Directory UMM :Data Elmu:jurnal:L:Livestock Production Science:Vol66.Issue2.Oct2000:
Teks penuh
Gambar

Dokumen terkait
Porcine colostrum and milk contain not only highly digestible nutrients but also numerous bioactive compounds, including various types of growth factors, including epidermal
developed, e.g., in mice (Saffrey and Burnstock, Dogs do not obtain a MMC until 15 days post- 1994; Liddle, 1997), it is important to study whether natally, whereas sheep and
In addition, there are considerable effects on hormones (especially on concentrations of insulin, glucagon, insulin-like growth factor-I, including its binding proteins, and
Because of gestion that the cow’s udder might grow rather than the exponential nature of mammogenesis, a doubling regress during declining lactation assumed that pro- of cell
However, it was not possible to establish any During myogenesis, the frequency of nuclei ex- clear correlation between the expression pattern of pressing myf-3 did not change
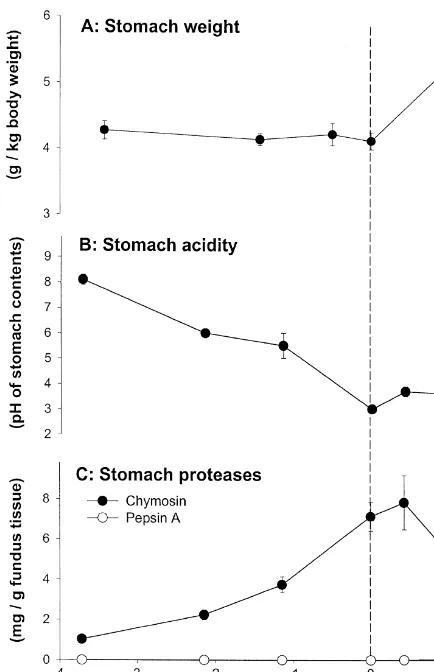
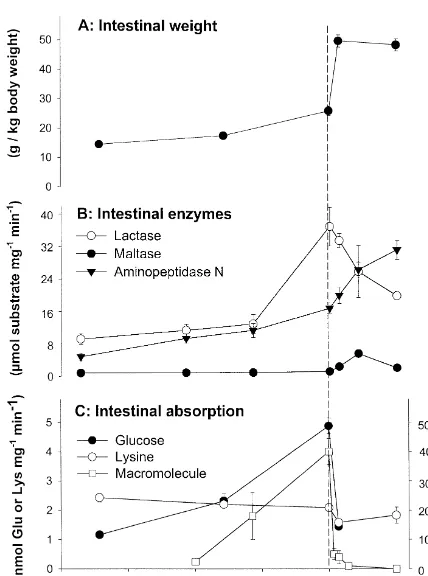
Maternal milk and maturation of the intestine thought to be taken up by the neonate and to compensate for the immature function of neonatal Colostrum and milk feeding have been shown
The combined preference priorities are calculated as follows: (1) the preference priority given by a certain customer to a certain service element is multiplied by the
Thus, the deleterious rhizobacteria (DRB) (Fredrickson and Elliott, 1985; Schippers et al., 1987), are so-called because they are considered to adversely influence root health and