LEARNING ACHIEVEMENT
(A Correlational Study at the Eighth Grade Students of SMP Ibu Pertiwi)
By:
NURMAW `IZATILLAH
1110014000041
THE DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
THE FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
iv
Involvement and Student’s English Learning Achievement (A Correlational Study at the Eighth Grade Students of SMP Ibu Pertiwi, West Jakarta). Skripsi. Department of English Education, Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers Training, UIN Syarif Hidayatullah (State Islamic University). Jakarta, 2015.
The principal objective of this study is to find the empirical evidence for the relationship that presumably exists between parents’ involvement and student’s English learning achievement. The researcher used a correlational descriptive method employing quantitative approach. The instruments of this study are questionnaire and the students' score in English exercises, assignments and examinations. The questionnaire used was the one adapted from Schute et.al. While the Pearson Product momentformula is used to investigate whether or not parents’ involvement has a significant relationship on their children's English learning achievement. The research findings show that rxy>rtable= 0.986 > 0.80.
v
Involvement and Student’s English Learning Achievement (A
Correlational Study at the Eighth Grade Students of SMP Ibu Pertiwi, Jakarta Barat). Skripsi. Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2015.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menemukan bukti empiris adanya hubungan antara keterlibatan orang tua dengan prestasi pelajaran bahasa Inggris siswa. Penulis menggunakan metode korelasional deskriptif dengan pendekatan kuantitatif. Instrumen yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah angket dan nilai rapor semester genap siswa pada mata pelajaran bahasa Inggris. Angket yang digunakan diadaptasi dari Schute, et.al., dengan menambahkan butir pertanyaan sesuai indikator yang telah ada. Kemudian, Pearson Product Moment Formula digunakan untuk menginvestigasi apakah terdapat hubungan yang signifikan antara keterlibatan orang tua dengan prestasi pelajaran bahasa Inggris siswa. Hasil dari analisis data menunjukan rxy>rtable = 0.986 > 0.80 yakni Ha diterima.
vi
In the name of Allah, the Beneficent, the Merciful. All praises be to Allah,
the Lord of the world who has given His Mercy and Blessing upon the writer in
completing this Skripsi. Peace and salutation always be upon the prophet
Muhammad Shallallahu ‘Alaihi wa Sallam, his family, his relatives, and his
faithful followers.
In this occasion, the writer would like to dedicate this Skripsi to her late
father (Alm. H. Ramli Aminoto) who could not live to see it and gives her
gratitude for all of cares and loves he poured. She feels also obliged to express her
utmost respect and gratitude to her beloved mother (Hj. Sa`adah) for her valuable
support, continuous prayers and moral encouragement in motivating the writer to
finish her study.
The writer also would like to express her greatest appreciation, honour and
gratitude to her advisors, Nasifuddin Djalil, M.Ag., and Maya Defianty, M.Pd.,
for their advice, guidance, corrections, and suggestions in finishing this Skripsi.
She sincerely prays for them –may they always be blessed and be successful in
whatever they are doing.
Her gratitude also goes to:
1. All lecturers of the Department of English Education who have taught and educated the writer during her study at UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
2. Dr. Alek, M.Pd., the Head of the Department of English Education.
3. Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum., the Secretary of the Department of English
Education.
4. Prof. Dr. Ahmad Thib Raya, M.A., the Dean of Faculty of Tarbiyah and
Teachers Training.
5. Her academic advisor, Didin Nuruddin Hidayat, M.A.,TESOL., for his
vii
Quraisy, Hr., and Fairuz Hammurabi, Hr., who teach her to show life that she
has thousand reasons to smile when life gives her hundred reasons to cry.
7. Her brother and sister in laws and also her lovely nephews and nieces who
have been sharing the laugh and bringing happiness to her life.
8. Her loyal best friends, dr. Arganita Kusuma Dewi, Fathimah Azzahra, Lc., and
Hanny Hardianty, S.Pd., who were always helping her during accomplishing
the skripsi.
9. Her beloved best friends, Listianty Ridayu Maksum, Nadya Yani Saniyatul
Amaniy, Ranny Junita A., Sita Pradhita N., Ummu Salamah, Robiatul
Adawiyah, Sari Febrianti, Nur Pratiwi, Siti Afifah and the best classmate,
Aisyah Mulyani, for sharing knowledge, care, motivation, time, support,
laugh and happiness in gaining Bachelor Degree.
10.Her beloved friends in English Education Department Academic Year 2010,
especially, EED class A, for giving their cares and supports all this time.
11.Any other person who cannot be mentioned one by one for their contribution
to the writer during finishing her Skripsi. The words are not enough to say any
appreciations for their help.
May Allah bless them for all of what they have done.
Finally, the writer feels that it is really a pleasure for her to receive critics
and suggestions to make this Skripsi better. She also hopes that this Skripsi would
be beneficial, particularly for her and for those who are interested in it.
Jakarta, March 2015
viii
ENDORSEMENT SHEET ... i
APPROVEMENT SHEET ... ii
SURAT PERNYATAAN KARYA SENDIRI ... iii
ABSTRACT ... iv
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vi
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... viii
LIST OF TABLES ... x
LIST OF FIGURES ... xi
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. The Background of the Study ... 1
B. The Identification of the Problem ... 4
C. The Limitation of the Problem ... 4
D. The Formulation of the Study ... 4
E. The Objectives of the Study ... 5
F. The Significance of the Study ... 5
CHAPTER II: THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Literature Review ... 6
1. Student’s English learning Achievement ... 6
a. Definition of Learning ... 6
b. Definition of Student’s Learning Achievement ... 7
c. Student’s English Learning Achievement in Indonesia ... 9
d. Factors Affecting Student’s Achievement ... 10
2. Parents’ Role in Student’s Academic Lives ... 13
a. Parents’ involvement Based at Home and School ... 13
b. Parents’ involvement in Student’s English Learning Process ... 16
B. Conceptual Framework ... 20
C. The Previous Related Study ... 21
ix
C. Research Population and Sample ... 25
D. Research Instrument ... 25
E. The Data Analysis Technique ... 28
F. Statistical Hypotheses ... 30
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS A. Findings ... 32
1. The Description of the Data ... 32
a. The Data of Parents’ Involvement and Student’s English Learning Achievement ... 32
b. The Relationship between Parents’ Involvement and Student’s English Learning Achievement ... 33
2. Analysis of the Data ... 34
a. The Frequency of the Data ... 35
b. The Histogram ... 36
c. The Normality test ... 38
d. The Correlational Result ... 40
3. The Interpretation of the Data ... 41
B. Discussion ... 42
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion ... 45
B. Suggestion ... 45
REFERENCES ... 47
x
Table 3.1 Indicators of Parents’ Involvement ... 26
Table 3.2 The Questionnaire Scoring ... 26
Table 3.3 Valid Items of Parents’ Involvement ... 27
Table 3.4 The Reliability of Questionnaire ... 28
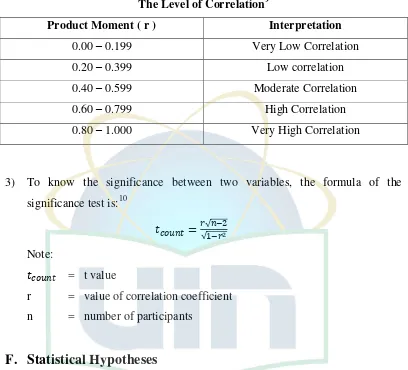
Table 3.5 The Level of Correlation ... 30
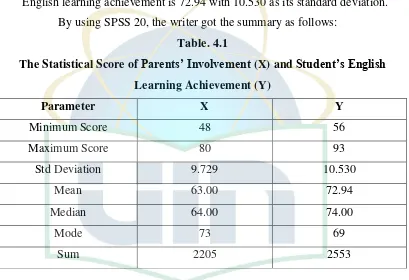
Table 4.1 The Summary Score of Parents’ Involvement (X) and Students English Learning Achievement (Y) ... 33
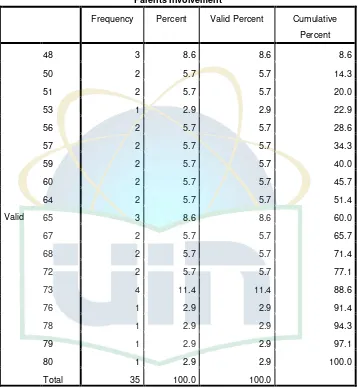
Table 4.2 The Frequency of Parents’ Involvement ... 35
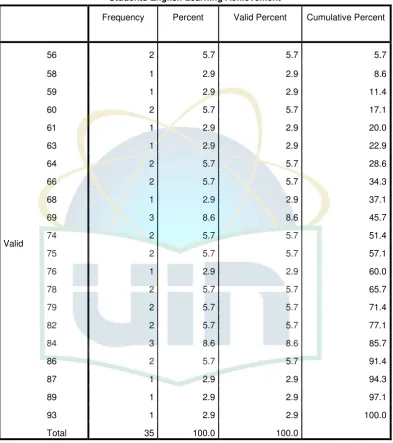
Table 4.3 The Frequency of Student’s English Learning Achievement ... 36
Table 4.4 The Normality Data of Variable X and Y... 38
Table 4.5 The Result of Correlation Calculation ... 40
xi
Figure 4.1 Parents’ Involvement ... 37
Figure 4.2 Student’s English Learning Achievement ... 37
Figure 4.3 The Normal Q-Q Plot of Parents’ Involvement ... 39
Figure 4.4 The Normal Q-Q Plot of Student’s English
xii
Appendix 2 The Questionnaire of the Correlation between Parents’ Involvement
and Student’s English Learning Achievement
Appendix 3 The Distribution of Questionnaire Score and The Student’s English Lesson Score
Appendix 4 The Recapitulation of the Questionnaire
Appendix 5 The Correlation Score
Appendix 6 Open Ended Question
Appendix 7 The Recapitulation of Open Ended Question
Appendix 8 The Result of Open Ended Question
Appendix 9 Triangulasi data Kuesioner dan Open Ended Question
Appendix 10 Surat Permohonan Izin Penelitian
Appendix 11 Daftar Nama dan Biodata siswa SMP Ibu Pertiwi Tahun Pelajaran 2014-2015
Appendix 12 Surat Keterangan dari Sekolah yang bersangkutan
Appendix 13 Surat Pengesahan Proposal Skripsi
Appendix 14 Surat Bimbingan Skripsi
1
A.
Background of Study
English is considered to be important to learn because it is one of
international languages used to communicate and develop relationship with the
countries in the world wide and the competence in it is important in career
development. Thus, students need to understand and use English to improve their
confidence to face global competition.
In Indonesia, English language is one of the compulsory subjects that are
tested in the National Final Exam- Ujian Nasional (UN). The government makes
English as the first foreign language to be taught in Indonesian schools as stated in
the 1994 GBPP that English is the first language which is considered important to
gain and develop science, technology and to make relationship with other
countries.1 It is learned by the students from junior high school, senior high school up to university level. Therefore, Indonesian students are expected to master
English as stated in the curriculum which its aim is mastering communication
skills in English covering listening, speaking, reading and writing because this is
what students need to face globalization and information era in the 21st Century.2 Furthermore, in the Indonesian curriculum, the aim of the curriculum is
drawn into the objective of study that students should reach. The objective of study is specifically drawn from Based Competence-Kompetensi dasar (KD)
which is developed from Standard of Competence-Standard Kompetensi (SK). In
English subject SK and KD cover the attainment of four skills; listening,
speaking, reading and writing as written on School-based Curriculum-Kurikulum
Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP).
Unfortunately, the English subject’s objective of study has not completely achieved yet because there are many schools in Indonesia that still could not fulfill
1
Departement Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, Kurikulum: GBPP Mata Pelajaran Bahasa Inggris. (Jakarta: Depdikbud, 1993), p. 1.
2
the standard achievement of the current curriculum. One of the schools which
have not reached the objective of English subject is SMP Ibu Pertiwi Jakarta Barat
where the writer did a pre-research in. Based on the data of the result of student’s
English score given by the teacher, there are many of the first, second and third
grade students who got low score and could not reach the school’s minimum standard criteria of English subject (65) at the school. Moreover, the result of the
interview with the English teacher also showed that there are many students who
cannot reach the Minimum Standard Criteria-Kriteria Ketuntasan Minimal
(KKM) in the middle and final exam of the school. The teacher said that there
were several possible factors which could cause the problem and affect the
students’ achievement, for instance, learners’ motivation, learners’ intelligence,
learner’s family condition and school facility.
In addition to the facts that the writer found at the school, the writer
assumed that there are many factors may affect the students’ learning
achievement. Intelligence is not the only determinant of academic achievement.
According to Muhibbinsyah, the other factors such as internal factors (physiology
and psychology aspect), external factors (social factors and non-social factors) and
approach to learning can influence achievement.3 It is in line with the English
teacher statement about the factors which may influence students’ achievement.
Further, M. Ngalim Purwanto also states that there are some social factors
which influence the students’ learning and achievement.4 Those social factors are family condition, teacher and teaching method, equipment which used in teaching
learning process, learning environment, and social motivation.
As one of factors which influence students’ achievement, parents have an
important role in affecting students’ learning achievement. It is supported by
Pena’s findings and statements about parents. Parents who involve in student’s academic lives have many positive benefits for students, the most important of
which is enhanced student’s achievement. In her long year studies, Pena did a case
3
Muhibbin Syah, Psikologi Pendidikan dengan Pendekatan Baru, (Bandung: PT Remaja Rosdakarya, 2010), p. 129.
4
study about the influence of parents’ involvement in a large urban city in
America. The findings show that parents could actually give their best
involvement to school activities and potentially give benefits to influence
student’s achievement. Further, the studies draw that the involvement of parents
could be in a variety of roles and areas and mostly become partners in education
of their children.5
Other supported data which shows the importance of parents who involve
in education and influence student’s learning achievement are stated in
Pomerantz’ journal article. Firstly, how parents react toward the students is critical to the success of their involvement in their academic lives and it gives more
benefit to some students. Secondly, parents’ involvement also gives benefits not
only for children’s achievement but also for their psychological functioning more
broadly.6
However, in Indonesia, parents have misinterpretation about responsibility
of educating. Parents’ responsibility to educate their children is mostly taken by formal and non-formal educational institution or it may be taken all. These make
parents’ control weaken and schools lessen parents’ authority on their children. Most of parents thought their responsibility has been given to the school. They do
not realize that education takes place at home, in school and in a community. In
line with this, Rosita states that parent is critically needed to know that education
takes place not only in school but also at home.7
Therefore, the focus of the study is on parents’ involvement based at
school and based at home because student’s achievement is not only from
teaching learning process in the school but it is also determined by the role and the
influence of parents in giving motivation and guidance to their children from the
early childhood to throughout school years at home. Finally, based on the
5
Delores C. Pena, Parent Involvement: Influencing Factors and Implications, The Journal of Educational Research, Vol. 94, No. 1, 2000, p. 42.
6
Eva M. Pomerantz, et. al., The How, Whom and Why Parents’ Involvement in
Children’s Academic Lives: More Is Not Always Better, American Educational Research Assosiation, Vol. 77, No. 3, 2007, p. 376.
7
background drawn, the researcher initiates to do the research about the
relationship between parents’ involvement and the students’ English learning
achievement in SMP Ibu Pertiwi.
B.
Identification of the Problems
Based on identification of the background drawn, the problems are
identified as follow:
1. Students still have a low score and could not reach the school’s minimum
standard criteria of English subject (65) at SMP Ibu Pertiwi;
2. Students who got a low score possibly get influenced by the factors which
come beyond the students like parents;
3. Parents still have misinterpretation about responsibility of educating;
4. Parents still have limit understanding of getting involve in children’s academic
lives;
5. Parents still do not realize that they have a big role in influencing student’s
learning achievement in school.
C.
Limitation of the Problem
As identifying the problems, one problem that is interested to be
investigated is that the relationship between parents’ involvement and students’
learning achievement in English lesson at Eighth Grade students of SMP Ibu
Pertiwi, Jakarta Barat.
D.
Formulation of the Study
After conducting the limitation of the problems, the research problem is
formulated into “Is there any significant relationship between parents’
E.
Objective of the Study
The objectives of this research is to find out empirical evidence of whether
or not there is any significant correlation between parents’ involvement and
student’s English learning achievement at 8th grade students of SMP Ibu Pertiwi Jakarta Barat.
F.
Significance of the Study
The result of this research is expected to be an input for teachers, parents
and students. By knowing and understanding the possibility of parents’
involvement which can influence students’ learning achievement, teachers are
able to inform parents about students condition in the school and parents could
give a proper feedback by giving more cares and supports toward their children’s
academic lives. The writer also hopes this research will be useful for them who
are interested in parents’ involvement as they can do deeper and better than this
6
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A.
Literature Review
This literature review presents the two topics. The first topic discussed
about student’s English learning achievement comprising the definition of learning, students’ learning achievement, student’s English learning achievement in Indonesia and factors affecting student’s learning achievement. The second
topic is considered about Parents’ role in students’ academic lives including parents involvement in education both home and school, and parents’ involvement in student’s English learning process.
1. Student’s English Learning Achievement a. Definition of Learning
Generally, learning is process which happens in a period of time and
through many steps of activities. And as an impact, it will make someone change
on certain aspect in his own self.
The lines are similar with Whittaker statement who defines learning as a
process by which behavior originates or is altered through training or experience.1 Further, Spears said that learning is to observe, to read, to imitate, to try
something themselves, to listen, and to follow direction.2
Further, Winkel defines learning as a relatively permanent change in
behavior that occurs through experience while the pupil grows.3 The similar line is stated by Bower and Hilgard that “learning refers to the change in a subject’s behavior or behavior potential to a given situation brought about by the subjects
repeated experience...”4
1
M. Alisuf Sabri, Psikologi Pendidikan, (Jakarta: Pedoman Ilmu Jaya, 1996), p. 55.
2
Ibid., p. 54.
3
W. S. Winkel, Psikologi Pengajaran, (Yogyakarta: Media Abadi, 2009), p. 18.
4
Both definitions define that an alteration of learning is relatively stable.
Through experience, students will learn that they need to study in order to do well
on a test. A student who has ability will have successful experience and better
change in behavior. In contrast, a student who has less ability may have
unsuccessful experience and bad change of behavior.
In summing up, learning is process where the students’ alteration in
behavior is depended on the ability of students’ experience and practices.
b. Definition of Student’s Learning Achievement
Generally, achievement refers to something that somebody got after
accomplished it up to particular point of time. Besides, achievement in learning
refers to the knowledge that students have learned up and usually is drawn by
numeral or letter as a realization of achievement.
Similarly, Hornby states that achievement is a thing done successfully,
especially with an effort and skill.5 Further, Gronlund defined achievement as “it
is what a pupil has learned”6
and it is added with Nunnally statement that
“achievement is how much students’ have learned up to particular point of time”.7 Additionally, Sukmadinata gives a specific meaning about students’ achievement. He said that achievement of students can be seen from mastering the
subject that they have taken up. He also said that the achievement of students in
their school is signed by numeral (0-10) or letter (A, B, C, D).8 On the other words, achievement can be drawn both by a numeral or letter as a realization of
students’ achievement.
Moreover, achievement means all things the people obtain from his/her
effort. But in education, achievement means the result of test design to determine
5
A. S. Hornby, Oxford Advanced Learner Dictionary, (Oxford: Oxford Universisty Press, 1995), p. 10.
6
Norman E. Gronlund, Mesurement and Evaluation in Teaching, (New York: Macmillan Publishing Co., Inc., 1976), p. 331.
7
Jum C. Nunnally, Educational Measurement and Evaluation, (New York: Mc-Graw Hill Book Company, 1964), p. 345.
8
a student’s mastery of a given academic area.9
Achievement is what a person has
already learned. It means achievement is the child’s past learning that is his accumulated knowledge in a particular field.10 Further, the other definition of learning achievement is the extent to which a person has achieved something
acquired certain information or mastered certain skills, usually as a result of
specific instruction.11
Related to achievement, Jihad and Haris have quoted the definition of the
achievement from experts’ opinion, and then they conclude that learning
achievement is “pencapaian bentuk perubahan perilaku yang cenderung menetap dari ranah kognitif, afektif, dan psikomoris dari proses belajar yang dilakukan
dalam waktu tertentu yang sesuai dengan tujuan pengajaran.”12 In addition to definition of learning achievement, some experts express their idea, as follows:
1) Romizowski says that learning achievement is outputs from an input process
systems, and
2) Sudjana states that learning achievement is one’s ability that he has after he got learning experience.
Furthermore, Sadker and Sadker express learning achievement as students’ actions that they have discipline minds and adhere to traditional moral and
behavior. They demonstrate their competency in academic subjects or traditional
skills through tests and writing.13 In conclusion, learning achievement is the result of students past learning after instructional process in harmony with the
instructional objective in particular period of time.
9
Julian C. Stanley, Measurement in Today’s School, (New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 1964), p.2
10
Louis J. Karmel, Testing in Our Schools, (New York: The Macmillan Company, 1966), p. 38.
11
M. Chabib Thoha, Teknik Evaluasi Pendidikan, (Jakarta: Raja Grafindo Persada, 1996), p. 44.
12
Asep Jihad and Abdul Haris, Evaluasi Pembelajaran, (Yogykarta: Multi Pressindo, 2008), p. 14-15.
13
c. Student’s English Learning Achievement in Indonesia
English achievement is learner’s ability to use the target language.14 Similarly, Thornburry stated that English achievement is what learner has learned
about target language – English, over a week, months, term or entire course. Moreover, English achievement is how much a foreign language that students
know.15 Students have to struggle through a course or learning experience of some sort to achieve a certain amount of control of the language.
Beside those definitions, Huebener said that English achievement is the
skills and the knowledge the pupils have acquired in each of the various phases of
the language learning.16 Concluding some definitions about the English achievement, it is the students’ ability, skill, knowledge in English which they have acquired in particular time. In education, achievement is sign by scores,
which may be taken from average of daily scores and final test where the test is
used to measure the achievement and it is usually called achievement test.
In indonesia, students’ achievement has been describe at the rules of the minister of National Education-Peraturan Menteri Pendidikan
Nasional-(Permendiknas) No. 22, 2007, about Education Assessment Standard- Standar
Penilaian Pendidikan. It is explained at section 1 point 1: “Assessment of learning outcomes of students in primary and secondary education implemented based on
the educational assessment standard that is applied nationally.”
To fulfill Education Assessment Standard, the students should reach the
objectives of study from Based Competence-Kompetensi Dasar (KD) which is
developed from Standard of Competence-Standar Kompetensi (SK). In English
subject, SK and KD cover the attainment of four skills; listening, speaking,
reading and writing as written on School-based Curriculum-Kurikulum Tingkat
Satuan Pendidikan (KTSP). As the aims of English subject in Indonesia, student
at secondary level are expected to have capabilities as described below:
14
Geof Brindley, Language Testing in the 1990s: The Communicative Legacy, ed. J. Charles Alderson and Brian North, (Hertfordshire: Macmillan, 1995), p. 154.
15
Robert Lado, Language Testing: The Construction and Use of Foreign Language Tests, 9th Ed., (London: Longman, 1977) p. 369.
16
1) To develop oral and written communicative competence to attain literacy
functional level;
2) To have awareness of the nature and the importance of English to improve the
nation’s competitiveness in the global community;
3) To develop students’ understanding of the interrelationship between nations and cultures.
Student „achievement reflects the attainment of KD. It can be measured by
achievement test. Achievement test is “any test of acquired ability or skill, a typical example being a test of scholastic attainment.” It measure what a pupil has learned. Achievement testing plays major important role in the school program
because it will show what the students have achieved at the past. The primary goal
of achievement test is to find out the student’ past learning. Hence, it reflects past progress of the student.
The result of the achievement test should pass the Criteria of Minimum
Learning Mastery-Kriteria Ketuntasan Minimum (KKM). It is used by the
education unit as the standard of Graduated Competence-Standard Kompetensi
Lulusan (SKL). Based on KTSP, every education unit or school has to determine
their own KKM. In SMP Ibu Pertiwi, for instance, the score of KKM is 65 (sixty
five). If the score of the students are under 65, they can take remedial test.
Moreover, the students’ achievement can be seen from the result of the achievement test administrated by the teacher during the learning process. The
result is usually written in the student’s report card. The score in the student’s
report card is the calculation of daily, middle and final test. Therefore, to know
English achievement of the students at eighth grade SMP Ibu Pertiwi, the writer
used the score of English subject that is in student’s report card.
d. Factors Affecting Student’s Achievement
There are a lot of factors that influence the achievement of student. Some
1) Internal factors in which includes physiology aspect and psychology aspect.
a) Physiology aspect
Students’ physical condition is considered as one of factors that
influence achievement. MuhibbinSyah states that “Kondisi jasmani siswa
meliputi kebugaran fisiknya akan sangat memengaruhi kualitas ranah cipta
(kognitif) sedangkan kondisi organ khusus seperti panca indera yang kurang
baik dapat menimbulkan masalah dalam proses penyerapan informasi.”17 Therefore, the one who learn need to be in healthy condition or if they are not,
teacher or parents should have more consideration and attention to the students
or children.
b) Psychology aspect
In psychology aspect, intelligence degree is dominantly affecting
students’ achievement. “Intelligence is regarded as a potential capacity. This potential capacity is probably a function of heredity, congenital development
and growth. The growth of intelligence toward the potential capacity may be
impeded by environmental stresses and strains or maybe accelerated by proper
stimulation.”18
It is important to keep in mind that intelligence is complex and that
individual have many kinds of abilities and strengths, not all of which are
measured by traditional IQ tests. Many students whose academic performance
has been weak have experienced considerable success in second or foreign
language learning.19
Another important variable in learning is motivation. “Motivation
involves the learners’ reasons for attempting to acquire the second language
but precisely what creates motivation is the crux of the matter.”20 And the last
17
Muhibbin Syah, Psikologi Pendidikan dengan Pendekatan Baru, Edisi Revisi, (Bandung: PT. Remaja Rosdakarya, 2010), p. 130.
18
James, M. Sawrey, and Charles W. Tellford, Educational Psychology, 4th Ed., (Boston: Allyn and Bacon, 1973), p. 424.
19
Christopher N. Candlin and Neil Mercer, English Language Teaching in Its Social Context, (London: Routledege, 2001), p. 31.
20
variable in affecting achievement which is considered as psychology aspect is
attitude, aptitude and interest.
2) External factor in which includes social and non-social environment.
Environment is one of the important components of instructional process
because it can influence the students. Social environment consist of parents
(family), teachers, and society (community).
Family is primary community for the children because it is primary
educational environment. Children got their first education and counseling as they
spend the entire of their time growing in the family. Additionally, parents and
siblings can focus attention on one child and so opportunity for interested,
motivated natural help is available covering considerable amounts of time. In
conclusion, bad environment may cause stress for students and may influence
students to have worst achievement.
3) Approach to learning including high, middle, and low approach learning.
Beside internal and external factors, approach to learning also influence
the learning process and students’ achievement. For example, students who apply
deep learning approach may have better achievement than students who only
apply surface or reproductive learning approach while they are studying.
Clearly, MuhibbinSyah shows a table of factors that influence students’ achievement.
Table 2.1
Factors that influence students’ achievement21
Ragam Faktor dan Elemennya
Internal Siswa Eksternal Siswa Pendekatan Belajar Siswa
1. Aspek Fisiologis:
a. Tonus jasmani
b. Pancaindera
2. Aspek Psikologis
1. Lingkungan Sosial:
a. Keluarga
b. Guru dan staf
c. Masyarakat
1. Pendekatan Tinggi
a. Speculative
b. Achieving
2. Pendekatan Sedang
21
a. Inteligensi
b. Motivasi
c. Minat
d. Sikap
e. Bakat
d. Teman
2. Lingkungan Non-sosial
a. Rumah
b. Sekolah
c. Peralatan
d. Alam
a. Analytical
b. Deep
3. Pendekatan Rendah
a. Reproductive
b. Surface
However, in this research, the researcher focused on parents as one of factors that
is affecting students’ achievement.
2. Parents Role in Students’ Academic Lives
The child is born into family – his first socializing group and the most basic agency of socialization in all societies. The family is not only the first group
to which he is exposed, but also is in many ways the most influential.22 It is in line with Robertson who states that one reason for importance of the family is that it
has the main responsibility for socializing children in the crucial early years of
life. The family is where children establish their first close emotional ties, learn or
acquire language, and begin to internalize cultural norms and values.23
As the unit of society, the home sets the pattern for social development
and adjustment to form the attitudes and behavior habits. A child’s physical,
mental, and emotional potentialities reflect the physical, mental, and emotional
characteristic of his parent. They are formed by the interaction between the child
and the parent.24
a. Parents’ Involvement Based at Home and School
The term parents’ involvement is used broadly in this writing. It includes several different forms of participation in education. Parents get
involved in their children’s education because one of their functions is giving education for their children.
22
Cole S. Brembeck, Social Foundations of Education: A Cross-cultural Approach, (New York: John Willey and Sons, Inc., 1967), p. 121
23
Ian Robertson, Sociology, (New York: Worth Publisher, Inc., 1978), p. 108.
24
The children’s education is primarily a concern of the family, not the society as stated on the law of Republic Indonesia, law 23 of the year 2002,
article 26 about Child Protection. Parents obligate and assume responsibility
for:
1) Nurturing, taking care, giving education and protecting the child;
2) Developing their child’s ability, talent and interest.
Parents’ involvement can be defined as a process that the parents use
all their ability to develop their children potency.25 Parents obligate as positive habit former for strong foundation in informal education. By the habits parents
show, the children will adapt and adopt their parents.26 This way, parents have
important roles in developing their children’s potency.
Drawing on several diverse lines of theory and research, Grolnick and
Slowiaczek cited on Pomerantz, et.al. journal article defined parents'
involvement in children's schooling as parents' commitment of resources to
the academic arena of children's lives. They make the broad distinction
between involvement based at school and that based at home. The distinction
is used because it is a closer one that may be used with ease by researchers,
policy makers, educators, and parents. Moreover, the distinction between
involvement on the school front and that on the home front is of import
because the two may embody distinct ways that parents become involved in
children's schooling, with distinct effects on children.27
School-based involvement represents practices on the part of parents
that require their making actual contact with schools. Practices in this vein
include, but are not limited to, being present at general school meetings,
talking with teachers (e.g., attending parent-teacher conferences, initiating
contact with teachers), attending school events (e.g., open houses, science
fairs), and volunteering at school. Parents commonly become involved on the
25
Soemiarti Patmonodewo, Pendidikan Anak Prasekolah, (Jakarta: Rineka Cipta, 2008), p. 124.
26
Abu Hamadi, op. cit., p.92.
27
school front through their presence at general school meetings and
parent-teacher conferences.
Parents' school-based involvement may also include involvement at a
higher level, such as being a member of the school board and attending school
board meetings. Epstein, on the journal article by Pomerantz, et.al., labeled
this involvement in governance and advocacy, distinguishing it from
school-based involvement at a lower level. The direct impact on children may be
quite small, given the limited interactions parents and children may have in its
context.
Home-based involvement represents parents' practices related to
school that take place outside of school, usually, though not always, in the
home. Such practices can be directly related to school, including assisting
children with school-related tasks, such as homework (e.g., creating a quiet
place for children to study, helping children in completing homework) and
course selection, responding to children's academic endeavors (e.g., choices
about the topic of a school project, performance on a test), and talking with
children about academic issues (e.g., what happened in school, the value of
doing well in school). Also characteristic of parents' home-based involvement
is engaging children in intellectual activities (e.g., reading books with
children, taking them to museums) that may not be directly related to school.
Parents' involvement on the home front may sometimes be tied to
parents' involvement on the school front. For example, parents may use
knowledge gained at parent-teacher conferences in assisting children with
homework.
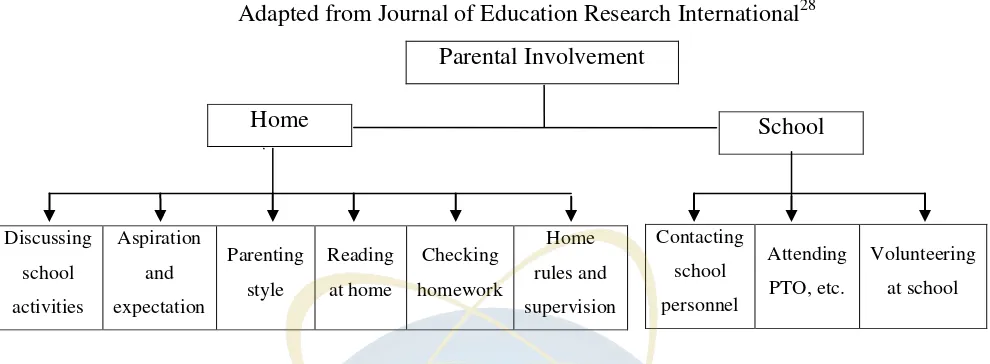
In conclusion, to make a clear explanation, the researcher used the
Figure 2.1 Parents Involvement
Adapted from Journal of Education Research International28 Parental Involvement
b. Parents’ Involvement in Student’s English Learning Process
Children acquire a large percentage of their language from their
parents. The home environment is the dominate factor in shaping early
language development for most children then for fulfilling this role, the home
provides a natural setting.29 The type of language a child is exposed to in the
home domain is a critical factor in determining that child’s proficiency in the language. According to Milner’s opinion which has been quoted by Gary N. Chamber, there is a model of attitudinal influence to which three processes
contribute:30
1) Direct tuition from parents,
2) Indirect tuition, for instance, the attitudes of the parents are implicit in
their behavior,
3) Role-learning, for instance, the behavior of the children reflects the
behavior of those around them.
28
Valerie J. Schute, et. al., A Review of a Relationship between Parental Involvement and Secondary School Students’ Academic Achievement, Journal of Education Research International, 2011, p. 3.
29
Rolland J. Van Hattum, Developmental Language Programming for the Retarded, (Boston: Allyn and Bacon, 1979), p.51.
30
Gary N. Chambers, Motivating Language Learners, (Clevedon: Multilingual Matters, 1999), p. 82.
Home School
Discussing
school
activities
Aspiration
and
expectation
Parenting
style
Reading
at home
Checking
homework
Home
rules and
supervision
Contacting
school
personnel
Attending
PTO, etc.
Volunteering
Moreover, Milner stated that within the context of foreign language
learning, the success of these three processes may depend largely on: (1)
positive attitudes of parents to learning in general and language learning in
particular; (2) the level of parent’s foreign language competence; and (3) their willingness to demonstrate this competence not only when helping with
homework but also when in the company of native speakers of the target
language.31
The influence of a parent’s view is possibly on the attitude which the pupil brings to the foreign language lesson. Astuti divided parents’ role on teaching and learning English as foreign language into32:
1) As motivator
The family is the primary and most important social source of motivation
in the student. They largely reflected the attitudes and beliefs of their parents.
It is within the family that the basic foundation of the social motivational
system is laid down.33
Parental attitude toward foreign language learning and indeed learning in
general may be influenced by educational, socio-economic, socio-cultural,
ethnic and linguistic background. Learners with the most positive motivation
toward learning foreign language tend to be integrative-oriented and to come
from homes where parents have a basic integrative orientation in combination
with pro-English attitudes.34
It is important to encourage the children. There is much that parents can
do. They can actively demonstrate the value for learning. Parents also can
congratulate the children for their success. Then, while they do not perform
well in academic, parents should support them. This will help them to see
how important to keep trying. This covers some involvement at home such as
(a) aspiration and expectation and (b) parenting style.
31
Ibid., p. 83.
32
Sri Astuti, Language Proficiency Starts at Home, Jakarta Post, January 27, 2008, p. 29, col. 1.
33
Sawrey, op. cit., p. 493.
34
2) As advocate in economy
One factor can influence instructional process is economy. Parent’s
economy condition will affect the education and every economy status has
different ways to educate the children.
To some, socioeconomic level is the major familial influence after
heredity on intellectual functioning.35 Children coming from homes of higher socioeconomic status are not only have come from more brilliant parents
initially but also have been provided better opportunities for development
intellectually, physically, and emotionally. Not only favorable heredity but
also a stimulating environment continues to favor intellectual growth.36 The higher socioeconomic family will easier to support the educational
facilities at home. The facilities provided can help students to develop their
English achievement.
3) As monitor
Parents can monitor their child’s academic achievement by giving attention on their student’s learning. They also should monitor homework given by teacher, out-of-school activities for example setting limits on
television watching, and arranging for after school activities.
Gary N. Chambers stated that if pupils equate parental encouragement
with the willingness and ability of their parent to offer and provide them with
help to do their homework, it may be interesting to ascertain how many pupils
perceive their parents as being in a position to provide assistance with
foreign language homework.37 If the parents monitor and give assistance to their children, the children will have more awareness to get better in English
achievement.
35
Lita Linzer Schwartz, Educational Psychology: Focus on the Learner, (Boston: Holbrook Press, 1972 ), p. 107.
36
Sawrey, op. cit., p. 621-622.
37
4) As model
As the home is the first classroom, the family members are the first
teachers. The mother is the most important figure in this process but all
family members contribute. If family members can understand that the child
is receiving stimuli from his environment even though reaction may not be
noted to signal this, they will be a more effective teacher.38 Some insight may be gleaned nevertheless from pupils’ thought on the encouragement they think their parents give.39
In foreign language learning, input is an essential component for
learning. It provides the crucial evidence from which learners can form
linguistic hypotheses.40
After getting input by hearing the surrounding, the children try to
interact with the other people. Interaction facilities the process of acquiring a
second language and foreign language as it provides learners with
opportunities to receive modified input and to receive feedback, both
explicitly and implicitly, which in turn may draw learners’ attention to
problematic aspects of their inter language and push them to produce
modified output.41 Interaction is important because it is in this context that learners receive information about the correctness and, more important, about
the incorrectness of their utterances.
In theory, pupils who hear their parent and friends at home interesting in
a foreign language with guests at home may have more appreciation of the
usefulness of the target language than those who do not have this opportunity.
The hypothesis of the research which has been done by Gary N. Chambers is
pupils who hear the target language spoken at home and who claim to know
38
Van Hattum, op. cit., p. 55.
39
Chambers, op. cit., p. 84.
40
Susan M. Gass and Alison Mackey, Theories in Second Language Acquisition, ed. Bill VanPatten and Jessica Williams, (New Jersey: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 2007 ), p. 177.
41
people, who speak the target language as their mother- tongue, may be more
aware of the usefulness of the target language.42
B.
Conceptual Framework
English which has been stated as a foreign language in Indonesia becomes
one of important subject that is needed to be learned because it is examined in the
National Final Examination in Indonesia. Students, parents, teachers and school
are trying to improve and achieve good goals for examination. Thus, students’ English learning achievement also seems to be concerned.
Students’ learning achievement can be influenced by many factors either internal factors including physiology and psychology or external factors including
social and nonsocial factor. All of the factors are allied to affect the students’
achievement and support each other.
Parents become one of the factors that influence students’ learning
achievement because children’s education starts from home. That way, parents have a big role in making their children reach a good learning achievement
especially in English lesson. Parents commonly involve in many aspect of their
children’s’ life especially education. Parents’ involvement, in this research is divided into two ways of involvement; they are home-based and school-based.
Students whose parents get involved in their education hopefully will have
encouragement to learn English. On the other words, it may be helpful if their
home environment and their parents’ involvement in their education are good. In conclusion, the students whose parents involve in their education may
get a better score in English subject. And there will be a positive correlation
between parents’ involvement and students’ English learning achievement.
42
C.
The Previous Related Study
The research about parents’ involvement and students’ academic achievement was done by Schute, et. al., Topor, et. al., Pomerantz, et. al., and
Fitriah AB.
Firstly, the paper discussed by Schute, et. al. on the title “A Review of a Relationship between Parental Involvement and Secondary School Students’
Academic Achievement”. This paper reviews the research literature on the
relationship between parental involvement (PI) and academic achievement, with
special focus on the secondary school (middle and high school) level. The results
firstly present how individual PI variables correlate with academic achievement
and then move to more complex analyses of multiple variables on the general
construct described in the literature. Several PI variables with correlations to
academic achievement show promise: (a) communication between children and
parents about school activities and plans, (b) parents holding high
expectations/aspirations for their children’s schooling, and (c) parents employing an authoritative parenting style. We end the results section by discussing the
findings in light of the limitations of non-experimental research and the different
effects of children’s versus parents’ perspectives on academic achievement.43 Secondly, the research that had done by Pomerantz, Moorman and
Litwack with the title “The How, Whom and Why Parents’ Involvement in
Children’s Academic Lives: More Is Not Always Better”. The researchers aim to
show that the factors beyond the extent of parents' involvement may be of import.
In this article, the case study is made to know about the consideration of the how,
whom, and why of parents' involvement in children's academic live is critical to maximizing its benefits. Evidence is reviewed indicating that how parents become
involved determines in large part the success of their involvement. It is argued as
well that parents' involvement may matter more for some children than for others.
Finally, the issue of why parents should become involved is also considered as a
significant influence to children’s academic live.44
43
Schute, op. cit., p. 1-11.
44
Thirdly, the related research that the researcher chose is from Topor et. al.
on the research “Parents Involvement and Student Academic Performance: A
Multiple Mediational Analysis”. The research is about parent involvement in a
child's education which is consistently found to be positively associated with a
child's academic performance. However, there has been little investigation of the
mechanisms that explain this association. The present study examines two
potential mechanisms of this association: the child's perception of cognitive
competence and the quality of the student-teacher relationship. This study used a
sample of 158 seven-year old participants, their mothers, and their teachers.
Results indicated a statistically significant association between parent
involvement and a child's academic performance, over and above the impact of
the child's intelligence. A multiple mediation model indicated that the child's
perception of cognitive competence fully mediated the relation between parent
involvement and the child's performance on a standardized achievement test. The
quality of the student-teacher relationship fully mediated the relation between
parent involvement and teacher ratings of the child's classroom academic
performance.45
The last is Fitriah AB, in her skripsi “The Correlation between Parents’
Involvement and Students’ English Achievement” (A correlational study at the eighth grade students of MTs Negeri Tangerang II Pamulang) aims to know the
influence of parents’ involvement on students’ English achievement at the first semester of academic year 2008/2009 at MTsN II Pamulang. She conducted a
correlational research by using quantitative descriptive. The techniques of
collecting data are questionnaire, documentation, interview and observation. The
finding of this study is that the influence of parents’ involvement is adequate on second grade students of MTsN II Pamulang. It is shown by the result of the
research (0.402) which belongs to medium correlation. It means that their parents’
45
involvement as the monitor, as an advocate in economy, as the motivator and as
the model is sufficient to support the students’ English achievement.46
However, of all four previous researches drawn, this study has four big
differences from them. Firstly, this research used a quantitative approach
employing correlational method to know the correlative calculation between the
variables and so it differs this study from the previous study which mostly using a
qualitative approach. Secondly, the parents’ involvement in this study was narrowed down into two kinds of involvement which are based at home and based
at school as it was adapted and adopted from Schute’s journal article. Thirdly, neither academic performance nor academic achievement, the researcher tried to
narrowed the study and only used a cognitive achievement from three academic
achievements in the school -cognitive, affective and psychomotor, to specified the
academic achievement. The last, the study was quite different from the research
done by Fitriah AB because the researcher used more data -an open ended
question about parents’ perception toward their contribution to their children’s
academic achievement, to triangulate the correlative result.
In conclusion, the researcher had done more varied techniques and data to
research the correlation between parents’ involvement and student’s English
learning achievement to provide the readers deeper about this issue.
D.
The Research Descriptive Hypothesis
The influence of parents’ involvement to the cognitive achievement in English lesson should be about 75%-90% because parents’ have a very close
related relationship to the students’ daily lives.
46
24
A.
Place and Time of the Research
This study was conducted in Sekolah Menengah Pertama (SMP) Ibu
Pertiwi. It is located at Jl. Let. Jend. S. Parman Kav. 69, Slipi, Jakarta Barat, DKI
Jakarta. The research was carried out on 2 June 2014 to 11 June 2015.
B.
Research Design
This writer used quantitative research method in conducting this research.
“Quantitative research is a type of educational research in which the researcher
decides what to study; asks specific, narrow questions; collects quantifiable data
from participants; analyzes these numbers using statistics; and conducts the
inquiry in an unbiased, object manner.”1
It means the writer collected and
analyzed the data statistically from the questionnaire distributed and students
report book of second semester to find out the correlation between parents’ involvement and student’s English learning achievement.
Further, this research is categorized into correlative method. Gay stated
that “correlational research involves collecting data in order to determine whether, and to what degree, a relationship exists between two or more quantifiable
variables”.2 The correlative method used by the researcher is to describe and measure the degree of relationship between two or more variables or sets of score.
In this research, the two variables are independent variable and dependent
variable. The independent variable (X) in this study is parents’ involvement while student’s English achievement will be dependent variable (Y).
1
John W. Creswell, Educational Research, (New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2008), p.46
2
C.
Research Population and Sample
1. PopulationArikunto states that “Population is all subjects of the research”.3In this research the population of the study is the whole students of eighth grade in SMP
Ibu Pertiwi, in the academic year of 2014/2015. There are six classes in this
school; each class has 35 students.
2. Sample
Sample is a representation of population which is observed. It means the
subject of population. Sample can be taken between 10% -15% - 25% if the
number of population is more than 100.4Besides, Gay stated that “The sample for a correlational study is selected using an acceptable sampling method, and 30
subjects are generally considered to be a minimally acceptable sample size”.5
Based on Gay’s line, in this research, the sample of the population is taken through purposive sampling. The 35 students in 8-C class were chosen for the
sample of this research.
D.
Research Instrument
The data in this study was obtained by compiling and making to answer the research question. Two techniques of data collection were used as follow:
1. Questionnaire
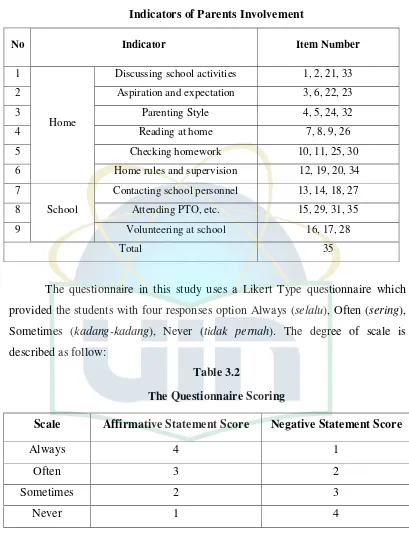
The research instrument that is used in collecting the data is a
questionnaire which is formulated and designed based on indicators of the
variables of parents’ involvement in students achievement. The questionnaire about parents’ involvement of students is given to students consisting 35 items. In
this case, it concerns about parents’ involvement in student achievement. The table is the blueprint of the questionnaire:
3
Suharsimi Arikunto, Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan Praktek, (Jakarta: RinekaCipta,2006), p. 173.
4
Ibid., p.174.
5
Table 3.1
Indicators of Parents Involvement
No Indicator Item Number
1
Home
Discussing school activities 1, 2, 21, 33
2 Aspiration and expectation 3, 6, 22, 23
3 Parenting Style 4, 5, 24, 32
4 Reading at home 7, 8, 9, 26
5 Checking homework 10, 11, 25, 30
6 Home rules and supervision 12, 19, 20, 34
7
School
Contacting school personnel 13, 14, 18, 27
8 Attending PTO, etc. 15, 29, 31, 35
9 Volunteering at school 16, 17, 28
Total 35
The questionnaire in this study uses a Likert Type questionnaire which
provided the students with four responses option Always (selalu), Often (sering),
Sometimes (kadang-kadang), Never (tidak pernah). The degree of scale is
described as follow:
Table 3.2
The Questionnaire Scoring
Scale Affirmative Statement Score Negative Statement Score
Always 4 1
Often 3 2
Sometimes 2 3
Never 1 4
The questionnaire is translated into Bahasa Indonesia. This is aimed to
avoid the possibility of different perception in understanding the statement.
Therefore, using Bahasa Indonesia in the statement will be useful for students to
a) Validity of Instrument
“Validity refers to the degree to which a test measures what it is supposed to measure and, consequently, permits appropriate interpretation
of scores.”6
Validity test is very important in all forms of research because
validity is the criteria of good instrument. In validating questionnaire, the
researcher conducted the research in 8-A class of SMP Ibu Pertiwi, Jakarta
Barat. The researcher got the standard coefficient validity minimum for
this instrument with N = 35 and coefficient validity is 0.334. To see the
validity instrument, the researcher use SPSS 20 to measure the validity of
questionnaire.
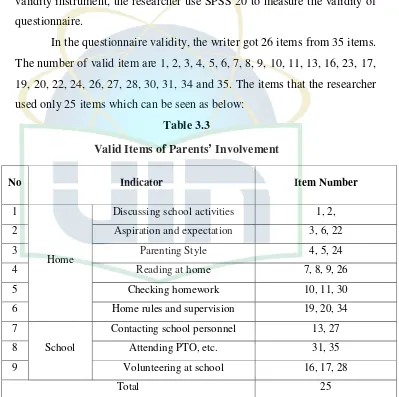
In the questionnaire validity, the writer got 26 items from 35 items.
The number of valid item are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 16, 23, 17,
19, 20, 22, 24, 26, 27, 28, 30, 31, 34 and 35. The items that the researcher
used only 25 items which can be seen as below:
[image:40.595.134.533.285.682.2]Table 3.3
Valid Items of Parents’ Involvement
No Indicator Item Number
1
Home
Discussing school activities 1, 2,
2 Aspiration and expectation 3, 6, 22
3 Parenting Style 4, 5, 24
4 Reading at home 7, 8, 9, 26
5 Checking homework 10, 11, 30
6 Home rules and supervision 19, 20, 34
7
School
Contacting school personnel 13, 27
8 Attending PTO, etc. 31, 35
9 Volunteering at school 16, 17, 28
Total 25
6
b) Reliability of Instrument
“Reliability means that scores from an instrument are stable and
consistent. Scores should be nearly the same when researchers administer
the instrument multiple times at different times.”7
The researcher used
SPSS 20 in order to know the reliability of questionnaire. The result can be
[image:41.595.115.511.251.563.2]seen as below:
Table 3.4
The Reliability of Questionnaire
The result shows that rresult= 0.932. In comparing to rtable with N=35 and 5% as significant level, that is rtable= 0.334, it can be concluded that the instrument is reliable because rresult > rtable= 0.932 > 0.334.
2. Documentation
The definition of achievement in this research is the result of what the
students has learned. In this research, English learning achievement is taken from
the scores that the students obtained in learning English after they have followed
teaching-learning process in English subject at the school. Thus, the writer took
the score from the report book of eighth grade students class C of SMP Ibu
Pertiwi for second semester in academic year 2014/2015 to be analyzed.
E.
The Data Analysis Techniques
After getting data from the students in the questionnaire, the writer needs
to analyze the data and correlate the questionnaire score and the students’ English achievement score.
In analyzing the data of the relationship between parents’ involvement and students’ English achievement, the researcher used correlation product moment
7
John W. Cresswell, Educational Research, (Boston, Pearson Education Inc., 2012), p. 159.
Reliability Statistics
Cronbach's Alpha N of Items
which developed by Carl Pearson.” Correlation product moment is used to show
whether there is a correlation between X variable and Y variable”.8
Data operation
technique is done through the steps below:
1) Finding the number of correlation using formula:
∑ ∑ ∑
√ ∑ ∑ ∑ ∑
Note :
r = Coefficient of correlation between X variable and Y variable
N = Number of respondents
∑XY = The sum of the multiplied of X and Y
∑X = The sum of X scores (parents’ involvement)
∑Y = The sum of Y scores (students’ English achievement)
∑X² = The sum of quadrate of each X scores
∑Y² = The sum of quadrate of each Y scores
(∑X)² = The sum of the quadrate of ∑X scores
(∑Y)² = The sum of the quadrate of ∑Y scores
Significant critical value : 0.05 and 0.01
This formula is used in finding index correlation „r’ product moment between X
variable and Y variable (rxy).
8
2) After the r was found then the writer interpreted the correlation based on
[image:43.595.108.516.179.549.2]following level of correlation.
Table 3.5
The Level of Correlation9
Product Moment ( r ) Interpretation
0.00 – 0.199 Very Low Correlation
0.20 – 0.399 Low correlation
0.40 – 0.599 Moderate Correlation
0.60 – 0.799 High Correlation
0.80 – 1.000 Very High Correlation
3) To know the significance between two variables, the formula of the
significance test is:10
√
√
Note:
= t value
r = value of correlation coefficient
n = number of participants
F.
Statistical Hypotheses
To know whether there is any significant correlation or not between X
variable and Y variable, the writer formulated Ha (Alternative Hypothesis) and Ho (Null Hypothesis) first as follows:
a) Alternative Hypothesis (Ha): there is significant correlation between X
variable (parents’ involvement) and Y variable (students’ English learning
achievement)
9
Sugiyono, Metode Penelitian Pendididkan: Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif dan R&D, (Bandung: Alfabeta, 2013), p. 257.
10
b) Null Hypothesis (Ho): there is no significant correlation between X variable (parents’ involvement) and Y variable (students’ English learning achievement)
Some assumptions are as follows:
a) If the result of calculation rxy is smaller than rt (r table), rxy≤ rt; so the null hypothesis (Ho) is accepted (Ha is rejected).
32
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS
A.
Findings
1. The Description of the Data
Since it has been discussed in the previous chapter, the study used
correlational study for investigating the case whether there is any significant
relationship between parents’ involvement and student’s English learning achievement or not.
To figure out and