ABSTRACT
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF READ, TELL, AND CHOOSE TECHNIQUE OF SPOOF ITEMS TO INCREASE STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION ACHIEVEMENT
AT SECOND GRADE OF SMA KARTIKATAMA METRO
By
Inggit Dwi Nuranggita Pristi
Guideline of Educational Unite Level Curriculum (KTSP) which is applied for all school levels in Indonesia leads the students to have real life skills. This implies that teaching English stated in KTSP in particular is to enable the students to master the four language skills; listening, reading, speaking and writing. Reading is one of the important skills that the students have to master. Students must improve their ability in reading comprehension, so they can get information from the text. As a matter of fact, the students’ ability in reading comprehension is far from the goal being expected. Many students have difficulties in comprehending the reading text. In fact the teachers in school do not teach reading comprehension using an effective technique in helping students understand reading comprehension easier.
This Classroom Action Research is conducted to find out how the implementation of Read, Tell and Choose (RTC) technique of spoof items to improves the students’ reading achievement and teaching learning process. This research is conducted in two cycles. The subject of the research is the second grade students of SMA Kartikatama Metro. The research lasted from March 21th until April 02th 2011.
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF READ, TELL, AND CHOOSE TECHNIQUE OF SPOOF ITEMS TO INCREASE STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION ACHIEVEMENT
AT SECOND GRADE OF SMA KARTIKATAMA METRO (Classroom Action Research)
By
Inggit Dwi Nuranggita Pristi
A Script
Submitted in a Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For S-1 Degree
In
The Language and Art Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
LAMPUNG UNIVERSITY BANDAR LAMPUNG
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF READ, TELL, AND CHOOSE TECHNIQUE OF SPOOF ITEMS TO INCREASE STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION ACHIEVEMENT
AT SECOND GRADE OF SMA KARTIKATAMA METRO (Classroom Action Research)
(A Script)
By
Inggit Dwi Nuranggita Pristi
LAMPUNG UNIVERSITY BANDAR LAMPUNG
CURRICULUM VITAE
The researcher, Inggit Dwi Nuranggita Pristi, was born on November 25th, 1987 in Gunung Madu. She is the second child of a wonderful couple, Hi. Ahmad Nurdin and Lilik Haryani, S.Pd., SD. She started her study from kindergarten at TK Satya Dharma Sudjana in 1993 and graduated in 1994. In the same year, she was registered Elementary School at SDN 1 Gunung Madu and graduated in 2000. She pursued her study at SMP Satya Dharma Sudjana Gunung Madu and graduated in 2003. She continued at SMA Kartikatama Metro and graduated in 2006.
DEDICATION
This piece of paper is proudly dedicated to:
The greatest inspiration of my life “My beloved parents” Thank you so much for the great love you’ve given to me and I love u
My beloved sister and brother and also my family Thanks for supports and spirits
My lovely “kakak”
Thanks for his attention, patience, supports, and his advice to me
My beloved friends and all English students 2006 Thanks for supports and help to me
CONTENTS
1.1. Background of the Problems... 1.2. Identification of the Problems... 1.3. Limitation of the Problems... 1.4. Formulation of the Problem... 1.5. Objective of The Research... 1.6. Uses of the Research... 1.7. Scope of The Research... 1.8. Definition of Terms...2. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK... 2.1. Reading Comprehension... 2.2. Teaching Reading... 2.3. Spoof Text... 2.4. Guiding Principles to The Teaching of Reading... 2.5. Read, Tell, and Choose (RTC) Technique... 2.6. Classroom Action Research……… 2.7. Procedure of Teaching Reading Comprehension of Spoof Items
Text Through RTC (Read, Tell, and Choose)... 2.8. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Read, Tell, and Choose
3. RESEARCH METHOD... 3.1. Setting of The Research... 3.2. General Description of The Research... 3.3. Research Procedures... 3.3.1. Planning... 3.3.2. Implementation and Action... 3.3.3. Observation and Interpretation... 3.3.4. Reflection and Analysis... 3.4. Indicators of The Research...
3.4.1. Learning Product... 3.4.2. Learning Process... 3.5. Instrument of The Research... 3.5.1. Reading Comprehension Test... 3.6.4. Counting The Total Score of Teacher’s Performance... 3.6.5. Counting The Average Score of Teacher’s Performance... 3.6.6. Students’ Learning Activities... 3.6.7. Teacher’s Performance...
4. RESULT OF THE RESEARCH
LIST OF TABLE
Table
1. Table 1 Table of Specification of Reading Test... 2. Table 2 Table of Specification of Observation Sheet for Students’
Activities... 3. Table 3 Table of Specification of Teacher’s Performance... 4. Table 4.1 The Frequency of the Students’ Reading Achievement at
Cycle 1... 5. Table 4.2 Students’ Observation Sheet at Cycle 1... 6. Table 4.4 The Frequency of the Students’ Reading Achievement at
Cycle 2... 7. Table 4.5 Students’ Observation Sheet at Cycle 2... 8. The Improvement of Students’ Reading Score from Cycle I to Cycle
II...
Page
35
38 39
47 49
65 67
LIST OF GRAPHIC
Graphic
1. Graph of the Students’ Reading Scores... 2. Graph of the Improvement of Students’ Participation...
Page
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendices
LIST OF GRAPHIC
Graphic
1. Graph of the Students’ Reading Scores... 2. Graph of the Improvement of Students’ Participation...
Page
LIST OF TABLE
Table
1. Table 1 Table of Specification of Reading Test... 2. Table 2 Table of Specification of Observation Sheet for Students’
Activities... 3. Table 3 Table of Specification of Teacher’s Performance... 4. Table 4.1 The Frequency of the Students’ Reading Achievement at
Cycle 1... 5. Table 4.2 Students’ Observation Sheet at Cycle 1... 6. Table 4.4 The Frequency of the Students’ Reading Achievement at
Cycle 2... 7. Table 4.5 Students’ Observation Sheet at Cycle 2... 8. The Improvement of Students’ Reading Score from Cycle I to Cycle
II...
Page
35
38 39
47 49
65 67
MOTTO
“Never tell people how to do things. Tell them what to do and they will surprise you with their ingenuity”.
ADMITTED BY
1.Examination Committee
Chairperson : Ujang Suparman, S.Pd., M.A., Ph.D……….
Examiner : Dra. Edhita Gloria Simanjuntak ……….
Secretary : Dra. Hartati Hasan, M.Hum. ………
2. The Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
Dr. H. Bujang Rahman, M.Si. NIP 19600315 198503 1 003
Research Title : THE IMPLEMENTATION OF READ, TELL, AND CHOOSE TECHNIQUE OF SPOOF ITEMS TO INCREASE
STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION ACHIEVEMENT AT SECOND GRADE OF SMA KARTIKATAMA METRO
(A Classroom Action Research)
Student’s Name : Inggit Dwi Nuranggita Pristi
Student’s Number : 0613042005
Department : Language and Arts Education
Study Program : English Education
Faculty : Teacher Training and Education Faculty
APPROVED BY Advisor Committee
Advisor Co-Advisor
Ujang Suparman, S.Pd., M.A., Ph.D. Dra. Hartati Hasan, M.Hum.
NIP 19570608 198603 1 001 NIP 19490928 197603 2 001
The Head of Language and Arts Education Department
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Alhamdulillahirobbil ‘alamin, Praise is merely to The Mightiest Allah SWT for the gracious mercy and tremendous blessing that enable me to accomplish this script entitled “ The Implementation of Read, Tell, and Choose Technique to Increase students’ Reading Comprehension Acheivement at Second Grade of SMA Kartikatama Metro. This script is submitted as a compulsory fulfillment of the requirements for S1 degree of English Education Study Program at Teachers Training and Education Faculty, University of Lampung.
It is important to be known that the script would never have come into existence without any supports, encouragements, and assistance by several gorgeous persons.
Here the writer would like to address her gratitude and respect to:
1. Ujang Suparman, S.Pd., M.A., Ph.D., as the writer’s first advisor, for his willingness
to give assistance, ideas, encouragement, and scientific knowledge within this time during this script writing process.
2. Dra. Hartati Hasan, M.Hum., as the second advisor, for her kindness, suggestions, and
patience in guiding the writer in finishing this script.
3. Dra. Edhita Gloria Simanjuntak, as the examiner, for her valuable suggestions, ideas,
and helps to make this script more valuable.
4. Drs. Deddy Supriyadi, M.Pd., as the writer’s academic advisor, thanks for his
guidances and expertise that are very beneficial for the writer to finish her study.
5. All the lecturers of English Education Study Program, for your contributions.
6. Aziz Muslim, S.Pd., as the headmaster of SMA Kartikatama Metro and Meliani,
S.Pd., as the English teacher of the second year of SMA Kartikatama Metro for their kindness during the research process.
7. All students of class XI IPS 1, academic year 2010/2011 at SMA Kartikatama Metro.
8. My beloved mother and father, for your endless love, support and continuous
guidance. May Allah SWT pay your love and devotion back within His never ending blessing.
9. My beloved sister, Swastika Nurhayuning Suharsanti and my beloved brother, Ahmad
Al Dino Fakih Nuri Mizan, and also my beloved family, pakde hudhi, bude tutik, om
yunit, om heru, bulek darti, bulek siti, om saiful, bulek tutut, mas koko, mbak yuli, mas wawa, mbak linda and all my big family who cannot be mentioned directly in this script. Thanks for your support and love for me.
10. My lovely brother, Fauzi, A.md or usually called Ozez, for his attention, advice,
11. My beloved friend, Gita Krisnawati, S.Pd. Thanks for your advices and help for the first time I made this script.
12. My close friends, Wuri Saputri, S.E. Thanks for your help and spirit.
13. My best friends at English Education Study Program ’06: Winda, Tri, Mbak Yu’, Ipit,
Elavia, Siska, Eby, Olla, Gita I, Amri, Arik, Agus, Nufus, Novi, Asri, Eka, Putri, Herlina, Kesi, Ade, Sigit, Ika, Pun, Shindy, Ridho, Galih, Yudi, Nurma, Eci, Ade, Sigit, Eka. Thanks for your nice friendship and togetherness, it will be forgotten.
14. All of my friend in SMP Dharmapala Bandar lampung Pak Yuzi, Pak Oman, Bu
Masitoh, Bu Yali, Pak Zulkifli, Mr Su, Mr Jo, Mbak Rini, Mbak Yani, Mbak Dewi, Mbak Dian, Mbak Yulia, Bu Ria, Bang Togar, Shesil, Mbak Devi, Mbak Emil, Desma, Mbak Eka, Mbak Mimin, Mbak Susi, Mas Slamet, Mas Joko Thanks for nice understanding, support and spirit for me.
15. My Friends in Mercy’s Bording House Vera, Pipit, S.Pd, Widia S.Pd, Betry, Meli,
Berlin, Eni, S.P, Naya, S.Pd, Diah, Ika. Thanks for your support and spirit for me.
16. Anyone who can’t be mentioned directly who has contributed in completing this
script.
Finally, the writer realizes that this script still has some weaknesses. Therefore, critics and suggestions are invited for its improvement. Hopefully, this script can give benefit to the readers or those who want to carry out further research.
Bandar Lampung, February 2012
CONTENTS
1.1. Background of the Problems... 1.2. Identification of the Problems... 1.3. Limitation of the Problems... 1.4. Formulation of the Problem... 1.5. Objective of The Research... 1.6. Uses of the Research... 1.7. Scope of The Research... 1.8. Definition of Terms... 2. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK...2.1. Reading Comprehension... 2.2. Teaching Reading... 2.3. Spoof Text... 2.4. Guiding Principles to The Teaching of Reading... 2.5. Read, Tell, and Choose (RTC) Technique...
2.6. Classroom Action Research………
2.7. Procedure of Teaching Reading Comprehension of Spoof Items Text Through RTC (Read, Tell, and Choose)... 2.8. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Read, Tell, and Choose
3. RESEARCH METHOD... 3.1. Setting of The Research... 3.2. General Description of The Research... 3.3. Research Procedures... 3.3.1. Planning... 3.3.2. Implementation and Action... 3.3.3. Observation and Interpretation... 3.3.4. Reflection and Analysis... 3.4. Indicators of The Research...
3.4.1. Learning Product... 3.4.2. Learning Process... 3.5. Instrument of The Research... 3.5.1. Reading Comprehension Test... 3.6.4. Counting The Total Score of Teacher’s Performance... 3.6.5. Counting The Average Score of Teacher’s Performance... 3.6.6. Students’ Learning Activities... 3.6.7. Teacher’s Performance...
4. RESULT OF THE RESEARCH
1
I. INTRODUCTION
1.1 Background of The Problem
The English curriculum of SMA states that there are four language skills namely:
reading, speaking, listening, and writing that are taught intergratedly. Reading is
emphasized because it is an important skill for the students in order to prepare them
to continue their study in education and to assist them in their future life. Surely,
most literatures related to learn English uses English Language. Based on that
reason, SMA students are expected to be able to read information which is mostly
written in English. Reading dominates the teaching materials in almost English text
book.
From the four skills, reading dominates the teaching materials in almost English
textbooks based on the reason that students are expected to get information for
increasing their knowledge which is mostly written in English. In order to achieve
the best result of learning a reading text, comprehension should be taught
intensively and extensively. Beside that reading as an active skill has
communicative function, so it can not be seperated from other skills: Speaking,
2
English students tend to have difficulty to get the main point of reading in English
in a simple form of story text or even to tell their ideas, utterances in English. This
condition may be causes by two reasons. First, it is causes by the minimal
participation of students during teaching learning process in the classroom. It might
be seen from the result in cycle 1, in students observation sheet. There are only 23
students from 33 students that actively involving to share their ideas in group, it’s
means only 69.69% students participation in cycle 1. The classroom activity is
teacher centered and directed. Students expect to be confused unless they call upon
to answer the question. This creates the unsupportive and discouraging environment
for language learners. As a consequence, most students can not participate in
reading English since they do not get enough exposure about the main point of
reading text in the language.
The second is the way teacher delivers the materials in the calssroom. Teacher only
depends on the textbook and it becomes the only source in the classroom. It was
happened in teacher teaching performance at cycle 1, the score for teacher teaching
performance for cycle 1 only 72, the fact is the goal of teacher teaching performance
is 80. It’s means that the way while the teacher teach the material is not interesting.
Commonly, reading test will happend in written task rather than oral activity.
Learning reading becomes a matter of book-based the topic and emphasizes largely
on grammar rules instead of giving reading test. As a result, reading target will not be
accomplised and the students will not learn to get the message of the text well
3
Based on writer’s pre observation in the SMA Kartikatama Metro, the researcher takes
40 students for sample, and the result is only 15 students who gets standard score of
reading, so most of the students are not able to read, reluctant to read and have low
ability in reading, because they think that reading is difficult and boring. That is why
their reading scores have not been achieved the standard (KKM) in the school yet.
This problem makes the writer interest in doing the classroom action research to
improve the students reading ability and hopefully the standard score for reading will
be achieved. The writer finds that when the teachers are asked to present the main idea
of the text, they get some difficulties in expressing their ideas so the listener can not
receive the message in communication well. There are lots of fillers, such as i…iand
mmmrr, in accuracy, there are many mismatch auxiliaries such as the story are good
and the actor don’t belive. In other words, their reading is not comprehendible even though they have learned English since they are students of elementary school. Their
ability to express their mind or ideas up is still too limited. This fact is find when their
reading are rated most of students fail to pass the standard goal that is 65.
In pre observation, researcher also finds the inappropriateness way of teaching used
by the teacher. The teacher teaches reading by explaining the form of sentence,
drilling it to students and asking students to do some written exercises at students’
work book or LKS (Lembar Kerja Siswa) these make the students passive and the
students only know the form of sentences but they are not able to implement it to their
real world. They are able to writing well but cannot implement it orally when it is
needed. So, reading class became writing class and students did not have enough
4
The low ability of students also due to the lack information about the context of
lesson that makes students have limited idea in discussion, If in percent it is only 50%
students ability to understand the information of the text. So, while the discussion
event during teaching learning, it become passive. This condition makes students’
performance at reading presentation in front of the class worse. The presenter can not
deliver their material well because they are not able to give the message and the
listener also can not respond it well because first, listener do not get the point of
material and secondly because they can not express their idea. So, discussion ran so
slow and boring. The last, reading goals can not be reached.
Due to the use of teaching aid, the teacher only used the text book. Students’ reading
ability becomes worse because they do not have sufficient sources as the references.
They just focuses on the example provided in their text book. Meanwhile the
successful language learner needed lots of chance to exercise. In reading and speaking
tend to be getting something done, exploring ideas, working out some aspects of the
word, or simply being together.
Due to the results of pre observation, researcher discussed with the teacher about the
problems in the classroom and researcher assumed that the students’ problems arefear
of being blamed, little chance for exercising, little sources, and boredom and in
appropriate way of teaching. By observing the problems of the students, the researcher
along with the teacher triggered to implement read tell and choose in classroom action
research due to its benefits.
To solve the problems above, it is very important for the teacher to find out a better
5
the way of teaching reading in order to make the students involve in teaching learning
process, and to build students interest in using English. Read tell and choose (RTC) is
considered as an alternative.
Read Tell and Choose is a concept of learning which helps teacher to relate the
materials being taught to the students’ real world and encourage students to relate
their knowledge in their reading skill. Therefore, the students have more time to
expose their skill in the classroom with the result that their reading achievement to
increase. Besides, RTC relates to subject matter content to real world situation that is
needed during the teaching learning process so that the students know the benefit of
learning in the classroom.
Now, here the researcher will use spoof text in this research. If readers are given the
word “spoof text”the readers can imagine its form and mention kind of spoof such as
funny story, short story, joke etc. But, if the reader want to know more about the
information included in the stories, the readers have to read the spoof text itself and
comprehend the content. This is one basic of the reason that people need to read, all of
people have different reasons, why do people need to read. There are six desires or
reasons why people need to read is that people read because of the need for
knowledge, the need to process and internalize the result of exploration, manipulation,
activity and stimulation, to resolve contradictions, to quest for solutions to problems
6
Because of this reason, the researcher as a teacher to be in the future and as reseacher,
wants to make the process of reading activity more interesting with a treatment
especially in reading spoof item text. In this reseach, I choose spoof item text because
that spoof item text is an excellent model of a research report and has even been used
for teaching the purpose, generic structure and grammatical features of this genre of
reading. Additionally, I choose spoof item text because it is stated in School Based
Curriculum (KTSP) that the students in the second grade senior high school must be
able to differentiate kind of the text and tell about the idea of the text orally or written.
The teacher should arrange the teacher’s talk by themselves. Therefore, they can
explain the lesson in their classroom based on KTSP. Beside that the teacher should
know about text types. It is called genre. In the KTSP, we can see there are many kind
of texts that should be taugh the student in the second grade of Senior High School.
They are report, narrative,analytical exposition, spoof, hortatory.
According to those previous statements, the researcher thinks that it is important to
apply a more interesting reading activity. So, in this research, the researcher is going
to focus on one technique of teaching reading comprehension of spoof item text. In
order to know the process of the teaching learning process of reading spoof item text,
the researcher entitles this research paper “The implementation of RTC (Read,Tell,
and Choose) technique in increasing students’reading comprehension achievement at
7
1.2 Identification of Problems
In Line of this part, for reference to the background of problem, the following problems
are identified:
a. Students get difficulties in comprehending ideas achievement in English
lesson during their interaction, If in percent it is only 50% students ability to
understand the information of the text. (interaction between one student with
other student). It might be caused by misunderstanding which are some
probably occurred.
b. Students’ learning strategies are inappropriate with their learning objective.
For example students learn English in order to be able to communicate in
English well both reading and writing. But they use learning strategies which
focus in grammar only. So it is not suitable.
c. Teaching learning process is not effective because the students are not
focused during teaching learning process. It will decrease the quality of
teaching learning process itself.
d. Students have negative attitude in learning English. It happened when the
students have a bad background knowledge about English lesson, may be
English is so complicated for them. So it is difficult for them to learn English
well because they regard that English is impossible to be learnt well.
e. Students’ motivation in learning English is still low. So it is difficult to
improve their English ability well, because the students almost being a
passive learner while teaching learning are happened.
f. Teachers uses inappropriate materials in teaching English. It can be seen
8
because the text given by the teacher is almost a monoton text with un
interesting topic. So it is difficult for students to improve their English
ability well.
g. The students’ reading comprehension achievement is still low. The students
almost get low score from standard minimum score.
h. The way or method for the teacher teaching performance is still low. The
material in the class usually becomes the source for that lesson.
1.3 Limitation of The Problems
Based on the identification of the problems above, the problems of the currents research
are limited in:
1. The students’ reading comprehension achievement
2. Teaching learning process in teaching reading comprehension
As the solution to overcome their problems, this research is intended to use the RTC
technique as one of technique in teaching learning strategies in order to avoid
misunderstanding between the students.
1.4 Formulation of The problem
In line with the limitation of the problems above, the research problems are formulated
as follow:
1. How can the implementation of RTC technique increase the students’ reading
comprehension achievement using spoof text?
2. How can the implementation of RTC technique increase the teaching learning
9
1.5 Objectives of The Research
In this line with the formulation of the problems above, the objectives of the research
were to investigate:
1. To find out how the implementation of RTC technique to increases the students’
reading achievement.
2. To find out how the implementation of RTC technique increases the teaching
learning process.
1.6 Uses of The Research
The results of this research are expected to be useful both theoretically and practically.
Theoretically:
the findings of the research are expected to support the existing theory about reading
comprehension for the researcher before who is going to concentrate on teaching spoof
text using any other technique, and to give contribution to EFL/ESL teachers and the
curriculum developers about the quality of spoof item task in reading comprehension,
the problems that they experienced, and the strategies that the high and low proficiency
readers used to cope with the problems in reading comprehension.
Practically:
the findings of the research are expected to be beneficial for:
1. As information for the readers about the teaching learning process using RTC
10
2. As information for the readers, on how to help the students improve their
reading achievement using spoof texts.
1. 7 Scope of The Research
This research was in form of classroom action research. It was conducted at SMA
Kartikatama Metro. The subjects of the research were the second year students of SMA
Kartikatama Metro. In this research, the researcher was focused on the implementation
of read, tell, and choose (RTC) as a teaching technique to increasing students’ reading
comprehension. The material were used based on 2006
English Curriculum for SMA.
The research would be gave in two cycles. The first cycle was based on the problem of
the research, and the second cycle was based on the result of the analysis from the first
cycle.
1.8. Definition of Terms
There are some terms used by the writer and to make it clearly, the writer give some
definition as follow:
1. Reading Comprehension is defined as an active cognitive process of interacting
with print and monitoring comprehension to establish the meaning. (Silberstine,
1987 ;Simanjuntak, 1988:15)
2. Spoof is a text which tells factual story, happened in the past time with
unpredictable and funny ending Ahdoy (2010 : 19).
3. Read Tell and Choose (RTC)is a technique in teaching and learning that relates
11
connection between knowledge and its application to their lives especially in
learning process.
4. A Techniqueis a way of presenting that actually takes place in language teaching
13
II. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
2. 1 Reading Comprehension
Before going to the concept of reading comprehension, it is important to define
what reading is. Clark and Silberstien in Simanjuntak (1988) define reading as an
active process of interacting with print and monitoring comprehension to establish
meaning. It means that when reading a reader not only gets information from text
but also manages to produce the point of the author from the text.
Along with those statements, Nuttal in Simanjuntak (1988) defines reading as the
meaningful interpretation of printed or written verbal symbols. It means that
reading is a result of the interaction between the perception of graphic symbols
that represent language and the readers’ language skills, cognitive skills, and the
knowledge of the world. In this process the reader tries to recreate meanings
intended by the writer.
Furthermore, Silberstain in Simanjuntak (1988:15) defines reading as an active
cognitive process of interacting with print and monitoring comprehension to
establish meaning. Reading is the instantaneous recognition of various written
symbols, simultaneous association of these symbols with existing knowledge, and
14
reader interacts with print, his prior knowledge combined with and the visual
(written) information results in his comprehending the message. Therefore,
reading is actually a conversation of sorts between a writer and a reader.
Mackay in Simanjuntak (1988:15) also defines reading as an active process. The
readers form a preliminary expectation about the material, then select the fewest,
most productive cues necessary to confirm or reject that expectation. This is a
sampling process in which the reader takes advantage of his knowledge of
vocabulary, syntax, discourse and ‘real world’. Therefore, reading involves an
interaction between thought and language.
From all the theories have mentioned above, it can be concluded that reading is an
active process of getting meaning or information from printed or written language
shared by the writer.
Comprehension means relating to what we do not know or new information, to
what we already know (Eskey in Nurmalasari, 2010:11). Therefore, in
comprehending a text, the reader relates new information from the text being read
to his previous knowledge that he has stored in his mind. Reading the words of a
composition in one thing, but comprehending is the vital point for the reader.
In addition to the statement above, comprehension in reading cannot be ignored.
As Simanjuntak (1984:4) states that the first point to be made about reading
process is reading comprehension; consequently, it can be regarded that
15
Furthermore, Dallman (1982) emphasizes that reading with comprehension means
constructing meaning from what is being perceived in writing. Referring to the
statement, it means that the idea of an author from the text should be well
understood by a reader. This involves the reader to activate his or her brain to
absorb the idea.
In addition, Heilman, Blair, and Rupley (1981:242) said that reading
comprehension is a process of making sense of written ideas through meaningful
interpretation and interaction with language. Comprehension is the result of
reading. Moreover, they categorize reading comprehension into three levels of
comprehension:
1. Literal Comprehension
Literal comprehension is the process of understanding the ideas and
information stated in the passage such as: knowing the meaning of the words,
recall of details directly stated or paraphrased in own words, understanding of
grammatical clues, subject, verb, pronouns, conjunction, so forth. Recall of
main idea explicitly stated and knowledge of sequence of information
presented in passage (Hielman, Blair and Rupley, 1981:242).
2. Interpretative Comprehension
Interpretative comprehension means understanding of ideas and information
not explicitly stated in the passage. For example: to understand the author’s
16
cause-effects relationship and also summarize the story content (Hielman,
Blair and Rupley, 1981:242).
3. Critical Comprehension
Critical comprehension is analyzing, evaluating, and personally reacting to
information presented in a passage. For example: personally reacting to
information in a passage, indicating meaning to the reader, analyzing the
quality of written symbol or information in the terms of standards (Hielman,
Blair and Rupley, 1981:242).
In conclusion, it can be stated that reading comprehension is a process of
absorbing the author’s idea and combining it with schemata to construct or
establish new concept in the reader’s mind.
2. 2 Teaching Reading
Reading skills are often regarded as receptive skills and likened to listening skills.
There are similarities, but one important difference is that the reader can take
control of input more easily. Woods (2005:62) states that a listening input is often
taped with pauses built in or controlled by teacher. When reading, however, a
reader determines the speed of the activity by himself so that this becomes one of
the positive things to stress to students in the teaching reading.
When trying to gauge how difficult a particular text will be for students, taechers
need to bear in mind not only the inherent difficulty of the text, but also the nature
17
tasks before, during or after students have studied the text. Woods (2005:63)
classifies the activities in reading class into three as follows:
1. Pre-Reading Tasks
This task can be in form of vocabulary games, word searches and matching
synonyms. These activities can help students to approach a text in a more
confident way. Other pre-reading activities that can help readers relate to the full
meaning of a text are ones which activate top-down skills, or schematic
.knowledge. All of them enable students to familiarize themselves with the
content of a text. The activities can be systematic (such as vocabulary exercise) or
schematics (such as thinking of the purpose of a text or predicting the content
from its title) Woods (2005:63).
2. While-Reading Tasks
These kinds of task, as Hedge in Woods (2005:63) states, have become more used
since the adoption of the idea of reading as an interactive process. These
encourage learners to be active as they read. Students can be given activities
which require them to do any of the following: follow the order of the ideas in a
text; react to the opinion expressed; understand the information it contains; ask
themselves questions; make notes; confirm expectations of prior knowledge or
18
3. Post-Reading Tasks
These tasks follow up the work covered and seek to extend candidates. Such
activities are directed writing activities, or role play and group discussion
activities.
The activities above are a part of a structured program of learning probably
chosen by teachers when teaching reading. All the above kinds of activity can be
undertaken on an individual or group basis. Reading is frequently thought as
being a solo and quiet activity, but group pre- and post-reading activities can
motivate the crucial while-reading activities, The tasks of the teachers in class is
to go beyond course books and to introduce the students to a challenging element
of the target language which can add a new dimension to their learning and which
can give them some autonomy Woods (2005:63).
2. 3Spoof Text
Spoof is a text which tells factual story, happened in the past time with
unpredictable and funny ending Ahdoy (2010 : 19).
Spoof textin this research refers to:
1. Social function of spoof text.
Social function of spoof text are consist of:
a) Its social function is to entertain and share the story.
19
2. The generic (schematic) structure of a spoof text is below:
The generic (schematic) structure of spoof text are divided into:
1. Orientation: orientation is mean sets the scene who were involved in
the story, when, and where.
2. Event(s): Event or events is tell about what happened in chronological
order.
3. Twist: Twist is mean provide the punch line and the funniest part of the
story.
3. Language features:
In this line, language features of spoof text are consist of:
a) Focus on individual participants: It is mean just concentration on
individual participants.
b) . Use of material processes: It is mean make material for teaching
process.
c) Circumstances of time and place: It is mean the condition
connected with place and time.
d) The use of action verbs:
(e. g. walked, laughed, ran away etc).
e) The use of connectives: It is mean use the related words to each
other.
(e. g. first. then, finally etc).
f) The use of adverbial phrases of time and place.
20
g) The use of the simple past tense:
spoof story is happened in past, so write spoof by using simple
past tense
(e.g. he walked away from the village).
2. 4 Guiding Principles to The Teaching of Reading
According to Gaudart and David (1993:102-103) guiding principles to the
teaching of reading are:
1. Reading is a “psycholinguistic guessing game” (Goodman 1967)- the
reader use of our background knowledge to interact with the text, making
predictions based on samples of the text and confirming or rejecting our
predictions as the reader read along.
2. Reading is more than a decoding of texts. The reader do not construct
meaning from texts by beginning first with letters, and then with words,
moving up to phrases, sentences and so on. Good readers do not in fact
read word by word; instead, they make use of both information in the text
and their background knowledge to construct meaning form the text.
3. Good readers interact actively with the text. They make predictions about
the information in the texts. They relate the content of the text to their own
experience and they may modify new knowledge acquired to suit the
existing knowledge structures (schemata) in their memory.
4. Reading entails the emotional involvement of readers- Readers react
21
“dialogue” with the text, questioning or evaluating the content of what
they read.
5. Readers select what they extract from the text based on their reading
purpose. In real life, readers select only relevant information for a
meaningful purpose. Readers moreover, do not normally have attain 100%
(complete) understanding of the text they read.
6. In reading class, the readers attention should be focused on meaning, not
form. We should encourage students to read for meaning, and not to read
because they want to learn grammar or vocabulary. Activities focusing on
form, if carried out at all, should only be done after the reading activity.
7. Reading should not be tough tas a separate skill in isolation- Reading and
the teaching of reading should be integrated with the other skills of
writing, speaking and lsitening. Talking and writing about what one has
read helps to reinforce reading skills acquired beside making the reading
class a more active and interesting one.
8. The reader learn to read, and to read better, by reading (Eskey 1986,
Smoth 1985). Reading involves the simultaneous interaction of miltiple
skills (bottom-up decoding, utilising background knowledge, skimming,
scanning, recognising rhetorical patterns and infer/ intra-sentensial
relationship, making inferences, etc.) such skills are best practised
simultaneously rather taught in isolation one at a time. Reading is
therefore caught not taught (Peter Roe, Aston University, personal
22
9. The provision of comprehensible text is of vital importance to reading
improvement. Students should be able to understand the texts they are
reading in order to improve their reading ability. As Smith (1985:139)
says. “Children learn to read by reading, so teachers must help children to
read by making reading easy, not difficult.” Text may therefore be
challenging but never frustating students.
2. 5 Read-Tell-and-Choose (RTC) Technique
A technique which will be used in this research is called read-tell-and-choose
(RTC) Technique because as Gaudart and David (1993:104) said:
1. Read: what learners have to do-they read the text.
2. Tell: tell their partners what they have read.
3. Choose: choose the best to be re-narrated.
It will be noted that the activity adheres to many of the principles mentioned
earlier. It adopts an integrated-skills approach which involves learning in reading,
writing, speaking and listening activity. The reading purpose provided by the
task-to tell the other group member what they have read and task-to select the best stask-tory
among them-is meaning-focused.
2. 6 Classroom Action Research
Allwright (1991:42) simply defines Classroom Action Research as a research
which involves taking action and systematically observing what follows.
Furthermore, Mettetal in his essay defines Classroom Action Research as
23
Classroom Action Research is a way for instructors to discover what works best in
their own classroom situation, thus allowing informed decisions about teaching.
In addition, Kemmis and Henry in Allwright (1991:44) defines Classroom Action
Research as a form of self-reflective inquiry undertaken by participants in social
situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of their understanding of
these practices and the situations in which these practices are carried out.
Kemmis and Mc. Taggart (1982 : 3) also state that action research is deliberate,
solution-oriented investigation that is group as personally owned and conducted.
It is characterized by spiraling cycle of the problem identification, systematic data
collection, reflection analysis, data-driven, action taken, and finally problem
definition.
Action research in classroom follows a series of repeated steps. Strickland in
Allwright (1991:44) discusses the following sequence: 1. identify an issue,
interest, or problem; 2. seek knowledge; 3. plan an action; 4. implement the
action; 5. observe the action; 6. reflect on your observations; and 7. revise the
plan. The cycle then begins once more, with the revisions incorporated in a new
action, which is itself observed, and so on. This process allows the teachers who
wish to investigate events in their own classrooms to take constructive steps
toward solving immediate problems, systematically reflecting on the outcome.
Thus the goals of action research are achieving local understanding and
24
In addition, action research teacher not only work alone, but can make
collaboration. Collaboration means entangling other people in the research. There
are many involvements in action research; such as partnership with the other
teachers or relationship between teacher and students.
From all the theories mentioned above, it can be concluded that Classroom
Action Research is an action in a research, which can be done by the teacher,
researcher, and the teacher with his/ her colleague, and allows the teachers to
investigate events to take constructive steps toward solving immediate problems
and systematically reflecting on the outcome.
2. 7 Procedure of Teaching Reading Comprehension of Spoof Items Text
through RTC (Read, Tell and Choose) Technique
It is clear that in RTC technique, the students are the most active candidates. The
teacher has the function as a guide or a consultant to help the students’ difficulties.
The teaching procedures are adapted from Abbott ,Greenwood, McKeating, and
Wingard (1981:104-106) and have been modified by the writer. The teaching
procedures can be described as follows:
A. Pre-Activity.
1. Greeting.
2. The students are given brainstorming the material based on their
background knowledge. It is used to build the students’ thought
25
3. The students are informed the material they are going to learn, the
goals of learning to achieve and reading technique the students use.
B. While-Activity.
1. The students are asked what they know about spoof text.
2. The students listen the teacher introduces RTC technique to the
students, tell those procedures and how to learn the lesson through its
procedures.
3. The students are divided into group. Each group consists of 3 or 4
members.
4. The students are given the reading text to the students.
5. The students listen the teacher begins the procedures of RTC
technique.
1. Read; teacher asks the students to read the text for about five
minutes.
2. Tell; teacher asks the students to retell the content of the text for
about five minutes.
3. Choose; teacher asks the students to determine which story is spoof
text for about ten minutes.
6. The students’ work are check by the teacher.
7. The students’ are rehearsed about the process of RTC by delivering a
new question (for instance about details of the text).
26
9. The leader of group comes in front of the class to read the answer of
his group.
10.The students’ answer are given revision and response by the teacher
toward or additional information that the students have not conveyed
yet and also leads the discussion into a conclusion.
C. Post-Activity.
1. The students’ are asked about the difficulties related to the topic.
2. The students’ are supposed to make inferences about what theyhave
just already learnt.
3. Closing the meeting.
2. 8 Advantages and Disadvantages of Read, Tell, and Choose (RTC)
Technique
As stated before, Read, tell, and Choose technique helps the teacher to relate the
material to students’ reading ability. However, it also has some advantages and
disadvantages. They will be as follows:
A. The advantages of RTC are:
1. Read, Tell and Choose technique give a deep understanding or
comprehension to the students because it is simple technique.
2. Read, Tell, and Choose technique give learners more control over their
27
3. Read, Tell, and Choose technique will become more useful if the text
gives current or recent information.
4. Read, Tell, and Choose technique will be more interesting if the text
includes or containsthe information about the learners’ experiences.
5. Read, Tell, and Choose technique the difficulties of the exercise can be
easily adjusted according to the amount of information which is provided
in the exercise.
B. The Disadvantages of RTC are:
1. The class will be noisy. This happens because Read, Tell, and Choose
technique invites the students to have discussion among them; therefore
the class will be noisy.
2. It will take longer time. In reading activity, the students have to fill
information which is presented in different form. So that the students have
to analyze the material first and they also have to understand the exercise.
This will take longer time.
3. The material selection. The material should be selected carefully, because
sometimes the same material cannot be applied, the students will be bored
28
III. RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Setting of The Research
In this reseach, the researcher used a classroom action reseach because this research was
done based on the problem faced by the students and the teacher when they were in reading
class. Based on the problem found by the researcher, the researcher examined the causes of
the problem and then founds the solution for that problem. (Arikunto, 2007: 5)
The subjects of the research were the second year students of science program of SMA
Kartikatama Metro. The researcher used one class from the second grade that consist of 40
students as the target of the research. Researcher found that the students in second grade of
SMA Kartikatama have difficulties in reading class. The low ability of students also due to
the lack information about the context of lesson that makes students have limited idea in
discussion
This research focuses on how to improve student’s reading comprehension achievement
using a certain technique. The teacher thought reading through read tell and choose suitable
for students at senior high school. The teacher thought about how to increasing student’s
29
The researcher chooses this class because they were the low achievers class in second grade
of SMA Kartikatama because their ability of reading was so low. Based on the researcher’s
observation, researcher found that students have low ability in reading especially in
vocabulary, background knowledge of the students and also meaning or point of the text. It
might be seen from their low average score in reading test which could not reach 65 as the
minimum score, when the teacher asked the students, many of them got confused because
misunderstanding of reading text.
In this classroom action research, the researcher acted as the observer, meanwhile the
teacher of SMA Kartikatama as a teacher and taught the students by using read tell and
choose. The teacher made the lesson plan and she performed in the class based on the
lesson plan. So, during the research, the researcher and the teacher would be observed
activities occurred in the classroom when they were learning reading.
3. 2 General Description of The Research
Classroom Action Research was characterized by problems in class and done actions to
solve problems. Based on the problem identified by the researcher, the researcher would be
examined problem causes and tried to find the problem solution. Problem solution that
would be conducted was teaching reading of spoof text through RTC technique. The
teacher made lesson plan and taught the students based on the lesson plan. Then, the
teacher and the researcher took the notes about the important things occurred during the
30
In doing the research, the researcher was doing the collaboration with the English teacher to
improve the students’ reading comprehension achievement through Read Tell and Choose
(RTC). While the researcher was applied RTC in the classroom, the collaborator observed
the teaching learning process and made some necessary points from that process.
Furthermore, the researcher analyzed and discussed the observation results during teaching
and learning process (the strength and the weaknesses found by the teacher and students
teaching and learning process of reading spoof text using RTC technique) and learning
product (the reading comprehension test). Learning process analysis would be done based
on the researcher and her partner observation. It focused on the weaknesses of the previous
cycle.
3.3 Research Procedures
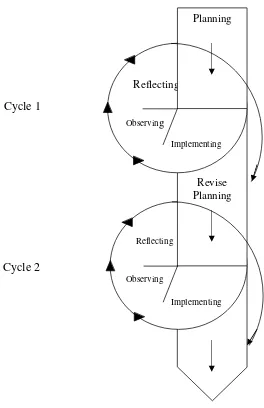
The research divided into some cycles. Each cycle consisted of four stages: (1) plan, (2)
implementing or action, (3) observing, and (4) reflecting (Arikunto, 2006:16). The stages
31
Figure 1. The cycle of Classroom Action Research Adopted from Kemmis and Taggart (in Wiriaatmadja, 2008:66)
Reflecting
Implementing
Revise Planning Reflecting
Implementing
Planning
Observing
Observing
Cycle 1
32
The Cycles are classified as Follow:
3. 3.1 Planning
Based on the problem of the research, the researcher prepares the lesson plan; selecting
material based on the syllabus for the teaching learning process through RTC technique.
The reading material wasspoof textswhich was taken from many sources. Additionally, the
researcher prepared observation sheets, and also reading test for the students in the form of
multiple choice.
3.3.2 Implementing
The teacher here was an English teacher from the school. In this step, the teacher taught the
students based on the lesson plan. Here, RTC technique was implementing in teaching
reading of spoof texts process.
3.3.3 Observing
The teacher helped by the researcher as an observer who took a note toward teaching and
learning activity. While the teacher implemented the technique, the observer monitored the
learning process and the students’ activities. Besides, the observer also observed the
teacher’s performance in implementing the RTC technique. The important things would be
33
3.3.4 Reflecting
In this step, the researcher and the teacher analyzed the result of the reading test of the
students as the learning product. The researcher also analyzed activities occurred in the
teaching learning process based on the observation sheets. It would be done to find out the
improvement after the teacher implemented the RTC technique in teaching reading
explanation text in the classroom. In analyzing, the researcher and the teacher doing a
reflection to discover the weaknesses and the strength of the implementation of RTC
technique, and also to knew the problems would be face by both the teacher and the
students during teaching and learning process. By doing so, the researcher and the teacher
knew what should be improved for the next cycle. If the indicators of the research have not
been fulfilled in the first and in the second cycle, the researcher and the observer planed the
next step to improve the quality of the learning process in the next cycle. On the other hand,
if the indicators were already achieved the researcher and the observer did not need to hold
the next cycle.
3.4 Indicators of The Research
The success of this classroom action research was divided into two parts: learning product
34
3.4.1 Learning Product
The target of learning product that determined by the researcher and the teacher was 65 or
more. It would be done because 65 was the standard minimum score or KKM stated by the
school for English subject. So, if at least 80%of students’ score got65 or more for reading
comprehension test, it was mean the RTC technique could improved students’ reading
comprehension achievement.
3.4.2 Learning Process
In learning process, there were two aspects which become the focus of this research: the
students’ activities and the teacher’s performance toward the implementation of RTC
technique.
Based on the result of the discussion with English teacher in conducting this research, it
was decided that the target of the learning process is 80% of the students actively involved
in learning process during the application of researcher. It was also decided because
according to Arikunto (1993:210), if more than 75% of students were actively involved in
teaching and learning activities, it could be categorized as a good level.
Besides observing the students’ activities, the researcher also observed the teacher’s
performance during teaching and learning process. It was expected that the teacher’s score
35
means she could teach students well. There were some aspects thatscored for the teacher’s
performances; it involved activities in the teaching and learning process from pre-activity,
main activity and post activity. The teacher’s performance in applying RTC technique was
observed in main activity.
3.5 Instrument of The Research
In collecting the data, the researcher used two kinds of instruments: (1) Reading
comprehension tests, and (2) Observation sheets. Each kind of instruments explained as
follows:
3.5.1 Reading Comprehension Tests
The tests would be reading test in form of multiple choice test. The result of this test was
considered as the data of students’ reading comprehension’s improvement. The researcher
made a table of specification that helped the test constructor plans the test.
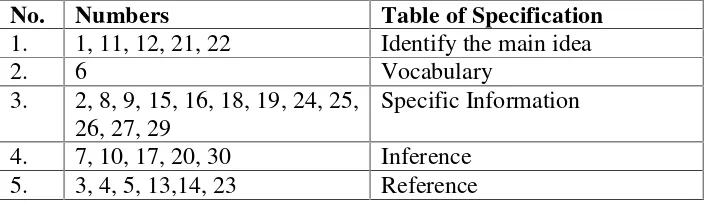
Table 1. Table of specification of reading test.
No. Numbers Table of Specification
1. 1, 11, 12, 21, 22 Identify the main idea
2. 6 Vocabulary
3. 2, 8, 9, 15, 16, 18, 19, 24, 25, 26, 27, 29
Specific Information
4. 7, 10, 17, 20, 30 Inference
36
There were 20 items in this test asking about three components of reading comprehension,
they were unstated information, stated information, and vocabulary.
The test would be administered at the end of every cycle in the learning process.
3.5.2 Observation Sheets
There were two observation sheets in this research, observation sheets for the students’
activities and that for the teacher’s performance. The two observation sheets were fulfilled
by the researcher as an observer. The Observation conducted in every cycle during the
teaching learning process. When teaching and learning process occurred, the teacher
together with the researcher as an observer observed the process which was happened in the
classroom.
3.6 Data Analysis
In analyzing the data, the researcher classified the data into two categories; the data of the
learning process and the learning product. The data Analysis would be done during and
after the data have been collected from every cycle (1st, 2nd, …) if the data from the first
cycle have been collected, the teacher together with the researcher as observer analyzed the
data and doing reflection based on them. From the analysis and reflection, the researcher
knew the weaknesses and the strengths from the first cycle. Besides, both teacher and
37
3.6.1 Learning Product
To know the learning product, the researcher used reading test to collect the data. To know
the percentage of the students who got ≥65, the following formula was used:
(Source: Dep. Pendidikan Nasional, 2009)
3.6.2Learning Process
To get data from the learning process, the researcher used observation sheets. The result of
the observation sheets analyzed after every cycle conducted. In this step, the researcher
counted the sum of scores from all aspects. The aspects scored were every aspect in each
step of pre activity (2 aspects), main activity (7 aspects), and post activity (1 aspect).
3.6.3Observation Sheet
Since the observation done for observing the students’ activities and also teacher’s
38
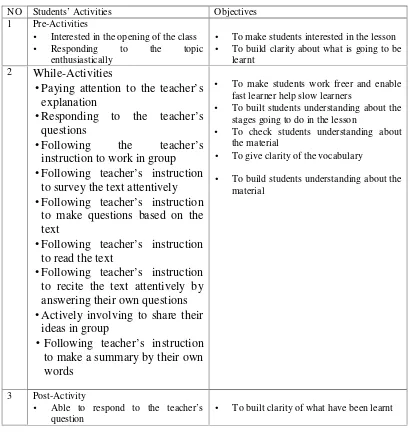
Table 2 Table of Specification of the Observation Sheet for Students’ Activities
NO Students’ Activities Objectives
1 Pre-Activities
• Interested in the opening of the class
• Responding to the topic
enthusiastically
• To make students interested in the lesson
• To build clarity about what is going to be
learnt
•Following the teacher’s
instruction to work in group
•Following teacher’s instruction
to survey the text attentively
•Following teacher’s instruction
to make questions based on the text
•Following teacher’s instruction
to read the text
•Following teacher’s instruction
to recite the text attentively by answering their own questions •Actively involving to share their
ideas in group
•Following teacher’s instruction
to make a summary by their own words
• To make students work freer and enable fast learner help slow learners
• To built students understanding about the
stages going to do in the lesson
• To check students understanding about
the material
• To give clarity of the vocabulary
• To build students understanding about the
material
3 Post-Activity
• Able to respond to the teacher’s
question
• To built clarity of what have been learnt
39
Table 3 Table of Specification for Teacher’s Performance
No. Aspects Obeserved Score (by giving a tick)1 2 3 4
1 Pre-activities
• The teacher was prepared and
well-organized in class. .
The prepared goals/ objectives were apparent.
2 While-activities
A. PRESENTATION
• The class material was explained in an
understandable way
• The lesson was well-paced
• Directions were clear and concise and
students were able to carry them out
• Material was presented at the students’
level of comprehension.
• The teacher knew when the students were
having trouble understanding.
• The teacher showed an interest in, and
enthusiasm for, the subject taught
B. EXECUTION/ METHODS
• There were balance and variety in
activities during the lesson.
• The teacher was able to adapt to
unanticipated situations.
• The teacher moved around the class and
made eye contact with students.
• The teacher knew students’ names.
• Student responses were effectively elicited
( i.e., the order in which the students were called on ).
• Examples and illustrations were used
effectively.
40
C. PERSONAL CHARACTERISTICS
• Patience in eliciting responses.
• Clarity, tone, and audibility of voice.
• Initiative, resourcefulness, and creativi
D. TEACHER/ STUDENT INTERACTION
• Teacher encouraged and assured full
student participation in class.
• The teacher was able to control and direct
the class.
• The students were attentive and involved.
• The teacher was aware of individual and
group needs.
E. Evaluation
• Monitoring the students’ improvement
after the teacher explains the lesson.
• Doing a final evaluation which is relevant
to the competence.
3 Post-activities
• Doing a reflection/making summary of
the lesson by involving the students’ participation.
• Doing a follow-up by giving direction or
41
Total Score
Description of score
(Source: Dep. Pendidikan Nasional, 2006) Note:
1 = Poor 2 = Enough 3 = Good 4 = Very Good
Description of Scores:
1. 40– 59 : Poor
2. 60– 69 : Enough
3. 70– 79 : Good
4. 80–100 : Very Good
In analyzing the data got from observation of the students’activities, the researcher counted
number of students who were actively involved in the teaching learning activities and also
calculated the percentage of the students. In addition the researcher made abstraction or
description then selected the important ones which were related to the activities of the
students.
Meanwhile, in analyzing the data found by from observing teacher’s performance, the
researcher doing the following steps:
3.6.4 Counting The Total Score of Teachers’Performance
In this step, the researcher counted the sum of scores from all aspects. The aspects scored,
were for every aspect in each step of pre activity (4 aspects), main activity (9 aspects), and
42
3.6.5 Counting The Average Score of Teacher’s Performance
The average score would be important to be decided in order to decided if the teacher
reaches the indicator or not. To find out the average score the following formula used:
3.6.6Students’ Learning Activities
After gathering data from observing the students’ learning activities, counting the number
of activities done by the students were the steps that would be done in this activity.
A. Calculating the percentage of students’ activities
For calculating the percentage of the students’ activities, the following formula used:
% A =
Note:
% A: percentage of students’ activities
A: number of students’ activities observes
n: number of students in the class
43
3.6.7 Teacher’s Performance
In analyzing the data from observation of the teacher’s performance, the researcher made
the description for the data that have been analyzed.
It was similar to analyzing thestudents’ activities, to analyzing the teacher’s performance,
the researcher made description from the collecting data which enriched and support the