Vol 8, No 3, July - September 1999 Hyoid bone
release
193Hyoid
bone
release
and end-to-end
anastomosis
on
stenosis
of the trachea
Hartono Abdoerrachman, Bambang Hermani
Abstrak
Di bidang THT, stenosis trakea masih merupakan keadaan patologi yang sulit diatasi. Dari waktu ke waktu, berbagai usaha telah dilakukan untuk mendapatkan cara yang tepat dan terbaik guna merxgatasi stenosis trakea. Kelihatannya cara yang terbaik sangat lergantung pada berat-ringannya penyakit dengan melihat situasi dan kondisi lcasus per lasus. Kadang-l<adang diperlukan tindalan berulang, dan kombinasi dari beberapa cara harus dipertimbangkan. Beberapa cara ),ang dianjurkan oleh para
ahli
akan dibahas dalan makalah ini. Juga dilaporkan sebuah kasus stenosis trakea yang disebabkan intubasi lama, dengan kombirnsi tindakan mruk mengatasinya. Penglepasan os hyoid akan memperpanjang takza yang direseksi dan kombinasi end-to-end dan pemasangan T-tube mencegah timbulnya kembali stenosis di daerah takeayang dijahit.Abstract
In
thefield
of Otorhinolaryngology, the treatment of tacheal stenosis is still subject to great problems. Anempts to treat the tracheal stenosis had been done from time to time in order to establish the proper and the best method. It seems that the proper methodof treatment depends on the severity of the disease as well as the situation and conditiott of each case. Sometintes repititive treatment is necessary and moreover, combination ofthe procedures should be considered. Several methods advocatedby the experts were discussed in this paper. A case of stenosis of the trachea due to prolonged intubation is reported, and the combined treatrnent is discussed. Hyoid bone release enables longer resection and approximatiott oflrachea and combination ofend+o-end anastomosis
anl
ùuertion ofT-rube preven.ts the reoccurance of stenosis on stitched area.Keywords: tracheal stenosis, end to end anastomosis, T-tube instalation
Tracheal
stenosis
is
a rarely found
case
and
still
aproblem
anddifficult
to
be solved,
which
sometimesneed a continues
handling
or
repeatedinterventions,
evencombination
of
the procedures.There have been
severalprocedures advocated
by
the experts, aslisted
below.
End-to-end
anastomosisis one
of
the attemptto
over-come the stenosis, andin this
case the anastomosis wascombined with insertion
of
aT-tube
asa
stent
for
acertain period
of
time.
Stenosis of the trachea is a
narrowine of tracheal
lumen
up to
or
more
than 707otor reductËn of
thediameter
of
the lumen up to 3 mm.
Hençe, a
tube with
outer
diameter
of
4.5 rnm
could not
pass the stenotic area.2Andrew
and Pearson found 17 .57o outof
103tracheos-tomized-cases, suffered
from
different
degree of
stenosis.3
Departtnent of O torhinolaryngolo gy, Faculty of Medicine, University of ltulonesia, Jakarta, Indonesia
Soejak
in
Surabaya
found 5
stenosis cases
within
5years.4
Our
case collection
in
ENT
Dept. RSCM
reveals24trachealstenosis
within l5
yearsof
accumu-lated
data.sAs the etiology
of
tracheal stenosis, several factors
could
be listed:6-
high volume
of
thecuff
: this
causesischaemia on
tracheal
wall,
leading
to
necrosis and
finally
stenosisduring
healing process.
-
impaired vascularisation on tracheal mucosa : this
condition
leads
to
ischaemia, necrosis
andfinally
stenosis.-
infection
around
thecuff
will
also cause necrosis
and leads to stenosis.-
piston action
will
cause
laceration, and
leads
to
stenosis on healing process.-
tracheal movements oncoughing
will
causelacera-tion,
and leadsto
stenosis on healing process.Several predisposing
factors facilitate the
stenosis process asfollows:z
t94
Ab doerrachman and H ermani-
repeated andtrauma on
intubation
-
configuration
and sizeof
endotracheal tube-
material
of
the tube-
high tracheostomy
-
badhumidification
-
systemic
diseaseThe types and classification
of
tracheal
narrowing,
stenosis can be
classified
in
several ways:Based
on
tissue
forming
types, stenosis,can
be
clas-sified
ashard
cicatrical
andsoft stenosis.'
The
secondclassification
of
stenosis,is
basedon
theshape
of
the
stenosis:8-
annular
stenosis-
tubular
stenosisbelow
thelevel
of
theCricoid
-
tubular
stenosisstomal
site-
lateral collaps
of
thetracheal lumen.
The
third classification of
the stenosisis
basedon
thelocation
of
thelesion.
-
above the stoma-
atthe
stoma site-
at thecuff
site [image:2.595.83.590.86.718.2] [image:2.595.80.580.443.696.2]-
at thedistal
endof
canuleFigure
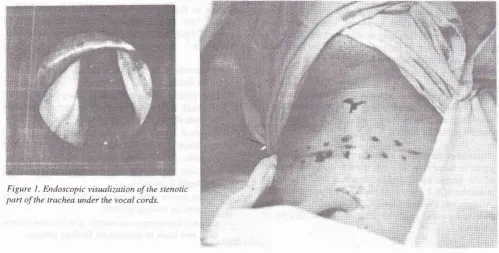
I.
Endoscopic visualization of the stenotic part of the trachea under the vocal cords.Med J Indones
Treatment attempted
to
overcome
the
stenosis
are asfollows:
-
dilatation with
or
without injection
of
steroid
-
dilatation
andprolonged stenting
-
luminal
augmentation
-
resection
of
the
stenosis
with
primary
re-anstomosis.
CASE REPORT
A
young
manof l8
yearsof
age had atraffic
accident
and suffered
from
cerebral
contusion.
Prolonged
in-tubation
has lead to the stenosisofthe first
and secondring of
trachea.Figure
I
showed the stenotic partof
the trachea, beneath thevocal
cords,visualized
endoscopi-cally. A
T-tube
was insertedto overcome the
stenosis,and
6
months
later the tube was removed,
but
the stenosisre-occurred.
Resection
of
thestenotic
areafollowed by
end-to-end
anastomosis was planned
for
permanenttreatment.
To
prevent re-stenosis
atthe stitched
area,A T-tube
wasinserted
and act as a stent.Figure
2 showed thehorisontal
incision line
onskin
of
theneck.
Horisontal incision
will
result
in
acosmeti-cally
better wound healing.
tr: r': ;,,
Vol 8, No 3, JuLy - September 1999
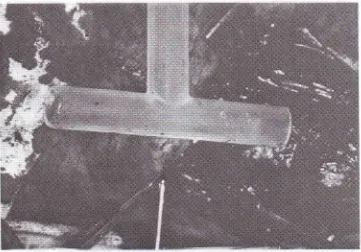
The
hyoid
bone waslocalized,
as shownin figure 3,
toperform hyoid
bone release, enabling
longer
ap-proximation of
the resected trachea.Hyoid bone
release
195The
tracheawas exposed, and
incision
was made
onthe upper and the
lower part
of
stenotic
area, as shownin figure 4.
[image:3.595.146.511.148.406.2]Figure 3. The hyoid bone localisation, to perfonn hyoid bone release
[image:3.595.141.510.451.715.2]196
AbdoerrachmanandHermaniFigure 5
showed the
T-tube to
be inserted
andact as
tracheal stent to prevent restenosis on the stitched area.
[image:4.595.151.512.145.397.2] [image:4.595.149.517.450.720.2]Med J Indones
Figure
6
showed theremoved part
of trachea,
leaving
the stenotic
area uncovered.Figure 5. T+ube to be inserted and act as tracheal stent to prevenl re-slenosis on the stitched area.
Vol 8, No 3, JuIy - September 1999
Figure
7 showed
the
T-tube inserted through
the resected partofthe
trachea, as trachealstentpreventing
re-stenosis at the resected area.
The upper
and
lower part
of
resected
areawas
thenapproximated
and sutured, asshown
in figure
8.Figure 7. Insertion ofT+ube through the resected
part ofthe trachea.
Hyoid bone
release
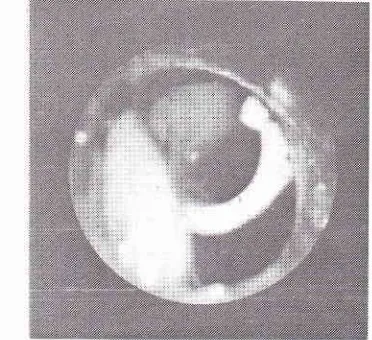
197Figure
9 showed theposition
of the upper end ofT-tube
within
the
trachea
on
post-operative
endoscopic
visualisation.
Figure 8. The upper and lower part of resected area
was then approximated and sutured.
Figure 9. The position of the upper end of T-tube within
198 Ab do e rrac hman and H e rmani
Six months later
theT-tube
was removedsuccessfully,
and the
patient
live uneventfully, without
evidence
of
re-stenosisor respiratory
distress.DISCUSSION
Stenosis
of
the tracheais
a rare case, but onceit occurs'
we
might
faceproblems to
evercome, even sometimesunsolved.
Many
experts
had beenemploying
andadvocating or
facilitating
methods and procedures
to
overcome
theproblem
but
it
seems that thereis no
standardmethod
to treat this pathology.
It should
bejudged
andcon-sidered case
by
case,carefully
calculatedby
looking
atthe
entire situation
andcondition of both
the
diseaseand the
patient. Sometime
theproblem
needs repeatedmanipulation
due
to
the
stubborn
lesion,
and
some-times,
a
combination
of
methods and
procedures
should be considered.
In our case,
dilatation
andprolonged
stenting by meansof
T-tube insertion
wasperformed
andlasting for
about6
months.
Onextubation it
was shown that the stenosisreoccur.
We
decided
to
carry
out
resection
of
thestenotic
area andfollowed
by end-to-
end anastomosisof
the trachea.
Hyoid
bone
release wasperformed to
enable
longer resection
andapproximation of
trachea.But
due
to
apprehension about restenosis
of
thestitched
area, aT-tube
was inserted and act
as stent.Some experts
mentioned
that a stent was not necessaryin
such case.However,
dueto
our
experiencethat
theinciclence
of
secondary and nosocomial
infections
Med J Indones
were high,
besidesgiving high
doseantibiotic,
weput
a stent on
to prevent
restenosis.Six months later
theT-tube
wasextubated
successful-ly,
and
on
the
follow
up no
signs
of restenosis or
respiratory
distress was noted.REFERENCES
1.
Hommerich KW and Fleming I. Classification of Laryngeal Stenosis. ORL, 1974; 36:100-6.2.
Holinger PH, Kutrick SL, Schild JA. Subglottic stenosis in infants and children. Ann. Otol. 1976; 85:591-9.3.
Andrews MJ and Pearson FG. Incidence and Pathogenesis of Tracheal injury following cuffed tube tracheostomy with assisted ventilation: Analysisof
a Two Year Prospective study. Ann. Surg.l97l;
173:243-63.4.
Sardjono Soedjak S, Harmadji. Stenosis trakea. Dilebarkan dengan operasi trakeo-fisur dan kauterlistrik.
Kumpulan Naskah Konas PERHATIV
Semarang, 1917 4Ol-5.5.
Abdoerrachman H, Rusmaryono, Hermani B, and Munir M. Pemasangan Pipa - T Silikon pada penyempitan trakea. PITI
IKABI
Jakarta, Nov. 17, 1982.6.
RainerWG,
SaucesM,
and LopezL.
Tracheal stricture secondaryto
cuffed
Tracheostomy tubes. Chest 1971; 59:1 15-8.7.
GatesGA
and FernandezAT.
Laryngotracheoplasty foracquired subglottic stenosis
in
infants and children' Ex-perience with six cases. Laryngoscope 1978; 88:1468-76.8.
EliacherI,
Birkin JH, Simon K, Joachins HZ. Emergency management of tracheal stenosis' Retrograde tracheal boun-ginage. Ann. Otol. 1980;89:46-8.