ii ABSTRACT
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION ACHIEVEMENT OF NARRATIVE TEXT BETWEEN STUDENTS WHO ARE
TAUGHT THROUGH GRAPHIC ORGANIZER AND THROUGH LITERAL TRANSLATION AT THE FIRST GRADE OF SMAN 1 NATAR
By
AYU PRATAMI PUTRI
The reading skill becomes very important in the education field, and reading is indispensable for the students because the success of their study depends on their ability to read. Therefore, the researcher intends to compare graphic organizer and literal translation for teaching reading. The objectives of the research are to find out whether there is significant difference in the improvement of students reading comprehension achievement of English narrative text between students taught through graphic organizer and taught through literal translationand to find out which one is more effective technique. The research was conducted at SMAN 1 Natar especially the first grade. To gain the objective of the research, the researcher conducted quantitative design with pre-test posttest experimental group design.
The test result showed that the mean of posttest in the experimental group one was 79.8and the mean of the posttest in the experimental class two was 72, probability level (p) was 0.000. The experimental class two gained the lower average score in posttest than experimental class one. The mean difference was 7.87. It was lower than 0.05. It means that H1was accepted and H0was rejected since 0.00<0.05. It proves that the treatments given by the researcher had
better effect of the students’ achievement. Based on the data, the researcher concludes that the application of graphic organizer improves students’ reading comprehension achievement
ADMITTED BY
1. Examination Committee
Chairperson :Prof. Dr.CucuSutarsyah, M.A. ………
Examiner : UjangSuparman, S.Pd., M.A., Ph.D. ………
Secretary : Budi Kadaryanto, S.Pd., M.A. ………
2. The Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
Dr. Hi.BujangRahman, M.Si. NIP. 19600315 198503 1 003
A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF STUDENTS’ READING COMPREHENSION ACHIEVEMENT OF NARRATIVE TEXT BETWEEN STUDENTS WHO ARE TAUGHT THROUGH GRAPHIC
ORGANIZER AND THROUGH LITERAL TRANSLATION AT THE FIRST GRADE OF SMAN 1 NATAR
By
Ayu Pratami Putri
A Script
Submitted in a Partial Fulfilment of The Requirements for S-1 Degree
in
The Language and Arts Education Department of The Faculty of Teacher Training and Education
UNIVERSITY OF LAMPUNG BANDAR LAMPUNG
Research Title : A COMPARATIVE STUDY OF STUDENTS’
READING COMPREHENSION ACHIEVEMENT OF NARRATIVE TEXT BETWEEN STUDENTS WHO ARE TAUGHT THROUGH GRAPHIC ORGANIZER AND THROUGH LITERAL TRANSLATION AT THE FIRST GRADE OF SMAN 1 NATAR
Student’s Name : Ayu Pratami Putri
Student’s Number : 0913042031
Department : Language and Arts Education Study Program : English Education
Faculty : Teacher Training and Education Faculty
APPROVED BY
Advisory Committee
Advisor Co-Advisor
Prof. Dr. Cucu Sutarsyah, M.A. Budi Kadaryanto, S.Pd., M. A. NIP 19570406 198603 1 002 NIP 19810326 200501 1 002
The Chairpersons of
The Department of language and arts Education
ADMITTED BY
1. Examination Committee
Chairperson : Prof. Dr. Cucu Sutarsyah, M.A. ………
Examiner : H.M. Ujang Suparman, M.A., Ph.D. ………
Secretary : Budi Kadaryanto, S.Pd., M. A. ………
2. The Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
Dr. H. Bujang Rahman, M.Si. NIP 19600315 198303 1 003
APPROVAL FOR JOURNAL
Research Title : A Comparative Study of Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement of Narrative Text between Students who are taught through Graphic Organizer and through Literal Translation at the first grade of SMAN 1 Natar.
Student’s Name : AyuPratamiPutri
Student’s Number : 0913042031
Department : Language and Arts Education
Study Program : English Education
Faculty : Teacher Training and Education Faculty
APPROVED BY
Advisory Committee
Advisor 1 Co-Advisor
KEMENTERIAN PENDIDIKAN NASIONAL UNIVERSITAS LAMPUNG
FAKULTAS KEGURUAN DAN ILMU PENDIDIKAN JURUSAN PENDIDIKAN BAHASA DAN SENI
Jl. Sumantri Brojonegoro No. 1 Kampus Gedung Meneng Bandar Lampung
Hal : Undangan Seminar Hasil KepadaYth.
Judul : A Comparative Study of Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement of Narrative Text between Students who are Taught through Graphic Organizer and through Literal Translation at the first grade of SMAN 1 Natar.
Pembimbing : 1. Prof. Dr. CucuSutarsyah, M.A. 2. Budi Kadaryanto, S.Pd., M.A. Pembahas : H. M. Ujang Suparman, M. A., Ph.D,
Maka kami mengundangBapak/Ibupada seminar yang akandilaksanakanpada:
Hari/tanggal : Selasa/ Maret 2013 Pukul : 10.00 WIB s.d.selesai
Tempat : Ruang Seminar Bahasa FKIP Unila
Demikianundanganini kami sampaikan.Atasperhatiannya kami ucapkanterimakasih. Bandar Lampung, Maret 2013
Mengetahui,
Koordinator Seminar
xi
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
1. Table specification of try out... 37
2. The homogeneity test of the students’ Pre-test scores in both classes... 46
3. The homogeneity test of the students’ Post test scores in both classes...47
4. The students’ achievement in experimental class one... 46
5. The students’ achievement in experimental class two... 49
xii APPENDICES
Appendix Page
1. Try out test... 64
2. Lesson Plan I... 73
3. Lesson Plan II... 78
4. Lesson Plan III... 84
5. Pre-test/Post Test... 94
6. Upper Group Try Out Test... 105
7. Lower Group Try Out Test... 106
8. Difficulty Level and Discrimination Power of Try Out Test... 107
9. Reliability Analysis of Try Out Test... 108
10. Students’ Score of Pre-test and Post Test... 109
11. Table of Frequency of Pretest... 120
12. Table of Frequency of Post Test... 121
13. Random Test... 122
14. Normality Test... 123
15. The Homogeneity Test... 124
60
REFERENCES
Alyousef, H. S. 2005. Teaching reading comprehension to ESL/EFL learners. The reading matrix Vol. 5, No. 2, September 2005. Update on 5th January 2007. http.acrobat/rider.co.id.
Arthur, W. Heilman, TimothyR. Blair, and William H. Rupley. 1981. Principles and Practices of Teaching Reading: 5th edition. Ohio: Charles E. Merril Publishing Company
Brookbank, D., Grover, S., Kullberg, K., &Strawser, C. 1999. Improving student achievement through organization of student learning. Chicago: Master's Action Research Project, Saint Xavier University and IRI/Skylight. (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED435094).
Depdiknas. 2006. Materisosialisasidanpenelitiankurikulumtingkatsatuan pendidikan (KTSP). Jakarta: Depdiknas.
Doyle, B.S. 2004. Main idea and topic sentence. London: Ward Lock educational.
Duke, N.K., Caughlan, S., Juzwik, M.M., & Martin, N. 2010. (in press). Doing genre with purposein the K–8 classroom. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann
Ellis, E., & Howard, P. 1998. Framing Main Ideas and Essential Details to Promote Comprehension. University of Alabama.
www.GraphicOrganizers.com. Retrieved at 28 October 2012
Ellis, Edwin. 2004. Q & A: What’s the big deal about graphic organizers?
Retrieved at 22 November 2012. http//www.graphicorganizers.com
Estes, Thomas H. 1991. Reading in Content Areas. University of Virginia. http://www.readingquestorg/links.html. Retrieved at 23 October 2012 Fry, Ron. 1996. Improve Your Reading. Book-Mart Press: USA
Hatch, E &Farhady. 1982. Research design and statistics for apllied linguistic. University of California: Los Angeles Pers: Rowley, London, Tokyo. Heaton, J. 1975. English Language Tests: a Practical Guide for Teachers of
English as a Second or Foreign Language. Virginia: Longman. Langford, P. A., Rizzo, S. K., & Roth, J. M. 2003.Improving student
61
Professional Development. (ERIC Document Reproduction Service No. ED478769.)
Meyen, E., &Vergason, G. 1996. Strategies for Teaching Exceptional Children in Inclusive Settings. Denver, CO: Love.
Meyer, D. J. 1995. The effects of graphic organizers on the creative writing of third grade students.Unpublished thesis.
Muth, K., and D. Alvermann. 1999. Teaching and learning in the middle grades. Needham Heights, MA: Allyn& Bacon.
Noviansari, Dian. 2012. The Use of Graphic Organizer Method to Teach Narrative Text in Senior High School. (Unpublished paper). Mojokerto: Muhammadiyah University.
Nuttal, C. 1985.Teaching reading skill in a foreign language.London : British Library Cataloguing in Publication Data.
Nuttal, C. 1982.Teaching Reading Skills in a Foreign Language. London: Heinemann Educational Books.
Potter, H. Abbot. 2008. Introduction to Narrative. Cambridge: Cambridge.
Richards, J. C. 1976. The role of vocabulary teaching.TESOL Quarterly, 10(1), 77-89.
Simmons, D. C., Griffin, C. C., &Kameenui, E. J. (1988). Effects of teacher-constructed pre- and post-graphic organizer instruction on sixth-grade
science students’ comprehension and recall.Journal of Educational Research, 82 (1), 15-21.
Sinatra, R. C., Stahl-Gemake, J., & Berg, D. N. (1984).Improving reading comprehension of disabled readers through mapping.The Reading Teacher.
Shohamy, E. 1985.A Practical Handbook in Language Testing for the Second Language Teachers. Tel-Aviv: Tel-Aviv University.
Smith, F. 1982. Understanding reading. New York: Holt Rinehart and Winston.
Suparman, U. 2005. Understanding and developing reading comprehension. Bandar Lampung: Unila Press.
Thompson, Max., and Julia. 2004. Learning-Focused Strategies Notebook. Teacher materials. Boone: Learning Concepts, Inc.
62
Unila Press.
ix
LIST OF APPENDICES... xii
I. INTRODUCTION 1.1 Background of Problem... 1
1.2 Identification of Problems...5
1.3
Limitation of Problems... 61.4 Formulation of The Problems... 6
1.5 Objectives of the Research... 6
1.6 Uses ofThe Research... 7
1.7 Scope of the Research... 7
1.8 Definition of Terms... 8
II. FRAME OF THEORIES 2.1 Review of Previous Research... 9
2.2 Concept of Reading ... 11
2.3 Concept of Reading Comprehension... 12
2.3.1 Literal comprehension... 12
2.3.2 Interpretative comprehension... 13
2.3.3 Critical Comprehension... 13
2.4 Concept of Teaching Reading... 14
2.5 Concept of Graphic Organizer... 15
2.6 The Advantages of Graphic Organizer... 17
2.7 The Disadvantages of Graphic Organizer... 18
2.8 Types of Graphic Organizer... 18
2.9 Concept of Literal Translation Technique... 21
2.10 The Advantages of Literal Translation... 22
2.11 The Disadvantages of Literal Translation... 22
2.12 Concept of Graphic Organizer and Reading Comprehension... 23
2.13 The Concept of Literal Translation and Reading Comprehension... 24
2.14 The Concept of Narrative Text... 25
x
2.16 Teaching Reading of Narrative Text using Literal
TranslationTechnique...
... 29
2.17 Theoretical Assumption... 30
2.18 Hypothesis... 30
III. RESEARCH METHOD 3.1 Research Design... 31
3.2 Population and Sample...32
3.2.1 Population... 32
3.2.2 Sample... 32
3.3 Data Collecting Technique...33
3.4 Research Procedures... 34
3.5 Criteria of Good Test... 36
3.6 Data Analysis... 40
3.7 Treatment of the Data... 40
3.8 Hypothesis Testing... 42
IV. RESULT AND DISCUSSION 4.1 Results of Research... 44
4.1.1 Result of TryOut Test... 44
4.1.2 Result of Pre-test... 45
4.1.3 Result of Post-test... 47
4.1.4 The Increase of Students’ Reading Comprehension Achievement.... 48
4.2 Result of data treatment... 50
4.2.1 Random Test... 50
4.2.2 Normality Test... 50
4.2.3 Discussions of Findings... 51
V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS 5.1 Conclusion... 58
5.2 Suggestions...59
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF READING ACHIEVEMENT OF
NARRATIVE BETWEEN STUDENTS TAUGHT THROUGH GRAPHIC
ORGANIZER AND TRANSLATION
AyuPratamiPutri, CucuSutarsyah, Budi Kadaryanto, Ujang Suparman Email: [email protected]
Mobile Phone: +628996424551 Institution: Lampung University
Abstract:The reading skill becomes very important in the education field, and reading is indispensable for the students because the success of their study depends on their ability to read. Therefore, the researcher intends to comparegraphic organizer and literal translation for teaching reading. The objectives of the research are to find out whether there is significant difference in the improvement of students reading comprehension achievement of English narrative text between students taught through graphic organizer and taught through literal translationand to find out which one is more effective technique. The research was conducted at SMAN 1 Natar especially the first grade. To gain the objective of the research, the researcher conducted quantitative design with pre-test posttest experimental group design.
The test result showed that the mean of posttest in the experimental group one was 79.8and the mean of the posttest in the experimental class two was 72, probability level (p) was 0.000. The experimental class two gained the lower average score in posttest than experimental class one. The mean difference was 7.87. It was lower than 0.05. It means that H1was accepted and H0was rejected since 0.00<0.05. It proves that the treatments given by the researcher had
better effect of the students’ achievement. Based on the data, the researcher concludes that the application of graphic organizer improves students’ reading comprehension achievement
of narrative text.
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF READING ACHIEVEMENT OF
NARRATIVE BETWEEN STUDENTS TAUGHT THROUGH GRAPHIC
ORGANIZER AND TRANSLATION
AyuPratamiPutri, CucuSutarsyah, Budi Kadaryanto, Ujang Suparman Email: [email protected]
Mobile Phone: +628996424551 Institution: Lampung University
Abstract:Kemampuanmembacamenjadisangatpenting di bidangpendidikan, danmembacajugasangatdibutuhkanparasiswakarenakesuksesanbelajarmerekatergantungpadak
emampuanmerekauntukmemahamibacaan. Olehkarenaitu,
penelitimencobamembandingkangraphic organizerdanliteral translation dalampengajaranmembaca.Tujuanpenelitianiniadalahuntukmenemukanapakahadaperbedaansi gnifikan di dalampeningkatanpembelajaranmembacapadateksnaratifyang diajarmelaluigraphic organizerdanmereka yang diajarmelaluiliteral translationdanuntukmenentukanteknikmana yang lebihefektif.Penelitiandilaksanakan di SMAN 1 Natarkhususnyakelassatu.Untukmemperolehsasarandalampenelitian, penelitimenggunakankwantitatifdesaindenganekperimenpre-testposttest.
Hasilpenelitianmenunjukkanbahwa rata-rata posttestpadakelaseksperimensatuadalah 79.8 dan rata-rata yang posttestpadakelaseksperimen II adalah 72.Kelaseksperimen IImemperolehnilai rata-rata posttestlebihrendahdibandingdengankelaseksperimen I. Rata-Rata perbedaanadalah 7.87, dimanatingkatanprobabilitas( p) adalah 0.000danlebihrendahdari 0.05. Iniberarti H1ituditerimadan H0ditolakkarena 0.00<0.05.Hal inimembuktikanbahwaperlakuanyang diberiolehpenelitimemberihasil yang lebihbaikterhadappencapaiansiswa.Berdasarkanpada datadapatdisimpulkanbahwapenerapangraphic
organizermeningkatkanprestasipembacaansiswatentangteksnaratif.
INTRODUCTION
Transferring new modern science, technology, and information can be done through reading
process. Almost at all of Senior High School, applying teaching reading has less the effectiveness so the students feel boring in reading process. The reading skill becomes very important in the education field, and reading is also something crucial and indispensable for
the students because the success of their study depends on the greater part of their ability to read.Smith (1982) says that reading certainly implies comprehension, and reading is
something that makes sense to the reader. The reader tries to understand and get the meaning and information in the written texts form of symbols, letters, graphs, etc. Thus, they grasp the
writers’ messages from the texts.
Meanwhile Nuttal (1985) defines reading as the meaningful interpretation of printed or written symbols. It means that reading is a result of the interaction between the perception of
graphic symbols that represent language and the readers’ language skills, cognitive skills, and the knowledge of the world. In this process, the reader tries to recreate the meaning intended by the writer.
According to Doyle (2004), comprehension is a skill in attaching meaning beginning at the
same level and proceeding to attaching meaning to an entire reading selection. All
comprehension revolves around the readers’ ability in finding and determining main idea and
topic sentence from the text.
comprehension into three levels of comprehension; literal comprehension, interpretative comprehension, and critical comprehension.
According to School Based Curriculum or Kurikulum Tingkat SatuanPendidikan (KTSP) for
the first grade of Senior High School, the students are expected to be able to construct meaning from text. Basically it is the same as comprehending the stated and unstated
information from a text.
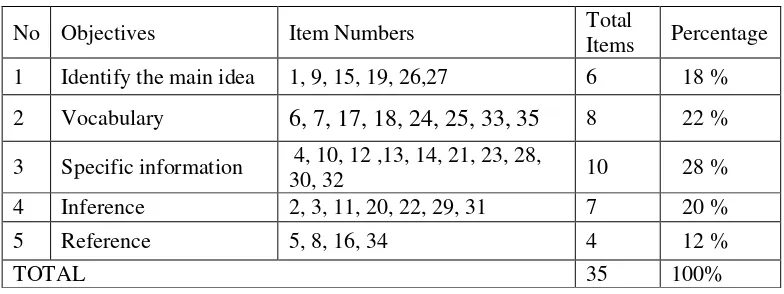
In addition, on the Passing Grades Standard (Standard KompetensiKelulusan/SKL) of Senior High School for reading skill is stated that the students should be able to identify the main idea, explicit and implicit specific information, reference, the word meaning, phrase, and
sentence of short simple text. It can be said that after graduating from Senior High School, students are expected to be good in reading, able to comprehend the simple text and to
construct better understanding toward the content of the text before they continue their study to the higher level.
To solve the problem, teachers are requiredto provide effective and applicable technique for
their students. They must invent potential problems that arise during the reading classroom instruction and put some efforts to find or create the effective techniques that are important to improving students’ reading comprehension achievement. Alyousef (2005:143) says that in reading, contemporary reading tasks, unlike the traditional materials, involve three-phase procedures: pre-, while-, and last-reading stages. In teaching reading, appropriate and
Graphic organizer would be possible to be applied by the Senior High School students in their reading.
According to Meyen, Vergason and Whelan (1996) graphic organizer is “visual displays teachers use to organize information in a manner that makes information easier to understand
and learn” (p.132). They will be interested to the text or learning material that consist of picture or other non-verbal information such as diagram, tables, graphs, graphic, etc. Based on this reason, the researcher is interested to apply graphic organizer in teaching reading
comprehension. Classroom activities that encourage interaction with texts, like graphic organizer, may improve students' reading comprehension. Graphic organizer is basically visual ways to represent information. Graphic organizer helps the readers to visualize the
main concept of what they are reading, thus, graphic organizer ease the readers comprehend the text.
Graphic Organizer improves reading comprehension by emphasizing text structures such as
story maps and improves different aspects of comprehension, such as literal and relational comprehension, recall, and vocabulary learning. Graphic organizer pairs with strategy
instruction can be more effective than traditional basal instruction and can be used effectively as advance organizers prior to reading (Simmons et al., 1988).
Graphic organizer is a general term for schematic diagrams that help students identify key
concepts and make relationships among them (Muth&Alvermann, 1999). It provides students with visual clues that they can relate to the written or spoken words to which they are exposed.
Translation is one of technique that can be used for teaching reading. Richards (1976:1) says
language (source of language) to other language (target language) whether the language in written or spoken forms. It means that translation is the process of giving the closest meaning
or natural equivalent of the words, phases, and sentences of one language into another language whether in written or spoken forms.
This research focuses on the improvement of students’ reading comprehension achievement by comparing graphic organizer and literal translation. The participants of this research are the first year of SMAN 1 Natar. In this research, the researcher would focus on narrative text
because the students’ comprehension in reading narrative is still low. They still have difficulty in finding the main idea and specific information of narrative text.According to Potter (2008:13), narrative is the representative of an event or a series of events. In addition,
prince stated, “narrative is essentially mode of verbal presentation and involves the linguistic recounting or telling of events”. The purpose of narrative stories may have other purposes
such as for explaining a phenomenon (myth and legend). Meanwhile, according Duke et al
(2010) reading narrative is making students to share and make meaning of experience, as with fairy tales, realistic fiction, and many true stories.
According to Max and Julia Thompson (2004:10), there are five main categories of graphic
organizer. They are Venn diagram, story board, story map, tree map, and cause effect. The focused type of graphic organizer researcher used is story map. This type is recommended to
help students in reading comprehension achievement of narrative text by emphasizing text structures. The reading comprehension here is involving achievement of identifying the main idea, specification information, vocabulary, inference, and reference. The text uses as the
METHOD
In this research, the researcher intends to find out the significant increase of students’ reading comprehension achievement by comparing graphic organizer and literal translation in reading. To gain the objectives of the research, the researcher conducted quantitative design with pretestposttest experimental group design. The researcher selected two classes, one as
the experimental group one and another as the experimental group two. According to Hatch and Farhady (1982:22) the design of the research is described as follows:
G1 : T1 X1 T2
G2 : T1 X2 T2
Notes:
G1 : experimental group one
G2 : experimental group two
T1 : pre-test
T2 : post-test
X1 : treatment for Experimental Group one (Graphic Organizer Technique)
X2 : treatment for Experimental Group Two (Literal Translation Technique)
RESULT AND DISCUSSION
This study has shown that the use of graphic organizer could improve students’ reading
comprehension of narrative text. The graphic organizer made the students aware of the
statement was supported by Ellis’s study (2004:2) that by showing how information is
structured can be powerful way to facilitate understanding.
The explanations of Graphic Organizer made students active in the class. They always asked
every step they need to do. Similar experiences were also encountered by Yunita (2007) when she applied Graphic Organizer. It seems that students would be active if they should
apply a strategy they have never faced before in a reading comprehension lesson. Graphic Organizer improved students’ ability to find detailed information of the text. Meanwhile,Brookbank had done previous research in 1999, he investigated graphic organizer can help students in comprehending the text and mastering vocabulary.
The increase of students’ reading comprehension achievement is proven by the data thatthe experimental class one, there was increased 528 point for the total point after being given the
treatments. The highest score, 80 in pretest increased into 92 in the posttest, and the lowest score in pretest improved from 48 into 60 in the posttest. Moreover, the mean of the pretest
that was 63.375 increased to be 79.875 in the posttest.Besides, the students’ reading comprehension score also increased in the experimental class two even though it was not as significant as in the experimental class one. Intable 2 describes that the experimental class
two, there was increased 260 point for the total point after being given the treatments. The highest score, 80 in pretest increased into 84 in the posttest, and the lowest score in pretest
improved from 48 into 56 in the posttest. Moreover, the mean of the pretest that was 63.875increased to be 72 in the posttest.
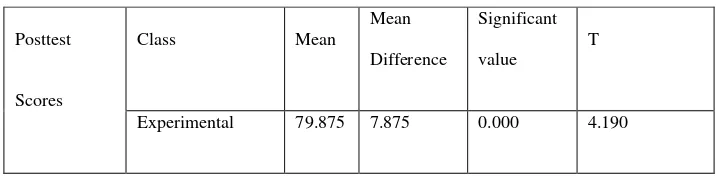
Table 1.The comparison of Students’ Reading Comprehension Score in Both Classes
Class One
Experimental
Class Two
72
By observing the Table 1 above, there are three aspects that are compared. The first is the
mean of both classes; 79.875 for experimental class one and 72 for experimental class two. The experimental class two gained the lower average score in posttest than experimental class
one. The mean difference was 7.87. The second is the significant value of students, that was
0,000 (p=0,000). Based on the table above, it can be found that the students’ significant score
was lower than 0.05 (0,000<0.05). The last was t-ratio>t-table (4.190>2.000) and therefore,
H0 was rejected. In other words, H1 is accepted that there was a significant difference of
students’ reading comprehension achievement between those who were taught through
graphic organizer and those taught through literal translation. Lastly, the increase of both classes was gained significantly different.
Since the students who were taught through graphic organizer gave higher result than those
who were taught through literal translation, it was considered graphic organizer was better than literal translation. Besides, it was also because graphic organizer was designed to teach
students to be active and to determine the main idea, supporting details, the reference of the noun, the new vocabulary and the generic structure of the text without they have to fully
understand the meaning of sentence in the text. Although literal translation was also applied Independent Samples Test
,471 ,495 4,190 62 ,000 7,87500 1,87930 4,11834 11,63166
in class, but the result was not as effective as the graphic organizer. It was the students which were taught through literal translation were not well structured. But, it is the strength of the
literal translation when they translate the sentence in the text, they can really understand the meaning then see main idea and details in the text, but it also is a problem because teaching learning process run passively so that those who are good are getting better, who are bad are
getting worse. After all, graphic organizer was more appropriate and possible to use to
increase student’s reading comprehension achievement of English narrative text significantly and applying graphic organizer can help students in reading comprehension of narrative text.
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
In line with the results of the data analysis and discussion, the following conclusions are
drawn:
a. There was a significant difference of students’ reading comprehension achievement between those who were taught through graphic organizer and those who were taught
through literal translation at the first grade of SMAN 1 Natar. The mean or average score of posttest in experimental class one is higher than experimental class two (79.87> 72).
The mean difference is 7.87, meaning that the experimental class one gained 7.87 score, higher than experimental class two in posttest. Besides that, the significant value of the posttest in both classes was 0,000 that was lower than 0.05 (0,000<0.05). T-value is
higher than T-table (4.190>2.000).
b. Graphic organizer is more effective technique than literal translation. The mean
difference after implementing graphic organizer is higher than the one after implementing
was higher than in experimental class two. The significance value (2-tailed) in experimental class was p = 0.00<0.05 that meant there was a significant difference. It was
also found that the students followed the reading class enthusiastically in experimental class. They enjoyed working in group and the media attracted and helped them much. Discussion happened during the class since the teacher monitored them.
According to the conclusion above, the researcher suggests that the teacher should apply graphic organizer in teaching because the technique has advantages:
1. The teacher can use graphic organizer as an alternative way in teaching reading since
it can be used to improve the students’ reading comprehension achievement.
2. The teacher should pay more attention to students’ difficulty dealing with determining main idea of a text and comprehending unfamiliar vocabulary. This can be done while the reading process. The teacher can ask the students to get used to determining main ideas and supporting details. The teacher also should give more examples in doing this correctly.
3. The further researchers should apply graphic organizer to improve the students’ reading comprehension achievement. They should apply other kinds of texts, i.e., descriptive, exposition, spoof, report text, etc.
REFERENCES
Alyousef, H. S. 2005. Teaching reading comprehension to ESL/EFL learners.The reading matrix Vol. 5, No. 2, September 2005. Update on 5th January 2007. http.acrobat/rider.co.id.
Arthur, W. Heilman, TimothyR. Blair, and William H. Rupley. 1981. Principles and Practices of Teaching Reading: 5th edition. Ohio: Charles E. Merril Publishing Company
Depdiknas. 2006. Materisosialisasidanpenelitiankurikulumtingkatsatuan pendidikan (KTSP). Jakarta: Depdiknas.
Doyle, B.S. 2004. Main idea and topic sentence. London: Ward Lock educational.
Duke, N.K., Caughlan, S., Juzwik, M.M., & Martin, N. 2010. (in press). Doing genre with purposein the K–8 classroom. Portsmouth, NH: Heinemann
Ellis, Edwin. 2004. Q & A: What’s the big deal about graphic organizers? Retrieved at 22
November 2012. http//www.graphicorganizers.com
Hatch, E &Farhady. 1982. Research design and statistics for apllied linguistic. University of California: Los Angeles Pers: Rowley, London, Tokyo.
Meyen, E., &Vergason, G. 1996. Strategies for Teaching Exceptional Children in Inclusive Settings. Denver, CO: Love.
Muth, K., and D. Alvermann. 1999. Teaching and learning in the middle grades. Needham Heights, MA: Allyn& Bacon.
Nuttal, C. 1985.Teaching reading skill in a foreign language.London : British Library Cataloguing in Publication Data.
Potter, H. Abbot. 2008. Introduction to Narrative. Cambridge: Cambridge.
Richards, J. C. 1976. The role of vocabulary teaching.TESOL Quarterly, 10(1), 77-89.
Simmons, D. C., Griffin, C. C., &Kameenui, E. J. (1988). Effects of teacher-constructed pre- and post-graphic organizer instruction on sixth-grade science students’ comprehension and recall.Journal of Educational Research, 82 (1), 15-21.
Smith, F. 1982. Understanding reading. New York: Holt Rinehart and Winston.
Thompson, Max., and Julia. 2004. Learning-Focused Strategies Notebook. Teacher materials. Boone: Learning Concepts, Inc.
Universitas Lampung. 2000. Pedomanpenulisankaryailmiah. Bandar Lampung: Unila Press.
Yunita, B. F. 2008. Utilizing Graphic Organizer in Increasing Students’ reading comprehension Ability to the First Grade of SMA Negeri 10 Bandar Lampung. Bandar
I. INTRODUCTION
This chapter concerns certain points.Introduction deals with background of the
problem, formulation of the problems, objective of the research, uses of the research, scope of the research, and definition of terms clarified like the following.
1.1 Background of Problem
Transferring new modern science, technology, and information can be done through reading process. Almost at all of Senior High School, applying teaching reading has
less the effectiveness so the students feel boring in reading process. This problem is also happened at SMAN 1 Natar. The reading skill becomes very important in the education field, and reading is also something crucial and indispensable for the
students because the success of their study depends on the greater part of their ability to read.Based on this statement the researcher considers that reading is a very
important skill in order to increase our knowledge and our way of thinking.
There are four skills of language to be mastered in learning English. They are listening, speaking, reading, and writing. Regarding the reason that the students are expected to read and to get information for increasing their knowledge that is mostly
2
According to School Based Curriculum or Kurikulum Tingkat SatuanPendidikan
(KTSP) for the first grade of Senior High School, the students are expected to be able to construct meaning from text. Basically it is the same as comprehending the stated
and unstated information from a text.
In addition, on the Passing Grades Standard (Standard KompetensiKelulusan/SKL) of Senior High School for reading skill is stated that the students should be able to
identify the main idea, explicit and implicit specific information, reference, the word meaning, phrase, and sentence of short simple text. It can be said that after graduating from Senior High School, students are expected to be good in reading, able to
comprehend the simple text and to construct better understanding toward the content of the text before they continue their study to the higher level.
Many students at SMAN 1 Natar still get low score in their reading comprehension
achievement. It is supported by the data of semester test the English teacher from recent examination test. There are only 93 students from 288 students who can pass the standard mastery learning. It means that only 32.29 % students who can answer
the question correctly and there is 61.25% students who cannot answer the question correctly. The minimum standard score of SMAN 1 Natar is 65. It means that there
are more than 50% students of class XI-1 SMAN 1 Natar who cannotpass minimum standard score, the researcherargues that student still have difficulty in
comprehending the idea in reading a text. Some factors that may cause the students
3
English skill that can support the reading comprehension; reading, writing, speaking,
and listening, (3) difficulties in finding the main idea and its detail information, (4) lack of background knowledge, (5) lack of vocabulary mastery, and (6) ignoring
reading technique.
In classrooms, teaching learning of English, especially in reading lesson, often appears monotonous and boring. It still depends primarily on media such as a
textbook, a workbook, a reader book, or a reference book. Teaching learning, which should be interesting and enjoyable remains tend to be boring for the students. Teacher only brings materials that are stated in the textbook or guidance book.
Seeing this opinion, teachers are requiredto provide effective and applicable
technique for their students. They must invent potential problems that arise during the reading classroom instruction and put some efforts to find or create the effective
techniques that are important to improving students’ reading comprehension
achievement. It is also urgent to create good condition related to students’ motivation in reading, so that reading class can be more meaningful and enjoyable be doing those
ways, teacher can attract the students’ interest in reading so that it can help students
to improve their achievement on reading comprehension of English text.
Furthermore, most of the students are visual learner. According to Meyen, Vergason
4
or other non-verbal information such as diagram, tables, graphs, graphic, etc. Based
on this reason, the researcher is interested to apply graphic organizer in teaching reading comprehension. Classroom activities that encourage interaction with texts,
like graphic organizer,may improve students' reading comprehension.Graphic organizer is basically visual ways to represent information. Graphic organizer helps the readers to visualize the main concept of what they are reading, thus, graphic
organizer ease the readers comprehend the text.
The graphic organizer can be used to improve anyone’s’ learning ability in any kinds of texts, and the kinds of graphic organizer itselfis unlimited. Anyone can create a
new kind of graphic organizer anytime. One common trait finds among graphic organizer is that they show the order and the completeness of a students’ thought process-strengths and weakness of understanding become clearly evident. The use of graphic organizer helps students comprehend better and students’ master key
vocabulary skills and also students’ critical thinking skills are enhanced. Regarding all the aforementioned above, the researcher assumes that graphic
organizer is a teaching reading technique that can be used as an alternative way in
5
1.2 Identification of Problems
1. The students get difficulties in comprehending the reading text. They get
difficulties in getting information from the text, finding the main idea,
finding the details, the answer to the questions based on the text and making inference from the text. As the results the students got difficulties in retelling or in transferring the information from the text.
2. The students are not aware of the appropriate technique of reading which are
needed to be applied in various types of text they interact. During learning
process, they only apply same technique for all types of reading texts. The result is that they do not have ideas in their mind of their reading
3. The students get difficulties in comprehending English text because there
may be some misunderstandings from students and their English teacher in the teaching learning interaction.
4. The students’ motivations in learning English are still low. So it is difficult to improve their English ability well.
5. The students have no good self confidence in learning English. So it is
difficult for them to learn English well because they regard that English is difficult to be learnt well.
6. The teachers use inappropriate materials in teaching English. So it is difficult
for students to improve their English ability well.
7. The teachers use inappropriate media in teaching English. So it is difficult in
6
8. The students are lazy to memorize the words and practice English in their
daily life. So they cannot use English well.
1.3 Limitation of Problems
In line with the identification of the problems, the researcher realizes her capability in
doing her research. As the solution to overcome their difficulties, the researcher is interested in discussing teaching technique which is regarded to be effective in
helping students in construct their schemata and give them the concrete illustration of the text that make it easier for the students to comprehend the text.
1.4 Formulation of Problems
In accordance with the limitation of the problems above, the formulation of the research problems is as follows:
1. Is there any difference in the improvement of students’ reading comprehension achievement of English narrative text between students taught through Graphic Organizer and those who are taught through Literal Translation technique? 2. Which technique is more effective in improving students’ reading comprehension
achievement of English narrative text?
1.5Objectives of Research
In relation to the research problems above, the objectives of this research are: 1. To find out whether there is difference in the improvement of students reading
comprehension achievement of English narrative text between students taught through Graphic Organizer and those whoare taught through Literal Translation
7
2. To find out which technique is more effective in improving students’ reading comprehension achievement of English narrative text.
1.6 Uses of Research
The results of this study are expected to be beneficial both theoretically and
practically as follows: 1. Theoretically
The result of this research is expected to support the existing theory on reading strategies and to give useful information for English teachers, students, and for the development of the theory on teaching reading. 2. Practically
This study can function as information to English teachers that Graphic
Organizer can be used to help students in improving their reading comprehension achievement and understanding English text easily. 1.7 Scope of The Research
This research focuses on the improvement of students’ reading comprehension achievement by comparinggraphic organizer and literal translation. The focused type of graphic organizer researcher used is story map.This type isrecommended to help
students in reading comprehension achievement of narrative text by emphasizing text structures. The reading comprehension here is involving achievement of identifying
8
1.8 Definition of Terms
1. Reading comprehension refers to an activity of understanding printed text
through making sense a written text by relating written language to what we already know and to what we want to know.
2. Graphic Organizer is visual way to represent information on the text. It
illustrates concepts and relationships between concepts in a text or using
diagrams. In addition, it employs lines, circles, and boxes to form images which
depict four common ways information is typically organized: hierarchic, cause/effect, compare/contrast, and cyclic or linear sequences. These images
serve as a visual cue designed for student to gather information, to generate and develop ideas of text, to establish cause and effect, to think logically and to seek patterns, and to form opinionsabout text.
3. Narrative text is one of the texts that contain a series of events that is created in a
constructive format that describes a sequence of fictional or non-fictional events. The purpose of narrative text is to amuse the readers with actual or imaginary
II. FRAME OF THEORIES
This chapter discusses certain points related to the theories used in thisstudy, such as review of the previous research, concept of reading, concept of reading
comprehension, concept of teaching reading, concept of graphic organizer, types of graphic organizer and concept of narrative text, involving the procedures of teaching reading of narrative text using graphic organizer, theoretical assumptions, and
hypothesis.
2.1 Review of Previous Research
The researcher interested in discussing review of previous research that investigate
that reading to know Graphic Organizer or Literal Translation that was more effective in teaching reading of Narrative text. There had been several studies proving that
study about graphic organizer.
Brookbank had done previous research in 1999, he investigated graphic organizer can help students in comprehending the text and mastering vocabulary.Meanwhile, Meyer
10
between the mean scores of the samples to warrant the use of GOs in the third grade
classroom.
Fitria in 2008 at SMAN 10 Bandar Lampung had done another previous research; she conducted an experiment using graphic organizer to find out whether it might
increase students’ reading comprehension. She found the students’ scores within
treatment class increased significantly from 60.75 to 74.00 point while the increase of
students’ score. She convinced that graphic organizer technique carries benefits
toward students’ reading comprehension.
Langford in 2003 implemented reading strategies focuses on advance organizers and
self-assessment were selected as intervention strategies. Various graphic organizers, an observation checklist, and a document analysis were incorporated into the daily
curriculum in the targeted classrooms. Post-intervention data indicated an improvement in accessing prior knowledge, organizing ideas, and strengthening connections to understanding
On the other hand, the researcher would compare teaching reading of narrative text
11
2.2 Concept of Reading
Reading is important for human because they would deal with written text in their daily life. They do reading for searching information or only for pleasure (Fry:2006).
Nevertheless, reading is not an easy activity. There are many definitions of reading from several experts.
Smith (1982) says that reading certainly implies comprehension, and reading is something that makes sense to the reader. The reader tries to understand and get the meaning and information in the written texts form of symbols, letters, graphs, etc.
Thus, they grasp the writers’ messages from the texts.Meanwhile Nuttal (1985)
defines reading as the meaningful interpretation of printed or written symbols. It
means that reading is a result of the interaction between the perception of graphic
symbols that represent language and the readers’ language skills, cognitive skills, and
the knowledge of the world. In this process, the reader tries to recreate the meaning
intended by the writer.
According to Doyle (2004), comprehension is a skill in attaching meaning beginning at the same level and proceeding to attaching meaning to an entire reading selection.
All comprehension revolves around the readers’ ability in finding and determining main idea and topic sentence from the text.
12
understanding while reading. Comprehension occurs when studentsare able to
understand, remember, retell, and discuss with others about what they have read. One
aspect that becomes essential in students’ reading is the reading technique. It has direct “link” in comprehension and strategy or technique. The researcher assumes that
reading comprehension is students’ competence in comprehending the specific information, word and surface meaning in texts is described by students’ score with
an appropriate technique.
2.3 Concept of Reading Comprehension
There are two kinds of reading activity, namely reading aloud and silent reading. What the studentsare doing in silent reading is to use their eyes and their ability to understand the meaning of the written sign, thus comprehending the text would be
given more emphasize in silent reading. Someone has a purpose when he is reading. Usually the purpose of reading a passage is to find ideas from the reading passage. As
Suparman (2005:1) states that there are two major reasons for reading (1) reading for pleasure; (2) reading for information (in order to find out something or in order to do
something with the information studentsget)
Reading comprehension is ability which depends on the accuracy and speed of grapheme perception, that is, perception of written symbol, control of language
relationship and structure, knowledge of vocabulary items and lexical combination, awareness of redundancy, the ability to use contextual clues and recognition of
13
Heilman, Blair, and Rupley (1981:242) said that reading comprehension was a
process of making sense of written ideas through meaningful interpretation and interaction with language. Comprehension is the result of reading. Moreover, they
categorize reading comprehension into three levels of comprehension; literal comprehension, interpretative comprehension, and critical comprehension.
Literal comprehension is the process of understanding the ideas and information
explicitly stated in the passage such as: knowing the meaning of the words, recall of details directly stated or paraphrases in own words, understanding of grammatical clues, subject, verb, pronouns, and conjunction, so forth. Recall of main idea
explicitly stated and knowledge of sequence of information presented in passage.
Here the researcher sees that in reading comprehension, it is important that the reader should be able to interpret what they read and associate with their experience, not
only see and identify the symbol in front of them. This is necessary because when a reader reads a text, the communication process between the reader and the writer has happened. The reader tries to interact with print, his/her prior knowledge combined
with the visual (written) information result in his comprehending the text. In short, the researcher argued about reading comprehension is a combination of recognition
14
At last, literal comprehension has been considered as the way to comprehend the text
in this research. The reason is that it is suitable to the level of the first grade of senior high school students as it only deals with understanding the ideas or information
explicitly in the passage such as finding main ideas of paragraph, synonym of the words based on the context, and the information.
2.4 Concept of Teaching Reading
Alyousef (2005:143) says that in reading, contemporary reading tasks, unlike the traditional materials, involve three-phase procedures: pre-, while-, and last-reading
stages. The pre-reading stage helps in activating the relevant schema. For example, the teachers can ask students questions that stimulate their interest while previewing the text. The aim of while-reading stage (or interactive process) is to develop
students’ ability in tackling texts by developing their linguistic and schematic
knowledge. The last reading includes activities, which enhance learning
comprehension using exercises, cloze exercises, out-up sentences, comprehension questions.
The aim of teaching reading is to develop students’ skills that they can read English texts effectively. To be able to do so the studentsshould have particular purposes in their mind before they interact with the text. Effective and efficient reading
15
In short, in teaching reading the teacher should provide strategy to the students with
purpose for reading to anticipate different type of reading texts. Therefore, reading technique should be matched to reading purpose to read efficiently and effectively.
The researcher assumes that in teaching reading, appropriate and possible strategy should be applied based on the purpose of reading in order to get the comprehension. They use reading strategy to make their reading efficient and effective. Graphic
organizerwould be possible to be applied by the Senior High School students in their reading.
2.5 Concept of Graphic Organizer
Graphic organizer is visual displays teachers use to organize information in a manner
that makes the information easier to understand andlearn. Estes (1991:1) states that graphical organizers are composed of boxes (or other closed figures) and lines that show the basic expository pattern of the text. The boxes contain the basic ideas of the
text and lines show the connections among ideas.
Graphic organizer illustrates concept and relationship between concepts in a text by using diagram. Graphic organizer is also called pictorial organizer, webs, maps, and
concept maps. Graphic organizer is visual ways to represent information. The maps can be created to arrange information:
According to main ideas, subtopics, and details
In sequence
16
According to the similarities and differences between two or more concepts.
Along with its components, as in the elements of a story.
Graphic organizer is a communication device that shows the organization or structure of concepts as well as relationship between the concepts. Spatial arrangement
depicting the information structure reduce the cognitive demands on the learner (Ellis, 2004:1)
Based on the explanation above, it can be seen that graphics are visual instructional
tools used to illustrate the concepts of a reading text influence by a student or a
class’s prior knowledge about a topic or section of the text, using lines, boxes, etc. that show the connection each others.
Using graphic organizer in teaching reading English comprehension can be very helpful for the teacher to improve students’ performance in teaching reading and also for the students to improve their ability in reading comprehension because they can
help students comprehend information through visual representation of concept, ideas, and relationships among the topic, main idea and the details of the text. They provide the structure for short and long-term memory and turn the abstract concepts
into concrete visual representations. Teacher can guide the students to create and to manipulate the graphics.
Regardless of the label, graphic organizer can help students focus on concepts and
17
organizer,comprehension and retention skills play an important role since the students
should firstly distinguish between main idea and supporting details. Then they infer the ideas in form of graphic organizer by writing them down in boxes or lines that
showing the relation among the ideas. In graphic organizer students uses inferences andconclusion skill in the process of their reading to create the graphic organizer of the text they read. They infer the ideas in the text and draw their own conclusion
about the message of the text.
In addition, in creating the graphic organizer of text, the students also use critical thinking and analysis skills. The students should analyze the ideas and think critically
to determine which are the main ideas and supporting details of the text.
2.6 The Advantages of Graphic Organizer
According to Ellis (1998), there are advantages of graphic organizer as follows: 1. The content of the text easier to understand and learn.
Students are considerably more likely to understand and remember the content subject you are teaching. Simply put, the information tends to be less “fuzzy” and more precise. Graphics help students separate what is important to know from
what might be interesting, but not essential information.
2. Graphic organizer can reduce information processing demands.
18
Showing (as opposed to just telling) how the information is structured can be a
powerful way to facilitate understanding.
3. Students become more strategic learners.
Reading and writing skills, communication skills, and analytical, critical, and creative thinking skills are all subject to improve when students learn recognize these patterns of thinking, construct, and use graphic organizers.
2.7 The Disadvantages of Graphic Organizer
Besides graphic organizer has advantages, it is also have disadvantages, they are: 1. Graphic organizer has complex
2. In teaching reading by using graphic organizer, the teacher spends more time
and energy to explain and give example how to construct it.
3. Some students have difficulty building concept maps and using these graphic
organizer.
2.8 Types of Graphic Organizer
In accordance with Ellis (2004:2), graphic organizer can be divided into two
categories: those that depict the six basic information structures (whole to part, cause
and effect, to compare or contrast information, chart the story structure, etc.) and those that serve specialized needs (i.e., a graphic which structures project planning,
19
According to Max and Julia Thompson (2004:10), there are five main categories of
graphic organizer. The explanation is as the followings: 1) Venn Diagram
The graphic is used to compare or contrast and evaluate information from two sources.
2) Storyboard/Chain of Events
It is used to show process, sequence of events and chronology within a text.
3) Story map
20
4) Tree map
This one is used to show classifications, pedigrees, analysis, structures, attributes,
examples, and brainstorming.
5) Cause and effect
21
Based on the types of graphic organizer aforementioned above, the focused type of
graphic organizer researcher used is story map. This type is recommended to help students in comprehension achievement of narrative text by emphasizing text structures.
2.9 Concept of Literal Translation Technique
Literal Translation refers to a translation technique that can be used when the
languages involve share parallel structures and concepts; not to a translation made word for word: Literal translation carries the imprint of the original. This technique is used when it is possible to transpose the source language message element by
element into the target language and obtain a text that is idiomatic. Ideational choices are seldom taught from the point of view of function. Generally the focus is on the
isolated meaning of each item, e.g. literal translation of these words. The researcher believes that if teachers make students realize the context in which such elements are used and trained them in inferring meaning from context, they wouldfind better
results.
The goal of this technique is to be able to read and translate literary masterpieces and classics. Classes are conducted in the native language. Eventually, entire texts would
be translated from the target language into the native language and tests would often ask students to replicate classical texts in the target language. Very little attention is placed on pronunciation or any communicative aspects of the language. The skill
22
2.10 The Advantages of Literal Translation
Translation technique has some advantages, they are:
1. Translation can be done quickly. Therefore, it can help the teacher to keep
balance between the time allocation and the number of students in every classroom.
2. Translation is not limited, as it can be used to explain many different types of
words.
3. The using of native language will give a set of clear of objective that finally
will give the students the security since they can understand most of the instruction.
2.11 Disadvantages of Translation Technique
Besides translation technique has advantages, it is also have disadvantages, they are:
1. Translation is considered too quickly. Therefore, it takes away time that could
have been used to exposure the learners to English.
2. Not every English word has exact equivalence in native language.
3. The use of native language will reduce learners’ experience of English in class.
2.12 Concept of Graphic Organizer and Reading Comprehension
Nuttal (1982) states that in reading comprehension, nonverbal material (i.e. Pictures, diagrams, graphs, tables, etc.), and a list of diagrams may give useful illustration or
23
specific help in learning to read effectively. It is also a great assistance for the reader
in interpreting the text. In term of teaching and learning English
readingcomprehension in the classroom, teacher and students can create their own
non-verbal material in form of graphic organizer. They can build up a list of graphic or diagrams according to the text as visual illustration to show the relationship between the content of the text.
Graphic Organizer improves reading comprehension by emphasizing text structures such as story maps and improves different aspects of comprehension, such as literal and relational comprehension, recall, and vocabulary learning. Graphic organizer
pairs with strategy instruction can be more effective than traditional basal instruction and can be used effectively as advance organizers prior to reading (Simmons et al.,
1988).
Graphic organizer is a general term for schematic diagrams that help students identify key concepts and make relationships among them (Muth&Alvermann, 1999). It provides students with visual clues that they can relate to the written or spoken words
to which they are exposed. It can be used prior to reading or other classroom activity
to help focus students’ attention and help them make connections. It can be used, for
example, to organize students’ knowledge about a topic prior to reading, having a
discussion, and so on. Using prior to reading, it can be used as a guide and to build background, especially for difficult or dense text. When used after reading (or
24
diagrams, story maps, timelines, discussion webs, word webs, clusters, thinking maps
and so forth.
By showing, how the information is structured can be a powerful way to facilitate
understanding. Moreover, students aremore likely to become strategic learners. Reading and other communication and creative thinking skill are all subjects to improve when students learn recognize these patterns of thinking, construct, and use
graphic organizer.
2.13 The Concept of Literal Translation and Reading Comprehension Translation is one of technique that can be used for teaching reading. Richards
(1976:1) says that translation is general term referring to the transfer of thought and ideas from one language (source of language) to other language (target language)
Whether the language in written or spoken forms. It means that translation is the process of giving the closest meaning or natural equivalent of the words, phases, and sentences of one language into another language whether in written or spoken forms.
Reading comprehension is students’ competence in comprehending the specific
information, words and surface meaning in texts is described by students’ score with
an appropriate technique. Reading includes translating process in order to get the
information by relating word to word. The most widely chosen by teacher when the activities designed to evaluate reading comprehension are translation, questions, identification and explanation of new vocabulary, multiple choice, true or false and
25
It is known that literal translation technique can be regarded as one of the techniques
applied to teach reading comprehension. Literal translation belongs to traditional ways of teaching English which is grammar translation method (GTM) included at Elementary school, Junior High School, and also Senior High School. The reason is
in sense related to the condition of the school, teachers’ ability, time allocation and
number of students in every class.
2.14 The Concept of Narrative Text
According to Potter (2008:13), narrative is the representative of an event or a series of events. In addition, prince stated, “narrative is essentially mode of verbal presentation
and involves the linguistic recounting or telling of events”. The purpose of narrative
stories may have other purposes such as for explaining a phenomenon (myth and legend)
Narratives generally follow a similar structure, but the student should be guided by
the purpose for an audience of their text in their use of the following structure: 1. Orientation : an introduction in which the characters, setting, and time of
the story are established, usually answer who, when, and
where.
2. Complication : problems in the story, the complication usually involve the
26
3. Resolution : there needs to be a resolution of the complication.
Complication may be resolved for better or worse, happily or unhappily.
The examples of genres that fit the narrative text structure:
Folktale : a very told traditional story from a particular place that was
originally passed on to people in a spoken form.
Fairy tale : an old story about magic things happened intended for amusing
and giving lessons, meaning, and moral values.
Fable : a traditional short story that teach moral lesson, especially one
with the animals as characters; this story is considered as one group
of animal stories.
Myth : a story from ancient times, especially one that was told to explain
about natural events or to describe the early history of place or
people.
Language features that are used in narrative text are: 1. Simple past tense is used in most narratives.
2. In chronological order, using connectives that signal time, e.g., once upon a time,
one day, then, next, after, meanwhile.
3. Focused on individual or group participants, for example, in third person: he, she,
and they, or second person: the young man.
27
From the explanation above, the researcher assumes that narrative text is a kind of
text, which tells about series of events and also provides the resolution for the problem that happen in the past. In this research, the researcher would focus on
narrative text because the students’ comprehension in reading narrative is still low.
Even though narrative text is one of reading text that is mostly used in the reading test but many students in the first year of Senior High School do not really comprehend
this sort of text. They still have difficulty in finding the main idea and specific information of narrative text.
2.15Teaching Reading of Narrative Text using Graphic Organizer
In developing students’ reading comprehension of narrative text, the researcherwould like to present the application of graphic organizer technique. The researcher
elaborates and constructs the following procedures of teaching reading
comprehension of English narrative text. The researcher takes some steps in the presentation of graphic organizer as follows:
Pre-reading Activity
Before giving the reading material, the students to firstly doing some steps as follows: 1. The students greets the teacher.
2. The students discuss about the goals of the lesson and the roles of teacher and
students in the lesson.
3. The students are asked leading question related to the topic of text.
28
While reading activity
1. The students reviewabout narrative text 2. The students are given the text
3. The studentsdiscuss the text together based on their schemata by asking some
question related to the topic.
4. The students are introduced the graphic organizer technique and explained its
function as visual illustration that can help them to comprehend the text easier. 5. The students are explained about story map and show how to construct story map. 6. The students show and explain to the relation between the lines in the story map or
storyboard (main idea and its detail information), reference of the pronoun, and difficult vocabulary in constructing the graphic organizer.
7. The students are given discussion ofgraphic organizerin the class
8. The students are explained the generic structure of the narrative text based on the
story map.
9. The groups of students are asked to discuss story map according to the text. 10. The students are asked to practice applying graphic organizer in reading
comprehension of the given text individually
11. The student are evaluated their reading comprehension through reading test.
Post Reading activity