Graduate Certificate in Clinical Instruction Graduate Diploma of Education kandidat Diploma in Graphic Communication Educatio. Kommunikationsteknologi Uddannelse Graduate Diploma in Mathematics Education Graduate Diploma in Student Welfare Graduate Diploma in Technology Education Graduate Diploma in Curriculum.
The general aims of the EO policy are
In order to achieve the aims of the EO and/or AA policies
S ubjects Available
P lanning a Course
W Normally orkload a student will not be permitted to enrol for subjects totalling more than 100
P oints and Involvement Time
Students commencing a course seeking leave of absence for up to twelve months must apply in writing or complete the appropriate form available from the Office of the Academic Registrar.
A ssessment Students are advised to keep a copy of all written assignments or materials submitted for
Additional Notations
P olicy on Assessment of Individual and Joint Work
E mergencies
ERC staff provide instruction and guidance on the location and use of tools and equipment. Instructions for using CD-ROM databases are available upon request at the print circulation desk.
M ulti Media Open Access Location: Level 3 Rm 3105
All incoming students are offered a user education program on the effective use of ERC services and resources. Sources of material in other libraries can be identified through the National Union Catalog of Monographs (NUCOM) or the National Union Catalog of Serials (NUCOS) held at the print circulation desk.
S tudent Information Austudy
Copiers for student use are located on the third floor in the Educational Resource Center. Phones for student use are located in the Student Lounge next to the Cafeteria on the first floor.
The Institute specialises in the professional expertise area of
Diploma of Teaching (Technical & Further Education)
Diploma of Teaching (Technology)
Bachelor of Education
Bachelor of Training and Development A three year full-time, or equivalent part-
Graduate Certificate in Educational Studies (Teaching English to Speakers of
Graduate Certificate in Clinical Instruction This initial course is an opportunity for
Graduate Diploma of Education
Graduate Diploma in Information and Communications Technology Education
Graduate Diploma in Mathematics Education
Graduate Diploma in Student Welfare This course is designed to increase partici-
Graduate Diploma in Technology Education This course assists teachers to assess technol-
Graduate Diploma in Curriculum
Graduate Diploma in Educational Administration
Articulation of The University of Melbourne courses within Hawthorn Institute
GDTE GDME
GDGCE*
GDSW H
M ethods of Assessment
The University of Melbourne Courses
O verseas Students
Conditions of Study in Australia and Immigration Regulations
Extended part-time study due to illness may result in a student not continuing to meet course requirements. If the leave of absence is approved, the student is not allowed to stay in Australia but must return to the country of origin.
Health Insurance
Your student visa lists the conditions that apply specifically to you and a breach of any of these conditions may result in the termination of your permission to remain in Australia. If the illness is of long duration, a student is expected to return to the home country and not return to Australia until fully recovered.
The provision of sharply focused studies in English has been and continues to be a
Unit
The Commercial Unit employs a wide range of skilled personnel who seek to meet not only the academic and vocational needs, but also the welfare needs of the international students studying within the Unit. Consequently, all Unit programs and courses are based on extensive consultation with the client and are evaluated both during and after implementation to ensure trainee and client satisfaction.
Training and Development
Center staff advise and assist in the development of comprehensive training plans for these industries. Over 200 Victorian industries and government sectors offer the Institute's accredited occupational health and safety courses through the Partnership Scheme.
The strength of the training provided through the Center lies in the flexibility of its delivery methods and attention to the needs of clients. Key consultancy services available through the Center include Vocational Analysis, Training Needs Analysis and Skills Audits plus the development and production of advanced training courses for the industrial, commercial and government sectors.
Course Listing
Associate Diploma in Training and Development** 30 Diploma of Teaching (Technical and Further Education) 33
Graduate Certificate in Clinical Instruction 69 Graduate Certificate in Educational Studies (TESOL) 72
Graduate Diploma in Educational Administration 78 Graduate Diploma in Graphic Communication Education** 90
Graduate Diploma in Mathematics Education 106
Graduate Diploma in Technology Education 114
Refer to The University of Melbourne Handbook 95 (Volume 5-Education)
Last intake was in 1994
COURSE CO-ORDINATOR: ROSALIND KING, ROOM 2259,
TELEPHONE: (03) 810 3295
Course code
Entry requirements
Period of candidature
Credit
Recognition for prior learning credit programs
Course structure and progress
From the beginning of 1995 the Associate Diploma in Training and Development will have no further student intakes.
Conversion from the Associate Diploma in Training and Development to the Bachelor
Subject desc ri ptions
771-102 TRAINING AND PRESENTATION SKILLS 1B Credit points: 21.7
771-103 NEEDS ASSESSMENT AND PROGRAM DESIGN 2A
771-104 EVALUATION AND COMPUTER BASED TRAINING 28
Content: CBT activities; concepts and skills in program design; CBT programming; student and learning assessment;. Assessment: A major task involving the production of a linear design CBT program together with a logic diagram, objective objectives, student assessment approaches, student response instruments and self-assessment documentation (100 percent).
771 - 105 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS 3 Credit points: 5.0
771-106 TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT IN ORGANISATIONS 4
771-107 INTERPERSONAL AND CONSULTATIVE SKILLS 5A
771-108 INTERPERSONAL AND CONSULTATIVE SKILLS 58
771 - 109 MANAGEMENT OF THE TRAINING FUNCTION 6A Credit points: 19.6
1 demonstrate the communication and interpersonal skills and commitment to education that contribute to collaborative learning.
771-110 TRAINING ADMINISTRATION 68 Credit points: 19.6
771-111 CONTEMPORARY ISSUES OF TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT 7
771-112 MAJOR PROJECT 8 Credit points: 21.8
INITIAL COURSE ENQUIRIES: VIRGINIA BRANTON
TELEPHONE (03) 810 3317
COURSE CO-ORDINATOR: JOHN DAVID, ROOM 1311, TELEPHONE (03) 810 3142
Course entry
Course advice
Assessment
Course structure
Schedule A
Subject descriptions
Assessment: Make up exercises; large task (70 percent); and a minor assignment or 3 minor assignments (30 percent).
772-272 TEACHING, LEARNING AND CURRICULUM 2 Credit points: 16.7
772-273 LANGUAGE AND COMMUNICATION 2 Credit points: 8.3
772-274 EDUCATION, TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETY 1 Credit points: 8.3
7 72-395 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
772-396 INITIAL TEACHING SKILLS Credit points: 4.0
772-398 TEACHING EXPERIENCE Credit points: 33.4
Basic teaching competencies are included in a Learning to Teach Agreement, while advanced teaching and learning activities comprise the Phase Two Agreement.
772 - 377 TEACHING, LEARNING AND CURRICULUM 3 Credit points: 11.2
772-378 EDUCATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY 2 Credit points: 5.6
772 - 379 LANGUAGE AND COMMUNICATION 3 Credit points: 8.3
772 - 380 EDUCATION, TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETY 2 Credit points: 8.3
772 - 383 TEACHING, LEARNING AND CURRICULUM 4 Credit points: 8.3
772-381/772-391 TEACHING/FIELD EXPERIENCE 2A AND 2B
772-384 ADULT EDUCATION Credit points: 8.3
772-385 SPECIALISED COMPUTER APPLICATIONS IN EDUCATION
772-386 STUDIES OF EQUAL OPPORTUNITY IN EDUCATION
772-387 MATHEMATICS IN VOCATIONAL EDUCATION Credit points: 8.3
The second component of the course is the Supplementary study which makes up the third year and consists of two parts. The second part consists of the Technology Education Program in which you follow studies designed to extend and broaden your understanding and skills in various aspects of technology education.
771-127 TECHNOLOGY STUDIES 1A Credit points: 5.6
771 - 129 LANGUAGE AND COMMUNICATION 1A Credit points; 11.2
771 - 131 TEACHING, LEARNING AND CURRICULUM 18 Credit points: 11.1
771 - 132 TECHNOLOGY STUDIES 18 Credit points: 5.6
771-133 EDUCATION, TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETY 1 Credit points: 8.3
771-134 LANGUAGE AND COMMUNICATION 18 Credit points: 8.3
771-136 TEACHING, LEARNING AND CURRICULUM 2 Credit points: 11.1
771-137 TECHNOLOGY STUDIES 2 Credit points: 5.6
771-138 EDUCATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY 2 Credit points: 5.6
Assessment: Completion of the set computing package (40 percent); and set tasks of about 1,500 words (60 percent).
771 - 139 LANGUAGE AND COMMUNICATION 2 Credit points: 5.6
771 - 140 EDUCATION, TECHNOLOGY AND SOCIETY 2 Credit points: 5.6
771-144/145/146/147/148 ADVANCED SPECIALIST STUDIES PROGRAM
Assessment A class presentation and 500 word written report (30 per cent); class exercises (20 per cent); and set assignments of approximately 1000 words (50 per cent). Content: The school will offer a range of 36 hour programs depending on student interest and staff availability.
771-149 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION PROGRAM Credit points: 50.0
771-156 TEACHING EXPERIENCE Credit points: 33.2
774-149 TEACHING EXPERIENCE 2 Credit points: 33.2
COURSE CO-ORDINATOR: JOHN O'SULLIVAN, ROOM 2325,
TELEPHONE: (03) 810 3234
The Bachelor of Education is intended for students completing a Diploma in Teaching (Technical and Further Education) or a Diploma in Teaching (Technology). The goal of the course is to provide a synthesis of practical experience and theoretical study that expands the student's knowledge and understanding of education and increases their ability to contribute effectively and flexibly in the processes of after-school and technical and further education.
Involvement time and teaching methods
After admission, you follow a follow-up study of at least one and at most two academic years as a full-time student, or during at least two and at most four academic years as a part-time student, unless you have had another application that has been approved by the Academic Council on the advice of the faculty. The total number of points to be obtained for prior education and/or following other course units may not exceed 50 points.
773-101 TEACHING AND LEARNING 1773-102 TEACHING AND LEARNING 2
773-001 GENDER STUDIES IN EDUCATION AND TRAINING
773-002 COMPETENCY BASED TRAINING Credit points: 16.7
773103 CURRICULUM DEVELOPMENT Credit points: 16.7
773 - 104 CURRICULUM INNOVATION Credit points: 16.7
773105 INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN IN EDUCATIONAL MEDIA
773-106 INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN IN EDUCATIONAL MEDIA: PILOT STUDY
Contents: The role of TAFE in post-secondary education;. characteristics, needs and motivations of adult students; adult learning models; principles and practices in adult education. After completing this course, students should be able to: understand adult education in a national and international framework; to evaluate adult education issues addressed in the literature; synthesize from their reading and experience an Australian perspective on adult education; and. make analytical comparisons of adult education in Australia with that in other countries.
773 - 111 METHODS OF EDUCATIONAL RESEARCH Credit points: 16.7
Contents: History and development of personnel management: policy development; personnel selection and introduction: personnel development; Performance Review.
773 - 112 RESEARCH PROJECT Credit points: 16.7
773-113 EDUCATION IN A MULTICULTURAL AUSTRALIA
773114 MOVEMENT AND ACQUISITION OF MOTOR SKILLS
Content: Intellectual disabilities; specific learning difficulties; emotional disturbances; recognition of learning difficulties and appropriate forms of remedial assistance. Assessment: A 1,500-word paper on special education and student social service provision (30 percent); a 3,000-word case study about an individual with a learning disability (70 percent).
773-119 INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIPS Credit points: 16.7
773 - 120 TECHNOLOGY AND VALUES Credit points: 16.7
773 - 121 MANAGING DIVERSITY Credit points: 16.7
COURSE CO-ORDINATOR: ROSALIND KING, ROOM 2259,
Special entry
Although the methods used to teach the subjects differ, the Bachelor of Training and Development follows principles of adult learning. Conversion from the Associate Diploma in Training and Development to the Bachelor in Training and Development.
776-108 THE PSYCHOLOGY OF THE LEARNING CLIMATE
Content: Communication models and their implications for training and development; personal development needs of individuals, interpersonal skills and communication styles and their impact on group dynamics in training and development situations in the workplace; effective communication as a critical element of leadership in training and development activities; development of personal creative approaches to problem solving through experience of a range of strategies and techniques appropriate for staff development and training, including evaluation and feedback, interviewing and counselling, mediation and negotiation, conflict resolution and discipline procedures; the relationship between group process and learning outcomes in training and development contexts within organizations;.
776-109 SOCIOLOGY OF WORK Credit points: 16.7
776-110 THE TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT PROFESSION
An analysis of current literature and ethical issues; history of education and development; the major basic studies of training and development such as economics, education, sociology and psychology; research traditions; Content Program design and implications for training and development practice; factors affecting program design and the resulting training and development impacts that may affect the organization; program design models, including product-based, content-based, process-based, research-based; training needs analysis models such as communicative and technical and their connections with program design.
776 - 204 WORK ORGANISATION AND TECHNOLOGY Credit points: 16.7
776 - 205 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT ISSUES Credit points: 16.7
776-206 TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT CONSULTANCY
776-207 HUMAN RESOURCE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS AND ISSUES
776-208 MARKETING IN ORGANISATIONS Credit points: 16.7
776-301 MODELS OF EVALUATION Credit points:16.7
Assessment: Describe and analyze an approach to the design and implementation of an evaluative study of 1000 words (20 percent); a comparative analysis of 4,000 words (80 percent).
776 - 302 PRAXIS IN TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT Credit points: 16.7
776 - 303 POLICY AND MANAGEMENT Credit points: 16.7
776-304 ORGANISATIONAL CHANGE AND DEVELOPMENT
Assessment: A 2500 word essay requiring application of theory to the student's workplace (50 per cent): a 2000 word essay describing and analyzing a change taking place in the workplace (50 per cent). The practicum component of the course will involve a minimum of 45 days of supervised practice teaching in an approved environment.
Program One
A person who has qualified for a degree at the University or has qualified at another university or institution for a degree or diploma may be admitted to the Graduate Diploma of Education course. Candidates who have completed the Graduate Certificate in Clinical Instruction are eligible to join the course with advanced standing and, on successful completion of the final three subjects of the programme, as set out below, will be awarded the Graduate Diploma of Education.
Program Two
To follow the 'Practicum' course, you arrange an internship yourself at a recognized institution, with a recognized supervisor or mentor.
Program Three
Course requirements
Subject descriptions Program One
Assessment: Completion of a Learning Agreement, negotiated within the subject, to develop an occupation-specific learning design/experience of 1500 words or equivalent (100 per cent).
772-168 DESIGN, MANAGEMENT AND EVALUATION OF LEARNING 1
772-169 PSYCHOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES IN ADULT LEARNING
Content: The content of the internship is clearly defined in an individualized, formal Learning Agreement, which is prepared, negotiated and developed by a trio of the student, a supervisor/mentor on site and a Hawthorn Education Institute manager. The Hawthorn Manager's professional judgment based on the mentor's report and the candidate's portfolio.
771 - 167 METHODS OF TEACHING
771 - 168 INTEGRATED PROGRAM
771-169 PRACTICUM (FULL-TIME SECONDARY) Credit points: 30.0
Content: The teaching experience program is based on the assumption that individuals progress at different rates through stages of concern about their practice. The teaching objectives are documented in the Teaching Learning Agreement, which is reviewed during the course.
771 - 173 PRINCIPLES AND METHODS OF TEACHING 1 Credit points: 12.5
771 - 176 PRINCIPLES AND METHODS OF TEACHING 2 Credit points: 12.5
771 - 175 PRACTICUM (PART TIME SECONDARY) Credit points: 30.0
Content The context of the teaching experience is built on the assumption that students progress at different rates through the stages of concern for their practice. Content: This course is delivered as two separate integrated courses: (i) stress management; Communication abilities; classroom management strategies; behavioral analysis; adolescence and/or adulthood and group dynamics; (ii) Exploration of topics selected from the areas of personal skills, personality and behaviour, learning and thinking.
771-183 EDUCATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY 2 Credit points: 5.0
771-179 EDUCATION AND SOCIETY 1 Credit points: 5.0
771-182 EDUCATION AND SOCIETY 2 Credit points: 5.0
771-122 PROJECT - SPECIAL METHOD TEACHING PROJECT
INITIAL COURSE ENQUIRIES: JACQUI KLAUS
TELEPHONE: (03) 810 3297
COURSE CO-ORDINATOR: BOB CROSTHWAITE, ROOM 2535,
TELEPHONE: (03) 810 3247
Prerequisites: Completion of, or concurrent enrollment in, Introduction to Learning and Teaching Processes and Design, Management and Evaluation of Learning 1. Prerequisites: Location in an approved teaching or training context and completion of or current enrollment in Introduction to Learning and Teaching processes and Design, management and evaluation of learning 1.
EducationalStudies(TESOL)
773-128 PSYCHOLOGICAL PRINCIPLES AND PROCESSES IN CLINICAL INSTRUCTION
773129 CLINICAL INSTRUCTION EXPERIENCE PROGRAM
COURSE CO-ORDINATOR: JAMES BROWN, ROOM 2311,
TELEPHONE (03) 810 3209
The course is a ms to upgrade andor retraining of graduated teachers in the teaching of English to speakers of other large,:ages in prnary. Preference for the course offered at the Hawthorn Campus will be given to applicants from the Adult Education and TAFE sectors.
773-122 LANGUAGE AND LANGUAGE ACQUISITION Credit points: 16.7
To qualify for the certificate, the first half of the requirements of the Postgraduate Diploma in Educational Studies (TESOL) offered at the Parkville campus will be met.
773-123 TESOL METHODOLOGY AND CURRICULUM DESIGN
773124 TESOL PROFESSIONAL PRACTICE Credit points: 16.7
INITIAL COURSE ENQUIRIES: JACQUI KLAUS
COURSE CO-ORDINATOR: DR RICHARD COTTER, ROOM 2253,
TELEPHONE (03) 810 3124
A student who, after having completed other equivalent higher education programs, registers for the diploma course, may, with approval, be credited in subjects corresponding to the other higher education programs, provided that the amount of credit must not exceed 50 percent of the course's requirements. Credit will not be given for similar studies in a course for which the student has already received an award or which was used to gain entry to the Graduate Diploma in Curriculum course.
Cross credits
After being admitted, a candidate must pursue a course of higher education for a minimum of one and a maximum of two academic years.
Teaching methods
For course descriptions for electives in the Graduate Diploma in Educational Administration or Graduate Diploma in Student Welfare courses, please refer to the relevant section of the Guide. Note: Courses from the Graduate Diploma and Student Welfare course will not be taken into account when meeting the requirements for enrollment in the one-year full-time Master's degree in Education.
Program for 1995
Content: Students will investigate and analyze the social, organizational and epistemological elements of curriculum design and implementation and how they relate to each other, different models of curriculum development will be studied; production of practical proposals related to the current work situation of students; how to manage curriculum change is a central focus.
774-114 MANAGING CURRICULUM EVALUATION Credit points: 16.7
774-115 CURRICULUM CONTEXT, POLICY AND GOALS Credit points: 16.7
774-116 ASSESSMENT AND REPORTING Credit points: 16.7
774-117 APPLIED PROJECT Credit points: 16.7
774-118 ADVANCED TEACHING PRACTICE Credit points: 16.7
773-199 RESEARCH METHODS
COURSE CO-ORDINATOR: LAWRIE DRYSDALE, ROOM 2257,
TELEPHONE: (03) 810 3375
Special entry requirements
Students are expected not only to demonstrate that they have reviewed the relevant material and/or administrative situations, but also to pose appropriate questions for consideration by their colleagues in the course. Explanations of the specific requirements for assignments for each subject are indicated in the detailed syllabuses.
773-139 THE LEADER IN ACTION Credit points: 16.7
773-131 EDUCATION AND THE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT PROCESS 1
773-132 EDUCATION AND THE FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT PROCESS 2
Contents: General systems of industrial relations; industrial relations in student organizations, industrial relations matters (eg, conditions, grievance procedures); skills development (eg, negotiation). Content: Roles of financial management; funding for educational institutions; accounting systems and records for educational institutions; budgeting in educational institutions; cost effective management of resources;
773-144 COMPUTERS IN EDUCATION Credit points: 16.7
773146 DEVELOPING PERSONAL RESOURCES Credit points: 16.7
773-147 MANAGEMENT OF HUMAN RESOURCES 1 Credit points: 16.7
773-148 THE COMMUNITY AND THE ADMINISTRATOR This subject is not offered in 1995
773-150 STRESS AND THE ADMINISTRATOR Credit points: 16.7
773 - 151 MANAGEMENT OF HUMAN RESOURCES 2 Credit points: 16.7
773 - 152 PHILOSOPHICAL ISSUES IN ADMINISTRATION Credit points: 16.7
773 - 153 MARKETING IN EDUCATION Credit points: 16.7
773 - 154 ADMINISTRATION OF CURRICULUM 1 Credit points: 16.7
Contents: Curriculum questions for the administrator; different models and philosophies of curriculum development and their implications for the management of education; the policy of governing the curriculum; managing curriculum implementation processes; purposes and styles of curriculum evaluation and their organizational implications.
773-155 ADMINISTRATION OF CURRICULUM 2 Credit points: 16.7
773-156 LEADERSHIP IN SMALL GROUPS Credit points: 16.7
773-157 WOMEN IN MANAGEMENT Credit points: 16.7
773-158 PLANNED CHANGE IN ORGANISATIONS Credit points: 16.7
Content The content is determined by the participant and the supervisor and is approved by the subject teacher and the course coordinator. Content: The content is determined by the participant and the supervisor and is approved by the subject teacher and the course coordinator.
773-164 MANAGING DIVERSITY Credit points: 16.7
773-165 PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT AND TRAINING
773-166 ORGANISATIONAL DEVELOPMENT This subject is not offered in 1995
773-167 ASSESSMENT AND DEVELOPMENT FOR EDUCATIONAL ADMINISTRATORS
773-168 ORGANISATIONAL EVALUATION This subject is not offered in 1995
773-196 SCHOOL DEVELOPMENT Credit points: 16.7
773-197 INFORMATION SYSTEMS Credit points: 16.7
773198 PROPERTY DEVELOPMENT AND MAINTENANCE
Content: Development process of the school; project planning and control audit; public relations, marketing and fundraising; strategic planning, quantifying the strategic plan;. Content: objectives of development and maintenance of school property, human resource management issues, planning and permitting processes, legal requirements and obligations, project management, work scheduling, ergonomics and design.
773-199 RESEARCH METHODS
Gradu é Diploma in Graph
Communication _Education
COURSE CO-ORDINATOR: JOHN STINCHCOMBE, ROOM G259,
TELEPHONE: (03) 810 3347
Course availability
Students who provide evidence of completed related study and/or experience in these fields may be granted exemptions from some course requirements. Postgraduate studies in graphic and communication education can be obtained by a student who has fulfilled the prescribed conditions and achieved a total score of 100 points with passed or recognized credit in each of the compulsory courses.
775-118 APPLIED DESIGN STUDIES IN GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION EDUCATION 1- INFORMATION
A student who, after completing a second study at the tertiary level, enrolls in a course for a diploma in graphic communication, may be recognized with approval for courses that were equivalent to those taken at a second tertiary study, provided that the amount of credit must not exceed 50 percent of the course requirements .
775-119 GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION TEACHING AND CURRICULUM 1
Contents: History of graphic communication education in Victoria from 1869; an evaluation of the teaching of graphic communication from the preparatory grades to the tenth year; an assessment of twelfth year courses; an experimental analysis of the drawing process; the role of graphic communication in the general school curriculum; current curriculum issues and integrative approaches to curriculum programming. Content: Perceptual and cognitive theories; creativity and graphic communication; brain functionality; problem solving and learning styles; fallibility of sensory processing systems; visual illusions; color theories; learning disabilities related to graphic communication; gestalt modeling and spatial development.
775-122 APPLIED DESIGN STUDIES IN GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION EDUCATION 3 - ENVIRONMENTAL
775-123 GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION TEACHING AND CURRICULUM 2
Communications ethnology Education
COURSE CO-ORDINATOR: TERRY GUTHRIDGE, ROOM 1319
TELEPHONE: (03) 810 3335
A postgraduate study in information and communication technology can be obtained by a student who has fulfilled the prescribed conditions and achieved a total score of 100 points with completed or recognized eight subjects, of which seven are compulsory and one subject. is an optional subject. This strand is designed to provide students with a range of skills in information and communication technology.
Proposed Course Structure for I99S
Technology orientation Strand
Social Context Strand
In this part, students study the consequences of information and communication technology in education and develop appropriate curriculum models for the implementation of information and communication technology. Course descriptions for courses in the proposed fifth year postgraduate study in Information and Communication Technology will have a sign (#) before the course code.
775168 THE PROCESSING, MANAGEMENT AND COMMUNICATION OF INFORMATION - INTRODUCTION
775-169 THE PROCESSING, MANAGEMENT AND COMMUNICATION OF INFORMATION - THE MEDIUM OF
775-170 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING (PROBLEM SOLVING)
775-171 ELECTRONIC PUBLISHING Credit points: 16.7
775-172 INFORMATION PROCESSING Credit points: 16.7
775-173 MULTIMEDIA DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT Credit points: 16.7
775-174 INFORMATION, COMMUNICATION AND SOCIETY
Assessment A major assignment in which each participant will form a hypothesis early in the course about the possible social implications of the use of information and communication technology. A journal will be used to discuss this hypothesis in relation to work covered in the course.
775-175 INFORMATION SYSTEMS Credit points: 16.7
Content: current and planned information and communication technologies; work and leisure; science and technology as ideology; industrial and technological restructuring for economic development; the validity of concepts such as mass society and mass media; cross-border data flows: global time competitiveness. The hypothesis can be modified or reinforced or rejected through arguments presented in the journal (3000 words or equivalent) (70 percent); a case study (1500 words or equivalent) (30 percent).
775-176 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Credit points: 16.7
775-177 MEDIA ANALYSIS Credit points: 16.7
775-178 THE CURRICULUM OF INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGY IN
EDUCATION Credit points: 5.6
Assessment: Individually agreed project or evaluation of information and communication technology education in schools (1500 words or equivalent) (100 percent).
775-179 ACTIVE PARTICIPATION IN EDUCATIONAL CHANGE
775-180 FUTURE DIRECTIONS IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGY
775-168 THE PROCESSING, MANAGEMENT AND COMMUNICATION OF INFORMATION -
CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONS IN COMPUTING Credit points: 16.7
Assessment: A minor paper of 2000 words in which participants will research and critically analyze various information processing solutions (40 percent). A major project of 3,000 words in which students design a solution to an information processing problem using all techniques related to the information processing cycle (60 percent).
775-169 THE PROCESSING, MANAGEMENT AND COMMUNICATION OF INFORMATION: THE MEDIUM OF
Content: Practical experience in the production of multimedia programs, including recording, editing and production management. A major assignment of 3,000 words, in which each participant will formulate a hypothesis at the beginning of the course about the possible social consequences of the use of information and communication technologies.
775 - 175 INFORMATION SYSTEMS Credit points: 16.7
Content: Topics will include: current and projected information and communication technology; work and leisure; science and technology as ideology; industrial and technological restructuring for economic development; the validity of concepts such as mass society and mass media; cross-border data flow; and global time competitiveness. The hypothesis can be modified or strengthened or rejected by arguments presented in the journal (60 percent).
775 - 176 COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS Credit points: 16.7
775 - 177 MEDIA ANALYSIS Credit points: 16.7
775-178 THE CURRICULUM OF INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGY IN EDUCATION
775-180 FUTURE DIRECTIONS IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGY
775-181 ADVANCED APPLICATIONS IN INFORMATION AND COMMUNICATIONS TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION
After completing this course, students should be able to:. evaluate and critically analyze concepts, theories and current developments in information and communication technology applications; evaluate and critically analyze the use of these technologies in society and education; research and reflect on current trends in each of the studied areas of advanced technology. Assessment of a 3000-word paper (60 per cent) on the theoretical aspects of virtual reality and a 2000-word equivalent paper (40 per cent) on the practical application of the technology.
COURSE CO-ORDINATOR: MICHAEL BARRACLOUGH, ROOM 3131,
TELEPHONE: (03) 810 3265
No credit will be awarded for similar studies in a course for which the student has already won an award or used to access the Graduate Diploma in Mathematics Education course. The Graduate Diploma in Mathematics Education may be awarded to a student who has met the pre-requisites and achieved a cumulative score of 100 points by passing or receiving credit in three Core Studies subjects, two Level 1 studies in Mathematics subjects, two Level 2 Studies in Mathematics subjects and two subjects from the tutored options.
774-172 MATHEMATICS EDUCATION: YEARS 5-9 Credit points: 8.3
774-174 RESEARCHING MATHEMATICS TEACHING AND LEARNING
774-175 STUDIES IN MATHEMATICS: ALGEBRA AND PROBABILITY
Assessment: Compilation of an organized and comprehensive resource file based on all content topics covered in the unit (50 percent); and preparing and presenting a class report detailing and illustrating applications of mathematics relevant to one of the content area topics (50 percent). Content: Computing in mathematics education, including the use of Logowriter and spreadsheets; evaluation of commercially available software packages.
774-182 COMPENSATORY MATHEMATICS EDUCATION Credit points: 8.3
774-183 MAJOR PROJECT Credit points: 8.3
774-184 STUDIES IN MATHEMATICS: ANALYSIS Credit points: 16.8
774-185 STUDIES IN MATHEMATICS: FINITE MATHEMATICS
Graduate Diploma_ n Studen
COURSE CO-ORDINATOR: JON STEBBINS, ROOM 3103,
TELEPHONE: (03) 810 3354
The Postgraduate Diploma in Student Welfare can be awarded to a student who has met the prescribed conditions and achieved a cumulative score of 100 points by passing the six compulsory subjects or receiving credit.
775-111 HELPING INTERVENTIONS 1
775 - 112 HELPING INTERVENTIONS 2 Credit points: 20.0
775 - 113 HELPING INTERVENTIONS 3 Credit points: 15.0
775-130 STUDENT WELFARE: THE SOCIAL CONTEXT Credit points: 15.0
Models of Student Welfare - Guidance and Needs; a critical analysis of well-being roles and structures in schools and colleges; the relationships between student welfare and organizational structure, curriculum and discipline. A consideration of community-based student welfare and other models of school welfare work; the concept of 'community'.
COURSE CO-ORDINATOR: GEOFF RODGERS, FOR COURSE INFORMATION CONTACT JOHN
Teacher welfare - the link between teacher and student welfare; organizational stressors and staff welfare measures; development of personnel welfare policy; Change processes and student welfare - theories and models of change in relation to managing change in schools and colleges; the teacher as a change agent; the processes of policy development; implementation and evaluation of changes; action research methodology.
STINCHCOMBE OR GEOFF RODGERS, TELEPHONE: (03) 810 3232
A graduate in technological education can be obtained by a student who has fulfilled the prescribed conditions and achieved a total score of 100 points with passed or credit points in six subjects. Participants in the Postgraduate Technology Education course will be required to demonstrate success in six subjects, including a compulsory subject, by satisfactorily completing assessment tasks.
Program for I99S
The following are typical programs that may be selected by students seeking qualifications in some aspect of technology education. Perspectives on the role of technology in the formation of personal and occupational identity and the symbolic purposes it serves.
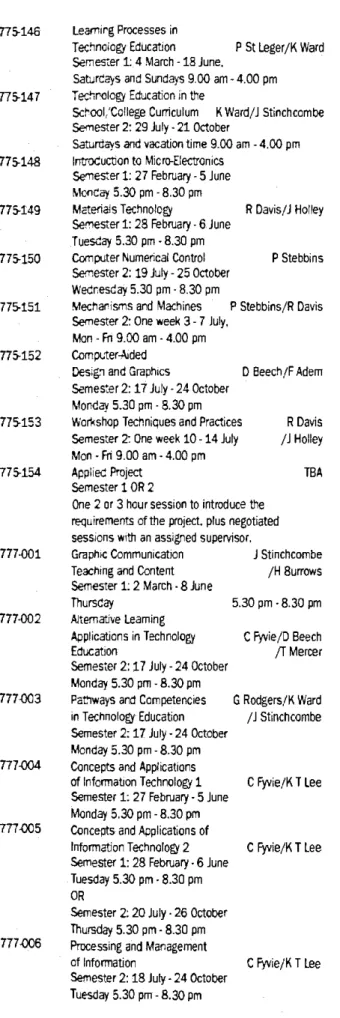
775-118 APPLIED DESIGN STUDIES 1 INFORMATION COMMUNICATION DESIGN
775-120 APPLIED DESIGN STUDIES 2 - PRODUCT DESIGN
775-122 APPLIED DESIGN STUDIES 3 - ENVIRONMENTAL DESIGN
Assessment: A minor assignment equal to 1500 words which is an output/folio oriented product based on the main assignment.
775 - 145 APPLICATION OF TECHNOLOGY Credit points: 16.7
775-146 LEARNING PROCESSES IN TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION
775-147 TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION IN THE SCHOOL/COLLEGE CURRICULUM
Content: Influences on the development of technology education content; an investigation into the various influences that shape technology education e.g. Evaluation and assessment; differences between assessment and evaluation; validity and reliability; formative evaluation in technology education.
775-148 INTRODUCTION TO MICRO-ELECTRONICS Credit points: 16.7
Curriculum planning; a critical analysis of curriculum planning in technology education; using resources, taking into account different learning styles and individual differences, using new delivery techniques for instruction and implementation; action research as a way of thinking about the curriculum.
775-149 MATERIALS TECHNOLOGY Credit points: 16.7
775-150 COMPUTER NUMERICAL CONTROL Credit points: 16.7
Composition of computer numerical control programming; the form and type of information required from design concepts: the process of identifying, obtaining, using and developing the required information. Identification of ways in which the principles of CNC machining can be applied in a specific teaching and learning context.
775-151 MECHANISMS AND MACHINES Credit points: 16.7
data transfer and graphic design processing; exploration of concepts related to the processing and transfer of data between systems. A large 3,000-word assignment in which participants compile a portfolio on computer numerical control, analyze and comment on the role of technology, design and manufacturing processes (60 percent).
775-152 COMPUTER AIDED DESIGN AND GRAPHICS Credit points: 16.7
Assessment: A small assignment corresponding to 2000 words based on a number of practical work requirements (40 per cent). Assessment: A minor assignment of 1500 words involving research into suitable computer systems (hardware and software) that can be implemented in a personal learning environment, taking into account the educational perspective, existing technologies and design factors involved in the development of such systems (30 per cent ).
777-005 CONCEPTS AND APPLICATIONS OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY II (CAIT II)
Contents: An overview of computer concepts; the nature of a computer; information processing cycle; computer systems components, software and an overview of information systems. A major assignment equal to 3,500 words involving interaction with an appropriate software package to carry out specific teaching-related tasks (70 percent).
777-006 PROCESSING AND MANAGEMENT OF INFORMATION (PMI)
end-user tools; analysis and evaluation of the most used software applications and their impact on users; key features of software applications; teaching aids and assistive devices in an educational environment.
777-007 INFORMATION SYSTEMS Credit points: 16.7
Non-imperative language: use a non-imperative language to determine the key elements that influence language structure by examining the applied relationship between an imperative and non-imperative language. Assessment A large assignment of 5000 words based on imperative and non-imperative languages - compare and contrast the two language styles and comment on the strengths and weaknesses of each language to solve the problem (100 per cent).
777-008 COMMUNICATION AND TECHNOLOGY Credit points: 16.7
Content: imperative language; use a compelling programming language to analyze elements of the structure and basic commands to achieve a desired result. Troubleshooting; explanation of problem solving techniques to gradually develop structured programming skills to learn how data is structured, represented and manipulated to find solutions to problems.
DIRECTORATE
SCHOOL OF TECHNOLOGY EDUCATION AND
DEVELOPMENT
Centre For Human Resources Development
STRONG
Centre For Studies in Adult and Vocational Development
Centre For Technology Education
MADNER
COMMERCIAL UNIT
Centre for International Teaching, Training and
Centre for Continuing Education and Training
Hawthorn English Language Centre [HELC]
CORPORATE SERVICES
Senior Management of the Faculty of Education 1995
UNRESTRICTED STUDENT
HAWTHORN