The primary objective of the study is to determine the role that middle managers play in the strategy implementation process within Brandhouse's sales department. The research results show that middle managers play a crucial role in facilitating the effective implementation of strategy.
Background
The Research Problem
The challenge to the idea that middle managers were merely involved in implementing the strategies developed by senior managers comes mainly from the amalgamation of three separate ideas. The author studied Brandhouse to provide a more detailed example of the difficulties of the role played by middle managers within the sales force department.
Research Objectives
Purpose of the study / Objectives
Research Questions
Research Methodology
Limitations of the study
Conclusion
The context of the study will be reviewed through a literature review in the next chapter to gain a deeper understanding of the role that middle managers play in the strategy implementation process.
Literature Review
Introduction
Defining Strategy
He also describes strategy as the bridge between high-order goals or policy on the one hand and concrete or tactical action on the other. According to (Lynch, 2013), a company strategy is the plan or pattern that integrates organization's main objectives, policies and action sequences into a unified whole.
Strategy Implementation
- Action Planning
- Organizational Structure
- Human Resources
- The Annual Business Plan
- Monitoring & Control
Most organizations and leaders make common mistakes by not taking responsibility for the strategy implementation process. All necessary technology must be in place to ensure management keeps up with implementation.

Middle Managers
First, top management should be involved in strategy formulation to ensure full support for the strategy and in the development of their action plans. But in order to be actively involved in strategy implementation, it is crucial that they believe in themselves as the main driving forces and at the forefront of strategic change (Doll, 2013).
Uncertainty
Middle managers play a crucial role in driving strategic objectives defined by top management, they drive the strategic change programs and they are the key strategic drivers of the emergence of strategic changes. In many cases, middle managers are seen as the drivers of change, the drivers of strategic change.
Strategic Planning
Structure forms the framework for the organization's activities and must harmonize with the organization's goals and objectives. Most organizations develop strategies to move the organization from the current state to the desired future state.

Resistance to strategic change
Restructuring – The current organizational change can handle a change involving a sudden change in market conditions. Evolution – This strategy involves fundamental changes in the way the organization must deal with the situation, but this can only happen overtime.
Reasons for resistance and how to overcome resistance
Adaptation – Incremental change can be facilitated by actual organizational change to achieve desired goals. The ideal situation is that the organization should become a learning organization in order not to manage this change.
Elements of the implementation process
- Main elements of the implementation process
The role of leaders in any organization is to decide which strategy the organization will follow and the chosen strategy will then have to be put into action to achieve the desired goals.
Nine schools of thoughts
This is where all steps in the strategic planning process must be followed to prepare the plan. Dynamic Competition – This statement identifies action and implementation as being more important simply because the ever-changing environments in which organizations operate therefore invalidate positioning frameworks as well as static planning.

Strategy - Competitive Advantage
Suppliers can influence the availability, cost and quality of raw materials for organizations in the industry. ii) Purchasing power. Competitors offering undifferentiated products and services in the market will reduce the attractiveness of the market. iv) Threat of substitution.

Strategy as a learning process
Close substitutes can increase the chances of customers switching to alternative products due to price. v) Threat of new entry. New entrants to the markets are driven by so many reasons, but the main driver is a profitable market.
Strategic Influencing
Sharing information, knowledge, observations, and opinions with more senior management about issues related to strategy formulation, strategy execution/implementation, or the organization's ability to respond to market or competitive movements. Strategic leaders must understand that without the ability to influence all directions across the organization, the long-term success that influences strategic action may be limited.
Strategic Thinking
Convince people of the wisdom of a particular strategic initiative so that there is real commitment as opposed to mere compliance (or even passive or active resistance); Strategic leaders must also understand that the key to real success is relationships – both professionally and personally (Daives, 2012).
Strategic Leadership Teams
Strategic Acting
Strategic Learning
The widespread feeling that everyone in the organization has a role to play in leading the business. Strategic leadership involves discovering what the organization needs to do well and more importantly can do well in order to grow in the future.

Strategy as a systematic process
According to (Ungerer, 2007), the emphasis is on ensuring that organizations can best translate and own the strategy at all different levels. After implementing the strategy, it is critical that progress is monitored and regular feedback on the strategy is provided.
Strategy as a resource
Product development – organizations look to increase sales by introducing improved products for their current markets.
Blue and Red Ocean Strategy
Renee (2011) looks at the principles that guide the successful formulation and flawless execution of blue ocean strategy and these principles mitigate the six risks presented below;.
Factors affecting strategy implementation
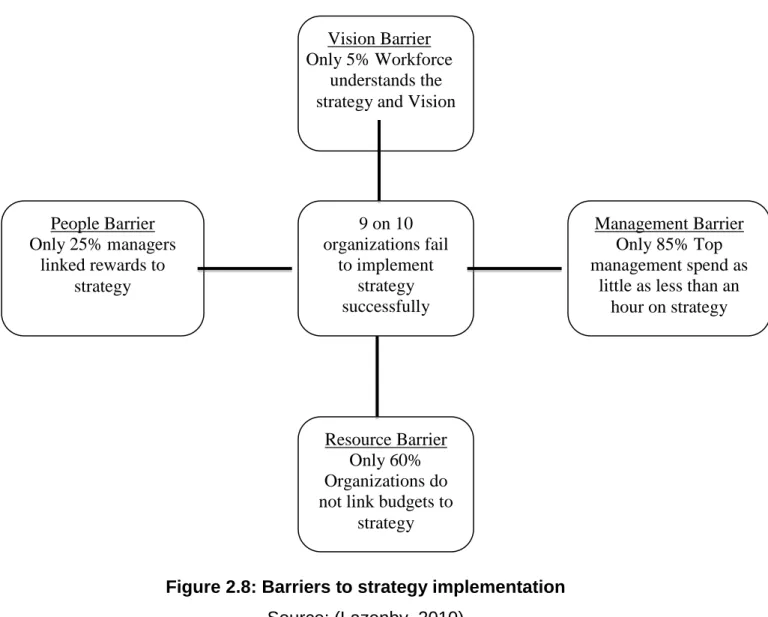
Employees must be involved in the formulation of a strategy process up to the implementation phase, and employees must be involved in the strategy pursued by the organization, giving them enough time to gain more clarity and provide feedback. Determine why there are barriers to implementation or why it is necessary to carry out a certain option and not the other. Lazenby, 2010) states that one of the main barriers to strategy implementation is the inability to possess the management skills.
Some of the reasons that organizations often experience when trying to implement strategies are related to lack of management skills and these problems include;. But since budgets are often not linked to the strategic plan, the discussions can completely avoid any focus on the true value drivers in the company.
Middle managers and strategy implementation
And since budgets are the traditional tools for planning the allocation of human and financial resources, strategic plans and strategic initiatives can fall short in terms of needed resources. This has led to middle managers being unsure of the necessary step to follow and uncertainty can lead to ineffective strategy implementation (McKinley, 2000). In today's environment, middle managers need to integrate horizontally, influence upwards and engage in more diverse initiatives, not through mere downward implementation strategy.
Floyd, 2011) plotted these different roles based on two dimensions; integrating versus diverging and upward versus downward. Middle managers can also facilitate adaptability by establishing experiments without too much association with the top.

Linking the Balanced Score Card to Strategy
McKinsey 7s Model
The model was developed by McKinsey consultants Robert Waterman, Tom Peters and Julien Phillips in the 1980s. Since its inception, the model has been widely used by practitioners and academics and has remained one of the most popular strategic tools.

Conclusion
Research Methodology
- Introduction
- Research Design
- Research Methodology
- Scientific Research Process
- Sampling Methods
- Population
- Sample Size
- Sources of Data
- Description and purpose of Instrument
- Validity and Reliability
- Validity
- Reliability
- Analysis of Data
- Ethical considerations
- Conclusion
It is therefore possible to answer the research question and achieve the goals that require the researcher to statistically assess the characteristics of the population from the sample. Bougie (2014) describes a population as the entire group of interest that the researcher wishes to investigate and draw conclusions about, while an element is a single member of the population. The population of interest in this study consists of the middle managers within the sales division at Brandhouse.
Leedy (2013) notes that the size of a sample should be a function of the variation in the population parameters being studied and the estimation precision required by the researcher. Content validity refers to the extent to which the questionnaire provides adequate coverage of the probing questions.

Results Presentation
- Introduction
- Reliability
- Data Analysis
- Brandhouse Employees Profiles
- Demographics
- Effectiveness of the implementation of the strategy
- Link between budgets, rewards and the intended strategy
- Barriers in implementing the intended strategy
- Key changes in the organizational strategy
- Understanding the vision and strategy
- Role of middle managers in strategy implementation
- Role in strategy implementation
- Support from senior managers
- Clearly defined goals and well understood
- Necessary skills and expertise
- Key factors to successful strategy implementation
- Detailed action plan and tactics
- Appropriateness of organizational structure
- Human resources as the main factor in strategy implementation
- Strategy Communication to all members of the organization
- Purpose of the strategy clearly communicated
- Future vision clearly communicated
- Importance of communication to ensure employee alignment
- Clear communication between employees and managers
- Chi-Square
As shown in Figure 5.2 below, more than half of the participants were male (59%) with 40.86 female participants. As can be seen in Figure 5.9, in response to the question „Do employees understand the vision and strategy?‟, 2.17% do not agree at all, 5.43%. Figure 5.15 shows that 46.15% of respondents agree that the organizational structure corresponds to the intended strategy, 4.40% strongly agree.
According to Figure 5.17, which is an answer to the question 'Does the organization ensure that the strategy is closely monitored and monitored to ensure it is not derailed and is on track?', 0% strongly disagree, 10, 87%. According to Figure 5.19 about the future vision, 60% indicate positively that this is clearly communicated by the leaders to the rest of the organization.

Discussion of results
- Introduction
- Participation
- Treatment of data
- Demographic profile of respondents
- Objectives of the study
- Link between budgets, rewards and the intended strategy
- Key changes in the organizational strategy
- Understanding the vision and strategy
- Role of middle managers in strategy implementation
- Role in strategy implementation
- Support from senior managers
- Clearly defined goals and well understood
- Necessary skills and expertise
- Key factors to successful strategy implementation
- Detailed action plan and tactics
- Appropriateness of organizational structure
- Human resources as the main factor in strategy implementation
- Strategy Communication to all members of the organization
- Purpose of the strategy clearly communicated
- Future vision clearly communicated
- Importance of communication to ensure employee alignment
- Clear communication between employees and managers
- Summary
This section looks at the evaluation of the effectiveness of the strategy implementation at Brandhouse (Pty) Ltd. The majority (79%) of participants indicated that the most important changes in organizational strategy that may affect employees are clearly defined. More than half of the participants reported that top management provides sufficient support to middle managers and the rest of the organization in implementing the strategy.
Brandhouse senior management must ensure that all drivers of the implementation process clearly understand their roles in the process of strategy implementation. About two-thirds (66%) of the participants mentioned that the organizational structure fits the intended strategy.
Conclusion and Recommendations
- Introduction
- Summary of findings
- Managers implications
- Recommendations for Brandhouse
- Recommendations for future research
- Conclusion
The results of the research on the role of the middle manager in the strategy implementation process have been achieved. The research showed that Brandhouse middle managers play a key role in the implementation of organizational strategies. The survey also revealed that about three-quarters of the participants positively mentioned that there are unrealistic goals and expectations that hinder middle managers from implementing the planned strategy.
Top management must provide adequate support to middle managers and the rest of the organization in implementing the strategy. 34,
Questionnaire
Do you feel that the most important changes in organizational strategy that may affect employees are clearly defined? Does senior management provide sufficient support to middle managers and the rest of the organization in implementing the strategy? Do you feel you have the necessary skills and expertise to ensure the successful implementation of a strategy?
Is the detailed action plan and tactical steps necessary for the successful implementation of the strategy clearly defined? Is the vision of the future clearly communicated by the leaders to the rest of the organization?
Ethical Clearance
Gatekeepers Letter
Brandhouse Case Study


