The Academy of Science of South Africa (ASSAf) was inaugurated in May 1996 in the presence of then President Nelson Mandela, patron for the launch of the Academy. The current accreditation system for the Ministry of Education is not designed to meet the needs of other participants in the national innovation system.
CHAPTER ONE: Introduction and background (W Gevers)
The importance of the second starting point was that, in principle, it establishes the preconditions for the validity of the first; this cannot be overemphasized because all or most of the arguments for publishing research in the country become counter-arguments for NOT investing resources of time, effort and money into the field if the journals published in the country are poor. quality in terms of the above-mentioned criteria. No analysis of research publication can avoid emphasizing the critical role of editing and peer review in maintaining a global system of knowledge production, accumulation, and use.
CHAPTER TWO: A bibliometric assessment of South African research publications included in the internationally
A survey of editors’ opinions and related information (X.Mati)
Of the 213 journals captured in the database, five journals were listed in the International Bibliography of the Social Sciences (IBSS) and 15 in the Thomson Scientific (Thomson ISI) databases, while the other 193 South African journals were only accredited by the DoE. A core panel of peer reviewers was maintained by 141 of the 213 editors, of whom 171 believed that they used a "blind" peer review system, mostly referring to anonymous referees.
Global e-Research trends and their implications for South African research publishing in
All open access repositories can be configured to be globally interoperable through the use of the OAI Protocol for Metadata Collection (PMH), defined internationally by the Open Archive Initiative. Open access publishing will have to attract benefits if researchers are to be encouraged to use it.
Conclusions and recommendations for a strategically enhanced role of research publishing in South Africa (W. Gevers,
Good textbooks and reviews cannot be written in the absence of published evidence and insights that can be traced in the "literature". This would be based on principles and guidelines developed in this report and supported by continuous observation and analysis of the field of research publication in the national and international domain.
AGGREGATED AND INTEGRATED RECOMMENDATIONS
The rationale for this broad recommendation is fully described in the chapters of this report. If the Academy is to be involved in the national research publication system in related, significant ways (see the recommendation below for a quality assurance system for Syd.
TOWARDS A NEW STRATEGIC FRAMEWORK FOR SOUTH AFRICA’S RESEARCH JOURNALS
INTRODUCTION AND BACKGROUND
POINTS OF DEPARTURE
NECESSITY OF A NEW STRATEGIC APPROACH TO SOUTH AFRICA’S RESEARCH JOURNALS
CONSULTATIVE WORKSHOP, SEPTEMBER 2002
The total number of (scholarly) journals published in South Africa, relative to the number of publishing scientists, was unusually high;. Different authorities with an operational interest in article publications have benefited from a successful ASSAf project on the strategic management of SA research journals.
SUB-PROJECTS WITHIN THE LARGER ASSAF JOURNALS PROJECT
Moving from the national to the continental dimension, while feasible, should not be done unilaterally from a South African base. Publication for "Public Communication of (South African) Science": The ASSAf Council decided in 2004 to establish a new science magazine ("Quest: Science for South Africa") to promote local scientific achievements and pre-professions (in South -Africa published) to showcase. and foreign journals) to a wide audience of senior school-based learners, higher education institutions and science councils, overseas readers and the general South African public.
THE ISSUE OF THE PRIMARY PURPOSE OF A RESEARCH PERIODICAL OR JOURNAL
Electronic publishing: There is considerable concern that the ease with which electronic publication of existing or new journals can be carried out may act as a "lifesaver" for weak journal titles and may thwart efforts to strategically organize the system: many of the advantages of electronic publishing must be achieved without an avalanche of published garbage.
FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES OF RESEARCH PUBLISHING PROVIDING THE BUILDING STONES OF THE MATRIX OF HUMAN KNOWLEDGE
Special attention should be paid to the first “main author” (sometimes explicitly shared), and to the inclusion in the authorship list of only persons who directly contributed to the production of the work at an intellectual/conceptual level. Acknowledgment of funding sources and potential conflict of interest must be full, and authorship affiliations must be provided that reflect both the period of the study and the current situation.
THE CORE ROLE OF THE EDITOR AND THE PEER REVIEW SYSTEM
The existing relevant literature must be appropriately and fairly cited; in this regard, efforts are always made to ensure that reference is made to the first report of a find rather than a later elaboration. This study has proceeded from the firm belief that the core functions of journal editorial and peer review are fundamental to the global system of orderly knowledge accumulation and cannot be diluted or lost in a set of recommendations for the future viability of South Africa's public research. system.
THE COMING WORLD OF ELECTRONIC DISSEMINATION OF RESEARCH INFORMATION
This is not to say that new and better ways of achieving the goals of editorial and peer review cannot or should not be found or implemented, or that the publishing system of a relatively small but emerging country cannot and should not be held hostage to the momentum of a skewed current world system for scientific production, it is only to emphasize how important these fundamental elements are and always will be to achieve real quality in our own national system of innovation and to achieve international recognition that goes along with contributing significantly to the development of our country and continent.
For this purpose, inclusion in ISI's three citation indexes – the Science Citation Index, the Social Sciences Citation Index and the Arts and Humanities Citation Index – remains currently the most appropriate approach for the bibliometric assessment of journals in relation to international literature. standards. The second issue addressed in this chapter relates to the citation impact (see below) of indexed South African articles in the various fields.
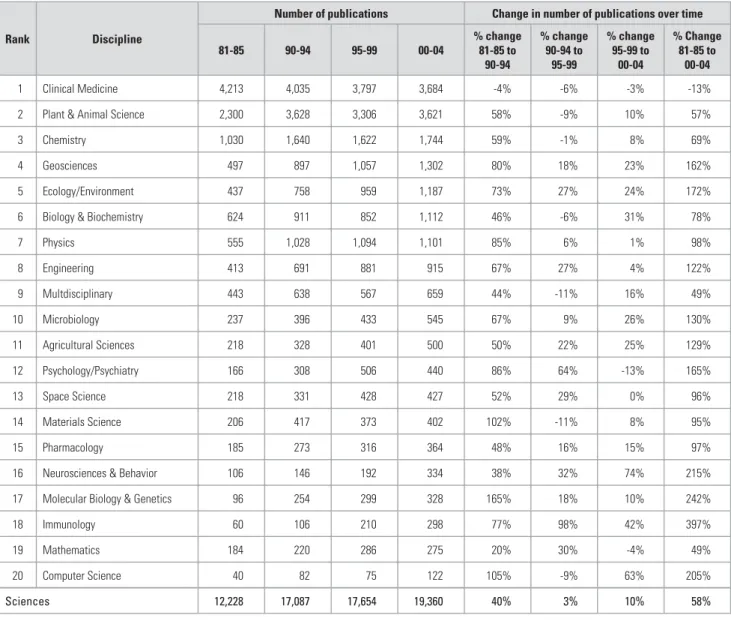
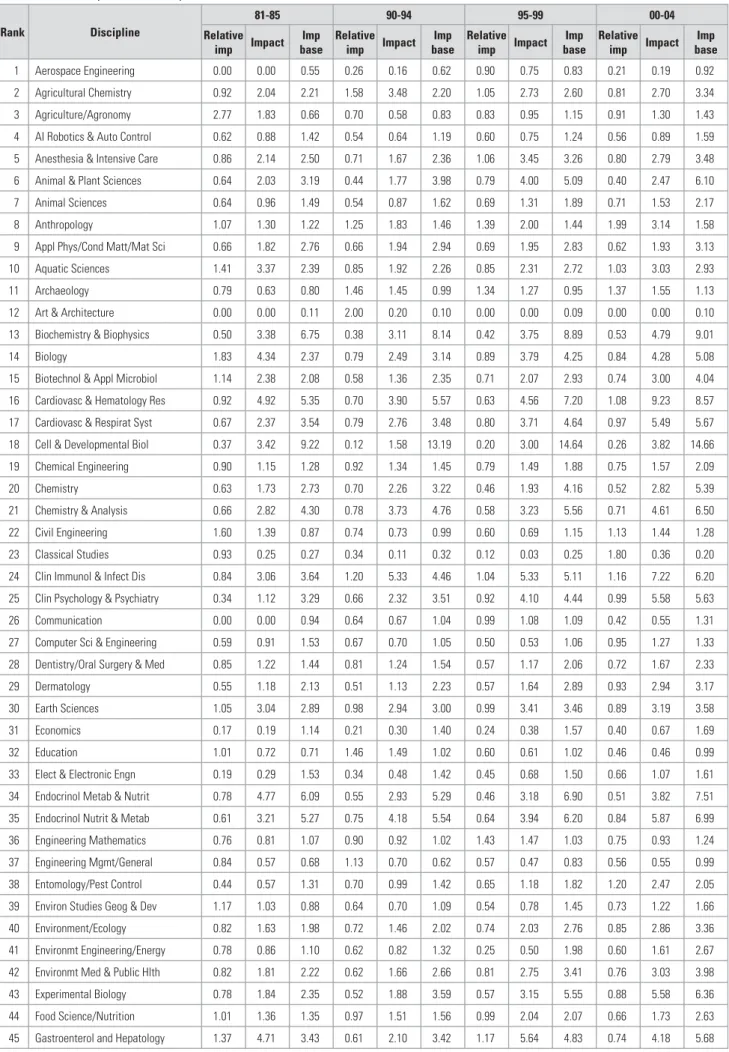
TRENDS IN SOUTH AFRICAN RESEARCH PUBLICATIONS: 1981-2004
A BIBLIOMETRIC ASSESSMENT OF SOUTH AFRICAN RESEARCH PUBLICATIONS
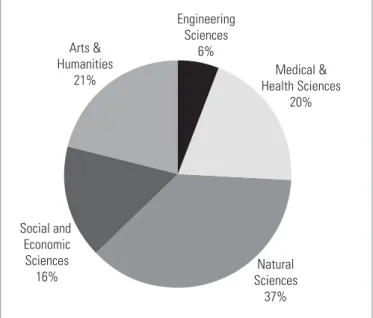
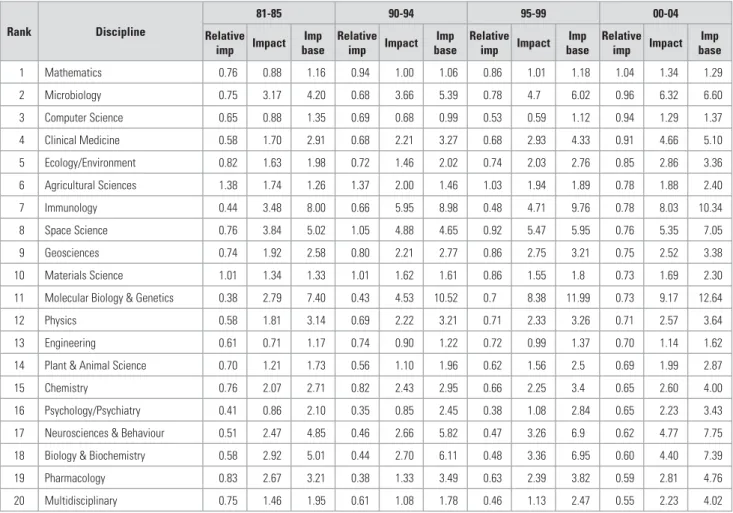
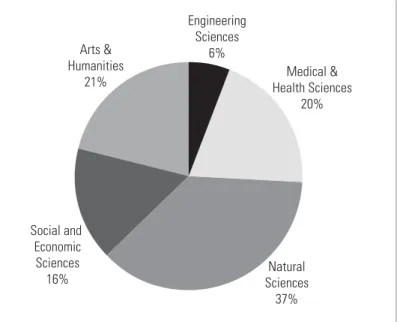
Tables 2, 3 and 4 aggregate the number of publications into larger disciplinary groupings: Table 2 shows the number of South African publications in 20 broad natural science disciplines, while Table 3. High growth rates in the number of publications in the social sciences and the humanities and arts ( however, as groups) may indicate possible opportunities for the establishment of journals covering these broad fields.
THE CITATION IMPACT OF SOUTH AFRICAN PUBLICATIONS
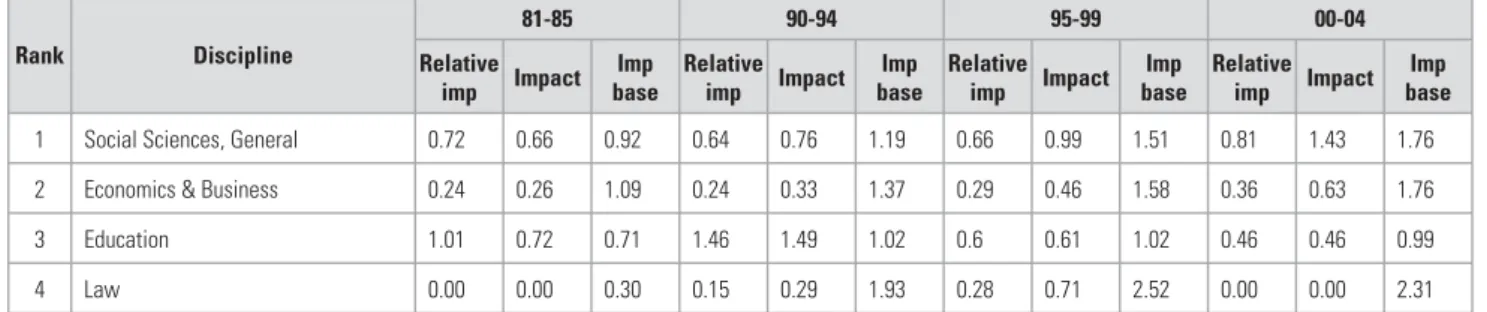
The caveat that groups with a small number of items may have higher relative impacts than larger groups becomes evident; only one discipline had a relative impact of one or higher, i.e. Tables 7 and 8 show the impact factors of social sciences, and arts and humanities disciplines, respectively; Attention is again drawn to the biases introduced by the small number of articles in these disciplines.
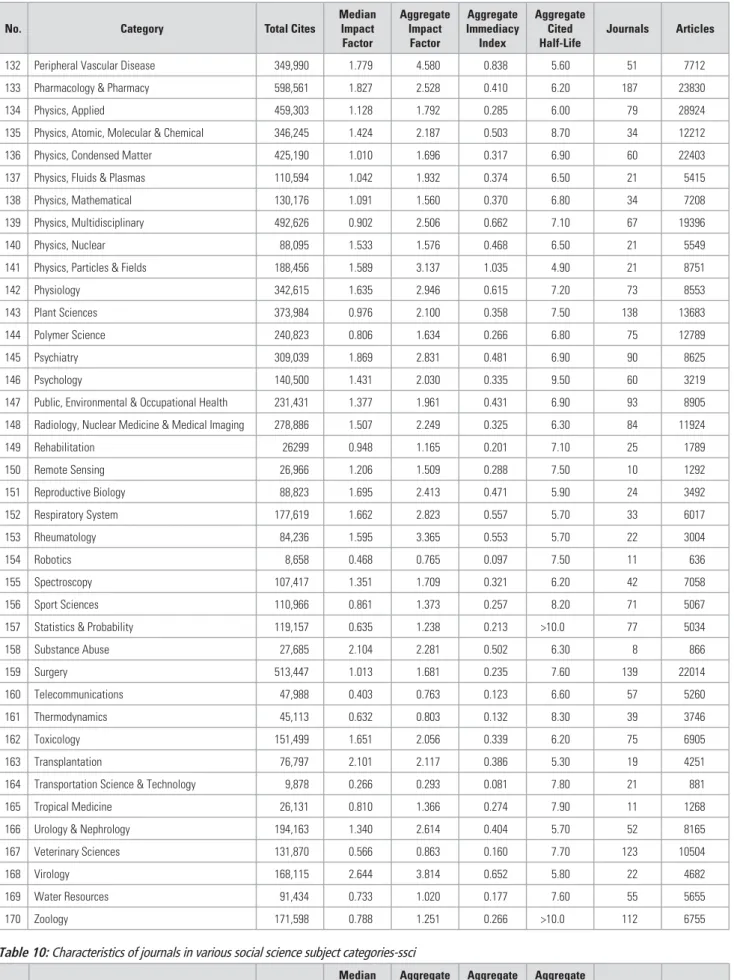
CHARACTERISTICS OF SA JOURNALS INDEXED IN ISI
Of the 19 journals in the list, 17 are indexed by the SCI and 2 by the SSCI. Veterinary medicine and zoology are the only subject categories that appear twice in the list of journals.
DISCUSSION
As we can search: comparing key features of the citation-based and citation-enhanced databases of Web of Science, Scopus, and Google Scholar. 2005) Beyond SCI Citations – New Ways to Evaluate Research. 2005) Citation analysis of scientific journals and measures of journal citation.
BACKGROUND
The purpose of this chapter is to provide an in-depth and systematic analysis of a large set of South African research journals4. Basic demographic analyzes of South African writers: race, gender and age, by scientific field.
THE HISTORY OF JOURNAL ACCREDITATION IN SOUTH AFRICA
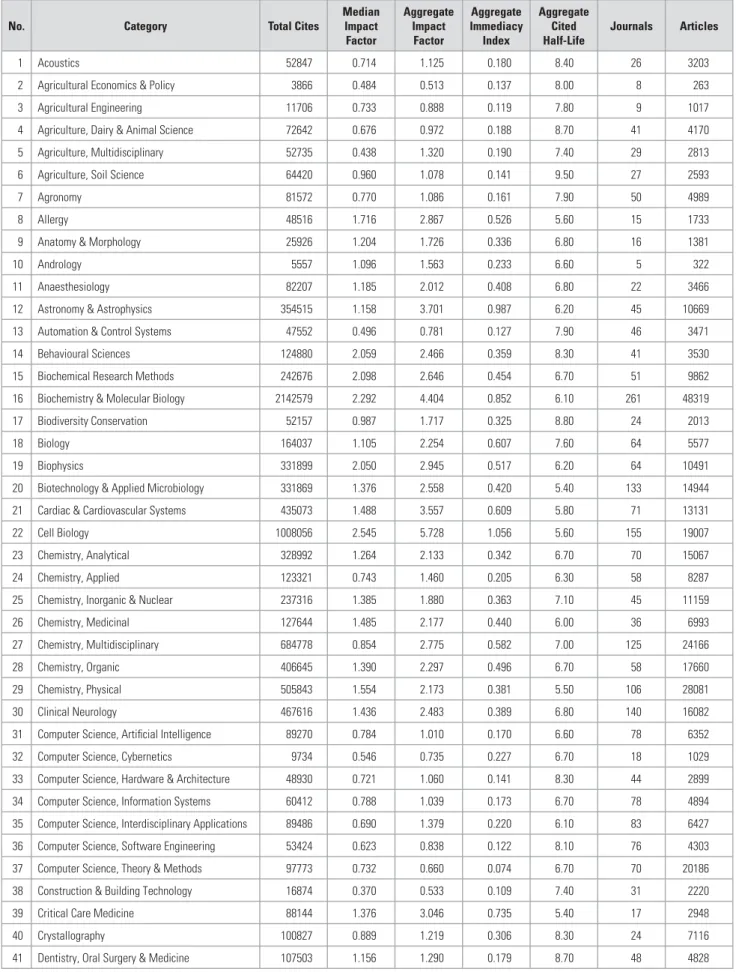
A COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS OF SOUTH AFRICAN RESEARCH JOURNALS
However, this number of 255 cannot be seen as being fixed, as any change to one of the international indexes (ISI or IBSS) will mean adding or reducing the total list of accredited journals7. It is not clear whether, under the new policy or otherwise, the Department of Education will add or remove journals from the 220 titles it accredited to the 2004 list, although that was stipulated in the published policy.
DATABASES
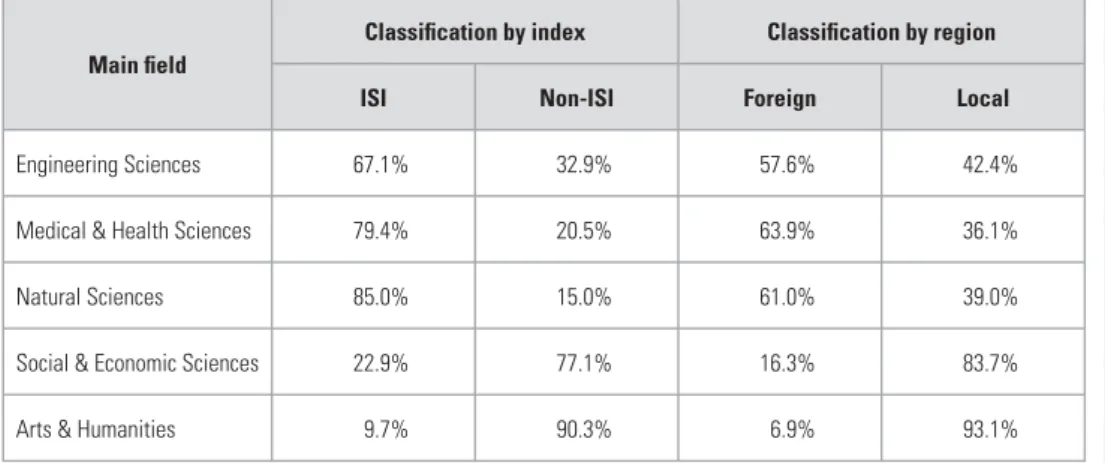
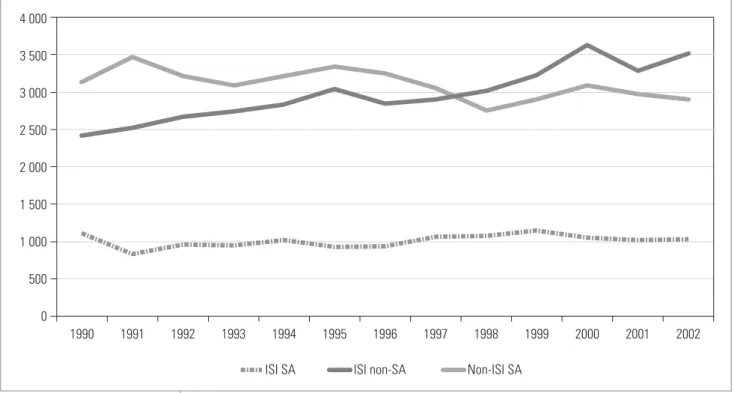
Most of the rest consists of citations to articles in ISI-listed journals that are not peer-reviewed original articles (and therefore not indexed in the sense of being included in the denominator function when calculating the impact factor), 'non-ISI' citations to. If you look at the situation in 1990 – the heyday of apartheid academic isolation – when only 36% of all articles were published in foreign journals, with the situation in 2002, when almost half (47%) were published in foreign journals, great progress has been made . made by breaking out of the isolation mold.
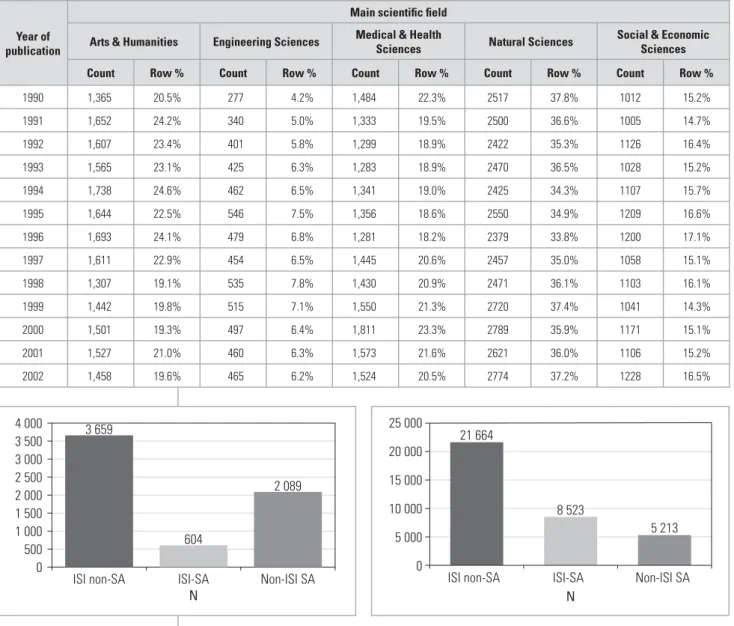
PUBLICATION DATA BY MAIN SCIENTIFIC FIELD, AND OVER TIME
It is not surprising that more than two thirds of articles from these fields are published in ISI journals. These results revealed some interesting "differences" in the profiles, with large proportions of articles in engineering sciences (42%), natural sciences (almost 40%), and medical and health sciences (36%) appearing in local journals.
AN ANALYSIS OF ARTICLE NUMBERS BY JOURNALS AND SCIENTIFIC FIELD
The high proportion of articles in the humanities appearing in local journals is not surprising, especially when one considers that the arts and humanities would include work in the fields of indigenous languages, theology, law, music, theater - all fields. that are embedded locally. A separate study has shown (Mouton, 2005) that higher proportions of articles in these fields are still published in Afrikaans, which makes it inevitable that they appear in local journals.
ARTS AND HUMANITIES
HEALTH AND MEDICAL SCIENCES
In terms of journal proliferation, the most striking feature of this list is the apparent dominance of the South African Medical Journal in this field, accounting for 11.67% of all articles published during this period. Geneeskunde, South African Family Practice and South African Journal of Surgery) account for a further 13.85% of all articles during this period.
NATURAL SCIENCES
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Department B-Ray Interactions with Materials and Atoms ISI & Non-SA 250 0.70. With the exception of the South African Journal of Science (which accounts for 5.38% of published articles) and which is probably best characterized as a "general science" journal, no single journal dominates this table.
ENGINEERING SCIENCES
What is striking is that of the first 34 journals listed, no fewer than 29 are local journals, of which 17 are included in the ISI (although the SA Statistical Journal has recently been delisted from the ISI). As in the case of Medical and Health Sciences, a few journals dominated production in this field, notably two journals: South African Mechanical Engineering (15%) and The Journal of the SA Institute of Mining and Metallurgy (9%) accounted for nearly a quarter of all articles published by South Africans in the field.
SOCIAL SCIENCES
Sixteen magazines account for 50% of production in this area, with an equal split of eight South African and eight foreign magazines. Twenty-one journals in the social and economic sciences account for 50% of all articles produced in this field.
INSTITUTIONAL PATTERNS IN JOURNAL PUBLICATION
In each case (Table 11), the top 3 – 5 South African institutions were then listed, each with the number of authorships in that journal. The results of this analysis of institutional contributions to selected South African journals reveal some disturbing trends.
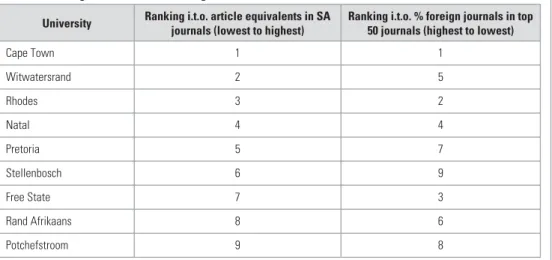
BASIC DEMOGRAPHIC ANALYSES OF SOUTH AFRICAN AUTHORS: RACE, GENDER AND AGE BY SCIENTIFIC FIELD
In each case, one wants to see if the age profiles of articles written by South Africa differed significantly. The final demographic analysis is devoted to the gender profiles of articles written by South Africa.
NOVEL COMPARATIVE MEASURES TO ASSESS THE IMPACT FACTORS AND CITATION PROFILES OF SOUTH AFRICAN JOURNALS
NOVEL COMPARATIVE MEASURES TO ASSESS THE IMPACT FACTORS AND CITATION PROFILES OF SOUTH AFRICAN JOURNALS. Perspectives in Education, Journal of the South African Institute of Mining and Metallurgy, South African Journal of Animal Science, South African Journal of Surgery and South African Journal of Economics).
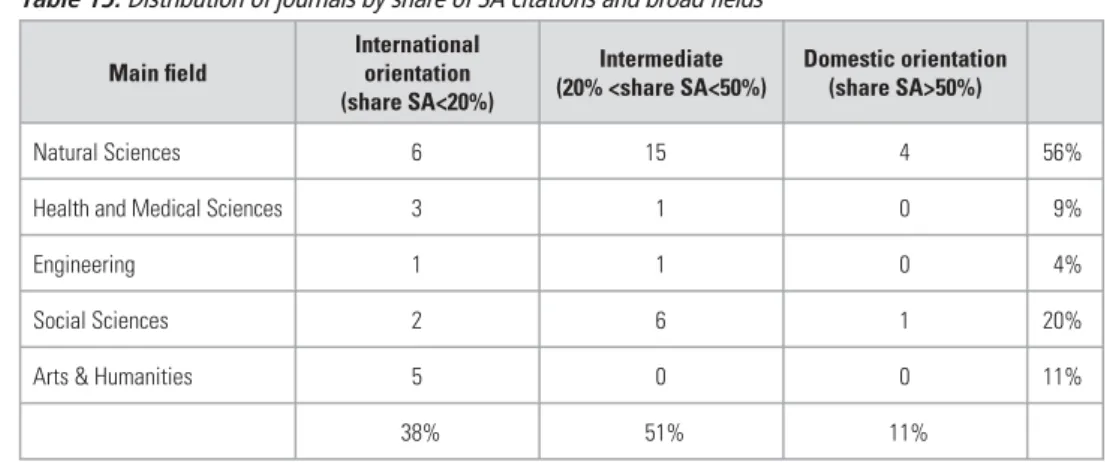
SUMMARY COMMENTS AND CONCLUSIONS
This in itself raises a big question about the international visibility (or lack thereof) of most South African magazines. And perhaps somewhat surprisingly, the five South African arts and humanities journals that generated significant citations all fall into the high international category.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
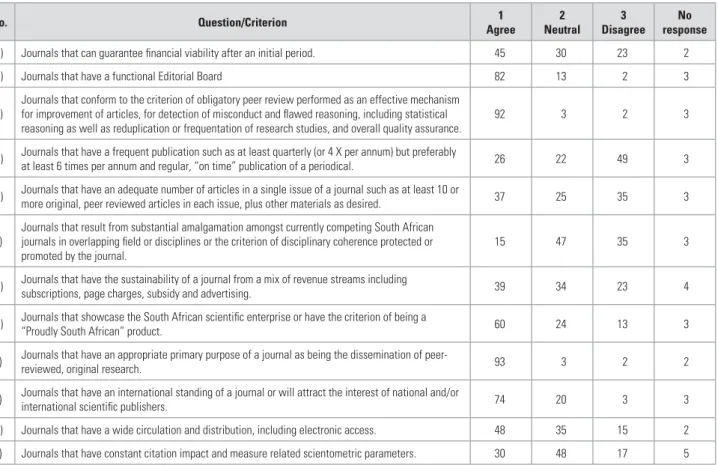
The aim was to obtain relevant opinions and relevant information from this sector, focusing on the project criteria for the accreditation of South African research journals drawn up by the Steering Committee for this project (see Chapter 1) All editors returned the questionnaire by April 2005 and data were captured and consolidated using standard techniques. The following analysis of survey data provides some indication of where South African research journal editors stand in relation to the draft accreditation criteria mentioned above, and examines whether their collective views provide empirical support for these criteria.
THE CRITERION OF HAVING A WELL-FUNCTIONING EDITORIAL BOARD IN PLACE
SURVEY OF EDITORS’ OPINIONS AND RELATED INFORMATION
Only half of the editors responded to this question, and the reason for the low response rate is not immediately apparent. The pattern of interaction was fairly similar for ISI- and DoE-listed journals, but board members of 18 DoE journals and one IBSS journal only interacted annually.
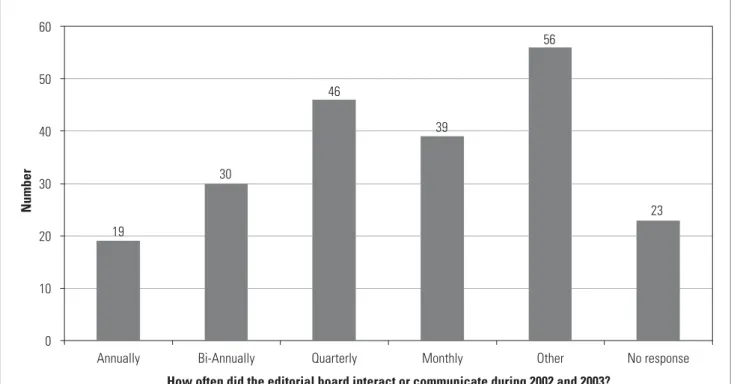
THE CRITERION OF OBLIGATORY, EFFECTIVE PEER REVIEW OF ALL ORIGINAL ARTICLES
One hundred and forty-one of the 213 journal editors indicated that they have a core panel of peer reviewers and 57 said they did not; only three of the fifteen journals included in the ISI list indicated that they had a core panel. One hundred and seventy-one of the magazines indicated that they believed they had a.
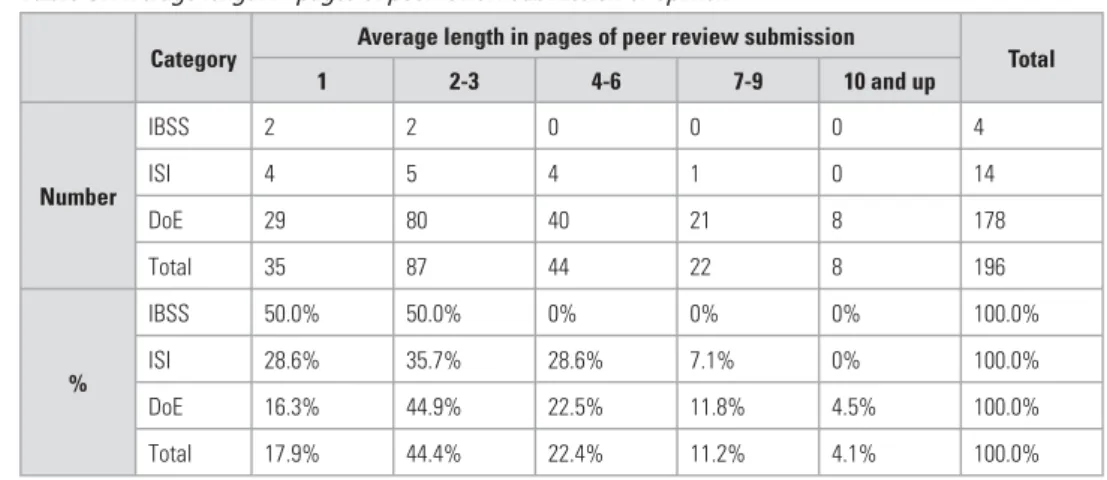
THE CRITERION OF FREQUENT, REGULAR AND ON-TIME PUBLICATION
There are also very compelling arguments for introducing a code of ethics for reviewers and enforcing it at editor or even editorial level where appropriate. While peer review is one of the most fundamental indicators of a research journal's quality, it is how it is used that reflects the journal's standards and indicates the overall quality of the research presented in its pages.
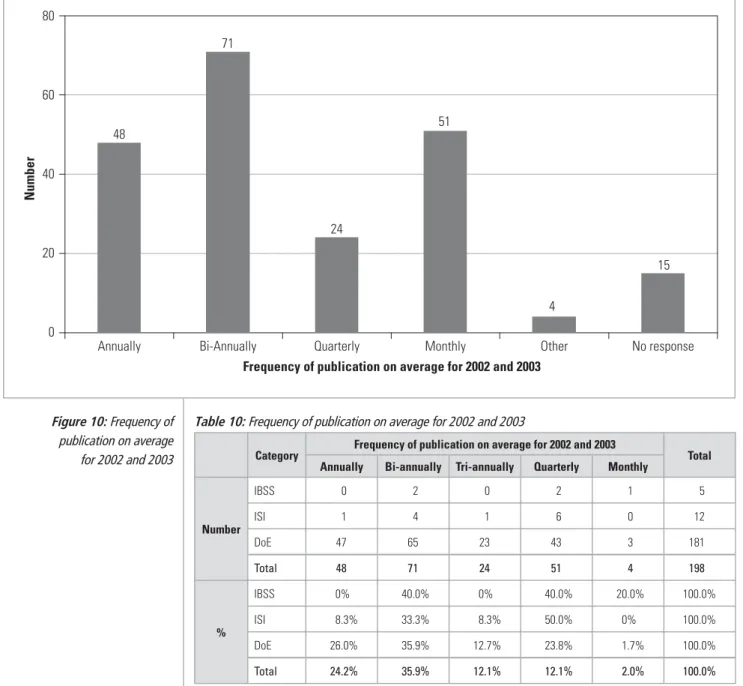
THE CRITERION OF AN ADEQUATE NUMBER OF ARTICLES IN ANY GIVEN ISSUE
THE CRITERION OF DISCIPLINARY COHERENCE, PROTECTED OR PROMOTED BY THE JOURNAL
Smaller fields such as Home Economics and Computer Science do not generate as many articles as larger fields such as Social Sciences and Social Studies, Education and Languages, Linguistics and Literature. Another conclusion could be that the social sciences and humanities were more homeland-focused than, for example, the natural sciences and engineering, either because their quality is not competitive in international terms, or because they are deliberately aimed at a local audience.
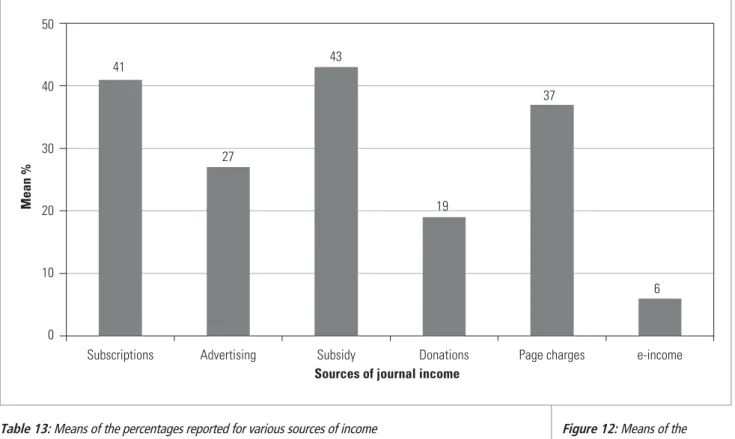
THE CRITERION OF SUSTAINABILITY OF A JOURNAL, ON THE BASIS OF A MIX OF REVENUE STREAMS
Resolution of this matter is critically important to South African scholarship, and one could perhaps distinguish between negative causes (requiring remediation) and positive causes by a more detailed examination of the history of articles submitted to South African journals, ie. THE CRITERION OF THE PRIMARY PURPOSE OF THE JOURNAL IS DISSEMINATION OF ORIGINAL, PEER-REVIEWED RESEARCH.
THE CRITERION OF THE PRIMARY PURPOSE OF THE JOURNAL BEING THE DISSEMINATION OF ORIGINAL, PEER-REVIEWED RESEARCH
THE CRITERION OF INTERNATIONAL STANDING OF THE JOURNAL
THE CRITERION OF PEER REVIEW OF A JOURNAL ITSELF
BIBLIOMETRIC CRITERIA
THE CRITERION OF WIDE CIRCULATION AND DISTRIBUTION, INCLUDING ELECTRONIC ACCESS
The print runs of journals are depicted in the histogram below and a further breakdown is presented in Table 17. In the vast majority of cases the print run was less than 1000; more than 50% of DoE-listed journals had a circulation of less than 500.
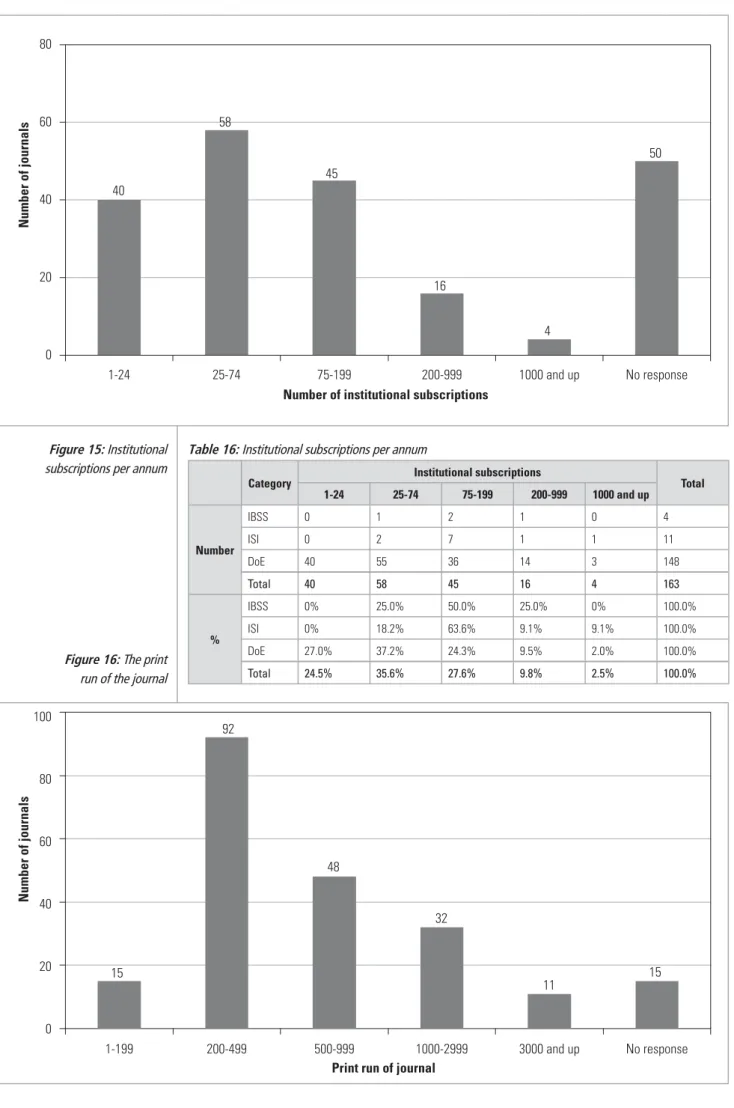
VERIFICATION OF SOME DATA BY DIRECT INSPECTION OF JOURNALS
Low circulations reflect low subscription rates and high costs, as high circulations provide significant economies of scale, including more effective advertising and therefore revenue from this source as well as from the subscriptions themselves. Given that there are now only 21 higher education institutions, albeit several with multiple campuses, the numbers for libraries and teaching departments appeared to be adequate and the journals appeared to be adequately available in South Africa.
EDITORS’ GENERAL OPINIONS REGARDING CRITERIA FOR ACCREDITED JOURNALS
i) Journals that have an appropriate primary purpose of a journal as being the distribution of peer-. revised, original research. 93 3 2 2 . j) Journals that have an international reputation of a journal or the interest of national and/or.
INTRODUCTION
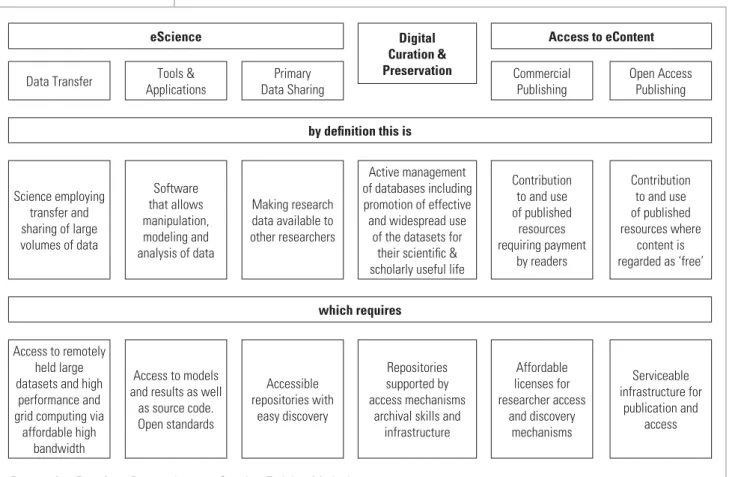
BACKGROUND TO ERESEARCH
Active management of databases, including promotion of efficient and widespread use. of the datasets for their scientific &. Formal (published) scholarly discourse now takes place on the dual playing field of the well-established but embattled terrain of commercial publishing and the emerging Open Access system, which is the main subject of this chapter.
THE INTERNET AND RESULTING NEW DYNAMICS IN SCHOLARLY DISCOURSE
GLOBAL ERESEARCH TRENDS AND THEIR IMPLICATIONS FOR SOUTH AFRICAN RESEARCH PUBLISHING
The search for truth through research depends on the willingness and ability of researchers to expose their new discoveries to peer scrutiny for validity and to participate objectively in the examination of the work of others. Furthermore, the entire community should not be invited to solicit comments as part of the process.
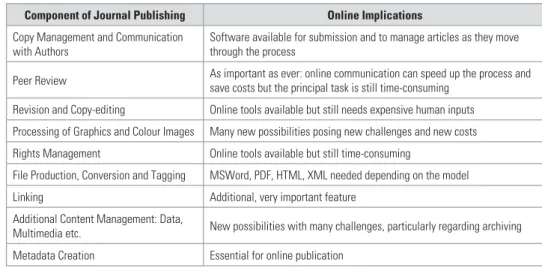
PUBLISHING COSTS
It should be clear by now that online publishing is no simpler than print, and in fact new skills are needed to do it well enough to create the environments users will expect. One of the main advantages of online publishing, visibility, can also be the downfall of non-professional publishers: any mistake will be visible to the whole world.
ACCESS COSTS
In addition, restrictive licenses involve several payments: Universities and research institutions pay for subscriptions and also for copyright and other permissions to use the articles they need.
THE SERIALS CRISIS
The importance of quality maintenance via peer review by active researchers and by editorial judgment remains absolute despite the opportunity and need for improved practice. The role of peer review as a developmental competence for researchers must never be underestimated, nor must it be forgotten that peer review and editing are costly activities.
OPEN ACCESS (OA)
Open Access Statement by the Australian Research Information Infrastructure Committee (ARIIC), 17 December 2004 http://www.caul.edu.au/. The policy will mandate open access to virtually all publicly funded research in the UK.
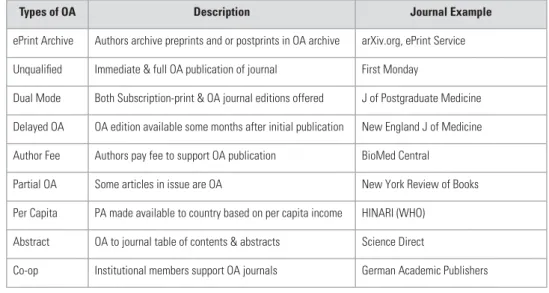
THE VALUE AND IMPACT OF OPEN ACCESS
A 2004 study by Thomson Corporation, publisher of the ISI citation databases, described a survey of 239 OA journals in the Web of Science (WoS) and Web of Knowledge (WoK). The online version of the article may not be used as a postprint, unless explicitly permitted.
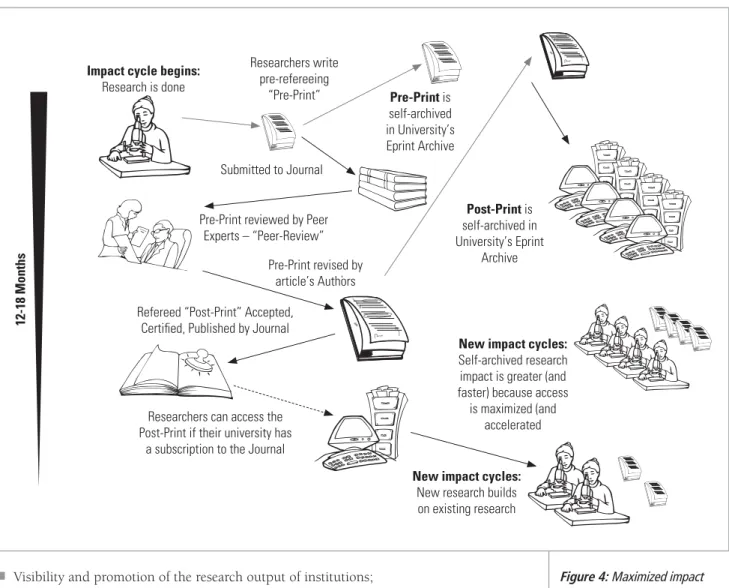
SOUTH AFRICAN DEVELOPMENTS IN PERSPECTIVE
The South African Journal of Science Website (www.nrf.ac.za/sajs/index.stm), as an example of the local situation, is not yet on par with the best international journals. Linking to the full text of the articles is more or less non-existent unless subscribers come in through some other route.
Overlay Journals
UP Research Journal
UP Medres
The value of local journals as a professional communication medium (eg South African Medical Journal, SAMJ) versus their global role in science. Open Access Archiving: A Fast Track to Building Research Capacity in Developing Countries, viewed 22 Dec 2005,
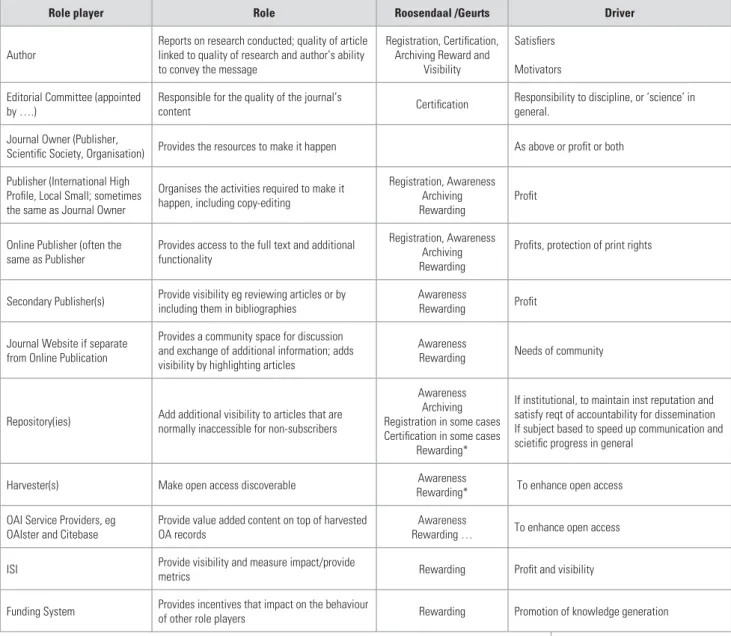
A RESEARCHERS AT HIGHER EDUCATION AND OTHER INSTITUTIONS
CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS FOR A STRATEGICALLY ENHANCED ROLE OF RESEARCH PUBLISHING
What does the research environment demand strategically from the national publishers of research journals. Finally, the issue of the Ministry of Education's accreditation system must be addressed in the system.
B DIRECT AND INDIRECT FUNDERS AND SUPPORTERS OF RESEARCH/QUALITY ASSURERS OF RESEARCH
C NATIONAL BENEFICIARIES OF RESEARCH
D EDITORS AND PUBLISHERS OF LOCAL RESEARCH JOURNALS
Of the journals, 14 are owned by CSIRO while the rest are partnerships with various societies. Summarizing the demands of South African research journal editors and publishers in the context of this chapter is made difficult by the fact that their collective voice has already been heard in Chapter 4.
E ANALYSTS AND EVALUATORS OF RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT (R&D) ACTIVITY
Publications in the peer-reviewed literature, however, are much easier to accept because. This may be an example of a country "pulling itself to its feet" and making a significant contribution to the global issues underlying science in the modern era.
F LEARNERS AND TEACHERS AT SOUTH AFRICAN SCHOOLS
He was twice president of the South African Biochemical Society and president of the South African Academy of Sciences (he is now its executive director). Johann Mouton, MASSAf, is Director of the Center for Research in Science and Technology (CREST) and Professor in the Department of Sociology at the University of Stellenbosch.
THE ORIGINS OF THE ASSAF
About the Academy of About the Academy of Science of South Africa Science of South Africa. Parliament unanimously approved the South African Academy of Science Bill on 26 October 2001, and the Act formally came into force on 15 May 2002.
THE ASSAF IN THE NEW MILLENNIUM
After the appointment of four current members (at least two from personal knowledge of the candidate), new members of the Academy are elected by secret ballot. ASSAf is a member of the InterAcademy Panel (IAP), which has more than 90 members and is based at the Developing World Academy of Sciences (TWAS) in Trieste, Italy.