ABSTRACT
IMPROVING STUDENTS’ LISTENING COMPREHENSION THROUGH VIDEO AS MEDIA AT THE SECOND YEAR STUDENTS OF SMA NEGERI
1 PRINGSEWU BY
FERDY ARYANDA PRASETYA
Listening is the key success of communication. Listening is receptive skill that should be acquired first in learning English. There are 5 aspects of macro skill of listening that should be learned. The aspects of listening include of indentifying main idea, specific information, reference, inference, and vocabulary. In fact, students still get difficulties in listening because teachers’ selecting in appropriate media. The use of video as media is able to improve students’ listening comprehension.
Therefore, the aims of the research are to find out the aspects of listening comprehension that significantly improve students’ listening comprehension and to find out the students’ problems in listening comprehension through video. The subject of this research was class 4D IPA of the second year of SMA Negeri 1 Pringsewu. This research applied one group pretest posttest design.
CURRICULUM VITAE
The researcher’s name is Ferdy Aryanda Prasetya. He was born in Pringsewu, on July 19th, 1992. He is the third child of great parents, Slamet Riadi and Agatha Waniati. He has two sisters, Indah Puspasari and Diah Novitasari, and one brother, Kristian Aji Nugroho.
He stared his study from kindergarten at TK Xaverius Pringsewu in 1996. He joined elementary school at SD Fransiskus Xaverius Pringsewu in 1998 then graduated from elementary school in 2004. He went to SMP Xaverius Pringsewu and graduated in 2007. Afterwards, three years later, he graduated from SMAN 1 Pringsewu in 2010.
DEDICATION
This script is proudly dedicated to:
My beloved parents: Slamet Riadi and Agatha Waniati
(Thanks for your affection, your prayers, your forbearance and everything)
My beloved sisters and brother , Indah Puspasari, Diah Novitasari, Kristian Aji Nugroho
My lectures
My friends
MOTTO
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Praise and thanks go to the almighty God, Allah SWT for the gracious mercy and tremendous blessing so that the writer is finally able to finish this script entitled
“Improving Students’ Listening Comprehension through Video as Media at the
Second Year Students of SMA Negeri 1 Pringsewu”. This script is submitted as compulsory fulfillment of requirement for S1 degree of English Department at the Faculty of Teacher Training and Education (FKIP), Lampung University.
It is necessary to be known that this script would never have come into existence without any supports, encouragement, and assistance. The writer would like to express his deepest gratitude to all those who gave his possibility to complete this script. The writer would like to address his respect and gratitude to:
1. Dr. Muhammad Sukirlan, M.A., as the first advisor for his patience, kindness and suggestion in guiding and giving advices.
2. Drs. Ramlan Ginting Suka , as the reseacher’s second advisor who have given suggestions and guidance.
3. Prof. Ag. Bambang Setiyadi, M.A, Ph. D., as the researcher’s examiner, who has given her constructive suggestion to complete this script. 4. Drs. Sudirman, M.Pd., as the reseacher’s academic advisor.
5. All lectures of English program, who have contributed their knowledge and guidance for the writer.
6. Drs. Yulizar, M.M., as the Headmaster of SMA Negeri 1 Pringsewu for giving his permit and opportunity to conduct research.
7. Novita Dianawati, S.Pd., as the English teacher of SMA Negeri 1 Pringsewu who have supported the research.
9. The researcher’s beloved parents, Slamet Riadi and Agatha Waniati, S.Pd, sisters and brother, Indah Puspasari, S.P., Diah Novitasari, Kristian Aji Nugroho, little niece, Ratu Kayla, for the love, pray, trust and support, and encouragement to finish his script.
10.Eva Suasiawati, for support, prayer, patience, and loyalty. Thank for always accompanying me during this script writing process.
11.All English ’10 generations: Fajar Prayoga, Lucky Nugroho, Dani Erfan Saputra, Abdul Haris Adnan, Tanjung Wulandari, Nandita Wana Putri, Fadhil Arief Primadi, Imelda Ayu Mustika and all friends who cannot be mentioned one by one, thank for everything.
12.My team, JPMT Graffiti, NO IDEA Art Team
Nothing in this world is perfect and this final project is no exception. I hope this final project will be useful and beneficial for the readers, especially those who involved in English teaching profession.
Pringsewu, July 2014
The Writer,
i
1.2.The Formulations of the Problem ... 5
1.3. The Objectives of the Problem ... 5
1.4.The Uses of the Research ... 5
1.5.The Scope of the Research ... 6
1.6. Definition of Terms ... 7
2. FRAME OF THEORIES 2.1 Review of Previous Research ... 8
2.2. Listening ... 9
2.2.1 Macro Skill... 10
2.2.2 Micro Skill ... 12
2.3. Listening Comprehension. ... 12
2.4. Teaching Listening Comprehension ... 14
2.5. Audio Visual Aid ... 17
2.6. Video ... 19
2.7. Teaching Listening through Video ... 20
2.8. Procedure of Teaching Listening through Video ... 21
2.9. The Advantages and Disadvantages ... 23
2.10. Theoretical Assumption ... 24
2.11. The Hypotheses ... 25
3. RESEARCH METHODS 3.1.Research Design ... 26
ii
3.3.Variable ... 27
3.4.Data Collecting Technique ... 28
3.5.Procedures of the Research ... 29
3.6.Research Instrument... 32
3.7.Criteria of a Good Test ... 32
3.7.1. Validity ... 32
3.7.2. Reliability of the Test... 34
3.7.3. Index of Difficulty ... 35
3.7.4. Discrimination Power ... 36
4.1.3. Result of Students’ Listening Comprehension Achievement ...43
4.2.Aspects of Listening Comprehension ...45
4.3.Students’ Problems in Listening ...52
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
Table 1. Table specification of Listening Comprehension Try out Test ... 34
Table 2. Percentage of Listening Aspects in Pretest ... 40
Table 3. Percentage of Listening Aspects in Posttest ... 42
Table 4. Increase of Students’ Listening Comprehension Achievement ... 43
Table 5. The Improvement of the Mean of Pretest and Posttest ... 44
Table 6. The Improvement of Students’ Listening Aspects ... 45
Table 7. Main Idea ... 47
Table 8. Specific Information ... 48
Table 9. Reference ... 49
Table 10. Inference... 50
Table 11. Vocabulary ... 51
LIST OF GRAPH
Graph 1. Listening Aspects in Pretest ... 41
Graph 2. Listening Aspects in Pretest ... 42
Graph 3. The Improvement of the Mean of Correct Answer ... 44
Graph 4. The Improvement of the Mean of Students’ Score ... 45
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1. Try Out Test ... 74
Appendix 2. Reliability Analysis of Upper Group of Tryout Test ... 79
Appendix 3. Reliability Analysis of Lower Group of Tryout Test ... 80
Appendix 4. Reliability Analysis of Tryout Test ... 81
Appendix 5. The Coefficient of the Reliability ... 82
Appendix 6. Table of Difficulty Level and Discrimination Power ... 83
Appendix 7. Pretest ... 84
Appendix 8. Posttest ... 89
Appendix 9. Transcription of Video in Pretest and Posttest ... 94
Appendix 10. Specification of Pretest and Posttest ... 97
Appendix 11. The Result of Pretest and Posttest ... 98
Appendix 12. Analysis Pretest of Students’ Listening Comprehension ... 99
Appendix 13. Distribution of Students’ Correct Answer of Pretest ... 100
Appendix 14. Students’ Listening Aspects Achievement in Pretest ... 101
Appendix 15. Analysis Posttest of Students’ Listening Comprehension ... 102
Appendix 16. Distribution of Students’ Correct Answer of Posttest ... 103
Appendix 17. Students’ Listening Aspects Achievement in Posttest ... 104
Appendix 18. Result of SPSS Analysis ... 105
Appendix 19. T-table ... 111
Appendix 20. Transcription of Interview ... 112
Appendix 21. Lesson Plan 1 ... 117
Appendix 22. Lesson Plan 2 ... 121
I. INTRODUCTION
1.1Background of the Problem
English is a language that is very important because it has been used by people globally. Many people around the world use English to communicate with other people who have differences in languages, races, and cultures. In this era of globalization, English as international language is needed for communication purposes. There are many reasons for the people to master English, some of them are: 1) English is as an access to global knowledge; 2) English is required for jobs and overseas scholarships; 3) English as lingua franca used to establish communication and good relationship with global community.
2
communication, people use receptive and productive skills. Without the skills, communication may be not working well.
In the process of learning language, the four basic skills link each other. It means that we learn to listen first, to understand the message of what we have heard. After accepting the information from what we have heard we try to deliver the information orally. It continues to two other skills, reading and writing. It can be illustrated, when a baby learns a language, before he/she can speak words, he/she tries to imitate what his/her parents say by listening it first. Other two basic skills are usually obtained in school, he/she learns to read and write.
Listening serves as the key of communication process. We cannot communicate if we do not understand message from the speakers. We cannot respond and reply what the speakers say if we do not understand the message. Listening takes a big part in communication. One spends his/her time for listening more than speaking, reading or writing. By listening, someone can receive important and useful information. Listening is also required to gain information from media such as television or radio.
3
From the data of students’ score in listening subject, the researcher found out some
students get low score in listening subject. Then during Teacher Training Program/Program Pengalaman Lapangan (PPL), the researcher found out that the students get problems in learning listening skill. They feel difficult to understand the meaning of audio material which is given by teacher. They get difficulty in understanding the system of target language. The students may get the problem in understanding the difficult words or phrases. It happens because they may lack of vocabulary. Phonology aspects also become the factor of students’ problems in listening. They cannot distinguish the words they have heard. It makes students are unable to understand the meaning of the audio material. Learners are expected to comprehend the meaning of messages in target language.
Other factor is that students may lack of motivation to the listening subject. They assume that it is not important to practice listening because listening is not included in most of English examination. They feel that listening to the tape recorder is a boring thing that they do while teaching learning process in the class. Listening material for teaching-learning process is also seldom taught in class. It happens because the school does not have media that can be used to teach listening material. Therefore, teacher as facilitator should utilize media for teaching listening material. Not only the students get the problems, teacher also gets problem about what the
students’ difficulty in listening comprehension. Teacher has to know the difficulties
4
According to Hamalik (1986), the use of teaching media in teaching-learning process can raise new desire and interest; generate motivation and stimulation of learning
activities, moreover has an impact on students’ psychological effects. Therefore,
teaching learning process needs media to improve students’ motivation. If there is no motivation in learning process, students will not able to understand the materials that are given. So it is important to teacher to uses the appropriate media as an aid to
improve students’ listening comprehension.
In this research, the media that used by researcher is video. Video is used to stimulate
students’ speculation and prediction that can lead to their schemata in listening
comprehension. In order to make teaching and learning process run effectively, students should be lead to use all their sense and the teacher are supposed to stimulate students to use their senses. Video also improves students’ interest and motivation. In Canning-Wilson (2000) and Putri (2011), they stated that the use of video as the media is able to improve students’ listening comprehension.
Based on the explanation above, listening is one of language skills that is important to be mastered by learners in foreign language class. It is the basic skill that will lead students to success in learning English as second language. And the use of video as
media in listening class is hoped can improve students’ listening comprehension.
5
1.2Formulations of the Problem
In reference to background of the problem explained above, the formulations of the problems are:
1. What aspects of listening significanly increase students’ listening comprehension after being taught through video at the second year of SMA Negeri 1 Pringsewu?
2. What problems are faced by the students who get low score in improving
students’ listening comprehension through video at the second year of SMA
Negeri 1 Pringsewu?
1.3Objectives of the Research
Based on Formulation of the Problem, the objectives of the research are:
1. To find out what aspects of listening significanly increase students’ listening comprehension after being taught through video at the second year of SMA Negeri 1 Pringsewu.
2. To find out students’ problems in improving students’ listening skill through video at the second year of SMA Negeri 1 Pringsewu.
1.4Uses of the Research
6
1. To improve students’ listening comprehension and motivation at SMA Negeri 1 Pringsewu.
2. To help English teachers of SMA Negeri 1 Pringsewu and others English teachers find appropriate media about teaching listening to improve
students’ listening comprehension.
3. To be used as reference for the next researcher who will do research focus
on students’ listening comprehension and the aspects of listening
comprehension.
4. To verify the previous theories which deal with the uses of video in second language acquisition.
5. To inform the readers, English teachers, other researchers, syllabus designer, how video can improve students’ listening comprehension.
1.5Scope of the Research
7
are in form of identifying main idea, specific information, reference, inference and vocabulary.
1.6 Definition of Terms
In order to avoid misunderstanding concerning to the term used. The definition of terms are:
Comprehension means process which the reciever try to understand the meaning of verbal or non verbal information.
Improving means to raise more excellent quality or condition or make something
better. In this case is students’ listening comprehension.
Listening is an active process where the listeners plays very active part in constructing the overall message that eventually exchange between listener and speakers. (Lukong, 1998)
News items is a text that informs the readers about newsworthy or important events of the day.
II. FRAME OF THEORIES
This chapter consists of several concepts that relate to the research. This chapter explains about review of previous research, concept of listening, listening comprehension, teaching listening, audio visual aid, video as teaching media, teaching listening through video, procedure of teaching listening through video, the use of video, advantages and disadvantages of using video as teaching media.
2.1Review of Previous Research
Video as media in teaching listening comprehension have been a focus of several language studies. The researchers believe that there are many advantages of using as media in teaching listening. They believe that it can develop listening skills. It reinforces grammar and vocabulary. It stimulates language production such as speaking.
9
is effective to improve students’ listening comprehension. In Putriani (2013) also finds that there was a significant increase of students’ achievement in listening
comprehension taught through video.
In Karlina’s research (2010), she conducts a comparative study of students’ listening
comprehension between audio tape and video as teaching media. In his comparison study, she finds that the use of video can increase students’ motivation and students’ listening achievement. From the data that she gets, the students’ average score in
video is significantly higher than students’ average score in audio tape. It shows that
teaching listening through video is better than using audio tape as media.
Considering the previous research above, video can be used as a media and it is effective to teach listening in classroom. Beside, to find whether the significant increase of the student’s listening comprehension. The different between this research
and other previous research was this research focuses on the five aspects of listening and students’ problem in listening. In addition, the researcher uses news items material.
2.2Listening
10
for learner, any learning cannot start that will lead to speaking. It means that listening is fundamental to speaking and other language skills. Listening skill provides an input will affect to speaking skill and then develop to the next skills.
Lukong (1998) defines that listening is an active process where the listener plays very active part in constructing the overall message that eventually exchange between listener and speakers. It means listener is required to be active to understand the meaning of the message that sent by the resources.
Hughes (1991) mentions two skills in listening that work together and involve. They are macro skill and micro skill of listening.
2.2.1 Macro skill
Macro skill simply means understanding what someone says, but in this skill listener has to understand three essential things like getting main idea of the text, and listening for specific information. And this research will focus on macro skill that deals with getting main idea or gist of the text, listening for specific information and identifying reference and vocabulary. Each term will be explained below:
a. Identifying the main idea
11
details. In order to get the main topic, the listener should listen well to the text. It need more attention to listen and should be careful to find the main idea from text. b. Identifying specific information
Putriani (2013) states that specific information develops the topic sentence by giving definition, example, facts, comparison, analogy, cause and effect statistics and quotation. In order to understand the text, listener should listen well to get the specific information to the text. The information can be facts, comparison, analogy, cause and effect statistics and quotation.
c. Identifying inference
Inference refers to a prediction about something untold from the information of the text. An inference can be made when the requisite general knowledge necessary to make that inference is available (Cain and Oakhill, etc, 2001).
d. Identifying reference
References are words or phrases used either before or after the reference in comprehension material. When such word are used, they are signals to the listener to find the meaning elsewhere in the text. (Putriani, 2013:13)
e. Vocabulary
12
2.2.2 Micro Skill
Listening is not only getting main idea of the text, identifying specific information, identifying inference or vocabulary. Listening also means interpreting intonation pattern (stress and rhythm) and recognition of faction of structure, detecting sentence constituent, or recognizing discourse maker detecting sentence constituent, or recognizing discourse maker. In addition, micro skill means evaluating and analyzing listening process. Danaher (1994:2) states that macro skill of listening within the foreign language learning is the most important skill for the beginner students, in order to prepare them for speaking and later for reading and writing. The researcher will focus on the aspects of listening in term of identifying the main idea, specific information, reference, inference and vocabulary from the text to developing students’ listening comprehension.
Based on explanation above, listening is an active process of understanding or comprehending messages from what the listener heard. Listening provides input for learner. Listening is one of most important skill in language that has influence to develop other language skill such speaking.
2.3 Listening Comprehension
13
the process by which a person understands the meaning of written or spoken language. In addition, James (2006) states that listening comprehension refers to understanding spoken language. Thus, listening comprehension means the ability to get and understand the meaning of the message from spoken language.
According to Hedge (2000) divides listening process into two classifications, they are bottom-up process and top-down process.
1. Bottom up process
Bottom up process refers to decoding process. The decoding of language into meaningful unit, from sounds waves into meaning. The listener replies on the language in the message that is combination of sounds, words, and grammar that creates meaning. The bottom up process might include: 1) listening for specific detail, 2) recognizing word order pattern, and 3) recognizing cognate.
2. Top down process
In top down process, the listener taps down into background knowledge of the topic, the situation or the context, the type of the text and the language. The background knowledge activates a set of expectation that helps the listeners to interpret what is heard and anticipate what will come next. The top down process include: 1) predicting, 2) identifying the speaker, 3) evaluating the themes, 4) finding the main idea, 5) finding the supporting details, 6) making inference and
14
Wong (2005:4) states that the way of learning listening by focusing on how to get the main idea, the gist of meaning in listening material even when it is clear that the learners have not been to identify may speech sound is often called the top down processing. This approach will help students to identify or find main idea, specific information, inference and vocabulary in order to develop their listening skill. The researcher will focus on top down approach because this approach is appropriate to use to develop their listening comprehension.
2.4Teaching Listening Comprehension
There is much information that we can get by listening, this is why listening is very fundamental in language learning. It is important to understanding what we hear to gain such information. Brown (2001:247) states that in classroom, students always do more listening than other skills like speaking, listening competence is “larger” than speaking competence. It means that listening takes big portion in language learning.
15
According to Swift (2007:18) teaching listening suggest that we need to take a more active approach to improve listening abilities, by focusing on the specific problems that the students have and planning listening activities, which will help to resolve the problem. It means the teacher are expected to able to choose and apply appropriate approaches, method, or teaching aid to develop students’ listening comprehension.
Cited from Christine Switzer’s article on synonym.com about modern methods of
teaching listening skills, there are some methods can be applied to develop students’
listening skill.
a. Interpersonal Activities
An effective way for students to develop better listening skills is through interpersonal activities, such as storytelling and interview. Teacher assigns the students to small groups, and then gives them a particular listening activity to accomplish.
b. Group Activities
16
c. Audio Segments
The usual methods is listening skills through audio segments of radio programs, online podcasts, instructional lectures and other audio messages. Teacher should model this interactive listening process in class with students, and then instruct them to repeat the exercise on their own.
d. Video Segments
Video segments are helpful resources to improve students’ listening skills, including short news, clips, documentary, interview segments, and dramatic and comedic material. As with audio segments, the length of the video segment is depend on the skill level of the students. First, watch the video in silent sound and then discuss it together. Then asking the students to identify what they think will be the content of the segment. Then, watch again with sound, ask students to take notes. After that, teacher asks students to write a summary of the video, or teacher can take time to discuss it.
e. Instructional Tips
17
their skill and confidence level, and then strengthen their confidence by celebrating the ways in which they do improve, no matter how small.
There are many effective methods to teaching listening to increase students listening skill. In this research, the researcher will use video as a teaching aid to develop students’ listening comprehension. The researcher will apply video as teaching media
because video brings benefits such as the authenticity of language, the provision of cultural context, and the existence of visual support and enhancement of motivation.
2.5 Audio Visual Aid
When there are an interaction between learner and his environment, learning process happens. In formal education, the environment can be teacher, students, curriculum, teaching material, media, etc. According to Putri (2011:20), in development of education and technology, a teacher is expected to be able to use teaching media provided by the school/institution. It means that teachers are required to have knowledge and ability to use media in teaching learning process.
The use of media or teaching aid has an impact in teaching learning process. Media as teaching aids also determine the success of students’ learning process. According to Arsyad (2006), there are many positive effects gave by the use of media in teaching learning process, such as:
18
2) Increasing students’ motivation in learning,
3) Creating a interactive classroom,
4) Facilitating students to understand teacher’s instruction,
5) Reinforcing students’ understanding toward the context of lesson.
Teaching media that are used to deliver a lesson can be book, tape recorder, video, film, slide, pictures, graphics, computer, and many more. Thus, media are effective equipment that delivers a lesson to the students and it motivates students and help students to learn.
Teaching aids are divided into two kinds, they are visual aids and audio-visual aids. Commonly, these teaching aids used to help teacher in teaching learning process. Visual aid concerns with the learner’s sight sense. In the other hand, audio-visual aid
is combination of learner’s sight and hearing. Therefore, these teaching aid both visual and audio-visual aids are effective in teaching listening skill.
Arsyad (2002) states that visual and verbal stimulus cause better result of learning. Visual stimulus can give positive effect in learning dealing with memorization, recall and association. On the other hand, verbal stimulus can give positive effect in learning dealing with sequential memorization. Double-sense learning will make students learn better rather than they use audio and visual sense separately.
19
2.6 Video
Video is one of audio-visual aid that concerns with learner’s sight and hearing sense and can be used in language teaching. In teaching listening, video provides visual stimuli that can lead to and generate prediction, speculation, and chance to active students’ background schemata. Audio-visual equipment used by teacher to transfer the concept, idea and experiences in order to make students understand the material taught. Sadiman (2005:29) defines that video is storage of pictures and sound information system where audio-visual signal is not only recorded on magnetic tape but also on disk. Video disk allows the teacher to do: 1) reverse and fast forward, 2) speed or slow motion, upward or backward, 3) single frame, upward or backward, 4)
speech search facility and 5) stereo sound.
Furthermore, Gill (1984) in Putri (2011) cited that video used in language classroom should possess the following features:
Freeze-frame device (still frame facility)
This feature is effective for: 1) prediction of language used in the frozen sequence of language that will be used or action that occurs after the frozen sequence, 2) repetition of dialog during the second viewing, 3) discussion of the setting who are involved in the video, where are they. Etc
Memory button
20
mean that the teacher will be able to locate the beginning of an episode quickly and without wasting too much time.
Speed Search Facility (fast picture, shuttle search, sue and review)
The feature allows the teacher to speed through the tape forward and backward at between five and times normal play back speed. The picture remains on the screen while this is taking place and thus this is an extremely helpful facility I locating a point quickly and accurately on the tape.
Remote Control Handset
This allows the teacher to control the video from anywhere in the classroom and is especially useful for group works.
Based on the previous definition, video is a kind of audio-visual technology that consists of pictures and sound information system. In this research, video will be used as media in teaching listening skill.
2.7 Teaching Listening through Video
21
Listening is not only a passive skill; it is also a vital part of language skills that must be mastered by students. Listening comprehension is the process to get and understand the meaning about the topic. Listening comprehension can be developed by using media in teaching learning process, such as video. As explained before, video provides visual and audio stimuli that promote students’ listening comprehension. As Putriani (2013) says that, the use of video is appropriate media to attract the students’attention and the students’ interest in understanding the unknown
words since the teaching language through video makes language more alive and meaningful and helps to bring the real world into the classroom. Teaching listening through is good to be used in classroom because video can stimulate and motivate students’ interest.
2.8 Procedure of Teaching Listening through Video
In developing students’ listening comprehension, the researcher will present the
application of video as media in teaching listening. The aim of the research is to increase students’ listening achievement and students’ motivation.
The procedure of teaching listening comprehension through video is conducted as following steps:
Pre activity
Teacher greets the students, checks students’ attendance list, and prepares
22
Teacher brainstorms the students by asking question based to the material
Teacher asks several questions to stimulate students’ background knowledge
Teacher tells the material will be learned (News Items)
While Activities
Teacher explains about news items text (definition, social function, example)
Teacher views video without the sound.
Teacher asks students to make prediction about the video
Teacher divides students into 5-6 groups
Teacher plays the video
Teacher asks students to make a notes about the specific information based
the video
Teacher gives question related to the video and asks students to discuss
in-group.
Teacher plays the video again with subtitle and asks the students to fill the
blank in video subtitle
Teacher asks students to presents their work
Teacher evaluate the students’ work
Post Activities
Teacher discusses the students’ work and asks for students’ answer. If there
23
Teacher asks the students about material that have been taught
Teacher concludes the material and closes the meeting
2.9 The Advantages and Disadvantages
There are some advantages and disadvantages of using video in teaching listening.
1. Advantages
Video brings language in the context of life in realistic setting to the
classroom
Video is an excellent medium for use in language classroom. It is so close to
language reality containing visual as well as audible cues. (Karlina, 2010:33)
Video generates students’ excitement then increase students’ motivation.
Video provides practice in listening comprehension.
Video help students increase their comprehension skills. Visual media makes
students can guess meaning of new words and meaning. (Putriani, 2013:23)
Video offers foreign language learners a chance to improve their ability to
understand comprehensible input. (Canning Wilson (2000)
Video helps learner in improving comprehensible and aid in the retention of
information (Canning-Wilson 2002:2)
Video can be controlled present to a group of students, individuals or
24
Video can increase awareness of target cultures, and strengthen audio visual
linguistic perception simultaneously (Canning-Wilson 2000:2) 2. Disadvantages
According to Putriani (2013:23), the use of video has some disadvantages.
It takes time for the teacher to preview authentic video.
It is difficult to and selects videos and then to prepare activities for learners.
The use of video depends on the electrical problem.
Video may be boring if overused and do not foster interaction among students
and between students and teacher if the teacher does allows the video control.
Video cannot be conducted in the schools that have not been facilitated
language laboratory of computer laboratory.
2.10 Theoretical Assumption
25
Therefore, the researcher decides to choose video as a teaching media. The researcher assumes that the use of video is expected can help students to understand the meaning of the text easily and create good atmosphere in the classroom. The researcher hopes the students are able to improve their listening comprehension.
2.11Hypothesis
Based on the theoretical assumption, the researcher formulates the hypothesis as follow:
III. RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter explains the design of the research, population and sample, variables, data collecting technique, procedure of the research, research instrument, criteria of a good test, data analysis, hypothesis testing.
3.1. Research Design
The researcher conducted this research by using One Group Pretest-Posttest Design. The researcher intends to find out the significant increase of students’ listening comprehension achievement before and after using video as teaching media. In this research, the researcher chooses one class as an experimental class. Probability sampling is applied to select the experimental class. Based on the design, the students are given a pretest to measure students’ listening ability before the researcher gives treatments and post-test. Thus, the formula of the research design is showed as below:
27
T1 = Pre-test
X = Treatment (using video as teaching media) T2 = Post-test
(Setiyadi, 2006: 133)
3.2.Population and Sample
The population of this research is the second grade students of SMAN 1 Pringsewu. There are six classes in the second grade of SMAN 1 Pringsewu. The researcher takes one class in this research, that class is 4 D IPA. The sample class is selected by using random sampling technique through lottery. That class is consisting of around 35 students are taken as the sample of research. It is done to avoid subjectivity and to guarantee every second grade class get the same opportunity. The experimental (4 D IPA) class are given pre-test, treatment (teaching listening through video), and post-test to measure students’ listening comprehension.
3.3.Variables
28
is what the researcher measure. The independent variable is the use of video as teaching media because it affects dependent variable and it can be selected and be manipulated by the researcher.
3.4.Data Collecting Technique
Data collecting technique means the way to get the data of the research, which the researcher needs in research. The data of this research are the students’ listening comprehension achievement before treatment (pre-test) and after treatment (post-test), and students’ data from interview. The data are used to find the increase of student’s listening comprehension. Meanwhile interview is given to the students’ to find out the students’ problem in listening comprehension through video. For more
details, the ways of data collecting are explained below:
Try Out
29
Pre-test
Pre test is the test conducted before the researcher gives treatment to the students. The purpose is to measure students’ basic listening comprehension achievement. This test is conducted to the experimental class (4 D IPA). It contains 30 items of multiple choices (A, B, C, D, and E) that were revised.In this test, the researcher does not use video as the media. The researcher uses audio source in the test.
Post-test
Post-test is the test that is conducted after the treatments are given to the students. It measures students’ listening comprehension achievement after being taught by
using video. The post-test and pre-test are used the same test that consists of 30 items of multiple choices that were revised. But the order of the question and the distracters are changed from those in the pre-test. The post-test has same difficulty as the pre-test. The researcher uses video source.
Interview
In order to find out students’ problems in listening comprehension through video,
the reseacher conducts interview. Interview is given after post test to the students who get low score in listening comprehension. The reseacher asks some questions related to students’ difficulties in listening comprehension.
3.5.Procedures of the Research
30
The population of the research is the second grade students of SMAN 1 Pringsewu. The experimental class (4 D IPA) is selected randomly. The researcher uses two classes, as try-out class (4 C IPA) and experimental class (4 D IPA).
2. Administering Try Out test to know the quality of the test
Try Out test is multiple choices test (30 items). It is held to measure index of difficulty (FV) and discrimination index (D) to find out the reliability and validity of the test. The purpose of try out test is to revise the test and create the better quality of the test.
3. Preparing the material
The researcher uses video as teaching media. The materials are taken by the researcher from http://www.reuters.com/video (News report items). The format videos are flash video/FLV in form of news report. It is played by using media player that are used in the class to present the materials. There are various topics were presented.
4. Administering the pre-test and finding the result
Pre-test is conducted before the treatment to see the students’ listening comprehension. It is conducted without using video as teaching media. The numbers of the items are 30 items of multiple choices (A, B, C, D, and E).
5. Giving Treatment
31
6. Administering the post-test
Post-test is given after the treatment to find out the increase of students’ listening comprehension after using video as media. The result of the post-test are compared with the result of pre-test. The test consists of 30 items of multiple choices. The researcher uses video source in the test.
7. Conducting Interview
Interview is conducted by the reseacher is to find out students’ problems. It is
given to 10 students who get low score after post test. 8. Analyzing the result
After pre-test, treatment, and post-test, and giving interview, the researcher analyzes the data of pre-test and post-test by using T-test. It is used to know whether the use of video increase students’ listening comprehension. The data is calculated through SPSS (Statistical Package for Social Science).
9. Concluding the results
After analyzing the result of pre-test, post-test, and interview, the conclusion is explained based on the result data.
10. Reporting the results
32
3.6.Research Instrument
The instruments of the research are a listening comprehension test used for try out, pretest, post-test, and interview. The numbers of the items is 30 items of multiple choices. In first pre test, the students are given a listening comprehension test which use audio source as media. The researcher converts the video in FLV format to mp3 audio format using video converter. And in post-test the researcher uses audio visual source (video) in the test. This researcher uses interview is given to the students’ to find out the students’ problem in listening comprehension through video.
Theinteview is focus on the students’ problem in listening comprehension through video.
3.7.Criteria of a Good Test
There are some criteria should be considered to know whether the test is good or not. They are: validity (content and construct validity), reliability, level of difficulty and discrimination power.
3.7.1 Validity
33
Construct validity is concerned with whether the test is actually in line with the theory of what it means to know the language that is being measured. It is capable of measuring certain specific characteristics in accordance with theory of language behavior and learning. It is the existence of certain learning theories or constructs underlying the acquisition of abilities and skills.
Content Validity is concerned with whether the test is sufficiently representative and comprehensive for the test. It depends on careful analysis of the language being tested. It should contain a representative sample of the course; the relationship between the test items and the course objective always being apparent. The test relates to the materials that have been taught to the students. The items of the test are decided by the expert jugdement (English teacher or lecturer). It is done to measure the degree of agreement.
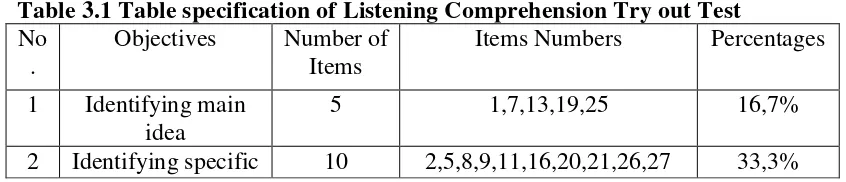
In comprehending the massage, listening and reading have the same purpose. Listening comprehends the oral messages and reading understands the written or printed messages. The aspects of listening comprehension in the instrument are determining the main idea, finding specific information, identifying reference, inference, and vocabulary. Here, the specification table of listening comprehension tests.
Table 3.1 Table specification of Listening Comprehension Try out Test No
34 candidates on different occasion (with no language practice). To measure coefficient of reliability between even and odd group, researcher uses Pearson Product Moment formula. The formula is as follows:
� = xy
x2 �2
rl : Coefficient of reliability between odd and even number items x : Odd number
35
To know the coefficient correlation of whole items, Spearmen Brown’s prophecy
formula is used. The formula is as follows:
� = 2�
1 +�
rk : the reliability of the test
rl : the reliability of the half test
(Hatch and Farhady: 1982: 246)
The criteria of reliability are:
0.80 – 1.00 : very high
0.50 – 0.79 : moderate
0.00 – 0.49 : low
(Hatch and Farhady: 1982: 247)
3.7.3 Index of Difficulty
Index of difficulty is related to how easy of difficult the item is from point of view of the students who takes the test. Index of difficulty is generally expressed as the fraction (percentage) of the students who answered correctly. The formula is:
FV=�
36
FV : Index of difficulty
R : the number of students who answer correctly N : the total number of students following the test
The criteria are:
<0.30 = difficult 0.30 - 0.70 = average >0.70 = easy
3.7.4 Discrimination Power
Discrimination Power refers to the extent to which the item differentiates between high and low level students on the test. Discrimination power (D) indicates the extent to which the item discriminates between the testees, separating the more able testees from the less able. It tells us whether the students perform well overall test tended to do well or badly on each item of the test.
The formula:
��= � − �
1 2 �
DP : Discrimination Power
37
The criteria are: 0.00-0.20 = poor 0.21-0.40 = satisfactory 0.41-0.70 = good 0.71-1.00 = excellent
(Negative) = bad items (should be omitted)
3.8.Data Analysis 3.8.1.Test
The researcher analyzes the data statistically using repeated measure t-test. Because this research compares 5 aspects of listening and only takes one class for experimental class. It is used statistical test for comparison of more than two means in order to analyze how significant the improvement of the students’ aspects of listening comprehension. The researcher uses these following procedures:
1. Scoring the pre-test and post-test
2. Tabulating the result of the test and calculating the mean of pre-test and post-test
38
3.9.Hypothesis Testing
The researcher used hypothesis testing of this research is to prove whether the hypothesis proposed in this research was accepted or rejected. The hypothesis is “There is a significant increase of the aspects of listening after being taught through
video at the second year of SMA Negeri 1 Pringsewu.” The hypothesis is statistically tested using repeated measure t-test through computing with SPSS. It is used to draw the conclusion in significant level of 0.05 (p<0.05). It means that the probability of error in the hypothesis is only about 5%.
3.10. Schedule of the Research
No Day/Date Activities
1 Monday, May 5th, 2014 Observation
2 Wednesday, May 7th, 2014 Administering try out test in 4C IPA 3 Monday, May 12th, 2014 Administering pre test in 4D IPA 4 Tuesday, May 13th, 2014 First treatment in 4D IPA
5 Thursday, May 15th, 2014 Second treatment in 4D IPA 6 Monday, May 19th, 2014 Third treatment in 4D IPA
V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
This chapter describes the conclusion of the research and suggestion for other researchers and English teachers. It explains the result of the research in improving students’ listening comprehension through video as media.
5.1. Conclusions
Based on the result of data analysis in chapter IV, the researcher draws a conclusion as follow:
68
students’ listening comprehension achievement after being taught trough
video. So, teaching listening through video as media is appropriate and effective to be used in improving students’ listening comprehension
achievement.
According to the analysis of the result of pretest and posttest in listening aspects, it showed the improvement of each aspect. The highest improvement was main idea (20.00), which increased from 29.14 up to 49.14. Meanwhile, the lowest improvement was reference (5.14). The results of SPSS analysis showed that the aspects of listening significantly increased after treatments were main idea, specific information, and vocabulary. And the aspects of listening didn’t significantly increase significantly after treatments were reference and inference. The results of analysis of all aspects of listening can be compared each other. Main idea has t-value was higher than t-table (4.381>2032) and Significance 2 tailed (p=0.000, p<0.05). In Specific information, t-value was higher than t-table (3.067>2032) and Significance 2 tailed (p=0.004, p<0.05). Reference, t-value was lower than t-table (1.717<2.032) than p=0.095 (p>0.05). Inference has t-value was lower than t-table (1.974<2032). And Sig. (2-tailed) or p=0.057. And vocabulary point out that value was higher than t-table (3.482>2032) and p was lower than 0.05.
69
researcher found out that the most problems and difficulties faced by students who got low score were pronunciation, vocabulary, speed of the speech, speech/accent of the native speaker.
5.2. Suggestions
Referring to the results of and discussion, suggestions are presented as follow:
1. Based on the results of data analysis in listening aspects, the lowest aspect of listening was main idea and the lowest improvement was reference. And the one aspect of listening didn’t increase significantly was inference. The
researcher suggests that the teacher should give students more practice in identifying the main idea, reference, and inference.
2. Based on the results of interview, the one of students’ difficulties in listening comprehension was vocabulary. So, teacher should pay attention to develop students’ vocabulary. Giving more practice to increase students’ vocabulary
and giving the students practice to recognize the spoken words.
3. English teachers should prepare the video appropriately. Teacher should choose news video which no longer than 2 minutes. The speed of the speaker should not be too fast. Teacher can reduce the speed of the video by using software. The topic should be interesting for students and appropriate with curriculum.
70
REFERENCES
Anderson, A. and Lynch, T. 1988. Language Teaching: A Scheme for Teacher Education. New York: Oxford University Press
Arsyad, A. 2006. Media Pembelajaran. Jakarta. PT BumiAksara.
Bilokcuoglu, H. 2014. A Schematic Approach to Teaching Listening Comprehension. EUL Journal of Social Sciences (Vol 1). (Online),
(en.lau.edu.tr/euljss/si515.pdf. Retrieved on 20 August 2014)
Brown , HD. 2001. Teaching by Principles: An Interactive Approach to Language
Pedagogy, Second Edition. New York: Longman Inc.
Cain, K. and Oakhill, J. V., etc. 2001. Comprehension skill, inference-making ability, and their relation to knowledge. Memory & Cognition. Vol 29 (6), 850-859.(Online),
(http://www.researchgate.net/publication/11639427_Comprehension_skill_inf erence
making_ability_and_their_relation_to_knowledge/links/0046351deabfbb8526 000000. Retrieved on 20 August 2014)
Canning, C. 2000. Practical Aspects of Using Video in the foreign Language Clasroom. The Internet TESL Journal. (Online),
(http://iteslj.org/Articles/Canning-Video.html. Retrieved on 31 January 2014) Danaher, M. 1994. Summary Report of a Study Investigating Issue of Concern to the Effective Teaching of Listening Skills in Beginning Students of Japanese as a Foreign language (JFL). QJER QR 10 Queensland
Researcher.http://education.curtin.edu.au/ieer/qjer/qr10/Danaher.html Hamalik, O. 1994. Media Pendidikan. Bandung: Penerbit PT Citra AdityaBakti Hatch, E. and Farhady. 1982. Research Design and Statistics for Applied Linguistics.
London: New Bury House Production, Inc.
Hedge, T. 2000. Teaching and Learning in the Language Classroom. New York: Oxford University Press.
71
James, R. 2006. Listening Comprehension. Reading Success Lab. Ju
Juan, E.U. & Flor, A.M. (2006), Current trends in the development and teaching of the four skills, Berlin: Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KB.
Karlina, L. 2010. A Comparative Study of Listening Comprehension Achievement between Students who are Taught by Using Video and Those Taught by Using
Tape Recorder at SMA N 1 Sukoharjo. Unpublished Script. Lampung
University Bandar Lampung.
Kathleen S.M.Chu. 1986. Teaching Listening with Video. BBC British Council Lukong. 1998.Concept of Listening.Retrieved on 31 January 2014 from
www.schoolar.google.comceptoflistening.com
Napa. P, A. 1991.Vocabulary Development Skill. Yogyakarta. Kanisius Nunan, D. 2002. Listening in Language Learning Methodology in Language
Teaching: An Anthology of Current Practice by Jack C. Richard. New York Cambridge University Press.
Putri, W. U. 2011.The Implementation of Video Movie in Listening Comprehension Class at the First Year Students of SMA YP Unila Bandar Lampung.
Unpublished Script. Lampung University Bandar Lampung. Putriani, D. 2013. The Use of Video Movie to Improve Student’s Listening
Comprehension Achievement at The First Year Student’s of SMAN 1 Natar
Lampung Selatan. Lampung University Bandar Lampung.
Rahayu, I. 2007. The Use of Animation Movie to Improve Students Listening Skill of Narrative Text at the First Year of SMA N 1 Kotagajah. Lampung University Bandar Lampung
Rost, M. 1994. Introducing Listening London: Penguin.
Sadiman. A. 2005. Media Pendidikan: Pengertian, Pengembangan, dan Pemanfaatan. Jakarta: Grafindo Pers.
Schacter, D. 2011. PSYCHOLOGY. USA: Catherine Woods.
Setiyadi, Ag. B. 2006. Metode Penelitian untuk Pengajaraan Bahasa Asing. Yogyakarta; Graha Ilmu.
Swift, S. 2007. An English Language Teaching
72
Switzer , C. Modern Methods of Teaching Listening Skill. Demand Media. http://classroom.synonym.com/modern-methods-teaching-listening-skills-2458.html
Underwood, M. (1994).Teaching listening. Longman Handbooks for Language
Teachers. New York: Longman Group Ltd.
Wong, R. 2005. Second Language Listening: Theory and Practice. Electronic Journal of Foreign Language Teaching.Vol 3 (1).
http://www.shkamiski.com/slasses/handouts/listening.html