EW OF TH EW OF AL RABLE PE EW OF BU EW OF BU EW OF BU DITURE ON LLOR AND LY TARGE ACTIONS HAVE L EXPEND. O mary of rev ntage grow ating Trans parison of osed Wate parison bet parison bet parison bet ng-reside parison bet. Overview of venue classes with i rev sfers and proposed r Tariffs between current current current between kur ousehold erating ex aintenance service services Pac. capital bid ects get Summ geted Fina fication) geted Fina.
Central Pla Budget Initiative Bu CFO City Manages Capital Consumer Re Development Departments Division Employment Energy Eff Executive Management M No Base Pay. Budgeted classification Budgeted as it contains Budgeted as it contains Budgeted classification that Finance.. of the Mun subsequent Media Bill. 6 The Council of the Metropolitan Municipality of the City of Buffalo, acting in accordance with 75A of the Local Government Act: Municipal Systems Act (Act 32 of 2000) adopts and approves with effect from 1 July 2012 the charges for other services set out in Schedule F.
8 That no new capital expenditure shall be made until a funding commitment is received by the Metropolitan Municipality of Buffalo City and Council approves such project. 9 Council notes that the draft MTREF budget for 2012/13 submitted for adoption is structured according to the votes and functions of the City of Buffalo at that time.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- KEY FOCUS AREAS FOR THE 2012/13 BUDGET PROCESS As per Circular 58 the following areas require particular attention
- NATIONAL PRIORITY – EMPLOYMENT OPPORTUNITIES a) Service Delivery and Labour Intensive Capital Projects
- BUDGET PRINCIPLES AND GUIDELINES
- CHALLENGES
The priorities and objectives of the 2011/2012 adjustment budget, as well as the basic allocations in that adjustment budget, were adopted as the upper limits for the new baselines for the 2012/13 draft MTREF budget; Tariff and property rate increase affordability and the fact that they are generally not allowed to exceed inflation as measured by the CPI, except when there are price increases in service inputs beyond the control of the municipality, for example the cost of bulk water and electricity. The need to re-prioritize projects and expenses within existing resources given the cash flow realities and declining cash position of the municipality;
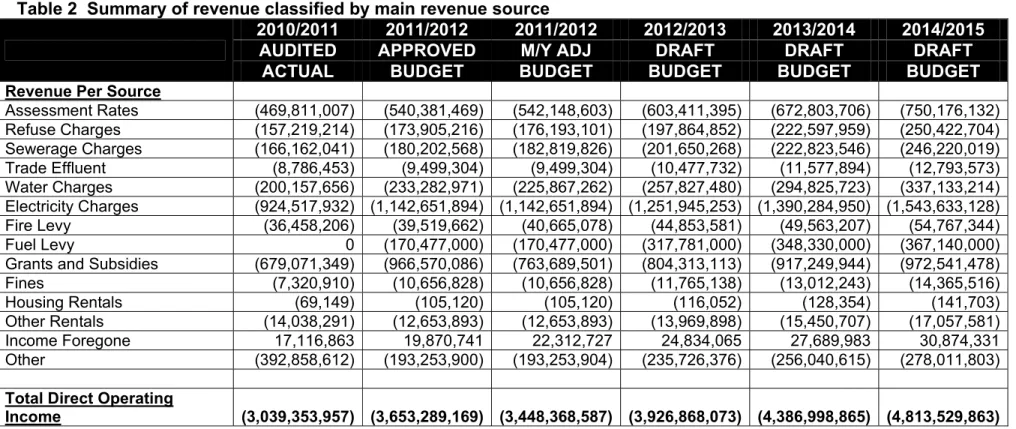
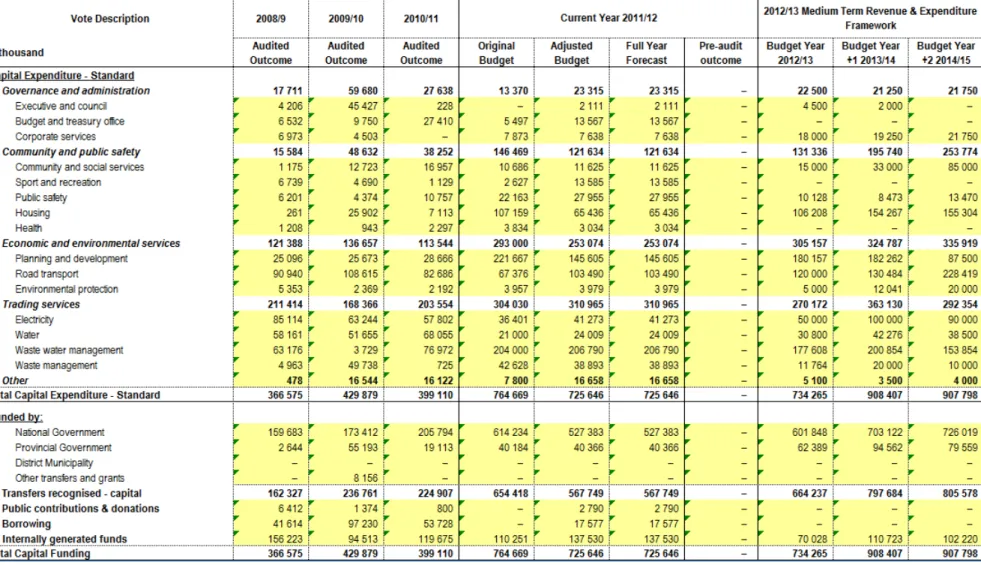
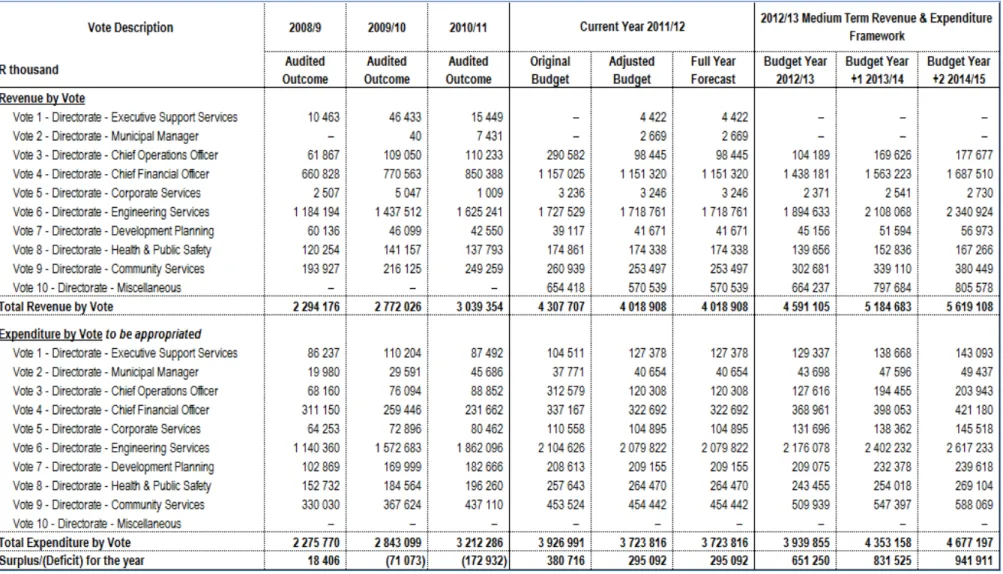
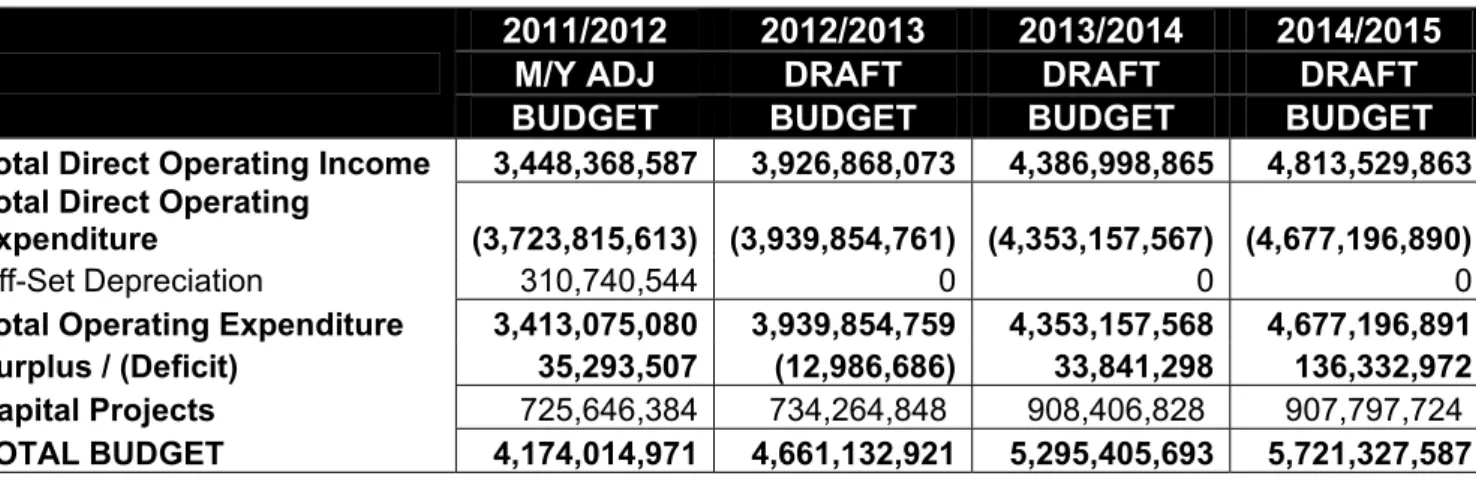
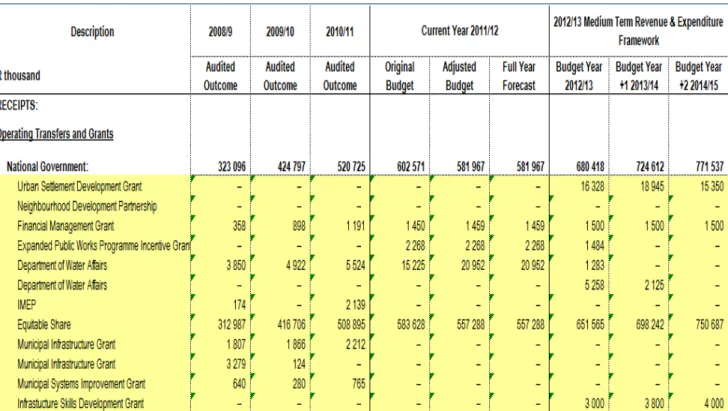
Affordability of capital projects – original allocations had to be reduced and operating expenses associated with the previous year's capital investments had to be included in the budget as part of the 2012/13 MTREF draft process. As stated above, the following table is a consolidated overview of the 2012/13 Medium Term Income and Expenditure Framework: USDG is mainly used to finance infrastructure programs in the "Built Environment".
The municipality must therefore ensure that it strives by all means to meet the conditions of the grant to ensure that service delivery is not hindered. The City is not taking out any new loans in the 2012/13 Draft MTREF period as it is currently reviewing its ability to borrow beyond the current debt-to-income ratio of 22.4%.
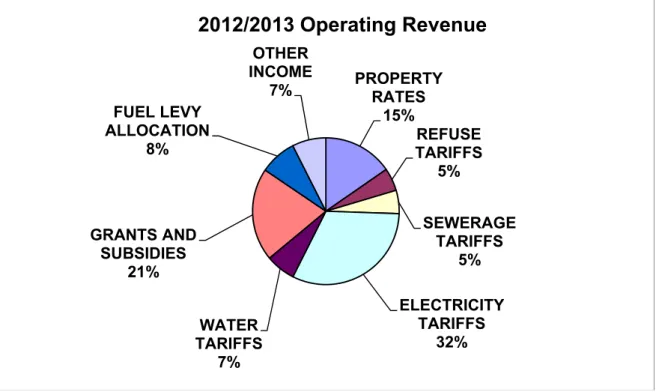
OPERATING REVENUE FRAMEWORK
2012/2013 Operating Revenue
- Property Rates
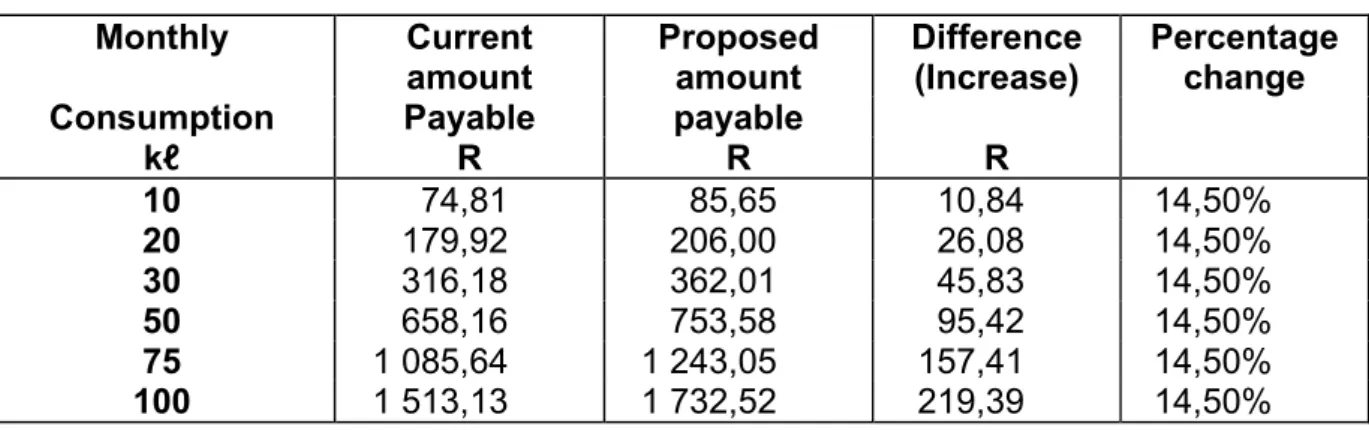
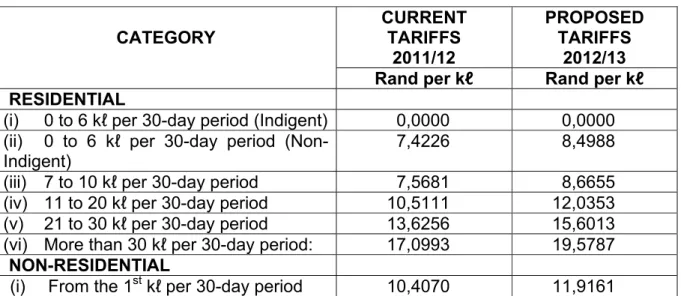
- Sale of Water and Impact of Tariff Increases
- Sale of Electricity and Impact of Tariff Increases
- Sanitation and Impact of Tariff Increases
- Waste Removal and Impact of Tariff Increases
- Overall impact of tariff increases on households
- OPERATING EXPENDITURE FRAMEWORK
100 percent rebate will be granted to registered needy in terms of the Needy Policy;. The following table shows the overall expected impact of the tariff increases on a large and small household, as well as a needy household receiving free basic services. Note that the overall impact of the rate increases on household bills was kept at an average of 11.3 percent in all cases.
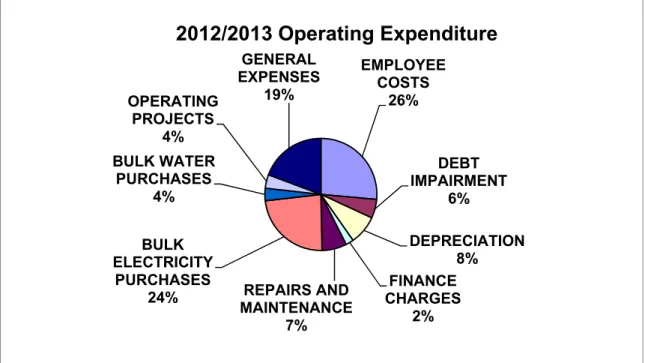
The City's spending framework for the 2012/13 budget and MTREF is informed by Sections 18 and 19 of the MFMA;. The budgeted allocation for employee related costs for the 2012/13 financial year amounts to R1,041 million, which is equal to 26,4% of the total operating expenses. Provision for depreciation is generally considered a proxy for measuring the rate of asset consumption.
Budget allocations in this regard amount to R330.5 million for the 2012/13 financial year and are equal to 8.4 percent of total operating expenditure. Other expenses consist of various line items related to the daily operations of the municipality.
2012/2013 Operating Expenditure
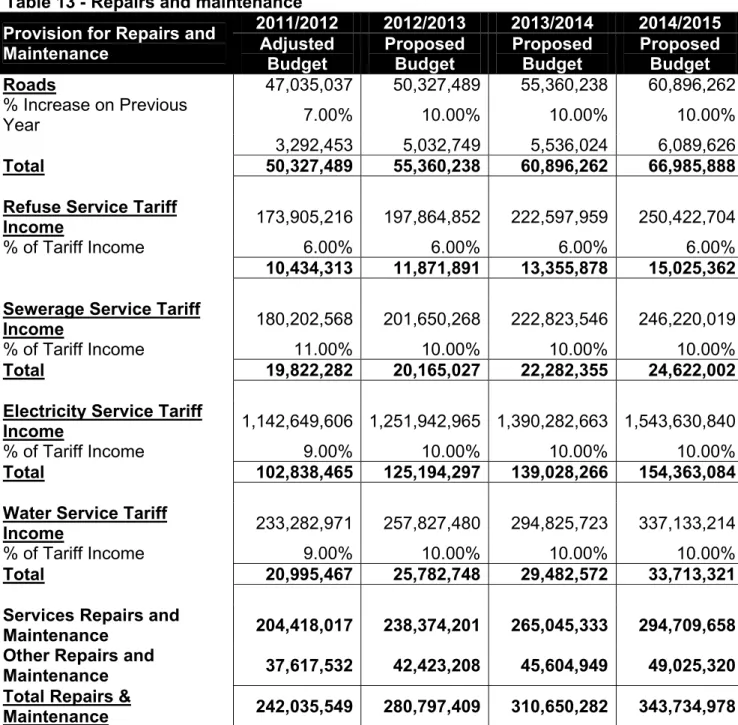
- Repairs and Maintenance
- Free Basic Services: Basic Social Services Package Table 14: Basic Social Services Package per household
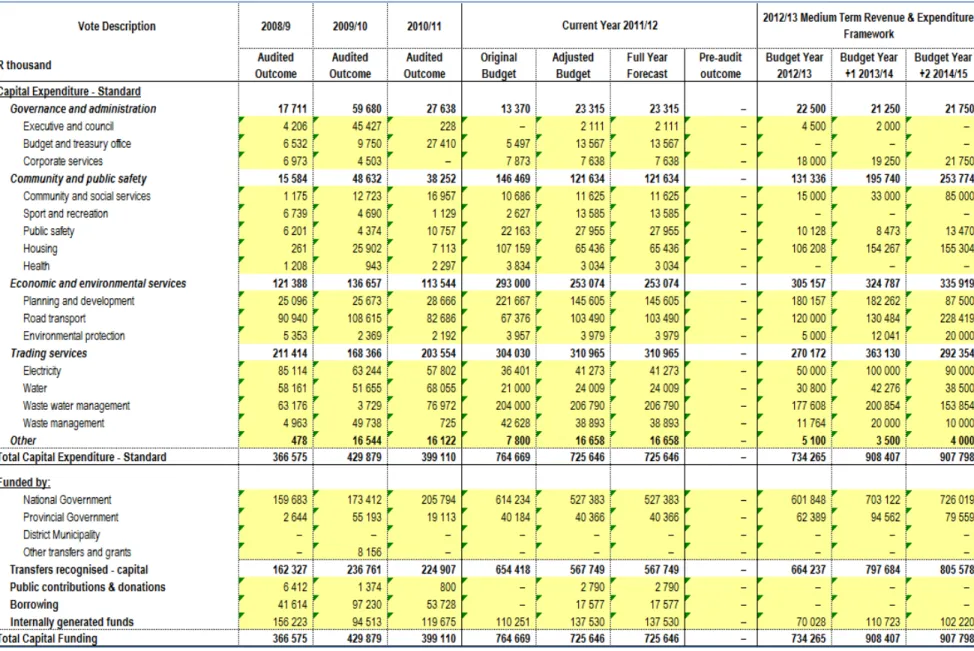
- CAPITAL EXPENDITURE
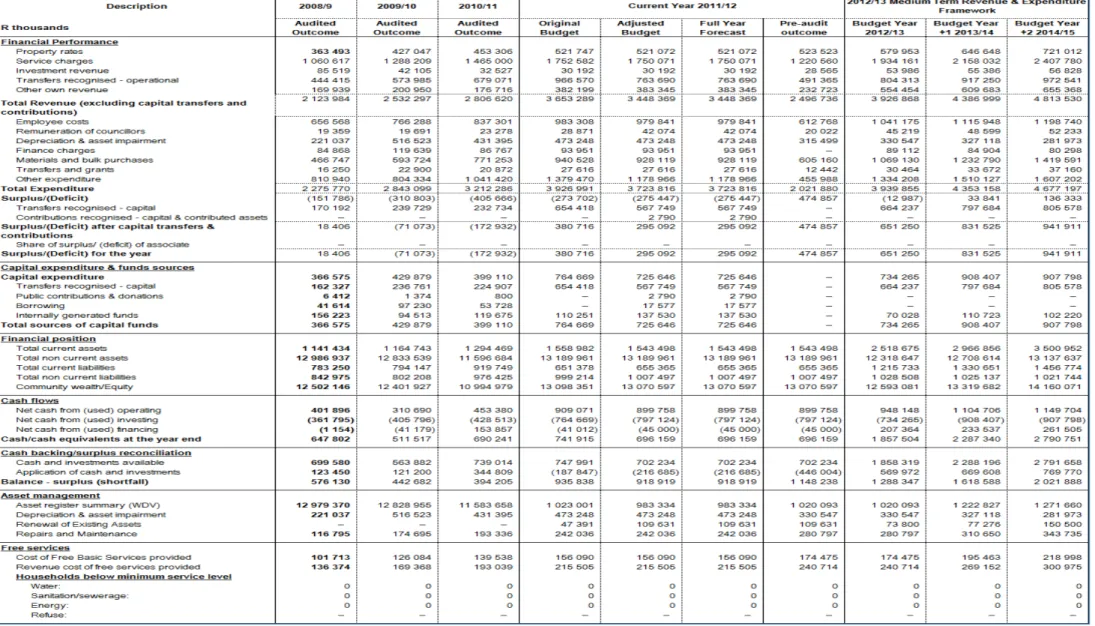
- ANNUAL BUDGET TABLES
- I In term
The city is striving toward a repair and maintenance of 10% of its overall operating budget due to the city's aging infrastructure and deferred historical maintenance. The welfare package helps families who are poor or face other circumstances that limit their ability to pay for services. To receive these free services, families are required to register under the City's Poverty Policy.
The goal is to register 70,000 or more needy households during the 2012/13 fiscal year, a process that is reviewed annually. The social package costs of the registered indigent households are largely funded by the national government through the local government's fair share received in terms of the annual Division of Revenue Act. The major contributors to this growth are the Urban Settlement Development Grant (USDG) and Human Settlement Development Grant awards for infrastructure and housing development.
Transport Planning received a grant of R450m, Electricity Infrastructure R240m, Roads and Stormwater R79m and Wastewater R532m. Ilitha Eradication of Wooden Houses to Formal Houses, Tyutyu Phase 2, Airport Phase 2A, Zone CC 18: Phase 2, Potsdam Ikhwezi Block 1 and 2, Potsdam North Kanana. The following twelve pages present the ten main budget tables as required by section 8 of the municipal budget and reporting regulations.
OVERVI
SUPPO
ANNUA
RTING
AL BUDG
DOCUM
GET PRO
MENTAT
OCESS
TION
IDP and Service Delivery and Budget Implementation Plan
The city's IDP is its most important strategic planning instrument, directly guiding and informing its planning, budgeting, management and development actions. This framework is rolled out into objectives, key performance indicators and targets for implementation, which directly inform the Service Delivery and Budget Implementation Plan. The IDP has been taken into a business and financial planning process up to the 2011/12 MTREF, based on the approved 2010/11 MTREF, Mid-year Review and adjustments budget.
The business planning process is then refined in light of current economic circumstances and the resulting revenue projections. With the compilation of the 2011/12 MTREF, each function/directorate had to review the business planning process, including setting priorities and objectives following the mid-year review against the 2010/11 Budget Service Delivery and Implementation Plan. Business planning relates to the priority needs of the city and reviewed the strategic objectives and fundamentally informed the operating budget allocations and the three-year capital program in detail.
The draft Service Delivery and Budget Implementation Plan (SDBIP) and draft performance contracts will be submitted to the Executive Mayor by 13 June 2012 in accordance with section 69 of the MFMA and the final SDBIP will be presented to Council for approval together with the performance contracts on 27 June 2012.
Financial Modelling and Key Planning Drivers
Community Consultation
OVERVIEW OF ALIGNMENT OF ANNUAL BUDGET WITH IDP
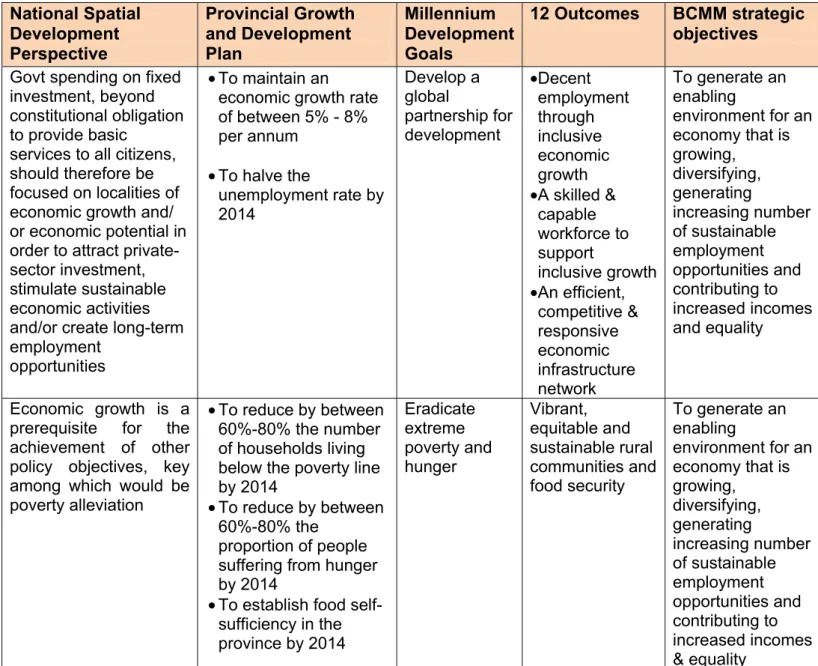
To generate an enabling environment for an economy that is growing, diversifying, generating increasing number of sustainable
To produce sustainable infrastructure that support social and economic development;
To be a well structured and capacitated institution that renders effective and efficient services to all by 2016
To enhance and protect all environmental assets and natural resources within Buffalo City Metropolitan Municipality by 2016
- MEASURABLE PERFORMANCE OBJECTIVES AND INDICATORS Table 34 - Table SA8 – Performance indicators and benchmarks
- Free Basic Services: Basic Social Services Package for Indigent Households The social package assists residents that have difficulty paying for services and are
- Providing Clean Water and Managing Waste Water
- OVERVIEW OF BUDGET-RELATED POLICIES
- Tariff Policy
- Rates Policy
- Credit Control Policy
- Indigent Policy
- Investment and Cash Management Policy
- Long-Term Borrowings Policy
- Supply Chain Management Policy
- Policy on Reserves and Asset Management Policy
- OVERVIEW OF BUDGET ASSUMPTIONS
- General inflation outlook and its impact on the municipal activities
- Credit rating outlook Table 36 - Credit rating outlook
- Interest rates for borrowing and investment of funds
- Collection rate for revenue services
- Growth in the tax base of the municipality
- Salary increases
- Impact of National, Provincial and Local policies
- Ability of the municipality to spend and deliver on the programmes
- Overview of budget funding
- Proposed Tariff Increases over the Medium-term
- Detailed Investment
- Medium-term outlook: capital revenue
- Details of Borrowings
- Cash Flow Management
- Cash Backed Reserves/Accumulated Surplus Reconciliation
- Funding compliance measurement
- EXPENDITURE ON GRANTS AND RECONCILIATIONS OF UNSPENT FUNDS
- COUNCILLOR AND EMPLOYEE BENEFITS
- MONTHLY TARGETS FOR REVENUE, EXPENDITURE AND CASH FLOW Table 51 - SA25 - Budgeted monthly revenue and expenditure
- CONTRACTS HAVING FUTURE BUDGETARY IMPLICATIONS
- CAPITAL EXPENDITURE DETAILS
- LEGISLATION COMPLIANCE STATUS
- In year reporting
- Internship programme
- Budget and Treasury Office
- Audit Committee
- Service Delivery and Implementation Plan
- Annual Report
- Policies
- OTHER SUPPORTING DOCUMENTS
Capital expenditure to operating expenditure is a measure of borrowing costs in relation to operating expenditure. In summary, various financial risks can have a negative impact on the municipality's future borrowing capacity. The liquidity ratio is a measure of the municipality's ability to use liquid assets to immediately meet or settle its short-term obligations.
For the financial year 2012/13, 70,000 registered needy people are foreseen in the budget. In terms of the Municipality's poverty policy, registered families are entitled to a fee of 6kℓ water, 50 kwh of electricity. These initiatives and interventions will translate into a positive cash position for the City and it is anticipated that available cash and cash equivalents will increase to RJ2.8 billion by the end of the 2012/13 MTREF period. What are the anticipated cash and investments that are available at the end of the budget year.
A deficit (deposits > cash and investment) indicates non-compliance with section 18 of the MFMA requirement that the municipal budget must be 'funded'. In accordance with the municipality's borrowing and investment policy, loans are drawn down only when expenditure is incurred for a specific project. For the purposes of monetarily secured reserves and reconciliation of the accumulated surplus, a provision in the amount of one month's operating expenses was foreseen.
Underperformance with regard to collections can put upward pressure on the city's ability to meet its creditor obligations. Long-term investments mainly consist of the sinking funds for the repayment of future loans. The municipality has reduced its cash reserves, which is a serious concern and should be considered a strategic risk to the city's financial stability.
As part of the planning strategy, this should be managed aggressively as part of medium-term planning objectives. The 2012/13 MTREF is informed by ensuring that the financial plan meets the minimum requirements of the MFMA. The City's cash position forecast was discussed as part of the budgeted cash flow statement.
This trend will need to be carefully monitored and managed in the implementation of the budget. Details of the city's strategy regarding asset management and repairs and maintenance are included in Table 51 SA34C. Under the City's Supply Chain Management policy, no contracts will be awarded outside the medium-term revenue and expenditure framework (three years).
Since the introduction of the internship program, the city has successfully hired and trained 11 interns through this program.