Understanding the key success factors of a new product development strategy remains unclear for many organizations in the dynamic telecommunications industry. Professor Bhowan for his advice in developing a model for successful new product development.
INTRODUCTION
Research Problem
CMG managers need to learn more about the complexities of product development. The research objective of this study is to assess the key success factors of CMG's new product development (NPD) strategy.
Subsequent Chapters of the Report
This chapter will include the results presented in relation to the research objectives stated in Chapter One. This chapter will give recommendations on how to solve the problems identified from the results.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Introduction
What Porter, essentially an economist, calls innovation is what business people, and especially marketers, refer to as new product development (NPD), which contributes to the main theme of this research project. Baker & Hart Since this research focuses on the field of marketing, new product development will be referred to as NPD, which is the accepted abbreviation for the term.
New Product Development Concept
This research project uses the term "new product development" to cover the process by which new products are developed in companies. In this dissertation, the terms new product development and product innovation will be used interchangeably, reflecting the interdisciplinary nature of NPD.
New Product Categories
Improved products: Products that are developments of existing products that represent a significant change, similar to the above category - improvements and revisions of existing products. Innovative Products: Products that are truly new to the market, similar to the first category above, New-To-The-World-Products (1987:11).
The Need For New Product Development Strategy
Imitator Products: Products that have already been introduced to the market by others, but are new to a particular firm, similar to the second category above - New Product Lines. In 1980/81 the Siemens Group, one of the world's leading electrical and electronic companies, spent over 3 billion deutschmarks (nine percent of total sales) on research and development.
Factors Affecting Success of New Product Development
Rather, it focuses on topics that research has shown to have an impact on NPD success rates, namely, corporate strategy, organizational structure, organizational culture, the role of management, the NPD process itself, the people responsible for implementation of it and how the information contributes to the process. These themes are revealed at two different organizational levels: (l) relating to the specific NPD project, i.e.
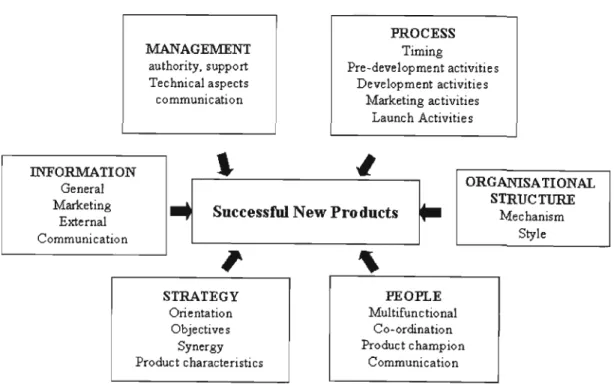
Strategic Issues
The purpose of this process is to ensure integration both in the aggregate and at the individual project level. A Financial Mail profile of the most successful companies states that product development is the most popular method of achieving business growth.
Project Related Issues
Many authors have investigated the extent to which the prescriptive activities of the NPD process take place. Access to knowledge technology is becoming one of the sources for innovation in the future.
A Model for Successful New Product Development
Team members work together from • Takeuchi & Nonaka (1991) start to finish during the NPD process. The role of information is • Ball and Asbury (1989) important in the NPD process for.
This research study aims to answer these questions by evaluating the company's new product development strategy. Information is constantly reworked in light of the changing circumstances during the NPD process. The overall objective of Part A of the Questionnaire was to evaluate the key success factors of CMG's New Product Development (NPD) Strategy.
Section Five of Part A of the questionnaire was linked to Section Five of the model regarding issues related to the NPD process. Information is continuously reworked in light of changing circumstances during the NPD process.
INTERPRETATION OF RESULTS
Introduction
High levels of synergy (i.e. the relationship between NPD and existing activities) exist within the company. New product development should be successful if senior management is committed and involved at all levels of the NPD process. The results of the pilot study (Refer to Question 8 in Appendix 13) and the diagram of the organizational structure (Refer to Appendix 7) support these results.
Functional coordination is identified as a critical factor contributing to the development of the new product. Functional coordination is identified as a critical factor contributing to the development of the new product.
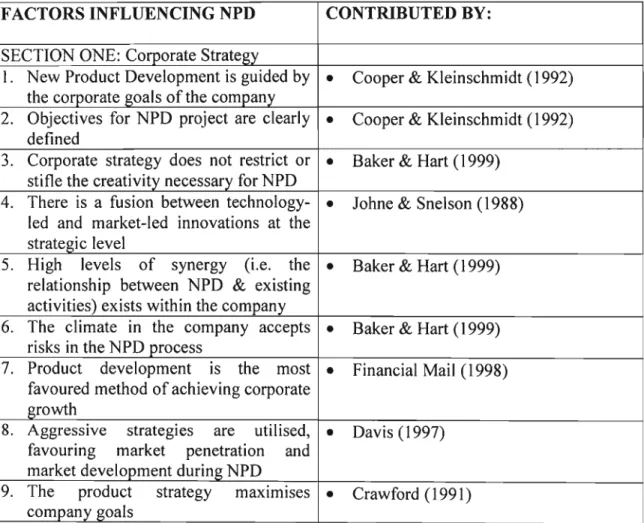
Interpretation of Chart 5.l : Aggregate Response for A1160 Questions
Interpretation of Graph 5.1: The Relationship between the Seven Key Factors
The differences in the percentage of disagreement and agreement for each of the seven factors shown in Graph 5.1, however, give some clues as to which of the seven factors are more problematic and which are not. Graphs 5.2 and 5.8 show the seven factors individually so that we have gained insight into each of the 60 characteristics. The seven factors were categorized according to sections one to seven of Part A of the questionnaire (see Appendix 1), which was based on the model of successful NPD (see Table 2.1).
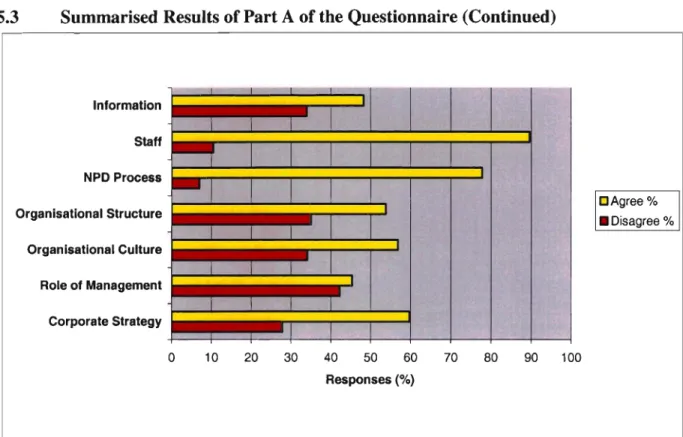
Interpretation of Graph 5.2: Corporate Strategic Issues
First, the results reveal that CMG's corporate strategy limits or stifles the creativity necessary for new product development success, while also revealing that CMG's corporate strategy is not aggressive. This implies that CMG's competitive strategies must be more effective if NPD is to be successful. Although the findings indicate that NPD is guided by the corporate strategy, it is important that the strategy is not so prescriptive that it limits or stifles the creativity necessary for NPD success.
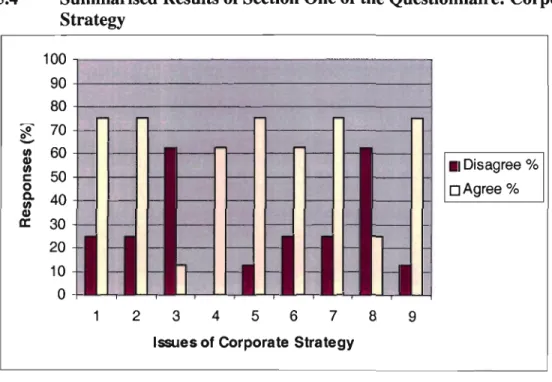
Interpretation of Graph 5.3: The Role of Management
This means that there is a higher level of negative attitude towards the above issues compared to other management issues. This may be the result of a company strategy that stifles the creativity needed to develop new products, as can be seen in graph 5.2. This could mean that the corporate strategy is causing the problem that senior managers are not fully involved in the NPD process.
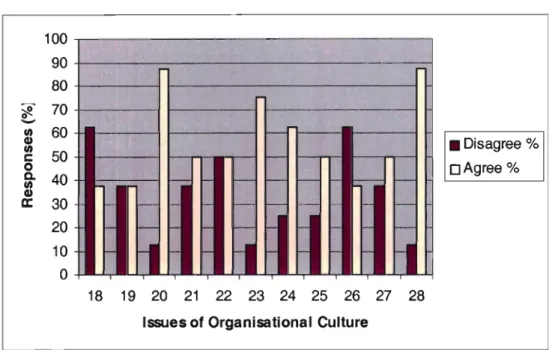
Interpretation of Graph 5.4: Organisational Culture
Therefore, the results show that the effectiveness of the CMG, in relation to the NPD strategy in relation to the company's corporate culture, is revealed in the above areas. The findings show that some negativity also exists within the company in their report, which states that "tensions in the workplace will have a negative impact on the company's performance" and ultimately on the NPD process. Corporate strategy as well as leadership style in the company can influence a positive attitude among staff members.
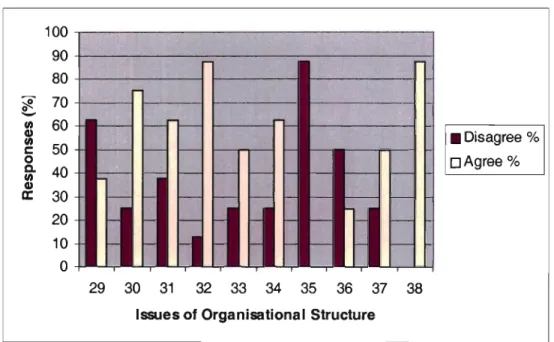
Interpretation of Graph 5.5: Organisational Structure
See graph 5.1. In order to understand why some of the answers were negative, a more detailed analysis of the company's structure is needed. The high levels of negative attitudes towards these issues compared to other organizational structure issues shown in Figure 5.5 reveal areas of great concern to CMG. This can be explained by the fact that the corporate strategy defines the rigid and hierarchical structures of the organization, which is responsible for many levels of authority, which negatively affects creativity.
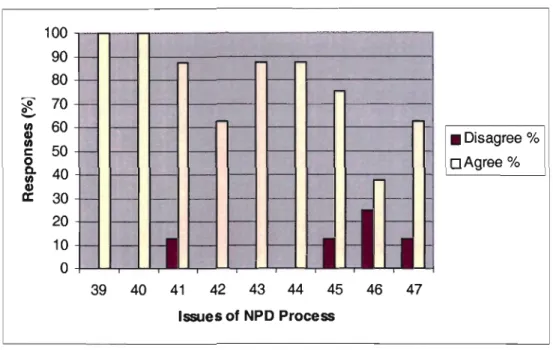
Interpretation of Graph 5.6: The NPD Process
The highest level of negativity occurred for Question 46 which relates to management's skills and time in the NPD process. The low level of commitment and involvement of senior management in the NPD process may be the result of the lack of skills as well as the result that management does not have enough time for NPD, as indicated by the negative response in Question 46. Even though did the results indicate that the steps in the NPD process are followed properly, the negative response of 25% of the product group shows that there is a problem at a strategic level and not really at the project level.
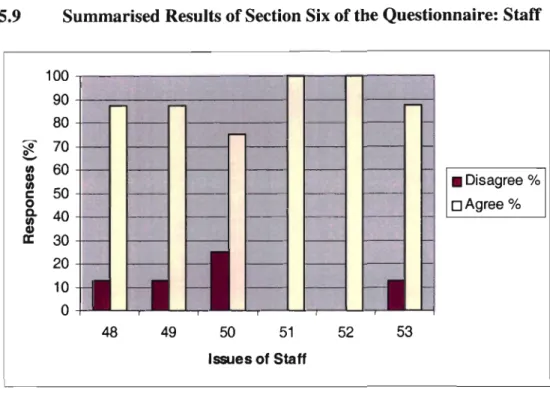
Interpretation of Graph 5.7: Staff
The reason for this may again be the result of rigid company structures, which may also limit staff and even management from being involved in all levels of the MDP Process. From the data collected in the pilot study it is clear that the company has specific people responsible for specific functions. These findings imply that at some points in the NPD Process there is an overlap of functions with team members in the CMG.
Interpretation of Graph 5.8: Information
Weaknesses in CMG's NPD information strategy were identified in the following areas:. See Appendix 11) However, the study reveals that this information system is not efficient enough, or perhaps the database is not accessible to all team members, reflecting a problem in the NPD strategy. This confirms that the information is not sufficiently accessible to speed up communication and reduce costs in the NPD process, which may be due to the lack of an effective centralized database as mentioned above.
The management style can be determined by the company's (strategic) structure, which in turn can prevent senior managers from communicating information with project team members and this can be the main cause of high costs during the Process (project) NPD. On the other hand, the findings show no significant difference between positive attitudes towards both strategic and project factors. This can only mean that CMG has most of the key characteristics of a leading innovator, but by looking at the factors one by one in detail, the strengths and weaknesses of CMG's NPD strategy were identified.
Introduction
Corporate Strategy
However, this is one of the risks CMG must be prepared for when nurturing creativity. Product development projects must be technologically aggressive, especially for companies active in the telecommunications market. For CMG, integrating customer service with technological innovation is essential for successful new product development.
The Role of Management
The organization must be undirected in the way it approaches tasks and communicates with other project team members. In other words, the management team will be more interested in how a particular proposal might affect their status in the company, rather than the effect of the proposal on the welfare of the organization. This means that any entrepreneurial orientation will be suppressed rather than encouraged due to the high level of risk that new orientations bring and the damage they can cause to an individual's status.
Organisational Culture
Third, management must allow innovators to help select projects for development, although this is often difficult. Linked to the attitude of staff members is the vision of the company, which is also a matter of corporate strategy. It is the one thing with which organizational members identify - "culture" - and it is the one thing that ensures a sense of belonging and therefore will create a positive attitude.
Organisational Structure
The NPD Process
After CMG product managers develop the product concept and marketing strategy, the business attractiveness of the proposal must be evaluated. If the product concept passes the business test, it moves into R&D and/or design to be developed into a physical product. Up to this point the product concept had to exist only as a word description, or a prototype.
Staff
In the rugby approach, the product development process emerges from the ongoing interaction of a carefully selected, multi-disciplinary team whose members work together from start to finish.
Information
The unwillingness or inability of research staff to communicate their ideas in terms that industry staff can understand.
The Relationship between the Strategic and Project-Related Issues
CONCLUSION
Summary
To summarize, it is believed by Pearson (1991), that the following steps can be taken to make the company more dynamic and innovative. Create a corporate environment that puts constant pressure on everyone to beat company-specific competitors in innovation. However, innovation is the challenge that CMG must meet because it is what builds market leadership and competitive momentum.
Suggestions for further research
Management: Building Competitive Advantage. Ed. 4. 2000).Powerful Products: Strategic Management of Successful New Product Development. A discussion of the relationship between the style and structure of an organization and its relationship to its market. Booz, Alien and Hamilton. (1982). New Product Management for the 1980s. New York: Booz, Alien and Hamilton.
Main Study - Introduction Letter and Questionnaire
The title of my research is An Evaluation of a Telecommunications Solution Provider's New Product Development Strategy. Thank you for your willingness to participate in this study related to new product success. New product strategy Disagree Agree or agree. between functional coordination and the NPD process.
Pilot Study - Introduction Letter and Questionnaire
2a) Does the company have a product development strategy that defines the new products to be developed? No . 7b) Describe the organizational culture (informal structures) and shared values that exist to encourage new product development. No . 9b) Describe the type of leadership style that senior management uses in new product development.
McKinsey's 7Ss Framework
Computer Tabulations
Descriptive Statistics
CMG SWOT Analysis
CMG Organisation Structure
CMG Mission Statement
CMG Company Objectives
Product Policy Enhancements
CMG Core Roadmap Process
CMG Business Plan for NPD
Summarised Results of Pilot Study
CMG's resources are one of its most valuable assets and we employ people with years of industry experience. A realization that the industry is rapidly evolving, where meeting new product requirements is an essential requirement for continued success, or even existence, in the marketplace. QA: Quality assurance for our own developed products or in the case of third party products they are responsible for integration testing and quality assurance.