INFORMATION AND ADOPTION OF ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR EFFECTIVE FACILITY MANAGEMENT IN THE ENERGY SECTOR. Artificial intelligence (AI) is a form of "deep learning" that enables machines to analyze information at a highly sophisticated level on their own, allowing them to perform complex functions such as facial recognition and speech recognition [1].
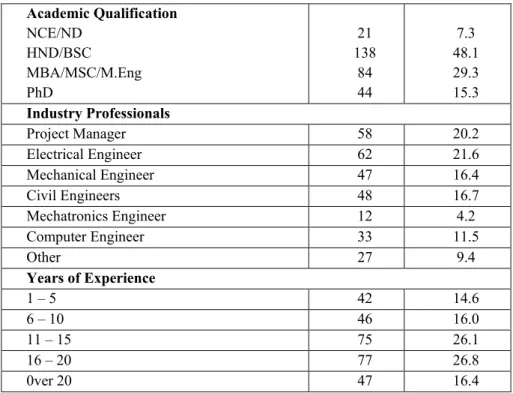
3 Results and Discussion
- Background data of respondents
- Awareness of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the Energy Sector
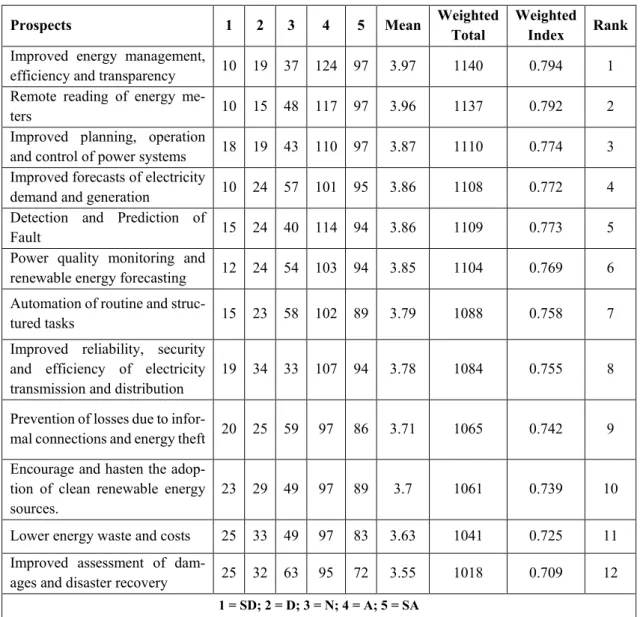
- Prospects of the adoption of artificial intelligence in the energy sector Another objective of this research was to determine the prospects of AI in the energy
- Prospects 1 2 3 4 5 Mean Weighted Total Weighted
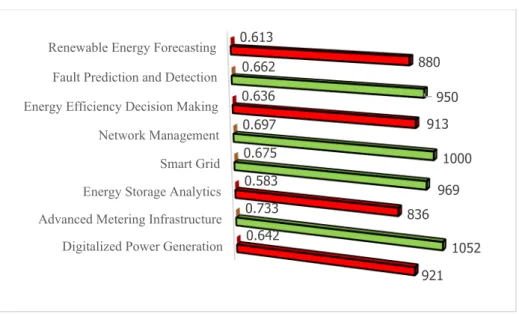
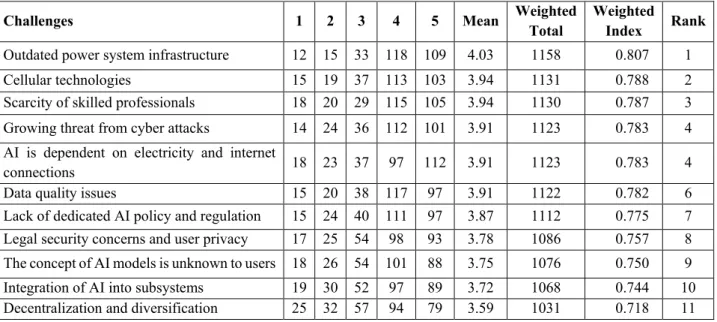
- Factors challenging the adoption of AI in the energy sector
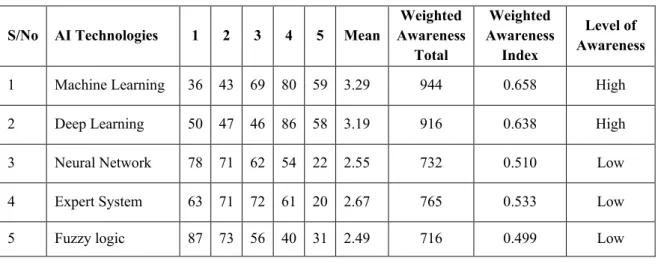
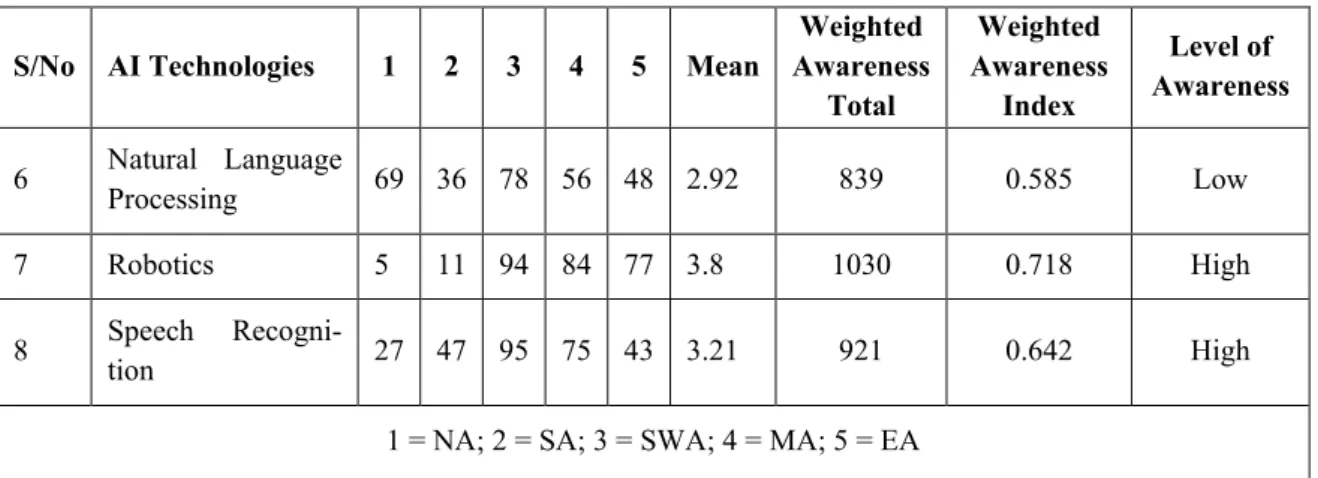
In addition, weighted index (WI) was further used for analysis to ascertain the level of awareness (WAI) of AI technologies and the level of application. To determine the level of knowledge about AI, respondents were asked to rank their level of awareness of AI applications in the energy industry.
4 Conclusion and Recommendations
The lack of these necessary infrastructures constitutes a significant obstacle to the use of AI in the management of facilities in the energy sector. Funding basic and applied research to produce significant advances in the theory, technology and applications of AI in the energy sector.
5 Acknowledgment
6 References
Tived, Artificial Intelligence in the Solar PV Value Chain: Current Applications and Future Prospects future prospects.
7 Authors
The Effects of Prepaid Metering Systems on Customer Satisfaction in Niger State, Nigeria
1 Introduction
Materials and Methods
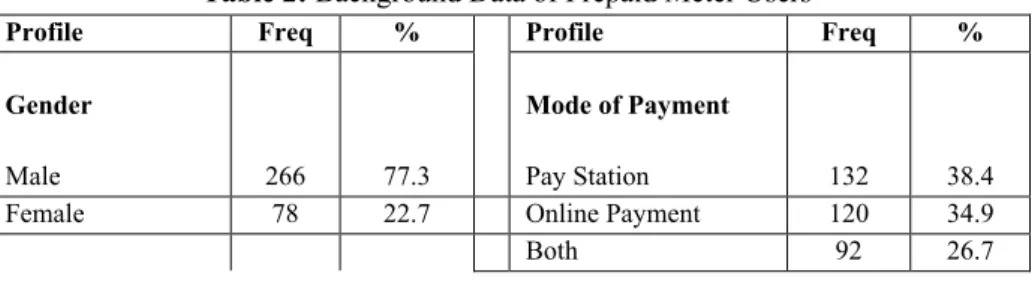
- Background data of prepaid meter users
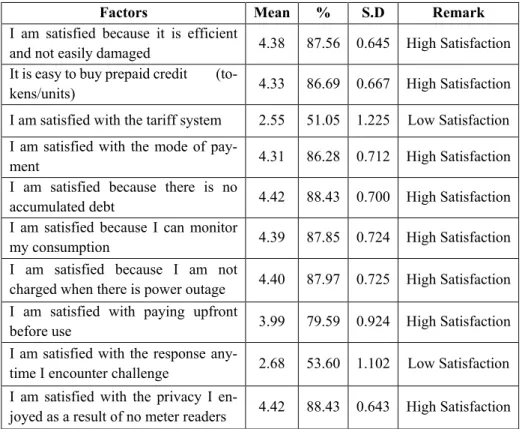
The result of the relationship between customer satisfaction and prepaid metering system is shown in Table 3. This indicates that the higher the reliability of the prepaid metering system, the higher the customer satisfaction.
Conclusion and Recommendation
This is because they no longer have to rely on others to read their meters for them, and they are satisfied that they no longer have to worry about inaccurate readings or strangers posing as meter readers. With "no accumulated debts", users are very satisfied because they pay before consumption and bills are not delivered to their homes.
34; Evaluation of Customer Satisfaction of Prepaid Meter Usage in Asokwa District of ECG in Kumasi Metropolis." PhD diss., 2016.
6 Authors
Farmers-Herders Conflict and Nigeria’s Quest for Food Security: The Imperative Need for Information
Communications Technology
Theoretical Explications
Social conflict theories emphasize the importance of conflict in determining social circumstances and the dynamics of social life. According to social conflict theory, conflicts for power and control are the main source of conflict in society.
Thematic and Content Analysis of Findings
- Farmers-Herders Conflict in Nigeria: Dynamics and Causes
- The Farmers-Herders Conflict Implications/Consequences on Food Security in Nigeria
- A Review of Government's Strategic Response to the Herdsmen-Farmers’ Conflict in Nigeria
- Establishment of Grazing Reserves in 1965
- The Establishment of National Commission for Nomadic Education (NCNE) in 1989
- The Armed Forces deployment to Curb Internal Security
- The National Grazing Reserve Bill of 2016 Initiative
- Prohibition of Open Grazing Legislation
- The Federal Government’ Great Green Wall Agency
On the other hand, the scourge of farmers-herdsmen continues to be a recurring theme in the country. The participation of the Nigerian Armed Forces, as provided for in the constitutional mechanism, is one of the urgent actions of the federal government to address farmer-herdsmen disputes [53].
The Imperative for Information and Communications
Technology towards Food Security and the Resolution of the Farmers-Herdsmen Conflicts
- Conclusion
- Acknowledgment
- References
- Authors
Similarly, the lack of technological inventions in the quest for a peaceful resolution to the ongoing conflict between fame and shepherds has exacerbated the conflict. These and many other factors remain Nigeria's greatest challenges to meaningful food security and a sustainable peaceful resolution of the conflict between farmers and pastoralists. The apparently visible lack of ICT use in the search for a sustainable solution to the conflict between farmers and herders, which has had negative consequences for food security in Nigeria, has also become a key factor why the conflict has remained never-ending.
Kwara State Council of Chiefs Proceedings of the 1st Royal Summit on Peace and Security in Kwara State.
Modelling the Impacts of Climate Change on the Yield of Crops
Methodology
- Area of study
- Materials
- Methods
- Regression Analysis – Multiple Linear Regression (Development of Crop Yield models)
- Temporal/Trend Analysis
This region is characterized by uneven, steep terrain that stretches from the west to the Benue Mountains in the east. The third, known as Savanna Sahel, is found in the far north of the country and has a desert environment with annual rainfall of less than 500 mm. The northern part of Nigeria's geography is lowland, with relatively level terrain stretching from Lake Chad to the Sokoto Plain.
This technique was used to estimate the significant trend in the observed yield of the crops throughout the periods covered by the research work.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
- Developed Crop models
- Crop Yield Changes under ICHEC Climate Scenario
- Crop Yield Changes under NOAA Climate Scenario
- Crop Yield Changes under NCC Climate Scenario
- Observation on Crop Yield Changes
These projected changes in yield are significant (P<0.001) except in Kaduna, Kogi and Plateau States. The other sixteen (16) states projected a decline in cassava yield with the observed decline predicted to range from 1.17% to 11.52%, also significant (P<0.001). The decrease projected is observed in ten (10) states, with them being significant (P<0.001), except for Ekiti and Akwa Ibom States which are not.
Ensemble averages of climate parameters obtained from four (4) Global Climate Models (GCMs) were used to estimate the yield of cassava, rice and soybean in Nigeria and the result indicated that there will be an increase in crop yield in some countries.
Cassava
Rice
Soybean
National Mean Crop Yield
Climate change impacts on cassava, rice and soybean yields were further modeled on a national versus state-by-state basis in Tables 2 – 5. For soybeans, yield increases are predicted using the four (4) ) climate scenarios . The above finding is consistent with [38] where it was reported that due to the predicted increase in food demand worldwide by 2050, there must be increased yields, more needs to be done to meet the targeted increase of approx. 20% in the yield of crops to tackle food sufficiency.
Research [34] also concluded that the net effect of climate change on oil palm yield in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria is positive, consistent with the positive effects of climate change on crop yield considered in this study.
Conclusion
These studies applied approaches different from the one used for this study to model the impact of climate change on crop yields around the world. Contribution of Working Group I to the 4th Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Stocker, T.F., D.
Effects of climate change on global food production under SRES emissions and socioeconomic scenarios.
Assessing Theoretical Frameworks, Human Resources Management Implications and Emerging Technologies on
Methodology
Theoretical Framework of Water, Energy, and Food (WEF) Nexus
According to Leese and Meisch [66], the WEF nexus is a security issue, influenced by the securitization theory of Weaver [135] of the Copenhagen School of security studies. According to Madani, et al., [74] games are defined as a mathematical framework, which consists of some players, strategic moves and payoffs of players (utilities) for a possible fusion of the outcome of the game, through which the player's decisions in the game are fueled by their potential profit. In addition, the author opined that an understanding of the WEF nexus involves synthesizing fundamental concepts, discourses, interests and institutions.
Simplicity and Ease of Use: This is based on the ease of use and application of the technology.
![Figure 1: Technology Acceptance Model [140].](https://thumb-ap.123doks.com/thumbv2/pubpdfnet/10385319.0/104.918.209.864.270.616/figure-1-technology-acceptance-model-140.webp)
Human Resource Management Implications on WEF Nexus
In addition, the introduction of the importance of human resources in the theoretical framework of the WEF nexus emphasized the utilization aspects of human resource management, but did not mention the procurement, compensation and reward aspects. Lack of nexus thinking among WEF nexus managers has been the bane of the nexus. Therefore, this article argues for consideration of WEF nexus thinking in the recruitment policies of the sectors of the three resources.
This will help manage the interdependencies, synergies and trade-offs of the three resources quickly and efficiently.
Effect of emerging technologies on management of Water, Energy, and Food (WEF) Nexus
Mabhaudhi, et al., [72]) of the South African Water Research Commission stated the lack of coherence among human resource managers in the energy and agricultural sectors in Mpumalanga and Limpopo provinces in South Africa. In addition, the compensation and reward system should be effective in the sectors and emphasize the management of WEF resource trade-offs, the reduction of waste and the identification of innovation synergies. In the energy subsystem of the WEF nexus, IoT applications include Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AIM), Control and Operation of Energy Consuming Devices (Co – ECD), Battery Energy Management (BEM), Micro Grid (MG), Control of Electric Energy System and Utility (CEESU), Nano Grid (NG) and Energy System Reliability and Stability (ESRS).
Therefore, the essential effect of new technologies is the emergence of innovations in the water, energy and food area, thereby shaping the nature of the context.
Conclusion and Recommendation
Analytic technology is a technique for modeling the WEF link where there are no dependencies or underlying assumptions between variables, and data is the fundamental input to the model. As a result, it is less prone to errors and uncertainties, evolves quickly, and shows trade-offs in the nexus, highlighting areas that will negatively impact sustainability issues in the nexus. In addition, artificial intelligence (AI), big data analytics, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are important technologies driving the water, energy, and food space.
110 resource investment in new technologies shaping the WEF connection to mass commercialization and adaptation of innovations introduced in the water, energy and food fields.
Water-Energy-Food Nexus A new approach to support food security and sustainable agriculture. Tracing the water-energy-food nexus: Description, theory and practice: Tracing the water-energy-food nexus. International Journal of Ethics & Society (IJES), 2(3), p. 1991) 'Development of an instrument to measure perceptions of adoption of and information technology innovation'.
Linkage approach to water-energy-food security: an option for climate change adaptation.
The Design and Performance Evaluation of a Wireless Sensor Network Based Irrigation System on Different
Soil Types
Due to limited freshwater supply, an efficient and cost-effective way of irrigation has emerged as the need of the hour, especially in countries severely affected by lack of freshwater reservoirs. The efficient use of water in agriculture is one of the most important agricultural challenges that modern technologies help to address [6]. The efficient use and management of water is one of many countries' major challenges today.
Irrigating 25% of the world's crops, which provide 45% of the world's food, is expected to require about 70% of the world's fresh water.
2 Related Work
Real-time control could be added to the system to be more dynamic and efficient. Using a wireless sensor network and GPRS module, the automated irrigation system in [4] used soil water balance concepts to plan irrigation levels and duration. The resulting analysis showed that it was insufficient and there was a need for the system to become more robust.
More features, such as the use of weather forecasting to predict rainfall, could be added to the system to make it more robust and efficient and help regulate the system's operation.
3 Materials and Methods
- Field Capacity
- Integration of WSN
- Data Collection Level (Router)
- Control Level (Coordinator)
- Gateway Level
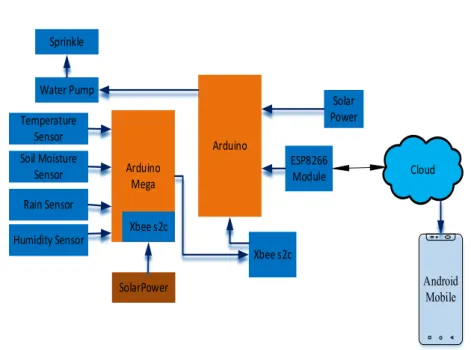
- Design and Overview of the System
The field capacity of the soil refers to the amount of water that remains in the soil. 130 The system connection is depicted in Figure 1 by a block diagram in which the router module is wirelessly connected to the coordinator node using the ZigBee connection protocol. The entire sensor is connected to one component of the system and transmits data wirelessly to the other part for decision making.
The system overview in Figure 4 shows the physical representation of the system integrated into agricultural land.
4 Result and Discussion
The performance of the system was evaluated based on the response time and saturation time of the soil. The module is connected to the application and ready to accept data when the system prints (ping: "number in ms"). The user can also turn the system on/off manually using this panel if needed.
A response time of less than 1 second for all three network service types indicates that the system is efficient.
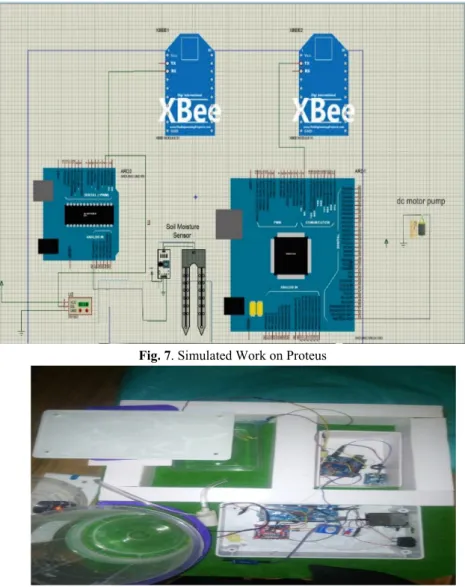
5 Conclusion
Muralter, “An overview of iot sensor applications and challenges using RFID and wireless sensor networks,” Sensors (Switzerland), vol. Pornillos et al., "Smart irrigation control system using wireless sensor network via Internet-of-Things", 2020 IEEE 12th Int. Pooja, “Design of a smart water-saving irrigation system for agriculture based on a wireless sensor network for better crop yield,” Lec.
Ramesh, “Automated irrigation system using weather forecasting for efficient use of water resources”, IOP Conf.
7 Author