We hereby declare that this project was carried out by ourselves under the supervision of Assistant Professor Tanvir Ahmed Chowdhury, Department of Textile Engineering, Faculty of Engineering, Daffodil International University. We also declare that neither this project nor any part of this project has been submitted elsewhere for the award of any degree or diploma. Firstly, we are grateful to the Almighty who gives us sanity and sound health to successfully carry out this project.
His endless patience, scientific guidance, constant encouragement, energetic supervision, constructive criticism, valuable advice, reading many inferior drafts and correcting them at all stages have made it possible to complete this project. This report presents a comparative study between the turquoise color dyeing and the normal color dyeing (reactive dye). In this report, we discuss turquoise dye and normal dye of reactive dye.
Here we also compare the color fastness to washing and rubbing fastness of turquoise colored fabric and normal colored fabric. We know that turquoise is a hot brand dye where normal color dyes are in lower temperature. After all, our study is essential to make a comparison between turquoise dye and normal color dye.
19 Figure 3.6: Process curve of color fastness to washing 20 Figure 3.7 : Crock Meter (Left) & Light Box (Right 21 Figure 4.1: Multi-fibre after washing with light shade 23 Figure 4.2 : Multi-fibre after washing with medium shade 23 Figure 4.3: Multi-fibre after washing with dark shade 24 Figure 4.4: Multi-fibre after washing with light shade 24 Figure 4.5 : Multi-fibre after washing with dark shade 25 Figure 4.6: Multi-fibre after washing with dark shade 25 .
Introduction
- Turquoise color
- Turquoise Dyestuff
- Turquoise Variations
- Some turquoise example with features
- Dyeing of turquoise various shade
Dyeing is a process in which dye is transformed into a textile material to create permanent or permanent color. There are different types of dyes used in the textile industry for dyeing textile goods. Reactive dyes are organic color compounds which are capable of forming covalent bonds between the reactive group of the dye molecule and the nucleophilic groups in the polymer chains within the fiber.
Reactivity of the dyes can be reduced when desired by blocking one of the reactive chlorine atoms giving H-type Procions [3]. Due to different types of classification, dye affinity and fastness of the dye to fiber show different characteristics. Turquoise dye is a hot brand reactive dye that has low affinity and less fastness properties than cold brand reactive dyes.
Hot brand dyes require a high temperature of around 70 to 90˚C, while cool brand and medium brand require a low temperature. But the hot brand dyes, such as turquoise dye, have lower affinity and persistence properties due to their molecular structure and reactive group. Here we compare the dyeing process and fastness properties of turquoise hot and cool dyes.
Knowledge of the dyeing process of turquoise (hot brand) dyes and conventional (cold brand) dyes. Knowledge of the fastness properties of turquoise (hot brand) dyes and regular color (cold brand) dyes. It is a common brand name hot dye and the dyeing process or the process of getting the color is a bit complicated than reactive dyes the normal color dyeing process.
According to the reactivity of reactive dyes, the cold brand dye contains a reactive group with high reactivity. A research paper- “Turquoise shade dyeing technique with in-depth analysis on shade, utility consumption and physico-chemical properties in relation to identical color batches” by Shamim Al Azad, Hridam Deb, Md. Another article named – “Comparison of properties of cotton dyed fabric with pigment and reactive dye” by Tanveer Hussain & Rasid Ali Published on March 2, 2009 is related to variation and comparison shade, dyeing process and fastness of reactive dye and dye of pigment when dyeing cotton fabrics.
No journal report has been made based on the comparison of turquoise and reactive dyes with normal color (cold mark). But having few journals and books published on based on reactive dyes and turquoise dyeing process.

11
- Equipment List
- Experimental Procedure
- Basic Difference between Reactive dye normal colour & Turquoise color
- Turquoise color dyeing Process
- Flowchart of Turquoise dyeing
- Normal color dyeing process
- Flowchart of dyeing normal color
- Testing of color fastness to wash
- Calculation
- Process Flow chart
- Testing of Color Fastness to rubbing
- Testing Procedure
- Assessment Technique
Our experimental project is based on three different shade percentages of turquoise and cool brand colors for light shade, medium shade and dark shade. Our experiment is about the difference in dyeing processing and fastness between Turquoise hot brand reactive dyes and cool brand reactive dyes. So the dyeing of the turquoise dye and the cool brand dye is done and then the fabric is gathered.
After dyeing and finishing, the fabric is tested to measure resistance to rubbing and color fastness to washing. Affinity The turquoise dye has a lower affinity, but the quality of the dye and the company play an important role in good dye persistence. Dissecting the stitch and measuring the change in color and color staining with gray.
A square of white test fabric (5 cm x 5 cm) is taken, which is plain woven, desized, bleached, but without finished cotton fabric (as ready to dye). The tested sample compared to colored sample and under light box using D65 light source and evaluated using color change gray scale. Dry rubbed crock cloth also visually assessed under a light box with a D65 light source and assessed using color staining gray scale.
In the case of the wet rubbed fabric, it was first evaluated after drying the baking fabric, the procedure was the same as for the dry rubbed fabric.
22
- Result of Turquoise color (Light shade)
- Result of Turquoise Color (Medium shade)
- Result of Turquoise Color (Dark shade)
- Result of Normal color Reactive dye (Light shade)
- Result of Normal color Reactive dye (Medium shade)
- Result of Normal color Reactive dye (Dark shade)
- Assessment for Rubbing fastness of turquoise dye
- Assessment for Rubbing fastness of Normal color Reactive dye
- Differences of the results between Reactive normal color (cold brand) and Turquoise
- Result in Chart
- Result in Chart for Rubbing fastness
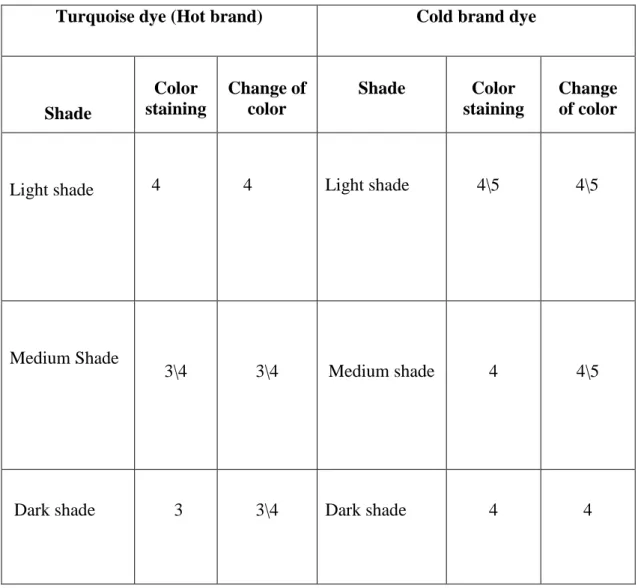
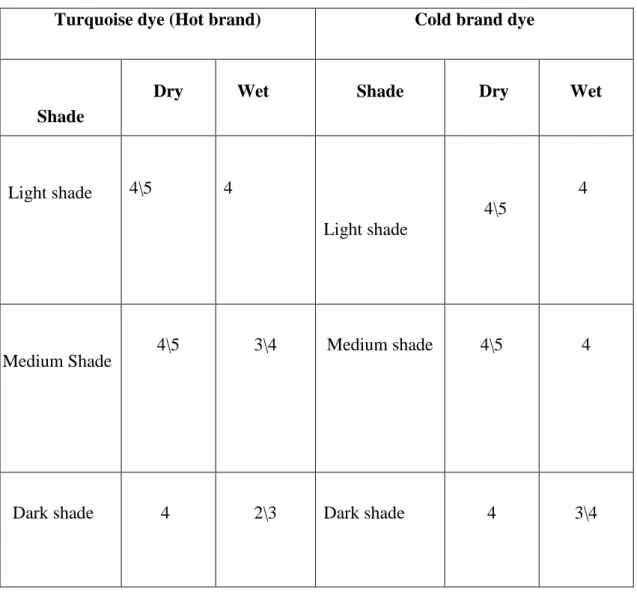
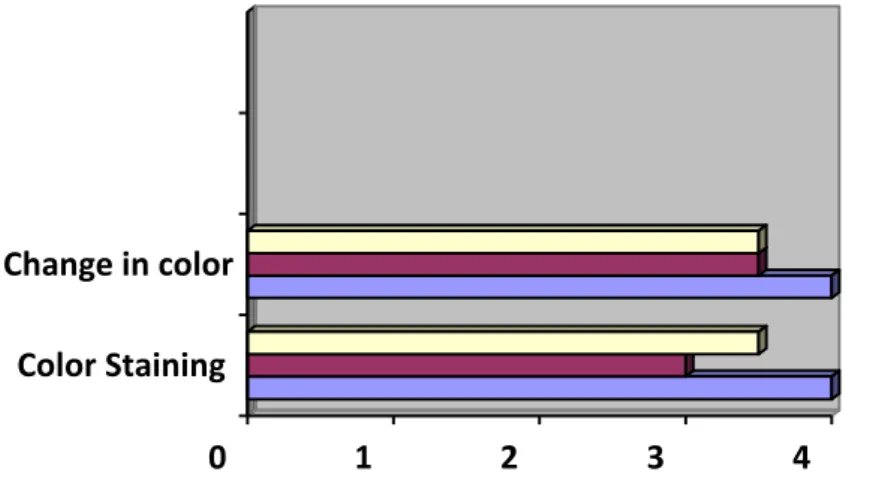
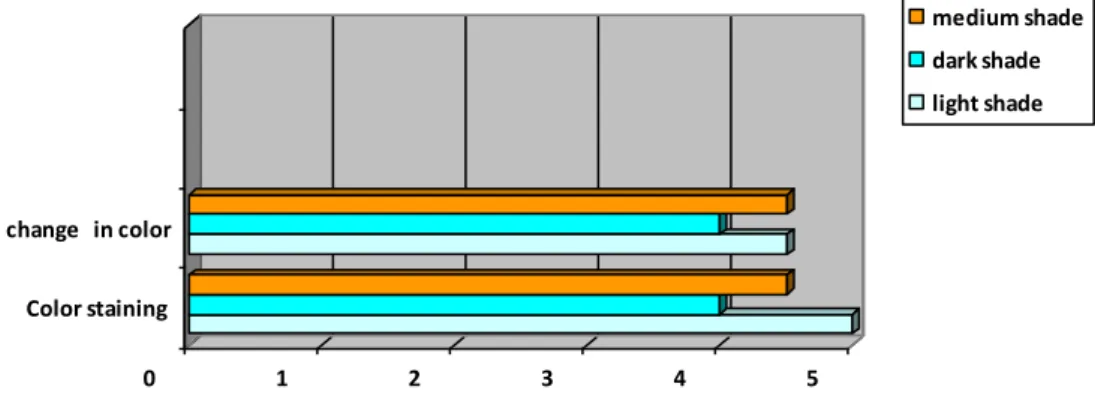
Figure 4.5: Multi-fibre after washing with medium shade Table 4.5 Grading of dyeing (Multi-fibre) for medium shade. After doing all those tests, we found a comparative result between Turquoise (hot brand) and cold brand of reactive dye. The result of color fastness to washing is shown in Table-4.13, the result of color fastness to rubbing is shown in Table-4.14.
When the tint percentage is less, the fastness properties of both the turquoise and cool brand colors are almost the same, but when the tint percentage increases, the turquoise dyed samples offer less fastness than the cool dyed sample. cool brand.

31
We know that now a days reactive dye is the most popular dye to dye the cellulose fibers due to high affinity to cellulose fibers. By forming covalent bond reactive dye molecule bond with fiber structure and shows moderate to good authenticity properties. According to the reactivity of these dyes, turquoise dye, which is warm brand dye, has less affinity than cold brand dye.
So during dyeing with turquoise color due to less affinity high temperature is required for color production for the fabric where cold brand required less temperature than hot brand color. This poor affinity to fiber also causes weak color fastness properties of the fabric and for good affinity of cold brand colors, it shows better fastness properties than turquoise dye. For light shade, both dyes show almost the same authenticity properties, but in medium and dark shade we see the difference.
Although turquoise dye has less affinity, quality dye and company play an important role for good color fastness. We hope that this work will be essential and useful for the readers and people in the industry to do further work with.