vol11_pp41-50. 139KB Jun 04 2011 12:05:52 AM
Teks penuh
Gambar

Garis besar
Dokumen terkait
By using this property it is possible to define a Fourier transform on the entire Hilbert space of the harmonic oscillator, which is its own inverse and satisfies the Parseval
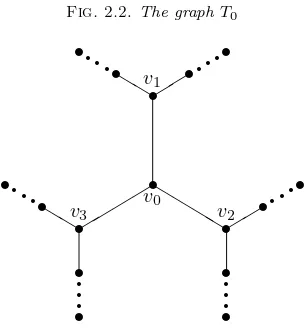
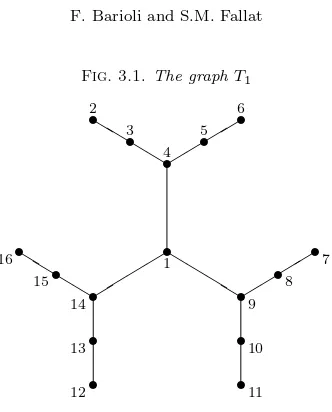
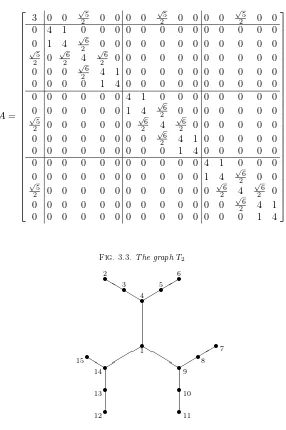
Inverse eigenvalue problem, Symmetric stochastic matrix, Symmetric nonnegative matrix, Distance matrix.. AMS
The problem of determining the multiplicities of an eigenvalue of a product of companion matrices appears in the study of Random Walks in a Periodic Environment (RWPE), a type of
were carried out using a particular, in this case MATLAB, programming language... In this paper we have focused on implementing the parallel algorithm for com- puting the group
In particular, joint semigroup densities of the eigenvalue processes of the generalized matrix-valued Ornstein-Uhlenbeck and squared Ornstein- Uhlenbeck processes are
A recent theorem in [3] provided a link between a certain function of transition probabilities of a strong Markov process and the boundedness of the p -variation of its
Several equivalent conditions are given showing their particular role influence on the connection between the sub-Gaussian estimates, parabolic and elliptic Harnack
We prove here (by showing convergence of Chen’s series) that linear stochastic differential equa- tions driven by analytic fractional Brownian motion [6, 7] with arbitrary Hurst index
