My parents, brothers and sisters for their support and encouragement and for instilling in me the desire to continue my studies. A debt of gratitude is extended to the heads of departments and level 1 educators for their willingness to provide research data.
INTRODUCTION 4
Purpose of the study 6
But despite the fact that teachers are attending workshops, EMS teachers are still unsure of what and how to teach in the EMS learning area. This could in part reflect their lack of fundamental knowledge of the EMS curricular area and/or lack of sufficient knowledge of general issues related to outcomes-based education and the integration of EMS with other curricular areas.
Research questions 7
Delimitations
Limitations 7
- Heads of Department 8
- Fundamental knowledge
- Professional development
- Learning area
It also outlines the objectives of in-service education and training (INSET), PD approaches and lists some of the challenges of professional development. A thorough discussion of the purposes of INSET was explored, followed by the different approaches to professional development. The role of the researcher in the professional development workshop was that of facilitator, participant and observer.
Due to the lack of sufficient EMS materials, the educator reported at the workshop that. Educators have difficulty connecting the theory with the practical aspects of EMS. However, a closer look at the answers in the questionnaire showed that one educator was of the opinion that.
It was also found that the EMS support materials provided were not sufficient to meet the requirements of the curriculum. Therefore, it can be concluded that there is a mismatch between the needs of the EMS educators and the provisions set by the department for professional development (PD).
Organisation of the study
Introduction 10
This literature review chapter on professional development (PD) provides a theoretical perspective for this study. This study is based on the assumption that the professional development of educators must include aspects of curriculum development.
The growth of professional development
Thus, those who introduce such courses pretend to "know what the needs of the organization were and frame the study accordingly" (Murphy leads to what Henderson and Perry in Pather (1995) characterized as the existence of a mismatch between needs teacher and course content Merely implementing a top-down set of workshops does not necessarily meet the needs of an organization or an individual educator.
Aims of INSET
- The integration of experience with theoretical studies
- Provision of upward mobility
- Supplying teachers for the system
- Combating bum-out
- Educating teacher to serve as initiators of change and Change
- Management of change
The main concern and one of the main purposes of INSET must be to devise. This approach assumes that outside experts impose curriculum changes and teachers' competence can be easily developed to satisfy all the needs of the changed curriculum.
Professional development approaches
- Organic approach
- Ad-hoc approaches
- Process-based approaches
- Consultancy approach
- Objective approaches
- Support
Professional development strategies must therefore recognize that EMS is a new addition to the curriculum and therefore assist teachers with this new change imposed on them. According to Bush (1994), professional development in these approaches is reactive and opportunistic and lacks any systematic attempt to bring together organizational and individual needs within a managed program. These approaches include models of professional development that emphasize reflection, analysis, and self-generated evaluation.
In this approach, professional development IS done through the use of outside agencies, such as non-governmental organizations, business consultants, etc., to analyze the education system holistically within schools/districts or provinces.
Some challenges of professional development
- Integration of authority and support
- Theory-practice tension
- The tensions around place and time
Although many INSET programs are currently being implemented, there appears to be little or no monitoring and support of the implementation process at school level. Accordingly, the Teacher Development Strategy (NCS Concept Paper June 2004) advocates that "the role of the school principal and SMTs in both the orientation and targeted training phases is central to implementation". One of the tensions in teacher development programs is what Adler (2002:5) calls the 'theory-practice tension'.
However, in other training programs, time constraints extend beyond the allocation of time within the program to the duration of.
Emerging issues
The aim of this study was to investigate the capacity building strategies of heads of department, curriculum coordinators and level 1 educators in the teaching area of Economic and Management Sciences (EMS) in 5 primary schools in the Ethekwini Region of the KwaZulu-Natal Department. . Education.
Research design
This is important as case studies provide fine details that provide powerful human-scale data from which to make decisions about development strategies where theory can be infused with practice. It also provides an opportunity to intensively analyze the multiple phenomena affecting EMS educators' capacity to teach EMS. This approach was appropriate for the study because, although I exercised little or no control over events, it gave me the opportunity to explore the rich and vivid descriptions of events that informed the curriculum coordinators' ability to manage the EMS curriculum, influence.
In recognition of the costs, time, and administrative support required for the successful completion of this study, a non-probability sampling strategy was used to select a sample of 5 elementary schools in Phoenix County.
The respondents
Data collection methods
- QuestIOnnaire 40
- Observation
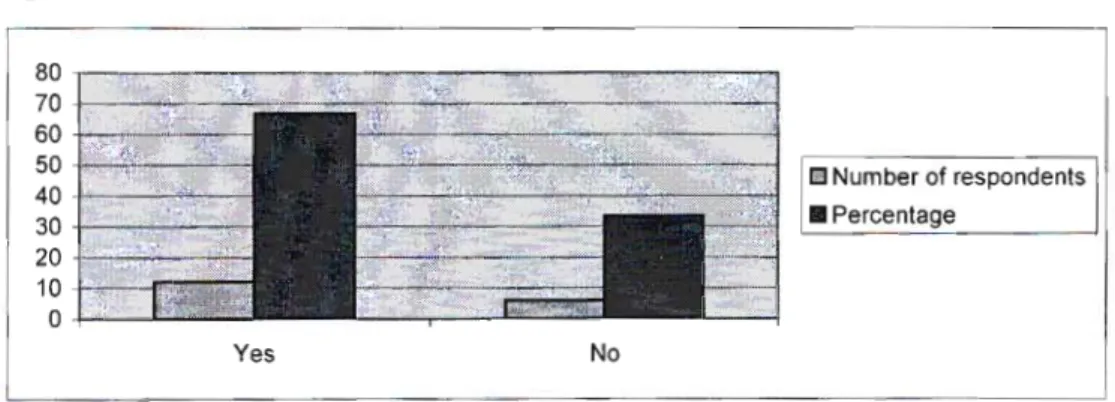
With permission from the principal, the HODs were asked to hand out these questionnaires to the EMS educator who had taught the longest in each of the 4th, 5th, 6th, and 7th grades. Since this represented 67% of the respondents in the sample, a personal visit was made. asked if educators needed additional time to fill out the questionnaire. This study used face-to-face semi-structured interviews with senior/intermediate managers of EMS learning area departments.
Educators were also surveyed for their level of readiness for the transformation from teacher to facilitator of the SMM curriculum.
Data analysis procedures
As a member of the Directorate of Teacher Development, charged with the professional development of educators, I was able to observe EMS teachers as participants in the workshops they conducted in Ikhwezi, as well as in their natural work environment in schools. The focus of the observation was to determine the level of content knowledge of educators in EMS and the level of integration of generic knowledge with content knowledge. The observation period lasted 2 years, and the workshops were conducted over 2 days.
Data from discredited sources were triangulated to help the researcher maintain the credibility, accuracy, representativeness and authority of the research.
Limitations of the study
Capacity development needs of department heads in providing appropriate support to educators were classified as category C, while category D addressed the challenges experienced by department heads in managing the EMS curriculum.
Summary
The aim of this study was to investigate the capacity building strategies of heads of department, curriculum coordinators and Level 1 teachers in the Economic and Management Sciences (EMS) learning area in 5 schools in the Ethekwini Region of the KwaZulu-Natal Ministry of Education. . Through methodological triangulation of data from questionnaires, observations and interviews, the data was analyzed and the findings are presented and discussed in this chapter. Section B discusses the level of EMS content knowledge of department heads, curriculum coordinators, and Level I teachers, while Section C identifies and discusses professional development strategies for EMS teachers.
Section D discusses the challenges of in-service training programs (INSET) and some of the strategies that department heads have put in place to address some of these challenges.
Section A - Biographical data
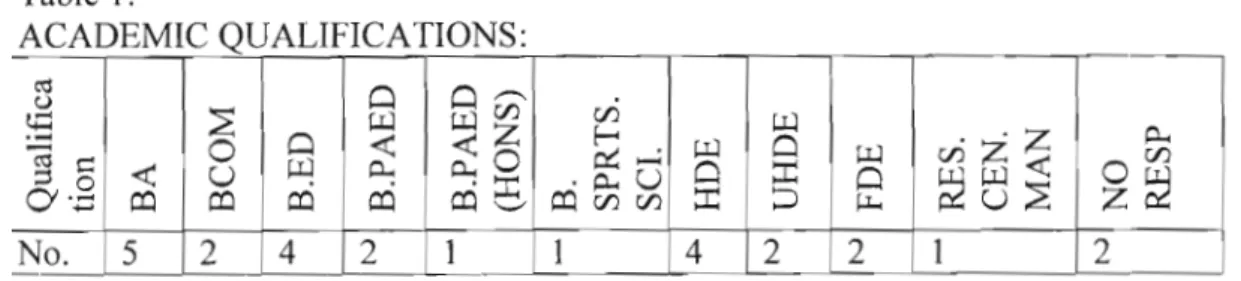
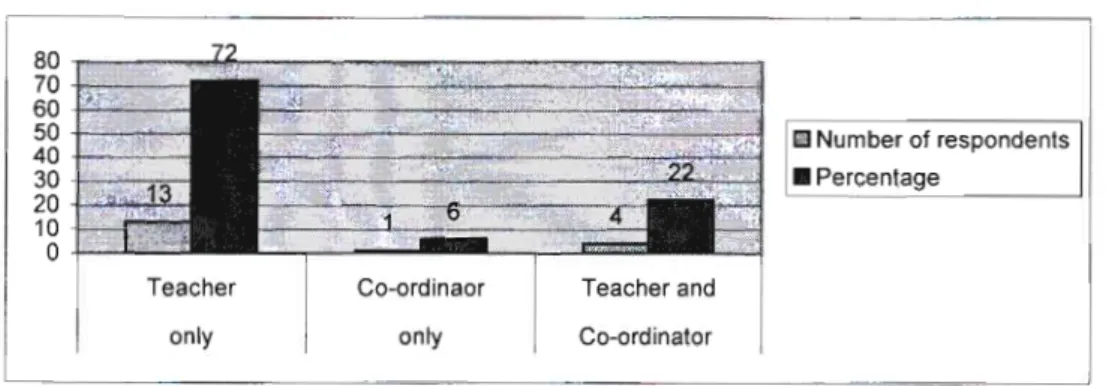
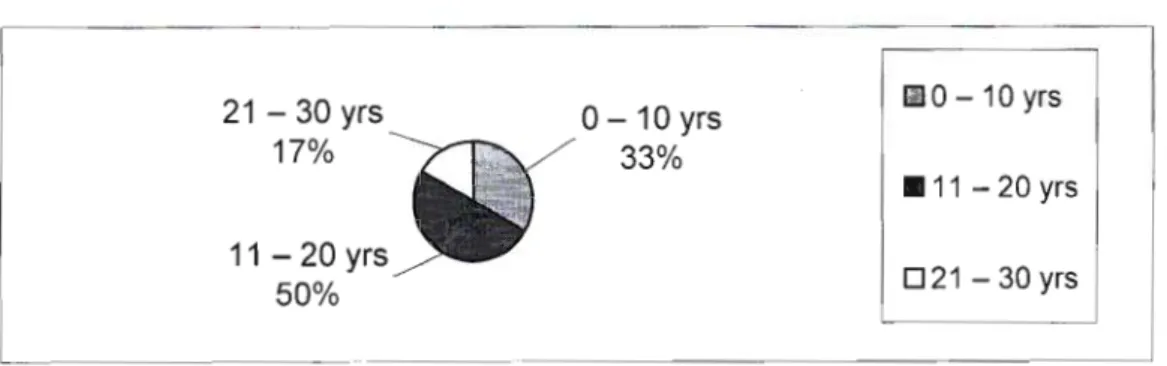
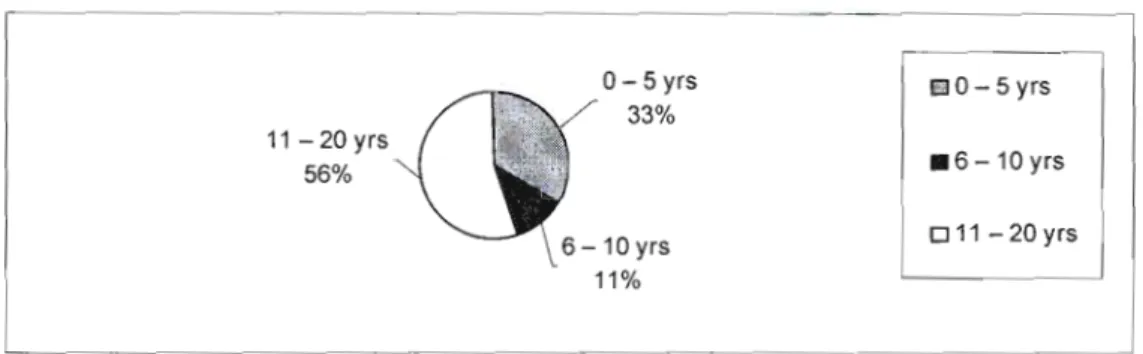
For the purposes of ease of understanding and presentation, the research findings are presented in four categories. This section simply identifies basic educator information that has a material impact on educators' competence and capacity to facilitate the EMS curriculum. This indicated that the respondents enjoyed a relatively stable working environment where professional development could be carried out gradually with the same group of educators.
Earlier studies by Pather (1995), where 22 percent of educators were found to be unqualified, suggest that the supply of qualified educators in the system has not improved.
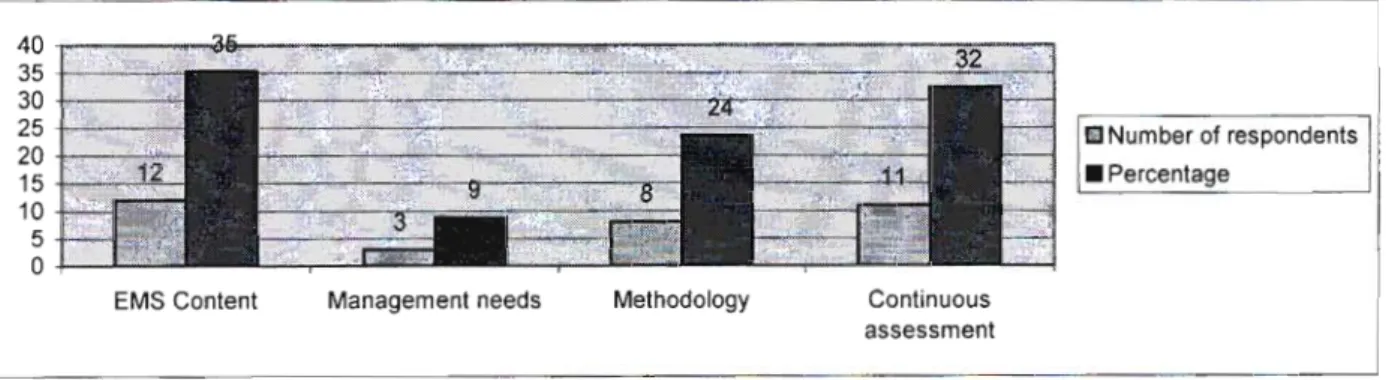
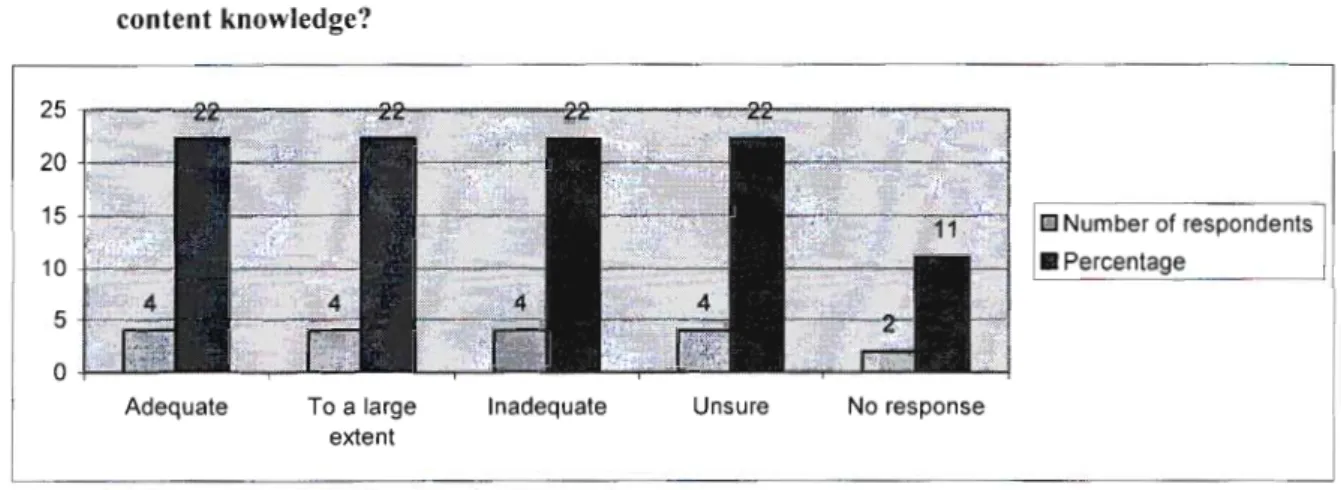
Section B - Content knowledge of EMS 47
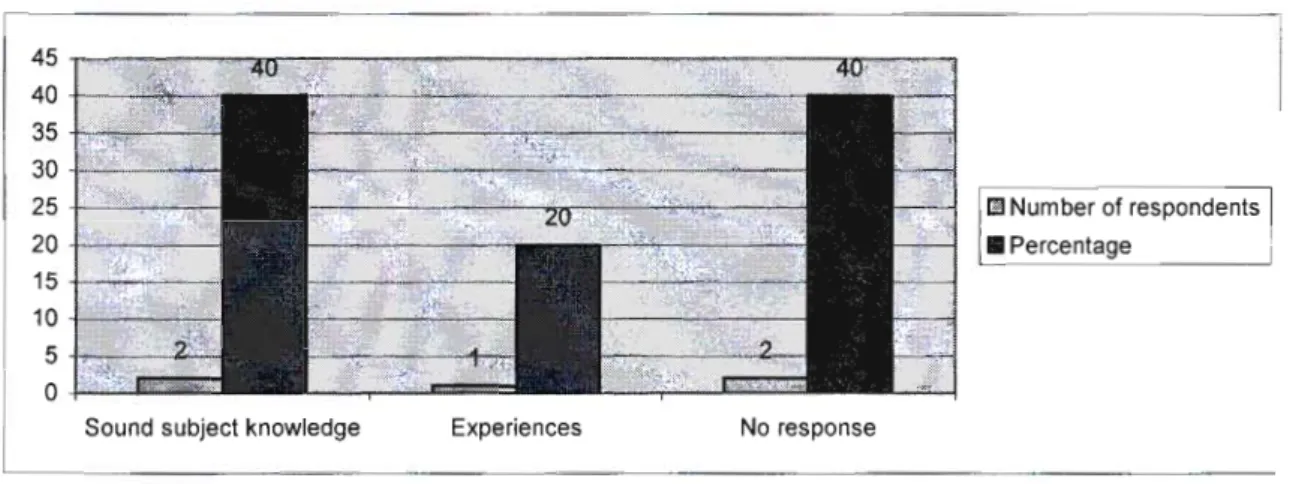
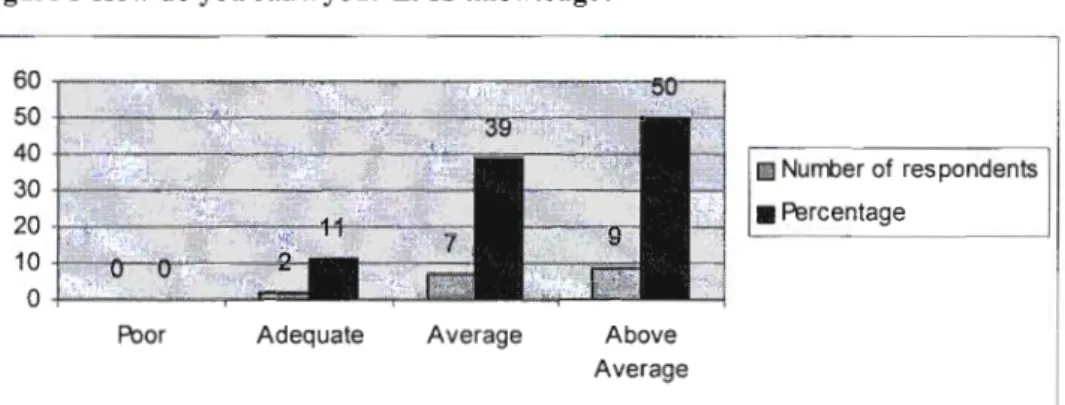
The lack of basic knowledge in SMM affects not only the efficiency of the teaching and learning process, but also has wider implications for the professionalism of educators. From a management perspective, interview responses indicated that HODs felt that INSET training did not empower them. This leads to what Henderson and Perry in Pather (1995:75) called a "mismatch between teacher needs and course content".
Teachers from the same learning area sit together and discuss the work plans to develop uniformity at the district level.
Section D - Challenges of INSET programmes
Berg and Hartshorne in Pather (1995) also found that the realities of the individual South African school contexts from which participants came had little or no influence on course design. This correlates with Maharaj's research where it was found that "teachers are responsible for operationalizing the curriculum. Students should be given the opportunity to participate in the planning and implementation of additional training programs.
Analysis of their reasons, as stated in the questionnaire, showed that they believe that control causes tension and therefore should not be combined with support.
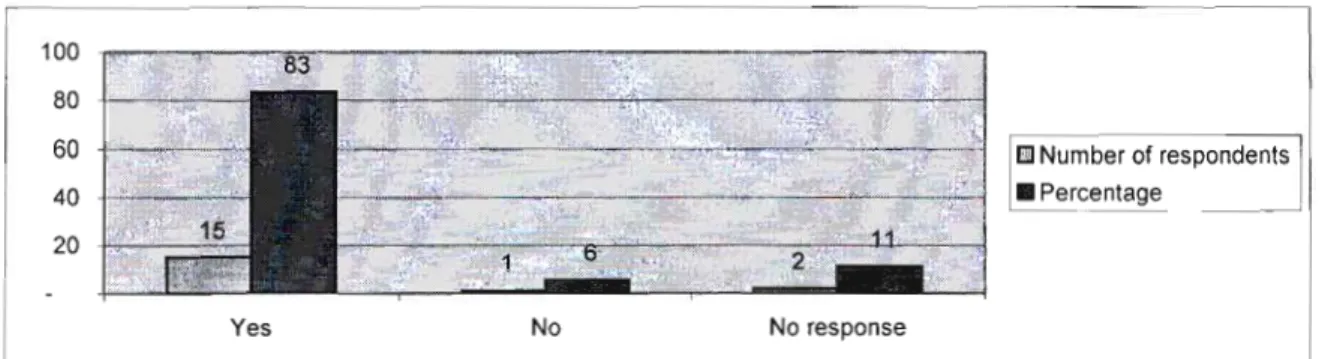
Emerging issues
Section D has identified that one of the challenges for INSET programs was the need to include the needs of educators in program design. The findings of this research therefore confirm that a lack of basic knowledge exists among all educators in the EMS learning area and that unless proper measures are put in place, EMS will continue to be marginalized. The results also showed that the existing INSET strategies are not necessarily effective in changing the landscape of the EMS learning area.
The purpose of this study was to examine current strategies of capacity building of EMS educators regarding their nature and degree of effectiveness and subsequent challenges with particular reference to primary schools.
Conclusions
This was partly indicative of the lack of basic knowledge in the field of EMS learning. It is the recognition of the diverse nature of educators' teaching and learning experiences that would add greater value to what is to be offered and to which curriculum designers should be sensitive in developing INSET programmes. Please list some of the challenges you face in teaching and/or managing EMS.
What do you think are some of the solutions to the challenges identified in Question 25?