The goals of the study were to determine whether unfair discrimination in employment is being eliminated; to determine whether a diverse workforce representative of the population is being achieved and to find out whether economic development and workplace efficiency are being promoted. The final goal of the study, therefore, is to find out if the Sharks Board is promoting economic development and efficiency in the workplace; indicates that this process has started.
BACKGROUND OF THE STUDY
Finally, the report showed that the implementation of Employment Equity legislation in South Africa was a steady process. Just as the activists of the developing world are angry that even after the 14th World AIDS Conference not enough was done to stem the tide of death and the disease, the same applies to the Equal Employment Act, as not much progress has been made. place to achieve expected results.
MOTIVATION FOR THE STUDY
Through questionnaires and face-to-face interviews, he audited staff perceptions of Employment Equity to understand current perceptions, beliefs and attitudes within the organization and the results will enable Natal Sharks Board management to identify those processes that will drive recruitment. Equity, as well as those who will undermine it. The results will enable Natal Sharks board leadership to identify those processes that will promote employment equity and those that will undermine it.
PURPOSE OF THE STUDY
AIMS OF THE STUDY
HYPOTHESES
SIGNIFICANCE OF THE STUDY
In Canada, the Employment Equity Act and the Federal Contractors program announced in 1986 were designed in similar ways to the American Affirmative Action Program. This study aims to provide a formal audit of the perceptions of the Employment Equity Act at the Natal Sharks Board and correct any unfounded perceptions.
LIMITATIONS OF THE STUDY
Changes in conditions within the Natal Fisheries Board, discussed in the organizational survey, further necessitated this study.
DEFINITION OF CONCEPTS
NATAL SHARKS BOARD is a provincial statutory body established in terms of Regulation No. 1 0 of 1964, as amended, for the principal purpose of approving, monitoring and initiating measures for the protection of swimmers from shark attacks.
ORGANIZATION OF THE STUDY
CONCLUSION
INTRODUCTION
In their analysis of businesses in post-apartheid South Africa, Adam and colleagues (1997) found that the great inequalities in South African society were structured along racial lines and arose mainly from uneven development arising from. The democratic government in South Africa has begun implementing strategies that address the need for strategic intervention in the economy.
THE EMPLOYMENT EQUITY ACT
The concept of social equality in the South African context cannot only be seen from a human rights perspective. This had to be done with enormous conviction if the South Africans were to meet the challenges ahead.
THE PURPOSE OF THE EMPLOYMENT EQUITY ACT
Although the wording of Section 20(5) is open to different interpretations, it is suggested that the intention of that section is to prescribe that unfair discrimination based on a person's lack of relevant experience is unlawful. The requirement does pose a challenge to recruiters on how to assess a person's ability to acquire skills, particularly in light of the restriction on the use of psychometric tests.
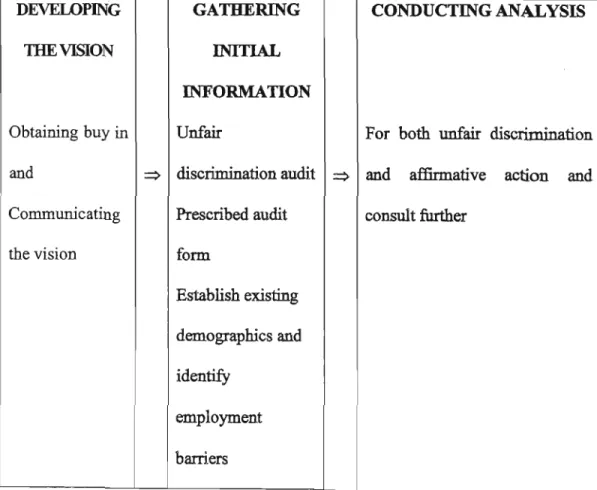
THEORETICAL PERSPECTIVES ON EMPLOYMENT EQUITY
In the context of South Africa, where the majority have been excluded by discriminatory practices, this means that a significant part of the productive population is underutilized. Eliminating the inequalities of the past and ensuring sustainable growth and development in the future. Finally, the Institute's response to the bill, as it then stood, warned that there was a threat that US case law might cloud our Court's interpretation of the Act.
One of the most important pieces of legislation to deal with leaders and managers at all levels within South African organizations is the Employment Equity Act No.55 of 1998. It is believed that the extent of implementation by employers can be categorized eventually under these three main headings: -.
PREVIOUS STUDIES ON THE EMPLOYMENT EQUITY
Third, considerable experience of Affirmative Action in practice, both of a positive and negative nature, has been gained in the United States of America. Companies had to realize that Affirmative Action is not limited to black people, but also includes women and the disabled - all of whom have been disadvantaged in the past. Affirmative Action was not new to South African business, although it had existed under different banners in the past.
Limiting our policy goals to formal workplace equality in South Africa would similarly ignore the social context of inequality and disadvantage. Some of the inadequate assumptions about the characteristics of the ideal worker that served to marginalize women in the labor market were as follows: -.
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT & EFFICIENCY IN THE WORKPLACE
It also tells us that without legislation, employers will not address the inequalities our history has created. To this end, Natal Sharks Board tenders are awarded by the Ministry of Works in accordance with the attractive procurement policy. A thesis conducted by Gounden (2000) concludes that the National Department of Public Works encouraged greater participation of favorable business firms in the economy through its affinnative action policy and that the adoption of the affirmative action policy resulted in the government bearing a limited financial premium compared to the original intended results and overall benefits. The road to establishing women as human beings and ordinary workers clearly remains long, as does the road to equal opportunities in the labor market.
In the words of Canadian Justice Abella, who reported to the Royal Commission on Employment Equality: "Equality is not a concept that creates the same results for everyone. Employment equality is access to the greatest opportunity to realize an individual's potential. Sometimes equality means treating people the same , despite their differences, and sometimes that means treating them as equals by accommodating their differences.
CONCLUSION
Employers generally recognize the need for workplace transformation - the debate is exactly how that transformation should be managed. There have also been arguments that the Employment Equity Act perpetuates racism and that similar initiatives internationally such as in the US have been unsuccessful and are currently being rolled back. Perhaps it would be fair to summarize these opinions as acknowledging the need for transformation, but not accepting that social engineering will necessarily be successful.
CHAPTER THREE
INTRODUCTION
RESEARCH METHOD
- RESEARCH METHOD
- ORGANISATIONAL SURVEY
- RESEARCH INSTRUMENTS
- QUESTIONNAIRES
- INTERVIEWS
- ETHICAL GUIDELINES
- DATA COLLECTION
- DATA ANALYSIS METHOD
- CONCLUSION
Validity depends on the skill Validity depends on the researcher's competence. Because organizational surveys require the allocation of valuable resources, their timing and frequency are critical. The timing of any organizational research is a key aspect of the entire process. Codes of ethics for conducting research with human participants state that such research must be conducted with respect and concern for the dignity and well-being of the people participating in the study.
To achieve the objectives of the study, data were collected through questionnaires and face-to-face structured interviews. Permission to conduct the tID.S study was obtained from the CIDef Executive Officer of the Natal Sharks Board.

CHAPTER FOUR
INTRODUCTION
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE RESPONDENTS
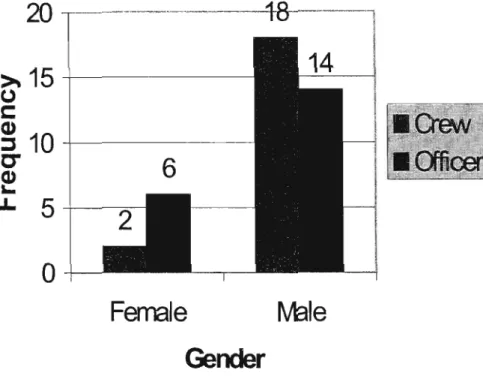
Female
Gender
IVtale
QUANTITATIVE DATA : DISTRIBUTION OF RESPONDENTS' RESPONSES TO DISCRIMINATION QUESTIONS
However, a significant majority believed there was racial discrimination in relation to work environment and facilities (28%), training and development (28%) and promotions (23%), while a significant minority did not know or did not respond to related to demotions (40%), succession planning (38%) and pre-employment testing (28%).
QUANTITATIVE DATA : DISTRIBUTION OF RESPONDENTS' RESPONSES TO DISCRIMINATION QUESTIONS
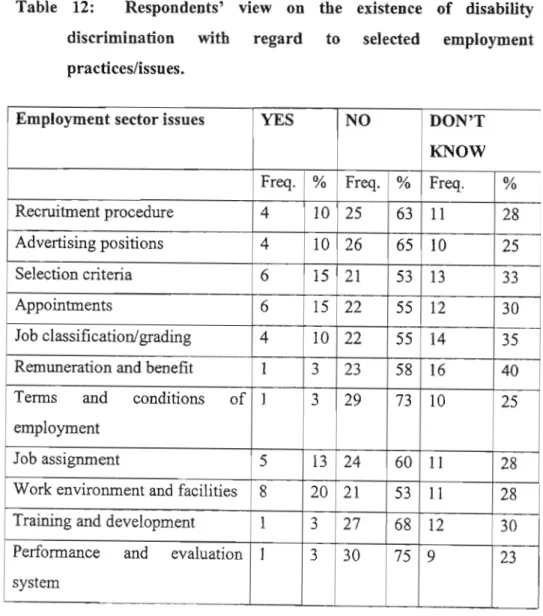
Nevertheless, a significant minority believed that there was gender discrimination in terms of hiring (20%) and job duties (20%). Another significant minority did not know or did not answer regarding the selection criteria (33%) and remuneration and benefits (33%). Nevertheless, a significant minority believed that there was disability discrimination in relation to working environment and facilities (20%), while a significant minority did not know or did not answer in relation to remuneration and benefits (40%), promotions (38%), job classification /grading (35%), succession planning (33%), selection criteria (33%) and pre-employment testing (33%).
QUALITATIVE DATA: RESPONDENTS' RESPONSES ON THE FOLLOWING SECTIONS
- Retirement Benefit and employment equity in relation to race, gender and disability discrimination
Statements about discrimination based on race, gender and disability in relation to advertising were made by 47.5% of respondents. Statements of discrimination on the grounds of race, gender and disability in relation to appointments were made by 65% of respondents. 77% of respondents made positive statements about race, gender and disability discrimination in job assignment.
Statements of discrimination based on race, gender and disability in relation to transfers were made by 20% of respondents. Positive statements regarding race, gender and disability discrimination in relation to demotions were made by 80% of respondents.
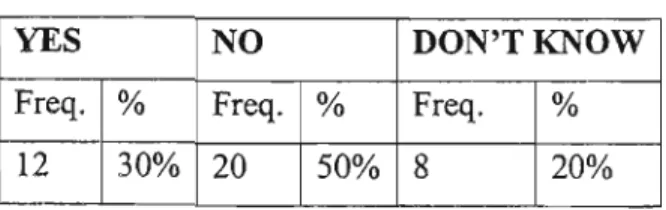
CONCLUSION
INTRODUCTION
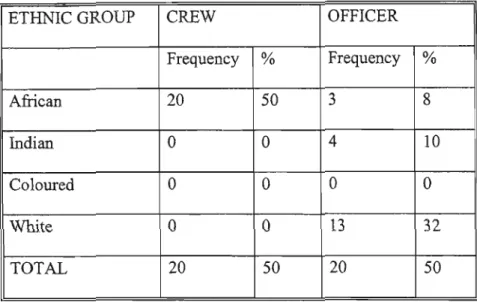
CHARACTERISTICS OF THE RESPONDENTS
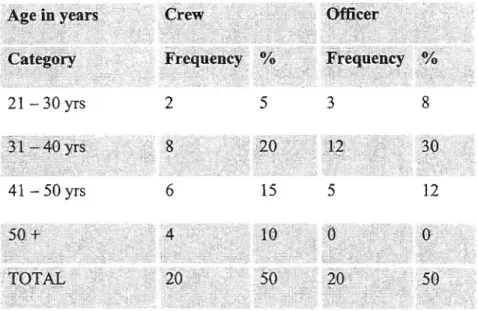
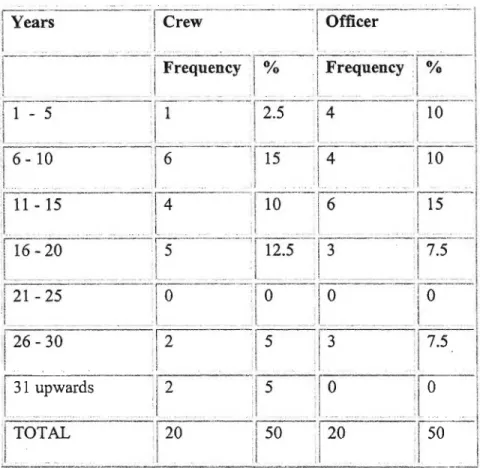
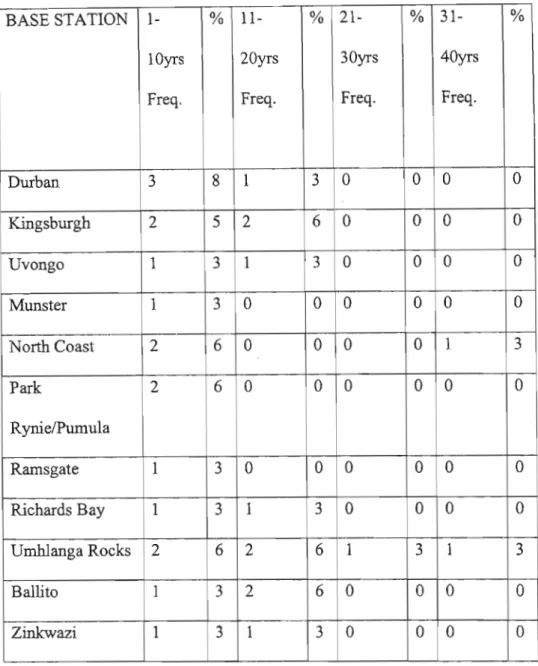
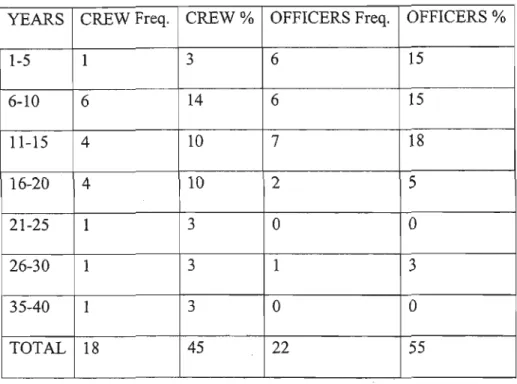
Of the Crew participants, 16 had a work experience between 1 and 20 years, while 4 of them had a work experience of more than 26 years. Of the Officer participants, 17 had work experience between 1 and 20 years, while 3 of them had work experience of more than 26 years. Similar findings were made by Eberhad and Van Horen (1996), who found that there is enormous inequality in South African organizations, structured according to uneven development arising from the policies of the previous government.
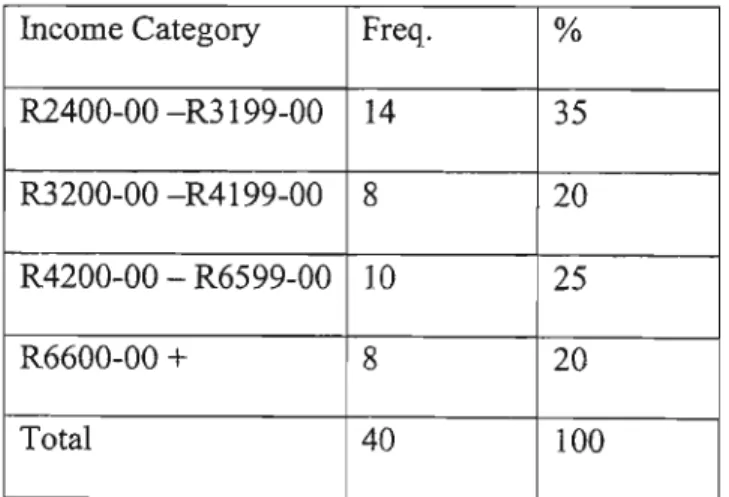
His study even made recommendations that strategic interventions by the state are needed, primarily based on the promotion of social justice. Westcott (1998) argued that if a cleaner in one of the large South African companies receives RI800-00 per month, the CEO is likely to earn more than R50 000-00, a ratio.
ELIMINATION OF EMPLOYMENT
When the new Employment Equity Bill becomes law, the government can sink its list back into the belly of corporate South Africa by wrestling the ratio down to just twelve.
THE PROCESS OF ACHIEVING A REPRESENTATIVE WORKFORCE
PROMOTION OF ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT AND EFFICIENCY IN THE WORKPLACE
CONCLUSION
The objectives and hypothesized statements of the study were clearly stated, as well as the manner in which they were measurable. The issue of the review of the Employment Equity Act 55/1998 based on perception among the Natal Sharks Board entity was clearly identified as something in need of investigation as undertaken in this study. Thus, without an employment equity law, the racial practices of the past are likely to continue in practice.
The results of the study as well as the literature show that an elimination of discrimination at work is observed and that there is a change in the diversity of the workforce as well as economic development and efficiency at the Natal Sharks Board. . That there should be further research into the implementation of effective strategies for economic development and efficiency at the Natal Shark Council; as soon as the Natal Sharks Council takes over the responsibility of the process of economic development at the Works Department.