Employees in the decision-making process 64 Table 5.3: Cross tabulation of work level and responses regarding non-participation e. Employees have in the decisions made within their enterprises 67 Table 5.7: Frequency and percentages of responses to the degree of participation in.
Abstract
Chapter One: Problem Statement and Purpose of the Study
- Introduction
- Problem Statement and Purpose of the Study .1 Problem Statement
- General Purpose of the Study and the Main Research Questions
- Research Objectives
- Delimitations and Limitations of the Study
- Significance of the Proposed Study
- General Structure of the Dissertation
- Rwanda in Context: its Localisation
The purpose of the study is to determine the state of employee participation in decision making in public enterprises, especially in the communication area in Rwanda. In this regard, the issue of employee participation in decision-making (in public enterprises) is not well studied.
I TANZANIA
It seems necessary to briefly locate Rwanda to give readers a general idea of this country.
Chapter Two: Theoretical Framework
Participation Concept
- Definition
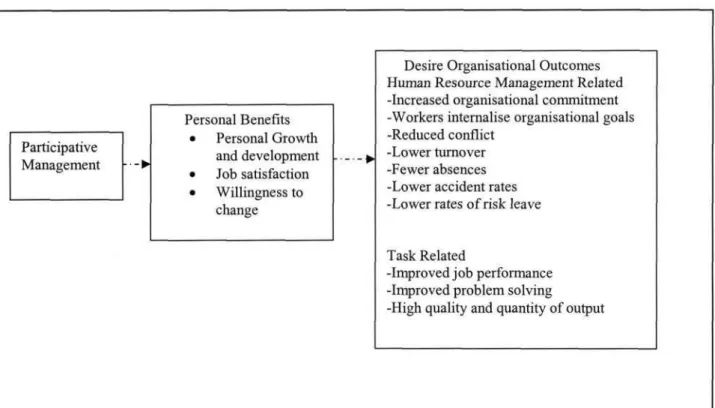
- Reasons for Employee Participation
- The Promotion of Satisfaction and Personal Development of the Worker
- The Extension of Democracy
- Participation as a Means of Improving Industrial Relations
- Participation as a Means of Increasing Efficiency
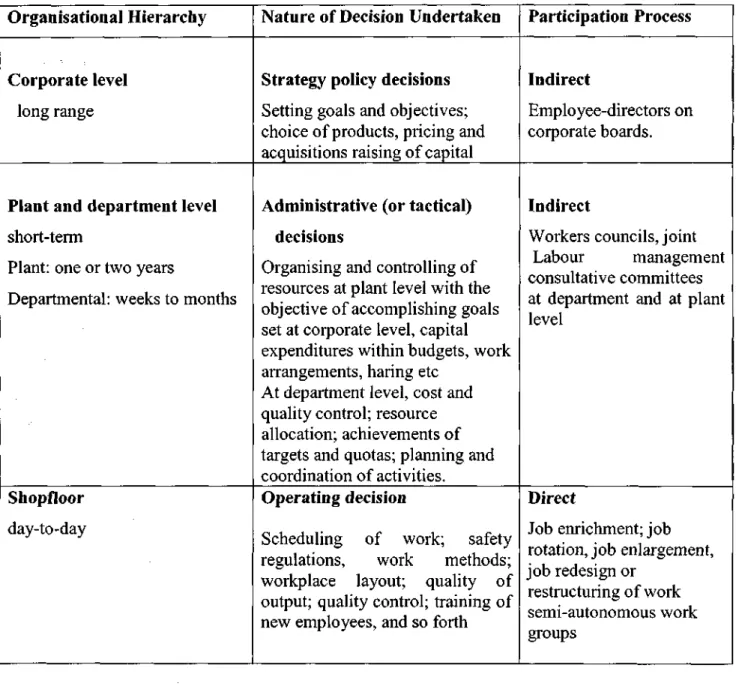
- Types of Employee Participation
- Direct Participation
- Indirect Participation
- Forms of Employee Participation: an Overview
Viteles cited in Clarke et al. have indicated that employee participation in decision-making in a democratic atmosphere created by "permissive" management facilitates. Torres makes a strong case that the essence of workplace participation lies in being involved in decision-making.
Collective Bargaining
The ultimate goal of some proponents of power-oriented participation is to change the basic authority relationship in the industry as a means of changing the character of society (Clarke et al., 1972).
Works Councils
Workers' Representation on Company Boards
Shop-floor Participation
- The Degree of Employee Participation
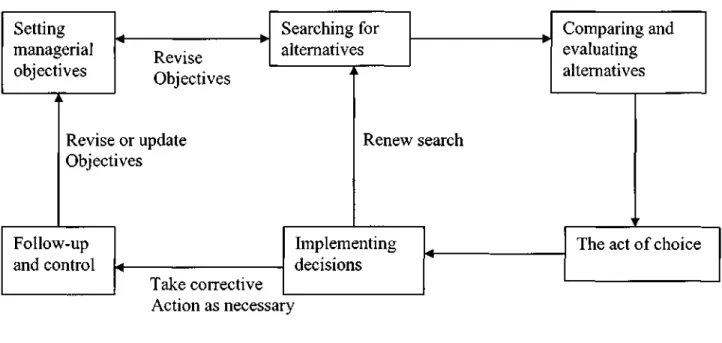
- Decision-making Concept
- Steps of the Decision-making Process
- Types of Decisions
- Some notions on Public Enterprise Concept
- What is a Public Enterprise?
- Why Public Enterprises?
- Public Enterprises in Rwanda: A brief Overview
From the definition of the term 'decision' it is clear that a decision-making activity is generally not accomplished by the isolated action of the decision maker. In the case of the bounded rationality model, the decision maker uses the satisficing technique by selecting the first alternative that meets the minimum criteria. 2nd step: Search for alternatives: In the decision-making process, the search for alternatives involves scanning the internal and external environment of the organization for information.
Choice is a moment in the ongoing process of decision making when the decision maker chooses a given course of action from a set of alternatives. Bass cited by Harrison (1987) indicates that decision making is an orderly process that begins with the discovery by the decision maker of a discrepancy between the perceived state of affairs and the desired state. According to him, groups provide an excellent vehicle for carrying out many of the steps in the decision-making process.
Chapter Three: Literature Review
Employee Participation in Decision-making: General Research Studies
Levine and Tyson (1990) (cited in Maree, 2000) conducted research that examined how employee participation in decision-making affects corporate performance. Thus, Locke and Schweiger, despite their critical attitude towards employee participation in decision-making, found that in 60% of the cases they analyzed, participation improved employee morale and job satisfaction. It was therefore impossible to draw conclusions about the effect of only the participation of workers in decision-making.
Of the twelve multivariate field studies reviewed by the authors, between two and nine changes were implemented along with employee participation in decision-making. Schweiger and Locke (1979) (cited in Maree (2000)) argued that the benefits that empirical studies show of employee participation in decision making are usually of two types. However, it is much more common for employee participation in decision making (WPD) to result in better morale and job satisfaction than greater productive efficiency (Maree, 2000).
Employee Participation in Decision-making in Public Enterprises
In this regard, organizational leaders in the public sector should emphasize changing organizational culture from the traditional pattern of hierarchical structure to participative management and empowerment. Based on a survey of government agencies, Berry and Wechsler (1995) cited in Soonhee (2002) found that a participatory process, such as the inclusion of lower level staff in a strategic plan development, is one of the trends in the evolution of strategic planning in the state is. agencies. For example, the number of employee grievances in the Postal Service was significantly reduced, and delivery routes were reconfigured for efficiency improvements.
The findings, particularly related to the postal service as a public enterprise, showed that for many years, particularly in the 1960s and 1970s, Australia Post was regarded as an inefficient and strike-prone organization that embodied the worst aspects of public sector management and industrial relations and employees. In the latter half of the 1980s and early 1990s, however, it embarked on a major program of consultation-based structural and technological change. 34;While significant progress has been made with structural efficiency, management will need to maintain momentum for change and persist in consultation and collaboration if Australia Post is to continue to raise performance levels" (Lansbury and Davis.
Conclusion
Chapter Four: Research Design and Methodology
- Research Methodology and Procedure
- Research Design
- Population and Sample
- Sampling Methods and Selection of the Subjects
- Source of Information
- Instrumentation
- Validity and Reliability of the study
- Data Analysis Methods
- Descriptive Statistics
- The Chi-Square Test
- Conclusion
On the one hand, it had the potential to increase the degree of representativeness of the study. Documentary sources thus played an important role because they helped the researcher to understand the concepts more clearly and orient the research based on the previous research studies. Regarding the extent of participation, respondents were asked to indicate whether this was Very high (code = 1 ), High (code = 2), Average (code = 3), Low = (code 4) and Very low ( code = 5) according to their daily observations.
In conventional usage, the term validity refers to the extent to which an empirical measure adequately reflects the real meaning of the concept under consideration (Babbie and Mouton, 2001). Reliability: Showing that research operations in terms of data collection, data analysis and so on can be repeated and the same results obtained. In short, this part of the research seems to be a fundamental factor in giving the importance of this study, because thanks to it the validity and reliability of the study can be established and achieved.
Chapter Five: Results and Discussion
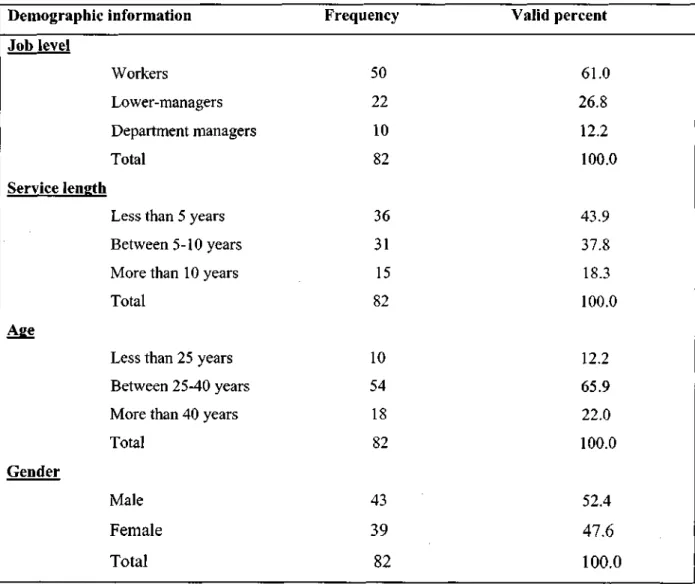
- Demographic Results and Discussion
- Perceptions of respondents Regarding the State of Employee Participation in the Public Enterprises of Communication
- Non-Participation of Employees in the Decision-making Process
- Degree of Influence which Employees have in the Decisions Made at Different Levels
- Degree of Participation in the Public Enterprises of Communication within Rwanda
- Desire for Participation
- Forms of Participation Practiced in the Public Enterprises of Communication
- Impediments to Employee Participation in Decision-making
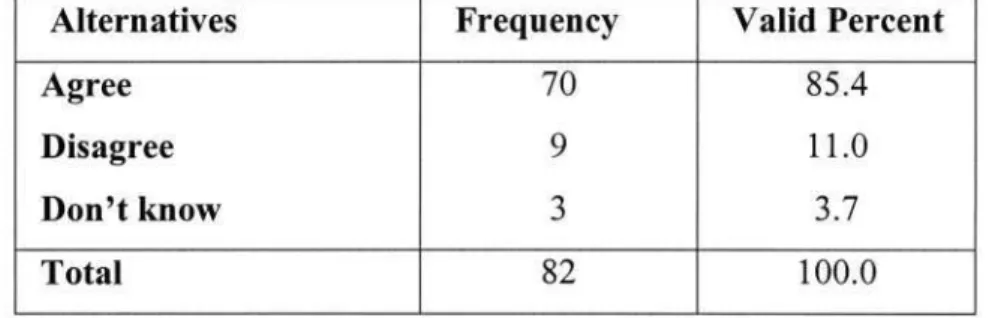
From these findings, it can be seen that most of the respondents, 85.4 percent, have recognized the existence of non-participation of employees in the decision-making process. Therefore, the degree of influence that employees' ideas (viewpoints) have can be an important indicator that can reveal a situation of employee participation in the decision-making process. Based on these findings, some conclusions can be drawn about the state of employee participation in the decision-making process.
First of all, it can be confirmed that the majority of employees do not participate in the decisions that are made in public communication enterprises. In other words, there is a major exclusion of subordinate categories of lower managers and workers in the decision-making process. On the basis of the above test, it can be concluded that there is a statistical connection or relationship between the hierarchical level of employees and the extent of participation in the decision-making process within public communication enterprises.
Chapter Six: Conclusions and Recommendations
Conclusion
The results show that the level of participation in public communications companies in Rwanda is very low. The “person Chi-Square” output confirmed that the observed differences are statistically significant. Therefore, it was concluded that such differences exist within the public communications companies. Considering the above findings, the participatory communication process within the public sector enterprises must take place at a number of levels, that is, at all levels, but with the greatest emphasis on the workplace.
According to the results, personal participation is widely needed within the public enterprises of communication in Rwanda through the emphasis on a greater say at task levels. On the other hand, the results showed that even the representative form, which was introduced in the public communication companies in Rwanda, it does not work correctly or effectively. From the results it was noted that there are other participatory form used in the public communication companies in Rwanda.
Recommendations
- Government
- Top management
The Rwandan government must realize that employee participation in decision-making is one of the most important elements that can improve the management of public enterprises in general and communications companies in particular. This local organization should help support and maintain employee participation in the decision-making process in this area. In this regard, future research on employee participation in decision-making in Rwanda should focus on the following areas:
Perceptions of public company managers about employee participation in decision-making process within the public companies. A comparative study of employee participation in the decision-making process between public and private enterprises in Rwanda. The influence of participation in decision making within the enterprise bargaining context: implication for job satisfaction and affective commitment.
Questionnaire
If you disagree, or want to have a personal say in the decisions you make in the workplace. I would like more say in the decisions related to the management of my own department I I I would like more say in the management of the entire institution I Do you think that your representative has enough say in the decisions made in your workplace.
I would like him (her) to have more say in matters directly related to my work and working conditions. I would like him (her) to have more say in decisions regarding the management of my Department. Apart from the forms of participation mentioned in the eighth question, are there any other forms of employee participation in decision-making in your enterprise.
Section A: Information Demographique
Sujet : Participation des salariés à la prise de décision au sein des entreprises publiques : cas des entreprises de communication rwandaises. Cette recherche est menée pour identifier les perceptions des employés des entreprises publiques de communication (Rwandatel et Post) quant à leur participation au processus de prise de décision. Votre entreprise (comme d’autres entreprises publiques) est critiquée pour la non-participation des salariés aux prises de décisions.
Lorsque les décisions sont prises à tous les niveaux, les opinions des employés ont une certaine influence. Participation des employés à travers des conseils ou comités d'employés • Participation des employés aux niveaux départementaux inférieurs I I. Outre les formes de participation mentionnées à la question 7, il existe d'autres possibilités de participation des employés à la prise de décision dans votre entreprise.