Vol 8, No 2, April - June 1999 Histopathological aspects
of
breast cancer 133Histopathological
aspects
of breast
cancer
in
relation to
some
epidemiological
risk
factors
Esti
Soetrisno*, Gunawan
Tjahjadi*, Goi Sakamoto',
JoedoPrihartonot, Yoshiyuki Ohnof,
Didid Tjindarbumi#,
Santoso
Cornain*,
Setyawati
Budiningsiht,
SadaoSuzuki4
Muchlis
Ramli#,
Idral
Darwis#, Endang
Sri Roostini*,
Kenji Wakai[
Drupadi
SDillon.
Abstrak
Penelitian epidemiologik dengan cara kasus kontrol pacla 300 kasus kanker payudara di Rumah Sakit
Dr
Cipto Mangunkusumo,telah clilakukan pada tahun 1989-1991. Dengan menggunakan klasifikasi yang dianjurkan oleh Japanese Breast Cancer Society,
gam-baran histopatologik kanker payuclara menunjukkan bahwa dari tipe karsinoma duktus invasif,
jenis
skirus ditemukan pada 147 kasus(49VoI jenis padat tubuler pada 79 kasus (26.33Vo) danjenis papiLotubuler pada 39 kasus (t3Vo). Sednng dengan menggrmakan
klasi-fikasi WHO ( 1981 ), ditemukan 265 kasus (88.337o) invasif duktus karsinoma, karsinoma invasif lobuler pada 7 kasus (2.337o), karsinoma moduler pada 17 kasus (5.68Vo), karsinoma adenoid kistik pada
I
kasus (0.33Vo), penyakit Paget pada puting 2 kasus (0.67Vo) dan 4kasus pada karsinoma noninvasif adalah karsinoma duktal insitu. Analisa terhadap faktor-faktor risiko yang bermakna pada kanker
payudara wanita Indonesia menuniukkrtn bahwa faktor-faktor: aktivitas seksuaL dini, tinggal
di
daerah perkotaan, traluna payudara, obesitas (kegemukan), haid pertama,/menarche yang terlambat, siklus haid yang tidak teratut; menopause, konsumsi makanan berlemak dan yang mengandung santan dapat meningkatkan risiko. Juga telah dianalisa hubungan antara faktor-faktor risiko yang bermakna tersebut dengan jenis histopatologik. Hasilnya menunjukkan bahwa Konsumsi makanan bersantan meningkatkan kemungkinan jenis karsinoma duktus invasif. Pengaruh tersebut berhubungan dengan ketiga subtipe histologik, yaitu papiler tubule4 solid tubuler clanskirus. Konsumsi minuman clengan santan/air kelapa dan sayuran segar menurunkan kemungkinan jenis tersebut, dengan sifat tklak bergantung kepada subtipe histoLo gik.
Abstract
Case control epidemiological study of 300 breast cancer casès from
Dr
Cipto Mangunkusumo HospitaL has been performed in 1989-1991. By applying the Japanese Breast Cancer Society classification, the histopathological pafiern ofbreast cancer showed that from the invasive ductal carcinoma type, scirrhous type was foundin
147 cases (49Vo), solid-tubular typein
79 cases (26.33Vo) and papilotubular type in 39 cases (I3Vo). According to WHO classification (1951); they were diagnosed as: invasive ductal carcinoma in 265 cases (88.33Vo), invasive lobular carcinoma in 7 cases (2.33Vo), medullary carcinoma inI7
cases (5.68Eo), adenoid cystic carcinomainI
case(0.33Vo),purePaget'sdiseaseof thenipplein2cases(0.67Vo)and4cases(l.33Eo)of thenoninvasivecarcinomawereductal carcinoma in situ. Analysis of the signfficant riskfactors among the Indonesian female breast cancer revealed that the following factors:living at urban area, young sexual activity, trauma, obesity, late menarche, irregular cycle, menopause, fafiy diet and coconut milk
con-taining food consu'mptiolx increased the risk. Relationship of the riskfactors to histopathological types has been stastistically analyzed. The resubs showed that increased possibility to have the invasive ductal carcinoma was related to consumption of coconut milk containing food. The effect was relatecl to the three histological subtypes, namely: papillary tubuLar, solid tubular arul scirrhous types. Coconut milk drinks andfreshvegetables showed decreasing effect, whichwas irrespective to subtypes.
Keywords: Breast cance4 histopathological, epielemiological, riskfactors.
* Department
of Anatomic Pathology, FacuLty of Medicine, University of Indonesia, Jakarta 10430, Indonesia
' Department of Pathology, Cancer Institute Hospital,
Tbkyo 170, Japan
t
Department of Community Meclicine, Faculty of Meclicine, University of Indonesia, Jakarta 10320, Indonesiall Department of Preventive Meclicine, Nagoya University
School of Medicine, Nagoya 466, Japan
# Department of Surgery, Faculty of Metticine,
University of Indonesia, Jakarta 10430, Indonesia
I
Department of Nutrition, Faculty of Medicine,University of Indonesia, Jakarta 10430, Indonesia
INTRODUCTION
134
Soetrisno et alPaget's disease
of
the nipple.
In
1986,
the
JapaneseBreast Cancer Society
suggested
to
observe
more
carefully on the
most
common invasive
breastcarci
noma:
IDC. As
the result
of
their
study,
there
are 3
IDC
which were easily identified by
ic
examination, namely:
Papilotubu-bular IDC,
andScirrhous
IDC.
These3
subtypes
of
IDC
have
l0
years survival rate
of
77 .4Vo, 64.9Vo and6I.ZVo respectively.a
Age influences on
some breast cancer types
in
rela-tion
to
prognostic
decision. For example:
lobular
car-ular
c
disease,
usually
elder
ma
onreproduc-in
wo
der
age
in
men,Junevile secretory carcinoma
on
childhood,
muci-nous
carcinoma among the 5th
decade,medullary
car-cinoma
in
the
lower
decade.In
general,
it
wasknown
that
some breast cancertypes have a specific
biologic
behavior: indolent, circumscribe
or
aggressive,
dif-fuse/massive
invasive.5-12Some
difference
on
histological type might
be
found
among
different
races.In
comparative study between
Japanese
and
American female
breast cancer,
it
wasrevealed
that
lobular carcinoma
among
Japanesefe-males
was
significantly
lower
than
that
among
American
females.
The
Japanesebreast cancer cases
had
better
survival
compared to
theAmerican
cases.5ogical
ighest
carci-noma
wasreported more
frequently
among
theblack.
In this
paper,
we
present the analysis on the
relation-ship between
certain histological
types
of
breastcan-cer
to
certain demographic characteristics and risk
factors.
MATERIALS
AND METHODS
Co
nicopathology
of
s (rqsq_rqgO)
usi
matched
con-Based on
Tjahjadi
etal.l3
andS
al.t4 data,
it will
be studied whether
histo
I
types
of
breast cancer
showed
any
to
someepidemiological
data.
The result
of
casedistribution
Med
J Indones
by
histological types was as
follows:
noninvasive
ductal carcinoma (DCIS)
4
cases
(l.33Vo), invasive
ductal
carcinoma
(IDC)
265
cases(88.3
ing
of
3
subtypes
papilotubular
IDC
39solid-tubular
IDC 79
cases(26.33Vo),
sI47
cases (49Vo),
mucinous
carcinodra
6
cases17 cases
(5.68Vo),
in-7 cases (2.33Vo), ade-33Vo)
andPaget's
dis-vo).The distribution
according
to tumor location
showed
that tumors were
mostly
located
atthe
left
breast
I72
cases
(57.33Vo),
followed by
right
breast
lI7
(39Eo)and
11 cases (3.67Vo)were
bilateral.
The
epidemiological
study on the 300
casesof
breastcancer revealed several
significant risk factors, listed
as urbaner,
young
first
sexual
contact, trauma,
obe-sity, late
menarche,
irregular cycle,
coconut
milk
food, no
vegetable,
and as significant
at
lVo
meno-types,
3tubular,
to
inva-ation to
certain
risk
factors. Thus,
living
area,
menopausal
of
coconut
food
tables
were
st thesive
ductal
com_pared
to
other types.
They
were
further
evaluated
against
the three histological
subtypes.
The
propor-tions were
compared
by chi-square calculatiôn with
correction
for
continuity.l6
16r,
for
trend was
per-formed using loglinear
regression
model
with
pàis-son error.15
RESULTS
Basic results
of
our
300
cases
breast cancer
study
presented
in
the
following
tables.ive
the
ma
of
ductal type (DCIS):
l.33Vo, paget,s
diseaseof
the
Vol 8, No 2,
April
- June 1999
Table
1.
Histological types and case distribution of breastcan-cer (1989-1991)
Histological types Number of
cases
%2.
t. Noninvasive carcinoma
-
Ductal-
Lobular Invasive carcinomaa.
Invasive ductal carcinomaa.1. Papilotubular
a.2. Solid-tubular
a.3. Scirrhous
b.
Special typeb.
l.
Mucinousb.2. Medullary
b.3. Invasive lobular
b.4. Adenoid cystic
Pagets disease
4 0
39 79 l4'1
6
17 7
I
2
1.33 0.00
r 3.00 26.33
49.00
1.33
5.68 z-J.t 0.33
0.67
Total 300 100.00
Source: Tjahjacli et aL. 1993
Tâble
2.
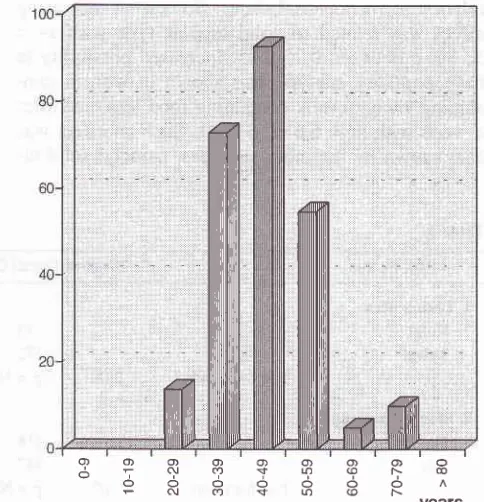
Case distribution by age at operation/biopsyAge at operation/biopsy Number of cases E
HistopathoLogical aspects
of breast cancer
t3s
o
@
years Figure 1. Histogram offrequency tlistribution by age of group
of
300 cases of breast cancar
(IDC)
type was analyzed
in
relation
to living
area,menopausal status, consumption
of
coconut
milk
containing
food
and drinks,
fatty
meat
and
fresh
vegetables.
The results are given
in
Table 3.
There
was
no
significant
or
difference
in
relation
to
IDC
type
or
IDC
type comparing between
rural
and
urbanarea,
with
x2
=
0.009.
Similarly,
if
they were
com-pared according
to
menopausal status,
with
x2
-0.400.
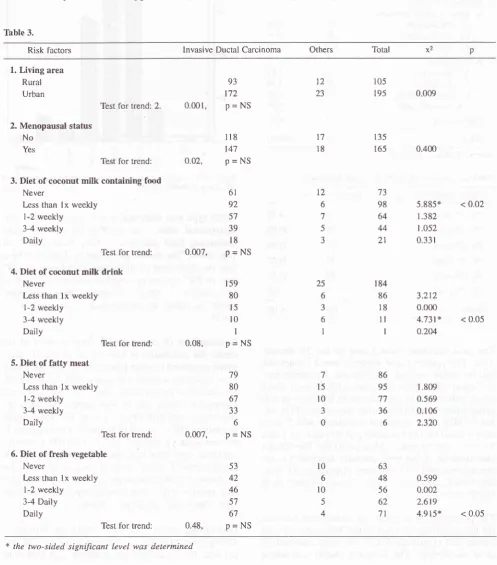
Consumption
of
coconut
milk
food
seemed
to
in-crease
the possibility
to
have invasive
ductal
carci-noma compared
to
other types.
Significant difference
was
shown
by women who
consumed
coconut
milk
food
lessthan once a week,
with
x2=
5.885,
p<
0.02.Somewhat
similar pattern was shown
by
consump-tion of
coconut
milk
drinks, except
for
significantly
decreasing
effect
related
to frequent consumption
(3-4
times
weekly), with
x2=
4.731,
p <
0.05.
Consum-ing fresh
vegetablesdaily
showed to
decrease therisk
significantly. Further
analysis
was
performed
by
evaluating the three
subtypes
of IDC,
namely
papil-lary
tubular type,
solid
tubular
type
and
scirrhous
type.
The results
aregiven in
Table
4.Accordingly,
there was
no significant
difference
among three
histological
subtypes
in
relation
to
liv-ing
area.However, there
wasmarginal significance in
oro)ooroooo,
AFN([email protected]c!s)<t(n@t.
20 - 29 years
30 - 39 years
40 - 49 years
50 - 59 years
60 - 69 years
70 - 79 years
t3
'72
93
55
58
9
4.33
24.00
31.00
18.33
19.33
3.00
Total 100.00
The
peak incidence was
found
in
the
5th
decade:3lVo.
The
youngest
casereported was
2i
years old,
and
the oldest
case was75
yearsold.
The young
peo-ple
group
(less
than
30
years
old)
showed
much
lower
percentage
in
comparison
to
the older
people
group (more than 40
yearsold),
they were
4.33Vover-sts
77.66Vo.
The
mucinous carcinoma
which
were
only
4
cases(1.337o)
occurring
at30
years,44
years,
51 years and 54
years
old respectively. The lobular
and
medullary
types
were similarly distributed in
the ageinterval
over 20to
70
years.Among our
11bilat-eral
breast cancer
cases,only
2
casesof
them
were
lobular
type.
The possibility
of
any
kind
of
relationship
betweenthe
histopathological
types
of
the 300 cases
of
breastcancer and significant
risk
factors was
etnalyzedby
cross tabulation.
The
invasive
ductal
carcinoma
300
[image:3.595.325.567.90.341.2]136
Soetrisno et aLrelation
to
menopausal status.
Somewhat
increasing
effect
was related
to
solid
tubular
type
with
x2
=
3.786,
p
between 0.25-0.05.
Increased
possibility
to
have
papillary
subtype was shown
in
women
con-suming coconut
milk
containing food
lessthan
oncea
week
with
x2
=
6.685,
p<0.01.
Such an
effect
wasalso shown
by
the other
subtypes,
namely:
solid
tu-Table 3.
Med
J
Intlonesbular type
with
x2=
4.014,
p<0.05
and scirrhous
type
with
x2=
4.857, p<0.05.
The
testsfor trend
were
not
significant at
p
level
of
0.05.
No
significant
differ-ence was seen
for
coconut
milk drinks, fatty
meat andfresh
vegetables
consumption
relative
to
respective
histological
subtypes.Risk factors Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Others Total x2
1. Living area Rural Urban
Test tbr trend: 2.
2. Menopausal status No
Yes
Test for trend:
3. Diet of coconut
milk
containing food NeverLess than
lx
weeklyl-2
weekly 3-4 weekly DailyTest tbr trend:
4. Diet of coconut
milk drink
Never
Less than
lx
weeklyl-2
weekly 3-4 weekly DailyTest for trend:
5. Diet of
fatty
meat NeverLess than
Ix
weeklyl-2
weekly 3-4 weekly DailyTest for trend:
6. Diet of fresh vegetable Never
Less than
lx
weekly1-2 weekly 3-4 Daily Daily
Test for trend:
93
172
0.001,
P = NS1r8
147
0.02,
p = NS6l
92 57 39l8
0.007,
P = NSr59
80
l5
t0
I
0.08,
p = NS79 80 67 JJ
6
0.007,
P = NS53 42
46
57 67
0.48,
p = NS5.885+
< O.O2t382
1.052
0.33 t
0.400
3.212
0.000
4.73t*
< 0.050.204
t.809
0.569 0.106
2.320
0.599 0.002
2.619
4.915*
< 0.05 1223
105 195
r35
165
0 009
t7
l8
t2
6 7 5 J
25 6 3 6
1
73 98 64
44
21
t84
86
l8
ll
1
63 48 56 62 71 7
15
l0
J0
l0
6l0
54
86 95 77 36
6
[image:4.595.84.582.174.739.2]VoL B, No 2, ApriL
-
June 1999Thbel
4. Analysis of risk factors
and histological type of 300 breast cancer casesHistopathologicaL aspects
of
breast cancerHistological type
Risk f'actors Papillary
tubular IDC
Solid tub.
IDC
Scirrhous IDC
x2 Others Total
1.
)
3.
Living
area Rural UrbanMenopausal status No
Yes
Diet of coconut
milk
containing food NeverLess than lx weekly
1-2 weekly 3-4 weekly Daily
Test
for
trend: Diet of coconutmilk drink
NeverLess than lx weekly
l-2 weekly
3-4 weekly Daily
Tbst
for
trend:Diet of
fatty
meat NeverLess than lx week'ly
1-2 weekly 3-4 weekly Daily
Test
for
trend:Diet of fresh vegetable Never
Less than lx weekly
1-2 weekJy
3-4 weekly Daily
Tbst
for
trentl:19 20 23 56 2',1 52 52 95 '72 75 6.685+* 4.593* r.610 0.652 0.222 4.014* 0.729 0.280 0.301 1.341 4.857+
0.8 t9
1.379
r.863
0.612
12
10523
195135 16s
l2
6 7 5 3 0.642 0.217 0.617 0.308 2.297 0.001 1.813 0.846 0.130 0.469 3.421 0.2730 077 0.1 05 1.321 2.022 0.101 3.786 3.368 0.068 2.136 0.085 0.091 o.201 3.625 0.03 8
2.929 0.004 0.708 0.675 0.238 0.290 2.536 0.4r6 2.475 0.021 1.502 3.291 2.383 184 86 18 11 1 6 t4
l2
5 22l
28 t7 10 -) 34 48 28 24 13 t5 98 64 442t
4. 28 9 1 I 0il
lt
t0 6 1 9 5 9 8 8 85 46 9 6 I 25 6 J 6 I 7 15l0
3 0l0
6 r0 5 4 46 25 5 J 0 5. 29 21 20 8I
39 48 3t 19 4 86 95 77 36 6 3.207 1.004 0.0r 83.182 t.437 6. r8 t4 l3 l5 t9 39 48 37 34 40 63 48 56 62
7I
0.525 0.077 1.222 3.1 48 0.142'k
Significantdffirence
at p<0.05;"{'
Significantdffirence
at p<0.01DISCUSSION
The
agedistribution of the
Indonesian
female
breastcancer showed
that
a
significant
increase
of
the
pro-portion of cases
hasstarted
atthe
third
decade (2480) andpeaked
at thefourth
decade (37Vo).The
datasug-gested
that the
breast cancer
in
Indonesian
females
started at younger
ages
compared
to
the American
and
the
Japanese cases.s-13The proportion
sharply
declined at the
seventh decade,
similar
to the
Japa-nese cases
but
differs
from
the
American cases,
which declined
atthe eighth
decade.The
histological typing
showed that the
majority
wasI
38
Soetrisno et alinvasive ductal carcinoma
and 9.67Vo
special
type.
Thus,
only a few
non-invasive carcinoma
(l.33%o)and Paget's disease
of
the nipple
(0.67Vo).The
pro-portion
were different
from
the
Japanesg ç4sss,5-13with
higher non-invasive
cases (1.4Vo),
lower
inva-sive ductal carcinoma (80.4Vo),lower special
types(1I.4Eo) and
similar
Paget's
disease (0.7Vo).The
pre-sent
study
hasanalyzed the
relationship
between
sev-eral
significant risk
factors
and thehistological
types.The data
showed
that consumption
of
coconut
milk
containing
food
increased
the possibility
to
have
in-vasive ductal carcinoma
ascompared
to other
histo-logical types,
while
coconut
milk
containing drinks
and
fresh vegetables
haddecreasing effect.
It
is
of
in-terest
that the
increasing
effect
of
coconut
milk
con-taining
food
related
to papillary tubular type
and
thedecreasing
effect
of
coconut
milk
containing drinks
was related
to
scirrhous type.
It
appearedthat
thefor-mer effect was evident
in
all
three histological
sub-types.
The
decreasing
effect
of
fresh
vegetables
wasnot preferentially
related
to
any
histological
subtype.Such
relationship
might
be value
for
better
under-standing
on
the
role
of risk
factors
in influencing
thedevelopment
of
breast cancer.The
relationship
of
his-tological
types
of
gastric cancer
to
demographic
datahas
been also analyzed
by
others.lT
Further study on
bigger
samples
is
suggested
to
en-able
the analysis on other histological
types and
theevaluation on important epidemiological risk
factors
such
asethnic
difference.
Acknowledgments
The authors would
like to
thank
to
the
nurses, Ms.
Ros and
Emi,
andpublic
health
nurses,Ms. July
andMs.
Erlaini for
excellent
epidemiological
datacollec-tion. We are
also indebted
to EDP
staffs
for
helping
in
data processing.
This work was
supported
by
theMinistry of
Education, Science, Sports
andCulture
of
Japanese
Govemment,
GrantsNo.
0 IM2007,
MM20
13andO6042006;
and waspartially
supported
by
theIn-donesian
Cancer Foundation. This
collaborative
study was
apart
of
Special
Cancer Research
project
in
Monbusho
International Scientific
Research
Pro-gram,
with
the
approval
of
the
Dean,
Faculty
of
Medicine
University of
Indonesia,
No.
43831PTO2.H4.FK/E/88.
Med
J
IndonesREFERENCES
I
.
Mc.Divitt RW, Steward FW, Berg JW. Tumors of the Breast:Atlas
of
Tumor Pathology. znn series. Washington: AFIPI 968.
2.
PageDL,
Anderson TJ. Diagnostic Histopathologyof
the Breast. Edinburg: Churchill Livingstones 1987.3.
International Histological Classificationof
Tumors: Histo-logical typing of Breast Tumors. WHO 1981.4.
Japanese Breast Cancer Society. The General Rules forclini-cal and pathologiclini-cal recording
of
breast cancer. Jpn J Surg 1989; 19: 612-32.5.
Sakamoto G, Sugano H, Hartmann WH. Comparative patho-logical study of breast carcinoma among American andJapa-nese women. In: McCuire WL, editor. Breast Cancer. Nash-ville: Plenum Publishing Corp.,
l99l;
4: 211-31.6.
Berg JW. Clinical Implicationsof
Risk Fâctorsfor
Breast Cancer. Cancer 1984; 1: 589-91 (supplement)'l
.
Gump FE. Premalignant Diseasesof
the Breast: SurgicalClinical North America 1984; 64: 1051-59.
8.
Ohno Y. Metodology and evaluation of dietary factors inJa-pan. In: Mettline CJ, Aoki K, editors. Recent Progress in Re-search on Nutrition and Cancer, pl1-20. Wiley-Liss 1990.
9.
Claus EB, Risch N, Thomson WD, Carter D. Relation be-tween Breast Histopathology and Family History of Breast Cancer. Cancer 1993;7l:147-53.
10, Hurliman J, Gebhard S, Gomez F. Estrogen receptor, pro-gesteron receptor, pS2, ERD 5, HSP27 and cathepsin D in in-vasive ductal breast carcinoma. Histopathology 1993; 23: 239-48.
ll.
Azzopardi JG, Ahmed A,Millis
RR. Problem in BreastPa-thology W.B.Saunders 1 979.
L2. Page DL. Prognosis and Breast Cancer. Recognition of lethal
and t'avorable prognostic types. Am J Pathol 1991; 15: 33+49.
13. Tjahjadi G, Sakamoto G, Tjindarbumi D, Watanabe S, Pri-hartono J, Ohno Y, et al. Pathological aspects of breast câncer
in
Indonesian fèmales, Emphasizing on the modified WHO classification. Med J Indones 1995; 4: 156-62.14. Budiningsih S, Ohno Y, Prihartono J, Ramli
M,
WakaiK
Cornain S, et al. Epidemiological analysis of risk factors forbreast cancer in Indonesian females. Med J Indones 1995;4:
I 63-8.
1 5, Ri mm AA, HarTz AJ, Kalbfl eisch JH, Anderson AJ, Hoffman
RG. Basic Biostatistic in Medicine and Epidemiology. Apple-ton Century Crofts, New York, 1980.
16. Clayton D, Hills
M.
Statistical Model in Epidemiology. Ox-ford University Press, Oxford, 1993.