1
I. INTRODUCTION
This chapter discusses certain points: introduction deals with background of the problem, identification of problems, limitation of the problem, formulation of the problem, objectives of the research, uses of the research, and scope of the research.
1.1Background of the Problem
Language is a means of communication for the people to interact with another. English is one of the foreign languages which is spoken by the people all over the world. In Indonesia, English is taught at formal education settings, from Elementary School at grade 4 (even some of which starts teaching English in the first grade), Junior High School level, Senior High School level, and University in Indonesia. There are four skills of language that should be mastered in learning English, i.e., listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Students are hoped to master these skills.
2
language skills. This objective is basically the same as comprehension of reading texts where the students are faced with the text written in English then they are hoped to read it in order to gather information from it. In this case, students use skill of reading in order to understand the written text. In other words, they access knowledge by reading skill.
To get the knowledge from the text, it is important for students to have a good reading comprehension. Without comprehension, reading would be empty and meaningless. Comprehension is not only intended to know what the letters stand for, but also involved power of fully understanding. Reading involves more than words recognition; that without comprehension, no reading takes place. It means that comprehension determines the essence of the reading process.
Reading comprehension requires motivation, mental frameworks for holding the ideas, concentration and good study techniques. There are many ways to be good at reading such as the readers should know the purpose in reading, they also should have awareness of type of the material they are reading, and kinds of learning strategies can also be used in reading that can help them in comprehending the reading text.
3
students do not have good self confidence in learning English, and the students have low motivation in learning.
There are some factors that cause the students to get difficulties in comprehending the text. The first is interest in the material (the text), it is one of important factor, if the students are not interest in material, they have motivation in their self to get information from the material. The second is schemata, schemata is schema is a cognitive framework or concept that helps organize and interpret information, it is important to understanding material and usually students not have clear schemata to the material which they are learning about, then that is one of causes the students difficult in comprehending the text . And the third is ignorance of reading techniques, students usually ignore the reading technique because they do not understand about it, so they read without using reading technique.
In teaching learning process the teacher’s functions as a facilitator who has
responsibility to help the students to choose and create an interesting technique in order to reach the aims of teaching and learning stated in the curriculum.
In selecting the material, it is better for the teacher to consider which material is the most effective in teaching reading, so that the teaching of reading comprehension can be useful to help the students to comprehend reading materials.
Based on researchers’ observation and interview to the first year students and
4
achievement in English especially in reading skill. English teacher in SMA Negeri 1 Gunung Sugih still used traditional technique, the technique is translation.
From the statement above, the writer would like to solve the problem by having comparative study between two technique, retelling story and translation from folktale. These materials are applicable for teaching reading comprehension. This research is aimed to find out whether one or both of them are effective or not
for increasing student’s reading comprehension achievement.
There are many materials that can be used to reading ability such us newspaper, bulletins, magazines, literary text and others. In this research is used folktale literary text to develop students’ reading ability. By studying literature materials the students will have a wide range of vocabulary and develop all of skills. While feeling entertaining by this interesting material, the students simultaneously can understand the folktale. In this way it is easier to know the meaning of the words of the folktale presented.
Teacher’s duty is not only to explain the materials, or select suitable material but
teacher also should give guidance, advice, support, and motivation to the students
whenever they need it. In order to improve students’ reading comprehension, the teacher should choose suitable technique and concern with students’ obstacles and
difficulties in learning reading.
5
technique, the students were supposed to be able to read a reading passage in the
target language into the students’ native language.
On the other hand, reading can also be taught through retelling story. Retelling story can be used to explain complex ideas or make important points about very real situation about the story. Teacher can use this technique to motivate students to understand and comprehend the story. In this technique, the students will be brought into an interesting and enjoyable situation, so students would be easier to comprehend the meaning and to find out the main idea of the text.
Considering these techniques above can be used for teaching reading. The writer did a research to see which one of the two techniques is more effective for teaching reading at Senior High School. The researcher is interested in comparing retelling story and translation in teaching reading comprehension through folktale.
1.2. Identification of the Problems
In relation to the background of the problem above, the following problems can be found:
1. The students get difficulties in comprehending the reading text. They get difficulties in getting information from the text, finding the main idea, finding the details, answering to the questions based on the text and making inference from the text. As the results the students got difficulties in retelling or in transferring the information from the text.
6
3. The students’ motivations in learning English are still low. So it is difficult to improve their English ability well.
4. The students have no good self confidence in learning English. So it is difficult for them to learn English well because they regard that English is difficult to be learnt well.
5. The teachers use inappropriate technique in teaching English. So it is difficult in helping students understand reading comprehension.
1.3 Limitation of the Problem
In line with the identification of the problems, the researcher realizes her capability in doing her research. Therefore, she focused her study only on the
students’ difficulties in comprehending the reading text because of inappropriate technique in reading.
1.4 Formulation of the Problems
Based on the limitation of the problem above, the writer formulates the problem as follows:
1. Is there any difference of student’s reading comprehension achievement between the students who are taught through retelling story and those who are taught through translation from folk tale?
2. Which of the two techniques is more effective for teaching reading?
1.5 Objectives of the Research
7
1. to find out whether there is any significant difference of student’s reading comprehension achievement between the students who are taught through retelling story and those who are taught through translation from folk tale. 2. to find out which technique is more effective for teaching reading.
1.6 Significances of the Research
The findings of the research may be beneficial not only theoretically but also practically:
1. Theoretically, the results of the research are expected to support previous theories dealing with retelling story and translation.
2. Practically, the finding of this research may give information to the English teacher that one of the two ways in this research is more effective in
improving the student’s achievement in reading comprehension.
1.7 Scope of the Research
8
students’ reading comprehension, the researcher measured the score of a set of pre-test and post-test.
1.8 Definition of Term
1. Reading comprehension is an activity of understanding printed text through
making sense a written text by relating written language to what we know and what we want to know.
2. Retelling story is requires the students to think more conceptually, to look
at the bigger picture rather than answering specific question about the text (Karen : 2001).
3 . Translation is changing a communication (a word, phrase, and sentence) to
other terms or to another form (verbal or symbolic) or to another level abstraction (simple or more complex) (Garrow : 1972)
4. Folktale is a very old traditional story from a particular place that was originally passed on to people in a spoken form.
5. Achievement in this research is the change or improvement of student’s
27
III. RESEARCH METHOD
3.1 Research Design
To conduct this research, the researcher used Pretest Posttest Control Group Design. This design belongs to true experimental designs. True experimental
designs have three basic characteristics: (1) a control group is present, (2) The sample are randomly selected and assigned to the groups, and (3) a pretest is administered to capture the initial differences between the groups (Hatch and Farhady 1982:22).
The researcher used this design because she wants to give special treatment to the experimental class using retelling story in teaching reading comprehension. There were two classes of this experimental study; one was experimental class which got treatment through retelling story and another as a control class which got treatment through translation.
The pretest was administered first before the treatment. It was intended to measure
the students’ basic ability of both in order to ensure their entry point. Control class was needed for comparison purposes because it lets the writer interpret her findings more confidently. Both of them got the same materials.
28
G1 (Random) : T1 X1 T2 G2 (Random) : T1 X2 T2 Notes:
G1 = experimental Group
G2 = control Group
T1 = the pretest
T2 = the posttest
X1 = treatment by the researcher (Teaching reading through retelling story technique )
X2 = treatment by the teacher (Teaching reading through translation technique)
3.2 Population and Sample
The population of the research was the first year students of SMAN 1 Gunung Sugih. The researcher was chose the first year students in the second semester of academic year 2011/2012. There were four classes of the first year students, that was XA, XB, XC, XD and each class consisted of 32 students. Their ages range from 15-16 years old.
The class as the sample was taken through lottery, because all the classes have the same opportunities to be chosen as the sample of this research. One was the experimental class I, and the other one was the experimental class II. In this case, the researcher asked the leader of each class to take a small piece of paper in order to know which the class would be as experimental class I or experimental class II.
3.3 Data Colleting Technique
In collecting the data, the researcher used reading test as the instrument. There were two kinds of test, pre-test and post-test. Pre-test administered in order to
29
and post-test administered after presenting the treatment in order to know the achievement of reading comprehension. The test designed based on School Based curriculum for the ten grade students.
3.4 Try-Out
The try-out was administered to determine the quality of the test that was used in taking the data. Before conducting the pre-test and post-test, a try out test was carried out. This test was administered in order to determine the quality of the test as instrument of the research.
3.4.1 The Validity
Validity is the extent to which a test measures what it claims to measure. It is vital for a test to be valid in order for the results to be accurately applied and
interpreted. Validity isn’t determined by a single statistic, but by a body of
research that demonstrates the relationship between the test and the behavior it is intended to measure. A test can be said valid if it measures the object to be measured and suitable for the criteria (Hatch and Farhady, 1982: 251).
There are four basic types of validity: content validity, criterion-related validity, face validity, and construct validity, (Hatch and Farhady, 1982:251). To determine the validity of the test, the researcher emphasizes only on content validity.
30
content validity of a test, the content of whatever the test will measure must be carefully defined.
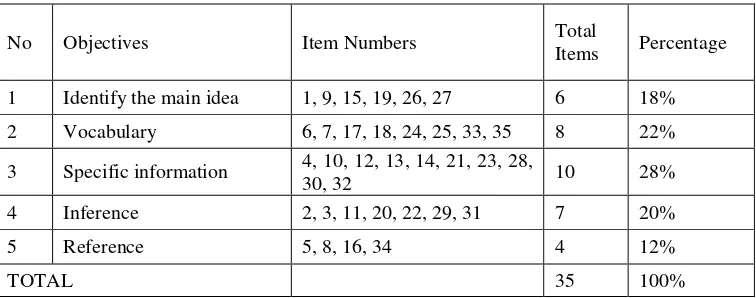
Table 3.1. Tabel of specification of try out test
No Objectives Item Numbers Total
Items Percentage
1 Identify the main idea 1, 9, 15, 19, 26, 27 6 18%
2 Vocabulary 6, 7, 17, 18, 24, 25, 33, 35 8 22%
3 Specific information 4, 10, 12, 13, 14, 21, 23, 28,
30, 32 10 28%
4 Inference 2, 3, 11, 20, 22, 29, 31 7 20%
5 Reference 5, 8, 16, 34 4 12%
TOTAL 35 100%
3.4.2 The Reliability
Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure. A test was considered reliable if we got the same result repeatedly. For example, if a test was designed to measure a trait (such as introversion), then each time the test was administered to a subject, the results should be approximately the same. Unfortunately, it was impossible to calculate reliability exactly, but it can be estimated in a number of different ways.
31
Notes:
R : coefficient of reliability between odd and even numbers N : number of the students correctly. It was calculated by the following formula:
Notes:
LD : the level of difficulty
R : the number of the students who answer correctly N : the total of the students in the higher and lower group (Heaton,1975:182)
The criteria of the difficulty level are < 0.30 = difficult
32
3.4.4 Discrimination Power
The discrimination power (D) is the proportion of the high group students getting the items correct minus the proportion of the low-level students who getting the items correct. The discrimination power of an indicate item the extent, to which the item discriminates between the test taker from the less able. The formula of the discrimination power is:
Notes:
D : discrimination power
U : the number of students from the upper who answer correctly L : the number of students from the lower who answer correctly N : the number of the students
(Shohamy, 1985:82)
The criteria of discrimination power are:
1. If the value is positive, it has positive discrimination because large number or more knowledge students than poor students get the item correct. If the value is zero, it means that there is no discrimination. 2. If the value is negative, it has negative discrimination power because
lower and higher level of the students gets the item correct.
3. In general, the higher discrimination index is better. In the classroom situation most items should be higher than 0.20 index.
(Shohamy, 1985:82)
Ha = L-ratio is higher than L-table (the distribution of the data is not normal)
From the calculation, the distribution of the data is normal (L-ratio is smaller than L-table)
3.5 Procedures of Taking the Data
33
The researcher took two classes to determine the experimental class I and experimental class II.
2. Administering try-out.
The try out administered to determine the quality of the test. 3. Administering pre-test.
The researcher and the teacher administer the pre-test on both groups experimental class I and experimental class II.
4. Conducting treatment. 5. Administering the post-test.
The researcher and the teacher administered the post-test, experimental class I and experimental class II.
6. Scoring the student’s work.
The researcher scored the learner’s work in order to get the data. 7. Analyzing the data.
After collecting the data, the researcher analized the data. 8. Testing hypothesis.
After analyzing the data, the researcher tested the hypothesis.
3.6 Scoring System
In scoring the result of students’ test, the researcher used Percentage Correct (Lyman, 1971:95). The score is 1 for each correct number. In order to make scoring easier, each correct answer divided by total number of the test and
34
The researcher calculated the average of the pre-test and post test by used this formula:
T R X%c 100
(Lyman, 1971: 95) Where:
X%c = percentage of correct score
R = number of right answers
T = total number of items on test
3.7 Data Analysis
The writer computes the students using the following steps: - Scoring the pre-test and post-test.
- Tabulating the results of the test and calculating the score of the pre-test and post-test.
- Drawing conclusion from the tabulated results of the pre-test and post-test administered, that was by statistically analyzing the data using statistical computerization i.e. Independent Groups T-Test of Statistical Package for Social Science (SPSS) version 20.0 for windows to test whether the
increase of students’ gain is significant or not, in which the significance
35
3.8 Treatment of the Data
In order to determine whether the data were good or not, the researcher analized the data by:
1. Scoring the pre-test and post-test
2. Tabulating the result of the thesis and calculating the mean of the pretest and posttest. To compute the average score or mean of the pretest and posttest, the researcher used a very simple statistic formula as follows:
Notes:
: mean (average score)
∑x: total number of the student’s score N : total number of the students
(Hatch and Farhady, 1982:5)
3. Calculating from the tabulated results of the pretest and posttest administered, that was by statistically analized the data using t-test to test whether or not the
difference between pretest and posttest was significant. It was used as the data comes from the same sample or known as paired data (Hatch and Farhady, 1982).
4. Administering the Normality Test
This test was used to measure whether the data in two classes were normally distributed or not. The data are tested by One-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Formula (SPSS 20).
36
The hypothesis is accepted if the result of the normality test is higher than
0.05 (sign > α). In this case, the researcher used level of significance of 0.05
5. Administering the Homogeneity Test
This test was used to know whether the data of the posttest from the
experimental class 1 and from the experimental class 2 were homogeneous or not. The data tested by Independent Sample Test (SPSS 20). The criteria for the homogeneity of pre test are:
H1: There is no significant difference in the level of ability (equal) H0: There is a significant difference in the level of ability (not equal)
The criteria for the hypothesis is: H1 is accepted if the result of Homogeneity
test of pre test is higher than 0.05 (Sign > α).
3.9 Hypothesis Testing
After collecting the data, the writer recorded and analyzed them in order to find
out whether there is an increasing in students’ ability in reading comprehension of folktale or not after the treatment. The writer used Independent Group T-test to know the level of significance of the treatment effect.
37
X : Mean from the difference pre-test and post-test of experimental class
and control class
c
X : Mean from the difference pre-test and post-test of experimental class
9
II. FRAME OF THEORIES
2.1 Review of Previous Related Research
There are several studies which have been conducted in relation to the similar
topic under discussion. First, Kissner’s (2006) study, investigated retelling story.
She found that retelling was used for years as a dependent variable in reading research experiments. After a previous researcher has done some intervention —a teaching method, questioning strategy, and so on—and asked students to read a text, the benefits of that intervention were measured by asking the student to retell what was read. The retelling was then scored based on a list of criteria to be included. Some retellings were “cued,” with the student prompted to give specific information, either by a story grammar chart or direct questioning. Others were simply given on a free recall basis.
10
ones. Being able to talk through a story helps student to process what is going on, and come to a new understanding of events or information.
Furthermore, Marantina (2006) she found that teaching reading comprehension through retelling story gives higher result than through translation because in retelling story the students are able to bring them into an interesting situation and enjoyable situation and the students just pay attention for the explanation, this is easier way than students have look to dictionary to comprehend the story.
Based on all the findings of the previous research above, it can be stated that teaching reading comprehension through retelling story gives better improvement than through translation. Retelling story requires the student to think more conceptually, so bring the student into an interesting and enjoyable situation. Besides that retelling story makes students able to talk through a story, helps students to process what is going on, and come to a new understanding of events or information. But, there is one issue that remains unresolved. From all previous finding, the previous researchers did not mention folktale as the material to teach through retelling story and translation. In this research, researcher wanted to resolve that issue by teaching through retelling story and translation used folktale as the material.
2.2 Review of Related Literature
2.2.1 Concept of Reading Comprehension
11
is something that makes sense to reader and always should or Nuttal (1982: 45) who states that reading as the meaningful interpretation of printed or written symbol. He suggests that reading is an active process because it involves an interaction between thought and language. It means that the readers always activate their minds to get meaning and information while interacting with the written text.
Someone has purpose when he is reading. Usually the purpose of reading a passage is to find ideas from the reading passage. As Suparman (2005: 1) states there are two major reasons for reading (1) reading for pleasure; (2) reading for information. Both are need reading comprehension.
Furthermore, Smith (1982: 166) states that reading is a matter identifying letters in order to recognize words in order to get the meaning from what is read, involving making connection among words and ideas presented in the text and the
readers’ own background knowledge. Another linguist, Dallman (1982) states that
reading is more than knowing what each letter of alphabet stands for, reading involves more than recognition. That is without comprehension, no reading take place. Therefore, if the readers can read the word but can not understand what they read, they are not really reading. In reading, the readers are active and intentional constructing meaning using the message in the print and their own background knowledge.
12
fewest, most productive cue necessary to confirm or reject the expectation. This is sampling process in which the reader takes advantages of his knowledge of vocabulary, syntax, discourse, and the real world.
Richard (1986) defines comprehension as the process by which the person understands the meaning of the written or spoken language. It means that
comprehension is mind’s act or power of understanding what has been written.
From these statements, the writer assumed that comprehending is the process of
mind’s act understanding the meaning of written or spoken language.
According to these views, it is clear that reading and comprehension are regarded as one activity which can not be separated, and each program is depending on the progress of activity of mind. In other words, reading comprehension is an activity to grasp the meaning of written materials with fully understanding.
Heilman, Blair, and Rupley (1981: 242) in Amri (2011) said that reading comprehension is a process of making sense of written ideas through meaningful interpretation and interaction with language. Comprehension is the result of reading. Moreover, they categorize reading comprehension into three levels of comprehension:
1. Literal comprehension
13
so forth. Recall of main idea explicitly stated and knowledge of sequence of information presented in passage.
2. Interpretative comprehension
Interpretative comprehension means understanding of ideas and information not explicitly stated in the passage. For example: to understand the author’s tone, purpose and attitude, infer factual information, main ideas, comparisons, cause-effects relationship and also summarize the story content.
3. Critical comprehension
Critical comprehension is analyzing, evaluating and personally reacting to information presented in a passage. For example: personally reacting to information in a passage, indicating meaning to the reader, analyzing the quality of written symbol or information in the terms of standards.
From the explanation above, it is quite clear that comprehension is important in reading. Comprehension is the result of reading. By comprehension meaning that the readers use their previous knowledge to response with the written text. In comprehension, we process deeply the information, so that we can make a meaningful interpretation of it.
14
knowledge combined with the visual (written) information result in his comprehending the text. In short, we can say that reading comprehension is a combination of recognition intellect and emotion interrelated with prior knowledge to understand the message communicated.
2.3 Concept of Teaching Reading
Alyousef (2005: 143) says that in reading, contemporary reading tasks, unlike the traditional materials, involve three-phase procedures: pre-, while-, and last-reading stages. The pre-last-reading stage helps in activating the relevant schema. For example, the teachers can ask students questions that arouse theirs interest while previewing the text. The aim of while-reading stage (or interactive process) is to
develop students’ ability in tackling texts by developing their linguistic and
schematic knowledge. The last-reading includes activities, which enhance learning comprehension using exercises, cloze exercises, cut-up sentences, and comprehension questions.
The aim of teaching reading is to develop students’ skills that they can read
English texts effectively. To be able to do so the readers should have particular purposes in their mind before they interact with the texts. Effective and efficient reading is always purposeful and tends to focus mainly on the purpose of the activity. Then the purpose of reading is implemented into the development of different reading techniques. These can be real when the students read and interact with various types of texts, i.e. functional and monologue texts.
15
reading technique should be matched to reading purpose to read efficiently and effectively. As Suparman (2005) states that there are two major reasons for reading (1) reading for pleasure; (2) reading for information (in order to find out something or in order to do something with the information readers get).
The researcher assumes that in teaching reading, appropriate and possible technique should be applied based on the purpose of reading in order to get the comprehension. They use reading technique to make their reading efficient and effective. Retelling story and translation will be possible to be applied by the Senior High School students in their reading.
2.4 What is Folktale?
Folktale is one of genre in narrative structure text. Based on Larson (1984 ) narrative text is an account of events. It means that narrative text is one that contains a series of events that is created in a constructive format that describes a sequence of fictional or non-fictional events. The purpose of narrative text is to amuse the readers with actual or imaginary experiences in difference ways.
Narrative always deals with some problems which lead to the climax and then turn into a solution to the problem.
The examples of genres that fit the narrative text structure:
• Folktale : a very old traditional story from a particular place that was originally passed on to people in a spoken form.
• Fairy tale : an old story about magic things happened intended for amusing and giving lessons, meanings, and moral values.
16
group of animal stories.
• Myth : a story from ancient times, especially one that was told to explain about natural events or to describe the early history of
place or people.
In this research, the researcher will focus on narrative text especially folk tale. Thompson (1977) defines folktale is the mere report of a recent happening, a legend of long ago, or on elaborately contrived fiction, men and women have hung upon his words and satisfied their yearnings for information or amusement, for incitement to heroic deeds, for religious edification, or for release for the over powering monotony of their live.
A folktale is interesting material, so that the students can easily accept the material, and they can better comprehend in reading. The students usually like the interesting reading materials, such as those about love, comedy, or something that not boring. Folktale is one of interesting material that can be used to help the students increase their comprehension in reading skill.
Students can read the folktale and get information from the material. After getting the information, the students analyze the theme, characteristic, and the moral messages. If the students can explain all of the indicators to measure the reading comprehension, it means that the students accept the material.
17
understanding in the environment and natural phenomena. There are various tale stories. They can be adventures, romance, jealousy, comedy, or extraordinary.
As the definition above, folktale bringing entertainment and relaxation. That helps students to increase their understanding in reading material. Beside that, folktale has a moral message in every story that makes students not only get information from the story but also get moral message by the story.
Folktale as a reading material makes students relax, because the content of the story usually about comedy, romance or about historical of a place. First, students read folktale, after that students look for the information in the story. Then, students know about the conclusion of the story and can explain the story by their own critical thinking.
Concerning the description above, the researcher infers that folktale is the report of recent happening that can be means for moral teaching. Researcher will apply the material . The example of folktale : Lutung Kasarung, The Legend of Roti Island, Bawang Merah and Bawang Putih.
2.5 Concept of Retelling Story
According to Karen (2001), retelling does not mean memorizing, retelling means
recounting the same story into the students’ own word. Retelling story requires
the students to think more conceptually, to look at the bigger picture rather than answering specific question about the text.
18
but also use their own language to retell the idea of the text. It is helps the students to have good concept in thinking.
Students use retelling story to make their concept about text stronger. Before the students retell the idea of the text, students have to be able to identifying the main idea of the text and answer the specific question about the text. After that they retell the idea of the text or the story by their own words.
Brown and Cambourne (1987) state that in retelling story, the function of a teacher is as a tutor. The teacher helps the students to absorbs the information from the students to retell the story and encourage the students to retell the story The function of teacher is important in retelling story. Sometimes the students face the difficulty in understanding about the meaning of the text, teacher have to help the students by give some clues that related to the text.
In retelling story, teacher helps students to absorb the information. If the students face the difficulty, teacher help the student by give some clues, beside that, teacher gives the students some question that help students to get specific information.
Matthew (1994) states that there are some physical aspects in retelling story, that is: eye contact, volume, body movement and hand and arm gestures. In retelling story, a story teller can combine gestures and expression.
19
to get good performance when they retell the text or story, while the teacher knows some indicators to evaluate about the students retelling story performance.
The story teller visualizes the characters and setting, and then improvises the actual wording. In this technique, the students will be brought into interesting and enjoyable situation so that they will feel easier to comprehend the meaning of the words. Moreover, this technique is more suitable applied relate to condition and needs of the students.
Dealing with the idea above, Gambrell and Dromsky (2000) state that there are some tips that should be kept in mind by the teacher to engage students in retelling activities. Those tips are :
a. Model retelling
b. Use predictable texts and/ or familiar stories, such as fairy tales or folktales c. Retell a portion of a familiar text and ask the student to finish the retelling d. Ask the students to identify the most important part of the text
e. Have the students work with a partner to practice retelling
f. In retelling story, the teacher should prompt the students to tell about : - Identify main idea
- Vocabulary
- Specific information - Inference
- Reference.
20
of concrete materials. If the students are able to retell the story in sequence, with a beginning, middle, and end, it indicates that the students have a good
understanding of the story. The students’ answer to the teacher’s prompts also can indicate the ability of the students to infer the information from the text.
Teacher helps the students by absorb the information and give some question that related to specific information. The teacher gives an example about retelling story, and asks the students to practice retelling story based on the criteria that have
taught before. After that, the teacher gives evaluation to the students’
performance.
From all the theories that have been mentioned above, it can be stated that retelling story does not mean memorizing, retelling means recounting the same
story into the students’ own word. In retelling story, a story teller can combine
gestures and expression, the function of a teacher is very important in order to reinforce the students to comprehend a story through retelling story.
2.6 Procedure of Teaching Reading Comprehension Through Retelling Story
In doing her research, the researcher gives treatment to the students by teaching reading comprehension through retelling story. The researcher applies the teaching procedures based on tips by Gambrell & Dromsky (2000) as follows: 1. Pre activities
21
c. The researcher leads the students to the topic by asking some questions related to the topic presented, the she asks them to answer those questions together.
2. While activities
a. The researcher gives a piece of folktale.
b. The researcher asks the students to read the text individually. c. The researcher retells the story.
d. The researcher asks the students to identify the most important part of the text
e. The researcher asks the students to work with a partner to practice retelling
f. In retelling story, the teacher should prompt the students to tell about : - Identify main idea
- Vocabulary
- Specific information - Inference
- Reference
g. The researcher gives the test.
h. The researcher asks the students to answer it on their answer sheet. 3. Post activities
a. The researcher asks the students to express their problem in comprehending the text.
b. The researcher gives the students evaluation.
22
2.7 Concept of Translation
Translation has always played a role in language teaching. Translation is a general term referring to transfer of thought and ideas from one language (source of language) to other language (target language) whether the language in written or spoken forms.
According to Garrow (1972), translation is changing a communication (a word, phrase, and sentence) to other terms or to another form (verbal or symbolic) or to another level abstraction (simple or more complex). The definition above saying that in translation techniques, concept are built in the pupils mind from bites and pieces and from specific, and in this condition, the students will passively understand.
It is known that translation can be regarded as one of the techniques that applied to teach reading comprehension. Most of senior high school level, have low ability in English, because English is not a mother Language in Indonesia. Based on this reality, translation is one of solution techniques to teach English especially reading skill.
23
Dealing the ideas above, Stoddart (2000) states that teaching reading comprehension through translation gives students excellent practice in the sub skills of reading. For example, using L2 and L1 translation will improve, the following sub skills.
1. recognizing the script of the L2 (if different from L1) 2. identifying and familiarizing with style and register
3. deducing the meaning and use of unfamiliar lexical items and meaning-patterns in the second language (including metaphorical and non-standard language)
4. understanding conceptual meaning
5. understanding the communicative function of clauses, sentences and paragraphs.
6. familiarizing with cohesion 7. familiarizing with coherence
8. identifying important / relevant information 9. deducing meaning from context
10. heightening awareness of genres and identifying sources 11. heightening awareness of different schemata
12. skimming and 13. scanning
24
student have to know about meaning in their mother language, and translation is one way to help students translate English text to their mother language.
Stoddart (2000) also states, there are some strategies that the teacher can use to teach translation, for example:
a. To make students more aware of the equivalent affect of what they translate (i.e whether the effect of the target text will be equal to that of the source text) b. To ensure that text used are interesting, relevant and as far as possible,
authentic.
c. To make translation a process-based activity, including all student at all stages of the process. This will include giving time to plan, reflect, discuss, review and edit their work, also encourage meaningful, independent interaction in English
d. To try and provide students with learner-centered, cognitive translation activities to help them notice the differences (and similarities) between L1 and L2 meaning patterns (in the short term), and of the language system as a whole (in the long term). Hopefully, this will help them acquire the pattern of the L2 and lesson the influence of the L1 on their developing language.
25
2.8 The Procedure of Teaching Reading Comprehension Through Translation
In doing her research, the researcher gives treatment to the students by teaching reading comprehension through translation. The researcher applies the teaching procedures as follows:
1. Pre activities
a. The researcher prepares the material.
b. The researcher gives some question related to the text 2. While activities
a. The researcher gives a piece of folk tale.
b. The researcher asks the students to read individually.
c. The researcher asks the students to answer the question related to the text.
d. The researcher asks the students some question after reading to allow them to understand the folk tale.
e. The researcher guides students to understand the folk tale by translation with looking up dictionary.
3. Post activities
a.The researcher asks the students to express their problem in comprehending the text.
b. The researcher gives the students evaluation.
26
2.9 Theoretical Assumption
Based on the frame of theories the researcher assumes that reading through retelling story can increase students’ comprehension. So their comprehension in learning reading through retelling story may be better in comparison with translation.
The result of teaching reading through translation makes the students remain passive and lack of motivation because they just translate the words and the students became bored in learning English because it did not motivate them. Most of interaction in the classroom is from the teacher to the students.
Teaching reading through retelling story from folk tales would increase students’ motivation to learn, help the students to understand the story well and the students also will be brought into interesting situation and enjoyable situation.
2.10 Hypothesis
The hypothesis of this research can be formulated as follows:
H0 = There is no difference of students’ reading comprehension achievement in folktale between students who are taught through retelling story and students who are taught through translation.
54
V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
5.1 Conclusions
Given the results of the data analysis and discussion, the following conclusions are drawn:
a. There was a significant difference of students’ reading comprehension
achievement between those who were taught through retelling story and those who were taught through translation. The mean score difference is 7.87, meaning that the experimental class one gained 7.87 score, higher than experimental class two in posttest. Besides that, the significant value of the posttest in both classes was 0,000 that was lower than 0.05 (0,000<0.05). T-value is higher than T-table (4.173 > 2.000).
b. Retelling story is more effective than translation to improve students’ reading comprehension especially in identifying main idea. The mean score difference after implementing retelling story is higher than the one after implementing translation (16.5 >8.12). It indicated that the increase in experimental class one is higher than in experimental class two. The mean or average score of posttest in experimental class one is higher than experimental class two (79.75> 71.87). The mean difference is 7.87, meaning that the experimental class gained 7.87 score, higher than control class in posttest. The significance value (2-tailed) in experimental class was p = 0.00<0.05 that meant there was a significant difference. In experimental class two who are taught through
55
especially in finding the meaning of new vocabulary, but the increasing in experimental class two not too significant as in experimental class one.
5.2 Suggestion
In line with the conclusions above, the researcher suggests that :
1. The teacher suggested to apply retelling story because students who are taught through retelling story get significant difference of students’ reading comprehension achievement, especially in indentifying main idea than students who are taught through translation.
2. The teacher suggested to apply translation too because translation can
increase students’ reading comprehension achievements, especially in finding
the meaning of new vocabulary. The teacher can mix retelling story and translation technique depend on the material and reading aspects that want to be increase.
3. The other researcher who interest to investigate about retelling story and translation suggested to apply the other material such as recount text,
descriptive text or the other applicable text to make study about retelling story and translation more strength.
56
REFERENCES
Amri, A. 2011. The Implementation of Graphic Organizer Technique in
Improving Students’ Reading Comprehension of English Recount Text at the First Grade of SMA N 1 Kalianda. Bandar Lampung: Unpublished manuscript.
Brown, H., and Cambourne, B. 1987. Read and Retell: A Strategy for the Whole Language Natural Learning Classroom. Heinemman: Educational Book Ltd.
Carver, R.P. (1990). Reading Rate: A Review of Research and Theory. San Diego, CA: Academic Press. 28 Oktober 2009
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reading_process(Retrieved on 12 January
2012)
Dallman, R.L. 1982. Teaching of Reading. Washington: CBS College Publishing.
Doyle, B.S. 2004. Main Idea and Topic Sentence. London: Ward Lock Educational.
Gambrell, L. and Dromsky, A. 2000. Fostering Reading Comprehension. New York: Teacher College Press.
Gambrel, M., Pfeiffer, S., and Wilson, R. 1985. Using Children Literature in Preschool to Develop Comprehension. Chicago: International Reading Association.
Garrow, F. 1972. The Learning Game, Strategies for Secondary Teacher. Ohio: Merrill Publishing Company.
Hatch, E and Farhady, H. 1982. Research Design and Statistic for Applied Linguistic. London: New Burry, Inc.
Howart, P. 2006. Making Reading Communicative.12th January 2011.
http://academic.cuesta.edu.Htm. (Retrieved on 12 January 2012)
57
Kissner, E. 2006. Summarizing, Paraphrasing, and Retelling Skills for Better Reading, Writing, and Test Taking. Portsmouth: Heinemann A division of Reed Elsevier Inc.
Lyman, B.H. 1971. Test Scores and What Theory Mean. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall,Inc.
Mallikamas, K. 1975. The Book of Folklore as Heritage Literatures. Bangkok: University of Jakata.
Mathews, C. 1994. Speaking Solution. New York: Prentice Hall Regents. Marantina, N. 2006. A Comparative Study of Teaching Reading Comprehension
Through Retelling Story and Translation from Fairy Tale at SMP N 1 Bandar Lampung. Bandar Lampung: Universitas Lampung
Nuttal, C. 1982. Teaching Reading Skills in a Foreign Language. London: Heinemann Educational Books.
Richard, T. 1986. How to be a More Successful Reader. New York: Heinle and Heinle
Shohamy, E. 1985. A Practical Handbook in Language Testing for the Second Language Teaches. Tel Aviv: Tel Aviv University.
Simanjuntak, E.G. 1988. Developing Reading Skills for English Foreign Language Students. Jakarta: P2LPTK
Smith, F. 1982. Understanding Reading 2nd Edition. New York: Holt Renehart and Winston
Stoddart, J. 2000. Teaching Through Translation (The Journal of English Translation No.11 April 2002). Portugal: British Council Ltd.
Suparman, U. 2005. Understanding and Developing Reading Comprehension. Bandar Lampung: Unila Press.
Thompson, S. 1977. The Folktale. California: University of California Press. Universitas Lampung. 2008. Pedoman Penulisan Karya Ilmiah. Bandar Lampung:
Universitas Lampung.