Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Nita Sofiani
- Pengajar:
- Dr. M. J Dewiyani
- Tan Amelia, S.Kom, M.MT
- Anjik Sukmaaji, S. Kom., M.Eng
- Dr. Jusak
- Pantjawati Sudarmaningtyas, S.Kom, OCA
- Sekolah: Sekolah Tinggi Manajemen Informatika & Teknik Komputer
- Mata Pelajaran: Sistem Informasi
- Topik: Rancang Bangun Sistem Penelusuran Minat Dengan Tes The Rothwell Miller Interest Blank (RMIB) Berbasis Web
- Tipe: tugas akhir
- Tahun: 2012
- Kota: Surabaya
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. Introduction
The introduction outlines the significance of aligning educational pursuits with individual interests and talents. It emphasizes that students often choose fields of study based on external pressures rather than personal inclinations, leading to misalignment between their education and career aspirations. The Rothwell Miller Interest Blank (RMIB) is introduced as a tool to measure individual interests in relation to various professions. The development of a web-based application aims to facilitate interest assessments, making it accessible for clients regardless of geographical constraints, thereby enhancing the counseling process.
II. Theoretical Framework
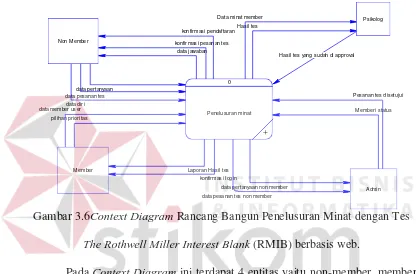
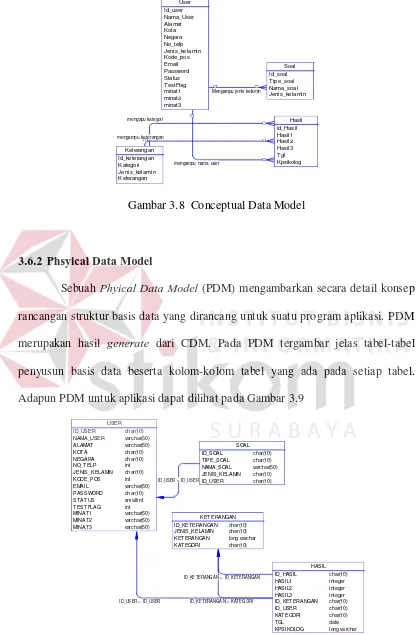
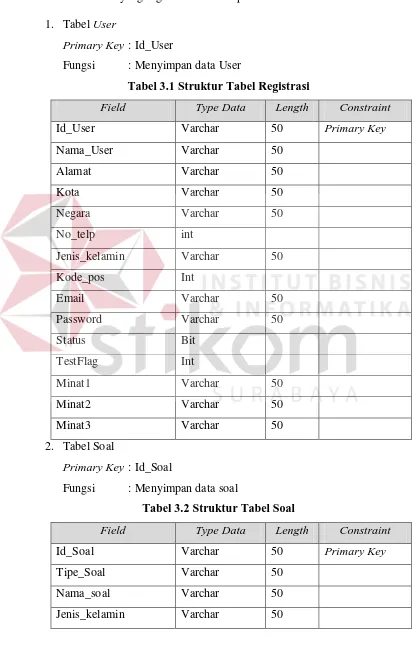
This section discusses fundamental theories related to information systems and their application in developing the RMIB-based interest exploration system. It covers definitions of systems and information systems, emphasizing their role in organizational decision-making. Additionally, it introduces data modeling concepts such as Entity Relationship Diagrams (ERD) and Data Flow Diagrams (DFD), which are crucial for understanding the system’s architecture and data management. The theoretical underpinnings provide a solid foundation for the system's design and implementation.
2.1 Basic Concepts of Information Systems
This subsection defines systems and information systems, highlighting their components and interactions. It explains how information systems support decision-making processes in organizations by integrating data, hardware, and software.
2.2 Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD)
ERDs are introduced as tools for data modeling that help visualize relationships between data entities. This section explains the components of ERDs, such as entities, attributes, and relationships, which are vital for database design.
2.3 Data Flow Diagram (DFD)
DFDs are discussed as a means to illustrate how data flows within the system. This subsection details the symbols used in DFDs and the importance of distinguishing between physical and logical representations of data flow.
III. Research Methodology
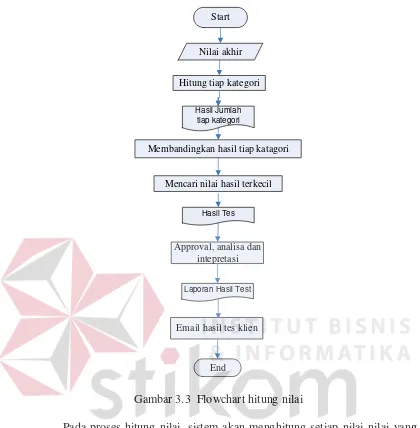
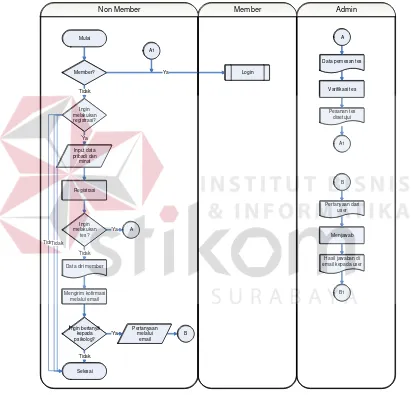
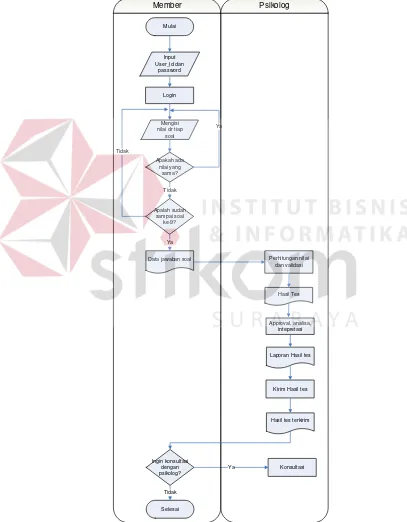
This section outlines the methodology employed in developing the web-based RMIB interest exploration system. It begins with identifying the core problem of assessing individual interests and the limitations of traditional testing methods. The research design includes a detailed analysis of system requirements and the implementation of the RMIB method. A block diagram illustrates the input-process-output model, providing clarity on how the system operates and interacts with users.
3.1 Problem Description
This subsection elaborates on the challenges faced by individuals in identifying their interests and the need for a systematic approach to interest assessment. It emphasizes the importance of aligning personal interests with educational and career choices.
3.2 Problem Analysis
The analysis identifies the single objective of the system: to facilitate interest exploration through the RMIB. It discusses the specific needs and expectations of users, guiding the development process.
3.3 Research Design
A detailed overview of the research design is provided, illustrating the systematic approach taken to develop the RMIB-based system. The block diagram highlights key processes, including user registration, interest assessment, and result interpretation.
IV. Implementation and Evaluation
This section discusses the practical implementation of the web-based RMIB system, detailing the hardware and software requirements necessary for its operation. It provides insights into the user interface design, including various application pages and their functionalities. The evaluation process is outlined, showcasing testing methods to ensure the system meets user needs and operates effectively.
4.1 Implementation
This subsection covers the technical aspects of implementing the system, including necessary hardware and software specifications. It highlights the steps taken to ensure a smooth deployment of the application.
4.2 Explanation of Program Usage
Detailed descriptions of various application pages are provided, including user menus, test pages, and report generation functionalities. This section aims to familiarize users with the system's interface.
4.3 System Testing
The testing phase is elaborated upon, detailing the various test cases conducted to ensure the system's reliability and accuracy. This includes functional testing of application pages and overall system performance.
V. Conclusion
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of the research, emphasizing the importance of the RMIB-based web application in facilitating interest exploration. It discusses the implications for educational practices and career counseling, highlighting how the system can enhance the alignment of students' educational paths with their interests and talents. Recommendations for future improvements and further research directions are also presented.
5.1 Conclusion
This subsection encapsulates the overall contributions of the project, reiterating the significance of the RMIB in personal and educational contexts.
5.2 Suggestions
Future recommendations for enhancing the application and expanding its reach to a broader audience are discussed, aiming to improve user experience and system functionality.