THE TRANSLATION STRATEGIES OF THE CULTURAL TERMS FOUND IN THE INHERITANCE OF LOSS
A Thesis
Submitted to Letters and Humanities Faculty in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for
The Degree of Strata One
Dede Nurillaila
1110026000029
ENGLISH LETTERS DEPARTMENT
LETTERS AND HUMANITIES FACULTY
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY OF SYARIF
HIDAYATULLAH
JAKARTA
FOUND IN THE INHERITANCE OF LOSS
Dede Nurillaila
1110026000029
ENGLISH LETTERS DEPARTMENT
LETTERS AND HUMANITIES FACULTY
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY OF SYARIF
HIDAYATULLAH
JAKARTA
i ABSTRACT
Dede Nurillaila, The Translation Strategy of the Cultural Terms Found in The Heritance Of Loss. A Thesis: English Letters Department, Letters and Humanities Faculty, State Islamic University of Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, March 2015.
This research investigates types of cultural terms related to social system and the strategies in translating them into Indonesian. The data were taken from the novel entitled The Inheritance of Loss in English and its translation in Indonesian translated by Rika Iffati Farihah.
The researcher uses the qualitative method by reading both English and Indonesian version novels, marking the cultural terms, classifying, selecting and analyzing them based on the theories of translation strategy which are taken from some relevant references.
iv
of my knowledge and belief, it contains no material previously published or written by another person nor material which to a substantial extent has been accepted for the award of any other degree or diploma of the university or other institute of higher learning, except where due acknowledgement has been made in text.
Jakarta, March 20th 2015
v
All praises be to Allah SWT, the Lord of Universe, on the overflow of graces and mercies to mankind, who amazingly guides the researcher in the process of making this thesis. Peace and Salutation be upon the greatest prophet Muhammad SAW, his family, companions and adherents, who had changed the world from the darkness into the lightness.
On this occassion, the researcher wants to say many thanks to her beloved parents (Hambali and EncunSuryani) and her oldersister (Payuningsih) and twoolder brothers (Awaludin and Maulana), who have kept, taught, advised and prayed for her success. The researcher also wants to give her gratitude to Mr. Dr. Muhammad Farkhan, M.Pd and Mr. M. Agus Suriadi, M.Hum, as the researcher’s advisors for their time, guidance, patience, kindness, contribution in correcting and helping her in finishing her thesis.
The researcher would like to express her appreciation to the following people, namely:
1. Prof. Dr. Sukron Kamil, M.Ag, the Dean of Letters and Humanities Faculty, State Islamic University of Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta;
vi
3. Mr. Drs. Saefuddin, M.Pd, the Head of English Letters Department and Ms. Elve Oktafiyani, M.Hum, the Secretary of English Letters Department;
4. All lecturers and the staffs of Adab and Humanities Faculty;
5. Special thanks to Agus Mujianto for being her fiancé, friend, beloved, figures, and shoulders to rely on, “You’re my everything”;
6. The researcher’s beloved FRIENDS: Siti Khodijah, Ratu Shodfatul Munifah, Hafizah Adha, Siti Lutfah Y, Sheila Khalidah W, and Aden Irmat. Thanks for all support and memories.
7. All friends of class B and Translation class;
8. The researcher’s friends in Translation Class:Dwi Santika and Khilda Nida.
9. To all people and friends that are not mentioned, “Thank you very much.”
May Allah, the all-Hearer and all-Knower, always bless’ protects, and gives them more than they have given to the researcher. Hopefully, this thesis will be advantageous for all people who read it.
Jakarta, March 20th, 2015
vii
A. Background of the Research ... 1
B. Focus of the Research ... 4
C. Research Question ... 4
D. Objective of the Research ... 5
E. Significance of the Research ... 5
F. Research Methodology... 5
B. The Strategy of Translation ... 11
C. Cultural Words ... 14
1. Definition ... 14
viii
D. Cultural Untranslatability Word ... 17
E. Types of Cultural Untranslatability ... 18
F. Translation Novel ... 20
CHAPTER III RESEARCH FINDINGS ... 21
A. Data Analysis ... 22
CHAPTER IV CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 32
A. Conclusion ... 32
B. Suggestion ... 33
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 34
1 CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Research
Language is the important aspect in the life of all beings. We use language to express our inner thought, to learn and to communicate each others. This is in appropriate with the definition of language in Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary
of Current English ―Language is the system of communication in speech and writing
used by people of a particular country‖.2
It means that language consists of the elements or components that are regularly arranged according to a certain pattern and form a unity. We must be able to speak by using language that is structured according to the correct system.
Essentially, language serves as a communication tool for people in the world that is used in various levels, and diverse interests. Therefore, using communicative language requires knowledge and skills using a wide variety of languages. In the field of translation, the translators are required to translating any text communicatively from various sources all over the world.
2
2
Meanwhile, translation is the liaison between countries in the world that have a different language and custom. Translation can connect people between the countries in the world, as Hoed states that, translation is the activity diverts messages from one language (source language/SL) to another (target language/TL).3
Basically translating text is translating culture, because language is essentially a product of a particular culture. As we know, language is a part of culture. Meanwhile there were so many kinds of different cultures in the world, because every country has its own culture, so that the language used varies also.
Moreover, every culture has its own incongruity that is not owned by another culture. This fact may cause many kinds of unique cultural products that make other people from different culture difficult to find the equivalence in their cultures and
languages. This is in line with Catford’s opinion that says ―The central problem of
translation practice is that of finding TL translation equivalents‖4. This means that the main problem in translation is to find the equivalent as precise as possible.
In order to find the cultural equivalent, the translator will deal with the concept of translatability and untranslatability. The larger the differences between source language and target language in their language structures and cultures, the
more the untranslatable factors are produced. For example, the word ―Kejawen‖ in
Indonesian was not found the equivalent in English word, and ―Halloween‖ in
English was not found the equivalent in Indonesian. The differences of cultural
3
Benny Hoed, Penerjemahan dan Kebudayaan, (Jakarta: Pustaka Jaya, 2006), p. 33. 4
between English and Indonesian language is the major problem that a translator needs to concern about. Therefore, the translator should make the readers understand about the message of the target language by giving an explanation about those cultural words.
For instance, when translating the novel text, the translator will face some problems of the way to translate a title, choose personal pronoun pronominal, and translate metaphor and idiom.5 All of problems and difficulties that appear when translating a novel text is a challenging job for a translator to produce the translation result which is equal to the source text and also acceptable in the target text.
4
States. Sai is a girl living in mountainous Kalimpong. Desai switches the narration between both points of view. The action of the novel takes place in 1986. In this novel, there are many words giving obstacles for translator to reach the equivalent word in the target language, because of the cultural differences between source and target language.
In this research, the researcher tries to find words containing cultural terms, to classify them based on the categories of cultural terms related to social system adapted from Ke Ping, indeed the researcher tries to analyze the translation strategies used by the translator to translate the cultural terms in The Inheritance of Loss. This research can lead the translator be more reasonable in translating cultural terms.
B. Focus of the Research
This research focuses only on the translation of cultural terms related to social system found in the novel entitled The Inheritance of Loss written by Kiran Desai and translated into Indonesian language by Rika Iffati Farihah also what translation strategies are used by the translator.
C. Research Question
1. What are the kinds of cultural terms related to social system found in
Kiran Desai’s novel The Inheritance of Loss and their translation in
Bahasa Indonesia?
2. What are kinds of translation strategies used by the translator to translate
the cultural untranslatability words in Kiran Desai’s novel The Inheritance
of Loss?
D. Objectives of the Research
Objectives of the research based on the problem statements are as follow: 1. To identify and classify the cultural terms related to social system found in
the novel based on Ke Ping’s classification.
2. To find the kinds of translation strategies used by the translator to translate the cultural terms in Kiran Desai’s novel The Inheritance of Loss based on
Mona Baker’s classisication of translation strategies.
E. Significances of the Research
The result of this research expectantly will be advantageous to the writer herself and the readers.
1. To know deeply about cultural terms found in the source language.
6
F. Research Methodology 1. Research Method
The method used in this research is descriptive qualitative method. The writer reads both English and Indonesian version of the novel The Inheritance of Loss, which tries to find the cultural terms and translation strategies applied by the translator (Rika Iffati Farihah).
2. Technique of Data Analysis
To analyze the data, the researcher uses descriptive analysis technique that is supported by the relevant theory, and the researcher uses the following steps:
1) Reading both version English-Indonesian novels, marking all cultural terms in both of versions and making notes about them in a piece of paper. In The Inheritance of Loss, one side of the paper consists of the English cultural term and the other side has the translation;
3. Instrument of the Research
The instrument of the research is the researcher herself by reading both version novels comprehend, observing, signing, and grouping the SL cultural terms and the target language translation used by translator in translating novel The Inheritance of Loss that will be analyzed for the report.
4. Unit of Analysis
Unit of analysis in this research is The Inheritance of Loss, a novel by Kiran Desai published by Penguin Group (Canada) in 2006 and its translation Senja di Himalaya by Rika Iffati Farihah in 2007 published by PT Mizan Pustaka. 5. Time and Place of the Research
The writer starts doing the research from December 2013 in English Letter Department, Letter and Humanities Faculty, State Islamic University of
―Syarif Hidayatullah‖ Jakarta. The research is located at the English Letters
Department, Library of State Islamic University of ―Syarif Hidayatullah‖
8 CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Translation
In this chapter, the researcher will express some theories about the notion of translation. Nowadays translation is seen as an important role in human activities and for the translator as a mediator between cultures. In this globalization era, the needs to the translated matter have increased intensely.
As quoted by Newmark of Jumpelt7, 20th century is said to be the century of translation. As well since the 19th century translation is the only way to communicate between the philosophy and other scientists.
1. Definition of Translation
There are a lot of understandings about translation which can be found in all the books about translation. Some linguistic experts have similar opinion
about translation but formulated in different ways. Catford stated, ―Translation
may be defined as follows: the replacement of textual material in one language
(SL) by equivalent textual material in another language (TL).‖8
Here, Catford emphasized that the subtitles should be commensurate with the original text.
7
Peter Newmark, Approach to Translation (Oxford: Pergamon Press, 1981), p. 3. 8
Here, Catford emphasized that the subtitles should be commensurate with the original text.Furthermore, Nida and Taber stated, ―Translating consist in reproducing in a receptor language the closest natural equivalent of a source language message firstly in terms of meaning and secondly in terms of style.‖9 It means, when process of translating a language into another language, it cannot omit the meaning and style. While Newmarkdefined translation as ―a craft consisting in the attempt to replace a written message and/or statement in one
language by the same message and/or statement in another language.‖10
It means the intention of the author of the text must be considered by the translator. Therefore, in translation the intention of the author in the source language used as a benchmark whether it is appropriate or not the meaning of the source language.
After explaining some definition above, the researcher makes a conclusion that translation is the process of rendering the source language to target language without changing the meaning. It means that before translating, the translator must be recognizing the target reader about the result of translating.
2. The Types of Translation
Practically, there are some types of translation that have their own characteristics and forms. To distinguish the concept of translation, Jacobson differentiate translation into:11
9
Eugene A. Nida and Charles R. Taber, The Theory and Practice of Translation (Leiden: E.J. Brill, 1982), p. 12.
10
Peter Newmark, Approach to Translation (Oxford: Pergamon Press, Ltd, 1981), p. 7. 11
10
a. Intralingual translation or rewording (an interpretation of verbal signs by means of other signs in the same language).12 This intralingual translation is the conversion of a text into another text based on the interpretation of the translator. For example, when we write back a poem into prose in Indonesian, then we do intralingual translation. b. Interlingual translation or translation proper (an interpretation of
verbal signs by means of the signs of some other language).13 This type of translation is a translation in the real sense. In this type, the translator rewrote meaning of the source language text or message text into the target language.
c. Intersemiotic translation or transmutation (an interpretation of verbal signs by means of the signs of a nonverbal system).14 This type includes the interpretation of a text into a form or another sign system. For example, interpretation of a novel into a soap opera with the same title.
Those concept are to seek the presence of translation equivalence, but Jacobson argued that the intralingual translation only have an idea of the process of transfer from the source language into the target language.
B. The Strategy of Translation
Strategy is a plan or method for achieving a specific goal (the whole text). Mona Baker states that there are eight types of translation strategy for professional translation.15
1. Translation by a more general word
This is one of the most common strategies to deal with many types of nonequivalence. As Baker believes, it works appropriately in most, if not all, languages, because in the semantic field, meaning is not language dependent. For example:
SL : My mother frightened about flooding at home constantly. TL :Ibuku selalu takut akan banjir dirumah.
*contantly translated selalu.
This is a common strategy used by the translator to find the equivalent of a variety words that do not have a direct equivalent.
2. Translation by a more neutral/ less expressive word.
This is another strategy in the semantic field of structure. This strategy is used to reduce the negative impression by the word in the source language, which is due to the meaning of which is owned by the words in the source language. For example:
SL : Sophie is still looking deadly bored and sleepy. TL : Sophie masih kelihatan sangat bosan dan ngantuk. *Deadly translated sangat
15
12
3. Translation by cultural substitution
This strategy involves replacing a culture-specific item or expression with a target language item considering its impact on the target reader. This strategy makes the translated text more natural, more understandable and more familiar to the target reader.
For example:
SL :Next week will be halloween party.
TL :Minggu depan akan diadakan pestatopeng.
4. Translation using a loan word or loan word plus explanation
This strategy is usually used in dealing with culture-specific items, modern concepts, and buzz words. Using the loan word with an explanation is very useful when a word is repeated several times in the text. At the first time the word is mentioned by the explanation and in the next times the word can be used by its own. For example:
SL :This is true of Bali where the unique ornamentation of the gringsing cloths of Tenganan village Are said to be designs painted in the sky, creations of BataraIndra.
TL :Begitupun di Bali ragam yang unik pada kain gringsing dari desa Tenganan, adalah desain yang terlukis di langit yang di ciptakan oleh Batara Indra.
5. Translation by paraphrase using a related word
This strategy is used when the source item in lexicalized in the target language but in a different form, and when the frequency with which a certain form is used in the source text is obviously higher than it would be natural in the target language. For example :
SL :Obama is an Afro-American man.
TL :Presiden Obama berdarah campuran Afrika-Amerika. 6. Translation by paraphrase using unrelated words
The paraphrase strategy can be used when the concept in the source item is not lexicalized in the target language. When the meaning of the source item is complex in the target language, the paraphrase strategy may be used instead of using related words; it may be based on modifying a super-ordinate or simply on making clear the meaning of the source item. For example:
SL :They have a totally integrated operation from the preparation of the yarn through to the weaving it.
TL :Mereka mempunyai semua langkah – langkah produksi dalam pabrik ini dimulai dari menyediakan benang hingga menggulungnya..
7. Translation by omission
14
SL : Tommy made the excuse of feeling tired and went up to his room. TL : Tommy beralasan bahwa dia capek, dan dia naik ke kamarnya.
The word ―feeling‖ is omitted this step was taken while not reducing the
important messages conveyed. 8. Translation by illustration
This strategy can be useful when the target equivalent item does not cover some aspects of the source item and the equivalent item refers to a physical entity which can be illustrated, particularly in order to avoid over-explanation and to be concise and to the point. For example :
SL: Beyond the veranda, speck insects suspended in a pod within which they jigged tirelessly.
TL: Diseberang beranda, serangga – serangga sangat kecil yang tergantung dalam sebuah kulit tempat mereka melompat – lompat tanpa lelah didalamnya.
C. Cultural Words 1. Definition
to several aspects, especially about culture. Translating the language that involves elements of culture is very challenging for translators because many translators who said that culture is difficult to be translated, or even impossible to translate.
According to Newmark, culture is ―… a way of life and its manifestations that are peculiar to a community that uses a particular language as its means of
expression‖. 16
And Larson says that culture is a complex of beliefs, attitudes, values, and rules which a group of people share.17 It can be concluded that cultural words is a word, a group of words, or compound word which states specifically on the cultural significance.
2. The Types of Cultural Words
Newmark sets the comprehensive cultural categories according to Nida’s divisions, to make it easier to understand the researcher categorizing into a table as following below:18
Table 1.1
Cultural Categories by Newmark’s classification
No. Categories Sub Catagories/ Elements
1. Ecology Concerns the geographical surrounding of nature such as flora, fauna, winds, plains, hills, etc.
2. Material culture This category includes what is related to every day supplies for instance foods, drinks, clothes etc.
16
4. Organizations, customs, activities, procedures, concepts
Political, religious, artistic activists.
5. Gestures and habits Body gestures and habits.
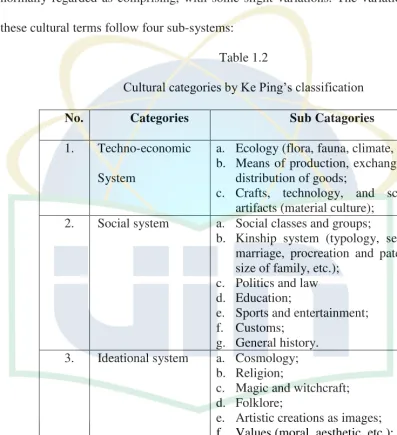
Another classification is done by Ke Ping.19 He defines that culture is normally regarded as comprising, with some slight variations. The variations of these cultural terms follow four sub-systems: b. Means of production, exchange, and
distribution of goods;
c. Crafts, technology, and science; artifacts (material culture);
2. Social system a. Social classes and groups;
b. Kinship system (typology, sex and marriage, procreation and paternity, size of family, etc.); 3. Ideational system a. Cosmology;
b. Religion;
4. Linguistic system a. Phonology and graphemics;
b. Grammar (morphology and syntax); c. Semantics and pragmatics.
Ke Ping’s classification of cultural terms is used in this research as the
background story of the novel. This is the most important point in using Ke Ping’s
classification. In addition, Ke Ping also gives the details of four classifications which are useful in classifying the terms and preventing ambiguity
.
D. Cultural Untranslatability Word
The translation that involves cultural items needs serious attention because the translator will be faced with complex problems, namely the untranslatability. Catford distinguishes two types of untranslatability, linguistic and cultural.20 Linguistic untranslatability occurs when there is no lexical or syntactic substitute in language for the Source language item. This is the result of the differences between the Source language and the Target language. Cultural untranslatability is due to the absence in the target culture of a relevant situational feature for the Source language text.
Translation is a part of a continuous process of intercultural transfer. The translator has to present the aspects of social culture that is unfamiliar to the receiving audience. They consist of elements of the material culture like food, dress and tools, factors of social structures like customs and law, features of the natural world like weather, flora and fauna, and social functions like festivals, rituals and ceremonies.
20
18
E. Types of cultural untranslatability
According to translation, cultural obstructions or cultural differences, reflects five aspects: historical culture, geographical and psychological culture, material culture, customs and traditions as well as religious culture.21
1. The historical culture
The historical culture refers to the culture settled and formed during the development of society. Different nations have different historical development, so their historical cultures are different. This kind of difference impedes the communication between languages. For example, the word
―prabu‖ must be translated in a direct way with the some explanations, for
there are lacks of such historical background in western country. 2. The geographical and psychological culture
Different nations’ geographical and psychological culture is also a main
barrier in translation. Because of the different geographical environment and different nation’s mentalities, the same word will have totally different
meanings in two different cultures. For example, ―East wind‖ in Chinese and
English is a vivid example. Chinese people and favors the east wind, for it is
always a symbol of ―spring‖ and ―warmness‖ while people in Britain dislike
the east wind, because the east wind is from the northern part of the European
continent, so it is always symbolize ―coldness‖ and ―sadness‖.
21
3. The material culture
Many words reflecting the distinctive material culture in the source language should be paid much attention to when translated them. For example,
the word ―cricket‖ is a peculiar word in the English language, for it is a
popular outdoor game in Britain, and plays an important role in people’s daily
life. There is a saying ―It is as significant as a game of cricket.‖ If we want to
translate this sentence, we should add some background information for the Indonesian readers, because playing cricket is rare in Indonesia.
4. Customs and traditions
The different customs and traditions in the daily activities and communications in Indonesia and Western countries reflect the different cultural mentality. The naming system is a good example, which reflects the different standards of the degrees of people’s close relations, the relations between people in the higher and lower levels. For example, in Indonesia people used to call others by their degree of family relation to show the respect while in western countries people call each other’s name directly to show the close relations.
5. The religious culture
Religious culture means the culture formed by a nation’s religious beliefs
20
F. Translation Novel
Novel is a literary work that reveals the stories are fictional using elements of character, plot, setting and style to express a particular theme. Novel much in demand among readers because the story is interesting, straightforward language, and its contents were impressed realistic due to reveal things that are very close to reality. As a work of imaginative, novel can be used for the researcher to express their thoughts and feelings. While novel translation is a novel that is structured by way of divert translated foreign novels into Indonesian.
In translation novel there are some differences with the original Indonesian novel. The difference is reflected in the language elements, customs, cultures, and values.Sayogie says that the good novel translation occurs when the impression of source language readers.22 It means that the translation of novel should be interesting in the way of presenting the wholly story and must gives the same message and impression between both source and target language readers. In translating novel, thereare some techniques of novel translationthere are:1) the translator should be masteringthe source language, 2) mastering the target language, 3) mastering the translated material, 4) familiar with all types of dictionaries, 5) easy and accustomed to seeing ―overall description‖ of the novel and 6) read as many other similar novel.
22
21 CHAPTER III RESEARCH FINDINGS
This chapter presents and discusses the results of the research. The cultural terms related to social system and strategies in translation are presented in one
section. The section discusses the types of cultural terms based on Ke Ping’s
classification and the strategies in translating the terms according to Mona
Baker’s classification.
A. Data Analysis
This section discussed the cultural terms found in the novel. There are 10 cultural terms related to social system found from the source text, the original version, and it can be classified under types of cultural terms related to social
system based on Ke Ping’s theory. There are 2 strategies of translation of this
novel which is related to social system, and it classified based on Mona Baker’s
theory of translation strategies.
Datum 1:
22
TL :Pesta pernikahan itu berlangsung selama seminggu dan sedemikian mewah sampai tak ada orang di Piphit yang meragukan bahwa keluarga tersebut hidup berkelimpahan ghee dan emas, jadi ketika Bomanbhai membungkukkan badan sambil mengucapkan Namaste dan memohon agar tamu-tamunya makan dan minum, mereka tahu sikap rendah hati ini cuma pura-pura— dan dengan demikian merupakan sikap rendah hati yang paling baik.
The term Namaste in sentence (8) above belong to the social system related to custom. Namaste is a common valediction or salutation originating from the Hinduism the Indian Subcontinent. It is a customary greeting when individuals meet, and a valediction upon their parting.20Namaste in this novel is also explained in the same way. When spoken to another person, it is commonly accompanied by a slight bow made with hands pressed together, palms touching and fingers pointed upwards, in front the chest.
Namaste is translated into Namaste, it can be said that the translator used the strategy of translation using loan word. The researcher identified that the translator borrowed Hindi cultural word by using italic for the word, so this
strategy can be mentioned as pure borrowing with ―wholly italic‖. In the
researcher’s opinion, the translator used italic form in the translation because SL word is used in italic form. This translation cannot be accepted as it is not clearly described the term, because the translator did not give more explanation and information about the term. Thus, the translation should be better added more explanation by putting it in the bracket, making a note or giving appendix of the term.
20
Datum 2 :
SL : "Babaji, just look outside—how are we to keep them dry? It is humanly impossible, they are getting wet as we transfer them from van to office."
TL : ―Babaji, lihat saja di luar—bagaimana kita bisa menjaga agar surat-surat itu tetap kering? Secara manusiawi, itu mustahil, surat-surat tersebut menjadi basah saat kami memindahkannya
dari van kekantor.‖
The example of kinship system is shown in datum (2). From this sentence, it can get an example of phrase related to paternity. The word "baabaa" [originally from Persian] means "daddy" still used with this meaning in Urdu. However, this word has come to signify an "old man". So, when one is addressing an old man (or anyone older for that matter) one adds "jii" (or jaan in Urdu) to convey respect.21
The term Babaji in the sentences above is not translated. The translator used the term as it is in the SL text. It’s function to introduce the Hindi culture about the social classes of calling for father. Though, it is still possible to translate the term to Indonesian as Bapak or Ayah. Thus, the way that the translator used in this case is translation using a loan word. This translation is cannot be accepted, because the translatoronly borrowing the term from source language without providing a clear explanation or information, so it will make the readers confused about the term. Thus, the translator would be better to addexplanation by putting it in the bracket of the term, or making a note and giving appendix.
21
24
Datum 3:
SL : ―Better get it straight before you get on the plane, bhai.‖
TL : ―Lebih baik kau paham itu sebelum naik pesawat, bhai.‖
Bhai in datum (3) belongs to social system which is part of kinship system. Bhai translated from hindi/gujarati as brother. Bhai used to call your younger brother if he has a stupid name you can't be arsed to say or to embarrass him in front of friends.22 In this novel, bhai was not described clearly. The term bhai in the novel used for talking in a friendly way to a man.
From the example above, the translation of the word bhai is transferred directly into the TL. Whereas, it still possible to translate the terminto Indonesian language as Mas or Abang. Therefore, the translation strategy used to translate this term is translation using a loan word. The researcher identified that the translator borrowed Hindi cultural word by using italic for the word, so this strategy can be mentioned as pure borrowing with ―wholly italic‖. In the
researcher’s opinion, the translator used italic form in the translation, because SL
word is used in italic form.
olderwoman familiar to the speaker.23 In the sentences above didi can be classified as social system, such as kinship system. Didi in this novel is used for talking in a friendly way to a woman.
The example above shows that the translator translates the term didi into didi. Though, the word didi is still possible to be translated in Indonesia as mbak or kakak. The translator translated the term directly in the target language. It can be said that the translator used the strategy of translation using loan word. In Indonesian culture the word didi is widely used by Indonesia society as a name of someone, so the translation of the term will exactly make the reader confused to understand and bring a different understanding as the translator translated didi as didi without italicizing the term or giving more explanation about the term.
Datum 5:
SL : ―A great shikari he was, Saibaby.
TL : ―Sungguh shikari yang hebat dia, Saibaby.
The term shikari in datum (5) above belongs to the social system related to kinship system. A shikari is a big game hunter or hunting guide in India.24 Shikari in this novel is also explained in the same way. Shikari is someone who is experienced in hunting, especially a wild animal.
The translation of the term in the target language clearly uses borrowing. It means that the translation uses the strategy of translation using a loan word.
26
addition, based on the context, there is an explanation of the word by putting it in the appendix in the novel, so it is not enough to just borrow that word. The word shikari is translated to shikari. It can be assumed that the translator wants readers to know that the word shikari is a foreign word. This translation is cannot be and poorest, the back-and-forth ones maintaining green cards. TL : Orang – orang India yang tinggal diluar negeri, yang paling kaya
dan yang paling miskin, orang – orang yang mondar mandir warga negara asing untuk tinggal dan bekerja di Amerika Serikat. According to the explanation of the text above, Green card is the example of social system related to politics and law. The translator does not put the explanation directly. The information puts in the foot note while the translator retains the original term of green card in order to inform to the Indonesian reader about the term.
25
In translating the two sentences above, the translator uses the strategy of using a loan word with explanation. The use of this strategy is needed with some of the considerations firstly, when the cultural term translated was not described clearly in the novel. Secondly, there are equivalent that if approached in the target language, although not entirely accurate. Third, the translator tries to retain the authenticity of the narrative.
Datum 7:
SL : A bit of ―sir sahib huzoor‖ for politeness’ sake, but that was just residual veneer now; he knew what they really thought of him. TL: Sekelumit ―tuan sahib huzoor‖ demi basa-basi, tetapi itu hanya
polesan sisa sekarang; dia sudah tau apa sebenarnya anggapan mereka tentang dirinya.
Huzoor is an Indian of high rank, or a title of respect for such a person.26 The term huzoor in the sentence can be classified as social system which is part of kinship system. In the bilingual Hindi-Indonesian dictionary, the term of huzoor has the same meaning as tuan. The translator not only put tuan as the similar meaning in Indonesian language, but also huzoor in the target language, so it has two terms in the sentences of target language.
The term huzoor in the sentences above is not translated. The translator uses the term as it is in the source language text. The aim is to introduce the Hindi culture about the kinship system of calling for master. It can be identified that the strategy which is used by the translator is translation using a loan word. This
26
28
translation is cannot be accepted as the translator only borrow the word without give more explanation or information of term, as it can make the reader confuse to understand the sentences. Thus the translator should give some explanation by putting it in the bracket of term or make a note and appendix in the novel.
Datum 8: equivalent as tuan. The term sahib is transferred directly into the target language without any change.
In this case, the translator uses the strategy of translation using loan word
to translate the term. In researcher’s opinion this translation is cannot be accepted,
because the translator only borrows the term from source language without provides a clear explanation or information, so it will makes the readers confused about the term. Thus, the translator would be better to adding more explanation by putting it in the bracket of the term, or making a note and giving appendix.
27
Datum 9:
SL : She had left India a meek bride, scrolled and spattered with henna, so much gold in her sari she set off every metal detector in the airport—and now here she was—white pantsuit, bobbed hair, vanity case, and capable of doing the macarena.
TL: Wanita itu meninggalkan India sebagai seorang mempelai yang penurut, terlukis dan terpecik henna, sarinya dihiasi emas begitu banyak sehingga dia menyalakan semua detector logam di bandara—dan sekarang inilah dia—mengenakan jaket dan celana panjang yang serasi, rambut dipotong pendek, tas make-up dan mampu bergoyang macarena.
Datum (9) shows, macarena as the cultural words that belongs to social system related to entertainment. Macarena is (often initial capital letter) a dance performed in a group line or solo and followed by arrhythmic pattern of arm, hand, and hip movements in time to a Spanish song.28 According to Oxford dictionaries Macarena is a dance performed with exaggerated hipmotion to a fast Latin rhythm.29 Yet, Indonesian culture does not have this kind of dance. Therefore, there is not an equivalent word in Indonesian language. It is identified that the translator uses translation using a loan word as the strategy to translate the term in which she preserves the term Macarena in its original word. It can be assumed that the translator wants readers to know that the word Macarena is a foreign word.This translation is cannot be accepted, because the translator only borrowing the term from source language without providing a clear explanation or information, because there is no term of such dance in Indonesian culture. Thus, the translator would be better to add explanation by putting it in the bracket of the term, or making a note and giving appendix.
28
http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/macarena?s=t, accessed on March 23rd 2015 29
30 berjalan bersama menuju Lapangan Mela, melalui gerbang masuk yang diatasnya dipasang patung Gandhi untuk memperingati kemerdekaan India. Petugas Keamanan, roughly translated as Association of Security Officers. In theory, a satpam is best equipped to guard your family in a dangerous situation. In reality, people would probably never need those services. His role is primarily to ensure people safety, open the gate, and screen visitors.30 However satpam is familiar to Indonesian reader and therefore provides a good cultural substitution.
The word watchman has several translation words such as penjaga, satpam and many other words. The translation believed watchman has the same
30
32 CHAPTER IV
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A. Conclusion
From the discussion in the previous chapter, it is found that most of the cultural terms related to social system are examples of kinship system. It is 7 from the total of 10 cultural terms. Custom is found 1 time and followed by entertainment 1 and law 1 term.
In translating these cultural terms, three different strategies are used by the translator. Those are translation using a loan word, loan word plus explanation, and translation by cultural substitution. From these strategies, translation using a loan word is the most used in translating cultural terms related to social system. It is because the terms are untranslatable, have no equivalence words in target language, or in order to create the exotics sense in the text. It is followed by translation using loan word plus explanation and cultural substitution which only occurred once.
B. Suggestion
From the conclusion of research findings, the researcher gives some suggestion for students of English Department, cultural translators, and other researchers as follows:
1. Students of English Department who are interested in the subject of material cultural terms translation, they should be aware that translation concerning culture is problematic, because each culture develops its own language. It is suggested that the student have wide understanding about material culture in subject observation. It is also suggested that a student has a deep understanding about the strategies in order to solve the problems of translation of cultural terms.
2. For the cultural translator, it is better to choose the words which have at least the closest meaning to the lexicon in source language and put the additional information or explanation about the source language material cultural terms which are unfamiliar among the target readers. 3. Since this research focuses only in the translation of cultural terms
34
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Books:
Baker, Mona. 1992. In Other Words, A Coursebook on Translation. Newyork: Routledge.
Catford, J.C. 1965. A Linguitic Theory of Translation. London: Oxford University Press.
Choliludin. 2009. The Technique of Making Idiomatic Translation. Jakarta: Visipro.
Desai, Kiran. The Inheritance of Loss. 2006. New York Grove Atlantic, Inc. Print. _____. Senja di Himalaya. Trans. Farihah, R.I. 2007. Jakarta: Penerbit Hikmah.
Print.
Hoed, Benny H. 1992. Penerjemahan dan Kebudayaan. Jakarta: PT Dunia Pustaka Jaya.
Larson, M. 1984. Meaning-based Translation. Lanham: University Press of America.
Machali, R. 2009. Pedoman Bagi Penerjemah. Jakarta: Grasindo.
Newmark, Peter. 1981. Approach to Translation. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Websites:
Anonym. Oxford Online Dictionary in www.oxforddictionaries.com. Accessed: November 24, 2014. Online.
Kitamura, Kanji. Cultural Untranslatability. Translation Journal, Vol 13, No 3 (2009) in http://translationjournal.net/journal/49translatability.htm. Accessed on September 26, 2014. Online.
Liyan, Huang. Cultural Differences and Untranslatability. Translation Journal, Vol 12, No 9 (2006) in http://www.21jfs.com/Item/596.aspx. Accessed on September 26, 2014. Online.
Ping, Ke. Cultural Presuppositions and Misreadings. META, Vol 44, No 1
(1999): 133-143. Retrieved August 27, 2014
36
APPENDICES
A. SYNOPSIS
The story is centered on two main characters: Biju and Sai. Biju is an illegal Indian immigrant living in the United States,
son of a cook who works for Sai’s grandfather.
Sai ia a girl living in mountainous Kalimpong with her maternal grandfather Jemubhai, the cook and a dog named Mutt. Desai switches the narration between both points of view. The action of the novel takes place in 1986.
In a crumbling, isolated house at the
foot of Mount Kanchenjunga in the
Himalayas lives an embittered judge
who wants only to retire in peace,
when his orphaned granddaughter,
Sai, arrives on his doorstep. The
judge’s cook watches over her
distractedly, for his thoughts are
often on his son, Biju, who is
hopscotching from one gritty New
York restaurant to another. Kiran
Desai’s brilliant novel, published to
huge acclaim, is a story of joy and
despair. Her characters face
numerous choices that majestically
illuminate the consequences of
colonialism as it collides with the