ABSTRACT
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF SIMULATION TECHNIQUE IN ENGLISH
SPEAKING CLASS AT THE FIRST GRADE OF SMAN 2 METRO
By
Sigit Prasetiyo
Teaching English stated in KTSP is particularly to enable the students to master the
four language skills; listening, reading, speaking and writing. The ability to
communicate is the primary goal of foreign language instruction that speaking is put
ahead on the other skills.
This Classroom Action Research was conducted to find out how the implementation
of Simulation Technique (ST) can increase the students’ speaking achievement and
improve the teaching learning process. The subject of the research was the first grade
students of SMAN 2 Metro consist of 32 students.
The result of the research shows that Simulation Technique (ST) improves the
students’ speaking ability. The indicators of the research concern with the learning
product and learning process. It was shown from the result in the learning product is
80% of the students pass the passing grade which is 65 while the learning process is
80% of the students active during the lesson and the teacher can get score 80 for
teaching performance. In the first cycle, students did not achieve the indicator
because the results were 17 students or 46.87% who achieved speaking score target
and 24 students or 75% for the students’ involvement, while the teaching
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF SIMULATION TECHNIQUE IN
ENGLISH SPEAKING CLASS AT FIRST GRADE OF SMA
NEGERI 2 METRO
(A Classroom Action Research)( A Script)
By Sigit Prasetiyo
0613042056
Advisors:
1. Hery Yufrizal, M.A., Ph.D. 2. Budi Kadaryanto, S.Pd., M.A.
English Education Study Program
Language and Arts Department
Faculty of Teacher Training and Education
Lampung University
CURRICULUM VITAE
The name of the researcher is Sigit Prasetiyo. He was born in Adijaya village, East Lampung on November 15, 1987. He is the last child of Bapak Mukijan and Ibu Warni. He has three older brothers and one older sister. He was so obsessed with traditional arts and military since he was a four-year old child.
He entered TK Pertiwi in 1992 and then continued his study in SD Negeri 1 Adijaya East Lampung in 1994. Having graduated from the elementary school in 2000, He entered SLTP Negeri 3 Metro, Kodya Metro and graduated in 2003. After that, He finished his high school at SMA Negeri 2 Metro in 2006.
After finishing his school, he followed the SMPTN (A National Selection
MOTTO
“SURADIRA JAYANINGRAT LEBUR DENING PANGASTUTI”
“The glory of evilness will be destroyed by goodness”
CONTENTS
D. Teaching Speaking Through Simulation ... 14
E. Procedures of Teaching Speaking through Simulation ... 16
F. Advantages and Disadvantages of Simulation ... 17
1. Cycle 1 ... 32
a. Planning ... 33
b. Implementing ... 33
c. Observing ... 35
d. Reflection ... 40
e. Recommendation for cycle 2 ... 42
2. Cycle 2 ... 43
a. Planning ... 43
b. Implementing ... 44
c. Observing ... 46
d. Reflection ... 52
B. Discussion ... 53
V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 61
1. Conclusions ... 61
2. Suggestions ... 62
REFERENCES
DEDICATION
This script is dedicated to:
My Father and Mother
My Grandfather and Grandmother
My Great grandfather and Great grandmother
My best friends who had assisted me
I. INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Problem
English is a foreign language taught in Indonesian schools. It has become a
compulsory subject from elementary schools up to university level. There are
four skills of English to be mastered, namely, listening, speaking, reading and
writing. Speaking is one of the central elements of communication. It is one of
the important skills that students have to master. By speaking, we can deliver
our ideas, information, and also maintain social relationship by communicating
with others. The primary goal of foreign language instruction is to be able to
communicate. That is why speaking is put ahead on the other skills. In addition,
a large percentage of the world’s language learners study English in order to be
able to communicate fluently.
Many language learners regard speaking ability as the measure of knowing a
language. That is why the main purpose of language learning is to develop
proficiency in speaking and communicative efficiency. They regard speaking as
the most important skill they can acquire and asses their progress in terms of
their accomplishment in spoken communication. For most students, speaking is
the most difficult part when they learn a foreign language. Based on
at SMP Negeri 7 Bandar Lampung, many students could not speak, or
expressing their ideas into spoken language. English students tend to have
difficulty to speak in English in a simple form of dialogue or even to tell their
ideas, utterances in English. It could be seen from their score when the teacher
did the speaking test.
This condition may be caused by two reasons. Firstly, it is caused by the
minimal participation of students during teaching learning process in the
classroom. The classroom activity is teacher centered and directed. Students
here tended to be silent unless they are called upon to answer the question. This
created discouraging environment for language learners. As a consequence,
most students could not participate in speaking English since they did not get
enough exposure to the language.
Secondly, the way teacher delivers the materials in the classroom. Teacher
depends on the textbook and it became the only source in the classroom.
Commonly, oral test was done in written task rather than oral activity. Learning
speaking became a matter of book-based activities and emphasized largely on
grammar rules instead of giving speaking practice. As a result, speaking target
would not be accomplised and the students would not learn to commincate
orally because language is solely from a book and written task. To solve this
3
According to Kayi (2006, 6), there are many techniques that can be apllied in
teaching English speaking skill such as role play, games, problem solving,
song, disscussion, and simulation. These techniques can be implemented in any
grade. Thus, the researcher here implemented a good technique of teaching
speaking by using simulation technique. By implementing this technique, the
researcher hopes to give new experience in learning English and have a fun
situation in the classroom.
In this paper, the research was conducted as a classroom action research. Action
research is classroom-based research conducted by teachers in order to reflect
upon and evolve their teaching (Kevorkian,1998). While according to Arikunto
(2006), classroom action research is overview from learning activity that rise
consciously in the classroom.
From the researcher’s pre observation in the SMA Negeri 2 Metro on January
2011, most of the students were not able to speak, reluctant to speak and have
low ability in speaking, because they thoght that speaking is difficult. That was
why their speaking scores have not been achieved the standard (KKM) in the
school yet. This problem made the writer interested in doing the classroom
action research to improve the students speaking ability.
Based on the phenomena above, the writer tries to find the solution to improve
the speaking ability of the first grade of SMA Negeri 2 Metro by employing
274), simulation can be students’ simulation a real-life situation (such as a
business meeting, on aeroplane cabin, or an interview) as if they are doing so in
the real world, either as themselves in that meeting or aeroplane, or taking on
the role of a character different from themselves or with thought and feeling
they do not necessarily share. Simulation encourages the students to be actively
participate in teaching learning process because this technique provided a way
of creating a rich communicative environment where students actively become
a part of some real word system and function according to predetermined role
as members of that group. It did not only make the students active but also
creative and critical. It stimulated real life situations and realistic environment.
In it also, students can bring any item to the class to create a real environment.
For example, if a student is a football player, he brings a ball to play it, or bring
a weapon toy if he roles as a soldier. Threfore, it was appropriate to use
simulation in teaching speaking skill. That is the reason of why this research
was focus on the simulation.
B. Research Problems
Based on the background above, the writer formulated the problem as follow:
How can the implementation of simulation technique increase the
students’ speaking score achievement?
How can the implementation of simulation technique increase the
students’ involvement during teaching learning process?
How can the implementation of simulation technique improve the
5
C. Objectives of the Research
In relation to the formulation of the problems above, the objectives of this
classroom action research is to find out how the implementation of simulation
technique can improve the students’ speaking achievement and students’
participation in teaching learning process.
D. Uses of the Research
The uses of this research are:
1. Theoretically
a. The result of the research can be used as the reference for those who want
to conduct a reseacrh in English teaching learning process.
b. The result of the research can be useful for English teacher in their
teaching learning process, especially in teaching speaking.
2. Practically,
This research can be useful for English teachers to implement simulation to
improve their students’ speaking achievement.
E. Scope of the Research
This classroom action research was conducted in the first grade of SMA N 2
Metro with one class as subject of the research. The class was X6 choosen by
random sampling technique by using lottery. The reason why the researcher
used this technique because it is the good way to find representing class. It
The focus of the research was teaching learning process within the
implementation of simulation technique. The researcher conducted the research
on the “on going” process by analyzing how the teaching learning process
occured in the implementation of Simulation technique in teaching speaking.
The research was limited only in particular themes taken from the 2006 English
Curriculum of senior high school.
F. Definition of Terms
There are some definition of terms presented in order to avoid misunderstading,
they are:
1. Speaking is the process of transferring knowledge of converse and how to
express one idea, thought, desires, and willingness into good pattern and
ordinary speech use to talk or recognize another.
2. Simulation is acting out or mimicking out an actual or probable real life
condition.
3. Simulation technique is one of the ways for teaching and promotes speaking
activity.
4. Teaching speaking means teaching how to use language for communication,
for transferring ideas, thought or even feeling to other people.
5. Classroom Action Research is an activity undertaken by teachers to improve
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
A. Concept of Simulation
The major problem of our students in schools are not able to make
connections between what they are learning and how that knowledge to be
used. This is because the way they process information and their motivation
for learning are touched by the traditional methods or techniques of classroom
teaching. Therefore, the English teacher should make an effort on searching
and creating a new model in presenting materials in order to reinforce, expand
and apply students’ academic knowledge and skills in a variety of in-school
and out-school settings in order to solve simulated or real-world problems.
According to Kayi (2006) simulations are very similar to role-plays but what
makes simulations different than role plays is that they are more elaborate. In
simulations, students can bring items to the class to create a realistic
environment. For instance, if a student is acting as a singer, she brings a
microphone to sing and so on. Role plays and simulations have many
advantages. First, since they are entertaining, they motivate the students.
Second, as Harmer (1984) suggests, they increase the self-confidence of
hesitant students, because in role play and simulation activities, they would
they do not have to take the same responsibility. While, according to Lynn
(2006) simulation is a structured, preplanned activity designed to stimulate the
real world that has rules, scoring, and defined procedures.
Simulation is the imitation of some real thing, state of affairs, or process. The
act of simulating something generally entails representing certain key
characteristics or behaviors of a selected physical or abstract system (Smith:
1999). Simulation can be used to show the eventual real effects of alternative
conditions and courses of action. Simulation is also used when the real system
cannot be engaged, because it may not be accessible, or it may be dangerous
or unacceptable to engage, or it is being designed but not yet built, or it may
simply not exist.
According to the simulation theory by Fraenkel (2007, 451), simulation is a
good and valuable method for second language learning. It can encourage the
student’s thinking and creativity, lets students develop and practice new
experience in a relatively no threatening setting, and can create the motivation
and involvement which are needed in learning process. In this research, the
researcher will describe this technique in detail. There is little consensus on
the terms used in the role playing and simulation literature. In role playing
students pretend they are in various social contexts and have a variety of
social roles. While simulations similar to role playing but what makes
different is in simulation students can bring real item to the class. There does
9
than role playing. For example, views simulations as complex, lengthy and
relatively inflexible, but role playing as quite simple, brief and flexible.
Simulation simulates real life situations, while in role playing the participant is
representing and experiencing some character type known in everyday life.
Simulation always includes an element of role play.
While, Jones (1982:113), Simulation clearly promotes effective interpersonal
relations and social transactions among participants. In order for a simulation
to occur the participants must accept the duties and responsibilities of their
roles and functions, and do the best they can in the situation in which they find
themselves. To fulfill their role responsibilities, students must relate to others
in the simulation, utilizing effective social skills.
Thus, it can be concluded that simulation is one of the activities which can be
used to promote speaking activity, since simulation is very similar to role
plays. What makes different is in simulation can bring the real items into the
situation, so it is entertaining for student. Simulation can also be said the
imitation of real thing, state of fair, or process. It has design, rules, scoring,
and procedures. Therefore, this technique could increase the students’ activity,
creativity, and their motivation. In simulation, students have their own duty
for the roles in the situation. It gives the students not threatening setting, and
can create the motivation and involvement that needed in the teaching learning
B. Concept of Speaking
Speaking is an essential tool for communicating, thinking, and learning. Oral
language is powerful learning tool. It shapes, modifies, extends, and organizes
thought. Oral language is foundation of all language development and,
therefore, the foundation of all learning (Hayriye, 2006, 1).
Speaking skills in learning is a priority for many second language or foreign
language learners. English learners often evaluate their success in language
learning as well as the effectiveness of their English course on the basis of how
much they feel they have improved in their spoken language proficiency
(Richards, 1990: 21).
Johnson & Morrow (1981) typifies speaking as an activity involving two (or
more) people, in which the participants are both hearers and speakers having to
react to what they hear, and make the contributions at high speed. In other
words, each participant must have an intention or set of intentions he wants to
achieve in the interaction. Each participant has to be able to interpret what is
said to him, and reply with the language he has which reflects his own
intention.
Speaking is the instrument of language and primary aim of speaking is for
communication (Tarigan, 1987: 5). From this definition, it is clear that the
11
communication, and in communication, a speaker has a choice not only about
what to say but also how to say it (Freeman, 1986: 130).
Byrne (1984: 81) says that speaking or oral communication is a two-way
process between speaker and listener and involves productive and receptive
skills of understanding. It means that we try to communicate with each other
and use our language to send our message to others (listeners). Hornby (1995:
826) speaking skill is the ability to perform the linguistic knowledge in actual
communication. The ability functions to express our ideas, feeling, thoughts,
and need orally.
Meanwhile, Lado (1961: 240) describes speaking as the ability to express
oneself in life situation, or the ability to report acts or situations in precise
words, or the ability to converse, or to express a sequence of ideas fluently.
This idea means that, speaking emphasizes more to the ability of an individual
to convey something whether it is in the form of expression, report, etc with the
language he has.
From the definition above, it could be concluded that speaking is two-way
process between speaker and listener and it involves both encoding and
decoding process. The former leads to the process of giving idea or making the
listener understand, while the latter leads to the process of getting the idea of
Speaking must fulfill these following aspects, they are:
1. Fluency
Fluency can be defined as the ability to speak fluently and accurately. Signs of
fluency include a reasonable fast speed of speaking and only a small numbers
of pauses. Fluency refers to the ease and speed of the flow of the speech
(Harris, 1974: 81). Fluency is the smoothness or flow with which sounds,
syllables, words and phrases are joined to other when speaking. It means that
when a person makes a dialogue with another person, the other person can
give respond well without difficulty.
2. Grammar
Heaton (1978: 5) defines grammar as the students’ ability to manipulate
structure and to distinguish appropriate grammatical form in appropriate ones.
Meanwhile, Syakur (1987) defines grammar as a correct arrangement sentence
in conversation.
3. Vocabulary
One cannot communicate effectively or express ideas in oral form if they do
not have sufficient vocabulary. Therefore, vocabulary means the appropriate
diction which is used in communication as what is stated by Syakur (1987).
4. Pronunciation
Pronunciation refers to the ability to produce easily comprehensible
articulation (Syakur: 1987). Meanwhile Harris (1974: 81) defines
13
5. Comprehension
Syakur (1987) defines comprehension for oral communication that requires a
subject to respond to speech as well as to initiate it. Comprehensibility denotes
the ability of understanding the speakers’ intention and general meaning
(Heaton, 1991: 35). This idea means that if a person can answer or express
well and correctly, it shows that he/she comprehends or understands well.
C. Concept of Teaching Speaking
Teaching speaking is the way for students to express their emotions,
communicative needs, interact to other person in any situation, and influence
the others. For this reason, in teaching speaking skill it is necessary to have
clear understanding involved in speech.
Teaching speaking means teaching how to use language for communication, for
transferring ideas, thought or even feeling to other people. The goal of teaching
speaking skills is to communicate efficiency. Learners should be able to make
themselves understood, using their current proficiency to the fullest. They
should try to avoid confusion in the message due to faulty pronunciation,
grammar, or vocabulary and to observe the social and cultural rules that apply
in each communication situation (Burnkart. 1998:2).
Moreover, Japerson in Marians (1978) in Viviani (2010: 17) write that the
essence of human language is human activity on the part of the individual to
make him understand by another and activity on the part of other understands
permits people to communicate with each other. Therefore, it is clear that
language is very important. We cannot only teach what will be spoken but also
the situation what we deal with. The teacher teaches speaking by carrying out
the students in imitating of real situation when the topic is being talked about.
The topic must be familiar with the students so what the ideas have an oral
command of the language need to describe the topic.
D. Teaching Speaking Through Simulation
Teaching means give the order to a person or give a person knowledge skill,
etc. While, speaking means use the words in an ordinary voice. Therefore,
teaching speaking is giving instruction to a person in order to communicate.
Speaking is a language skill that is developed in child life, which is preceded by
listening skill, and at that period speaking skill is learned. It means that
speaking is the basic language. The process of speaking skill has happened or
proceeded by listening skill. Increasing listening skill is very beneficial for
speaking ability. Tarigan (1990: 3-4) stated that, the goal of teaching speaking
skills is to communicate efficiency. Learners should be able to make
themselves understood, using their current proficiency to the fullest.
Dougill and Jones (1987) agreed that simulation is “mirror real life” and
“reality of function in a simulated and structured environment”, which means
that simulation is not real life; it is only a type of simulating real life in a
15
From the statements above, it could be concluded that teaching speaking
through simulation is the way the teacher teaches the students how to
communicate by using simulated situation and environment. When teaching the
students, the teacher tries to simulate the material in simulated situation
combined by role daily life simulation such as a singer, football player, or
buyer. Teacher has a role as a director of this simulation and the way of
teaching learning process. In teaching learning process hopes that this
technique can motivate students to speak more because they can bring
real-imitated things such as ball, microphone, or money.
In this research teacher have a few roles according Sam (2006), they are:
1. Controlling the class in order to make the situation run well and not off
from the design.
2. Teacher also become a model for the students usually in pre activity, in
the while activity students act based on the role and situation from the
dialogue given.
3. The teacher and the students can reflect what they have learnt in
reflection. This activity usually occurs in post activity.
4. The last the teacher can describe the real competence of students
through authentic assessment. Authentic assessment is not only done at
the end of period but also integrated together with teaching learning
E. Procedure of Teaching Speaking through Simulation
There are several procedures that should be done to implement simulation
technique in teaching speaking. The steps are not really different with other
steps in ordinary teaching steps. The difference is simulated situation during the
class. Adapted from Sam (2006), the procedures of teaching speaking through
simulation are as follows:
Activities:
Pre activities:
Teacher greets the students
Teacher checks the students attendant list
Teacher asks the students some questions about the topic being learnt at that
day.
While activity
Students write down their own information based on the topics learnt today.
Teacher gives the instruction to make a group consist of two or three students.
Students read the dialogue that given by the teacher with their friends in
group.
Teacher facilitates the students with the supported thing.
Students make their own dialogue with their friend in group.
Students practice the dialogue in group by what the teacher already given the
example for them.
Students perform or simulate their own groups’ dialogue in front of the class
in turn.
17
Post Activity
Teacher gives feedback to the students of what being learnt.
Teacher summarizes the materials by explaining what is being learnt today.
Teacher closes the meeting.
F. Advantages and Disadvantages of Simulation Technique
As stated before, simulation technique helps the teacher to relate the material to
the students’ imagination or simulated situation. However, it also has some
advantages and disadvantages. According to Sam (1990) there are several
advantages and disadvantages of simulation. They will be as follows:
1. The Advantages of Simulation technique
The advantages of simulation technique are:
1. Stimulates authentic conversations
Simulation activities stimulate authentic learner-to-learner conversational
interaction. The activities also develop conversational competence among
second language learners.
2. A fluency activity
It is where opportunities arise, the learner to use language freely and
creatively.
3. Suitable for consolidation
Since simulation activities are more practice/revision activities than teaching
activities, they are useful and more suitable for consolidating and practicing
4. Creates sensitivity and sense of awareness
Simulation brings the outside world into the classroom. This could have
affective aspects in terms of social interaction and cultural awareness.
5. Increase motivation
A simulation prompts mental and bodily activity. The activities require active
participation. Concentration is also often required and it is not easy for
students to stay passive for long. Situations are created for the students to use
the language meaningfully and this will motivate the students towards
participation. The less motivated students will be gradually drawn into the
activity when they see the rest of the group having a good time.
6. A break from routine
The use of simulation activities is a break from the usual text book teaching
and the ‘chalk and talk’ method of the teacher. The students have
opportunities to mix around and to act out different roles. The atmosphere in
the classroom is less formal and this can reduce tension
7. Prepare students for real life and unpredictability
Real life situations and communication are unpredictable. The students may
learn all the correct forms of communication but may not know when to use
them appropriately. Simulation provides opportunities to react to these
situations and to give the students a taste of real life.
2. The Disadvantages of Simulation technique
The disadvantages of simulation technique are:
19
The situations sometimes are artificial and not relevant to the needs of the
students.
2. Activities are difficult to monitor
With so much activity both physical and verbal going on, it is sometimes
difficult for the teacher to monitor a student’s performance. There is the fear
among teachers that the students are having too much fun and that no learning
is taking place.
3. Spontaneity is lost
Very often the students get too much caught up with what to say. They
hesitate to choose their words and do not interact spontaneously.
4. Timing lessons is to difficult
The teacher has to spend a lot of time in preparation work especially for
simulation. He is not able to predict the amount of class time that will be taken
III. RESEARCH METHOD
A. Setting of the Research
This classroom action research was done at the first year students of SMA N 2
Metro. It was done based on the problem faced by the students and the teacher
when they are learning in the class. In line with the problem found by the
researcher, examining the cause of the problem and finding the solution for that
problem. The major students’ problem was they could not express their idea
well this is because they have very little chance to speak up.
The subject of this research was the students in first grade of SMA N 2 Metro
that consist of 32 students. Students’ teaching learning at classroom was the
focus in this research. The teacher (researcher) taught the students speaking
through simulation technique. The students were taught with simulated
environment and using daily activity material. Based on the researcher’s
experience during pre research, most of the students had low ability in speaking
especially in grammar, fluency, vocabulary and pronunciation. It could be seen
from the result of oral test, when the teacher asked the students, many of them
21
In this classroom action research, the researcher acted as a teacher and also as
an observer, meanwhile the teacher of English at SMA N 2 Metro acted as
collaborator. The researcher made the lesson plan based on the technique that
was implemented and taught the students based on the lesson plan.
B. General Description of the Research
Classroom Action Research was developed by problems in the class and the
actions done to solve problems. Based on the problem identified, the researcher
examined the problem causes and tries to find the problem solution. The
simulation technique was conducted in teaching speaking in the class. The
researcher made lesson plan and taught the students. Thus, the collaborator
observed the students’ activities in teaching learning process.
The observation result during teaching learning process such as (weaknesses
and strength which has been done by the students using simulation technique)
and speaking test was analyzed and discussed by the researcher and the
collaborator.
The researcher and the collaborator also did reflection after knowing the result
of the analysis. Based on the analysis and reflection, it was decided whether the
next cycle would be held or not, and the next cycle would be focused on
C. Research Procedures
In conducting the research, the researcher used the procedure of classroom
action research designed by Arikunto. According to him, the research procedure
in a classroom action research consists of planning, implementing, observing
and reflecting (2006: 16). Therefore, this research is designed as follows:
1. Planning
The researcher prepared the lesson plan and selected the material. In designing
lesson plan, the researcher used the school syllabus as the basic of the lesson
plan. The lesson plan was aimed to teach speaking skill. It contains the standard
competence and the basic competence to achieve. It also contains the procedure
of presenting lesson, activities, and assignment in each meeting. The material
was correlated with daily activity. The researcher prepared observation sheet. It
was purposed to analyze the process of teaching learning.
The researcher made the indicator of success which was aimed to assess the
students’ ability in speaking correctly. The indicator of success was made to
determine whether the action throughout the first cycle has been successful or
not.
2. Implementing
The second step of Classroom action research was implementing the action. In
this stage, the researcher taught speaking by using simulation technique with
the material and lesson plan prepared.
3. Observing
Observation was done by the researcher and the collaborator. They observed
23
observation in the observation sheets. When the teaching learning process
occurred, the researcher and the collaborator interpreted the result of the
observation.
4. Reflecting
Reflecting was a stage where the researcher together with the collaborator
analyzed the result of the speaking of the students as the learning product. The
researcher also analyzed everything occurred in the teaching learning process
based on the observation sheets. The weaknesses and the strength of the cycle
were discussed by the researcher and the collaborator. It purposed to determine
what to do in the next cycle and to determine whether or the result of the cycle
is satisfied or not.
The cycle of Classroom Action Research (Arikunto, 2006: 16) Planning
Implementing CYCLE 1
Observing Reflecting
Planning
Implementing Reflecting
? Observing
D. Indicator of the Research
To see whether the simulation technique can improve speaking skill of the
students, the researcher used two indicators. They were learning product and
learning process. The learning product was formed in students’ speaking test
score, while learning process was in form of the observation report of the
collaborator.
1. Learning Product
In learning product the indicator was based on Standard Goal for Student
(KKM) stated that for speaking the standard goal is 65. Simulation technique is
able to improve students’ speaking achievement if 80% students get the target
score of speaking test, 65 (Diknas 2006).
Learning product focused on the production of sound, students’ speaking for
certain aspect which students mostly has difficulty in speaking. Here, the
teacher recorded the students when they are making a conversation, in group.
There are some aspects that would be observed in the scoring system, promoted
by Harris (1979: 68-69). The aspects as follows:
Pronunciation
20 Speech is fluent and effortless as that of native speaker.
16 Always intelligible though one is conscious of s definite accent
12 Pronunciation problems necessitate concentrated listening and
occasionally lead to misunderstanding.
8 Very hard to understand because of pronunciation problem must
25
4 Pronunciation problems too severe as to make speech virtually
unintelligible
Grammar
20 Make few (if any) noticeable errors of grammar or word order
16 Occasionally makes grammatical and/or word order errors which do
not, however, obscure meaning.
12 Make frequent errors of grammar and word order, which obscure
meaning.
8 Grammar and word orders make comprehension difficult must often
rephrase sentences and/or restrict him to basic patterns.
4 Errors in grammar and word order to severe as to make speech
virtually unintelligible.
Fluency
20 Speech is fluent and effortless as that of native speaker problems.
16 Speed of speech seems to be slightly affected by language problems.
12 Speed and fluency are rather strongly affected by language problems.
8 Usually hesitant, often forced into silence by language problems.
4 Speech is as halting and fragmentary as to make conversation virtually
impossible.
Vocabulary
20 Use of vocabulary and idiom is virtually that of native speaker.
16 Sometimes uses inappropriate terms and/or must rephrase ideas
12 Frequently uses the wrong words, conversation somewhat limited
because of inadequate vocabulary.
8 Misuses of words and very limited vocabulary make comprehension
quite difficult.
4 Vocabulary limitation to extreme as to make virtually impossible.
Comprehension
20 Appear to understand everything without difficulty.
16 Understand nearly everything at normal speed
12 Understand what is said at slower than normal speed.
8 Has great difficult following what is said.
4 Can not be said to understand even simple conversation in English.
The researcher evaluated the aspects of speaking ability based on the table
bellow. The lowest score is 4 and the highest score is 20. The total of the score
is multiple 5.
Scoring sheet of Speaking Test
Student’
name Pronun-ciation (4-20)
Grammar
(4-20) Fluency (4-20) Vocabulary (4-20) Compre-hension (4-20)
The score of speaking ability based on five elements can be shown in percentage
as follows:
27
2. Grammar : 20%
3. Fluency : 20%
4. Vocabulary : 20%
5. Comprehension : 20%
The researcher and observer took the score of a student, and the score would be
totalled and divided by the number of the teacher and the researcher to get the
final score. The calculation as follows:
The standard of the score would be at level 12 (for each aspect) Harris’s rating
scale. It refers to the ability of students in producing English speaking, in better
way, hear able, understandable although with some different native speaker’s
speaking.
2. Learning Process
In learning process, there was one aspect which becomes the focus of this
research that is the students’ activities. The observation of the process of
teaching would be based on the lesson plan which was made by the researcher
and the real process in the classroom. It would cover pre activity, while activity,
post activity. The target determined by the researcher concerning the students’
activities is 80% of students are active during the process. The researcher set
80% as the target since according to Arikunto (1993:210), if more than 75% of
students are actively involved in teaching and learning activities, it could be
categorized as a good level. Students’ activity would be measured through Final score: Score researcher + score teacher
written report of the collaborator and researcher in observation sheet. While the
researcher is teaching, collaborator and the researcher himself observed the
teaching learning process in the classroom and focused on the participation and
the involvement of students in the activity.
Besides observing the students’ activities, the researcher also observed the
teacher’s teaching performance during the teaching and learning process. It was
expected that the teacher could get score 80 in his teaching performance after
implementing Simulation technique. So, if the teacher can reach that target, it
means that the teacher’s teaching performance is very good. The scoring system
for teaching performance was based on the standard teacher’s teaching
performance proposed by Departement Pendidikan Nasional (2006). For the
teaching performance, there are some aspects scored, that is, the teacher’s
activities in pre-activity, while-activity, and post-activity.
E. Instrument of the Research
The researcher used two kinds of instruments as the source of data. The
instruments were speaking test and observation sheet. The instrument will be
described as follow:
1. Speaking Test
The test was conducted by asking students to play a simulation that they
have been created (for example playing as soccer player) and it was
recorded. The two observers, they were researcher and the teacher analyzed
29
of every cycle in the learning process. The students performed it in front of
the class as a speaking test. The students in his group was called in turn,
while they were practicing their dialogue, the observer recorded it and
analyzed their speaking based on Harris’ rating scale after the process.
2. Observation Sheet
In this part, observation was conducted in every cycle during the teaching
learning process. When teaching and learning process was occurring, the
researcher observed the process happened in the classroom. The researcher
used structured observation to know the students’ activities in the classroom.
So there was one kind observation sheets that is filled out by the researcher,
it was the observation sheet for the students’ activities.
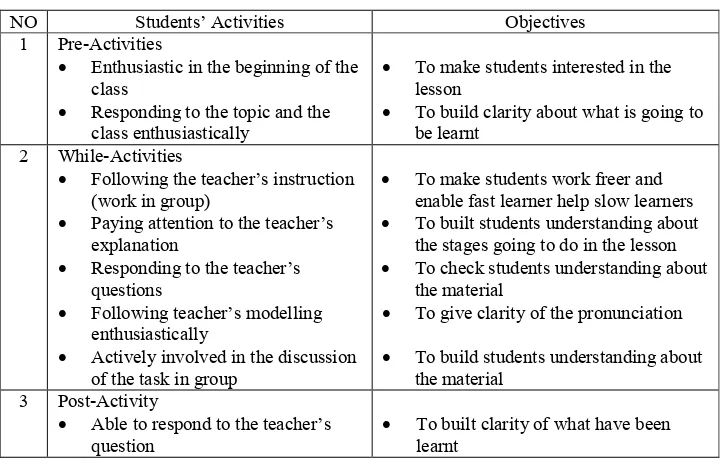
Table 3.1. Table of the Observation Sheet for Students’ Activities
NO Students’ Activities Objectives
1 Pre-Activities
Enthusiastic in the beginning of the class
Responding to the topic and the class enthusiastically
To make students interested in the lesson
To build clarity about what is going to be learnt
2 While-Activities
Following the teacher’s instruction (work in group)
Paying attention to the teacher’s explanation
Responding to the teacher’s questions
Following teacher’s modelling enthusiastically
Actively involved in the discussion of the task in group
To make students work freer and enable fast learner help slow learners
To built students understanding about the stages going to do in the lesson
To check students understanding about the material
To give clarity of the pronunciation
To build students understanding about the material
3 Post-Activity
Able to respond to the teacher’s
question To built clarity of what have been learnt
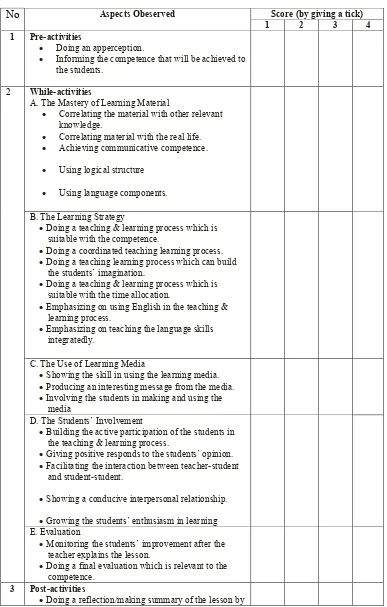
Table 3.2. Table of Specification for Teacher’s Performance
No Aspects Obeserved Score (by giving a tick) 1 2 3 4 1 Pre-activities
Doing an apperception.
Informing the competence that will be achieved to the students.
2 While-activities
A. The Mastery of Learning Material
Correlating the material with other relevant knowledge.
Correlating material with the real life.
Achieving communicative competence.
Using logical structure
Using language components.
B. The Learning Strategy
Doing a teaching & learning process which is suitable with the competence.
Doing a coordinated teaching learning process.
Doing a teaching learning process which can build the students’ imagination.
Doing a teaching & learning process which is suitable with the time allocation.
Emphasizing on using English in the teaching & learning process.
Emphasizing on teaching the language skills integratedly.
C. The Use of Learning Media
Showing the skill in using the learning media.
Producing an interesting message from the media.
Involving the students in making and using the media
D. The Students’ Involvement
Building the active participation of the students in the teaching & learning process.
Giving positive responds to the students’ opinion.
Facilitating the interaction between teacher-student and student-student.
Showing a conducive interpersonal relationship.
Growing the students’ enthusiasm in learning E. Evaluation
Monitoring the students’ improvement after the teacher explains the lesson.
Doing a final evaluation which is relevant to the competence.
3 Post-activities
31
involving the students’ participation.
Doing a follow-up by giving direction or tasks as a remedy.
Total Score Description of score
(Source: Dep. Pendidikan Nasional, 2006)
Note: 1 = Poor 2 = Enough 3 = Good 4 = Very Good
Description of Scores: 1. 40 – 59 : Poor 2. 60 – 69 : Enough 3. 70 – 79 : Good 4. 80 – 100 : Very Good
F. Data Analysis
In analyzing the data, the researcher classified the data into two categories: they
were the data of learning product and the data of learning process. The data
analysis was done during and after the data has been collected form every
cycle. The data from the first cycle was analyzed by the researcher as an
observer together with the teacher analyzed and did the reflection based on
them. From the analysis and reflection, the researcher knew the weaknesses and
the strengths of the first cycle. Therefore, the teacher and the researcher know
what should be improved for the next cycle.
1. Learning Product
For speaking ability improvement was analyzed by comparing the mean of
score from each cycle and the percentage of high score. If 80% of student has
improve students speaking ability. To see the percentage of student who gets ≥
In learning process, the researcher used observation sheets. The result of the
observation sheet was analyzed after every cycle was conducted. The
observation was done for observing the students’ activities.
2.1 Students’ Learning Activities
After gathering data from observing the students’ learning activities, the
next step is counting the number of activities done by the students.
A. Calculating the percentage of students’ activities
For calculating the percentage of the students’ activities, the following
formula is:
% A = A Χ 100% n
Note:
% A : percentage of students’ activities
A : number of students’ activities observed
n : number of students in the class
B. Making a description from the data that had been analyzed
When the data have been gathered, the researcher described the data. For
example, if the percentage of students’ activity is more than 80% means
33
2.2 Teacher’s Teaching Performance
In analyzing the data from observation of the teacher’s performance, the
researcher made the description for the data that has been analyzed.
It was similar to analyze the students’ activities, to analyze the teacher’s
performance, the researcher made description from the collected data
V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
Having conducted his research at the first grade of SMA Negeri 2 Metro and
analyzing the data, the researcher would like to state his conclusions and
suggestions as follow:
A. Conclusions
In line with the result of the learning product and learning process in the research,
it can be concluded that:
1. Simulation technique is applicable to improve the students’ English
achievement especially in speaking ability. The problem faced by students
can be solved after Simulation Technique was implemented.
2. Simulation technique can improve speaking score in learning product. It
can be seen from the increase of the students scores from cycle 1 (53.12%)
and cycle 2 (84.37%) after this technique was implemented.
3. In learning process, the improvement also occurs in students’
participation. By implementing Simulation technique, the students become
more active to follow the class and they become more comfortable in
learning speaking. Since Simulation technique provided a chance to the
students to work in group and share their ideas by performing it to other
79
Simulation technique also contributes a positive effect toward teacher’s
performance.
B. Suggestion
Referring to the conclusion, the writer would like to propose some
recommendations as follows:
1. English teachers are recommended to use Simulation technique in teaching
their students since it can improve students’ speaking achievement and it
can make the students involve in teaching learning process, enables the
students to be more active in the classroom activities.
2. The teacher should motivate students to be active in the classroom by
simulation, giving them the activity that can stimulate interaction because
they can express their style and not afraid of making mistakes by indirectly
correcting when they made mistake.
3. The teacher should be creative in creating media and using interesting
topic for the material, since it can attract the students and make them easy
to understand the content of the media itself. And also, the teacher should
manage their timing lesson carefully because it is important to reach our
purposes in teaching learning process. The teacher should make certain
timing when he/she conduct the teaching and learning process in the