i ABSTRACT
INCREASING STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION ACHIEVEMENT THROUGH THINK PAIR SHARE TECHNIQUE IN PROCEDURE TEXT AT THE FIRST GRADE OF SMA N 1 BANDAR
SRIBHAWONO
By
MIFTACHUR ROHIBAH
This research was conducted in SMA N 1 Bandar Sribhawono, East Lampung that the students still got low scores in reading comprehension test. This quantitative research was intended to find out whether there is a significant difference between the score of students’ reading comprehension achievement before and after being taught through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text, to know the most increase of five reading comprehension aspects, and to know the students’ reactions toward the teaching technique.
The sample of this research was chosen randomly. Class X6 was chosen as the tryout class and class X1 was chosen as the experimental class. The data was collected through tryout, pre-test, treatments and post-test. This research used one group pre-test and post-test test design. The treatment was conducted three times. The data was analyzing by comparing the mean score of pre-test and post-test using Repeated Measure T-test.
Based on the calculation of the t-test, the result showed that the mean score of
iv
CURRICULUM VITAE
v
DEDICATION
This script is fully dedicated to
my parents, Mujito and the late Umu Fadilah, my brother and my sisters, Ms. Sumiyati,
vi MOTTO
There can be miracle when you believe, though hope is frail it’s hard to kill, who
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Praise is for Allah SWT the Almighty God, for blessing the writer with health to finish this script. This script, entitled “Increasing Students’ Reading
Comprehension Achievement through Think Pair Share Technique in Procedure Text at the First Grade of SMA N 1 Bandar Sribhawono”, is presented to the Language and Arts Education Department at the Teachers Training and Education Faculty, Lampung University as a partial fulfilment of the requirements for S-1 degree in English Education.
Among many individuals who gave generous suggestion for improving this script, first of all the writer would like to express her sincere gratitude and respect to her first advisor, Dra. Editha Gloria Simanjuntak, and also her second advisor, Drs. Sudirman, M.Pd., who had contributed and given their evaluation, comments, suggestion during the completion of this script. The writer also would like to express her deepest gratitude and respect to Drs. Hery Yufrizal, M.A., Ph.D., as her examiner for his encouragement and contribution during the seminar until this script is finished.
viii
SMA N 1 Bandar Sribhawono, especially classes X1 and X6 for their nice cooperation during the research.
Most importantly her special gratitude should go to her beloved father, Mujito who always gives his prayer, love and support for every path the writer chose and her beloved mother, the late Umu Fadilah. Her thank is also due to Ms. Sumiyati, her brother, Nurcholis, her sisters Chusnul Chotimah and Choirul Muslimah for their encouragements.
The writer also would like to thank to her beloved companions English ’09, especially Dresti, Dwi (Jegeg), Imeh, Fera, Jessy, Yusni, Arini, Dea, Tri, Mitha, Widi, Eva, Fani and Kadek. Thank you so much for being such a great companion along the way in finishing this script. Moreover, she must extend her gratitude for love and supports to Hendri Firmanto and her beloved friends in boarding-house: Isti, Sriwi, Maul, Mb.Umi, Mb.Dedeh, Rina, Nuli and Anjar. Hopefully, this script would give a positive contribution to the educational development or to those who want to carry out further research.
Bandar Lampung, April 2013
ix 2.1 Concept of Reading and Reading Comprehension ... 7
2.2 Reading Comprehension Aspects ... 10
2.3 Concept of Cooperative Learning... 11
2.4 Nature of Think Pair Share Technique ... 13
2.5 Concept of Procedure Text ... 16
2.6 Procedure of Teaching Reading ... 18
2.7 Advantages and Disadvantages ... 20
2.8 Theoretical Assumption ... 21
2.9 Hypothesis ... 22
III. RESEARCH METHOD 3.1 Research Design ... 23
3.2 Population and Sample ... 24
3.3 Data Collecting Technique ... 25
x
3.8.4 Discrimination Power ... 35
3.8 Data Analysis ... 36
4.1.5 The Increase of Each Reading Comprehension Aspects ... 48
4.1.6 The Students’ Responses toward The Teaching Learning Reading Comprehension through TPS ... 49
4.2 Discussion of Findings ... 50
V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION 5.1 Conclusions ... 60
5.2 Suggestions ... 61
REFERENCES ... 63
xi
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
1. The Scoring System of Questionnaire ... 30
2. The Students’ Responses Data ... 30
3. The Students’ Responses Percentage ... 31
4. Specification Table of Tryout Test ... 31
5. Specification of Pre-test ... 42
6. Distribution Frequency of Pre-test Scores in Experimental Class ... 43
7. Statistics Computation of Pre-test Score ... 43
8. Specification of Post-test ... 44
9. Distribution Frequency of Post-test Scores in Experimental Class ... 44
10. Statistics Computation of Post-test Score ... 45
11. The Increase of the Students’ Comprehension Achievement ... 46
xii
7. The Reliability of the Data Collecting Instrument ... 80
8. The Difficulty Level and Discrimination Power of Data Collecting Instrument ... 81
9. Pretest ... 82
10. Posttest ... 87
11. The Students' Score of Experimental Class ... 98
12. The Computation of Distribution Frequency ... 99
13. Table of Frequency of Pre-test ... 100
14. Table of Frequency of Post-test ... 101
15. Increases of Students’ Reading Comprehension ... 102
16. T-Table ... 103
17. The Students Category and Students Grouping ... 104
18. Lesson Plan I ... 106
19. Lesson Plan II ... 111
20. Lesson Plan III ... 116
21. Students’ (in pair) Score ... 121
22. Questionnaire ... 122
23. Data Analyzing Students’ Questionnaire ... 123
24. Students’ Tryout Scores (The Highest and The Lowest) ... 124
25. Students’ Pre-Test Scores (The Highest and The Lowest) ... 125
26. Students’ Post-Test Scores (The Highest and The Lowest) ... 126
27. Students’ Treatments 1 Answer ... 127
28. Students’ Treatments 2 Answer ... 128
29. Students’ Treatments 3 Answer ... 129
30. Students’ Questionnaire ... 130
31. Surat Izin Penelitian ... 132
I. INTRODUCTION
This chapter describes the background of the problem that explains why the research is administered. It also consists of formulation of the problem, objectives of the research, uses of the research, scope of the research and definition of terms.
1.1Background of the Problem
Learning English cannot be separated from four language skills: listening,
speaking, reading and writing. Those are stated in standard competence and basic competence in syllabus of KTSP curriculum. As we know that listening skill refers to the ability to catch the message or meaning through audio or hearing; reading skill refers to the ability to understand or get the meaning of written or printed words; speaking demands the ability to use the language in the oral form; and writing skill refers to the ability of putting information or message in a piece of paper or in appropriate form. Thus, those four language skills are integrated one another which the students have learnt from elementary level up to senior high school level.
In Indonesia, reading skill is expected to be acquired by all of the education levels. It is important to carry reading activity as standard competence of English course. Reading activity that focuses on understanding context and getting new information of texts is reading comprehension. According to BSNP, 2011 the highest level of reading activity is carried out in senior high school. Moreover it is stated in competence standard of KTSP curriculum that students are expected to master reading comprehension of short functional text and short essay in the form of narrative, descriptive, and news item in daily context. Students of senior high school are expected to comprehend reading of some English texts.
Commonly, people read for general comprehension, whether for information or for pleasure, the objective is not to memorize most of specific detail but to have a good comprehension of the main ideas and to relate those ideas to background knowledge as appropriate.
Based on researcher’s pre observation at SMA N 1 Bandar Sribhawono, the researcher found out that the students’ reading comprehension test scores which are mostly stated lower than the minimal mastery criterion (KKM) of that school which requires the students getting score 75. It is caused by some problems, such as the technique of teaching. The students tend to be passive in reading class if the technique is dominated by the teacher (teacher-centered).
According to the researcher, to overcome the students’ reading comprehension
the opportunity to think and discuss in comprehending the text. The principle that is learning in group will increase their learning process than self learning. In doing the task, the students will get better in comprehending the text if they share their result with their friends. Further, Think Pair Share (TPS) can be used to big class, usually it consists of 30 to 40 students. Think Pair Share (TPS) is considered to be applied in this research because it is one of the techniques that give students a chance to learn cooperatively.
Reading is an activity that has purpose. The reading purpose depends on the information that the students need. Reading also has a purpose to find out the appropriate strategy to reading comprehension.
This research investigates the role of technique of teaching in promoting students’ reading comprehension ability. The main reason of conducting this research is based on assumption that reading comprehension achievement is one important component in second language proficiency.
1.2Formulation of the Problem
Based on the background of the problem mentioned previously, the formulations of the problem are:
1. Is there a significant difference between the score of the students’ reading comprehension achievement before and after being taught through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text?
2. Which aspect is the most increase of reading comprehension aspects? 3. What are the students’ reactions after joining Think Pair Share technique?
1.3 Objective of the Research
The objectives of this research are:
1. To know whether there is a significant difference between the score of the students’ reading comprehension achievement before and after being taught through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text.
2. To know the most increase of reading comprehension aspects.
3. To know the students’ reactions after joining Think Pair Share technique.
1.4Uses of the Research
The uses of this research are:
2. Practically, to inform the readers, English teachers, language researchers, other practicians, etc, how significant the difference between the score of the students’ reading comprehension achievement before and after being taught through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text, in order to develop English teaching technique further.
1.5Scope of the Research
This research is a quantitative research which was conducted by giving the pre-test and post-pre-test to help the students increase their reading comprehension achievement through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text. This research was focused on five reading aspects, they are determining main idea, finding specific information, finding reference, finding inference and understanding vocabulary. The material was given in several procedure texts based on KTSP curriculum of senior high school, which are considered to have suitable
vocabulary and grammar for their level. The data was collected from the students of the first grade students of SMA N 1 Bandar Sribhawono.
1.6Definition of Terms
The definition of terms are:
2. Reading comprehension means extracting the required information from the text as efficiently as possible (Grellet 1981).
3. Cooperative learning is variety of teaching methods in which students work in small groups to help each other learn academic content (Slavin, 1995: 20).
4. Think Pair Share is summarization strategy that can be used in any content area before, during and after a lesson. The activity involves three basic steps, they are thinking, pairing and sharing (Lyman, 1981).
II. FRAME OF THEORIES
This chapter elaborates the concepts that are related to the research, including concept of reading and reading comprehension, reading comprehension aspects, concept of cooperative learning, nature of Think Pair Share technique, concept of procedure text and related researches in increasing students’ reading
comprehension achievement through Think Pair Share technique.
2.1 Concept of Reading and Reading Comprehension
The meaning of „read’ is look at and understand something written or printed
(Oxford dictionary). In other words, reading can be defined as an activity of
understanding something written. Cameron (2001) in Noviani (2012) said that reading is actually about understanding not only understand the word or code but also the message is being conveyed by the text. It means that when someone reading, he not only understand the word, but also understand the message or main point of the text.
personal meaning to understand what they read. The meaning is not only based on the dictionary.
Mchorter (1989: 212) states that reading is a way of taking new ideas and
identifying information to be learned. It means that, when one is reading a text, he may find new things that he has not known yet. He may also find information that will help him learn something. In this case, his knowledge will certainly be better than before.
Just and Carpenter (1987), as Bernhardt, (1991) in Suparman (2007) include several factors in their definition of reading, they are:
1) What information in the text starts the process 2) How long the process takes
3) What information was used during the process
4) What likely sources of comprehension difficulties exist 5) What the reader has learned when the process is finished
“Reading may sometimes entails „comprehension’ and sometimes not …” (Smith,
Grellet (1981) states that reading comprehension means extracting the required information from the text as efficiently as possible. This view implies that a competent reader should first determine his purpose in reading e.g. when looking at a notice board to see if there is an advertisement for a particular type of
accommodation, he will quickly reject the irrelevant information and find only what he is looking for. In the case of reading a scientific article, it is not enough to understand the main point of the text; more detailed comprehension is necessary. So one should know what and why reads.
The first point to be made about the reading process is reading comprehension (Simanjuntak, 1984: 4). Dallman (1982: 23) says that reading is more than
knowing what each letter of alphabet stands for, reading involves more than words recognition; that comprehension is essential of reading, that without
comprehension no reading takes place.
Moreover, Simanjuntak (1988: 4) says that comprehension is always directed and controlled by the needs and the purposes of individual. So, reading
comprehension is an activity that has purpose. The reader read the text, because they want to know what they will find in the text.
Bernhardt (1991) in Suparman (2007) argues that in a cognitive perspective on reading, there are two essential factors of comprehension, that is, (1) “the
From the explanation above, we can conclude that reading comprehension is a process that occurs in reading activity. The measurement of reading
comprehension is when the students can understand, interpret, and answer the questions of the text given.
2.2 Reading Comprehension Aspects
There are five reading aspects (Nuttal: 1985) which help the students to comprehend the English text well, they are:
1. Main Idea
Main idea is called the topic sentence. It tells what the rest paragraph is about. In some paragraphs, the main idea is not explicitly stated in any one sentence. It is left to the reader to infer or reason out. So, main idea is the very important idea that the author develops throughout the paragraph.
2. Specific Information
Specific information or supporting sentence develops the topic sentence by giving definitions, examples, facts, an incidents, comparison, analogy, cause and effect statistics and quotation.
3. References
4. Inference
Inference is an educational guess or prediction about something unknown based on available facts and information. It is the logical connection that the reader draw between his observes or known and what he does not know.
5. Vocabulary
Vocabulary is the stock of word used by people or even person.
Concerning with those statements indeed vocabulary is fundamental for everyone who wants to speak or to produce utterances for reading.
2.3 Concept of Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning is one strategy for group instruction which is under the learner-centered approach (Brown, 2001: 47). There are some definitions of cooperative learning according to some experts of cooperative learning. Johnson and Johnson (1992) defined cooperative learning as a process of working in groups of two or five members in which “students work together to maximize
their own and each other’s learning. Slavin (1995: 20) stated that cooperative learning is a variety of teaching methods in which students work in small groups to help each other learn academic content. Then, he explained that in cooperative learning, students are hoped to help each other, discuss and argue with one another, asses each others’ current knowledge and fill in gaps in each others’
Lie (2004: 31) stated that cooperative learning is a group working where the teacher is only as a facilitator. It means that, students take a role important in the class. Students have to be active and if they do not know about something, they can ask to the facilitator. He also stated that not all of group work can be regarded as cooperative learning. It is not cooperative learning if students sit together in groups and work on problems individually and let one person do all the work.
According to Johnson, Johnson & Holubec (1993) cooperative learning should fulfill five principles. They are:
1. Positive Interdependence
Students perceive that they need each other in order to complete the group's task ("sink or swim together"). It means that one can not succeed unless everyone succeeds.
2. Face-to-Face Interaction
Students promote each other's learning by helping, sharing, and encouraging efforts to learn. Students explain, discuss, and teach what they know to classmates.
3. Individual Accountability
4. Interpersonal And Small Group Skills
Groups cannot function effectively if students do not have and use the needed social skills. In cooperative learning students have to learn how to make an interaction with the others in their group. They also learn how to convey their ideas in their group and it will be demanded special ability.
5. Group Processing
Groups need specific time to discuss how well they are achieving their goals and maintaining effective working relationships among members.
From the explanations above show that students who work in groups should have collaborative skills to achieve the teams’ goal. They also realize that their group
work is more than how to accomplish a task. They have to help each other to understand what they learn. So, there will be less change for students to behave passively.
2.4 Nature of Think Pair Share Technique 1. Concept of Think Pair Share Technique
According to Kagan (1992) some of cooperative learning techniques are Number Head Together (NHT), jigsaw, Students Team Achievement Divisions (STAD), Team Games Tournament (TGT), Team Assisted Individually (TAI), group investigation and Think Pair Share (TPS).
summarization strategy that can be used in any content area before, during, and after a lesson. The activity is consists of three basic steps. During the think stage, the teacher gives a problem or question that related with the lesson. This allows for wait time and helps students control the urge to impulsively shout out the first answer that comes to mind. Then, individuals are paired up and discuss what have they learnt and solve their problem. During this step students may revise or changes the original ideas. For the last step, they share their answer to the rest of the class.
Lie (2002: 57) Think Pair Share is defined as a technique which gives the opportunity to the students to work alone and also in group. It will make the students’ participation increase. Kagan (1992) stated that Think Pair Share is consists of three steps cooperative structure. During the first step, individual think silently about a question given by the teacher. Individual pairs up during the second step and exchange thoughts. In the third step, the pairs share their responses with other pairs, other teams, or the entire groups.
From the descriptions above, it can be concluded that Think Pair Share give the students the opportunity to think individually, discuss their ideas and provides a means for them to see other problem solving methodologies. Thus, Think Pair Share can be tried as one technique in teaching reading comprehension.
2. Team Formation in Think Pair Share Technique
Informal groups are often used to supplement lectures for a moment and may change everyday. On the contrary, in formal formation, students work with the same students for a longer period of time, sometimes for an entire semester. A formal formation, for instance, the teacher assigns groups by homogenous or heterogeneous grouping, random grouping, and interest grouping (Olsen and Kagan et al, 1992) as cited in Kessler (1992: 13).
First, homogeneous and heterogeneous grouping is formed when the grouping bases depends on the variety of the certain things such as ethnic, gender,
achievement level, language proficiency and so forth. Second, random grouping, conversely, is formed when the teacher distributes many color papers, shape or cards to students. Then, the teacher groups the students by the same color, shapes and cards. In this phase, there is no specific category like achievement, gender or linguistic skills. Third, interest grouping, is when the teacher assigns some topics by which the students may choose the topic that they are interested in.
2.5 Concept of Procedure Text
A procedure text is taught to first grade students in senior high school based on standard competencies and basic competencies. Besides, according to Derewianka (1990: 24), procedure text is a text which tells us information of making or doing something and how things work through several steps directions. Procedure text has generic structures and language features. There are three particular generic structures in procedure text namely goals, materials, and method (Derewianka, 1990: 27). According to Derewianka (1990), Watkins and Knapp (2005: 157), goal or purpose in procedure text is to give description for readers about what they are going to do. It is usually stated in the title of the text, for example, “How to Make a Pizza”.
Furthermore, ingredients or materials are something to be prepared and those are stated commonly in order of use. According to Derewianka (1990), Watkins and Knapp (2005), ingredients or materials are something to be prepared and those are stated commonly in order of use. Besides, a set of ingredients or the materials required to complete the task will often be presented in order of use. The last method is sequenced steps in doing or making something (firstly, take a spoon …, second, then, etc.). Then, a sequence of steps specifying how the goal is to
achieve.
completing a task; for example, “Cross Smith Street and turn right, walk to the
next cross street”. Meanwhile, verbs are in the simple present tense to create a
sense of timelessness. They are also stated as imperatives.
Second, procedure text focuses on specific people or things, such as, (first, you get ….) and focuses on generalized human agents such as “you put the tea”.
Procedure text usually uses temporal connectives to do with time or sequence of action and it can be used to link information (first, then, next, when, etc).
Finally, procedure text uses detail factual description of participants (shape, size, color, amount, etc.) and simple language due to the purpose to give clear
information and detailed information on how (mix it carefully); where (cut 6cm from the top); when (after you have folded the napkin) (Derewianka, 1990).
Here is an example of procedure text:
How to Make Pizza
Lots of us know pizza. Do you? Wouldn’t it be nice if once in a while we tried to make a pizza? Well, here the recipe.
INGREDIENTS: SAUCE:
1 package (1/4 ounce) active dry yeast 2 cans (8 ounces each) tomato sauce
2 cups warm water 1 ½ teaspoons grated onion
3 tablespoons vegetable oil 1 teaspoon dried oregano
1 ½ teaspoons salt ¼ teaspoon salt
4 to 6 cups all-purpose flour 1/8 teaspoon pepper TOPPINGS
4 cups (16 ounces) shredded part-skim Mozarella cheese 4 ounces beef, diced
1 package (3 ½ ounces) sliced pepperoni 1 medium sweet red pepper, sliced 1 medium green pepper, sliced
1 cup grated Parmesan cheese DIRECTIONS:
First, dissolve yeast in warm water in a large mixing bowl. Add oil, salt, and 2 cups flour. Then beat on medium speed for 3 minutes. Stir in enough remaining flour to form soft dough and turn onto a floured surface. Make sure you knead it until smooth and elastic, about 6-8 minutes. After that, place in a greased bowl, turning once to grease top. Cover and let in a warm place for 10 minutes.
2.6 Procedures of Teaching Reading Comprehension
In teaching procedures, the researcher used three elements in teaching reading procedure text through Think Pair Share technique. The researcher tried to make a general procedure of teaching which is adjusted to the English curriculum used in the school, i.e. KTSP, as follow:
Pre activities
1. Teacher greets the students.
2. Teacher constructs the students’ background knowledge that related to the topic.
For example:
What is your favorite food? Have you ever cooked it? What material did
you need? How did you make it? Do you get success?
3. Teacher tells the material that will be taught and introduce Think Pair Share procedures.
While activities
1. Teacher gives students a procedure text and asks the students to read individually.
2. Teacher asks the students to analyze the procedure text given and explains the generic structure and languages features.
3. Teacher applies the procedures of Think Pair Share as follows:
a. Think: teacher delivers students’work sheet and asks them to think about the exercise given silently and individually. (Think-time is
important because the students have a chance to formulate their answer
by retrieving information from their long term memory). Teacher asks
the students to write down their answers in a piece of paper and collect
them later.
For example:
Teacher: “Think about the following questions individually”.
b. Pair:teacherasks the students to work in pair. The students will be asked to discuss the results of their individual thinking with their
partners. (Pairing is important because it can solve the students’
misunderstanding when they answer the questions individually).
For example:
Teacher: “Now, turn to your partner. Discuss your answers with your
partner. If you make any changes in your statements, you can write
down on other piece of papers”.
peer-feedback because what one pair thinks and discusses always differ
with other pairs think).
For example:
Teacher: “Now, Ani and Rita please come to front of the class. Share
your answers to your friends. The other pairs may give any comments,
revisions and additional information toward your friends’ answers”.
4. Teacher gives commend toward the students’ answer by giving revision or
additional answer and conclude the answers.
Post activities
1. Teacher does a reflection by asking the students what they have learnt that day and asks the students whether they have any difficulties in understanding the lesson.
2. Teacher closes the class.
2.7 Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages of Think Pair Share technique according to Johnson and Johnson (2001):
1. Thinking time provision
2. Making students actively involved
This strategy provides an opportunity for all students to share their thinking with at least one other student. Pair and share time encourage students’ responses and allows quiet students to answer questions. Therefore, students become actively involved in group discussion and classroom participation.
3. Solving students’ misunderstanding
Students’ misunderstandings about the topic are resolved during peer -tutoring or peer-teaching; the lower ability’ students will learn from higher ability’s students, while the higher ability’s students can also internalize
their knowledge by teaching others.
The disadvantage of Think Pair Share technique (Lyman, 1981) is time
consuming. It means that applying Think Pair Share technique in the class may be time consuming if the process can not run well. The teacher should be able to give some rules and create an amusing classroom atmosphere to prevent.
2.8 Theoretical Assumption
The researcher chooses Think Pair Share as a technique in the research. Therefore, researcher assumes that the using of Think Pair Share in procedure text is
expected able to help understand the text easily in teaching learning process; automatically the students are hoped able to get better in the understanding of text.
2.9 Hypothesis
Based on the theoretical assumption above, the researcher formulates the hypothesis as follow:
1. There is a significant difference between the score of the students’ reading comprehension achievement before and after being taught through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text.
2. The most increase of reading comprehension aspects is on vocabulary aspect.
III. RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter includes research design, population and sample, variable, data collecting technique, research procedures, research instruments, scoring system, tryout, data analysis and hypothesis testing.
3.1 Research Design
In this research, the researcher intended to find out the significant difference between the score of students’ reading comprehension achievement before and after being taught through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text. It could be found by using pre-test before the treatment and post-test after the treatment. This research was a quantitative study which used one group pretest-posttest design. The researcher only selected one class as experimental class which had
treatments (teaching reading comprehension through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text). The research design is as follows:
T1 X T2 Where:
T1 = Pretest (before treatments)
X = Treatments (teaching procedure text through Think Pair Share) T2 = Posttest (after treatments)
The researcher gave pre-test before the students were taught the procedure text through Think Pair Share technique. It was conducted to find out the students’ reading comprehension achievement in procedure text. There were three treatments (teaching reading the students in procedure text through Think Pair Share technique). The researcher conducted the treatments by using different topics in every meeting or every lesson plan. Eventually, post-test was administered to find the students’ reading comprehension achievement in procedure text after they were taught through Think Pair Share technique as the treatments.
3.2 Population and Sample
The population of this research was the first grade of the students of SMA N 1 Bandar Sribhawono. Class X1 that consists of 30 students in 2nd semester, academic year 2012/2013 was taken as the sample of this research, the class that was given the treatments (teaching reading procedure text through Think Pair Share technique). This class was chosen by using simple random sampling technique by using lottery, the researcher wrote some peppers with named the class X (X1-X9) and put them in to the glass. The class that out of from the shaken glass would be chosen as the experimental and tryout class, so that all of the first grade classes got the same chance to be sample in order to avoid
3.3 Data Collecting Technique
Data collecting technique is the way to get the data for the research. This data was collected to find out the significant difference between the score of the students’ reading comprehension achievement before and after being taught through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text. In collecting the data, the research
procedure administered pre-test, treatment and post-test. Then, the researcher analyzed the result of those activities which could be clarified as follows:
1.Try-out
The try-out test was applied to know the quality of the test as the instrument of the research. The try-out test was conducted in another class which was chosen
purposively in the pre observation, out of experimental class. The numbers of the tests items were 40 items of multiple choice that consist of four options of each answer (A, B, C and D). Time allocated was 90 minutes. This test was given to the students in order to have a good quality which has not only good reliability and good validity, but also it was not too easy and too difficult.
2.Pre-test
The pre-test was conducted before the treatment of teaching reading
3. Treatment
After having the pre-test, the students in the experimental class were given treatments. The treatment was teaching reading comprehension through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text. The researcher taught the students the material based on KTSP 2006 curriculum of senior high school. There were three different topics every meeting that consists of 90 minutes.
4.Post-test
The post-test was given to the students after the treatments to find out the significant difference between the score of the students’ reading comprehension achievement after being taught through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text. The result of post-test was compared with the result of pre-test. The test consists of 30 multiple choices items consisting of four options (A, B, C, and D).
3.5 Research Procedures
In constructing the research, the research procedures used these following steps:
1. Determining the population and sample of the research
The population of this research was the first grade students of SMA N 1 Bandar Sribhawono. The sample or experimental class is class X1 that consists of 30 students. It was chosen randomly by using lottery.
2. Administering the tryout to know the quality of the test
discrimination power (DP) as well to find out the reliability and validity of the test.
3. Preparing the material which will be taught
The researcher took the material based on English book of first grade student.
4. Administering the pretest and finding the result
The pre-test was conducted before the treatment, to see the students’ base reading comprehension in procedure text. The pre-test was given as an objective test in the form of multiple choices. The numbers of the items in the test are 30 items of multiple choice tests with four options of answers, (A, B, C and D). The pre-test took 60 minutes.
5. Giving treatment
After having the pre-test, the students in the experimental class was given three treatments. The treatment was teaching reading comprehension through Think Pair Share technique. There were three different topics in each meeting that consists of 90 minutes.
6. Administering the post-test
7. Analyzing the test result
After conducting pre-test and post-test, the researcher analyzed the data by using T-test. It was used to know whether Think Pair Share is able to increase students’ reading comprehension achievement in procedure text or not. It was computed through SPSS.
3.6 Research Instrument
The instruments of this research were:
1. Objective reading test of procedure text that was used for tryout, pre-test, and post-test. Those tests were in form of multiple choices that consists of four options (A, B, C and D). The multiple choice test is used since its marking is rapid, simple and most importantly reliable, not subjective or influenced by the marker’s judgment (Heaton, 1975).
2. Questionnaire consisting of the students’ arguments about the use of Think Pair Share technique in teaching learning reading comprehension. The
questionnaire consists of seven statements, four positive statements and three negative statements. Every student chooses the answer based on their
3.7 Scoring System
There were two research instruments consisting of objective reading test and questionnaire. Then, the scoring system can be seen as follows:
a. The Scoring System of Objective Reading Test
There were 40 items in tryout test, 30 items in pre-test and 30 items in post-test. Each correct answer is scored one. In scoring the students result of the test, the researcher used Arikunto`s formula. The ideal higher score was 100. The score of pretest and post tests were calculated by using formula as follows:
S = 100 N R
Where:
S: The score of the test
R: The total of the right answers N: The total items
(Arikunto, 1997:212)
b. The Scoring System of Questionnaire
The data responses of the students about the application of Think Pair Share technique in teaching learning reading comprehension was found by
1. Calculate the questionnaire score based on the table. Tabel 1. The scoring system of questionnaire.
Statements Score
1 0
Positive (Agree) S TS
Negatif (Disagree) TS S
Note: S = setuju; TS = tidak setuju (modified from Rahayu, 2010:29).
2. Tabulating the data based on the classification, it aimed to give the frequency and the tendency from every answer in questionnaire statements.
Tabel 2. The students’ responses data toward the teaching learning reading
comprehension through Think Pair Share technique
No.
(modified from Rahayu, 2010: 31).
3. Calculate the percentage of questionnaire score by using formula as follows:
Where: P = Students’ answer percentage; f = frequency of answer; N = the total of students (modified from Sudijono, 2004:43).
P = x 100% f
4. Deciding the responses percentage based on the Hendro’s criteria (in Hastriani, 2006:43).
Tabel 3. The students’ responses percentage criteria
Percentage (%) Criteria 100
Tryout is the test that was given before pre-test and post-test. It was the multiple choice test that consists of 40 items and had four options A, B, C, D. It was given in order to know the level of difficulty and discrimination power of the test items before giving the pre-test and post-test to the class. The test could be said has a good quality if it has a good validity, reliability, level of difficulty and
discrimination power.
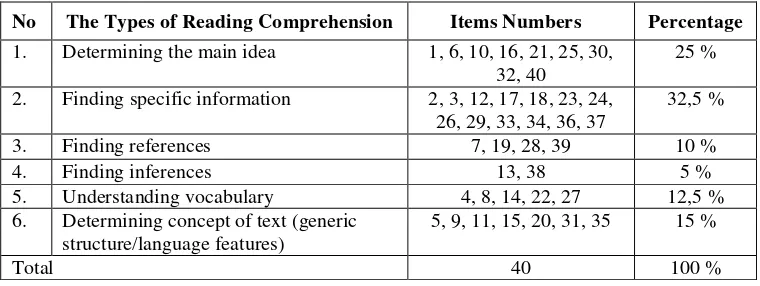
Table 4. Specification Table of Tryout Test
No The Types of Reading Comprehension Items Numbers Percentage 1. Determining the main idea 1, 6, 10, 16, 21, 25, 30, 6. Determining concept of text (generic
structure/language features)
5, 9, 11, 15, 20, 31, 35 15 %
3.8.1 Validity of the Test
The test can be said as the valid one if the test measures the object to be measured and it is suitable with the criteria (Hatch and Farhady, 1982:250). There are two basic types of validity (Hatch & Farhady, 1982: 250). They are content and construct validity. To measure whether the test has a good quality or not, the researcher used content and construct validity.
a. Content Validity
Content validity is concerned with whether the test is sufficiently representative and comprehensive for the test. Based on Hatch and Farhady (1982:251), since content validity is the extend to which a test measures a representative sample of the subject matter, the focus of content validity is adequacy of the sample of the appearance of the test. Therefore, since the test instrument was constructed to get the data of the students’ reading comprehension ability, the content validity of the test items were constructed by including reading material which was arranged based on the material already given and it was suitable with the curriculum. Thus, if the measuring instrument had represented all the ideas that connected with the material that was measured, that measuring instrument had fulfilled the aspect of content validity.
b. Construct Validity
KTSP 2006 curriculum of senior high school. Then, the test was determined according to the material that was taught to the students.
3.8.2 Reliability of the Test
Reliability of the test can be defined as the extent to which a test produces
consistent result when administrated under similar conditions (Hatch and Farhady, 1982:243). Pearson Product Moment formula that was used as follows:
rl: Coefficient of reliability between odd and even numbers items x: Odd number
y: Even number
x2: Total score of odd number items y2: Total score of even number items xy: Total number of odd and even numbers
(Lado, 1961 in Hughes, 1991:32) The criteria of reliability are:
0.80 – 1.00 = very high 0.50 −0.79 = moderate
0.00 – 0.49 = low
To know the coefficient correlation of whole items, “Spearmen Brown`s prophecy formula” will be used. The formula is as follows:
=
Where:
rk: The reliability of the whole test
: The reliability of the half test (Hatch and Farhady, 1982:246)
3.8.3 Level of Difficulty
Level of difficulty is related to how easy or difficult the item is from point of view of the students who take the test. To know the level of difficulty, the researcher used the following formula:
LD = N
R
Where:
LD: Level of difficulty
The criteria are:
<0.30 = difficult 0.30-0.70 = average <0.70 = easy (Shohamy, 1985:79)
3.8.4 Discrimination Power
The discrimination power refers to the extent to which the item differentiates between high and low level students on the test. A good item according to the criteria is one which good students will do well and bad students will fail. To know the discrimination power of the test, the formula that was used:
DP = N
L U
2 1
Where:
DP: Discrimination power
U: The proportion of upper group students L: The proportion of lower group students N: Total number of the students
0.41 – 0.70 = good 0.71 – 1.00 = excellent
(Negative) = bad items (should be omitted)
(Heaton, 1975: 182)
3.9 Data Analysis
The purpose of analysis is to reduce data to be intelligible and interpretable so that the relation of research problem can be studied. The researcher analyzed the data statistically using Repeated measure T-test because this research only take one class for experimental class. It is probably the most widely used statistical test for the comparison of two means because it can be used with very small and simple size. In order to analyze how significant the difference between the score of the students’ reading comprehension achievement before and after being taught through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text, the researcher used these following procedures:
1) Scoring the pre-test and post-test.
2) Tabulating the result of the test and calculating the mean of the pre-test and post-test.
To know whether there is a significant difference between the score of the students’ reading comprehension achievement before and after being taught through Think Pair Share technique or not, the researcher compared the result of test to the result of post-test. If the result of post-test was higher than the pre-test, it means that Think Pair Share technique could be used to increase students’ reading comprehension achievement in procedure text.
3.10 Hypothesis Testing
The hypothesis statistically tested using Repeated measures T-test. It was used as the data came from the same sample or known as paired data (Hatch and Farhady, 1982: 114). The data was calculated through computing with Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) version 17.0. It was used to draw the conclusion in significant level of 0, 05 (p<0, 05). It means that the probability of error in the hypothesis was only about 5%.
To determine whether the first hypothesis is accepted or rejected, the following
criteria acceptance that used:
H0 : There is no significant difference between the score of the students’ reading comprehension achievement before and after being taught through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text
The criteria are:
V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
This chapter presented the conclusion and suggestion based on the finding and discussion of the data analysis.
5.1 Conclusion
Based on the discussion of the research finding on the previous chapter, the researcher concluded that:
1. There is a significant difference between the score of students’ reading comprehension achievement before and after being taught through Think Pair Share technique in procedure text. This could be seen from the mean score of students’ pre-test was 68.27 and the mean score of students’ post-test was 81.33, with the gain was 13.06. The result of paired sample t-test in hypothesis test showed that the significant value (2-tailed) was p=0.000 (p<0.05), t
2. This research was focused on five reading comprehension aspects. Then, from the calculation, it can be seen that the most increase was on vocabulary aspect. 3. Teaching reading through Think Pair Share technique can be used to increase
students’ participation in contributing the group work clearly and has a good
positive result in teaching learning activities in the class. The students’
relationship within group or pair becomes stronger. Besides, students feel that think pair share technique is enjoyable, simplifies the group work assignment and improves responsibility.
5.2 Suggestion
Based on the data in the previous chapter and the conclusion, some suggestions are recommended:
1. Considering the advantages of Think Pair Share technique, the researcher suggested that English teachers of the class apply Think Pair Share technique as an alternative way in teaching reading because from this research and
previous researches, Think Pair Share can be used to increase students’ reading comprehension achievement. The English teachers should make highly good preparation before applying think pair share technique because it determines the success of teaching learning process.
2. The other researchers who are intended to write the similar research,
considering the time allocation for the treatments. The target of material can not be explained fully because the limitation of time.