This confirms that the thesis titled “Pavement Management System Using Deflection Prediction Model of Flexible Pavements in Bangladesh” submitted by Md. It is stated that the work “Pavement Management System Using Deflection Prediction Model of Flexible Pavements in Bangladesh” stated in this thesis was carried out under the supervision of Lecturer Khondhaker Al Momin, Department of Civil Engineering, Daffodil International University.
INTRODUCTION
- Introduction
- Rigid pavement is classified into four types
- Flexible Pavement is classified into three types
- Pavement Management System
- About AADT
- Some data table for determination of AADT
- Determination process of IRI
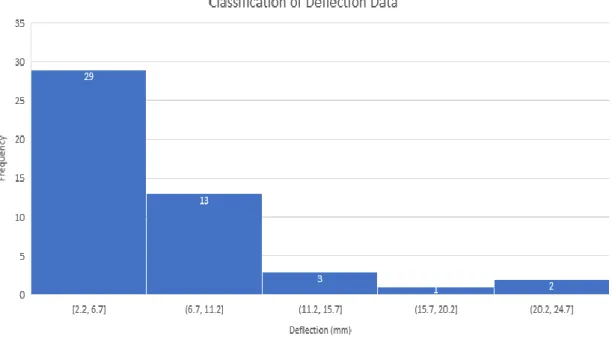
- Deflection
- Deflection Measurement
- About RHD
- Measurement Techniques
- Some benefits of using flexible pavements
Using a tiered system to create a flexible paving design relies on the retailer communicating aspects of the system (Hassan, 2015-12). An applied (static or dynamic) load causes a vertical deflection of the road surface, which is quantified as a deflection distance on the road surface.
LITERATURE REVIEW
- literature review
- Pavement in aspects in Bangladesh
- Pavements in Bangladesh Have a Long History
- Pavement Life Cycle in Bangladesh (As of the Present Situation)
- Pavement management system
- Factors of pavement management system
- Example of Pavement failure in Bangladesh
- Determination of Flexible Pavement Roads in Bangladesh
- Reclaimed Asphalt Pavement in Bangladesh
- Design of Flexible Pavement
- Difficulties of Pavement construction in Bangladesh
Rutting and pavement surface roughness were also considered in determining the final overlay thickness recommendations. Unless otherwise stated, all information in this study was obtained directly from the author's lodgings. At the end of the process, the results of the avoidance were used to determine the necessary reinforcement for the path (Younger, 1982).
During this investigation, the climatic condition of the area is taken into account. However, one of the main disadvantages of solid paving is the high cost of construction in the beginning. The CBR of the subgrade and the amount of traffic are two of the yield characteristics.
Due to the pooling of water, it is easy to see the lack of trainability of the pavements in Bangladesh. Stone quarries can be found in the northern tip of the country, near the border with Canada. Whatever the case, strengthening the mix through the use of proper treatment can help improve the road's base layer.
This layer of the pavement is often referred to as the drainage layer of the pavement (Alam, 2004).
DATA COLLECTION
Introduction
Site Selection
- For Predicting Actual Pavement Life
- For Evaluating the Overloading Impact on Pavement Life
- For Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Rigid and Flexible Pavement
- For Field Data Collection for Performing Laboratory Experiment
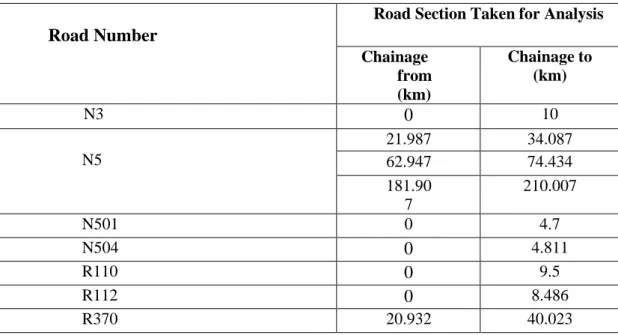
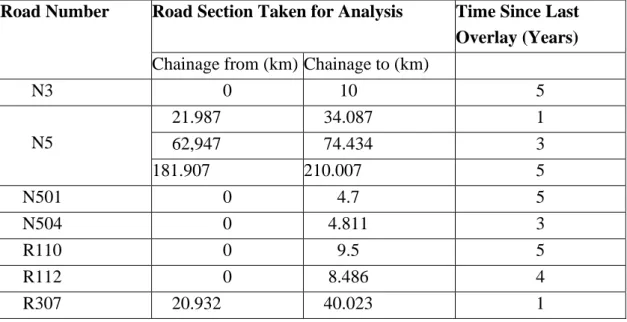
Initially, a pilot survey was conducted within the RHD road network to identify suitable road sections to collect adequate data to successfully predict actual pavement life. Representative samples covering all three types of road sections such as national roads, regional roads and Zilla roads. Thus, on the basis of the above-mentioned criteria, a total of nine road sections of approximately one hundred seven kilometers and six hundred and seventy seven meters (107.677 km) were selected for the final survey.
To assess the impact of overloading on the service life of the road surface, axle load data from heavy vehicles traveling on roads should be collected. During the pilot research phase, a search was made for the locations where axle load data can be found. Obtaining axle load data from the weigh station required necessary permission from the Executive Engineer, Manikgonj Road Division, RHD.
For the determination of the initial and life cycle costs of rigid and flexible pavement, several ongoing and completed projects were observed by RHD during the reconnaissance survey. These two construction sites were selected for the final survey to determine whether the correct method is being followed in the construction of flexible pavement undertaken by Dhaka City Corporation (DCC) engaging local contractors.
Description of Sites
- Site Description for Predicting Actual Pavement Life
- Site Description of N3
- Site Description of N5
- Site Description of N501
- Site Description of N504
- Site Description of R110
- Site Description of R112
- Site Description of R370
In order to ensure quality control during roadway construction, various field surveys must be conducted. To conduct field research related to various aspects of flexible pavement construction, data were collected from two construction sites in Dhaka city in the form of critical observation of construction practice, paving mix ingredients and samples were also collected from these two sites. These two road sections differed from each other in terms of geometric characteristics and traffic load patterns.
Four national roads N3, N5, N501, N504 of the Department of Roads and Highways were selected and six road sections from these selected national roads were taken for further analysis. Three road sections were taken from the three regional roads R110, R112 and R370 of the Department of Roads and Highways.
Basic Information
Site Description for Evaluating Overloading Impact on Pavement Life
To evaluate the impact of uncontrolled overloading on the service life of the pavement, the axle load station at Bathuli, Dhamrai, Dhaka, located on the Dhaka-Aricha highway, was selected. The stations are managed to control congested truck traffic through government-approved mechanisms to protect the national road network from the harmful effects of overloading. The station has an axle load measuring system for oncoming traffic on both sides of the highway.
On each side, the 600 m long installation includes two HSWIM (High Speed Weighing in Motion) and one LSWIM (Low Speed Weighing in Motion) equipment with integrated traffic sensors, video cameras, signs, signals, terminals, computing and communications equipment, connections, nodes and compatible software; control of buildings and annexes, approach roads including acceleration and deceleration lanes, landings, gates, fences, barriers, truck parking area, lighting, generator and other related features required for station operation. Approach roads consist of flexible pavement, rigid pavement and a modern underground drainage system that requires careful maintenance. However, they are responsible for the maintenance of the structures/installations constructed/included by them/any entity other than.
Site Description for Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Rigid and Flexible Pavement
- Description of Site-1
- Description of Site-2
The Debogram-Progoti Sharani Link Road or Purbachal access road is a proposed project constructed by RAJUK as a flexible pavement, and the Dhaka-Sylhet highway has already been constructed as a flexible pavement. In this cost comparison analysis, both road sections are analyzed as flexible pavement and then again as rigid pavement with the same data (soil conditions, traffic, etc.). The Sylhet-Bholaganj road project includes both flexible and rigid paving works and the project is currently under construction.
To determine whether the correct method is followed in the construction of flexible pavement, data is collected from two overlapping construction sites in Dhaka city. Site-1 is a light road segment located in the Khilgaon area near the Khilgaon flyover. The construction work consisted mainly of the restoration of the deteriorated pavement and was implemented by using an on-site prepared paving mix and laying it by hand.
It is a road section located in Shahbagh in the vicinity of PG Hospital which is mainly used by medium to heavy traffic. The construction of this site also consisted mainly of resurfacing the weakened pavement and was implemented using plant mix and paving.
Data Collection
- Pilot Survey
- Final Survey
- Prediction of Actual Pavement Life
- Evaluation of the Overloading Impact on Pavement Life
- Life Cycle Cost Analysis of Rigid and Flexible Pavement
Final investigation work is carried out after investigation of problems that had arisen in the pilot investigation. To create the survival curves, the IRI values are converted to Pavement Condition Rating (PCR) values and the time since the last overlay is used as described in the methods section of Chapter 3. After the engineer issued the permit on 23 October 2016, the necessary data was retrieved from HDM- Circle in the form of a Portable Document Format (PDF) file.
Axle load data was collected from the weigh station at Bathuli, Dhamrai, Dhaka by Regnum Resources Limited, which is the responsible party for maintaining the weigh station and collecting toll from the overloaded heavy vehicles authorized by the Roads and Highways Department. To calculate the percentage of overloaded trucks, data was also taken from the monthly report for penalty amount for overloaded trucks at Bathuli-Manikgonj axle load checking station. The monthly reports for the months of November 2016, December 2016 and January 2017 were collected from the office of Executive Engineer, Manikgonj Road Division, RHD for analysis purposes.
For conducting life cycle cost analysis of rigid and flexible pavements, pavement design data from Debogram-Progoti Sharani Link Road Project and Dhaka-Sylhet Highway Restrengthening Project were collected from the thesis titled. The pavement design data for both flexible and rigid pavements of Sylhet-Bholagonj Road Project was collected from the office of Technical Services Wing of Roads and Highways Department at Elenbari, Dhaka on 26 October 2016.
3.4.2.3.1 Design Data of Debogram-Progoti Sharani Link Road Project
3.4.2.3.2 Design Data of Dhaka-Sylhet Highway Restrengthening Project
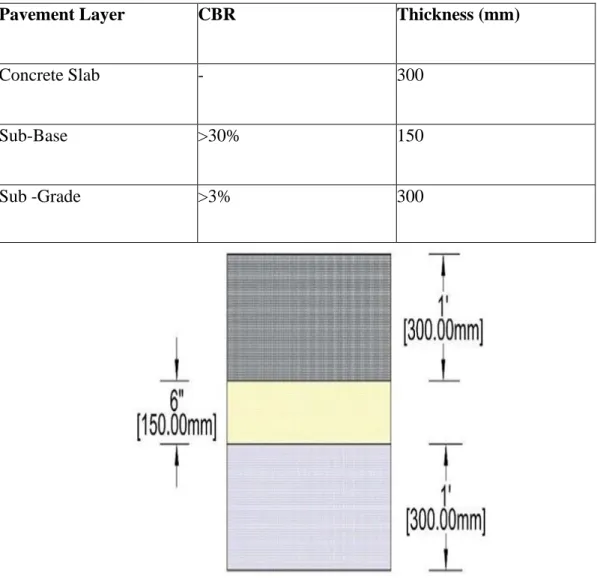
Figure 3.13 shows the design layer thicknesses of the rigid pavement together with the associated CBR values graphically.
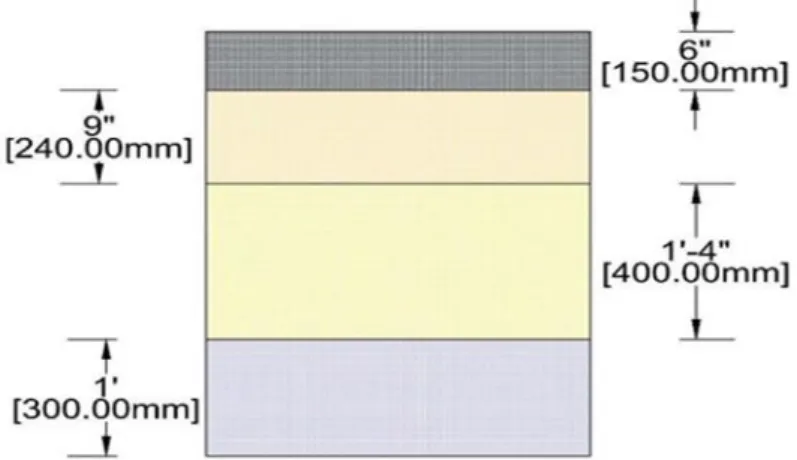
3.4.2.3.3 Design Data of Sylhet-Bholaganj Road Project
- Pavement Design (as national highway standard)
- Design of rigid pavement
- Field Data Collection for Performing Laboratory Experiment
- Problems Encountered During Data Collection
- Overview
- Review on road section
- Analysis on IBM SPSS v.26 Software
- Comments on Analysis
- CHAPTER 5 CONCLUSION
- Conclusion
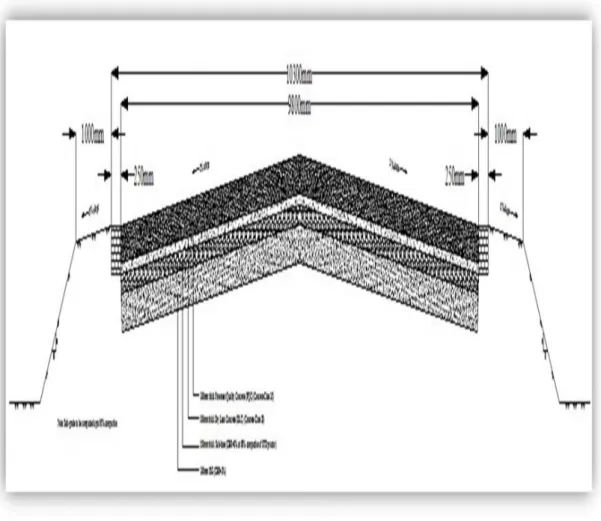
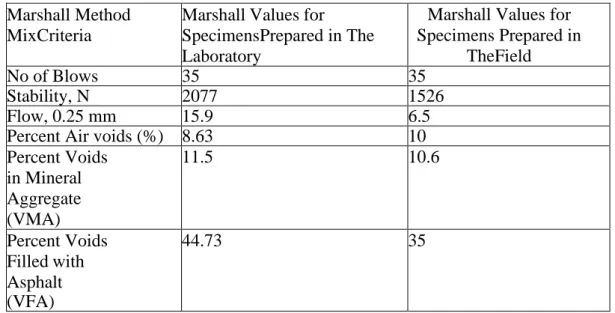
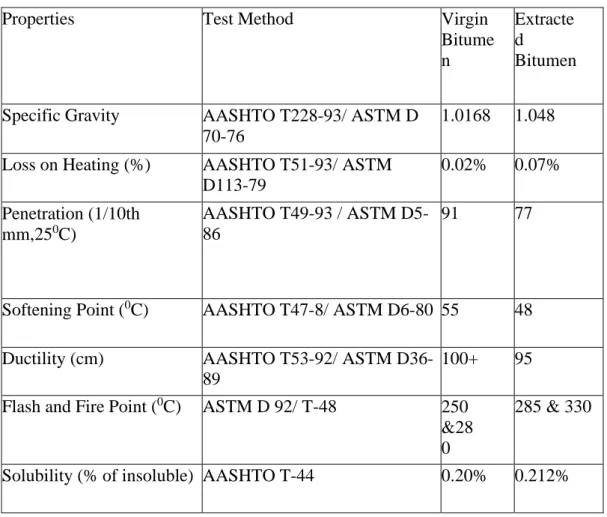
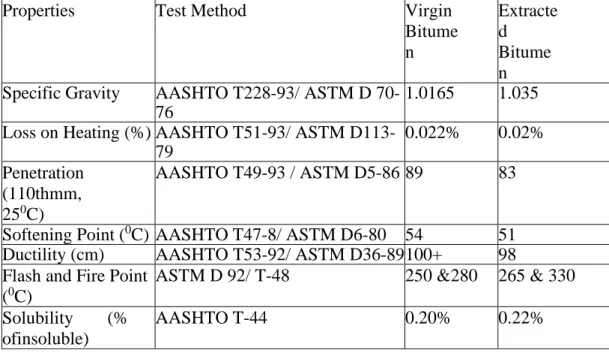
The joint details for rigid pavement such as contraction joint, longitudinal joint, expansion joint and corner reinforcement details are given in the design sheet with nice illustrations. For rapid disposal of rainwater, adequate drainage facilities should be provided. The pavement design sheet collected from the Technical Services Wing of Roads and Highways Department in collaboration with the Executive Engineer is available on the following pages. The test results obtained by performing various tests as mentioned earlier are arranged in tabular form in the following section.
Analysis of these data is prepared in the next chapter "Data Analysis" and observations along with comments on the results obtained are made by comparing with the standard values. So the data of the Roughness Survey conducted in the year 2013 was used to carry out the analysis work to achieve the objectives stated in Chapter 1 of this research work. For inspection of the quality control of pavement construction, a lot of time must be given in the field.
This chapter includes the data collection phase, which was carried out according to the methods described in the Methods chapter. Overall, this chapter contains all the data required for the analysis to be performed in the next chapter 4 called “Data Analysis” to achieve the objectives stated in chapter 1 titled “Introduction”. The constant or intercept as well as the regression coefficients (B) for each explanatory variable included in the regression model are presented in this table.
IRI and pavement time, i.e. the amount of time elapsed since the last overlay, have been identified as important indicator factors in determining pavement deflection.