DESCRIPTION OF THE APPLE INDUSTRY
- Apple production areas
- Apple production
- Apple cultivars
- Employment
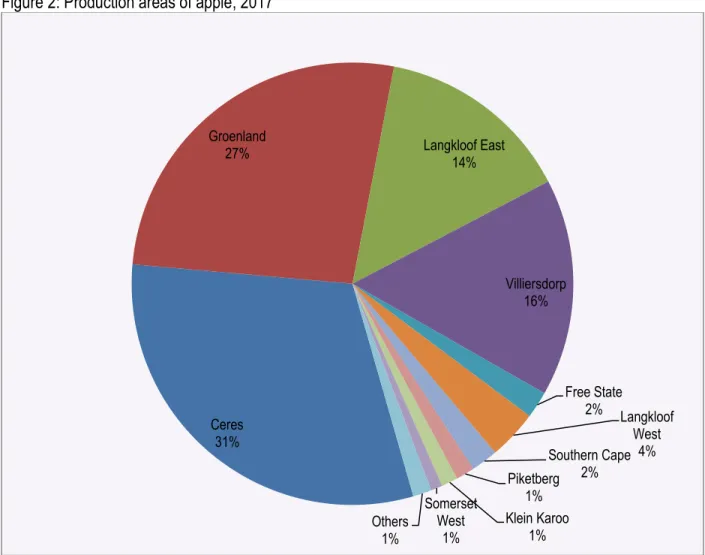
South Africa's main apple producing areas are Greenland, Ceres, Villiersdorp (all in the Western Cape) and Langkloof East in the Eastern Cape. The apple industry makes an important contribution to direct employment in apple production and processing.
MARKET STRUCTURE
Domestic markets and prices for apples
Prices in local markets are mainly influenced by seasonality in production, perishability of production and the quantity of apples exported (availability of apples in the local market). The impact of seasonality is mitigated to some extent by cold storage facilities that ensure regular supplies of apples to local markets.
Apple exports and imports
- Exports
- Imports
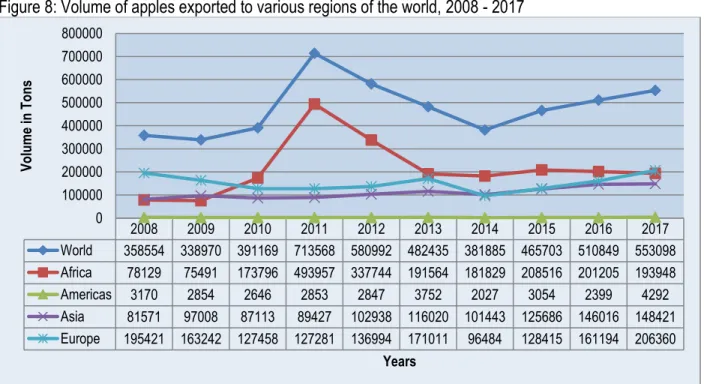
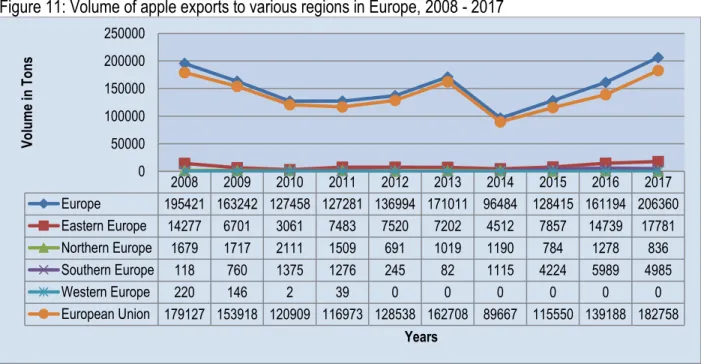
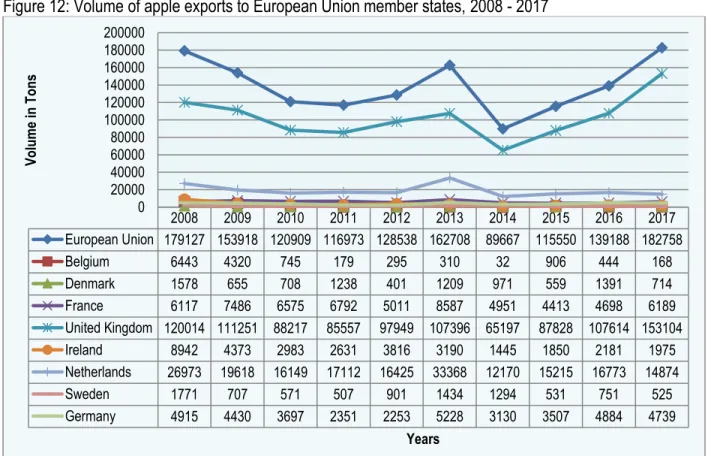
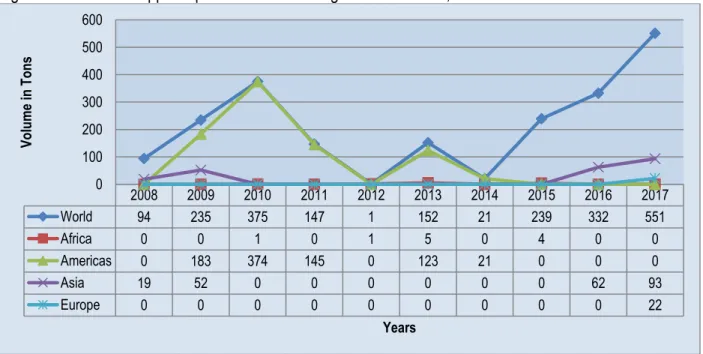
The volumes of South African apple exports to different countries over the last decade are shown in Figure 10 below. The volumes of South African apple exports to the different regions of Europe are shown in Figure 11.

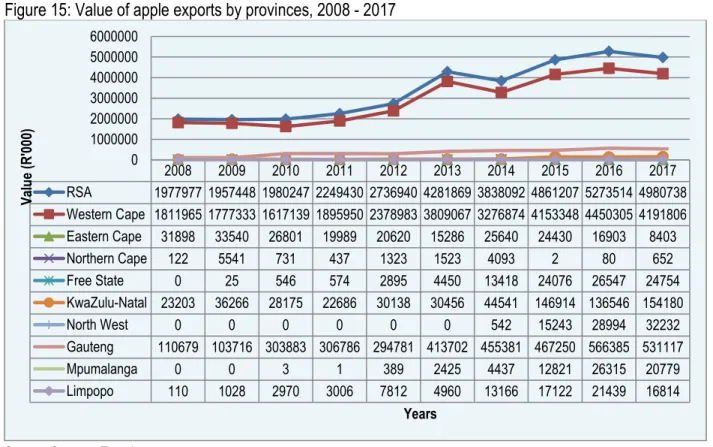
Provincial and district export values of South African apples
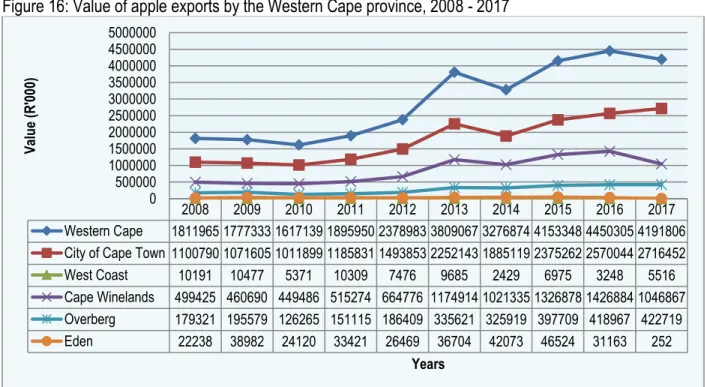
The following figures (Figures 16 – 24) show the value of apple exports from the various districts in the nine provinces of South Africa. Overall, there have been significant increases in the value of apple exports from the City of Cape Town and Cape Winelands since 2008. The value of apple exports has been unstable for the Ekurhuleni Metropolitan Municipality over the past decade.
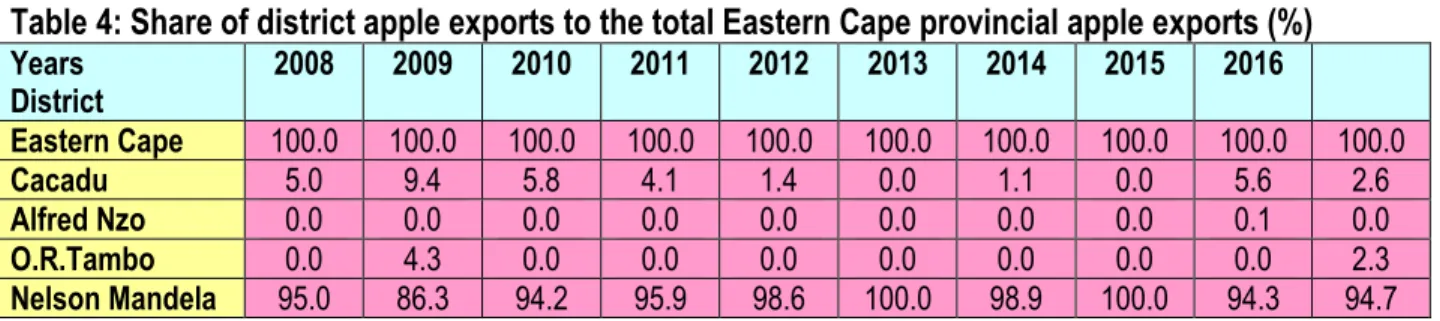
It can be observed in Figure 19 that apple exports from the Eastern Cape province are mainly from Nelson Mandela and Cacadu to a lesser extent. The value of apple exports from Cacadu district has been declining since 2007, and has remained below R annually for the past ten years. The value of apple exports from the Thabo Mofutsanyane and Fezile Dabi districts decreased by 12% and 100% between 2016 and 2017.
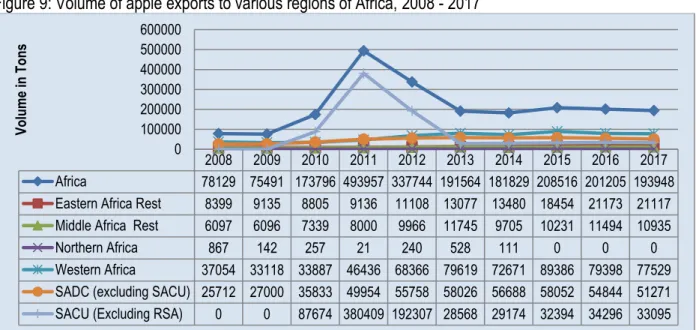
Apple exports from the Northern Cape province are mainly from the Namakwa and Siyanda district municipalities.
Share Analysis
It is clear from Figure 24 that in 2017 apple exports from Mpumalanga province were only from Ehlanzeni District Municipality and Gert Sibande. Together, the three districts accounted for over 99.7% of the total Western Cape provincial apple exports in 2017. The district's apple export shares of the Eastern Cape Province's total apple exports are shown in Table 4.
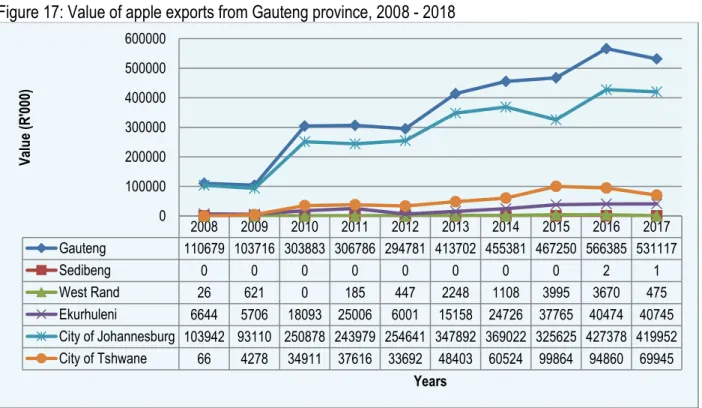
No apple exports were reported from Amatole and O.R Tambo districts in the last four years. Shares of county apple exports to total Gauteng provincial apple exports are shown in Table 7. Shares of county apple exports to total Limpopo province apple exports are shown in Table 9.
The EThekwini district is the leading municipality in terms of apple exports from KwaZulu Natal, accounting for 98.1% of total provincial apple exports in 2017.
Processing
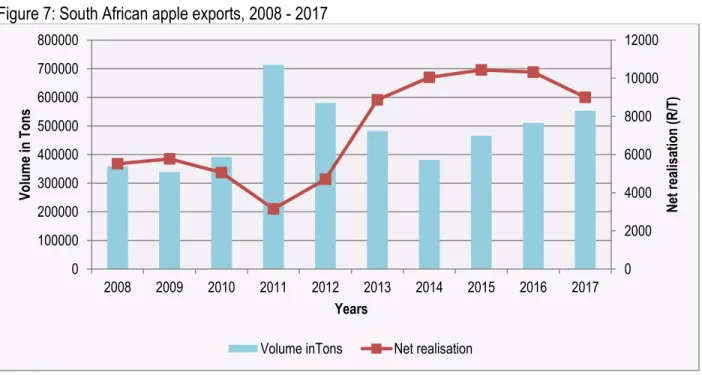
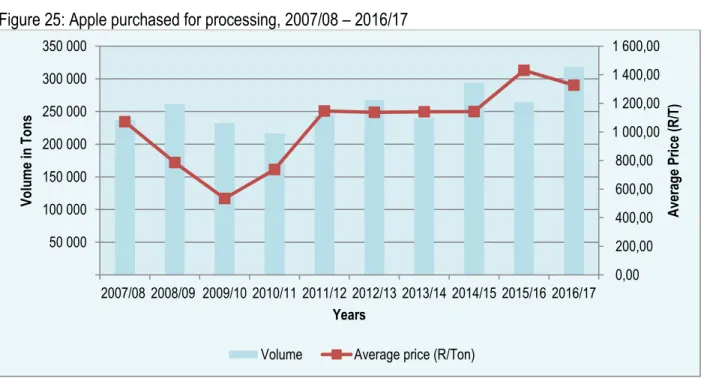
In 2017, almost all (88.9%) exports of apples recorded in the Northern Cape were from the Namakwa district (see Table 10). The amount of apples available for sale in a given production season depends on the volume of exports as well as volumes sold in the local markets. The increase occurs at the same time when the volume in the local markets decreased (see Figure 6).
Virtually all processed apples are subject to post-harvest activities that alter their chemical and physical properties. Apples are an important ingredient in many winter desserts, for example apple cake, apple crumble, apple crisp and apple cake. Similar treats in the US are candy apples (coated in a hard shell of crystallized sugar syrup) and caramel apples, coated in cooled caramel.
On the Jewish New Year, Rosh Hashanah, they eat apples with honey, which symbolize a sweet new year.
MARKET INTELLIGENCE
Competitiveness of South African apple exports
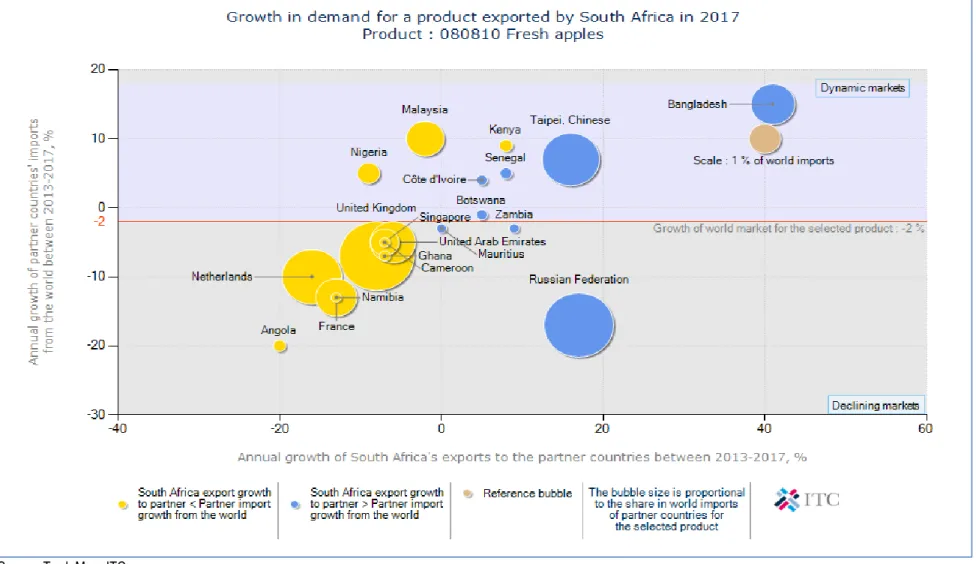
The United Kingdom, Malaysia, Bangladesh and Nigeria accounted for the largest market share of South African apple exports in 2017. While four countries dominate global apple imports, it is interesting to note that countries such as Nigeria, along with Zambia and Malaysia, have experienced higher annual growth. value (see Figure 26). It is important to note that the growth of all the mentioned countries was from a high base.
It is also important to note that imports of apples from the world to countries such as Zimbabwe, Saudi Arabia and Ireland declined and as a result these countries have recorded a negative growth rate.
South Africa vs. Southern hemisphere production
Certificate of conformity must be obtained by anyone who wants to export and sell fruit in the EU, if that fruit falls under the jurisdiction of the EU marketing standards. The essence of the directive is that it authorizes the Plant Protection Services to inspect a large number of fruit products on arrival in the EU. For the most part, it revolves around quality and the perception of European consumers about environmental, social, health and safety aspects of both the products and . the legal sense, they are becoming increasingly important in Europe and cannot be ignored by existing or potential exporters. i).
Delays due to deterioration of the supporting infrastructure within the supply chain (handling facilities at ports, roads and energy supply). Lack of storage capacity at certain times of the year, when apples and other fruits are harvested (mid-January to the end of February). Transporters are a key link in the fresh fruit supply chain by facilitating the physical transfer of the produce between parties such as the grower, cold store and terminal operator.
Under the PPECB Act (Act 9 of 1983), the PPECB is responsible for "the control of perishable products intended for export from the Republic of South Africa".
South Africa vs. Southern hemisphere exports in 2014
MARKET ACCESS
Tariffs, quotas and the price entry system
European Union (EU)
- Tariff barriers
- Non tariff barriers
- Legal requirements
- Non-legal requirements
- Consumer health and safety requirements
There are other non-tariff barriers, including the phytosanitary and food hygiene regulations set out in EU legislation, marketing standards and certificates of conformity, and the ever-changing demand patterns of EU consumers. When the value of the imported lot is between 92% and 94% of the entry price, 8% of the entry price will be added to the normal duty. When the value of the imported lot is between 94% and 96% of the entry price, 6% of the entry price is added to the normal duty.
When the value of the imported part is between 96% and 98% of the entry price, 4% of the entry price is added to the normal customs duty. When the value of the imported item is between 98% and 100% of the entry price, 2% of the entry price is added to the normal customs duty. If the cargo does not comply, it may not enter the EU, although some organisms may be fumigated at the expense of the exporter. iii).
The EU Commission lays down rules for materials that come into contact with food and that can endanger people's health or bring about an unacceptable change in the composition of the food.
United States of America (USA)
- Tariff barriers
- Non tariff barriers
Some products may be pre-cleared by International Services (IS) personnel stationed in the country of origin, either at export terminals or on-site inspections. The PPQ's main focus is to prevent the spread of diseases and pests to US agricultural resources, and it has staff stationed at all airports, seaports and border stations that check imported cargo and oversee the quarantine process. Exporters or importers must make a request to export/import a commodity, providing as much information as possible about the product, its region of origin and its status, i.e. whether there are any restrictions or regulations that apply to that particular product of that specific region before a permit is issued, together with the conditions of import (disinfection treatment) or mitigating measures.
Denials can be challenged and governments and companies can request a change in the status of a prohibited commodity (an investigation must be carried out by the PPQ scientific team), as long as sufficient conditions have changed or a risk assessment has not been carried out within deadline. 10 years. Establishing specific and maintained pest-free areas in a country (which obviously requires extensive cooperation between the country's plant health services and the APHIS IS division) or systemic approaches (field surveys, random inspections or various field treatments) In addition to phytosanitary regulations, the USDA's Food Safety Inspection Services (FSIS) regulates sanitary practices in food packaging, while the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), which is part of the US Department of Health, regulates packaging and labeling.
USDA quality standards for fruits and vegetables provide the basis for domestic and international trade and promote efficiency in marketing and procurement.
DISTRIBUTION CHANNELS
The Policy and Program Development (PPD) Department works with both divisions to determine long-term plans and procedures. They will also be responsible for clearing the products through customs, packaging and ensuring label/quality compliance and distribution of the products. The contract importers of fruit combine harvesters market and distribute the combine harvester products, clear customs, and in some cases handle and package it.
Few exporters have long-term contracts with wholesalers who deliver directly to retail stores, but with the increasing importance of standards (EurepGap, etc.) and the availability of fruit throughout the year, the planning of long-term contractual relationships is expected to increase.
LOGISTICS
Mode of transport
Cold chain management
Packaging
ORGANIZATIONAL ANALYSIS
- Producer and associated organizations
- Strengths, Weaknesses Opportunities and Threat analysis
- Strategic challenges
- Labour markets
- Infrastructure
- Other challenges
- Opportunities
- Producers
- Fresh produce markets
- Retailers
- Processors
- Cold storage operators and transporters
- Exporters
- PPECB
- Terminal and port operators
However, in the local scenario, laborers lack mobility as well as skills to find work outside the harvest. Inefficient handling operations at South African ports, giving rise to costly delays and interruptions in the cold chain. This provides an opportunity for Hortgro to provide matching funds for the implementation of targeted transformation projects in the province.
FPMs are the dominant player and form of wholesale in the South African apple and fresh fruit and vegetable (FFV) sector. The PPECB also acts as a "beneficiary" of the government within the meaning of the APS (Agricultural Produce Standards) Act (Act 119 of 1990) and is responsible for "control over the sale and export of agricultural and allied products". As more emphasis is placed on food safety and customers demand higher quality standards, the PPECB and other inspection bodies play an increasingly important role in the export of fresh produce from South Africa.
Terminal operators must notify exporters, PPECBs and other relevant parties in the supply chain such as carriers, producer associations, manufacturers and cold stores of port-related delays such as labor strikes, wind delays, terminal congestion and other traffic disruptions in port, which will affect the flow of fresh products to and from the port.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS