Where the work of others has been used, this has been duly acknowledged in the thesis. The findings of the study suggest that educators have positive attitudes towards the integration of ICT in education.
Information and Communications Technology Integration in Education
- Introduction
- Background and Rationale
- Research Problem
- Outline of Study
This means that teachers should become effective actors in order to use technology in the classroom. There are also a number of elements that are considered barriers to the use of ICT in the classroom.
Literature Review
Introduction
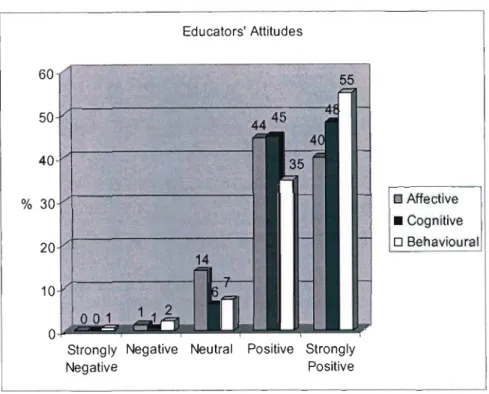
Educators' Attitudes
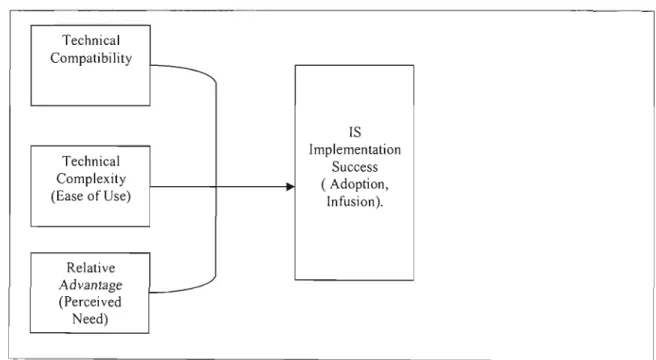
This study addresses the first 4 attributes above in determining educators' attitudes towards technology (Questionnaire, NoJl, Appendix A). Sooknanan's 2002 study in Trinidad and Togo found that relative advantage, compatibility, and observability are significantly related to educators' attitudes toward computers.
Theories Used in Information Systems (IS) Research
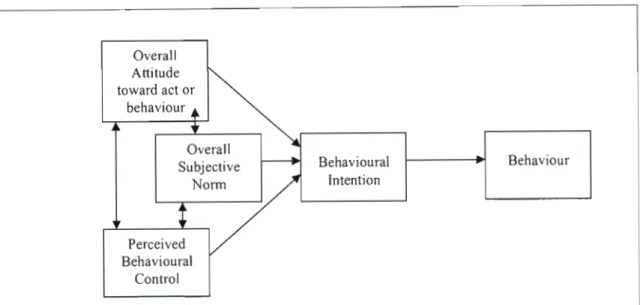
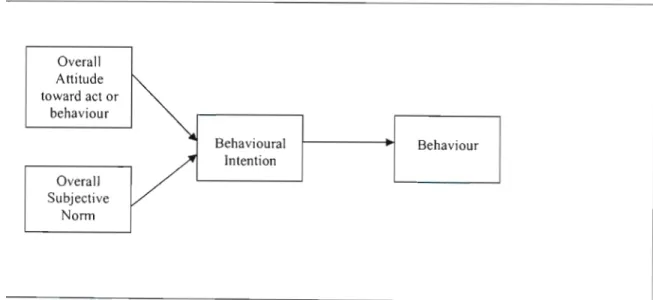
- Theory of Reas oned Action
- Theory of Planned Behaviour (TPB)
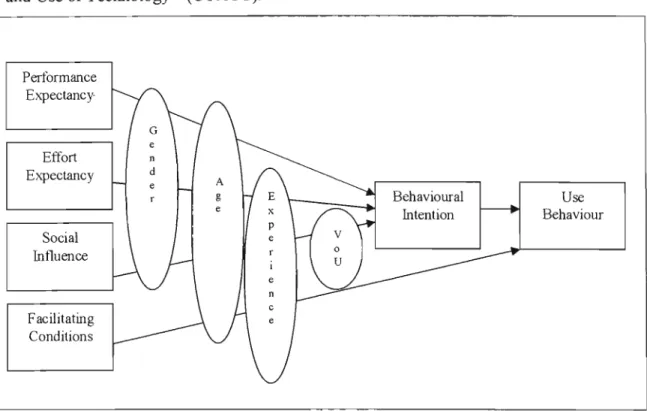
- Uni fied Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology
- Diffusion of Innovations (DOl)
This relates to the non-complexity/simplicity of using computers in the classroom (Questionnaire, No. II, 9-13, Appendix A). These activities focus on integrating the use of technology into the curriculum that a teacher works with.
ICT in Schools
ICT and its Impact
Apple Classrooms of Tomorrow
Discussions with Computer Studies lecturers in Ethekweni region, reveal that they are not aware of the above initiatives. One of the most successful approaches to educator development is the use of educator-led networks (Hadley & Sheingolds 1993).
Obstacles that Prevent the Use ofICT in Schools
Other Barriers to Technology Integration
Research on technology integration suggests that one of the most important factors related to successful integration of technology is effective leadership (Livesay & Murray 1992). A minority of staff remained unconvinced of the computer's potential, and many were dissatisfied with the quantity and quality of professional development in the use of the palm and in lCT in general.
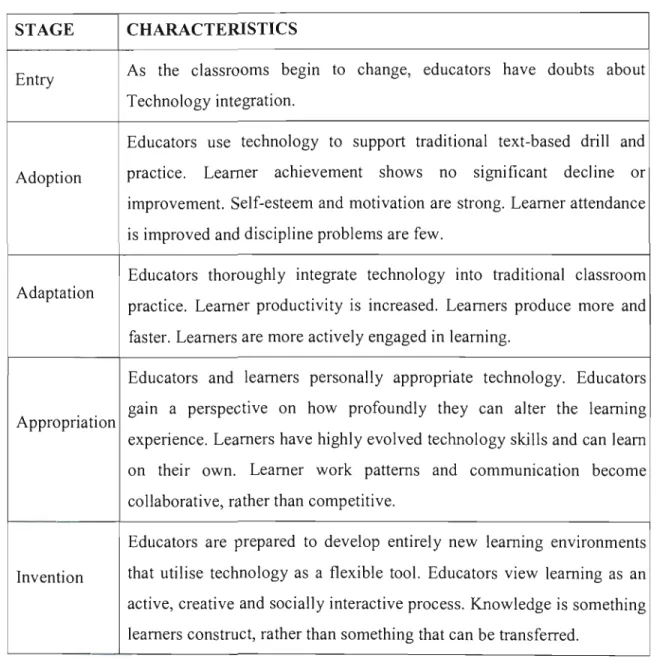
Stages of Development
Drill and practice in the South African context can be seen as automated excessive learning. They choose drill and practice software based on curricular goals and the needs of their learners.
Schools as Organisations
Cuban (ibid.) goes on to describe three possible scenarios for the class of 2003, which he calls the technophile, the conservationist, and the cautious optimist. Schools with computer labs for instruction, in this survey, fall very narrowly into the cautious optimist scenario.
Factors that Encourage Educators to Use Technology
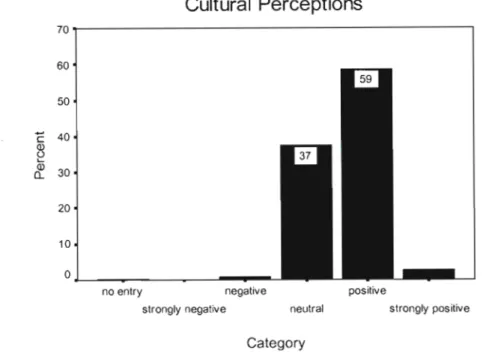
Many teachers (my colleagues) involved in teacher training do not integrate ICT into their teaching, even though they are moderate to very proficient in using computers. In this chapter, teachers' perceptions are analyzed on all the above variables. What are the teachers' perceptions of the cultural relevance of computers to South African society and schools?
The Role of the Educator in Relation to ICT and its Effect on Pedagogy
Studies of Educators Learning to Integra te Technology into their Teaching
McDougall & Squires (ibid) continue to locate each of the above foci within the framework provided by the Perspectives Interactions Paradigm. The total number of secondary schools in the Ethekwini region on the Ministry of Education's EMIS list is 403 per March 30, 2004. Due to the concentration of points, this further supports the use of a linear regression line analysis.
ICT Paradigms in Teacher Education
Reservations about ICTs
Costs and ICTs
It is driven by the changing nature of work, the realities of the information age, new. For each of the 4 topics, at least a level of moderate proficiency (score 3) is required to determine whether an educator has the core competency (score > 11) or not. It is the researcher's opinion that a positive attitude is a necessary, but insufficient, condition for the successful introduction of technology.
International Agencies and Strategies for ICTs and Lifelong Learning
- Ireland
- Portugal
- Finland
- United Kingdom (UK)
- Australia
- Japan
- Pakistan
Concluding Remarks
Ultimately, the adoption of technology is comparable to the adoption of other educational innovations; however, it is even more time-consuming, labor-intensive and expensive.
South African Government Policy Background
Introduction
A Synopsis of the Government's White Paper on E-Education
- Introduction
- ICTs in Schools in South Africa
- The Policy Framework
- Equity
- Access to ICT infrastructure
- Strategic Objectives
- Research and Development
- Concluding Remarks
This White Paper represents a new framework for cooperation between government and the private sector in the provision of KPK in education. 34; Every South African learner in the general and further education and training cohorts will be ICT literate (that is, use ICT confidently and creatively to help develop the skills and knowledge they need to achieve personal goals and be a full participant in the global community) by 2013. According to the White Paper, each school will have a dedicated educator to manage LeT facilities and protect the use of LeT- at school.
A Synopsis of the Government's Electronic Communications and Transactions
- Key Issues
- Chapter Summaries
- Concluding Remarks
Below is a brief description of those aspects of the act that were considered relevant to the school system, as interpreted by Michalsons Attorneys (2002) and Buys (2004). This part of the law defines critical words and phrases and defines the main objects of the law. Cyber inspectors can monitor school websites and investigate whether or not they are in compliance with the relevant provisions of the act.
Design & Methodology
The study
Methodology
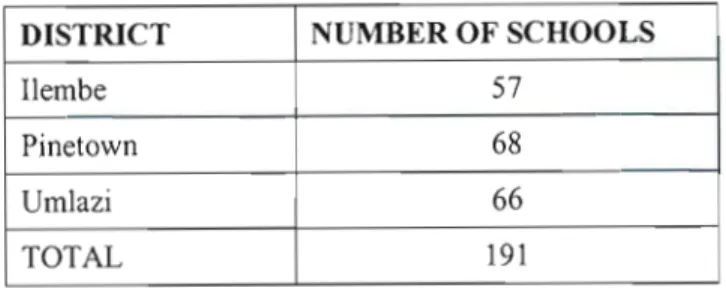
Beyond a certain point (at about 5000 or more), one must sample at least 400 of the population. The researcher believes that the sample is a truly representative sample because every alternative school in a district was selected and it represents 50% of the secondary schools in the Ethekweni region. It is interesting to note that in the Ethelcwini region some of the 403 secondary schools have computer rooms with 10 or more computers.
Questionnaire
Feedback was mainly used to ensure that the scales measure the content area of the study and are culturally and technically appropriate for the context of the study. Descriptive statistics are used to describe and summarize the characteristics of the mass of data collected from the respondents (Diamantopoulos & Schlegelmilch 2000). Regression analysis was used to determine the proportion of variance in teachers' attitudes towards ICT in education that could be explained by the selected independent variables, and the relative importance of each of them in explaining the dependent variable.
Attitudes of Educators
- Introduction
- Research Question One: What are the attitudes of high school educators in KZN
- Discussion of above Results
- Conclusion
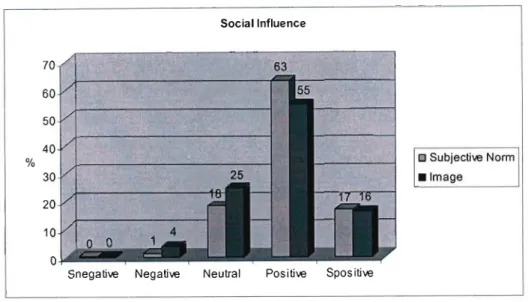
These positive attitudes will encourage the less technologically competent educators to learn the skills necessary for implementing technology-based activities in the classroom (Kluever et al. 1994). In fact, the behavior subscale of the computer attitude scale shows that the majority of educators (93%) intend to learn about computers and use them in the near future. This relationship between attitudes towards eT, and its use in the classroom, has been widely reported in the literature (for example, Blankenship 1998, Isleem 2003).
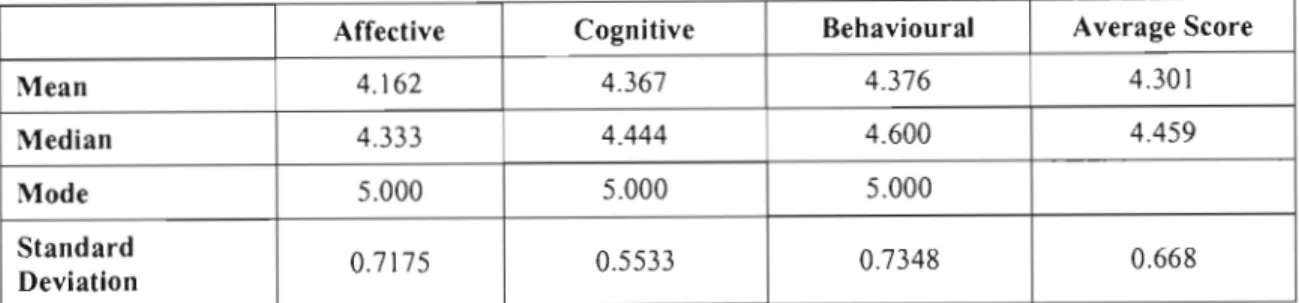
Perceptions' of Educators
- Introduction
- Research Question Two
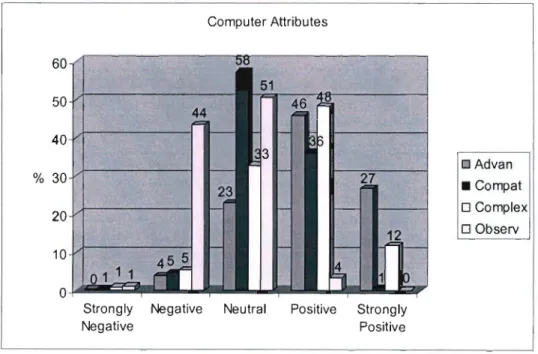
- What are the Educators' Perceptions of Computer Attributes?
- What are the educators' perceptions of the cultural relevance of computers to the South
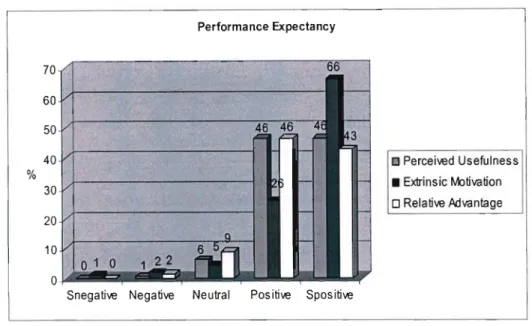
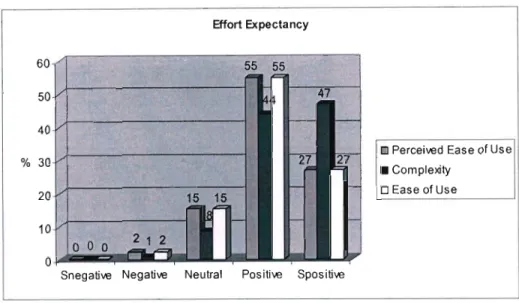
- What are educators ' perceptions of the different constructs extracted from different IS
- Discussion of above Results
- Conclusion
Effort Expectancy is defined as the degree of ease associated with using the system (Venkatesh et al. 2003). Facilitating Conditions are defined as the degree to which an individual believes that an organizational and technical infrastructure exists to support the use of the system (Venkatesh et al. 2003). For the construct "Perceived Ease of Use", at least 83% of respondents were of the opinion that using a computer will be effortless.
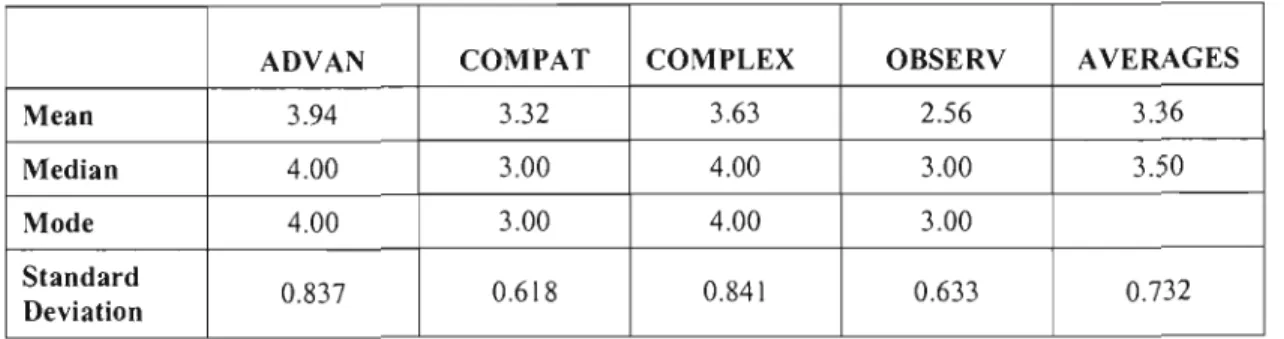
Best Predictor of Educators' Attitudes
Introduction
Research Question Three: What is the best predictor of educators' attitudes toward
- Regression Two - Educator attitudes as a function of the different IS constructs from IS
It is thus possible to reject the null hypothesis that there is no relationship between respondents' "computer attitude" and response to "advantages of computers" as a computer attribute. It is possible to reject the null hypothesis that there is no relationship between respondents' "computer attitude" and response to "computer complexity" as a computer characteristic. The model used is only able to account for 34% of the variance in computer attitude.
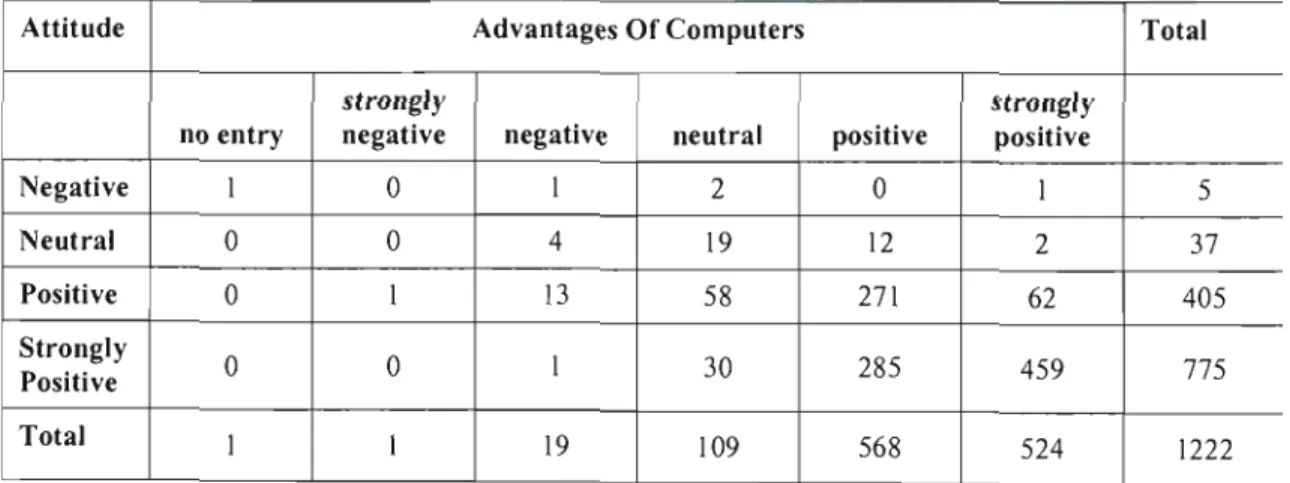
Concluding Remarks
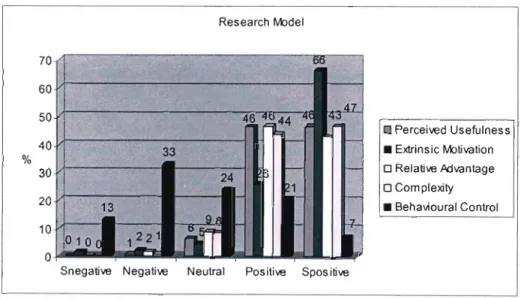
In the second regression analysis, a combination of the different constructs, as drawn from the different IS technology adoption models/theories, is used to attempt to determine the best predictor of teacher attitudes and thus technology adoption. The researcher has statistically shown that the constructs can be used to predict teachers' attitudes towards technology and therefore technology adoption. Our research model (which may be limited to education) has shown that the model can explain as much as 83% of the variance in teachers' attitudes towards technology and therefore technology adoption.
Using Perceptual Control Theory to Analyse Computer Usage
Introduction
Research Question Four: To what extent are educators using computers for general
This could be attributed to the lack of core skills, as well as the lack of access as. For some of these respondents, this is due to the lack of core competencies, as identified in Chapter 6, in which case appropriate training programs are needed. It is quite obvious that the lack of general computer use can be attributed to the fact that.
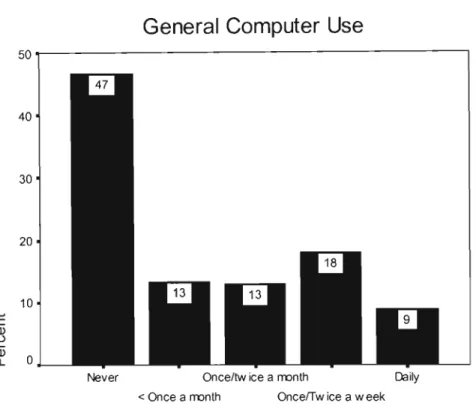
Understanding Purposeful Behaviour: Perceptual Control Theory
- The Control System
- A Hierarchy of Perception and Control
- The Integration of Technology: Why and Why Not?
An Auto-Pilot cruise control system shares a number of characteristics with all control systems. The example of the Auto-Pilot cruise control system can be fleshed out by placing a human pilot into the picture. An Auto-Pilot cruise control system can be used to maintain a constant speed, and so can a human pilot.
Concluding Remarks
The research model (Figure 21) that is proposed also shows a general lack of positive response for the construct Perceived Behavioral Control. A frequency analysis for the constructs of the various IS model theories shows that there is definitely a lack of positive responses for "Perceived Behavioral Control" and. 34;Perceived Behavioral Control' and 'Facilitating Conditions' could be improved, which could result in a better chance of technology adoption by educators.
Challenges for KZN Department of Education
- Introduction
- Research Question Five: What are the ICT related challenges faced by the
- Results
- Discussion
- Overall Proficiency in Technology
- Discussion
- Discussion
- Conclusion
Each of the country's nine provinces assumes responsibility for primary and secondary education within the provinces, through provincial education departments, while higher education continues to be administered by the National Ministry of Education. The South African Cabinet and Council of Education Ministers (CEMs) approved this recommendation in the year 2000. Within the KZN environment, the researcher identified teachers' lack of knowledge and skills as the main barrier to the department achieving their ICT goals. identified in the White Paper on e-Education (DOE 2003).
Issues and Recommendations in Educator Professional Development ................. 1 73
- Access
- Software Tools
- Curri culum Reso urces
- Overlo aded Curriculum
- Educator Preparedness
- Higher Order Teaching and Learning Theories
- Sustainable Educator Professional Development
- Modeling Behaviour
- Mentoring
- Practical Exarnples
- Educator Overload
- Educator Assessment
- Quality of Resources
- New Educational Structures
- Specialised Resource Centres
- Availability of Research
- Learner Success
- Other Points of Concern
- Knowledge-based Society
- Equity
- RateofChange
- Plannin g
- Funding
- Local versus Global
- Education Reforrn
- Quality Assurance
- A Proposed Process for Educator Professional Development
- Concluding Remarks
Without Internet access and sufficient quantity and quality of equipment, educators are unlikely to be highly motivated to participate in LeT-related professional development activities. Strategies should be developed that would capture the rural education population, which may not have access to the professional development activities of urban educators. There is always the question of whether professional development source material should be developed in the "home" country, or obtained from external sources.
Conclusion & Recommendations
Educators' Attitudes
Educators' Perceptions
Technology Use
Equal Access and Equal Competence
Recommendations
Professional Development
Conclusion