The beliefs of the Mathematical Literacy (ML) teachers changed as they identified with the content and pedagogical content knowledge of ML. The implications of the study in relation to the Department of Education The implications of the study in relation to the universities.
Acronyms
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
DEDICATION
CHAPTER ONE
The Advanced Certificate in Education in Mathematical Literacy Curriculum
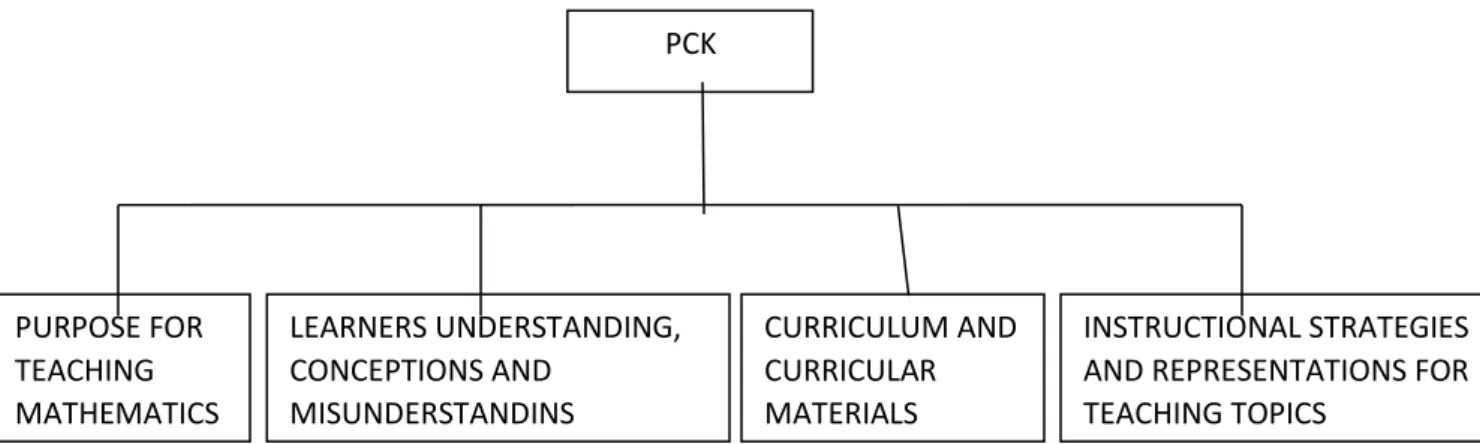
The curriculum of the ACEML program at UKZN was composed of eight modules of which four modules were closely linked to the content knowledge as set out by the DoE in the Learning Program Guidelines (LPG). The modules were Pedagogical Content Knowledge (PCK), and focused on the following: exploring the curriculum of ML, exploring how the content will be taught, designing tasks and assessment strategies suitable for their classrooms and identifying misconceptions that arise.
Purpose of the ACEML
This research is an exploration of how the ACEML program has impacted the professional development of the teachers who studied, in terms of their content knowledge, pedagogical content knowledge and the changes in their beliefs and identity, as well as the confidence level of the ML teachers. 2 How was the professional development of the teachers studying the Advanced Certificate of Education in Mathematical Literacy improved?
Limitations of the research
Chapter five is the final chapter that highlights a summary of the research findings and answers the research's critical questions as well as states the research's limitations and recommendations.
LITERATURE REVIEW AND THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
Introduction
- What is Mathematical Literacy?
- Introduction of the subject Mathematical Literacy in South Africa
- The need for training ML teachers and the challenges faced
- Professional development of teachers
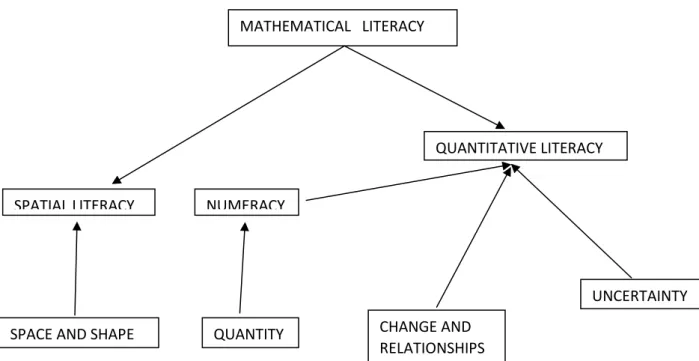
These different views of mathematical literacy have a tremendous impact on the professional development of the participants in this study. Mathematical literacy provides students with awareness and understanding of the role mathematics plays in the world.
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
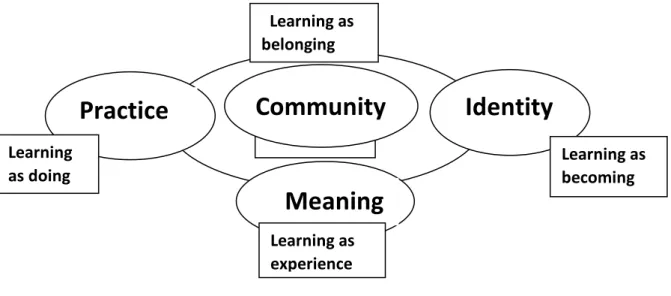
This description of the goals of ML is reflected in Wenger's third premise above that knowledge is about active engagement in the world. In the previous situation of the teachers, success would have been defined in the sense of facilitating the knowledge of the previous subject.
Learning
It is therefore analyzed separately, but viewed in relation to its components: meaning, identity, practice and community.” (Graven, 2002, p.129). The following figure shows Wenger's learning theory, including its four components, as explained by Graven (2002, p.153), namely meaning (our ability to experience the world as meaningful), practice (our ability to use historical and social resources, frameworks and perspectives that support mutual engagement in action), community (ability to talk about the social configurations in which our enterprise is defined and our participation is recognizable as competence), and identity (a way to talk about how learning has changed who we are) and combines his four principles on which his work is based;
Practice Community Identity Meaning
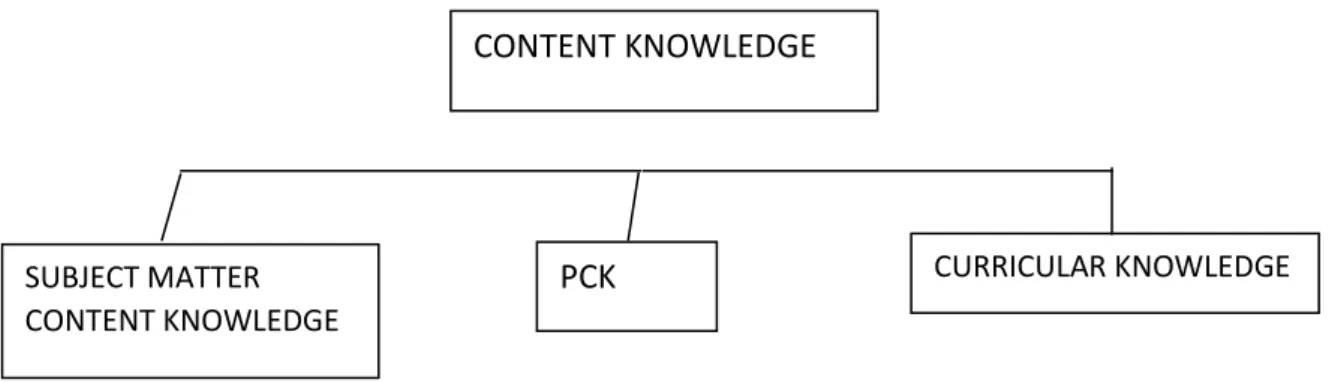
Dimensions of teacher knowledge
- Subject Matter Content Knowledge
- Pedagogic Content Knowledge (PCK)
- Teacher’s Professional Identity and Beliefs
Content knowledge consists of knowledge about a subject and its organizational structures (Grossman, Wilson, & Shulman, 1986b, 1987). Hill, Rowan, and Ball (2005) examined the specialized content knowledge and skills used in teaching and found that “teachers.
Introduction
Purpose Of The Research
Research Approach
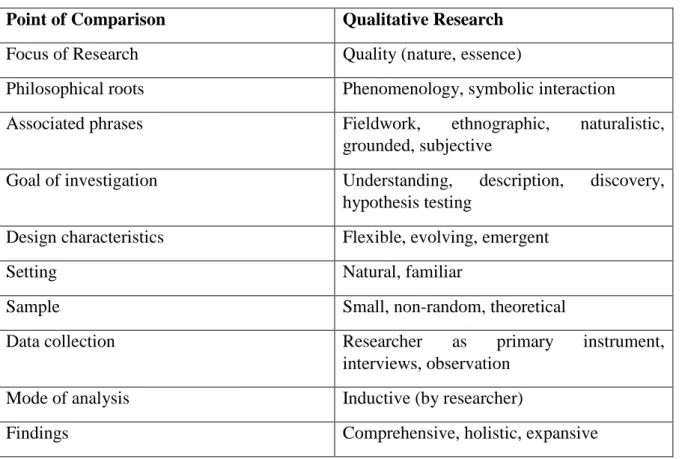
Data: The data collected may be subjective, as the data in this study are teachers' perceptions of how their studies affect their professional development. A combination of both qualitative and quantitative data provides a better understanding of the research problem than either approach alone (Cresswell, 2000).
- Participants in the study
- Data collection
- Data Analysis
- Issues of Validity and Trustworthiness
- Ethical Considerations
- Limitations of the Study
- Summary
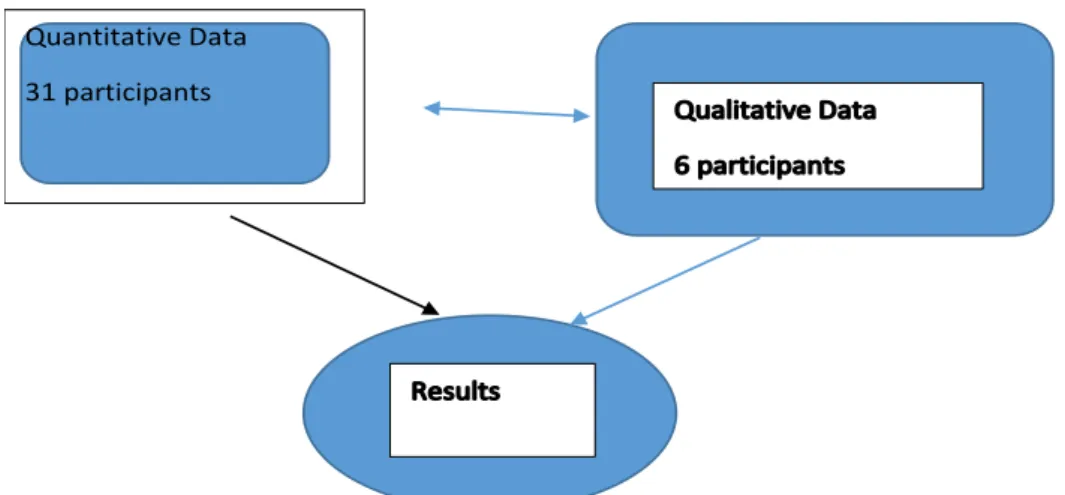
From the thirty-one participants who had completed the questionnaires, interviews were conducted with six of the participants. From the thirty-one participants who had completed the questionnaires, interviews were conducted with six of the participants.
CHAPTER FOUR RESULTS
SECTION A
ANALYSIS OF THE SELECTED SURVEYS
Background
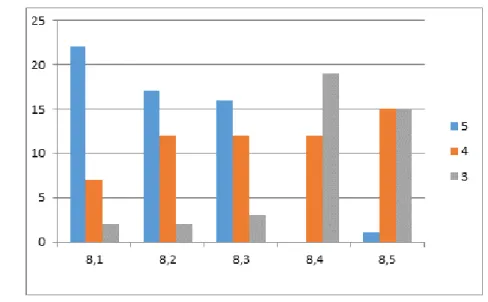
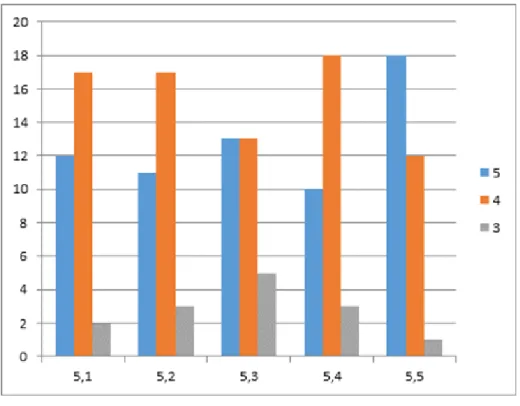
Six of the teachers were at level 2, one was at level 3 and twenty-four of them were at level 1. All had a qualification on a three-year teaching exam and twenty-eight of them were currently studying towards their honors degree in ML.
Impressions About The Program
- Impressions Of The Tutors and the Centres
- Results Of The Teachers’ Participation
- Factors That Helped Teachers Remain In The Program
- Modules That Were Most/Least Useful To The Teachers
- General
The teachers reported being overwhelmed by the results of their participation in the ACEML program. 98% of teachers also felt that the program introduced them to new strategies that they are now implementing in their classrooms.
SUGGESTIONS MADE TO NMMU AND UKZN FOR THE IMPROVEMENT OF THE PROGRAMME
JBD stated that he would ensure that the basics are thoroughly taught at the GET level so that no problems are encountered. SCM will ensure that teachers receive a comprehensive training session through support programs at the beginning of each semester so that they are well prepared for their lessons.
SECTION B
TASK DESIGNS BY THE PARTICIPANTS
- This task was designed by PJM
- This task was designed by GBN
- This task was designed by HDJ
JBM felt that all schools should have appropriate laboratory equipment and should ensure that teachers handle the equipment properly. TM would ensure that subject advisors are supportive so that they know exactly what to do in class with the help of prepared timetables.
SECTION C 4.5 Interviews
TERM
Their ability to measure and see measurement in the right perspective made the subject a "hands on subject". He also saw the context being integrated across other subjects. He said: "It was more empowering and it was relevant to the students and they could relate to the content because it's stuff they're experiencing in the real world." He also found that the Year 12 work they were studying involved a lot of maths and was very relevant to him.
Summary
She could also use the one-to-one strategy with her learners and explain to them until they understood all the concepts of mathematical literacy. She also used a lot of repetitive and remedial teaching so that her learners gained a good conceptual understanding.
CHAPTER FIVE
RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS
Introduction
RESEARCH QUESTIONS
Improvement of Content Knowledge
- The teachers learnt new knowledge in terms of the context
- The various kinds of learning experiences of the Teachers
Many teachers who have studied in the ACEML program have previously taught subjects in other disciplines. HDJ and the other participants reflected Lave and Wenger's (1998) theory of learning with meaning and.
A Learning from Tutors
SSG stated that “square, triangle, rectangle and circle always fascinated him and before I signed up for ML I avoided learning word problems. The data also revealed that one of the benefits of the ACEML program was that it offered different learning experiences, such as tutored learning, peer learning, and learning by engaging with different resources.
B Learning from Students
HDJ, PJM, SPM and NM confirmed that the tutors taught well and gave them additional notes and resources to take back to their classrooms and this enabled him to teach confidently in their classrooms.
C Learning by engaging in Resource Materials
- Integration of contexts and skills different from mathematics
- Emulation of teaching styles of tutors/peers
- Developing Skills in Task designs
- Developing Skills in Assessments
- Changes In The Identity And Beliefs Of The Teacher
- Improvement in the confidence levels and how teachers view themselves as professionals
- Development of beliefs and a change in identity in ML
- Access to Professional bodies and opportunities within the department of education
- A model to explain how the ACEML program enhanced the professional development of the teachers
- Implications of the study
- Implications of the study in relation to the teachers
As shown in the figure, the study has shown that the professional development of participating teachers has increased. As teachers' beliefs and identity changed towards ML, they felt more confident in the classroom.
Professional development
Implications of the study in relation to the school
The DoE should also set up tests for teachers to use in confidence to ensure that teachers are allowed to test themselves to see if they are competent in certain content and thus be trained in what they require as teachers and not on all the content they teach. DoE should also provide opportunities for lecturers in other subjects to study ML so that they can develop professionally and incorporate ML into their subjects such as hospitality studies, tourism studies, etc.
Implications of the study in relation to the universities
This study is based on teachers' perceptions of the contribution of the ACEML program. Regarding teacher support programs, universities should expand the ACEML program curriculum to include a greater depth of content knowledge.
Conclusion
In terms of pedagogical content knowledge, teachers were overwhelmed by the different and new strategies they were equipped with in the ACEML program. They became confident with their new content knowledge and the pedagogical content knowledge they learned in the ACEML program.
Bibliography
An exploration of the strategies used by grade 12 mathematical Literacy exam questions based on a variety of real-world contexts. Analyzing the relationship between the implementation of an Advanced Certificate of Education in Mathematical Literacy reskilling program and the transformation of teacher identities.
INTERVIEW QUESTIONS
INTERVIEW No. 1 INTERVIEWER: P BRIJLAL
INTERVIEWEE: TERM
It was to move from that kind of teaching, give the students problems, here we were all involved together, now there is more understanding between students and teachers when we teach mathematics. That's why I applied for Bed honors because I thought it would be the same only to find out it's very different, more of a theory now in honors.
END OF INTERVIEW
If you prepare your work, you will know what to expect from them, it will be easy to clear up those misunderstandings, you will sit with them and discuss with them, and you will know how they are approaching things and the reason behind it after their thinking and they have a problem. understanding this here and then this should be done like this, then it is easy to deal with it.
INTERVIEW NO 2
INTERVIEWER: P BRIJLAL B: INTERVIEWEE: HDJ
As for history in terms of time, space and measurement, taking the Taj Mahal and being shocked to find that the building was only 56 square meters inside, I could tell if the length was short by using it. Nothing else, looking at it globally, I was literally able to use a globe in geography and show students that you can use mathematical calculations to find time, distance and speed.
INTERVIEW NO 3
INTERVIEWER: P BRIJLAL B: INTERVIEWEE: PJM
He gave us all this support and I think that is the very policy of the institution. It is a fact that some students out there, that they do not understand the content, but the language.
INTERVIEW No. 4
INTERVIEWER : P BRIJLAL B: INTERVIEWEE: SPM
Do you think if you have a non-math teacher like an accounting teacher teaching math now, do you think it was necessary for them to have taught 8th and 9th grade math. If the university were to improve the ace math lit program, what do you think they should do.
INTERVIEW NO 5
INTERVIEWER: P BRIJLAL B: INTERVIEWEE: NM
Tieren always asks me what do you do in math, is it different from pure math. In mathematics task 2 class 12, it is a lot to think outside the box compared to the module we did in mathematics.
INTERVIEWER: P BRIJLAL B: INTERVIEWEE: GBN
In pure math it was very difficult to understand shapes and measurements, but in math it became easier as they did it. Ace was the third course I took, the second course I also took at work and I didn't have time and sometimes we were very helpless, and in the second module you have to fight alone and there was no teacher then, but in mathematics the teacher is everything time followed.