Rationale for the study
Sclerocarya birrea is one of the most important indigenous useful plant species in the Limpopo province. Indigenous people have important traditional knowledge about this species regarding its uses, management and population. However, the dynamics within its population must be understood to aid its sustainability.
Research questions
Aim and objectives of the study
Hypothesis
Structure of dissertation
Sclerocarya birrea fruits and seeds form an important component of the diet of rural people (Cunningham, 1988; Shackleton et al., 2000). Sclerocarya birrea (Marula) is a common and widespread species throughout the semi-arid, deciduous savanna of much of sub-Saharan Africa (Peters, 1988). An optional harvesting system must take into account the regeneration potential of the species (Orbiri et al., 2002).
Population structure
Evaluation of anti-inflammatory properties of Sclerocarya birrea (A.Rich.) Hochst (Family: Anacardiaceae) aqueous stem bark extract in rats. According to Xaba (2011), the African Marula (Sclerocarya birrea) is one of the most valuable indigenous fruit trees in the world. Research has proven that Marula species play an important role in the livelihood of the rural population.
Much knowledge about the use of Sclerocarya birrea is lost because it is not passed down from one generation to the next. Evaluation of anti-inflammatory properties of Sclerocarya birrea (A.Rich) Hochst. Family: Anacardiaceae) stem bark extracts in rats. Evaluation of analgesic anti-inflammatory and antidiabetic properties of Sclerocarya birrea (A.Rich) Hochst.
Inventory of Marula (Sclerocarya birrea subsp. caffra) stocks and fruit yields in community and conservation areas of the Bushbuckridge Lowveld, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Differences in size may cause the population of the same age to respond differently to the stimulus (Desmet et al. 1996). According to Klimas et al. 2007), population structure in forestry and ecological studies has been defined in terms of size class or stem diameter.
Most savanna tree species experience long-term dieback in the juvenile stage (Luoga et al., 2004).
Materials and methods
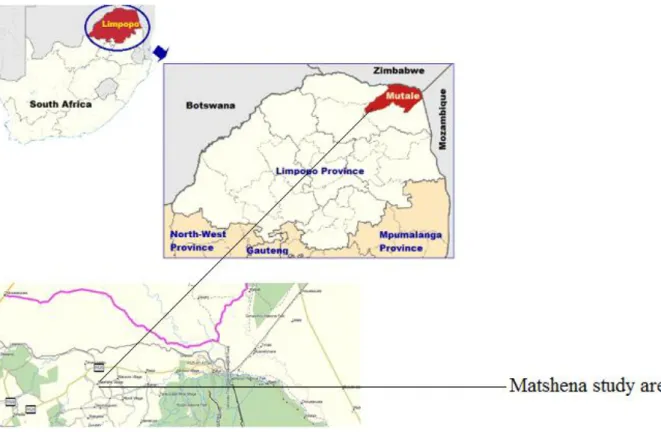
- Study area
- Methodology
The species is also gaining economic importance as products become more widely marketed (Gadd, 2002; Shackleton et al. 2002a). 2002) also state that Marula is a fruit bearer, which plays a very important role in the lives of many people in southern Africa. The present study therefore focuses on ethnobotanical inventory or Sclerocarya birrea use in the village of Matshena, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Limpopo is one of two provinces that are close to the Kruger National Park.
The province takes its name from the long, meandering Limpopo River that flows through the province, feeding the surrounding flora. The climate in Limpopo province is usually hot as the area bisects the Tropic of Capricorn. During the summer months, the heat is often interrupted by short thunderstorms, which are usually tolerable despite the sometimes extreme heat of the day.
Visitors to Limpopo province can expect sunshine, long summer afternoons and dry days for most of their stay. During this time of year, days usually start with a chill in the air to a warm midday and cool, dry afternoon. Thirty informants were interviewed in the former village of Matshena, Mutale Municipality in Limpopo Province, South Africa.
For those who were illiterate, questionnaires were administered in the vernacular Tshivenda, local language, with prior consent from them.
Results and discussion
- Informants profile
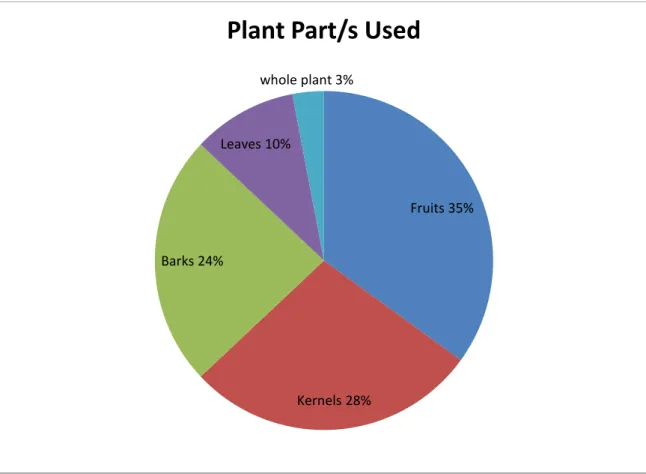
- Plant part/s used
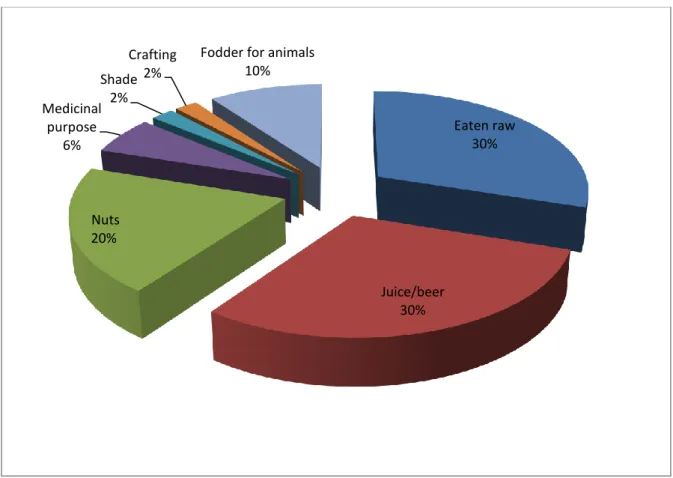
- Utilisation categories
Informants found available and willing to be interviewed when moving from house to house were interviewed about the use of Marula, most parts used and management. The convenience sampling method did not take into account the proportionality of the population of the village, as people were interviewed based on availability and willingness to participate. These findings on female dominance in information sharing are consistent with what has been stated by Shackleton et al.
They are therefore in a better position to know information about S use and to be willing to share information. Education levels were not considered for analysis in this study that focused on Indigenous knowledge generated through years of experience. Shackleton and Shackleton (2002) also address the use of fruit for eating (94.4%) in the domestic and commercial use of Marula products by Bushbuckridge households. The bark collected as shown in Figure 3-4 is used in the treatment of various stomach ailments, liver ailments, sore throats, rashes and malaria, and to relieve labor pains.
The stony seed coats are used to make baking soda which is used when cooking green vegetables. According to Hall et al. 2002), leaves are also mixed with bark in a variety of medical treatments. 2002b) indicated the uses of roots in the treatment of heavy menstruation, bilharzias, cough, weakness, sore eyes and heartaches.
Other uses for the wood include furniture, panels, flooring, laminated products, box shakers and manufactured articles such as shoe heels (Immelman et al., 1973).
Conclusions and recommendations
The study has revealed that people from Matshena village located in the former Mutale municipality, who are mainly women, have solid knowledge related to the use of Sclerocarya birrea. Effect of Sclerocarya birrea (Anacardiaceae) stem bark methylene chloride/methanol extract on streptozotoc in diabetic rats. Pharmacological activity of a procyanidin isolated from Sclerocarya birrea bark: Antidiarrheal activity and effects on isolated guinea pig ileum.
A book about indigenous and exotic trees in South Africa, about trees and timber in our cultural history and about our extensive silvicultural and timber industries. Ethnobotanical profile of indigenous protected tree species within the agricultural system of Mutale Local Municipality, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Potential stimulation of local rural economies by harvesting secondary products: A case study of the central Transvaal Lowveld, South Africa.
The use and trade of native edible fruit in the Bushbuckridge savannah region, South Africa. How long before resistance will make it possible to control some field strains of Haemonchus contortus in South Africa with one of the modern anthelmintics.
Introduction
Population size structure reflects past demographic structure and also indicates future demographic structure (Bullock et al. 1996).
Materials and methods
- Study area
- Methodology
The transects method was used to sample the population of Sclerocarya birrea using a 100 m tape measure which was laid down and all individuals of S. Stem girth measurements were taken at the base of the individuals using a tape measure (Figure 4.1 ). The assessment was interpreted as follows: 0 - 100% crown mortality, 1 - severe crown damage, 2 - moderate crown damage, 3 - slight crown damage, 4 - traces of crown damage and 5 - healthy crown.

Results and discussion
- Population structure
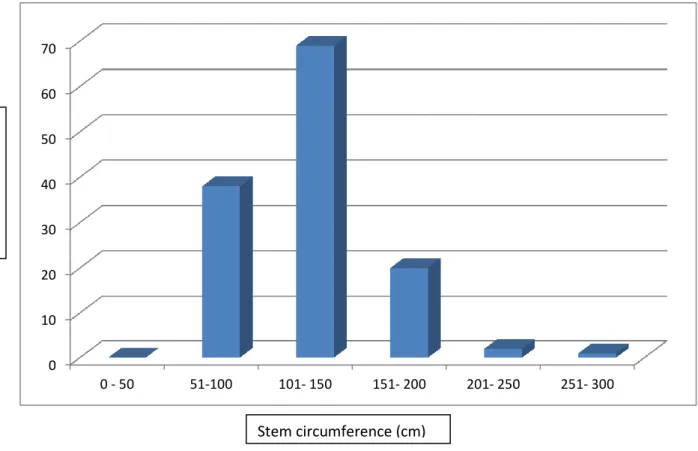
- Size class distribution
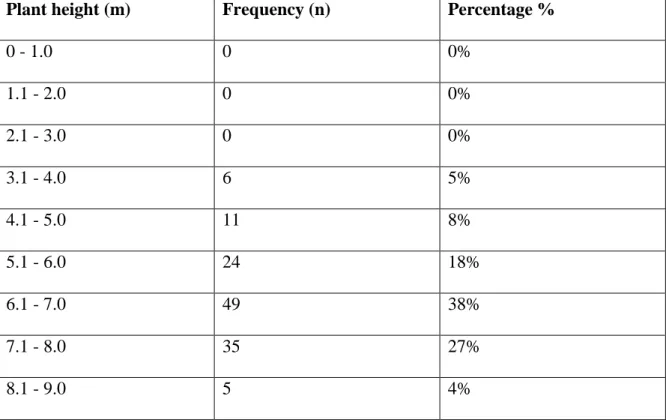
- Plant height measurement
- Crown health
The length class of 6.1 - 7.0 m has a large number of individuals and there is a huge decrease in the number of individuals of this class to 7.1 - 8.0 m, which is from thirty-eight percent (38%) to twenty-seven percent (27%) and eighteen percent individuals respectively. In this study the population of S. birrea is stable with only mature trees and little or no evidence of successful regeneration or recruitment. This finding has also been reported by Gouwakinnou et al. 2009) in that the largest trees are available in agroforestry area as.
The decline in seedling establishment was also due to human activities such as harvesting Maroela fruit by removing the seed from the population. During the winter season, many plants shed their leaves, but since data were collected during the summer month (February 13-19), most of the trees had healthy crowns. 2015), reported age as a contributing factor to severe crown defoliation in Tilia cordata tree species.
Conclusions
Demography of the plant ivory palm Phytelephas seemannii in Colombia, and the impact of seed harvest. The dynamics and sustainable use of high value tree species from the Coastal Pondoland Forests of the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. It also contains the research questions, aims and objectives of the study, hypothesis and the structure of the thesis.
In conclusion, it was found that the people of Matshena village do not use this species for commercialization like people of Bushbuckridge and Phalaborwa (Shackleton et al. 2000). According to Grundy et al. 1993) similar levels of kernel use were also observed in Owambo (Namibia) and Mbengarewa (Zimbabwe). Sclerocarya birrea is always present even during dry years and can therefore be useful as food security (Mojeremane et al., 2004).
According to Gouwakinnou et al. 2009), there were plenty of seedlings in agroforestry systems under mature trees that germinate during agricultural activities. These results on the population ecology of S. birrea in a municipal area using size class distribution, height and crown health cannot alone conclude or predict the future of the population. According to Condit et al. 1998), it takes time to predict the future population of a species.
An increased proportion of rural population and agricultural activities have a negative impact on various species (Gouwakinnou et al., 2009).
Recommendations
This area should be protected and people should be educated about harvesting the fruits. There should be a time frame for harvesting the fruit and after that time people should not be allowed to harvest. That the remaining fruits will fall off and be renewed, since they will not be harvested.
Regarding firewood, carving and bark removal for medicines, communities need to be empowered with the necessary knowledge for effective management and sustainable use of this population. Knowing these plants is important not only for their medicinal value, but also for their conservation aspect. According to Luseba and Tshisikhawe (2012), indigenous knowledge should be recorded and not transmitted to the new generation only orally.
It is important to document knowledge so that it can be useful to the next generation who may need this information in the future. Young scientists should be encouraged to use what scientists have found regarding native medicinal plants. Medicinal plants used to treat livestock diseases in the Vhembe Region, Limpopo Province, South Africa.
The use and trade of native edible fruit in the Bushbuckridge savannah region, South Africa.
Ethnobotanical knowledge questionnaire