AN ANALYSIS OF TRANSITIVITY IN TIME MAGAZINE: A CASE STUDY OF ARTS RUBRICS
A THESIS
BY
WINDA YUSTA UTAMI 050705024
ENGLISH LITERATURE DEPARTMENT FACULTY OF LETTERS
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH SUMATERA MEDAN
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Alhamdulillah, in the name of Allah SWT, I would like to thank to God, the Almighty for the blessing on me, where every day, guides me and gives me garce power and chance to acccomplish this thesis.
First and foremost, I would like to thank my supervisors and my co-supervisors, Dr. Eddy Setia, Med. TESP and Drs. Chairul Husni, MEd.TESOL for their guidance, support, advice and constructive comments during thev writing of this thesis.
My sincere gratitude also goes to the Dean of Faculty of Letters, University of North Sumatera, Drs. Syaifuddin , MA, Ph.D. the Head and the Secretary of English Literature Department, Dra. Swesana Mardia Lubis, M.Hum,
Drs.Yulianus Harefa, Med TESOL and all of the lecturers and the staffs of English Literature Department for the facilities and oppurtunities to me during my
study in this University.
My special thanks are expressed to my beloved mother, Asna and my sister Dini, for giving me a great love, support, and attention. My thanks to my father. And my great thanks are for my brother, Nurdin, and my brother in-law, Yono,my beloved nephews, Cindy and Nesha.Thanks for your love and kindness.
Big thanks are addressed to my best friends, Tila,Intan, Lia, Rini and Suranta. Thanks for your friendship and times that we spent together both in happy and sad situation. And great thanks are also given to Nina, thanks for your togetherness in advicing prosess.
Medan, 26th June 2009 The Writer
ABSTRACT
Skripsi yang berjudul An Analysis of Transitivity Process in Time Magazine: A Case Study of Arts Rubrics. Merupakan suatu kajian Linguistik Fungsional Sistemik pada majalah mingguan Time khususnya pada bidang seni. Untuk mendapatkan proses yang palind dominan digunakan formula yang dikembangkan oleh Bungin (2005,171-172). Analisis proses transitivity didalam skripsi ini menerapkan teori Linguistik Fungsional Sistemik (Systemic Functional Linguistics) yag dipelopori oleh Halliday.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ACKNOWLEDGNMENTS ... i
ABSTRACT ... ii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... iii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ... 1
1.1 The Background of the Analysis ... 1
1.2 The Scope of the Analysis ... 5
1.3 The Problems of the Analysis ... 5
1.4 The Objectives of the Analysis ... 6
1.5 The Significance of the Analysis ... 6
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 7
2.1. An Overview of Discourse Analysis ... 7
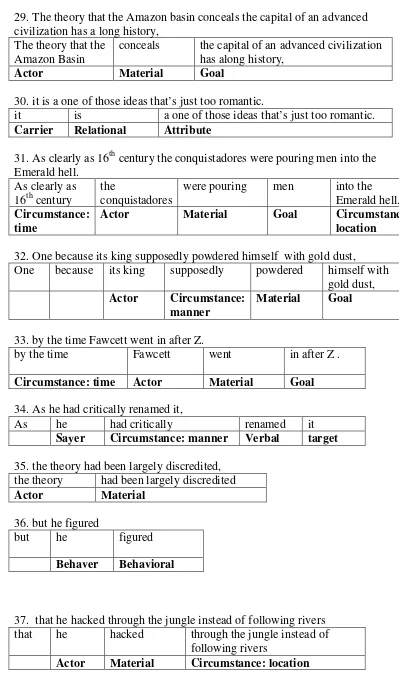
2.1.1 The Definition of Discourse Analysis ... 8
2.1.2 The Function of Discourse Analysis ... 9
2.1.3 Systemic Functional Linguistics ... 9
2.1.4 Metafunction of Language... 12
2.1.4.1. The Ideational Function ... 12
2.1.4.2. The Interpersonal Function ... 13
2.1.4.3. The Textual Function ... 15
2.2. Transitivity Process ... 17
2.2.1 Material Process ... 21
2.2.2 Mental Process ... 22
2.2.3 Relational Process ... 26
2.2.4 Verbal Process ... 29
2.2.5 Behavioral process ... 30
2.2.6 Existential Process ... 31
CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY ... 35
3.1 Research Method ... 35
3.2 Method of Collecting Data... 35
3.3 Method of Analysis Data ... 36
CHAPTER IV. ANALYSIS OF DATA AND FINDINGS ... 38
4.1 The Analysis of the Data... 38
4.2 No.6 : Television “Life After Earth ” ... 38
4.1.1 No.7: Movie “And Emmy Goes to…” ... 48
4.1.2 No.8 : Exhibition “The Art of Diplomacy” ... 55
4.1.3 No.9 : Books “Jungle Fever” ... 68
4.3 Findings... 75
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 77
5.1 Conclusion ... 77
5.2 Suggestion ... 77
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 78
ABSTRACT
Skripsi yang berjudul An Analysis of Transitivity Process in Time Magazine: A Case Study of Arts Rubrics. Merupakan suatu kajian Linguistik Fungsional Sistemik pada majalah mingguan Time khususnya pada bidang seni. Untuk mendapatkan proses yang palind dominan digunakan formula yang dikembangkan oleh Bungin (2005,171-172). Analisis proses transitivity didalam skripsi ini menerapkan teori Linguistik Fungsional Sistemik (Systemic Functional Linguistics) yag dipelopori oleh Halliday.
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
1.1The Background of the Analysis
Human beings live in the world in togetherness, and they live in
relationship to others as social creature. They make contact by communicating
and associating each others. All of these are best performed by language.
As a fundamental means communication, language is used to convey or
share ideas and express thoughts, human’s needs, wishes, intentions and desires.
Communication types can be a verbal or written. Both types of communication is
a purposeful activity. Communication can only take place successfully if the
means of communication is agreed upon by its users, and thus language has a
social, and conventional aspect. Communication exists with language.
“Language is a system of semiotics. It means language is realized in symbols or sign that has meaning”. (Halliday, 1978:44) In addition, Language is purely human and non instinctive method of communication ideas, emotion and desires by of system voluntary produces symbols”. (Sapir, 1921: 8).
From definition of language above, it can be concluded that language is a
system of arbitrary produced symbols to express the ideas, emotions, and desires
in communicating each others.
Language is a social phenomenon, it has the tendency as means of doing
than knowing. Language consists of three levels, namely Phonology (sounding
and writing), Lexicogrammatical (saying or wording) and Discourse
Semantic.“……., any text represents an actualization (a path through the system)
folk-linguistic term for the lexicogrammatical system). And of course the level of
sounding or writing” (Halliday 1978:40).
In other words, the level of meaning, the level of saying or wording, and
the level of sounding or writing in language are the system of semiotic expressed
by Lexicogrammatical, Phonology, and Discourse.
In the last few decades, language has been studied in scientific way. Many
linguists are appeared and interested in analyzing how language is structured and
used in conveying which are known as system for they establish a theory called
Systemic Linguistics. This theory stresses on communication. In other words, it
concerns with relation between language and context in which it is used.
The branch of linguistics that concerns with text is Discourse Analysis.
Discourse Analysis concerns with the relationship between language and
situation. Discourse is defined in two ways, a particular unit of language (above
the sentence a particular focus (on language use).
A particular unit of language that is larger than sentence is a structure way
and the use of language for social, expressive and referential. Then, a structure
way is called structuralism and the realization of functions is called functionalism.
Discourse Analysis has to be found on a study language system. The main
reason for studying the system is to throw light on discourse, on what people say,
write, listen, and read. Both system and text have to be in focus of attention. By
starting from the system we can see the text in its aspect as a process.
Language has three functions of metafunction of language. The ways in
a. Language is used to organize, understand and express perception of our own
consciousness. Ideational function is classified into two sub functions. The
experiential and the logical. The experiential function is concerned with
content or ideas, while the logical function is concerned with the relation
between ideas. The ideational metafunction consist of logical that is realized
by the clause system.
b. Language is used to enable us to participate in communicative acts with other
people, to express and understand feelings and attitudes. This function is
called as the interpersonal function. The interpersonal metafunction is realized
by the mood system.
c. Language is used to relate what is said (or written) to the real world or to other
linguistics events. It involves the use of language to organize the text itself.
This is called as the textual metafunction is realized by the system.
These metafunctions have a systemic relationship with the lexicogrammar
of the language (Halliday,1978:109)
In the concept of transitivity (Halliday, 2004:107) proposes three
components of a transitivity process:
(a) The process itself (realized by a verbal group)
(b) Participants involved in the process (realized by a nominal group)
(c) Circumstances associated with the process (realized by adverbial group
or prepositional phrase).
The process consists of Material process (process of doing), Relational
process (process of being), mental process (process of sensing), Behavioral
(process of saying), and Existential process (represents that something exists or
happens). The participants are directly involved in the process :the one that does,
behaves, senses, says, is or exists, participants are also centrally involved in the
process by being affected by it, the one that is done to, sensed etc. While
circumstances are typical adjuncts. They answer such questions as when, where,
why, how, how many and as what. They realize meanings about time, place,
manner, cause accompaniment, matter and role.
This study only concerned with the ideational function. In the ideational
function there is a system which called transitivity. The system of transitivity is a
presentation of meaning in a clause. The writer chooses the articles of magazine to
be analyzed. The writer takes “Arts” articles of Time Magazine to find the
transitivity process and get the most dominant process which characterizes this
article.
Time (The International Magazine of Events) Magazine is a weekly
general interest magazine. It was founded in 1923 by Briton Hadden and Henry
Luce. It is in America. Time has seven main topics: Briefing, Commentary, The
Well, Life, Global Business, Arts, and Cover Story. The writer only takes “Arts”
articles in February and March 2009 as the data of this study.
In analyzing the data, the writer uses the Systemic Functional Linguistic
(SFL) of Halliday as the basic of the analysis. The writer chooses SFL because
this theory often appears in social situation or our daily lives, either spoken or
written. This theory focuses on the purposes and the uses of language. This theory
also claims that language is functional and language use is unique and can be
1.2The Scope of the Analysis
In research, it is important to limit the analysis on specific data that has
been chosen, and to avoid over complicating the issues and analysis.
As we know that Discourse Analysis is not only concerned with the
description and analysis of spoken interaction but it is also concerned with written
text. In addition to all of our verbal encounters, we consume many of written and
printed words such as newspaper, articles, novels, short stories, comics,
magazines, instructions and notices.
In this thesis, the writer analyzes transitivity process found in “Arts”
articles of Time Magazine in February and March 2009 (Fourth edition, Vol 173,
No.6, 7, 8, and No.9).
The writer selects some of “Arts” articles as data for investigating which
described as follows:
- NO 6: Television “Life After Earth” article 16th , February 2009. - NO 7: Movie “And Emmy goes to….” article 23rd, February 2009.
- NO 8: Exhibition “The Art of Diplomacy” article 2nd, March 2009. - NO 9: Books “Jungle Fever” article 9th, March 2009
1.3The Problems of the Analysis
As we know, human beings have many experiences. In their experiences,
people get sense about what goes around them and inside them. People can differ
their experiences, is it happening, doing, sensing, meaning, being and becoming.
People express these experiences in language; they are called material process,
In accordance with the title of this thesis, there are two questions to be
raised that motivate the writer to do the analysis.
The problems are:
1) What are the transitivity processes appeared in “Arts” articles of Time
Magazine?
2) What is the dominant process in “Arts” articles of Time Magazine?
1.4The Objectives of the Analysis
Dealing with the analysis of transitivity process found in “Arts” article of
Time Magazine, the objectives of the analysis of this thesis are:
1) To find the transitivity processes which appear in “Arts” articles of Time
Magazine.
2) To find out the most dominant process found in “Arts” articles of Time
Magazine.
1.5The Significances of the Analysis
For practical purposes, language is a means of representing the world,
about what is going on or the real situation. Thereby, language plays a crucial role
in individual involvement with other people. The transitivity processes in
language’s representational function can be found in daily life, either in spoken or
written form. So, the writer chooses the transitivity process to be analyzed
because the writer hopes this thesis can help the language’s learners, especially to
find out and to analyze the transitivity process. And hopefully, this thesis will be
useful for the readers who are interested in studying transitivity process. Finally,
the writer hopes this thesis can be used as one the references in analyzing
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 An Overview of Discourse Analysis
Discourse analysis analyzes not only large units of language such as
conversation or written text but also attempts to achieve the exact meaning or at
least the closest meaning intended by the writer in the written texts or speaker in
conversation. In order to reach the aim of discourse analysis, there are some
function related to it, they are:
1. Enabling one to say why the text is or is not, an effective text for its own
purpose in what respects it succeeds and it what respects it fails, or even less
successful in order to get the evaluation of text
2. Enabling one to show how and what the text. This is the lower of the two
functions. It is one that should always be attainable based on grammar
According to Mc Carthy (1995:12) discourse analysis is not only
concerned with the description and analysis of spoken interaction. In addition to
all our verbal encounters we daily consume hundreds of written and printed
words: newspapers, articles, letters, stories, recipes, instruction, notices, comics,
billboards, leaflets pushed through the door, and so on. We usually expect them to
be coherent, meaningful communications in which the words and/or sentences are
linked to one another in a fashion that corresponds to conventional formula, just
as we do with speech. Therefore discourse analysis are equally interested in
2.1.1 The Definition of Discourse Analysis
Many linguists and scholars have proved that there is another unit of
language that is more complete and larger than sentences. They admit it as the
higher level of unit of language, which is known as Discourse. In short, discourse
is the larger linguistic unit which has meaning. Linguists have defined discourse
analysis in various ways.
-Stubbs (1983:10) says “Discourse analysis consist of attempts to study the
organization of language above the sentence or above the clause and therefore to
study larger units, such as conversational exchanges or written text.
-Mc Carthy (1991:12) says “Discourse analysis is not only concerned with the
description and analysis of spoken interaction. In addition to all our verbal
encounters we daily consume hundreds of written and printed words.
-Hartmann and Stork (1972:69) say” Discourse is a text which forms fairly
complete unit. It is usually restricted to the successive utterances of single speaker
conveying a message.
From the above definitions, we can understand that discourse has several
important elements, they are:
(1) The unity of language
(2) The most (complete the largest/ the highest language above the sentence or
the clause
(3) Tied well sense of coherence/cohesive of language
(4) Continuous written/spoken text
2.1.2 The Function of Discourse Analysis
Discourse is the larger unit of language . as we know that language holds a
very important role in human’s life because language is primarily an instrument of
communication among human beings in community. (Lyons, 1981:4)
“Language is the institution whereby humans communicate and interact
with each other by means or habitually used oral, auditory arbitrary symbols”
It means that human communicate and interact each others by using
language. It is important to gets the information details correctly from what we
have heard or read. That is why the speaker or writer should make what he says
or writes clear. Discourse is an appropriate unit for this purpose.
As the larger unit of language, discourse has the main function like the
function of language that is transmit the information in social communication and
its structure and also will qualify us to produce a well-performed discourse.
So, it can concluded that the function of discourse can be defined as to organize
larger idea of the writer or speaker. The other function is to arrange the idea into
coherent state in order to make the recipients will easily comprehend the writes or
speakers as a consequence the goal of language will be obtained.
2.1.3 Systemic Functional Linguistics (SFL)
Systemic Functional Linguistic (SFL) is theory about language as a
resource for making a meaning based on a context of situation and a context of
culture. SFL was developed by Halliday (1985, 1999), a professor of linguistics
from university of Sydney, Australia. This theory is based on Firth’s system
context of situation and context of culture. Is works were subsequently developed
by Halliday, whose theory of language-in-context is generally known as systemic
functional linguistic (SFL). The interesting development of systemic functional
linguistic theory in Malinowski and Firth’s time was the attention paid to the
study of the interrelatedness of language and context in theory and practice.
Modeling language-in-context theoretically, describing and applying the model in
question in various areas of human activity have been the trademark of Systemic
Functional Linguistic Theory (SFL).
SFL works on language-in-context are available in a great variety of forms
such as books and journals. It is also used to explore different ways of interpreting
things theoretically such as text, cohesion, coherence, discourse, context,
situation, culture and other phenomena. In General Systemic Functional Grammar
(GSF), The ‘S’ for ‘Systemic’ implies that theory pays to the systemic relations
and their probabilities in a system network of relating and choices starting from
general to specific features which are paradigmatic in nature. It is also implies that
the systems of meaning that are interrelated to the phenomena under study. The
‘F’ for ‘Functional implies that is concerned with the functional realizations of the
system in structures.
SFL can be used for analyzing text as form of discourse. Halliday
(1994:107 ) says” The aim has been to context a grammar for purposes of text
analysis “: one that would make it possible to say sensible and useful things about
any txt, spoken and written in modern English” The text that is analyzed,
It is obvious that when analyzing text, the grammar becomes prominent
thing to describe how language works. Therefore, grammar and meaning are
closely related. Grammar becomes a study of how meanings are built up through
the use of words when language acts are performed as the expression of meaning.
The way how language works involves the idea that a language consist of a set
system, each of which offers the speakers (or writer) a choice ways expressing
meanings because the forms of the language that is used by a speaker represents
meanings.
In using language to express meaning, a speaker has a linguistics choice
that allows him/her to change the order of groups of words or in other words, the
speaker is given allowance to use many ways of language use, for example: when
a speaker intents to know the time, she/he may use his/her own expressions the
language offers such as:
(1) What’s the time
(2) What time is it, please?
(3) Would you mind telling the time, please?
(4) Tell me the time, please
(5) I’d like to know the time.
Those are different form of expressions. The first and second one are
interrogative forms, the third is requesting form. The fourth one is imperative
form while the last one is declarative form.
Most of linguistics choices a speaker makes are unconscious. He/she never
makes a conscious choice among the available language form. He/she had chosen
meaning (semantic) are related each other either in spoken or written language.
SFL believes that such a kind of relation is one of realizations. Therefore, the
linguistics analyses of texts can help us to find out why some text are more
effective than other text at communicating information. Text analysis is
advantageous in giving us a better understanding of the nature of language use in
English in many fields.
SFL puts a great interest in the relation between language and context. If a
text can be understood by the speakers or writers, there is a great deal about the
context in which the text occurs can be revealed. Therefore, SFL has been
described as a functional semantic approach to language which explores how
people use language in different context, and how language is structured for use
as a semiotic system.
2.1.4 Metafunctions of Language
Systemic functional Linguistics (SFL) describes that language is
functional. In general, metafunctions of language is major function of language to
give the message which has good formulation. Metafunction of language consists
of three major functional components, they are: The Ideational Function, The
Interpersonal Function, and The Textual Function.
2.1.4.1 The Ideational Function
The Ideational function relates to the inner worlds of reality, it is
“language about something”. According to Halliday (1978:112), whenever one
reflects on the external world of phenomena or the internal world of one’s
consciousness, the representation of that reflection would takes the form of
- Experiential Meaning
Focusing the language on the clause level with respect to the notion of
clause as representation. Clause as a representation means that one function of the
clause is as representation of experience of both external realities (i.e. reality
outside oneself ) and internal reality (reality inside oneself). The experiential or
representational function of language (clause) is realized by the transitivity system
of language. The outer world of reality that is brought into the inner world of
reality in one’s consciousness, which is encoded in the transitivity system of
language, is interpreted as a what-is-going-on process, which is related to material
actions, events, states and relations. The what–is-going-on process falls into
various processes. Halliday has identified the encoding processes of the realities
under discussion, and he has also
linguistically (grammatically) classified the various process types: (1) material,
(2) mental, (3) relational, and he classified other processes into three subsidiary
process types: (1) behavioral, (2) verbal, and (3) existential (Halliday 1985d,1994)
2.1.4.2 The Interpersonal Function
The interpersonal function is an interpretation of language in its function
as an exchange, which is a doing function of language; it is concerned with
language as an action. This meaning represents the speaker’s meaning potential as
an intruder that takes intro account the interactive nature of relations between the
addresses (speaker/writer) and the addressee (listener/reader).
At the grammatical level of interpretation with respect to the clause
that involves speaker, writer, and audience (listener or reader). Clauses of the
interpersonal function as clauses of exchange, which represent speech role
relationship. As Halliday (1985d:68-71) suggests, whenever two people use
language to interact, one of the things they do it is establishing a relationship
between them. In this, he sets out two most fundamental types of speech role or
functions: (1) giving, and (2) demanding (Halliday, 1994:68-69).
The interpersonal meaning of language (clause) in its as an exchange, in
which clauses of the interpersonal meaning that function as clauses of exchange
representing the speech role relationship, is realized by the mood system of
language (clause), the mood system of the clause is represented by the mood
structured of the clause, which comprises two major elements: (1) mood and (2)
residue. A mood element of an English clause typically consist of a subject and a
finite, whereas a residue element of a predicator, one or more complements(s),
and any number of different types of adjuncts.
An act of speaking is in interact, i.e. an exchange, in which there is
something either given, which implies there is something received, or else
demanded, which implies there is something given. If not, there is no interaction.
In other words, in an interaction involving speaker and listener, the speaker is
either giving something, which implies the listener is giving something in
response. What is exchange (demanded/given or given/received) is a kind of
commodity exchanged falls into two principle types: (1) good & services, and (2)
information. These two variables or types of commodity exchanged defined the
four primaries speech function of (1) offer, (2) command, (3) statement, and (4)
1. May I help you? (offer)
2. Shut up! (command)
3. John can type 45 words per minute. (statement)
4. When will he join the army? (question)
The interpersonal meaning of the clause can be observed on two levels. On the
first level, the speaker/writer as the producer of the clause can speaker or write
from a position carrying the authority of a discipline or an institution. In this, the
way the interpersonal meaning is delivered is determined by the knowledge or
power relationship exiting between the speaker/write and listener/reader. On the
other level, the speaker/writer may choose to communicate with the
listener/reader. appositions as a person, with no authority of a discipline, an
institution, or the like. For example: The lecturer says, “submit our homework
next Wednesday !” (first level)
My friend said to me, “Will you join with us tonight
2.1.4.3 The Textual Function
The textual function of language is an interpretation of language is its
function as a message, which is text forming function of language. This is
interpreted as a function that is intrinsic itself, but is it at the same time a function
that is domain in which language (text) is embedded. At the clause level, the
textual function is concerned with how inter-clausal elements are organized to
form unified whole texts that make meanings. In this, the textual function
The textual function of language (clause) inn its function as a message is
realized by the theme of language (clause). The theme system of the clause is
represented by the thematic structure of the clause, which comprises two major
elements: (1) theme, and (2) rheme.
In analysis of a thematic of a thematic structure of a thematic structure of a
text, it is possible to examine language in terms of Halliday’s three metafunctions;
the textual, and the ideational
Example:
Right student today we Learn
grammar
Textual Interpersonal Topical
Theme Rheme
As the above clause represents, the theme choices is the language may be
of three kinds: (1) textual, (2) interpersonal, (3) topical. The topical theme creates
the topic that the speaker (we) chooses to make the point of departure of the
message. The interpersonal theme occurs at the beginning of a clause when a
constituent is assigned a mood label (we as seen in the example). The textual
theme thematic prominence to the textual elements and has the function of linking
one clause or clause element are related to each other as such that they form a unit
of whole text within contexts (see right the example). The rheme is lean grammar,
2.2 Transitivity Process
Transitivity system belongs to experiential metafunctions. When it looked
at the experiential metafunctions, that’s mean looked at the grammar of the clause
as representation. It is called so because the clause in its experiential functions is a
way of representing pattern of experience. Through the system of transitivity, it
can be explored the clause in its aspects such is:
Who = does = what = to =whom, when, where, why or how function.
When people talk about what a word or sentence means, it is kind of
meaning they have in mind. Meaning in this sense is related to content or idea. So,
here the clause that functions as the representation of processes explores by
transitivity system. Transitivity analysis offers a description of one of the
structural strands of the clause. Transitivity specifies the different types of
processes that are recognized in the language, and the structures by which they are
expressed
There are three semantic categories which explain in general way. How
phenomena of the real world are represented as linguistic structures. These are:
The process itself
Participants in the process
Circumstances associated with the process
These provide the frame of reference for interpreting experience of what goes on
Processes
We use term process and participant in analyzing what is represent through
the use of language. Processes are central to transitivity. They are also regarded as
necessarily involve different kinds of participant in varying circumstances. While
participants and circumstances are incumbent upon the doings, happenings feeling
and beings.
Processes can be subdivided into different types. There are six different
process types identified by Halliday:
1) Material doing bodily, physically, materially
2) Mental sensing emotionally, intellectually, sensorilly
3) Relational being equal to, or some attribute of
4) Verbal saying lingually, signaling
5) Behavioral behaving physiologically and psychologically
6) Existential existing there exist
Those kinds of processes are realized by verbs. Traditionally, verbs have
been defined as “doing words”. But, as the above list indicates, it is obvious that
some verbs are not doing words at all, but rather express states of being or having
the process types differentiate kinds goings-on, for example:
Diana gave some blood (Material)
Diana through she should gave give blood (Mental)
Diana said that giving blood is easy (verbal)
Diana dreamt of giving blood (behavioral)
There is a reward for giving blood (existential)
Diana is a blood donor (relational)
The process type system is what underlies the differences between those kinds of
paradigm. Furthermore, in analyzing transitivity structure in a clause, we have to
1. The selection of process: the process choice will be realized in the verbal group
of the clause:
Last year Diana gave blood
2. The selection or participants: participants will be realized in the nominal
groups:
Last year Diana gave blood
3. The selection of circumstances: circumstantial meanings which are expressed
through adverbial group or prepositional phrase
Last year
-Means : tells by what means and is probed by what with? Diana gave blood
The transitivity of a clause is its process type. Each process type has associated
with it certain functional participant roles. Any process type can have
circumstantial elements in it.
Circumstances
The circumstantial system is what differences between a simple clause,
such as Diana gave blood, and an expanded clause such as last……. Geneva.
Diana gave blood voluntarily and without pain with her sister at the clinic.
Circumstances answer such question as when, where, why how….. many and as
what. They represent meaning about:
Time (temporal) : tells when and is probed by when? How often? How long?
E.g.: he goes to theater every Saturday night
Place (spatial) : tells where and is probed by where? How far? E.g : he goes to theatre every Saturday night.
E.g.: he goes there by bus
-Quality : tells how and is probed by how?
E.g.: he loved his girl truly, madly, deeply.
-Comparison : tells like what and is probed by what like?
E.g.: he was jumping around like a monkey on a zoo
Cause : Why
-Reason : tells the purpose and is probed by why? Or how?
E.g.: the sheep died of thirst.
- Purpose : tells the purpose and is probed by what for
E.g.: He wants to the shop for cigarettes
Accompaniment : tells with (out) who or what and is probed by who or what else?
E.g.: I left work without any briefcase/
Matter : tells about what or with reference to what and is probed by what about?
E.g.: this movie is talking about friendship.
Role : tells what as and is probed by as what? E.g. : he lived a quiet life as a beekeeper
Various circumstances are involved in the clauses and associated with the
2.2.1 Material Process
Material process is process doing, that some entity does something and
undertakes some action which may be done to some other entity. Clauses with a
material process obligatory have a doing (process) and a does (participant).
Actions involve actors of participants
The dog barked
participant process
The entity who or which does something is the Actor
These optionally is an entity to which the process is extended or directed
this entity which may be done to is Goal.
The dog
Because some processes also have a
second participant
for example:
barked the stranger
participant process participant
↓ ↓
As an Actor as a goal
The police arrested
Actor process
↓ ↓
As an Actor as a process
The term “Goal” implies meaning of “directed at”. Goal is that participant
at whose the process is directed or to whom the action is extended. Another term
undergoes the process. Nevertheless, the writer will keep familiar term goal in the
present analysis. The goal is most like the traditional direct object which is
known as transitive verb may take
There are two variables of material processes:
1. Creative (a ‘bringing about’)
2. Despositive (a ‘doing to’)
In the creative type of material process, the Goal brought about by the process:
Frederick Douglas wrote a narrative story
Actor Material process goal
In despositive type, we have doings and happenings
He dismissed the secretary
Actor Material process Goal Material process reflects a ‘doing to’ action
The gun discharged
Actor Material
Material process reflects a happening
2.2.2. Mental Process
Mental process is process of sensing, feeling, thinking, perceiving. Some
processes involve not material action but phenomena described as states of mind
or psychological event. People are not always talking about concrete process of
doing. They very often talk not about what they are doing, but about what they
Halliday (1994:112-119) calls processes which encode meaning of thinking or
feeling as mental processes. These processes tend to be realized through the use
of verbs like think, believe, understand, know, feel, smell, hear see, smell, want,
like please, admire, repel, enjoy , fear, frighten.
There are three types of mental process:
1. Affective or reactive (feeling) → Which is recognized through the use of
verbs of liking, fearing.
2. Cognitive (thinking) → which is recognized through the use of verbs of
thinking, knowing, understanding.
3. Perceptive (perceiving through the five senses) → which is recognized
through the use of verbs of seeing, hearing.
Mental process is mental, covert kinds of goings-on, and the participant
involved within it, is not so much acting or acting upon in a doing sense, as
sensing-having feelings, perceiving or thinking. We can recognize that mental
process is different from material process because it no longer makes sense to ask
“what did X do to Y”?
I hate injections
What did you do to the injection? I hate it
She believe his excuses
What did she do to his excuses? She believed them
With these clauses, it makes more sense to ask: “What do you think or feel
to know about X”?
-What do you think about injections? I hate them
What makes mental process looks different from material one is that we
probe them differently. That when we probe, we find we are not asking about on
action or doing in a tangible, physical sense; but it’s about mental reaction; related
to a through, feeling or perception.
The participant role in mental process are “senser” and “phenomena”
associated with any mental process. Even if one participant is apparently absent. It
will need to be retrieved from the context for the clause to make sense.
She believed always implies she believed something or someone. One
participant in the mental process clause must be a conscious human participant.
Because only a conscious human being can perform a mental process this
participant is called the senser.
She
The senser who fells, think or perceives.
Must either be human or an anthropomorphized non-human. It must be a
conscious being:
believed his excuses
senser mental process
I hate injections
senser mental process
It is important to consider what label to apply to the second participant in a
mental process clause. Halliday labels the second participant as the phenomenon.
The phenomenon is that which is sensed: felt, through or seen by the conscious
She believed his excuses
senser mental process phenomenon
Do you want more soup?
senser mental process phenomenon
Halliday also identifies two types of embedded phenomena: Acts and Facts
1. Phenomenon: Acts
Acts occur with mental processes of perception: seeing, hearing, noticing
etc.
An act is realized by an imperfective non-finite clause acting as if it were a simple
noun.
I saw the operation taking place
senser mental process phenomenon : Act
2. Phenomenon: Fact
A fact is an embedded clause is, usually finite and usually finite and
usually introduced by a “that”, functioning as if it were a simple noun
She didn’t realize that is was a bomb
2.2.3Relational Process
Relational process involves states of being, including having. Relational
process is typically realized by the verb be or some verb of the same class (known
as Copular verbs) : for example, appear, become, seem or sometimes by verb such
as have, own, process. Relational process can be classified according to whether is
being used to identify something or to assign quality to something
Process which establish an identity is called Identifying Process while
process which assign a quality is called Attributive Process
You
. Each has its own
characteristic participant roles.
1. Identifying Process
An identifying clause is not about ascribing or classifying, but defining.
The meaning of an identifying intensive is that “X” serves to define the identity of
“Y”. In this process, the participant roles are token and value.
are the tallest one here
Token identifying process value
You is identified as the “holder” or “occupant” of the identity or laber of the
a. Token : Which stands for what is being defined
the
tallest one.
Grammatically, the defining involves two participants:
b. Value : Which defines
All identifying clauses are reversible, they can form passives
The tallest one here is you
The reversibility of identifying clauses raises the question of determining
which “side” of the clause is the token, and which one is the value. This can be
determined both semantically and grammatically.
Halliday (1985:115) points out that semantically, the token will be a
“sign”. Name, from holder or occupant of a value which gives the “ meaning
referent, function, status or role” of the token. While, the token is the nominal
group which contains the “name” which gives the classification.
-Token will always be subject in an active clause.
-Value will always be subject in a passive clause.
2. Attributive Process
In the attributive sub-type, a quality, classification or descriptive epithet
(Attribute) is assign to a participant (carrier) which is realized by a noun or
nominal group. Attribute is a quality or epithet ascribed to the carrier (means that
“Carries the attribute a”) while carrier (means “X is a member of the class a”)
You are very tall
token identifying process value
I won’t be a liar
carrier attributive attribute
She is a talkative person
On the contrary to identifying clauses, the essential characteristic of the
attributive clauses is that they are not reversible. In the other words, there is no
passive form of the clause: the subject can never conflate with the role attribute,
but it will always conflate with the role of carrier.
Relational process can be further sub-classified according to whether they
are: intensive (quality), possessive and circumstantial.
The option available of relational process can be shown as the following
Examples:
Cytoplas is soft of a jelly-like material
Carrier Attributive: intensive Attribute
Plant cells have a cell wall
Carrier Attributive: possesive Attribute RELATIONAL
PROCESSES
Attributive : carrier, attribute
Identifying : token, value
Intensive
The yolk is inside the albumen
Carrier Attributive: circumstantial Attribute
The nucleus is the brain of the cell
Token Identifying :intensive Value
The transducer is Dr. Buick’s
Token Attributive: possesive Value
2.2.4 Verbal Process
Verbal process is process of saying ore of symbolically signaling. A verbal
process typically three participants.
- Sayer
- Receiver
- Verbiage
The sayer is the participant responsible for the verbal process, who encodes a
signal source. Does not have to be a conscious participant (although it typically
is). But anything capable of putting out signal.
The receiver is the one whom the verbal is directed. Or the one to whom
the verbalization is addressed.
The verbiage is nominalized statement of the verbal process, a noun
expressing some kind of verbal behavior, a name for the verbalization itself.
I asked my teacher a question
sayer verbal receiver verbiage
(Human participant)
She told me a rude joke
sayer verbal receiver verbiage (Human participant)
The sayer (signal source)needs not to be a conscious being.
The sign says “no smoking”
sayer verbal
(signal Participant)
The alarm clock screamed
sayer verbal
(signal participant)
2.2.5 Behavioral Process
Behavioral process is a process of physiological and psychological
behavior, like breathing, dreaming, snoring, smiling, hiccupping, looking,
listening, watching, and pondering.
Halliday (1994:120) describes the process semantically as a “half way
hour” between mental and material process. It means that, the meanings they
realized are midway between materials on the one hand and metals on the other.
There is one obligatory participant: the behaver, and is typically a conscious being
(like a senser in the mental process clause). But, the process is one of doing, not
sensing, such as:
She lives in a big city
behaver behavioral process Circumstance: place
Behavioral process often occur with circumstantial elements, particularly
of manner and clause.
He coughed loudly
behaver behavioral process Circumstance: manner
Behavioral process may contain a second participant that is called as
behavior
He smiled a broad smile
behaver behavioral process behavior
2.2.6 Existential Process
Existential process is the process of existence. It represents that something
exists or happens. It also represents experience by positing that “there was /is
something”.
There is a gateway in the garden
There was snow on the roof
Existential process existent Circumstance: place
On the wall there hangs a picture of me
Circumstantial: place
existential process existent
There is were two of us
Existential process existent
It is easy to identify a clause contains existential process, as the structure
involves the use of the word there. “There” has no representational function, it
merely because all English clauses require a subject. The word “There” is left
unanalyzed for transitivity. Existential process typically employs the verb “be” or
synonyms such as exists, arise, occur the only obligatory participant in an
existential process is called the existent. This participant which usually follows
the “there is/ there are “ sequence, may be a phenomenon of any kind and is often
2.3 Relevance Study
In completing this thesis, the writer consults some related analysis based
on the transitivity system to support this thesis. Some of the related research to
this thesis can be mentioned under following here such as:
Halliday (1994: 14) says that“The grammatical system by which clause as
being a mode of action, of giving and demanding goods, and services, information
and reflection. the endless variation and flow of events is achieved as transitivity.
The transitivity system construes the world of experience into a manageable set of
process types”
There are six process types:
(1) Material process is process of doing
(2) Behavioral process is process of behaving
(3) Mental Process is process of sensing
(4) Verbal process is process of saying
(5) Relational Process is process of being
(6) Existential process is process of existing
Sinar (2007: 44-46) in her research GSFLT is a theoretical framework that
accommodates certain aspects and dimensions of interpretation that will in turn
enable analysis to make appropriate choices whereby the target direction and goal
can be achieved efficiently and effectively as an end of a discourse analysis.
Mandasari, (2001) in her thesis, “An Analysis of Six Types of Transitivity
Process in Kangguru Radio English Script” She explores the transitivity process
Systemic Functional Approach., she found material process as the most dominant.
From her thesis, the writer get the understanding the manner of analyzed her data.
Andriyani, (2008) in her thesis “Transitivity Process In Worldview’s
Articles of Newsweek” by adopting the Systemic Functional Approach, found
material process as the most dominant. From her thesis, the writer can get the
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY
3.1 Research Method
There are three kinds of research based on the location of the research
example library research laboratory, and field research. (Bungin, 2005:40-41). In
this thesis, the library research method is applied by collecting some theories and
information about transitivity process from books, thesis, internet and other
sources to support the writing.
3.2. Method of Collecting Data
According to Arikunto (2006:223-232) there are five kinds of method in
collecting data i.e. test, interview, questioner, observation, and documentation. In
this writing, the documentation method is used in collecting data. The data was
collected by using purposive sample. From articles of Time Magazine, the writer
chooses “Arts” article in February and March 2009 (Fourth edition, Vol 173).
- NO 6: Television “Life After Earth” article 16th , February 2009. - NO 7: Movie “And Emmy goes to….” article 23rd, February 2009.
- NO 8: Exhibition “The Art of Diplomacy” article 2nd, March 2009. - NO 9: Books “Jungle Fever” article 9th, March 2009
3.3 Method of Analysis Data
The data are analyzed by using descriptive quantitative and qualitative method by
Arikunto (2006:239) and applied some procedures or steps. Firstly, the writer
divides the text on each article into clauses. The total number of the clauses in
each articles become the population and also as the sample in the analysis.
Secondly, identifies their process and then classifies them into their process. And
thirdly, the writer tries to find the most dominant process in all of articles.
In order to get the most dominant process, the writer uses the following
formula from Bungin, (2005:171-172).
% 100 x N fx n =
Where, n = Percentage of types
fx = Total types frequency of the sub-category N = Total types of all categories
For example:
Taken from “Arts” article (Vol 173, No 8)
At a time more conventional channels of communication between Britain
and Iran have stalled, Mac Gregor’s cultural diplomacy is opening up another
avenue for dialogue.
This sentence consist of two clauses, they are:
(1) At a time more conventional channels of communication between Britain and
Iran have stalled.
(2) Mac Gregor’s cultural diplomacy is opening up another avenue for dialogue.
After dividing into some clauses, then they are identified and classified
Example:
At a time more conventional channels of communication between Britain and Iran
have stalled.
At a time More conventional channels of
communication between Britain and Iran
Have stalled
Circumstance: time Actor Process:Material
Mac Gregor’s cultural diplomacy is opening up another avenue for dialogue
Mac Gregor’s cultural diplomacy is opening up another avenue
Actor Process: Material Goal
After writer identifies and classifies them, the writer tries to get which
process is the most dominant process of all “Arts’ articles by using Bungin’s
formula. Finally, the writer draws conclusions and suggestions.
CHAPTER IV
4.1 The Analysis of the Data
4.1.1 No. 6: Television “Life After Earth”
In “Arts” article No.6: Television “Life After Earth”. It is discovered that
the process of Material gained 47 clauses, the process of Mental gained 10
clauses, the process of Relational gained 17 clauses, the process of Verbal gained
5 clauses, the process of Behavioral process gained 3 clauses and the process of
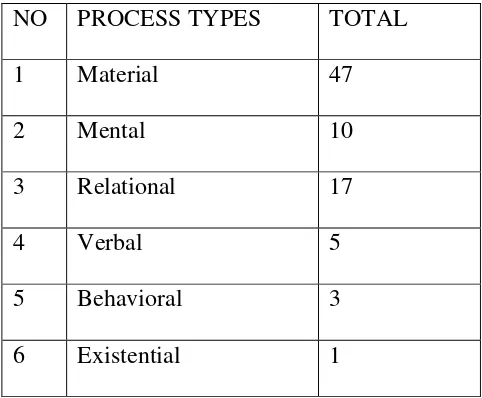
[image:44.595.107.348.318.517.2]existential gained 1 clause. It can be seen in this following table:
Table 1. Process Types of Transitivity of Arts article “ Life After Earth”
NO PROCESS TYPES TOTAL
1 Material 47
2 Mental 10
3 Relational 17
4 Verbal 5
5 Behavioral 3
6 Existential 1
From the findings above, it can be concluded that in this article has the
Material process as the most dominant process, and then followed by Relational
process, Mental process, while Verbal and Behavioral process has same number
and the last Existential process as the lowest process.
For more detail explanation, analysis of transitivity process in the “Arts”
article “Life After Earth” can be seen below:
1. Battlestar Galactica is more than a space chase: it’s became a lyrical tale of humanity under siege
Battlestar Galactica is more than a space chase: it’s became a lyrical tale of humanity under siege
Carrier Relational Attribute
2. Many Science-Fiction and Fantasy sagas are driven by the quest for One Big Solution: a singular objective,
Many Science-Fiction and Fantasy sagas
are driven by the quest for One Big Solution: a singular objective,
Recipient Material Actor Goal
3. that realized, fixes everything.
that Realized, fixes everything.
Mental Phenomenon
4. Someone throws a ring in a volcano
Someone throws a ring in a volcano
Actor Material Goal Circumstance: place
5. and Sauron is obliterated.
and Sauron is obliterated.
Actor Material
6. Someone kills the emperor
Someone kills the emperor
Actor Material Goal
7. and balance is restored to the force.
and balance is restored to the force.
Actor Material Goal
8. The One Big solution is us
The One Big solution is us
Carrier Relational Attribute
9. that is Earth.
that is Earth.
Carrier Relational Attribute
10. Somewhere a few thousand humans have escaped near genocide by the Cylons,
Somewhere a few thousand
humans
Recipient Material Circumstance: place
Actor
11. The survivor are driven by the search for a planet __Ours__
The survivor are driven by the search for a planet __ Ours__
Recipient Material Actor Goal
12. on which a religious legend says the “13th tribe” of man long ago settled. on which a religious legend say the “13th “ of a man
long ago settled
Sayer Verbal Verbiage
13. Be careful what you wish for.
Be careful what you wish for
Senser Mental
14. Last year, at the midpoint of BSG’s fort and final season the fleet landed on Earth,
Last year, at the midpoint of BSG’s fort and final seasaon
the fleet landed on Earth,
Circumstance: time
Goal Actor Material Circumstance:
place 15. to find a dead, nuclear wasteland.
to find a dead, nuclear wasteland.
Material Goal
16. It is as if Moses
It is Moses
Carrier Relational Attribute 17. had crossed the desert
had crossed the desert
Material Goal
18. to find that the promised land
to find that the promised Land
Material Actor
19. had fallen into the ocean. had fallen into the ocean.
20. The focus of human kind’s survival strategy and religious mythology instantly turned to radioactive ash.
The focus of human kind’s survival strategy and religious mythology
instantly turned to
radioactive ash
Actor Circumstance:
manner
Material Goal
21. Now returned for its final run of 10 episodes,
Now returned for its final run of 10 episodes Circumstance: time Material Goal
22. BSG asks an unusual question: What happens after the big solution turns our to solve nothing?
BSG asks an unusual
question:
What happens after the big solution turns our to solve nothing?
Sayer Verbal Target Verbiage
23.BSG began with a straightforward sci-fi premise: a space-Chase saga. BSG began with a straightforward sci-fi
premise
a space- Chase saga
Actor Material Circumstance: comitative Goal 24. There are no cute droids a la Star wars or sexy aliens a la Star Trek. There are no cute droids a la Star Wars or sexy aliens
a la Star Trek, Existential Existent 25. Its universe is dirty,
its universe is dirty, Carrier Relational Attribute 26. lived in and warn out.
lived in and warn out. Behavioral Circumstance: place 27. The ships are cramped.
The ships are cramped.
Actor Material
28. The humans carry guns
The humans carry guns
29. that shoot bullets
that shoot bullets
Material Goal 30. They also eat__ yum! __
They also eat yum!__
Actor Material Goal
31. processed algae processed algae Material Goal
32. vacuumed up from uninhabited planets. vacuumed up from uninhabited planets. Material Circumstance: location
33. And they are given for creative basic-cable profanity –frak being BSG’s Fword of choice.
And they are given for creative basic-cable profanity-frak being BSG’s Fword of choice.
Actor Material Goal
34. That’s not to say BSG is a bummer; it’s thrilling, lyrical, even funny. That’s not to say BSG is a bummer; it’s thrilling, lyrical,
even funny Verbal Verbiage
35. A politician says “wondering how to spin the news about Earth, real estate precise are low”.
A politician say “wondering how to spin the news about Earth, real estate prices are low”
Sayer Verbal Verbiage
36. But it is an adventure of exhaustion, not exhilaration.
But it is an adventure of exhaustion, not exhilaration Carrier Relational Attribute
37. What has kept that the diaspora going on
What has kept that the diaspora going on
Material Actor Material
38. this grim cruise is the promise of President Laura Roslin (Mary Mac Donnell), this grim cruise is the promise of President Laura Roslin
(Mary Mac Donnel
39. a bureaucrat who becomes leader
a bureaucrat who becomes leader
Actor Material Goal
40. After the government is vaporized After the government is vaporized
Behaver Behavioral 41. and who believes
and who believes Mental 42. she is a prophet
she is a prophet
Carrier Relational Attribute 43 to lead humankind home.
to lead humankind home. Material Goal
44. What keeps the viewer
What keeps the viewer
Material Actor
45. the cat-and mouse game with the Cylons, who can hide
the cat-and mouse game with the Cylons, who can hide
Actor Circumstance: comitative Material
46. among and interbreed with humans.
among and interbreed with humans.
Material Circumstance: comitative 47. The robots, at least, are sexy
The robots, at least are sexy
Carrier Relational Attribute
48. launched with a 2003 miniseries, launched with a 2003 miniseries Material Circumstance: comitative
49. BSG evolved into a sci-fi tale of the war on terrorism.
BSG evolved into a sci-fi tale of the war on terrorism.
50. Because Cylon “skin-jobs” pass for human __ some believe Because Cylon “skin-jobs” pass for human__ some believe
Senser Phenomenon Mental
51. They are human__
They are human__
Carrier Relational Attribute 52. The fleet feel into the kind of paranoia
The fleet feel into the kind of paranoia Senser Mental Circumstance: location 53. that post-9/II saw a sleeper-cell agent on every commuter flight. that post-9/II saw a sleeper-cell agent on every
commuter flight.
Senser Mental Phenomenon
54. It also dramatized the danger of religious extremism
It also dramatized the danger of religious extremism
Actor Material Goal
55. The Cylons are monotheist
The Cylons are monotheist Carrier Relational Attribute
56. who see their human creators (who worship a version of the Greco-Roman phanteon as heathens).
who see their human creators (who worship a version of the Greco-Roman phanteon as heathens).
Mental Phenomenon 57. The parallels were uncomfortable.
The parallels were Uncomfortable.
Token Relational Value
58. Admiral William Adama (Edward James Olmos, a far cry from the cuddly Lorne Greene of the 70’s BSG) unflinchingly over-rides civilian rule,
Admiral William Adama (Edward James Olmos, a far cry from the cuddly Lorne Greene of the 70’s BSG
unflinchingly over-sides civilian
rule
Actor Circumstance:
manner
Goal Material
59. when he sees fit for security.
when he sees fit for security.
60. Roslin is not above-box stuffing
Roslin is not above-box stuffing Carrier Relational Attribute
61. to ensure she leads the quest for Earth.
to ensure she leads the quest for Earth
Material Actor Material Goal
62. In season 3, when humanity lived under an Iraq-like occupation by Cylons In season 3, when humanity lived under an Iraq-like
occupation by Cylons Circumstance:
time
Behaver Behavioral
63. to reform rather than exterminate the survivors?
to reform rather than exterminate The survivors?
Material Material Goal
64. Characters turned Characters turned
Actor Material
65 to bombings and suicide attacks against Cylons and their human collaborators. to bombings and suicide attacks against Cylons and their human
collaborators.
Material Goal
66. Roslin is idealistic
Roslin is idealistic
Carrier Relational Attribute 67. but possibly blinded by beliefs,
but possibly blinded by beliefs,
Circumstance: manner Mental Phenomenon 68. Adama is high-handed.
Adama is high handed.
Carrier Relational Attribute
69. Even Swashbuckling pilot Starbuck (Katee Sackroff is unstable as often as heroic).
Even Swashbuckling pilot Starbuck (Katee Sackroff)
is unstable as often as heroic.
70. The Cylons, prove a fascinating society with doubt and riven by debate over their religious mission.
The Cylons, prove a fascinating society
with doubt and riven
by debate over their religious mission
Actor Material Goal Circumstance:
comitative
Goal
71. In its episode, unsettling revelations about Earth’s past come as the humans (Now allied with a breakaway group of Cylons,
In its episode, unsettling revelations about Earth’s
past come as the humans (Now allied with a breakaway group of Cylons), Circumstance: matter Material Circumstance:
role 72. wonder what to do next.
wonder what to do next
Material Goal
73. In the process BSG shifts from the topical to the timeless rising questions about the nature of humanity as the protagonist are forced
In the process BSG shifts
from the topical to the timeless
rising questions about the nature of humanity as the protagonist
are forced
Actor Goal Material Circumstance:
matter
Material
74. to redefine their purpose.
to redefine their purpose
Material Actor Goal
75. Can humankind save itself
Can humankind save itself
Actor Material Goal
76. not finishing some quest
not finishing some quest Material Goal
77. but understanding the threats of its own creation?
but understanding the threats of its own creation
Mental Senser Phenomenon
As this brilliant space saga comes to an end
Actor Material Goal
79. humans are forced humans are forced
Actor Material
80. to recognize that to recognize that Verbal target
81. the big solution is not out in the stars
the big solution is not out in the stars.
Token Relational Value
4.1.2 No.7: Movies “And Emmy Goes To……”
In “Arts” article No 7 “And Emmy Goes To….”. It is discovered that the
process of Relational gained 12 clauses, the process of Verbal gained 2 clauses,
the process of Behavioral process gained 1 clause and the process of existential
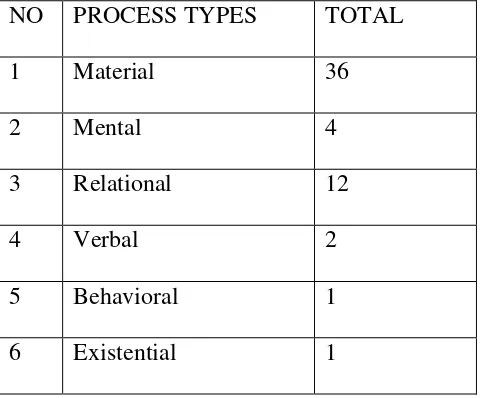
[image:54.595.109.349.209.408.2]gained 1 clause. It can be seen in this following table:
Table 2. Process Types of Transitivity of Arts article “And Emmys Goes To…..”
NO PROCESS TYPES TOTAL
1 Material 36
2 Mental 4
3 Relational 12
4 Verbal 2
5 Behavioral 1
6 Existential 1
From the findings above, it can be concluded that in this article has the
Material process as the most dominant process, and then followed by Relational
process, Mental process, Verbal process, and Behavioral process while Existential
process as the lowest process.
For more detail explanation, analysis of transitivity process in the “Arts”
article “And Emmys Goes To…..” can bee seen below:
“AND EMMYS GOES TO……”
1.Once again Hollywood has nominated little films for its big awards
Actor Material Goal 2. No, Not Slumdog Millionaire__ that is a breakout hit
No, Not Slumdog Millionaire__ that is a breakout hit
Carrier Relational Attibute
3. but worthy miniatures like Frost/ Nixon that look so good on the small screen but worthy miniatures like
Frost/Nixon
that look so good in the small screen
Behaver Behavioral Circumstance:
place
4. The members of the motion are still filling out their ballots, The members of the motion are still filling out their ballots,
Actor Material Goal
5. but right now the Anglo-Indian melodrama Slumdog Mill