COMPREHENSION AT SECOND YEAR STUDENTS OF SMAN1 KRUI
By
EGRA BETARIA
Guideline of School-Based Curriculum (SBC) which is applied for all school levels in Indonesia leads the students to have real life skills. This implies that teaching English stated in SBC, in particular, is to enable the students to master the four language skills; listening, reading, speaking and writing. Reading is one of the important skills that the students have to master. Students must improve their ability in reading comprehension so that they can get information from any text they read.
is far from the goal being expected. Many students have difficulties in comprehending reading text because teachers in school do not use effective technique for teaching reading comprehension.
Therefore, this Classroom Action Research is aliened, first, to improve the achievement through jigsaw, second, to
participation during the teaching learning process, and third to improve the , in this research is conducted in two cycles. The subject of the research is the second grade of SMAN1 Krui. The research lasted from February 22thuntil March 02th2012.
The result of the research proves that jigsaw technique can be used to improve the comprehension. There are two cycles in this research. In the first cycle, the indicators in this learning product and learning process could not be
fulfilled yet in cycle 1. For learning product, i %
Based on the data, the researcher concludes that the implementation of Jigsaw
technique achievement and teaching learning process.
The researcher She was born in Krui on February 6th,
1989. She is the sixth child of a harmonious and wonderful couple Hasmudin Ahsan, S.Pd and Ermaini. She has four brothers and three sisters: Herdi Wilismar, S.H, Deni Ishanda, S.Pd, Charles Arisandi, Febriyansah, Heryanti, S.E., Nora Elisa, S.Pd, and Yesi Sumarni, S.I.Kom.
She enterd SD Negeri 2 Gunung Kemala in 2000. Then she continued her study to SMP Negeri 3 Krui and graduated in 2004. She finished her High school at MAN Krui in 2007.
DEDICATION
This Script is dedicated to:
My beloved parents, Hasmudin AHsan, S.Pd and Ermaini:
My beloved brothers and sisters: Heryanti, S.E., Nora Eisa, S.Pd., Yesi Sumarni, S.I.KOM., Herdi Wilismar, S.H., Deni Ishanda, S.Pd.,
Charles Arisandi, and Febri Yansah.
My soul mates (Arie Setiawan): Thanks for your love, help, and Support
God helps those who help themselves
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Alhamdulillah, praises is merely to Allah SWT for the gracious mercy and tremendous blessing that enables the researcher to accomplish this research project. Then, sholawat is for our Prophet Muhammad SAW, with his family, The Implementation of Jigsaw Technique in Teaching Reading Comprehension at The Second Year Students of
SMA Negeri 1 Krui Department of
Teachers Training and Education Faculty of Lampung University as partial fulfillment of the requirements in accomplishing the S-1 Degree in English education.
It is important to be known that this script would never have come into existence without any supports, encouragement, and assistance by several generous persons. First of all the researcher would like to express her sincere gratitude and respect to her first advisor, H. M. U. Suparman, M.A., Ph.D. and for her second advisor, Dra. Hartati Hasan, M.Hum., who have guided, assisted and encouraged her during the completion of this script. The researcher also would like to express her deepest gratitude and respect to her primary examiner Dr. Muhammad Sukirlan, M.A., for his valuable suggestion.
Besides, the researcher wants to extend her deep appreciation to Iswanto, S.Pd. as the English Teacher of second grade of SMA Negeri 1 Krui, and to the XI IPS4 students of SMAN1 Krui in academic year 2011/2012 for their nice cooperation during this research.
Most importantly her special gratitude should go to her great father, Hasmudin Ahsan, S.Pd., and her great mother, Ermaini for their never ending love, pray, attention, and encouragement. For her brothers Herdi Wilismar, S.H., Deni Ishanda, S.Pd., Charles Arisandi, Febri Yansah, her lovely sisters, Heryanti, S.E., Nora Elisa, S.Pd., Yessi Sumarni, S.I.Kom., her brohers in law, Juhendi Hermansyah, Siswanto, S.Pd., Heri Aska, S.Ag., her sisters in law, Evi Sumarni, and Linda Yani, and her lovely nephews and nieces. Thanks for your love and support.
Moreover, the researcher would like to thank her foster brothers, Ledo Saputra (Dank Ledo), Roli Tamara (Bang Roli) and Yoga Sugama (Cik Yoga). Thanks for your support, time, and advises. For her beloved bestfriends, Yulia Helwana, S.Pd., (Yuyie), Dellia Astiti, SPd., (Moet), Lisa Epiya (Cha), dwi Chery (Chery), Eflin Pasaribu (Eflin), and Dora Carolina (Dora). Thanks for your support and time.
The researcher 7
Bandarlampung, June 2012 The Researcher
ABSTRACT
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF JIGSAW TECHNIQUE IN TEACHING READING COMPREHENSION AT SECOND YEAR STUDENTS OF SMAN1 KRUI
By
EGRA BETARIA
Guideline of School-Based Curriculum (SBC) which is applied for all school levels in Indonesia leads the students to have real life skills. This implies that teaching English stated in SBC, in particular, is to enable the students to master the four language skills; listening, reading, speaking and writing. Reading is one of the important skills that the students have to master. Students must improve their ability in reading comprehension so that they can get information from any text they read. As a matter of fact, the students’ ability in reading comprehension is far from the goal being expected. Many students have difficulties in comprehending reading text because teachers in school do not use effective technique for teaching reading comprehension.
Therefore, this Classroom Action Research is aliened, first, to improve the students’ reading achievement through jigsaw, second, to improve the students’ participation during the teaching learning process, and third to improve the teacher’s performance, in this research is conducted in two cycles. The subject of the research is the second grade of SMAN1 Krui. The research lasted from February 22th until March 02th 2012.
93.33% students were actively involved and the teacher was scored 85 for her teaching performance.
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter discusses introduction dealing with background of the problem, identification of the problems, limitation of the problems, formulation of the problems, objectives of the research, uses of the research, scope of the research, and definition of terms.
1.1 Background of the Problem
There are four skills to be mastered in learning English, namely: listening, speaking, reading and writing. Based on 2006 (SBC) the students are expected to learn English from various types of the text. It means that the students have to deal with many texts during the English lesson, for example descriptive text, recount text, explanation text, discussion text, reviews text and also narrative text. In the syllabus, it is stated that the students should be able to identify the topic from the text read, identify certain information, identify the meaning of the words in the text read and identify the meaning of sentences in the text read.
-observation conducted in SMAN1 Krui, it was found that the first class of social science program class II has several problems. First, the students still have difficulty in comprehending the reading text; as a result their reading scores were low. Second, the average of the students reading comprehension test score was 60 which were lower than the minimal mastery criterion (KKM) of that school which was 65. The researcher assumes that the problems happen because the students are unable to identify the main ideas, specific information, reference and interference of each paragraph of the text.
Due to the problems faced by the students, the researcher tried to find out the cause of the problem. From the pre observation, the researcher assumes that, one of the causes of the problem is the inappropriateness of teaching technique used by the teacher in teaching reading. So it is clear that English teacher should be creative to select the teaching techniques, especially in teaching reading comprehension to make the students understand the subject better.
3
comprehension, i.e. by using jigsaw technique. Jigsaw technique is considered as an alternative. Jigsaw technique was developed by Aronson 1978. This technique can be used in teaching listening, speaking, reading or writing. Jigsaw technique is an interesting activity which can activate students in reading because each student can be active learners by giving his/ her idea and share it to the other members when they have some problems in comprehending the topic.
Jigsaw is a complex form of cooperative learning and it is important that students have experience with small group learning skills before they are involved in jigsaw. Jigsaw is a cooperative learning technique that provides students with an opportunity to actively help each other in their learning. Each student is assigned
from different home groups. Students meet in their expert group to discuss specific ideas or solve problems. They then return to their home group, where all members share their expert knowledge.
There are many reasons why jigsaw technique is chosen as a technique in teaching reading. One of them is that through jigsaw technique all of the students have a chance to interact whit the other students. In this activity, the students will form a community that can make them love the teaching learning process. Besides, by using jigsaw each student can be active learners by giving his/ her idea and share it to the other members when they have some problems in comprehending the topic.
students will s
thinking and social skills to accomplish the learning task, and gain self-confidence through their contributions to the group effort
According to the previous statements, the researcher thinks that it is important to apply the more interesting reading activity. So this research is focused on one technique of teaching reading comprehension of narrative text. In order to know the process of the teaching learning process of reading narrative text, the researcher
1.2 Identification of the Problems
In reference to the background of the problem previously presented, the following problems can be formulated as follows:
a. Students get difficulties in comprehending the reading text. They get difficulties in getting information from the text, especially in finding main idea, social function of narrative text, text organization, and language features. b. Students do not have sufficient vocabulary mastery to comprehend the text.
c. Students do not have sufficient Reading skills which make them lazy to read the text.
d. motivations in learning reading are still low. It is difficult to improve their reading ability well.
5
f. Teacher uses inappropriate teaching technique in teaching Reading. So it is difficult in helping students in reading comprehension.
g. The students reading comprehension achievement is still low. The students almost get low score from standard minimum score.
1.3 Limitation of the Problems
Based on the identification of the problems above, the problems of the currents research are limited in:
1.
2. ng the teaching learning process.
3.
As the solution to overcome their problems, this research was intended to used the jigsaw technique as one of technique in teaching learning strategies in order to avoid misunderstanding between the students.
1.4 Formulation of the Problems
Based on the background above, the researcher tried to state the problem as follows:
2. How can jigsaw technique be used to improve the teaching learning process?
3. How can jigsaw technique be used to improve the performance in teaching reading?
1.5 The Objectives of Research
The objectives of the classroom research are: 1. To find out how jigsaw can be used to
comprehension achievement?
2. To find out how jigsaw technique can be used to improve participation during the teaching learning process?
3. To find out how jigsaw technique can be used to improve the performance in teaching reading comprehension?
1.6 Uses of the Research
The findings of this research are expected to be useful both theoretically and practically.
Theoretically:
7
2. To be used as a reference for the next researcher who will concentrate on
Practically:
The findings of the research are expected to be beneficial for:
1. As the information concerning with whether there is improvement
reading achievement and teaching learning process that are taught through jigsaw technique.
2. As a help to English teachers in finding and appropriate way to improve ing achievement.
1.7 Scope of the Research
This reseach was conducted at SMAN1 Krui Lampung Barat, while the subject of the reseach was the second year students of senior high school academic year. In this case, the material of reading taught was narrative text. The reason why the reseacher chose narrative because it is one of kind of fuctional text that should be mastered by the students in this level.
1.8 Definition of Terms
There are some terms used by the writer and to make it clearly, the writer give some definition as follow:
Reading Comprehension
comprehension revolves around the rea main idea and topic sentence from the text.
Jigsaw
It is refers to a complex form of cooperative learning and it is important that students have experience with small group learning skills before they are involved in jigsaw. Jigsaw is a cooperative learning technique that provides students with an opportunity to actively help each other in their learning.
Technique
It is refers to a way of presenting that actually takes place in language teaching or learning in the classroom.
Narrative
It is refers to a text which tells what happened. To amuse, entertain, and to deal with actual or vicarious experience in different ways.
Classroom Action Research (CAR)
CHAPTER II FRAME OF THEORIES
This chapter deals with the theories used in this study, namely concept of reading comprehension, concept of teaching reading, concept of jigsaw technique, the advantages and disadvantages of jigsaw technique, concept of narrative text, the procedures of teaching reading by using jigsaw technique, theoretical assumption.
2.1 Concept of Reading Comprehension
There are two kinds of reading activity, namely reading aloud and silent reading. What the readers are doing in silent reading is to use our eyes and our ability to understand the meaning of the written sign, thus comprehending the text will be given more emphasize in silent reading. Meanwhile reading aloud forms a foundation for the early literacy framework. By having stories read to them children learn to loves stories.
Caver (1990) defines reading as a complex cognitive process of decoding symbols for the intention of deriving meaning (reading comprehension) and/ or constructing meaning. Written information is received by retina, processed by the
means of language acquisition, of communication, and of sharing information.
the readers through the texts. The writer tries to encode the messages to the readers. Then the readers try to decode the messages that sent by the writer.
These concepts basically state that reading always deals with printed materials, which stresses on the grasping meaning from the printed language. It means that reading activity is the interaction between the perception of the graphic symbols
the knowledge of the world. In this process, the reader tries to create meaning intended by the writer.
Someone has a purpose when he/she is reading. Usually the purpose of reading a passage is to find ideas from the reading passage. As Suparman (2005: 1) states that there are two major reasons for reading (1)reading for pleasure; (2) reading for information (in order to find out something in order to do something with the information readers get).
At the same time, Pakhare (2007) states that reading comprehension can be defined as the level of understanding of passage or text. For normal reading rates (around 200-220 words per minute) an acceptable level of comprehension is above 75%.
According to these views, it is clear that reading and comprehension are regarded as one activity which cannot be separated, and each program is depending on the progress of activity of mind. In other words, reading comprehension is an activity to grasp the meaning of written materials with fully understanding.
12
finding and determining main idea and topic sentence from the text.
Referring to the definitions above, it can be said that in comprehending the texts the students have to know their strategy in reading. It means to make them easy to identify the specific information in the text. One aspect that becomes essential in is the reading strategy. The researcher assumes that reading
information, words and surface meaning in the texts which is described by re with an appropriate strategy.
2.2 Concept of Teaching Reading
Reading skills are often regarded as receptive skills and linked to listening skills. There are similarities, but one important difference is that the reader can take control of input more easily. Woods (2005: 62) states that a listening input is often taped with pauses built and or controlled by teacher. When reading, however, a reader determines the speed of the activity by himself so that this becomes one of the positive things to stress to students in the teaching reading.
When trying to gauge how difficult a particular text will be for students, teacher need to bear in mind not only the inherent difficulty of the text, but also the nature of the tasks they plan to set and whether they require student to attempt such tasks before, during or after students have studied the text. Woods (2005: 63) classifies the activities in reading class into three a follows:
This task can be in form of vocabulary games, word searches and matching synonyms. These activities can help students to approach a text in a more confident way. Other pre- reading activities that can help readers related to the full meaning of a text are ones which activate top-down skills, or schematic knowledge. All of them enable students to familiarize themselves with the content of text. The activities can be systematic (such as vocabulary exercise) or schematics (such as thinking of the purpose of a text or predicting the content from its title) Woods (2005: 63)
2.2.2 While-Reading Tasks
These kinds of task, as Hedge in woods (2005: 63) states, have become more used since the adoption of the idea of reading as an interactive process. These encourage learners to be active as they read. Students can be given activities which require them to do any of the following: follow the order of the ideas in a text, react to the opinion expressed; understand the information it contains; ask them selves questions; make notes; confirm expectations of prior knowledge or predict the next part of a text from various clues.
2.2.3 Post-Reading Tasks
14
The activities above are a part of a structure program of learning probably chosen by teachers when teaching reading. All the above kinds of activity can be undertaken on an individual or group basis. Reading is frequently thought as being solo and a quite activity, but group pre and post-reading activities can motivate the crucial while reading- activities, the task of the teachers in class is to go beyond course book and introduce the students to a challenging element of the target language which can add a new dimension to their learning and which can give them some autonomy Woods (2005: 19)
In short, in teaching reading the teacher should provide strategy to the students with purpose for reading to anticipate different type of reading texts. Therefore, reading technique should be matched to reading purpose to read efficiently and effectively.
2.3 Concept of Jigsaw Technique
Aronson (1978: 43) says that Jigsaw Technique is a technique which has a strong the group. This also means that can help the students to rely on each other for information in a way which puts on students above others. Finally, each student will be valuable in the group.
threatening for many students, (b) it increases the amount of student participation in the classroom, (c) it reduces the need of competitiveness, (d) it reduces the sroom. Consequently, Jigsaw Technique can
and help create an active learner-centered atmosphere.
Johnson, Johnson and Holubec (1993) put forward five principles for Jigsaw: a. Positive interdependence
success. Each group member has to make unique contributions to the joint
knowledge to
b. Face to face promotive interaction
Group others, check for understanding, discuss concepts being learned and associate the present learning with the past one.
c. Individual and group accountability
The size of the group should be kept small, for the smaller the size of the group is, the greater the individual accountability may be. The teacher is expected to give an individual test for each student, randomly examines
teacher or to the entire of the class, observes each group and records
appoints one student from each group as the leader who is responsible for asking other group members to explain the rationale underlying the group answers, and monitors students to teach what they have learned to the others.
16
Social skills are necessity for the success of Jigsaw leaning in class. Social skills include leadership, decision-making, trust building, communication, and conflict management skill and so on.
e. Group processing
Group members discuss how well they are achieving their goals and maintaining effective working relationship, describe what member actions are helpful and what are not, and make decisions about what behaviors to continue and change
Jigsaw Technique makes it possible for students to be introduced to material and yet bear a high level of personal responsibility. It helps develop teamwork and cooperative learning skills within all students and a depth of knowledge not possible if the students learn all of the materials on their own. Since students are supposed to repot their own findings to the home group in jigsaw learning, it quite
misunderstandings.
2.4 Advantages and Disadvantages of Jigsaw Technique
As stated before, jigsaw technique helps the teacher to relate the material to
disadvantages. They will be as follow:
2.4.1 Advantages of Jigsaw Technique
The advantages of jigsaw technique are:
1. It ensures the participant of the students because the students have unique,
material at a deeper level than students typically do when simply ask to produce on an exam.
3. It has a strong effect on attitude to learning and social relationship among students in group because each student has a chance to contribute meaningfully to a discussion, something that is difficult to achieve in group discussion. Each student develops an expertise and has something important to contribute (share information). So cooperation and communication are necessary and students are active participants in the learning process is needed.
4. It enables the students to understand the text because students requires to prepare in their answering specific question in order to insure adequate students preparation, students has a specific task that tasks students to plan how they will teach what they have learn. So, member of the group have to work together in order to establish a common goal. Each member is interdependent on each other. Cooperation and communication are necessary because no one can success completely unless each member contributes
2.4.2 Disadvantages of Jigsaw Technique
The disadvantages of jigsaw technique are:
18
2. It requires some time to make group which is heterogeneity in their ability, because there is one student as a leader, who is responsible for being fair and spreading participation evenly and in order to reduce a problem in their group.
be responsible in their information. Because students works with other individuals from other groups working on the same segment on the report. So that, students that do
possible to the other group and to add the group, they will be mention bad member and this event show that heterogeneity members.
3. It requires long time to arrange the seating, because in reading jigsaw activity, the teacher as facilitator and monitoring class activity and while activity the teacher needs to float from group to group in order to observe the process.
2.5 Concept of Narrative Text
Referring to 2006 (CBS) curriculum, there are some types of text that should be recognize and comprehend by the second year students of SMA/MA: report, narrative, analytical exposition spoof, and hortatory exposition text. In this research, the text that is expects is narrative text.
ning skill
Narrative text is the most famous type of any text. Various purposes are communicated in a narrative type. However the way it is construct is describing certain event, character or phenomena in detail. Narrative in prefer showing to telling and that the power of narrative. Reader will feel as his show by him self what happen in the text. Actually narrative can be fiction such as short story or novel and non- fiction like memoirs. (English Curriculum of SMA, 2006).
According to Madison smart bell, the narrative design, or what we call from or structure, is of first and final importance to any work of fiction. In that structure, we will find elements of story: characterization, point of view, theme and plot. Plot is the way of the story construct.
2.5.1 The Examples of Genres that Fit the Narrative Text Structure:
1. Folktale - a very old traditional story from a particular place that was originally passed on to people in a spoken form, e.g.,The Mighty.
2. Fairy tale - an old story about magic things happened intended for amusing and giving lessons, meanings, and moral values, e.g.,Cinderella.
20
4. Myth - a story from ancient times, especially one that was told to explain about natural events or to describe the early history of place or people, e.g., Tower of Babel.(Source: Dep Pendidikan Nasional, 2006).
2.5.2 Text Organization of Narrative Text:
1. Orientation
It refers to the characters, problem, place and time, such as: who is the character in the text, what is the problem in the text and where does it happen in the text.
2. Complication
It denotes a crisis arises. It comprises initiating event, subsequent event and climax aspects when the characters face the problems.
3. Resolution
It shows that the crisis is resolved. In this part, the character does the act of solving or settling the problem for better or for worse one.
4. Re-orientation
It indicates the optional point. This mean that a story not always uses this, and usually, it states the conclusions of the event based on the writer point of view. (Source: Dep Pendidikan Nasional, 2006).
2.5.3 Language Features of Narrative Text:
1. Focus on the specific and individualized participants. 2. The use of noun phrases
(First, before that, then, finally)
4. The use of adverbial phrases of time and place (In the garden, two days ago)
5. The use of simple past tense (He walked away from the village) 6. The use of action verbs
(Walk, sleep, wake up) 7. The use of saying verbs
(Say, tell, ask)
8. The use of thinking verbs, feeling verbs, verbs of senses
(She felt hungry; she thought she was clever, she smelt something burning). (Source: Dep Pendidikan Nasional, 2006).
Example of narrative text:
Beauty and the Beast
Orientation Once upon a time there was a beautiful girl named Beauty. She lived with her father and her two sisters. She was a hard worker; she always helped her father on the farm. Complication One day, her father set out for the city. He saw an old castle
22
The beast allowed her to go home. Her father was happy to see Beauty.
From the explanation above, the researcher assumes that a narrative text should consist at least of three items of text organization, those are orientation,
complication and resolution. Those there items make narrative text differs from other kind of texts.
2.6 The Procedures of Teaching Reading by Using Jigsaw Technique
In implementing jigsaw technique, the teacher needs to make every learner active. The students are divided into group (each group consist of 5 students). Each student has information to complete the given task. Meanwhile, the role of teacher is a facilitator of the students learning. Certainly, the teacher has many roles to fulfill, since the teacher is a manager of the classroom activities. During the activities, the teacher acts advisor, answering students question and monitoring their performance.
Aronson (1978) Suggests that the procedure of jigsaw in the class is divided into three terms: Pre activity, While activity and Post activity. The students are divided into group (each group consist of 5 students). These activities include in lesson plan and are applied in teaching learning process. Here are the procedures of teaching reading trough jigsaw.
In pre activity it is as an opening act to lead the teacher to the core of teaching and learning. Pre activity facilities students to build up their schemata before coming to the topic of the lesson.
The main purpose of giving pre- attention to
the topic. Stein and Hirasawa (1981: 183) state that if the teacher spend more time in introducing the reading, the result will be better. Intermediate- level students in particular benefit from careful reading preparation because it helps them to be more receptive to the content. There are many ways working into the reading upon the goals of the lesson and the needs of the students. In general, pre- reading activities that will do in the class as follows: brainstorming, showing picture, and asking question about Cinderella.
1 Greeting
2 The students brainstorm the material based on their background knowledge. It
text.
3 The students are informed the material they are going to learn, the goals of learning to achieve and reading technique the students use.
While Activities
24
1. The students listen to the explained of jigsaw technique and the rule how to study in cooperative.
2.The students were devided into six groups, based on their reading score. Each
3.The teacher appointed one student from each home group as the leader.
4.Each student from home group is asked to make expert group, which each expert group consist of one member of home group.
5.The students were provided the reading text. Each group has different text. 6.The students were in the expert groups are asked to read and discuss what is
the main idea, reference, inference, difficult vocabulary, and specific information of their text.
7.The students are asked to return to their home group
8.The students are asked to share, discuss their information since each students has different information
9. The students are given the reading test and they were asked to do the test.
Post Activities
1 Reviewing from what students have learnt.
2 Asking the students about the difficulty in understanding the lesson. 3 Giving the summary of the lesson. (Reflection).
4 Closes the meeting.
2.7 Theoretical Assumption
Referring to the frame of theories, the writer assumes that jigsaw technique can
be use g comprehension. In jigsaw technique
26
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter discusses the methods of research used in this study, that are: setting of the research, general description of the research, research procedures, determining indicator of the research, instruments of the research, and data analysis.
3.1 Setting of the Research
In this reseach, the researcher used classroom action research. This research was done at SMAN1 Krui. It was done based on the problem faced by the teacher in the class. Based on the problem found by the researcher, the researcher examined the cause of the problem and then found the solution for that problem.
The subject was the second year students of SMAN1 Krui class XI social science
department (IPS 4) which consists of 30 stu
-observation in that school she concluded that the students of that school were unable to identify the main ideas, specific information, vocabulary making reference and inference of each paragraph of the text. As the result their reading comprehension scores were low.
would perform in the class based on the lesson plan. So, during the research, the researcher observed everything occurring in the classroom when they were
learning reading comprehension. The data was taken eading
comprehension score.
3.2 General Description of the Research
The research was conducted based on the problem faced by the teacher. In doing the research, the researcher collaborated with the English teacher to improve the comprehension achievement through the implementation of jigsaw technique.
While the teacher was applying jigsaw in the classroom, the researcher observed the teaching learning process and made some necessary points from that process. In that process, the teacher also held reading comprehension test by asking the students to read and answer the question based on the text.
After that, the teacher and the researcher analyzed the result of the observation, and also the reading test. The teacher and the researcher did reflection after knowing the result of the analysis. Based on the analysis and reflection, the researcher and the teacher decide whether the next cycle need to be held or not, and the next cycle focused on eradicating the weaknesses in the previous cycle.
3.3 Research Procedures
28
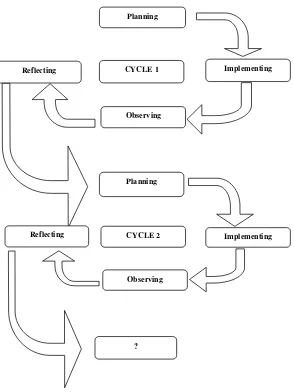
Figure 3.1 The Cycle of Classroom Action Research Adopted from Kemmis and Taggart (In Hopkins, 2004: 69)
3.3.1 Planning
Based on the problem of the research, the researcher prepared the lesson plan and selected the material from the textbook. The material was narrative text, which
was researcher prepared
classroom observation note, the reading test for the students.
Planning
Implementing Reflecting CYCLE 1
Observing
CYCLE 2 Planning
Implementing Reflecting
Observing
3.3.2 Implementing
In this step, the teacher implemented jigsaw technique while she was teaching reading comprehension. The teacher was teaching the material about how to identify the main idea, specific information, vocabulary, making reference and inference from narrative text given. Next, the teacher leads the students practice doing it. The researcher observed the situation in the class and made some necessary notes.
3.3.3 Observing
The researcher observed the activities happened in the classroom in every cycle and write the result of the observation in the observation sheets. The researcher also interpreted the result of the observation. This step started when teaching learning process was occurring.
3.3.4 Reflecting
30
fulfilled in the first cycle, the researcher together with the teacher planned the next step to made betterment in the next cycle. On the other hand, if the indicators were already achieved the researcher and the teacher did not need to hold the next cycle.
The activity began from planning, and came to the action where the researcher and applied what she had planned. During the implementation of the planning, the researcher observed the process of teaching learning. At the end, the researcher analyzed the result of the activity.
3.4 Determining Indicators of the Research
To find out the success of this classroom action research, the researcher determined the indicators, which deal with the learning product and the learning process.
3.4.1Learning Product
The target of the learning product determined by the researcher and the teacher was 65 or more. It was done because 65 is the minimum standard of passingrade
scores could reach 65 or more for the reading test, it meant that the Jigsaw The aspects of reading which measured are identify the main idea, specific information, vocabulary, making reference and inference.
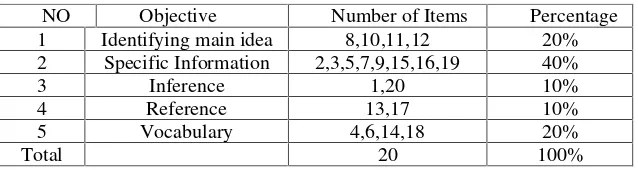
that the researcher wanted to test, then it was valid from that point of view. A table of specification is an instrument that helps the test constructor plans the test.
Figure 3.2 Table of Specification
3.4.2 Learning Process
In learning process, there were two aspects which became the focus of this research was
implementation of jigsaw technique.
The target determined by the researcher concerning vity was 80% of students were active during the process. The researcher decided to set 80% as the target since according to Arikunto (1993:210), if more than 75% of students were actively involved in teaching and learning activities, it can be categorized as
a good l measured through written report of the
collaborator and researcher in observation sheet. To set the target of the success of this CAR, the researcher also did a discussion with the English teacher of that school.
ching and learning process. It was expected that the teacher could got score 75 in her teaching performance after implementing jigsaw technique. So, if the teacher could reach that target, it means
that the s very good. For the teaching
NO Objective Number of Items Percentage 1 Identifying main idea 8,10,11,12 20% 2 Specific Information 2,3,5,7,9,15,16,19 40%
3 Inference 1,20 10%
4 Reference 13,17 10%
5 Vocabulary 4,6,14,18 20%
32
performance, there were some aspects scored that were pre-activity, while-activity, and post-activity.
3.5 Instruments of the Research
To gather the data, the researcher applied two kinds of instruments: the reading test and observation sheet.
3.5.1 Reading Test
Reading test was done as the product of the teaching learning process. The test focused on identifying the main ideas, specific information, vocabulary, making reference and inference of each paragraph of the text. The text used was narrative text in which students are asked to analyze in the text and answer the comprehension questions given. The result of the test considered as the data of the
In scoring the result of stu used percentage correct
(Lyman, 1971:95). The percentage correct score was used in reporting the result of classroom achievement tests. The researcher calculated the score test by using this formula:
X%c= 100
(Lyman, 1971:95) Where:
X%c : percentage of correct score
R : number of right answers T : total number of items on test
Observation was conducted in every cycle during the teaching learning process. When teaching and learning process was occurring, the researcher observed the process happened in the classroom. The researcher used structured observation to
s in the classroom. So there
are two kinds of observation sheet that are filled out by the researcher, that were and observation sheet for the
. activities, the researcher used table
from (Haggard, 1982) and (Ruddel, M.R., & Shearer, B.A. 2002). And for observe
performance, the researcher used
performance, adapted from (Dep. Pendidikan Nasional, 2006). Besides, the researcher also made some necessary notes in the observation sheet concerning
.
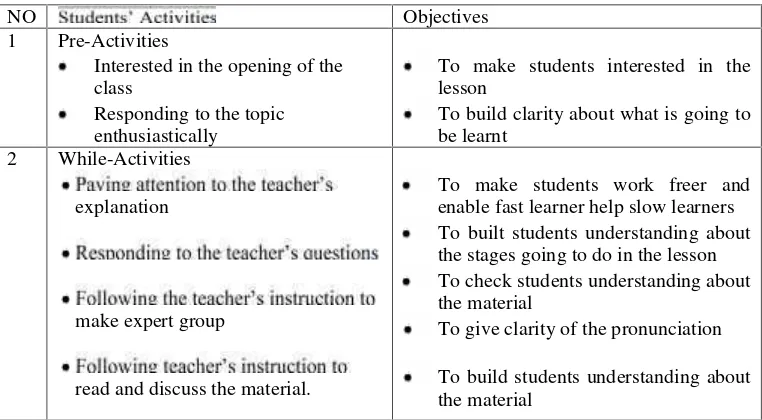
Figure 3.3
NO Objectives
1 Pre-Activities
Interested in the opening of the class
Responding to the topic enthusiastically
To make students interested in the lesson
To build clarity about what is going to be learnt enable fast learner help slow learners To built students understanding about the stages going to do in the lesson To check students understanding about the material
To give clarity of the pronunciation
34
make jigsaw group.
Actively involving to share and discuss and complete their information in group
answer the question by their own word.
make a summary by their own word 3 Post-Activity
question
To built clarity of what have been learnt
Adapted from Haggard (1982) and Ruddel, M.R., & Shearer, B.A. (2002)
Figure 3.4 Observation Sheet
NO Aspects Observe Scores (by giving a tick)
1 2 3 4
1 Pre-activities
- The teacher was prepared and well-organized in class.
The prepared goals/objectives were
apparent.
2 While- activities
A. A. Presentation
- The class material was explained in an understandable way.
- Directions were clear and concise and students were able to carry them out.
-level of comprehension.
- The teacher knew when the students were having trouble understanding.
- The teacher showed an interest in, and enthusiasm for, the subject taught
B. Execution/ Methods
- There were balance and variety in activities during the lesson
- The teacher was able to adapt to unanticipated situations.
- The teacher moved around the class and made eye contact with students.
-- Students responses were effectively elicited (i.e., the order in which the
students were called on)
- Examples and illustration were used effectively.
- Appropriate error correction.
C. personal characteristics
- Patience in eliciting responses
- Clarity, tone, and audibility of voice
- Initiative, resourcefulness, and creative
D. Teacher / Student Interaction
- Teacher encouraged and assured full students participation in class.
- The teacher was able to control and direct the class.
- The students were attentive and involved.
- The teacher was aware of individual and group needs.
36
- improvement
after the teacher explains the lesson.
- Doing a final evaluation which is relevant to the competence.
3 Post-activity
- Doing a reflection/ making summary of the
participation.
- Doing a follow-up by giving direction or tasks as a remedy.
In analyzing the data, the researcher classified the data into two categories that were, the data of the learning product and the learning process. The data analysis was done during and after the data had been collected from every cycle (1st, 2nd
3.6 1 Learning Product
To know the learning product, the researcher used reading test to collect the data. There were some steps which were used to analyze the data got from the test:
A. Giving the Reading Scores to the Students
score. Besides that, the researcher analyzed the result to know the errors mostly made by the students. This was very useful for betterment in the next cycle.
B Calculating the Number and the Percentage of the Students Who Get 65 or More
5, the following formula was used:
65
100%
(Source: Dep. Pendidikan Nasional, 2009)
3.6.2 Learning Process
38
After gathering data from observing the
number of activities done by the students was the step that would be going to be done in this activity.
A
ities, the following formula was used:
%A = A 100%
n Note:
% A A
n: number of students in the class
B Making a Description from the Data that Had Been Analyzed
3.6.2.2 Performance
Meanwhile, in analyzing the data go the researcher did the following steps:
A Counting the Total Score
In this step, the researcher counted the sum of scores from all aspects. The aspects
that were score -activity, while-activity, and
post-activity.
It was similar to analyze
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
In line with the result of the research, the conclusion and the suggestion are formulated as follows:
5.1 Conclusions
In line with the results of the data analysis and discussion about learning product and learning process in the research, it can be concluded that:
1. , Jigsaw can be used to
achievement in learning product. By using Jigsaw technique the students rerely get problem during learning process. The effects are that they understood what they wanted
comprehension achievement increased. If the students felt comfortable learning process, it is high possible
would be increased. It also could be seen from the improvement of the
implementing Jigsaw technique.
2. In teaching learning process, the implementation of Jigsaw technique made the students more interested in learning. The improvement occurred
them to work in group and share their ideas to other friends, they enjoyed the class during the teaching learning process, it can be found from the percentage
.
3. Jigsaw also contributes a positive effect on the
Since in implementing Jigsaw, the teachers were asked to create a strategy that made the students active in learning process. Moreover, the teachers were demanded to create interesting media materials since the interesting media and materials would
5.2 Suggestion
In line with the conclusions above, the suggestions are put forward as follows:
1. English teachers are recommended to use Jigsaw in teaching their students since Jigsaw can be used to
make the students involved in teaching learning process, enables the students to be more active in the classroom activities.
2. the teachers
and suggested to help students.
80
Page 1.1 Background of the Problems... 1
1.2 Identification of the Problems... 4
1.3 Limitation of Problem ... 5
1.4 Formulation of Problems ... 6
1.5 Objective of the Problems... 6
1.6 Uses of the Research ... 7
1.7 Scope of the Research ... 7
1.8 Definition of Terms... 8
2. FRAME OF THEORIES 2.1 Concept of Reading Comprehension ... 9
2.2 Concept of Teaching Reading... 12
2.3 Concept of Jigsaw Technique ... 14
2.4 Advantages and Disadvantages of Jigsaw Technique... 16
2.5 Concept of Narrative ... 19
2.6 Procedure of Teaching Reading by Using Jigsaw Technique ... 22
2.7 Theoretical Assumption ... 25
3. RESEARCH METHODE 3.1 Setting of the Research ... 26
3.2 General Description of the Research... 27
3.3 Research Procedures ... 28
x
3.3.2 Implementing ... 29
3.3.3 Observing ... 29
3.3.4 Reflecting ... 29
3.4 Determining of the Research ... 30
3.4.1 Learning Product ... 30
3.4.2 Learning Process ... 31
3.5 Instrument of the Research ... 32
3.5.1 Reading comprehension Test ... 32
3.5.2 Observation Sheets... 33
3.6 Data Analysis ... 37
4. RESULT OF THE RESEARCH 4.1 Result of the Research ... 40
4.1.1 Cycle 1 ... 40
4.1.2 Cycle 2 ... 56
4.2 Discussion ... 68
5. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS 5.1 Conclusion ... 78
5.2 Suggestion ... 79
LIST OF FIGURES
Page
1. Figure 3.1 Cycle of Classroom Action Research ... 28
2. Figure 3.2 Table of Specification ... 31
3. ... 34
4. Fi ... 35
5. ... 71
6. ... 73
x
Page
1. Table 4.1 Frequency of Students ... 43
2. Table 4.2 Frequency o ... 59
3. ... 69
4.
Cycle 1 to Cycle 2... 70
5. Cycle 1
To Cycle 2 ... 74
Page
1. Appendix 1Lesson plan 1 ... 81
2. Appendix 2 Lesson plan 2 ... 92
3. Appendix 3 Reading 1 ... 103
4. Appendix 4 Reading 2 ... 111
5. -observation 120 6. ycle 1 ... 121
7. Appendix 7 Frequency o Reading Score at Cycle 2 ... 122
8. at Pre-Observation ... 117
9. t Cycle 1 ... 118
10. t Cycle 2 ... 119
11. t Cycle 1 ... 123
12. ctivities at Cycle 2 ... 124
13. Appendix 13 Observation Sheet o at Cycle 1 ... 125
14. Appendix 14 Observation Sheet o at Cycle 2 ... 126
15. Appendix 15 Observation Sheet of 129 16. Appendix 16 Observation Sheet of 130 17. ... 135
THE IMPLEMENTATION OF JIGSAW TECHNIQUE IN TEACHING READING COMPREHENSION AT THE SECOND YEAR STUDENTS
OF SMAN1 KRUI (A Script)
By
EGRA BETARIA
ENGLISH STUDY PROGRAM LANGUAGE AND ART DEPARTEMENT
TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY UNIVERSITY OF LAMPUNG
REFERENCES
Alyousef, H. S. 2005.Teaching Reading Comprehension to ESL/EFL Learners. 5. http.acrobet/rider.co.id. Accessed on Tuesday, December 5, 2011, 03: 30: 32 pm.
Arikunto, S. 1993.Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan DikdatikJakarta: Rineka Cipta.
Aronson, E. 1978.Interdependent Interactions and Propocial Behavior. ELT Journal, 34 (2): 153-160.
Caver, R. P. 1990.Reading rate: A Review of Research and Theory.
htttp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/reading_process.Accessed on Monday, January 15, 2012, 12: 02: 30 pm.
Depdiknas. 2006.Materi Sosialisasi dan Penelitian Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP). Jakarta: Depdiknas.
Depdiknas, Dirjen Pendidikan Dasar dan Menengah. 2005.Menteri Pembelajaran Terintgrasi Bahasa Inggris- Pembelajaran Text Narrative.Jakarta: Depdiknas.
Doyle, B. S. 2004.Main Idea and Topic Sentence.London: Ward Lock educational. Haggard H. R, Ruddel, M. R., and Shearer, B. A. 2002.Toword More Effective
Learning and Teaching of English. Malaysia.: Cetaktama. Harmer, J. 1996.How to Teach English. Cambridge: Longman.
Heilman, W. A, Blair, R. T, and Rupley, H. W. 1981.Principles and Practices of Teaching Reading. Ohio: Charles E Merryl Publishing.
Hopkins, D. 2004.A Teacher's Guide to Classroom Research.Philadelphia: University Press.
Howart, P. 2006.Making Reading Communicative. http://academic.cuesta.edu.Html. Accessedon Monday, December 23, 2011, 10: 05: 25: 30 pm.
Larsen-Diane, Freeman. 1986.Techniques and Principles in Language Teaching. Oxford University: Oxford.
Lyman, B. H. 1971.Test Scores and What They Mean.Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall, Inc.
Ayashree, Pakhare. 2007.Efective Teaching Reading Comprehension. http.effective-teaching-reading-comprehension-strategies.Html. accessed onMonday, December 23, 2011, 11: 05: 25: 30 pm.
Purwantisari. 2004.Improving Reading Achievement Through Jigsaw Task of at SMA Negeri 1 Bandar Lampung. Unpublished Script. Bandar Lampung: Lampung University.
Seliger, Henber and Shohamy, Elena. 1990.Second Language Research Methods. London: Oxford University Press.
Stein, H. and Hirasawa. 1981.Testing English as a Second language. New delhil: Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing.
Suparman, U. 2005.Understanding Reading. Bandung: Arfino Raya.
Universitas Lampung. 2009.Pedoman Penulisan Karya Ilmiah. Bandar Lampung: Unila Press.
Woods, C. 2005.Teaching and Assessing Skills in foreign Languages. London: Cambridge University Press.
Nurmalasari. 2010.The Implementation of the Jigsaw Technique Through Extensive Type Exercises