A Skripsi
Submitted to the Faculty of Language Education in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of SarjanaPendidikan
Oka HanumPratiwi 20120540058
English Education Department Faculty of Language Education UniversitasMuhammadiyah Yogyakarta
i
The Impact of Teacher’s Talk Time on Student Motivation to Practice
Speaking in the Classroom
A Skripsi
Submitted to the Faculty of Language Education in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of SarjanaPendidikan
Oka HanumPratiwi 20120540058
English Education Department Faculty of Language Education UniversitasMuhammadiyah Yogyakarta
iii MOTTO
***Doing a little work consistently more useful than nothing to do***
iv
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Alhamdulillahirobil’alaminalhamdulillahirobilaminalhamdulilahirobilalam
in. I never tired to say alhamdulilahirobilalamin many times and also say that I do proud to the only one my Lord Allah SWT who always gives me his grace such as strength, healthy, happiness also sadness to face this undergraduate thesis. He give me everything and I do being grateful to know that you are tremendous, enormous also the almighty. I cannot finish this undergraduate thesis without Allah blessing. Thank My Lord, Allah SWT. Hereby, I would like to appreciate thanking to:
My beloved supervisor. My wise, my busy, my best supervisor to Miss Darcy (Sri Sudarsi, S.S., M.InT.), I love you so much ma’am! Nothing to say that I do appreciate your intention to guide me finished this thesis patiently. You are wonder women (who manage this department and many students patiently). You have to always amanahand stay strong Ma’am. Thank for your support, your advice, your valuable feedback also your encouragement ma’am.
My patiently examiners. Another support comes from my patient examiner Miss Maryam Sorohiti, S.S.,M.H.Sc. I do be thankful for your suggestion in helping me to complete my undergraduate thesis. Miss Mariska Intansari, S.S.,MA.thank you ma’am your advice very valuable for me.
v
my thesis. I know that you want me to finish soon and got the best score. Now, I can provide them to you mom! My best sister AdelliaAudryPramesti, thank you Lha! You give me opportunity that I can be your guide sister. You trust me If I do best to make you happy also my parents. Thank you that you caring our parents and our brother when I was not at home. I love you dek! For my one and only brother Muhammad BaariqHafidz, thank you very much you always show your happiness, your laughness and your cuteness. I got more spirit when I am with you dekapiz! Thank you for always entertain me, it worked to fresh my thinking.
My Future.Best Partner also annoying person in doing everything, FahmiNafisArifinS.Pd. Thanks for always accompany me, guide me, encourage me in every single things. Your advices inspire me to finish this thesis well. Success for us, darl, I love you and always beside me.
My Sisters.This thesis cannot finish without Mbejotdot community. I am happy to have you all guys.TyasAyuPuspaDewi (Incess) and AnisAstriani (Juchak). We have trough every single destination together. Thank you for being my source of energy during learning in this department guys. You introduce me good things also bad thing. You guide me to be independence women too. Thanks for the whole time, your happiness, your sadness might make me miss you! Thank you for coloring my day’s guys. Loveyou! haha
My B’rilliant Class. English Education Department Student 2012.All of
vi
motivate me in finishing this thesis. I wish, Brilliant Class element always extraordinary!
Pak Nanto’s Boarding House Member. I am glad to be acquainted with
vii
TABLE OF CONTENT
COVER ... i
APPROVAL SHEET ... ii
STATEMENT OF AUTHENTICITY ...iii
MOTTO ... iv
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... v
TABLE OF CONTENT ...viii
ABSTRACT ... x
Chapter One Introduction ... 1
Background of the study ... 1
Identification of the problem ... 5
Formulation of the problem ... 6
Purpose of the study ... 6
Significance of the study ... 7
Outline of the study ... 8
Chapter Two Literature Review ... 10
Teacher’s Instruction ... 10
Teacher’s Talk ... 13
Teaching across Proficiency Level ... 16
Motivation ... 18
Speaking Class ... 22
Review of Related Studies ... 24
Conceptual Framework ... 25
viii
Research Design ... 28
Research Setting ... 30
Research Participant ... 31
Research Instrument ... 33
Data Collection Method ... 34
Data Analysis ... 36
Chapter Four Finding and Discussion ... 37
Chapter Five Conclusion and Recommendation ... 58
Conclusion ... 59
Recommendation ... 61
References ... 62 Appendix 1. Interview Guideline
i
IMPACT OF TEACHER’S TALK TIME ON STUDENT MOTIVATION Abstract
Teacher’s Talk is often discussed in educational setting especially in teaching and learning process. This study’s aim is to find out the impacts of
teacher’s talk time on student motivation to practice speaking in the classroom.
This research involves student at English Education Department of UMY (EED UMY) who attended Listening and Speaking for Academic Purpose Class. They shared their individual opinion concerning on Teacher’s Talk Time in the
classroom. This study uses qualitative research design and provides descriptive qualitative research. The researcher used interview in collecting the data. There were four participants in this research and they were all student of 2015. The researcher used random sampling to choose participant in every classes. To analyze participants’ answer the researcher used three steps in qualitative research
namely open coding, axial coding and selective coding.
Research showed that EED UMY student perceived that they belonged to intermediate level. Teacher’s proportion talk time was around 50-60 % and
student talk time was around 25-40%. This research also revealed that Teacher’s Talk offered some advantages and disadvantages which had influenced student motivation in learning. These advantages were student had many inputs, student had a model and student had a better comprehension of material. This study presented some disadvantages about the effect of teacher talk in the classroom. These were student felt bored, lack of concentration, lack of motivation, lack of opportunity to speak, lack of self-confidence, and lack of student independence. Based on the research findings, some recommendations were finally presented.
Chapter One
Introduction
This chapter presents the problems and reasons of conducting the study. This chapter is arranged as follows: background of the study, identification and limitation of the problem, formulation of the study, purposes of the study, the significance of the study and the outline of study.
Background of the study
Teacher’s Talk (TT) is one of interesting issues to be discussed in
educational setting. It is one of teaching instruction which is used by teacher in teaching and learning process. According to Yan, (2006, p.6) Teacher’s Talk is defined as “the kind of language used by the teacher for instruction in the
classroom”. Teacher’s Talk is useful for the learner since it helped the learners to
understand the material that explain by the teacher. The students acquire foreign language by Teacher’s Talk in the classroom. Teacher considers their kinds of
language to talk with target language such as to talk with beginner, advance and intermediate students. However, the kind of language used by the teacher is able to influence target language to accomplish their goal (Brown, 2000). It means that, when the teacher taught advance level, the teacher need to consider the language used. The teacher uses kind of language that is able to accomplish their goal in order to increase students’ capability.
opportunity to practice the target language so that the teacher should reduce the amount of their talk to 20% to 30% of the class time, and students’ talk time
should be around 70% to 80% during the lesson time”. Language learner need
more time to acquire and absorb the material in their course. The advantages of teacher’s talk were based on the balancing percentage that it is used between
teacher and students. If the teacher reduce the percentage of his/her talks time in the classroom, it enhanced the students’ capability in speaking. There was an argument that too much teacher’s talk time can even decrease student motivation
in speaking (Setiawati, 2012).
Motivation plays an important role in improving speaking skill. Harmer (2011, p.51) defines that “motivation is some kind of internal drive which pushes
someone to do things in order to achieve something”. When students need
something and have desire in order to do things, then the motivation followed their willingness to reach their goal. For example, the student practices speaking in the classroom well so student motivation appears, then they achieve their goal. However, when the motivation does not appear, the students do not want to practice. It is because their goal does not clear enough.
In addition, the role of motivation does not only talk about the students and their peers but also the students with the teacher. Teacher’s contribution in the
reason why the teacher plays important role in motivating students and creating positive learning environment.
The challenge of student motivation is affected by two factors. These factors were known as extrinsic and intrinsic motivation. Brown (2000, p.59) investigated that “the most powerful rewards are those that are intrinsically motivated within the learner. Because the behavior stems from need, wants or desire within oneself, the behavior itself is self-rewarding; therefore, no externally administered rewards is necessary”. Actually, when the students think that
speaking was not important for them, the students’ desire could not appear
because speaking was not their necessity. Extrinsic motivations come from outside such as teacher’s explanation, rewards, possibility future travel or teacher’s feedback (Harmer, 2011). It shows when the students express their
opinion without teacher’s reward or teacher’s feedback. It makes student
motivation does not appear in the learning process.
There are several reasons why students do not want to practice speaking. The reasons as follow; students worry if they make a mistake. The mistake usually come from their pronunciation, vocabulary limitation and also lack of
teacher (Vargaz and Duenz, 2013). It means that teacher should give something which can build student motivation in speaking skill.
Based on the researcher’s experience, this condition also happened at
English Education Department of University Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta (EED UMY). In the English Education Department there were many students who did not want to speak up in the classroom. It was influenced by many reasons. First, the students were not confident with their knowledge. The students thought that their knowledge was in low level. Second, the students were not confident how they pronounce the word. The students were worried when the students make misunderstanding in their classroom by their false pronunciation. Third, students did not want to speak up in the classroom because the lesson did not interest them. Fourth, the teacher always talked more during learning process. The teacher did not talk about the material anymore but also an important thing like teacher’s
family which did not become an interest topic for the students.
Those are the problems encountered by the students in practice speaking which is one part of learning English. The problems came from both teacher and students. Actually, there were three major problems faced by students in the classroom such as students’ problem with the teacher, students’ problem with the
other students and students’ problem with their own self (Moore, 1990). However, these problems are always related to each other.
This research focuses on discussing students’ problem in relation to the
teacher. When the teacher talked more in the classroom, it could affect student motivation to learn in the classroom. Teacher’s Talk could decrease student
being active in the classroom because the teacher spend more time to talk in the classroom. The teacher and the students should have balance talk turn in the classroom. If one of them talked more it can decrease student motivation in learning. More specifically, this research focused on how teacher’s talk time
affects student motivation to practice speaking in the classroom. Identification of the Problem
There were areas that teacher and students relation in the classroom such as communication, reward and punishment, and misbehavior which is able to be researched. However, the researcher only focused on the Teacher’s Talk Time which is in line with student motivation in their learning. Teacher’s Talk is
teacher instruction which is important in teaching and learning process in the classroom. Teacher’s Talk is important for the teacher in delivering the material.
However, if the teacher talks more than the students, it will decrease student motivation to learn in the classroom. The student does not have opportunity to speak up in the classroom.
Successful teaching and learning process in the classroom is influenced by both teacher and students role in speaking. If the students’ and Teacher’s Talk
balanced, it relates to the effective teaching and learning process. The teacher and the students knew the goal of learning in the classroom. If they really know their goal, students and teacher get effective teaching and learning process. Afterwards, the students and the teacher are able to have motivation in order to reach their goal especially for the students during teaching and learning process conducted.
classroom is able to motivate the students practice speaking in the classroom. Motivation always helps the students to be responsible with their own
achievement. Student motivation will increase if the Teacher’s Talk time in the
classroom decreased. For example, the students do not want to practice speaking in the classroom because the teacher talked more. The students had no desire to speak up in the classroom. Hence, the researcher is interested in to investigate how Teacher’s Talk time is able to influence student motivation.
Formulation of the Problem
The researcher formulates the research question as follow:
What are the impacts of Teacher’s Talk Time on student motivation to
practice speaking in the classroom? Purpose of the Study
This research is intended to find out:
The impact of Teacher’s Talk Time on student motivation to practice
speaking in the classroom. The Significance of the Study:
Teacher. This study is useful for the teacher in the following ways. First, the study give contribution to the EED lecturers in UMY, in considering their Talk Time in the classroom activity. Second, this study is useful for English lecturers in getting information about how to motivate their students in practice speaking in the classroom activity. Third, this research reminded the lectures that Teacher Talk Time is able to be useful in the class but classroom environment and students’ characteristics should be considered.
Students. The results of this study have several advantages for the students. It can be used for the students to acquire teacher explanation by his talk time. Students had a role model that motivates them in practicing the language in the classroom. Furthermore, students get better comprehension of the material by the teacher talk in the classroom.
The researcher. This study is useful for the researcher in the following ways. First, this study gives useful information about using “Teacher’s Talk” and motivating the students to practice speaking in the classroom. Second, because the researcher will become a future teacher so that the researcher have to consider her Talk Time in the classroom. The last, the study is the real the researcher creation so it would give stronger confidence to the researcher to carry out other researches in the future.
Outline of the Study
This research consists of five chapters. Chapter one talks about introduction. Introduction has five parts namely background of the study,
identification and limitation of the problem, formulation of the study, purposes of the study, significance of the study and outline of the study.
Chapter two discusses some academic literatures, conceptual framework and previous studies. Furthermore, there are sub topics in the theories such as teacher’s instruction in the classroom, definition of Teacher’s Talk, the
advantages and the disadvantages of Teacher’s Talk, teaching across proficiency
level, definition of motivation, types of motivation, definition of speaking, classroom speaking activity and listening and speaking for academic purpose.
Chapter three explains the way the researcher conduct the data such as the design of the study, research setting, research participant, instruments of the study, data collection method and data analysis.
Chapter four reports the finding and discussion. In this chapter, the researcher found out six parts. First finding talks about students’ individual perception on their proficiency level. Second, talks about teacher’s and students’ proportion talk’s time in the classroom. Third finding discusses about the
advantages of teacher’s talk time in the classroom. Fourth, this chapter provided
the disadvantages of teacher students’ talk, teacher talk time. Fifth finding talks
about teacher talk and student motivation in the classroom. Sixth finding talks about students’ effort in their learning.
classroom. Beside that, the researcher presents some suggestions about the impact of teacher’s talk time on student motivation to practice speaking. Therefore, it
Chapter Two
Literature Review
This chapter presents some related information of the study. It intends to provide some theoretical concept which supports this study. First, this chapter explains about teacher’s instruction in the classroom. Second, the researcher talks
about Teacher’s Talk Time which consists of definition, and advantages and the disadvantages of Teacher’s Talk time. Third, it explains about teaching across
proficiency level. Fourth, it explains about the definition of motivation and the types of motivation. The last this study talks about speaking class which consists of practice speaking, speaking activity in class, and listening and speaking for academic purpose.
Teacher’s Instruction
Definition of Teacher’s Instruction. Teacher’s instruction is direct communication which is used by the teacher in learning process. According to Reigeluth (1999) as cited in (Hueet, Moneti, Hummel, 2009) they said that in the teacher instruction, the teacher should provide students’ opportunity to practice
and give information on how the intended audience learns and develops.
According to Rosenshine (2012,p.18) “the teacher might have students engage in
an activity that could be done more efficiently once the new content or skills have been mastered”. Teacher’s instruction includes the way teacher explain the
instruction is valuable for the teacher and students because both of them always relate to each other in order to gain successful learning process in the classroom. Without teacher’s instruction, the students do not know what they should do in the
classroom. Likewise, without students, the teacher does not know how far the teacher’s instruction is able to help students in improving skills in their learning
process.
Effective teacher’s instruction is applied to help students if the teacher
provides principle instruction in the classroom. There are three teacher’s principle instructions. According to Rosenshine (2012) who stated that there are three teacher’s principle instructions such as cognitive science, master teacher and
cognitive support. First, cognitive instruction is defined as an instruction which focuses on how our brains acquire information and when the brains limit their working memory. Second, master teacher is defined as an instruction which focuses on the way the teacher presents the lesson, examines students’
understanding and many other teacher’s instructional in the classroom which is
related to the teacher’s instruction. The last, cognitive support is defined as an
instruction which focuses on somebody being a model to help the students learn effectively and support the students to think aloud.
can see the connections in what they are asked to learn. If the teacher and the students do not work together it can decrease student motivation in learning process. Brenda (2000, p.5) investigates “students may become passive and lose
motivation if teacher-directed learning is overused”. Yuqin and Yanven (2010, p.76) pointed out that “the success of teaching depends to a large extent on the
way Teacher’s Talk and interactions that occur between teacher and students”.
Teacher’s instruction in the classroom. The teacher recalls students’ previous knowledge or learning in the classroom. It will make the students review the material that teacher explain in previous meeting. Recalling the students is used to know how students master the teacher’s material. The teacher uses five up to ten minute to recall the entire students’ material. The teacher be able to know
students’ outcome from the teacher’s input. Rosenshine (2012, p.13) argued that
helping students to recall their memory about the previous material is needed because students working memory is limited.
The teacher does not explain or present the material too much in the
classroom in one time. The teacher teaches in the small time then asks the students to practice. The teacher makes sure that to measure students’ understanding by ask them to practice before learn new material. Before the students are able to
practice, the teacher should be a model for the students. Rosenshine (2012, p.14) investigates that “some successful teacher teaches by giving a series of short presentation using many examples”.
teacher knows whether the students understand the material or not. The teacher makes students brave to ask question and make the students has big confidence and improve students’ independence (Rosenshine, 2012).
Teacher’s Talk
Definition of Teacher’s Talk. Teacher’s Talk is useful to support teaching and learning process in the classroom. This is the way teacher explains some material to the students. They are able to interact in the classroom to gain learning process goal. When the teacher explains, the students will be able to acquire knowledge from the teacher. Furthermore, Teacher’s Talk is used to
motivate the students’ to be active in learning process in the classroom.
Many researchers investigate the definition of Teacher’s Talk. Yan (2006) investigates the definition of Teacher’s Talk into some opinions. First, the kind of
language used by the teacher for instruction in the classroom is known as Teacher’s Talk (TT). Second, Teacher’s Talk is special communication that has own goal. The goal develops students’ foreign language proficiency. Third, Qican
(1999) as cited in Yan (2006) asserts that Teacher’s Talk is teacher’s instruction
and teacher managing classroom activities. The last, Nunan (1991) as quoted by Zue and Liu (2012) Teacher’s Talk is not only important for managing classroom but also in the process of acquisition.
Teacher’s Talk and Students’ Talk should be balance. If there is no balancing between the teacher’s and students’ talk, so it makes teaching and
considers the subject that teacher’s explains in the classroom. Furthermre, the
students will get nothing during classroom activity.
The researcher concludes that Teacher’s Talk has important part in every teaching and learning process in the classroom. It means that the role of Teacher’s
Talk should be considered to the target learners and the teacher need. Considering that there are different students’ and teacher’s goal in the teaching and learning
process.
The Advantages of Teacher’s Talk Time. The advantages of Teacher’s Talk Time are useful for the learner if Teacher’s Talk time is not dominant in the
classroom. The researcher’s experience find that Teacher’s Talk time in the classroom has some benefits. The students got much knowledge from the teacher’s explanation. The knowledge does not only talk about the subject
anymore but it also talks about everything which is able to improve students’
knowledge. The students have clear instruction when the teacher explains the material in front of the classroom. The students are easy to communicate with the teacher in the classroom environment.
Advantages of Teacher’s Talk Time may influence the students to be
active in the classroom. It is supported by English Teaching Journal (2007), there are advantages of Teacher’s Talk Time in the following ways. First, listening to
the Teacher’s Talk about real issues is more motivating than listening to or
conversation without using anecdotes and jokes may also stimulate interest during a lesson. Last, storytelling can improve students’ second language acquisition.
The Disadvantages of Teacher’s Talk Time. Despite the advantages of Teacher’s Talk Time, there are some disadvantages of Teacher’s Talk Time. The
disadvantage of Teacher’s Talk Time is affecting the students learning in the classroom. Some disadvantages of Teacher’s Talk Time are discussed below.
The students cannot be an autonomous learning and being active in the classroom. Teacher’s Talk is always explaining the material in the classroom, so that the students cannot be active in the classroom. In addition, teacher has big turn in speaking than the students. It is supported by Zu and Liu (2012) states that “teacher’s talk time dominants most of the class time, vary from 36%to 58%, and
the students talk time is less”. Further, teacher’s in Indonesia thought that
teacher’s are the only source of knowledge. Fitriana (2014) investigates that
“Indonesian teacher is big source of knowledge, so that they have to speak much
in the classroom.”
Many researchers extend the disadvantages of Teacher’s Talk Time in
different opinion. Davies (2011) stated that there are four disadvantages related with Teacher’s Talk time namely Teacher’s Talk time do not work effectively in
the classroom, it does not enhance students’ listening comprehension and
communication skills, reduce students’ occasion to practice L2 in a classroom and
decrease students’ concentration. Dan (2007) as cited in Davidson (2014) points
become passive and dimmed interaction in the classroom, the students are getting bored in the classroom, and detract students autonomous learner in the classroom. Teaching Across Proficiency Level
Defining Proficiency Levels. Teacher helps students to achieve their goal by understanding their proficiency. There are three levels of proficiency namely beginner, intermediate and advance (Brown, 2000). These three levels help teacher in understanding about different way to achieve goal in each level. There are four proficiency levels which is had by students such as speaking, listening, reading and writing.
Teacher considers instruction in the classroom based on each level. It is in line with Brown (2000, p.98) which stated that “since students at this level have little or no prior knowledge of the target language the teacher’s (and
accompanying techniques and materials) becomes a central determiner in whether students accomplish their goal.” This indicates that teacher’s instruction determine
how students achieve their goal.
Teacher’s’ Talk for Beginner Level. The students who are in beginner
level have different ability with students who are either intermediate or advance level. Students need more input toward material from teacher’s explanation or teacher’s talk for beginner level. The advantage in teaching for beginner level is
students have big enthusiasm in the learning activities. The students pay attention to the teacher’s instruction or Teacher’s Talk so that the Teacher’s Talk should be slow in explaining the material. It gives students’ comprehension input in the
teacher, the teacher talk should be around 70-80% during the lesson time (Tsegaye and Davidson, 2014). There will be no learning without input (Yan, 2006).
Teacher’s’ Talk for Intermediate Level. This level is higher level than the
beginner level. In this level, the teacher should have different way in teaching in order to give challenge for students in intermediate level. In this level, teacher is not allowed to talks more in order to make students speak in the classroom. Teacher is allowed to explain the material when students do not get clear explanation about the material. (Brown, 2000). The teacher should give opportunity to the students to talk in the classroom.
In addition, the teacher should expect how many time the teacher talks in the classroom. It helps teacher to influence students in practicing the language. Actually, based on Waren (2003), he has expected his talk time in the classroom around 20-40% during the lesson time, but his expectation is more than the target. The fact, in the intermediate level based on Waren (2003) percentage of Teacher Talk time around 40-60 % during the lesson time.
Teacher’s’ Talk for Advance Level. This is the highest level than two
previous levels. This level shows that the students have higher ability in receiving material from the teacher’s. The students’ challenge is Teacher’s Talk in choosing
the vocabulary, idioms, structures and the other languages (Brown, 2000). Teacher and Students talk should be commensurate and having natural speed in every situation (Brown, 2000). For this level, teacher’s role either becomes
opportunity to practice the target language so that the teacher should reduce the amount of their talk from 20% to 30% of the class time, and Students’ Talk Time should be around 70% to 80% during the lesson time”.
In conclusion, teacher need consider and expect their talk time before they teach in the classroom in order to give students e opportunity to speak and help the students to improve their achievement in the classroom.
Motivation
Definition of Motivation. Motivation is supporting someone to do something. The words “motive” supports which is related with someone interest
and attitude (Lestari and Alice, 1989). Motivation is ability to make someone reach achievement both in the classroom and outside the classroom. Every students has own motivation. It depends on their struggle and their willingness to do it. Supporting someone to do something is influenced by two factors such as motivation which either comes from inside or outside the students. Motivation which comes from students self is called by intrinsic motivation. Extrinsic motivation is motivation which does not come from students self. This can be from the students’ environment. Motivation is including some steps that should be
kept in order to reach the goal. Pintrich and Schunk (2002) as cited in Miller and Reynold (2003) “the term motivation comes from the Latin verb movere, which
means to move. Motivation is occurred to explain what gets people going, keeps them going, and helps them finish tasks. As the students, the students need motivation which occurs from their self. For example, the students should master speaking skill during learning process from the first semester until the last
process. The next students should keep going to speak in the classroom. Further, the students are able to finish their task in every process. The students are developing their speaking during their learning process in the colleague. It is called by motivation which has “movere” meaning.
Types of Motivation. Different researchers investigated different types of motivation in educational psychology. The different types have one goal which gains student motivation in learning. The students have different way in achieving their ability so that they need to know what will make them keep going to achieve that goal. Type of motivation which appears in educational psychology affects either students’ success or failure to acquire the second language. Success or
failure students acquiring the second language depends on the types motivation (Lightbrown and Spada 2001) as cited in (Mahadi and Jafari 2012) .
Types of motivation are useful both for students and teacher to know how far they are able to achieve their goal in the classroom. There are some researchers who classify types of motivation in different view Mahadi and Jafari (2012). He mentions type of motivation which is able to affect and control the procedure and outcome of the learning. Mun (2011, p.1) investigates that, “principally, there are
four distinct types of motivation concerned with second language learning such as intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, instrumental motivation and integrative motivation.”
Intrinsic motivation. It comes from students’ desire in order to achieve
oneself, the behavior itself is self rewarding; therefore, no externally administered is necessary (Brown, 2000, p.7).” (Brewster & Fager, 2000; Dev, 1997; Lumsden, 1994; Lepper, 1988) as cited in Blazer (2010, p.2) emphasize that “intrinsically
motivated students also tend to employ learning strategies that demand more effort, prefer more challenging tasks, feel more confident about their ability to learn new materials, and retain information and concepts longer”.
Extrinsic motivation. It comes from other people who are able to make target learners have motivation to do something. Extrinsic motivation needs reward to make target learner motivated. Appearing students’ extrinsic motivation is challenging because extrinsic motivation can be up or down when somebody ask the target learner to have motivation (Weller, 2005; Baldes et al., 2000; Kohn, 1999). Kohn (1999) as cited in Blazer (2010) states that “studies found that extrinsic rewards can actually have negative effect on student motivation and they argues that teacher actually the decline of student motivation by thinking it is necessary to reward students to do something.”
Extrinsic motivation is influenced by teacher and students interaction in order to achieve their goal in educational setting. Extrinsic motivation can be influenced by some factors in the classroom setting namely teacher’s feedback,
rewards, punishment and Teacher’s Talk time. Those are effective way to improve
Student motivation to be active in the classroom activity. The students and the teacher should work together.
Integrative motivation. It is the motivation that appears to gain somebody goal. According to Garden and Lambert (1972) as cited in Ahmadi (2011)
identify with the target culture. Base on Holt (2011) as cited in Yin (2011) argues that the learners which have integrative motivation usually integrate the culture of SLA to enclose learner target. It means that, the students has desire to speak or to gain their goal in order to full fill their cultural goal. According to Rehman, et al (2014, p.256) “an integrative orientation means that the learner is learning second
language both for social and cultural goals”.
Instrumental motivation. The students need to have instrumental motivation if they have to get higher career in the social environment. Instrumental motivation is learning the language as an instrument to achieve practical goal (Garden and Lambert, 1972 as cited in Ahmadi, 2011). Someone who focused on their educational setting and carrier area can be said as somebody who has instrumental motivation (Ahmadi, 2011). The purpose of instrumental motivation is useful for the learners who apply a job and translation work. It means that, instrumental motivation belong to gain advance social status rather than gain cultural setting (Yin, 2011). It means that, the students who has practical reason such us the students want to get salary or getting a job.
From these examples above, the researcher concluded that these types have different way to reach students’ goal. Instrumental motivation inclines with
Motivation and Language Learning
The Relation between Motivation and Language Learning. English Education students should have motivation to learn and acquire English. For the Indonesian people who learn foreign language they have to posses big desire motivation in order to acquire the foreign language.
Speaking Class
Practice Speaking. English has four skills that should be mastered by students’ namely speaking, reading, writing and listening. Speaking and Writing
are the productive skill then Reading and Listening are receptive skill in English subject. Fattah (2006, p.13) investigates that “speaking is one of the four language skills (reading, writing, listening and speaking)”.These skills are able to represent
students’ expression, speaking is productive skill that is useful in order to get
much knowledge and exchange other opinions. The students have to practice these skills in order to get master English skill. The students cannot master and
understand these skills without practice.
Speaking Classroom Activity. Nowadays, speaking is important ways to transfer message from the students and the teacher’s, from the teacher’s to the students and from the students and other students in the classroom. It might help them to create good environment because it influences Students to speak up and being active in the classroom speaking activity. They should have good relation in the classroom activity, if there is miscommunication or misunderstanding about the lesson so that speaking is useful for them to clarify about that conversation.
However, there are teacher’s problems in line with students’ speaking skill
classroom is one problem (McBain, 2011). The students have no motivation if the Teacher’s Talks more in the classroom. This is caused by it decrease students’
confidence to speak up in the classroom. The students might be felt uncomfortable with that problem.
The researcher concludes that speaking skill especially speaking for second language is not easy for the students. The teacher should help the students increase their motivation to express, share and speak up in the classroom by knowing the Teacher’s Talk in the speaking classroom activity.
Listening and Speaking for Academic Purpose. This is one example subjects that English Education Department forces the students to always practice the skill in the classroom. The teacher should encourage the students to practice speaking skill in the classroom. Considering that learning without practice is nothing.
Practice speaking in the classroom is important. The students will be easier to remind the words or the material if the students practice it. For example, the teacher gives explanation to the students then they imitate the teacher’s’ words,
pronunciation and teacher’s explanation. Furthermore, the teacher will be able to know students’ understanding about teacher’s explanation.
Review of Related Studies
Many researchers investigate many studies that is to find out the impact of Teacher’s Talk time on student motivation to practice speaking in the classroom.
Firstly, Davidson and Tsegaye (2014) reported study with the title “The
Ratio of Teacher Talking Time to Students Talking Time in Efl Classroom: A Case In Six Partner Preparatory Schools Of Haramaya University, Ethiopia. This study discussed about the proportion between Teacher’s Talk to students’ talk time in Language classroom Ethiopian context. This study took six teacher’s
preparatory from Haramaya University to be participants. This study used observation in the classroom activity. The result of the study showed that preparatory teacher used 83, 4% talk than the students 16, 6 % in the classroom activity. It proved that teacher’s talk time dominated in the classroom and the
teacher should reduce their talk. The students did not have opportunity to interact and communicate with the teacher and the other students in the classroom. This research recommended that teacher should minimize their talk and give the students opportunity to talk in the classroom.
Secondly, a study from Rehman, A , et al (2014) with the title “The Role of Motivation in Learning English Language for Pakistani Learners”. This study
explored motivation’s role in learning English for Pakistani learners. This study
found that motivation played an important role in every activity. Actually, there are some types of motivation but this study only focus on two types of motivation. This study wanted to know student motivation to learn English which is
research then questioner as the data collection. There are fifty (50) Pakistan students as the participant in this study. That participant included twenty five (25) female and twenty five (25) male. Instrument of this study used Likert scale. The research dividing the question into two, ten (10) questions talk about integrative motivation and ten (10) question talk about instrumental motivation. From the result, it can be concluded that there are seventy percent (70%) students who are motivated by Instrumental. This study found thirty percent (30%) students who are motivated by integrative motivation. Instrumental motivation is higher than Integrative motivation but both of them are able to influence student’s motivation
in learning SLA especially English.
In summary, according to those previous related studies, it becomes basic knowledge for the researcher to conduct this research. Many researchers conduct the study about the Teacher’s Talk time and student motivation and those previous
studies related with something discussed above. It becomes researcher’s reason to conduct the researcher since there is no study which does not discuss about the relation between the Teacher’s Talk time and student motivation.
Conceptual Framework
This explanation is mentioned in the previous that Teacher’s Talk is
teacher’s instruction which is used by the teacher to explain material in the
classroom. However, Teacher’s Talk should be considered in the classroom. If
teacher talked more in the classroom it could decrease student motivation to speak up in the classroom. Teacher’s Talk should be considered in order for limiting
Teacher’s Talk time affects student motivation practice speaking in the classroom
at English Education Department. It focused on the student motivation to practice speaking and how the impact of Teacher’s Talk time in the classroom.
Firstly, this study will be focused on the Teacher’s Talk time during the
teacher gives instruction. Classroom activity can be said as success if there is good interaction between students and teacher. Besides, there were many advantages and disadvantages of Teacher’s Talk Time. The advantages of
Teacher’s Talk Time as follows:students’ rich knowledge, real issue of the
teacher, and natural conversation. The disadvantages of Teacher’s Talk Time as
follows: decrease students’ autonomous learner, decrease students’ practice,
minimum students’ talk, and decrease students’ concentration.
Secondly, motivation plays an important role in educational setting. Motivation appears unconsciously to the students who learn second language acquisition in the university. Motivation was be able to promote the students desire in order to reach their goal in learning process. However, students had different variety to reach their goal in learning process. Motivation has some types which were included in different variety to help students in learning process these were intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, instrumental motivation and integrative motivation. However, this study was focused on the extrinsic motivation to know why students unmotivated to practice speaking in the classroom.
speaking in Foreign Language, it needed somebody to encourage them to practice speaking in the classroom. The researcher only focused on the Listening and Speaking for Academic Purpose Class. Students needed to practice speaking in the classroom. This class can be said as high motivation class for students to practice speaking rather than other classes. From the explanation above, extrinsic motivation could influence students to practice speaking in the classroom
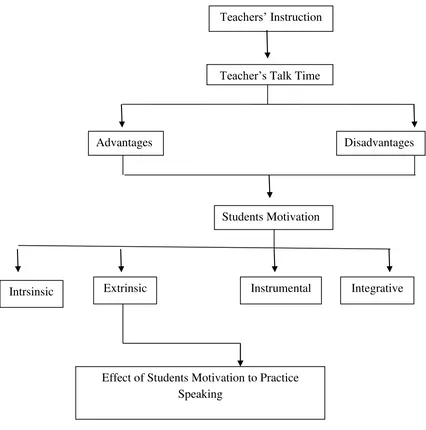
Figure 1. Conceptual Framework
Teachers’ Instruction
Teacher’s Talk Time
Advantages Disadvantages
Students Motivation
Intrsinsic Extrinsic Instrumental Integrative
Chapter Three
Methodology
This chapter presents information regarding the process of writing research design and the reason of choosing the design. Research setting and participant is used to know setting and the participant in the research. Data collection helps the researcher to explain the way the data are gathered. The last is data analysis method which is used to analyze the result after collect the data.
Research Design
This study aims at investigating the impact of Teacher’s Talk Time on
Student motivation to Practice Speaking in The Classroom at EED UMY batch 2015. Hence, the researcher required qualitative design to conduct her research.
The researcher used descriptive qualitative research in this study. Creswell (2012) asserts that qualitative research is the best method to address the research problems of phenomenon. The phenomenon talked about the impact of Teacher Talk related to the student motivation in practicing speaking at EED UMY. Creswell (2012) also points out that to address the research’ problems, it is actually needed to explore more detail information from participants. Sugiyono (2005) investigates that qualitative research is used to get deeper data which contains meaningful data. Qualitative research does not emphasize on the information from the generalization answer but it emphasizes the meaning.
The researcher’s reasons chose qualitative design was categorized into
participants. Qualitative research provides much information from the
participants. The researcher could get the information by giving interview session to the participants and followed up question. The researcher make follow up question if the participants’ answer does not clear. The reseacher did follow up question. This information was related to the student motivation in practicing speaking so the researcher chose qualitative design to dig in depth information from the participants.
Second, it needed emotional bond between the researcher and the participants. The contribution emotional bond between the researcher and the students could express their answer and give much information to the researcher easily, especially participants’ answer about the impact of teacher talk time on
student motivation to practice speaking in the classroom.
Third, Creswell (2012, p. 131) investigates that “qualitative research intent to explore or understand the central phenomenon with specific individuals as a certain research site. It means that the researcher is easy to get real information because the participants know central phenomenon that concern in how the Teacher’s Talk time affect student motivation to practice speaking in the
classroom.
Research Setting and Participant
Research Setting. The object of this research is English Education students at English Education Department Universitas Muhammadiyah
Speaking for Academic Purpose class which was taught at second Semester students.
These were following reasons of the researcher’s decision to choose EED
as the research setting. First, the participants were studying in the same college with the researcher so that it make easier to collect the data. Second, most of the students in this department want to become teacher in the future. It means when they want to become a teacher in the future, they should consider talk time and should motivate the students to speak during learning process in the classroom. Third, this research takes of Listening and Speaking for Academic Purpose so that the students have practiced speaking and expressing their opinion in the
classroom. The students are good in speaking skill and the students willing to speak up in this class than the other classes. Fourth, this department has many students who have different motivation to practice speaking in the classroom. From the explanation above, the researcher wanted to investigate the impact of how Teacher’s Talk on student motivation to practice speaking in the classroom.
Starting from May 2016, the researcher conducted interview to gather the data.
Research Participants. The participants of this research were English Education Students batch 2015 which attended Listening and Speaking for Academic Purpose.
Considering the researcher’s title which focuses on the impact of Teacher’s Talk time on student motivation to practice speaking in the class, the
the classroom. Second, student motivation to become an active learner in the classroom was influenced by the teacher. Third, the researcher has asked the student to have motivation in learning English because they were in the second semester. Hence, second semester is new member in the EED that the teacher has influenced them in motivate their self during learning in EED UMY. The last, it was accessible for the researcher since it conducted in EED UMY.
The researcher used Probability sampling. Sugiyono (2005) points out that probability sampling was the technique which gives the same opportunity toward the member population to be chosen as the sample. Sugiyono (2005) investigates that there were four (4) techniques sampling. These techniques were systematic simple random sampling, proportionate stratified random sampling, sampling area sampling and disproportionate stratified random. The researcher used random sampling to choose the participant. In the random sampling, the researcher chose the sample randomly. The researcher selected the participant use random
sampling based on Creswell (2012 p.143) who stated that “the intent of simple
random sampling is to choose individuals to be sampled who will be representative”.
The researcher took representative participants in each class of Listening and Speaking for Academic Purposes at English Education Department.
Considering the number of the participants, the researcher found theories that support researcher’s decision. Creswell (2012) stated that “qualitative research did
not think about the number of the participant but it talks about how useful the information to the researcher.” From the explanation above, the researcher took
females and two males. However, EED UMY had many female students than male students. Both of male and female have different perception about the study (Creswell, 2012)
Research Instrument
The researcher became research instrument. The researcher had been valid because it was able to help how far the researcher ready to do her research and started to collect the data. Sugiono (2005) pointed out that the validations toward the researcher as the instrument were including of how far the researcher masters the object to be research and the researcher knowledge about qualitative research. The researcher was the key instrument.
The researcher used interview guidelines and the researcher took note during interview process. The question of the interview focused on how the Teacher’s Talk time affects student’s motivation to practice speaking in the
classroom. Besides, the researcher used recorder in the interview session in order to replay participants’ recording and the researcher listened to participants’
accuracy in order to make the researcher easy to get clear information.
The researcher used semi structure interview as instrument to collect the data. Sugiyono (2005) investigated that the researcher is being flexible to do the interview than structure interview. The purpose of semi structure interview was to find the problem transparently and asked the participants to give their idea or opinion. Creswell (2012) stated “a qualitative interview occurs when the
supported by Creswell, (2012) Interview is ablet to conductby face-to-face or by telephone. In the interview, the researcher asked open-ended questions to the participant in order to get the information. By having interview, the participant expressed detail information to the researcher. Creswell (2012) investigated that some advantages are that they provide useful information when you cannot directly observe participants, and they permit participants to describe detailed personal information.
Data Collection Method
The researcher’s procedure to collect the data was described in several
steps. First, the researcher used random sampling. The researcher asked some students batch 2015 to be her participant. The researcher faced problems when the students did not want to be her participants. The problem was the student did not know about researcher’s research. The researcher asked other students. The researcher found two males and two females. That was researcher’s way in
selecting the participants.
Third, the researcher made an appointment to the respondents to dig out detail information as the researcher needs. The researcher explained the
participants’ rights before the interview started. The researcher conducted the
interview by face to face since it helped the researcher and the participants catching up the meaning in their conversation. The interview conducted around ten to twenty minutes for each participant. However, when the researcher satisfied and got enough information then the time stopped at that time. The researcher asked permission to the participant because she used recorder to gain the information so the participants’ answer did not left behind.
The researcher used Indonesian language in order to gain clear
understanding between the researcher and the participant. Indonesian language is the native language for both of researcher and the participants’ environment. The researcher and the participants used Indonesian language in their daily activity. It made the participants was easier to explore the answer during interview process. The researcher used voice recorder during the interview process. The recording was around seven to ten minutes. After that, the researcher transcribed the participants’ record.
Data Analysis
(2012) stated that, “transcription is the process of converting audiotape recordings
or field notes into text data (p.239)”.
The researcher used member checking in order to make the transcription appropriate with the participants’’ answer. Following the transcription, the researcher read the transcription and found the code in every important transcript carefully. That is called as coding. Cohen, Manion, & Marison, (2010) argued that “the process of disassembling the text in to line and paragraph (p.492)”. Coding is
the process of labeling text to form description and phrases (Creswell, 2012). In the coding there were three parts important. Cohen, Manion, & Marison, (2010) asserted “open coding involves exploring the data and identifying units of analysis to code for meanings, feelings, actions, event and so on (p.493)”. Second, the
researcher used axial coding. Creswell (1998) points out that “axial coding is a
procedure for interconnecting the categories (as cited in Cohen, Manion, & Marison, 2010, p.493)”. The researcher selected the data using selective coding.
Chapter Four
Finding and Discussion
This chapter reports the findings which answer the research question in this study based on the data interview. This chapter also provides further discussion that relate to some references which have been reviewed in chapter two. There were six findings from this study, such as students’ individual perception on their proficiency level, teacher’s and students’ proportion of talk
time in the classroom, advantages and disadvantages of teacher’ talk, the relation
of teacher’s talk time and student motivation in the classroom, and students’ effort
in their learning.
The researcher provide comprehension picture on the whole of the setting of the research, there are some points from the interview that should be presented such as students’ proficiency level and teacher and students’ proportions talk time.
These findings are not the major of the discussion but these findings are to support the reader’s understanding
Students’ individual perception towards their proficiency level in Listening and Speaking for Academic Purpose at EED UMY
Finding: Students proficiency level was in intermediate level. There were three proficiency levels that literature provided, such as beginner,
intermediate and advance level. However, all participants claimed that they belonged to the intermediate level. Brown (2000, p.98) stated that “since students
at this level have little or no prior knowledge of the target language, the teacher’s
(and accompanying techniques and materials) becomes a central determiner in whether students accomplish their goal.” This means that, teacher was needed to
be dominant in this level. Although the teacher’s was needed to be dominant in
this level, the teacher also gave students opportunity to practice speaking in the classroom. Furthermore, students of intermediate level could accept many inputs by listening to the teacher’s talks and reading the material that was explained by
the teacher in the classroom. All participants in this research reported that they could learn individually but they still needed teacher’s role in supporting them to accept the material in the classroom. Leopold (2011, p.4) stated that “the teacher can play a key role in creating an encouraging environment” The researcher
concluded that EED UMY students belonged to intermediate level that still needed teacher’s talk and did practice the language in order to make optimal
learning.
Teacher’s and Students’ Talk Proportion in the Classroom Activity
After the researcher found students proficiency level, the researcher asked participants opinion about students and teacher’s talk’s proportion in the
could motivate students in improving their skill. Besides, students also needed to be aware of how much they needed to practice speaking.
Finding: The proportion of Teacher’s Talk Time was bigger than Students’ Talk Time. One way to make teaching and learning process successful is by knowing teacher’s and students’ talk proportion in the classroom. This
finding talked about participants’ opinion toward students and teacher’s talk
proportion in the classroom. Based on the interview, most of participants reported that teacher’s and students’ talk proportion time happened when students have
time to speak and teacher only gave minimum talk time in the classroom.
Participant one stated that “in my opinion, we are students, so that we have
to have more time or being active to talk and the teacher should have less talk turn in the classroom activity”. EED students needed more time to deliver their opinion
in front of the classroom especially in Listening and Speaking for Academic Class. Participant one also explained that “the teacher has applied that the teacher need a little talk to explain the material”. It was supported by the previous finding
from Davies (2011, p.1), a good language teacher should be able to get students to do more work in the classroom”. EED teacher’s tried to talks as minimum as
possible and it was useful for students. The teacher was aware about the proportion of talking in explaining the material at Listening and Speaking for Academic Class.
Another participant informed the similar opinion:
I think the ideal proportion between teachers and students’ talk is when
material in a little time students can respond and have turn to talk easily. (P2.21)
Students need to speak in the classroom in order to habituate them to have a good speaking skill. Statement above was supported by Nunan (1999, p.216) who stated that to talk or to speak in the classroom, the learner not only know how they talk and consider the way consider linguistic competence but also they know well when, why, and what ways produce the language (as cited in Emma, 2015, p.25).
Some participants informed that teacher’s and students’ talk estimation
time in the classroom activity. It was shown by participant two “maybe the teacher’s talks for around 30 minutes in the class then students respond his/her
explanation about 15 minutes in every meeting”. EED teacher had managed his
talk to explain the material in front of the class but students talk opportunity still less than the teacher’s talks proportion. This finding was in line with Waren
(2003), who stated that teacher’s ideal proportion was around 20-40% of the
whole learning hour in the classroom.
Another participant added similar information
If I can say the ratio between teacher and students’ talk in one hour, the teacher’s talks around 35 minutes then 25 minutes for students to talk
everything, include ask question to the teacher’s. (P3.25)
Two participants stated that Teacher’s Talk in Listening and Speaking for
-40% in every meeting. Students needed more time to talk because students need to practice the language. Tsegaye and Davidson (2014, p.2) stated that “in
communicative EFL classes students need much opportunity to practice the target language so that the teacher should reduce the amount of their talk to 20% to 30% of the class time, and students’ talk time should be around 70% to 80% during the
lesson time.” It means that, students agreed if in Listening and Speaking for
Academic Purpose class, students needed more time to practice speaking than the teacher’s.
Students’ Perception on the advantages about Teacher’s Talks Time in the classroom
This study also tried to provide students’ perception about advantages and disadvantages of Teacher’s and Students’ Talk Time in the classroom. In this part,
the researcher reported the advantages of teacher’s talk time in the classroom.
Based on the interview, the researcher found some advantages such as, students had many inputs, had a model and had better comprehension of material.
Finding 1: The students had many inputs. Students can accept many inputs from teacher’s talk. All participants claimed that they had many inputs by
the teacher who talked more in the classroom. Participant one reported that “the advantages that I feel when the teacher talks more in the classroom, I have many input knowledge”. Second participant added similar opinion “the advantage is I
teacher’s talk time is students have many inputs, like students can improve their
second language by acquiring the material. It was in line with theory of Nunan (1991) who stated that teacher’s talk is a crucial of importance, not only for the
organization of the classroom but also for the process of acquisition.
Students of EED felt satisfied when the teacher explained more about the material in the classroom Students were satisfied because teacher’s who talked
more gave clear information about the material and they understood and acquired the material well.
Finding 2 : Students had a model. The researcher found that some students could have many inputs from the teacher who talked more. Beside that, Teacher’s Talk could also improve students’ skill. Participant two informed that
“when the teacher’s talk in front of the class using his/her own style it can also
improve my speaking skill because I try to imitate the teacher’s did”. The teacher
could made students improve their skill because students imitated teacher’s
speaking style by his talk.
Every teacher has his or her own style to teach students in the classroom. Teacher’s style could affect student motivation in class. Mahmood and Syeikh
(2014) pointed out that teacher’s teaching style become important things that help
students to have good motivation in the classroom. The researcher found one participant who agreed with that model. The participant informed that “by looking
Rosenshine (2012) stated that cognitive support is defined as an instruction which focuses on somebody being a model to help the students learn effectively and support the students to think aloud. Hong (2008) also stated that teacher’s takes role of model or being facilitator to students learning in the classroom.
Finding 3: Students had better comprehension of material. Better comprehension might facilitate students in joining classroom activities. Participant three informed that:
For the students, it can make them got clear information about the material that has explained by the teacher’s. So that I do not need to ask my friend
because the material was clear enough, certainly I understand. (P3.27)
Another participant showed similar information
For the advantages, maybe we get better comprehension and also we can absorb the knowledge from the teacher’s talk in the classroom. (P4.31)
From those findings, the researcher concluded that Teacher’s Talk Time in
EED gave motivation and brought some benefits for students. It was shown from those findings that teacher’s talk could be useful since the learner got many inputs
from the teacher’s, got model and got better comprehension about the material
Students’ perception on the disadvantages of Teacher’s Talk Time in the Classroom
The previous finding reported the advantages about teacher’s talk time in
the classroom. In contrast, some students also had different view about teacher’s who talked more in the classroom. Those disadvantages were that students felt bored, lacked of concentration, lacked of motivation, lacked of opportunity to speak, lacked of self-confidence, and lacked of students independence.
Finding 1: Students felt bored in the classroom. Based on the interview, feeling bored becomes the first thing that the researcher is going to discuss. Two out of six stated that teacher who talked more could made students bored in that class. Participant one reported “actually, there are a lot of disadvantages about
teacher’s who talked more in the classroom but what I dislike most is I felt bored,
absolutely bored”. Dan (2007) stated that teacher’s who talked more in the
classroom is able to make students bored (as cited in Davidson, 2014). EED students indicated that they were bored because they had to wait the teacher to give opportunity to speak up and it made them bored while waiting for teacher’s
instruction. That statement was supported by participant two:
The disadvantage is I have to wait teacher give opportunity to speak up. While waiting the teacher gives us opportunity to speak up, it made me bored to wait that time. (P2.31)
When students felt bored that it might be students felt sleepy and did not accept the material well. One out of four participants felt if teacher’s talked more,
Finding 2: Students were lack of concentration. The researcher found that students’ lacking of concentration also become one of disadvantages of teacher’s talk time in the classroom. One out of four participants claimed that
teacher’s talk time could decrease students’ concentration and not focused in
accepting the material. Here was participant one’s statement “then, I do confuse with the teacher’s explanation who talk more”. Participant one also repeated his
statement below:
... it showed when the teacher’s talk more so that the material is not focuses then it make me does not understand. The main point is I am not enjoyed and it decreases my concentration.
According to Davies (2011) teacher’s can interrupt students’ concentration
because of his talk. The researcher found that participants felt confused in receiving teacher’s material because the teacher’s talked more and it made
students’ concentration decreased. Students did not understand what the teacher
explained, because the teacher explained more about the material in the classroom.
Finding 3: Students were lack of motivation. Another disadvantages faced by students in the classroom was students’ lack of motivation. Ellis (1994)
that there is an argument that teacher talked more can even decrease student motivation in speaking. The students did not want to focus in listening teacher’s
talk in the classroom, because their motivation did not appear from themselves. Participant two also informed that “if the teacher talks more, I don’t have
motivation and I feel not focus in asking or listening”.
Finding 4: Students were lack of speaking opportunity in the
classroom. Lack of speaking opportunity became crucial thing in the Listening and Speaking for Academic Purpose Class. In that class, students have to practice speaking. Three out of four participants claimed that teacher who talked more was able to decrease students speaking turn in the classroom. Participant two claimed that “the disadvantage i