This Paper
Has fulfilled The Requirement for the Degree of Sarjana (SI) At The English Department the Faculty of Education
By:
DWIHARTATI
NIM. 0014000382 !
ENGLISH DEPARTMENT
FA CUL TY OF TARBIY A AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SY
ARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
A
PaperPresented to The Faculty ofTarbiyah and Teachers Training Jn Partial Fulfillm.:nl nCThe
Requirement for The Degree of Sarj ana ( 31 )
By:
!)Wl HJ},J(l:i\Tl
NIM.0014000382
Advisor:
NIP. l 50 244 682
ENGLISH DEPARTJYf.ENT
FACULTY OF TARRIYAH. AND TEACHERS
Ti<iAlNING
SYAHJ.F
HTDAYATULLAH
STATE
JSLAJ'vHC
UN!VERSrf':/
J.
セ@ F <, ᄋセᄋᄋイ@ 'J ,.a\..M.N. KA
Smart Education Center Villa Mutiara Jombang, Ciputat)" was examined at the
examination session pf the faculty of Tarbiyah of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic
University Jakarta on October 10, 2005. This skripsi has fulfilled the requirement for
the det,>ree of Sarjana (SI) at the English Department.
Jakarta, October I 0, 2005
Examination Committee
The Read of Committee The Secretary of Committee
Examiner I
セ@
Mas'ud Mada, M.A NIP. 150012951
r.HAziz.Fahrurrozi M .. A. NIP. 150 202 343
セMMMMMNNNN@
Praise be to Allah, the lord of the universe, peace and blessing be upon prophet
Muhammad saw.
Alhamdulillah, the writer has finished her skripsi, entitled: "Using Picture in
Teaching Vocabulary". The primary aim of writing this skripsi is to complete a partial
fulfillment ofrequireme\)its for sarjana degree in the Faculty ofTarbiyah
This Skri psi could not be completed without a great deal of help from many
people, especially Drs. Syauki M.Pd, as advisor who always guides and suggest the
writer to make a good skripsi, from the beginner until he end.
Fmihermore, it is pleasant task for her to extend this acknowledgement to:
1. Prof Dr. Dede Rosyada M.A., the Dean of Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher's
Training.
2. Drs. Nasrun Mahmud M.Pd., the Head of English Department, and Drs. Syauki
M.Pd the Secretary of English Depaiiment and her advisor, who had given her
valuable advice to the writer.
3. All Lecturers in English Department, who had given motivation and support
4. The Staff and Officers of Libraries UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, British
Council and Atma Jaya, who had given permission to use their books.
5. Drs. Subarja, The Head of Smart Education Center (S.E.C), and Mrs Lily Kartika
7. Her Boss (Djupri and Family) who had given permission to completed her
Skripsi.
8. The writer does not forget to say thanks to Akim and his family, Nana, Dina, Aam
and her family, Chaira Saidah, Risnawati, Dayat, Novi, Faris, Opunk, Ruslan,
Teguh and all of her wonderful friends of the English Department 2000.
May Allah Bless, Protect and Guided them all, Amin.
Jakarta, June 2005
TABLE OF CONTENT
UST OF TABLES
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION
111
v
«._A. Background of the Study... 1
.A'.: B. L)mitation and Formulation of the Study... 2
C. Statement of the Problem,<... 3
D. Objectives of the Study . . . 3
E. Method of the Study . . . .. 3
F. Hypothesis ... G. Orgapization of the Study. CHAPTER II: THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK /\. PICTURES I. The Meaning of Picture ... . The Types of Picture ... . 4 4 6 7 3. The Use of Pictures... 11
..f. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Pictures 12
13. VOCABULARY
I. The Meaning of Vocabulary ... .
The Types of Vocabulary ... .
3. The Use of Vocabulary ... . 14
16
A. Research Methodology
L The Purpose of 111e Research .. .. .. .. .. .. . .. .. . .. .. .. .. ... 2 l
2. Place and Time of Study .. . .. . .. . .. .. .. .. . .. .. .. .. .. . .. .. .. 21
3. Population and Sample .. .. .. .. . .. . .. . .. . . .. .. . .. . .. .. .. .. .. 21
4. Instrument of Research ... 21
5. Technique of Data Taking ... .' ... 22
6. Technique of Data Analysis ... 23
B. Research Finding I. Description of Data ... 24
2. Analysis ofData ... 27
3. Interpretation of Data ... 28
4. Discussion of Finding ... 29
CHAPTER IV: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion .. _ ... _ .. _ ... _ .. . . .. .. .. 30
t3 Suggestion ... 30
BIBLIOGRAPHY. APPENDIX ···-· ··· 31
Table III: The Comparison ofX and Y... 25
Table IV: The Pre-Test Score of Control Class (Y1) ... 83
Table V: The Post-Test Score of Control Class (Y2) ... 83
Table lV: The Pre-Test Score of Experiment Class (X1)-... 83
[image:8.518.33.445.141.488.2]English as a language for international communication is clearly needed by
many learners to deliver thoughts and interact in a variety of situation, as for foreign
travel, business or other professional reasons in Indonesia. English is one of
international languages, which takes the widest range of usage. English is used in
many fields such as in politics, economics, social and education.
In education field English is a main subject, which must be learnt from
kindergarten up to university level. Generally, English is still considered as a difficult
subject for the Indonesian students because English is completely different from
lndoncs1an language in the systems of strncture, pronunciation and vocabulary.
Vocabulary is one of the important aspects in teaching language, besides
grammar and pronunciation, as stated by Edward in his book "Vocabulary is one
important factor in all language teaching, student must continually be learning words
as they learn structure and as they practice the sound system. " 1
Therefore, the English teachers have to be able to organize teaching learning
activities. They have to give materials by using a suitable technique and master the
sub.1ect matter. A good technique may make students understand and master the
lesson.
1
Edward David Allen and Rebecca M. Vallete, Classroom Technique: Foreign langtmge and
Asking children to memorize words with their meaning is usually ineffective,
sometimes children remember their meaning for a short period of time, and moreover
they forget with the meaning.
To give solution of this problem, the writer gives an alternative technique to
enrich student's vocabulary by using pictures. Because the picture ean direct the
student see and speak about object from elementary school until university, especially
when the students are taught using English as ·medium of instruction and
communication.
Another reason for using picture in teaching vocabulary is that the picture is
effective and helpful in teaching learning process, so the students became easier in
understanding and studying English especially in studying vocabulary, and it may
save valuable classroom time in teaching learning process.
B. Limitation and Formulation of the Study
I. L1111//at ion of the problem
To avoid misunderstanding and to clarify the problem, it is necessary to
make limitation of the problem. The writer will limit the problem in using
picture in teaching vocabulary especially in noun and verb.
2. Formulation <>lthe problem
The formulation of the problem is: "which one is more effective in using
C. Statement of the Problem
The writer conducts the study to reveal whether usmg the pictures has
influence on teaching vocabulary. The problem of statement of the study is
formulated as follows: How effective is teaching vocabulary using pictures?
D. Objectives of the Study
The objectives of the study are, firstly, to encourage the use of pictures in
teaching vocabulary to basic level students, and secondly, to help students
learning vocabulary better with the use of pictures.
E. Method of the Study
The study is based on both library and field research. In library research she
got some information concern with the topic from the books, textbook, magazine,
newspaper. etc.
ln field research the writer collected data by teaching and observing two
classes, experiment class by using picture in teaching vocabulary and control
class without pictures in teaching vocabulary. The research is conducted in an
English Course institution in Ciputat, SEC (Smart Education Center) Ciputat,
F. Hypothesis
!he experiment hypothesis (Ha) is: there is significance difference in teaching
vocabulary before using picture and after using picture for the pre beginner
students of SEC.
The Null Hypothesis (Ho) is: Teacher vocabulary before using picture has no
inlluencc for the pre beginner students of SEC.
G. Organization of the Study
This "Skripsi" consists of four chapters, as follow:
The firsr chapter is introductions, which include background of study,
limitation and formulation or the problem, the statement of problems, the
objective or study. method of the study and the organization of study.
The second chapter is theoretical framework; it discussed about Pictures; the
meaning or pictures, the type of pictures. the use of pictures and the advantages
and disadvantages; Vocabulary: the meaning of vocabulary, the types of
vocabulary and the use of vocabulary; Teaching vocabulary by using picture;
Hypothesis.
!"he third dwpter is research methodology and findings which consists of
research methodology; purpose of the research, place and time of study,
population and sample. instrument of research, technique of data taking,
technique of data analyzing, research finding, description of data, analysis of data,
1. The Meaning of Picture
Pictures are kinds of visual instmction materials might be used more effectively to develop and sustain motivation in producing positive attitudes toward English and to teach or reinforce language-language skill. Some experts gave the explanation of pictures, as follow:
In Webster New World dictionary of American English, it can be seen that: ''Pictures is an image or likeliness of an object, person, or scene procedure on a flat surface, especially by paining, drawing or photography."2
Vernon S. Gerlacha stated:
'"Pictures are a two dimension visual representation of person, places, or things. Photo1,>raph prints are most common, but sketches, cartoons, murals, cut outs, charts, graphs, and maps are widely used ... " "A Picture may not only be worth a thousand words it may also be worth a thousand years or a thousand miles. Through pictures, learner can see people, places, and things from areas for out side their own picture can also represent images from ancient times or portray the future." 3
Andrew Wright pointed out that pictures are the most suitable for the revision of known language and for recombination or manipulation word, the picture or
2
Noah Webster, Webster New Word Dicliouary «f American English (Prentice
Hall. I 994).p. I 022
1
Vernon S.Berlach and Donald P. Elly, Teaching and Media a ,\:Vstematic Approach, 2nd (New
word acting as a cue for substitution the size and shape of the pictures are
excellent for speedy and stimulating words.4
The kinds ru1d nw11bers of pictures that the teacher should take with him to
carry out the activities in class can be taken from magazines, articles or others and
should be attractive and interesting to capture the students' attention. The purpose
of using pictures for the students is to give them an opportunity to practice the
language in real context or in situations in which they can use it to communicate
their ideas.
Picture is the non-verbal sources infonnation. The non-verbal helps us to
predict what the next might be about, and this ability to predict helps us to
recognize meaning more quickly that if we had to sort it out solely from what we
hear and read. Picture can represent these non-verbal sources of infonnation.
Indeed, they and what they represent are centrally bound up with the nature of
communication itself What we see affects how we interpret what we hear and
vice versa. 5
2. The Type of Pictures
There are two kinds of pictures that Grazyna Szyke finds especially useful
as teaching aids, they are:
a. Pictures of individual persons and objects.
1
Andrew Wright, Visual Material for language Teacher, Longman Group Ltd, 1983, p.73.
5
Andrew Wright, Picturesjor language Leaming, (New York: Cambridge University press,
Pictures of individual persons or thing may be used, mainly at the
elementary level, to introduce or test vocabulary items, for example: a man,
and a car. Portraits, pictures showing people in close detail, are useful for
intermediate and advance learners. The students can be asked question about
the age and profession of the model.
b. Pictures of situations in which persons and object are "in action".
Situation pictures that show or suggest relationships between objects and
or people can be perfect teaching aids for introducing, practicing, or reviewing
. l 6
grammatlca structures.
According to Betty Morgan Bowen, there are some types of pictures as
their shapes:
a. 'Wall Charts
h. \Vall Pictures
Wall Pictures is simply a large illustration of scene or event a set of scenes
or events. It is usually to be used with the whole class.
e. Sequence Picture
Sequence Picture is a series of pictures of a single subject. Its function is
to tell a story or a sequence of events.
· ·
-(, Cirazna Szyke, "(}sing l'icture as Teaching Aids", (English Teaching Foru1n,
Vol.XfX, No.4,0ctober, 1981)
d. Flash Cards
•!• Word flashcard, card with printed words on it can help up rapidly; the cards can be used to demonstrate exactly what the teacher wishes. •!• Picture flashcard, useful for the representation of a single concept,
such as an object or an action.
e. ·work cards
Include visual as well as text magazme pictures, drawing, maps and diagrams can be important part or work card at aJJ levels, used for variety of purposes.7
Meanwhile, Noor azlina Yunus in his book grouped the pictures into four groups:
a. Composite Pictures
These are large single pictures, which show a scene (Hospital, beach, canteen, railway station, street) in which number of people can be seen doing things. They enable students to see places, people and events that they would otherwise not see because of factors like distance, time and cost. Because of their size, composite picture are most appropriate for whole-class teaching rather than individualized learning or group work.8
7
Betty Morgan Bowen. Look Here!, Visual Aids r11 La11g11age Teaching, London: Essential
language teaching series, 1973, p. 13-31
'Noor Azlina Yu nus, Prepari//g and U>i//g Aids for English Language Teaching, (Kuala
b. A picture se1·ies
A picture series is a number of related composite pictures linked to fonn a
series or sequences. Hence, its main function is to tell a story or sequence of events.
A wide variety of picture series is available in textbooks, in comics and in cartoon
slri ps in magazines for the teacher to copy and enlarge. However the observant
teacher can find such series in other sources, for example calendars and wrapping
paper.
c. Individual pictures
These are single pictures of objects, person or activities. Such pictures ve1y in
size from small newspaper pictures and full-page magazine pictures to poster-sized
pictures, and can be mounted singly. There is an enormous variety of material
available from newspaper, magazines, catalogues, greeting cards, trail brochures,
advertisements, old textbooks and even \\'Tapping paper. 9
d. Specialized pictures (posters, charts, advertisements, brochures)
Wall posters arc not designed specifically for teaching, but rather for
advertising or propaganda purposes. Although they provide very little textual
information, they cannot be dismissed from the ESL class- room as they can be
used to i II ustrate topics and provide motivation for discussion.
9
3. The Use of Pictures
There are five roles of picture:
a. Pictures can motivate the students and make him or her want to pay attention and want to take part.
b. Pictures contribute to the context in which the language is being used. They bring the world into the classroom.
c. The pictures can be described an objective way or interpreted or responded to subjectively.
d. Pictures can cue responses to questions or cue substitutions though control practice.
e. Pictures can stimulate and provide information to be referred to in conversation, discussion and storytelling.
Beside those five roles in using picture, there are six reasons why pictures helpful in teaching learning process.
There are six reasons why using pictorial material:
a. Pictures are very useful for presenting new £,>rammatical and vocabulary items. They help to provide the situations and contexts which light up the meaning of words or utterances and, indirectly help the teacher to avoid resorting to
b. Pictorial material allows for meaningful practice of vocabulary and structures
presented by the teacher. Rather than have students repeat words or utterances
whose meaning may be unknown, the teacher can use cues or prompts.
c. Pictorial material can also provide a stimulus for using the language at the
reproduction and manipulation stages-to speak, to read and to write.
d. Pict"Ures can be used for revision from one lesson to another as well as for
long-tenn revision of vocabulary and structures.
e. Pictorial material can be used to supplement whatever textbook the teacher is
using or whatever course he is following. Pictures, of course can be used to
provide more practice of the exercises that students have done using the textbook.
f. Pictorial material is easy to collect, to make and to transport.
In an article, Edmundo J. Morn stated that the pictures could be used to give
students of English as a foreign language an opportunity to practice the language in
real context or in situations in which they can use it to communicate their ideas. 10
4. The Advantages and Disadvantages of using Pictures
a. The Advantages of using pictures
Following are some opinions concerning with the advantages of usmg
pictures.
According to Vernon S. Gerlach:
"'Edmundo J. Mora, "Using Pictures Creatively", English Teaching Fomm, vol. XXVI, No.4,
I ) They are inexpensive and widely available.
2) They provide common experiences for an entire group.
3) The visual detail makes it possible to study subjects, which would otherwise
be impossible.
4) They can help to prevent and correct misconceptions.
5) They offer a stimulus to further study, reading and research. Visual evidence
1s a power tool.
6) They help to focus attention and to develop critical judgment.
7) They are easily manipulated.11
Accurdmg ro A . .!. Romis::owski:
l) It is convenient to use the real thing
2) ;\ model or chart can better explain the principle being thought.
3) The real thing can not be seen any way
4) Requirement no equipment for use.12
b. The Disadvantages of using Pictures
Vernon S. Gerlach said:
I l Sizes and distances are often distorted
2) Lack of color in some pictures limits proper interpretations
3) Students do not always know how to read pictures13
-·---
-" Vernon S. Gerlach and Donald P. Elly, Op. Cit. p. 277
12
AJ. rッQQQゥウコッキウォゥセ@ 771e selection and use ofi11str11ctio11a/ Media: for hnproved classroom
Although the pictures have the disadvantages but from the statement
above, it can be concluded that there are many advantages, which can be taken
from the use of pictures in composing, they are:
,.. Represent things which are not available
;,. Motivate and stimulate the students
,- More Practice (can be used everywhere and anytime)
,.. Help both the students and the teachers in teaching-learning process, etc.
B.
VOCABULARY
I. The Meaning of Vocabulary
In this chapter the writer wants. to prepare vocabulary meaning because to
understand a language the learners must understand vocabulary first. It is difficult
to make one definition of vocabulary. So, the writer tries to take it from some
differences.
There are some experts who give definition of vocabulary. Hatch and Brown
define vocabulary as a list or set of words for a particular language or a list or set
of words that individual speakers oflanguage might use. 14
While according to Harimurti Kridalaksana, vocabulary is "Komponen
bahasa yang memuat semua informasi tentang makna dan pemakaian )cata dalam
I
"Vernon S. Gerlach and Donald P. Elly, Loe. cit
14
Evelyn Hatch and Cheryl Brown. Vocahulwy, Semantics and Language Education,
bahasa."1\Vocabulary is a component of language that maintains all infom1ation
about meaning and using words in a language.)
Webster Dictionary noted that, vocabulary is: "a list or collection of words
usually alphabetically arranged and explained or lexicon, stock of words used in
language or by class, individual, etc."16
According to Webster's ninth collegiate Dictionary, Vocabulary is:
1. A list of word and often phrases, abbreviation inflectional fonn, etc. Usually
arranged in alphabetical order and defined or otherwise identified as in a
dictionary of glossary.
An interrelated group of non-verbal symbols, signs, gestures, etc. used for
communication or expression in a particular art, skill, etc.17
The words that students know depend upon their experience. We hope that
our students know not only the meaning of words, but also know they are using
its in sentence. The vocabulary meant here, the English words as stated in the
secondary school curriculum of the elementary school.
"Zainuri, A.M. Vocabulary l UlN Jakarta, 2003,p. I
16
\Vebster's, 77u.! Largest Abridg111ent of}Vehster 's New Inter11ational dictiona1y of En.s;lish
l.a11g11age. Webster's Collage Dictionary. USA: G & G Merriam co, 1935, p. 1073.
17 z。ゥョオイゥセ@ Q|Nmセ@
2. The Types of Vocabulary
Vocabulary is frequently divided into four types; listening, reading,
writing and speaking.
That is possible for people to understand words they hear, and yet not use the
words themselves in speaking and writing. It is also possible that a word can be
read and understood, and yet not handled easily when heard in a listening, and at
the same time, contain dit1erent words that are understood or used frequently by
individuals. There is also a fifth vocabulary that we might consider-our
·'understanding" vocabulary. We know certain words well enough that we can
respond to them. We may, however, need to see or hear them in context, or need
someone to say something that helps us record the word meaning. 18
Fries say Vocabulary is of two, namely;function and content wordv.
!he timction words are a closed class, we cannot add to the preposition or
·auxiliaries or modals or any structure words of the language (with, for, May, will,
etc). 7/1e content word,, on the other hand, can be added to at any times as new scientific advances make new words and communication about new inventions
necessary (Pen, school, go, pretty, etc).
The content words can be divided into three general classes:
a) Words naming things, ideas, entitles, that we might call them nouns
b) Words naming actions called verbs
"Carol J fisher, Jerry, Childrm 's Language and the language Art. USA : Alemary Press, l977.
c) Words used to describe the qualities of those things or action called adjectives
and adverbs 19
John Haycraft distinguishes vocabulary into active and passive vocabulary.
a. Active vocabulary-words that the students understand can pronounce correctly
and used constructively in speaking and writing.
b. Passive vocabulary-words that the students recognizes and understand when
they occur in a context, but which cannot produce correctly him self2°
3. The Use of Vocabulary
Yocab1t!ary is important because it helps the students enjoy their classes. One
who masters enough vocabulary will find fewer difficulties than those who have
fewer vocabularies. When they read a certain text, they will easily get the
information from it since they can understand every word in the texi. On the other
hand, those who lack of vocabulary will face a lot of problems. Mastery of
vocabulary will be useful for the process of achieving language-teaching
objectives that is the mastery of language skills (reading, listening, speaking, and
writing).
If we want to communicate with other in certain language we must master the
language they belong to especially to know enough vocabulary of those
languages. Yang Zhihong who says that words are the basic unit oflanguage form
1
"z· . .
M 0 . ?セ。ゥョオョL@ A. . p c1t_,p ....
10
John Haycrat1, J111rod11ctio11 lo Ji)1g/ish liu1guage Teaching, (Harlow: Long1nan Group
supports it. Without vocabulary, one cannot communicate effectively or express
idea. He also states that having a limited vocabulary is also a barrier.21
Furthermore, Long and Richards explains that vocabulary like grammar is an
essential component of all uses oflanguage.22
C. TEACHING VOCABULARY BY USING PICTURE
Pictures for vocabulary teaching come from many sources. Jn addition to
those drawn by the students (or by the teacher) there are attractive sets, which are
intended for schools. Picture which have been cut out of magazines and newspapers
are also useful: many inexpensive books for children have attractive picture, which
show meaning of basic words.
Often a picture will show a situation or a scene in which there are several
different thing and persons. It is good for students to see the total scene or picture to
see how its parts are related to the whole. ft is also helpful (especially for beginner in
English) to see a picture of a single object or person as the only focus of attention.
Suppose, for example, we have a picture of each of the following: a church, a
taxi. a bus, a traffic light, a policeman, and a mailbox. Suppose each of the pictures is
large enough to be seen by all in the class. The students have seen and heard the
English word for each one, and have copied the word into their notebooks. Our aim
now is to help the students master the vocabulary, so we want to encourage the use of
21
Yang Zhihong. "Leaming Words" English Teaching Fonun,vol.38, no. J July,2000
22
Michael H. Long and Jack C. Richards, Methodology in 1ESOL: a Book of Readings, (New
each word for commw1ication. We consider possible techniques for making students feel it is important to know the English word. Here is one way:
l. The teacher arranges the pictures aJong ledge of the black board, saymg something like this: "We'll put the taxi here. That's the first picture. Then the bus ... then the traffic light ... then the clmrch ... then the policemen ... then the mailbox."
2. The teacher asks a member of the class (We'll call her Lia) to came to the blackboard.
TEACHER: Lia is going to move one of the pictures for us. We are going to tell her
which picture to move. Lia, please move the policeman. Put the policeman first (Lia moves the picture
(1.
1he policeman, placing it first in the row on the !edge ofthe blackboard).TEACHER: Put the taxi first. (Lia does so.)
3. The teacher indicates that vari0t1s members of the class should request Lia to make other changes in the order of the pictures using English, of course. For example:
A STUDENT: Move the church. Put the church first. (Lill does so.)
A STUDENT: Move the mailbox, etc
If the class has began to learn the ordinal numerals (first, second, third, etc) these may be reviewed in connection with this activity. After each rearrangement of the pictures. the teacher (and then various students) says: "Now the _is first; the
In the activity, which has just been described, students use English words while talking about changes in location of pictures and changes in relationships. To make such changes quickly and easily, we need pictures that can be moved and rearranged w(J:hout taking time to pin them or tape them to the wall.23
23
l. The Purpose of The Research
The purpose of this research is to find out whether there is a significance a
difference of using picture in teaching vocabulary or not.
2. Place and Time of Stndy
The research was held at SEC (Smart Education Center), which located on
Villa Mutiara Jombang, Ciputat. The field research was done from May 12Ll' until
June l 0'11
J. Populations and Sample
The population of the study consists of 20 students from pre beginner students
of Smart Education Center (S.E.C) from two classes. The sample was taken by
random sampling system where 10 students from experiment (Picture) class and
10 students are from control (drill) class.
Sampling is done in random in order to get representative data and make it
easy to calculate. In this research the writer presented a lesson using picture and
drill. And also she gave the explanation of doing test.
The instrument in this research was the final test. The material of test was
taken from the flash card, which taught in the class, like names of animals, tools
of school, occupation, and transportation. This test made by the English teacher.
This instrument was given only to experiment class during teaching learning
process.
5. Techn.ique of Data Taking
The techniques of data taking in this research are:
a. Observation
The observation in Smart Education Center (S.E.C), which is located on
JI Kccubung IV No.65, Sawah barn, Ciputat - Tangerang to research the
students of pre basic, the English teacher, the English teaching - learning
process in the classroom.
b. Ex1leriment
The experiment is conducted by dividing the students into two classes:
an experiment class and a control class. In the experiment class, writer teaches
students some vocabularies through the use of pictures. The material is for
c. Evaluation
The writer gives vocabulary test to the students then they have
answered the question. The test was held at first research (pre test) and at the
end of the research (post test) in each meeting.
6. Technique of Data Analysis
Data analysis is the last step in the procedure of experiment, in this case,
processing the data. Data processing is the step to know the result of both the
experiment class and control class also their difference.
To find out the differences of students' score in using picture technique in
teaching English vocabulary will be compared to the students; that using drill
technique in teaching English vocabulary the writer using T - test.
Before using T-test formula, the writer has to seek the differences of mean
variables by using formula as followed:
M1 =
>
and Mi=I
Ni Nz
And after getting mean variables, the writer has to seek the standard of
deviation of variable and standard error mean of variables by using formula as
followed:
セ。ョ、@
2. SEM1 =
セ@
N-1
and
The next step is seeking the standard error mean differences of variables by
using formula as followed:
SE,11 Ml= セsemQ R KseセQR R@
. Then the last is determining T - test by using formula:
To
-Ml-M2
B. Research Finding
l. Description of Data
As mentioned in this chapter, the writer conducted both library research and
field research. The \VTiter did field research by teaching two classes; Experiment
class (By using Picture technique) and control class (By drill technique). The
research of both methods was done four times for each method respectively. And
the writer got the data from pre-test and post-test. The pre-test was given before
the lesson began and the post-test was given at the end of the teaching.
There are fifteen items in the pre-test; the instrument of this research consists
oftwo types;
a. Multiple choice, there are ten items and each item scored 5, so the total of this
b_ Matching, there are five items and each items scored I 0, so the total of this
type is 50_
And there are twenty items for post-test; this research consists of three types;
a_ Multiple choice, there are ten items and each item scored 5, so the total of this
type is 50_
b_ Matching there are five items and each items scored 5, so the total of this type
is 25_
c_ Completion, there are five items and each items scored 5, so the total of this
type is 25_
Having finished the field research by using picture in teaching vocabulary and
without using picture in teaching vocabulary the writer obtained the score as
follows:
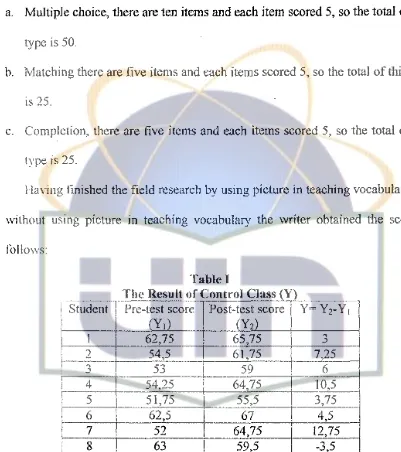
Table I
i
-Studentセヲィ・@ Result of Control Class (Y)
Pre-test score Post-test score Y=Y2-Y1
i
(Y1) (Yz)!
1 62,75 65,75 ' __,' 2 54,5 61,75 7,25
'
! 3 53 59 6
' 4 54,25 64,75 10,5
!
I
5 51,75 55,5 3,75
I
' 6 62,5 67 4,5
f
7I
52 64,75 12,758 ' 63
I
59,5 -3,5I
I
9 67 68 l
I
[image:33.521.46.447.114.566.2]Student
l
I 2
I
3 4l-
5 6I
nt \ ·---lI
I
··--r
.-AL
M1=94 75 JOM1 = 9,475
I
I 7 8 9 10x
12,5 17 16,5 6,75 2,75 7 7 l3 6,5 5,75D<=
94,75 Table IIThe Result of Experiment Class (X) Pre-test score Post-test score
(X1l (X2l
63,75 76,25
50,5 67,5
54,5 71
64,75 71,5
73,75 76,5
68,25 75,25
64,5 71,5
59,75 72,75
69 75,5
63,5 69,25
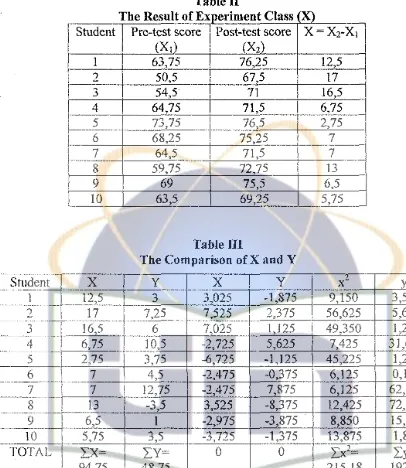
Table III
The Comparison of X and Y
y 3 7,25 6 I 0,5 3,75 4,5 12,75 -3,5 l 3,5
'LY=
48,75M'.ll. =48 75
lO
M2 =4,875
x
y3,025 -l,875
7,525 2,375
7,025 1,125
-2, 725 5,625
-6,725 -1,125
-2,475 -0,375
-2,475 7,875
3,525 -8,375
-2,975 -3,875
-3,725 -1,375
0 0
[image:34.521.37.443.37.505.2]2. Analysis of Data
In analyzing of the data the writer uses the comparative technique. The
comparative technique is analysis technique to evaluate hypothesis concemmg
differences between two variables that examined statistically.
Jn the comparative technique, 1J1e •;ariables are compared to know whether
di llcrenccs are very significant or they arc only happened by chance. The writer uses
T-tcst to find out the differences score of using picture in teaching vocabulary and
without picture in teaching vocabulary. The formula ofT-test is:
)· a. - Determining mean I with fomrnla:
:-x
= 94.75 = 9.475---'"'---
-N lO
b. Detennining mean II with formula:
セ@ 00 48.75 = 4.875
N 10
c. Determining of standard of deviation of variable I:
SDJ=
セ@ セ@
=
セ@ R[セᄋQX@
=Fl =
4.6d. Determining of standard of deviation of variable II
SDI=
セ@
=
セ@
192.53=
セ@
1_'.?.2--5=
4.3N !O
e. Determining of standard error mean of variable I:
SEM1
=
セ@
SD1=
セ@
4.6=
セ@
4.6=
"105l
=
0.71Ni-1 10-l 9
nm
SEM2=\j Bセ@
N1-l
セ@
4.3 =セ@
94.3 = ""0.47 = 0.69 10- I2. Determining of standard Error Mean difference of Ml and M2:
sEM1-M2
=JsEM/+sEM/
]jPNWQKPNVY]セ]QNQX@
3. Determining t0 with formula:
To= Ml -M2 = 9.475 - 4.875 = 4.6 = 3.89
SEML SEM2 1.18 1.18
4. Detennining t - table in significance level 5 % and 1 % with df:
The writer gained t - table:
At the degree of significance of 5 % = 2.10
At the degree of significance of l % = 2.90
The comparison between T - score with T - table:
5 % to : tt = 3. 89 > 2. l 0
I % ·-·to : tt = 3.89 > 2.90
So we can conclude that t - score is higher than t - table
3. Interpretation of Data
Based on the data collected from the test gained from the experiment class,
scores oftest in the experiment class was 9.475 while the mean scores oftest in the '
control class was 4.875.
From the explanation above the analysis of the result on the table above, we
can see that the using picture in teaching vocabulary is adequately success. It can be
seen on the table above that the students who receive picture in learning vocabulary
get higher score than the students who do not. It means that the influence of using
picture in teaching vocabulary in experiment class is bigger than teaching vocabulary
using drill in control class. It can conclude that picture have influence in teaching
vocabulary for the primary school students as (Basic class) in Smart Education Center
(S.EC).
4. Discussion of Finding
Based on the research finding, why there is significance influence between
using picture in teachmg vocabuJary and without it, perhaps there are some reasons to
discuss.
I. Using picture in teaching - learning process make student interested more m
learning vocabulary.
2. By using picture the students are faster and easier in memorizing vocabuJary
Based on data found in the previous chapter, it can be concluded that the use
of picture has significant influence in teaching English vocabulary. As can be seen
from the average score of test of the pre-basic class is (3.89)24 in using picture in
teaching vocabulary
From the result of the analysis, it is generally accepted that using picture is a
good technique and method in teaching vocabulary.
B. · Suggestion
In relation to the writer's conclusion, she suggests:
I. In teaching learning process, teachers are expected to process many ways and
methods in their teaching. Those ways and method function to make the class
alive. Especially in learning vocabulary that often make the students bored.
One of the ways and methods to make class alive is using picture.
Using picture in teaching vocabulary especially and in teaching English
generally is more effective and useful than without using picture. Therefore,
the writer suggests the English teacher to use media in their teaching.
2
Allen French Virginia, Technique in Teaching Vocabulary, Oxford University press
Berlach Vernon S. and Elly Donald P., Teaching and Media a Systematic Approach,
2'"
1 (New Jersey: Prentice Hall), 1980Bowen Betty Morgan., Look Here! , Visual Aitf.1· in Language Teaching, London:
Essential language teaching series, 1973
Fisher Carol .!, Jerry., Children's Language and The Language Art. USA: Almery
press, 1977
Hatch Evelyn and Brown Cheryl., Vocabulwy, Semantic and Language Education,
(Cambridge: Cambridge University press, 1995)
Haycraf John., Introduction to English Language Teaching, (Harlow: Longman
Group Limited, 1978)
Long Michel H. and Richards Jack C., Methodology in TESOL: A Book <>(Readings,
(New York: Newbury House Publisher, 1987)
Mora Edmundo J., Using Pictures Creatively, English Teaching Forum, vol. XXVI, no.4 October, 1988
Romiszowski.AJ., The Selection and Use of Instruction Aiedia: For Improved
( 'fassroom Teaching and Interactive, lndividuali::ed Instruction, London: Kogan page, 1988
Szyke Grazna., Using Picture as Teaching Aids, (English Teaching Forum, Vol. XIX,
no.4, October, 1981)
Webster Noah.,. Webster New word Dictionmy of American English (prentice Hall,
1994)
Wright Andrew, Pictures For l,anguage [,earning, (New York: Cambridge
University press, 1994)
Yunus Noor Azlina,. Preparing and [/.ving Aidv for English Language Teaching,
(Kuala Lumpur: Oxford University press, 1981)
Zainuri, A.M. Vocabulary I, UIN Jakarta, 2003
Nama Lembaga Level
Mata Pelajaran Terna
Waktu
RENCANA PEMBELAJARAN I
: Smart Education Center (S.E.C) : Pre Besic (Experiment Class) : Bahasa Inggris
: Animal : 90Menit
A Tujuan Pembelajaran Umum (TPU)
Siswa dapat menguasai kosakata dengan menggunakan kata yang tersedia.
B. Tujuan Pembelajaran Khusus (TPK)
l. Siswa dapat menyebutkan nama-nama hewan dengan bahasa [nggris secara lisan.
2. Siswa dapat menjawab pertanyaan guru tentimg nama-nama hewan dengan menggunakan bahasa Inggris dengan lisan.
3. Siswa dapat menyusun kata-kata baru.
4. Siswa dapat mencocokkan kata-kata dengan gambar.
5. Siswa dapat mengucapkan kata-kata yang diucapkan oleh guru.
C. Materi Pembelajaran (Terlampir)
D. Buku Panduan
Y.Cerstari,Bermain sambil belajar Bahasa Jnggris,Grasindo.1955 Smart Education center,English Class Book for Beginner level
E. Media Pembelajaran
Word flashcard and Picture flashcard (Terlampir)
·F. Kegiatan Pembelajaran
1. Pendahuluan (25')
>
Guru memberi salam dan bertegur sapa.,. Guru mengabsen kehadiran siswa.
Y Guru mengarahkan siswa pada topic yang akan dibahas dengan mengajukan
beberapa pertanyaan.
:r
Guru memberikan kertas Jatihan soal tentang materi yang akan di bahas.dan siswamengerjakannya dengan batas waktu 15 menit. (pre test) ,. Guru menjelaskan tujuan pembelajaran,
>
Guru menjelaskan kepada siswa kegiatan yang akan meraka lakukan: menghapal,mengerjakan latihan.
2. Peny4jian ( 60 ')
• Guru memperkenalkan nama-nama hewan dengan menggunakan kartu yang
• Guru memberikan pertanyaan yang berhubungan dcngan gambar yang ada di kartu
• Guru memberikan flashcard kepada siswa, masing-masing 2 11ashcard,dan siswa di haruskan menghapalkan kata-kata yang ada dalam flashcard tersebut.
• Guru mengambil flashcard yang telah diberikan pada siswa setclah 5 menit ditangan mereka.
• Guru menanyakan pada masing-masing siswa tentang nama-nama hewan apa saja yang ada pada flashcard yang ada pada tangan mereka.
• Guru membagikan kembali flashcard kepada siswa dengan gambar yang berbeda, dan siswa di haruskan menghapalkan kembali flashcard yang memiliki kata-kata yang berbcda, dan seterusnya sampai semua siswa mendapalkan semua flash card. • Guru memberikan pertanyaan kepada siswa secarn kescluruhan tentang
nama-nama hewan dalam bahasa lnggris .. Dan siswa di hitruskan menjawab secara serempak.
• Guru rnemberikan kesempatan untuk bertanya kepada siswa.
• Guru mcrnbcrikun soal-soal dalam kertas Jatihan yang berhubungan dcngan matcri (animal) kcpada siswa experiment class. (post test)
0 Guru rnengumpulkan pekerjaan sisv.la.
3. /'cnutup (5 ')
o GCirn mcnanyakan pada mercka apa yang sudah mcrcka dapal dari apa yang tclah mereka pelajari.
o Guru mengakhiri pelajaran, dengan penutup salam
G. \Vaktu
Pendahuluan Penyajian Penutup
: 25 l\'[ enit : 60 Menit
: 5 Menit
90 Menit
Mengetahui
Jakaita, J uni 2005
Penulis
Kelinci
i
I
ᄋセ@
·1I
'
'Three
' I
I
Seven.!
9
Nine'
t
i
!
I (\
·\
.. '._:·1 ' .
'
.
i
Four:!
. -·" ,_ . , .. ' ... , ___ ;_.'):,
-: .. .
·'"
',_. ,.;
j
Ii
El2ven 1
J
1
i '1
l
.I IFour)
::. _; ...• セHi@!
I [I
Kucingi
I
. I
l
\ I \Four)
.. !.
! I
8
Twelve
!2
··---...
'i
I
I
i
Eight!
12
Na1nc:
I. Choose the right answer of the following question by crossing A, B, C or D
1. It eats carrot, what is it.. ... .
a. Penguin b. Rabbit c. Horse d. Tiger
2. It lives in desert ... . a. Camel
c. Horse
b. Cat
d.Monkey
3. My ... like to eats fish
a. Elephant b. Snake c. Monkey d. Cat
4. It is very dangerous and has poison ... . a. Snake
c. Lion
b. Monkey d. Camel
5. lt is the king of the jungle ... .
a. Tiger c.Snake
b. Giraffe
d. Lion
6. The bird that can deliverletter.. .. a. Penguin
c. Rabbit
b. Pigeon d. Cat
8. The long neck animal is ... . a. Tiger
c. Cnnd
b. Cat d. giraffe
9.'Thc long nose animal is ... .
a. Elephant b. Swan c. Dog d. Octopus
J 0. The animal which lives in north pole ... .
a. I:aglc
c. Turke\·
b. Swan d. Penguin
j\
IL Match the left side of the following words into right side \ZZNZM\[MZZセLL@
!. T;gcc ( ) A. , ,
2. Crocodrle (
j
(jf
ャ|セNセセセ@
;j
|セᄋQ[|Iセセ@
4 I , \':.\ 1,\
B &.·
ZセセwLNjZゥG@
.
1. V'if\
v3. Giraffe ( )
」セLLセ@
4. Elephant ( )
4 . . . ' .
ッNセTェセ@
Name:
PRE BASIC LEVEL
I. Choose the right answer of the following questi. - 'crossing A, B, C or D
l.
c. Horse ·
c. Snake d. Monkey·
3. It always makes a sound "Meow"? a. Elephant b. Snake
c. Monkey d. Cat
4. What is the animal which likes to eat banana? a. Snake
c. Lion
b.Monkey
d. Camel 5. My ... Born three little puppies
c. Snake
b. Dog
d. Lion
6. An ... has a big body, big ears and long nose . a. Elephant b. Pigeon
c. Rabbit d. Cat
7. The bird has long leg and we usually see it at the beach? a. Monkey
c. Giraffe
b. Elephant
d. Pinguin
8. This 11nilmil hus long neck imd moat lives in Arabic? a. Tiger
c. Camel
b. Cat
d. giraffe
9. lt is a wild animal and likes to hunt another animal? a. Elephant b. Lion
10. A ... can help people to send the letter
a. Eagle
c. Turkey
b. Swan
d. Penguin
IT. Match the left side of the following words into right side
1. Cat
(
)
2. Crocodile ( )
3. rfiger ( )
4. Monkey ( )
5. Eagle
(
)
Ill. Arrange the letters to be right words!
l.G··l-R-E-T (Harimau):
2. T - A - B - l - R -B (Kelinci):
3. H-E-R-0-S(Kuda):
4. K-E-M-0-N-Y (Monyet):
5.G-A-L-E-E (Elang):
;·?
c(f
セセL@
a_) セ@•.i!....//
Nama Lembaga Level
Mata Pelajaran Tema
Waktu
RENCANA PEMBELAJARAN II
: Smart Education Center (S.E.C) : Pre Besic (Control Class) : Bahasa lnggris
: Animal : 90Menit
A Tujuan Pembelajaran Umum (TPU)
Siswa dapat menguasai kosakata dengan menggunakan kata yang tersedia.
B. Tujuan Pembelajara11 Khusus (TPK)
1. Siswa dapat menyebutkan nama-nama hewan dengan bahasa Inggris secara lisan. 2. Siswa dapat menjawab pertanyaan guru tentang nama-nama hewan dengan
menggunakan bahasa Inggris dengan lisan. 3. Siswa dapat menyusun kata-kata baru.
4. Siswa dapat mencocokkan kata-kata dengan gambar.
5. Siswa dapat mengucapkan kata-kata yang di ucapkan oleh guru.
C. Materi Pembelajaran (Terlampir)
D. Buku Panduan
E. Media Pembelajaran Papan Tulis dan spidol
F. Kcgiatan Pembelajaran
I. P endahuluan (25 ')
,.. Guru memberi salam dan bertegur sapa.
r Guru mengabsen kehadiran siswa.
,- Guru mengarahkan siswa pada topic yang akan dibahas dengan mengajukan beberapa pertanyaan.
r Guru memberikan kertas latihan soal tentang materi yang akan di bahas.dan siswa
mengerjakannya dengan batas waktu 15 menit. (pre test) ).;.- Guru menjelaskan tujuan pembelajaran.
;;. Guru menjelaskan kepada siswa kegiatan yang akan meraka lakukan: mengbapal, mengerjakan latihan.
2. Penyajian ( 60 ')
• Guru memperkenalkan nama-nama hewan dalam bahasa Inggris dengan
menulisnya di papan tulis.
• Guru mengajarkan bagaimana pengucapan nama-nama hewan dalam bahasa
PRE BASIC LEVEL
Name:
I choose the right answer of the following question by crossing A, B, C or D
1. lt eats carrot, what is it. ... (Kelinci)
a. Penguin b. Rabbit c. Horse d. Tiger
2. It lives in desert ... (Unta)
a. Camel b. Cat c. Horse d. Monkey
3. My ... like to eats fish (Kucing)
a. Elephant b. Snake c. Monkey d. Cat
4. It is very dangerous and has poison ... (Ular)
a. Snake b. Monkey c. Lion d. Camel
5. It is the king of the jungle ... (Singa)
a. Tiger b. Giraffe c. Snake d. Lion
6. The bird that can deliver letter. .... (Merpati)
a. Penguin b. Pigeon c. Rabbit d. Cat
7. The animal that likes to eat banana ... (Monyet)
a. Monkey b. Elephant c. Giraffe d. Horse
8. The long neck animal is ... (Jerapah)
. a. Tiger b. Cat c. Camel d. giraffe
9. The long nose animal is ... (Gajah)
a. Elephant b. Swan c. Dog d. Octopus
I 0. The animal which lives in north pole ... (Pinguin)
a. Eagle b. Swan c. Turkey d. Penguin
II. Match the left side of the following words into right side
l. Tiger ( ) A. Uhur-ubur
2. Crocodile ( ) B. Jerapah
3. Giraffe ( ) C. Harimau
4. Elephant ( ) D.Buaya
Name:
PRE BASIC LEVEL
I Choose the right answer of the following question by crossing A, B, C or D
1. What is the animal which has a Jong ear? (Kelinci)
a. Penguin Q. Rabbit c. Horse d. Tiger
2. What is the animal which has along body? (U1ar)
a. Camel b. Cat c.Snake d. Monkey
3. It always makes a sound "Meow"? (Kucing)
a. Elephant b. Snake c. Monkey d. Cat
4. What is the animal which likes to eat banana?
a. Snake b. Monkey c. Lion d. Camel
5. My ... Born three little puppies (Anjing)
a. Tiger b.Dog c. Snake d. Lion
6. An ... has a big body, big ears and long nose (gajah)
a. Elephant b. Pigeon c. Rabbit d. Cat
7. The bird has long leg and we usually see it at the beach?
a. Monkey b. Elephant c. Giraffe d. Pinguin
8. This animal has long neck and most lives in Arabic? (unta)
a. Tiger b. Cat c. Camel d. giraffe
9. It is a wild animal and likes to hunt another animal? (Singa)
a. Elephant b. Lion c. Dog d. Octopus
10. A ... can help people to send the letter
a. Eagle b. Swan c. Turkey
(Merpati)
d. Penguin
II. Match the left side of the following words into right side
1. Cat ( ) A. Monyet
2. Crocodile ( ) B. Harimau
3. Tiger ( ) C. Kucing
4.Monkey ( ) D. Buaya
5. Eagle ( ) E. Elang
Nama Lembaga Level Mata Pelajamn Terna Waktu
RENCANAPEMBELAJARANIIl
: Smart Education Center (S.E.C) : Pre Besic (Experiment Class) : Bahasa Inggris
: Tools of school : 90 Menit
A Tujuan Pembelajaran Umum (TPU)
Siswa dapat menguasai kosakata dengan menggunakan kata yang tersedia.
B. Tujuan Pembelajaran Khusus (TPK)
I. Siswa dapat menyebutkan aama-nama buah dengan bahasa Iaggris secara lisan.
2. Siswa dapat menjawab pertanyaan guru tentang nama-nama buah dengan menggunakan bahasa Inggris dengan lisan.
3. Siswa dapat menyusun kata-kata.
4. Siswa dapat mencocokkan kata-kata dengan gambar.
5. Siswa dapat mengucapkan kata-kata yang diucapkan oleh guru.
C. Materi Pembelajaran (Terlampir)
D. Buku Panduan
E. Media Pembelajaran
Word flashcard and Picture flashcard (Terlampir)
F. Kegiatan Pembelajaran
1. Pe11dah11lua11 (25 ')
r Guru memberi salam dan bertegur sapa.
r Guru mengabsen kehadiran siswa.
r Guru mengarahkan siswa pada topic yang akan dibahas dengan mengajukan
beberapa pertanyaan.
r Guru memberikan kertas latihan soal tentang materi yang akan di bahas.dan siswa
mengerjakannya dengan batas waktu .l5 menit. (pre test)
r Guru menjelaskan tujuan pembelajaran.
r Guru menjelaskan kepada siswa kegiatan yang akan meraka lakukan: menghapal,
ュ・ョァ・セェ。ォ。ョ@ latihan.
2. P enyqj ian ( 60 ')
• Guru memperkenalkan nama-nama buah dengan menggunakan kartu yang mana
nama-nama buah tersebut telah terlampir di dalam kartu dalam bahasa Inggris
• Guru mengajarkan bagaimana pengucapan nama-nama buah dalam bahasa Inggris
kartu
• Guru mcmbcrikan flashcard kepada siswa, masill,g-masing 2 11ashcard,dan siswa di haruskan menghapalkan kata-kata yang ada d:tlam flashcard tcrsebut.
• Guru mcngambil flashcard yang telah dibcrikan p:ida siswa selelah 5 mcnit
ditangan mcreka.
• Guru mcnanyakan pada masing-masing siswa ten!ang nanrn-nama buah apa s:ija yang aJa pada flashcard yang ada pada tangan mereka.
• Guru mcmbagikan kembali flashcard kepada sisw11 dengan gambar yang bcrbcda, dan siswa di haruskan menghapalkan kembali flashcard yang memiliki kata-kata yang bcrbeda, clan seterusnya sampai semua siswa mendapatkan semua flash card. • Guru memberikan pertanyaan kepada siswa secara kcseluruhan tcntang
nama-nurna buah dalam bahasa lnggris .. Dan siswa di haruskun mcnjawab secara serempak.
• Guru memberikan kescrnpatan untuk bcrtanya kepada siswa.
• Guru mcmberikan soal-soal dalam kc1tas latihan yang bcrhubungan dcngan
matc:ri J kcpada siswa experiment class. (post test)
• Guru mcngumpLdkan pckci:jaan siswa.
3. l\'llllllljJ (5 ')
Guru mcmnyakan pacla mereka apa yang sudah mcreka dapal dari apa yang tclah
イョ・イエセォ。@ pclajari.
Ciuru 111:.::ngakhiri pclajaran, dengan ーセョオエオー@ sa!attt
G. W:rktu
l'endalr u I u :111
Pcnyajian Pcnutup
(Lily Kar ilrn, S.pd)
: 25 M'enit
: 60 Menit : 5 tv1enit
90 lv1enit
Mengctahui
hkarta, Juni 2005
Pcnulis
セカZ@
t'IGH APUS
BOLPO\N
PAPAN TULIS
ENGGARlS
BUKU
---
セM/drlver}
PRE BASIC LEVEL Name:
I choose the right answer of the following question by crossing A, B, C or D I. The teacher writes on the ... .
a. Pencil c. Black board
b. Ruler d.Pen
2. l put the pencil in the ... .
a. Pencil b. Pen
c. pencil case d. Pencil sharpener
3_ The students write the exercise on the...
セ@
a. Rubberc. Blackboard
b. Book d. Ruler
4. Nita sharpens the pencil using ... .
a_ Book b. Chalk
c. Pen d. Pencil sharpener
5. Rani erases the mistake note using ... .
a. Rubber c. Chalk
b. Ruler d. Book
6_ lbnu writes on the Blackboard using ... .
a. Chalk b. Pen
c. Pencil d. Ruler
7. Tomakealineweuse ... .
a. Book b. Rubber
8. The ... teaches the student
a_ Dentist
c. Teacher
b. Nurse
d. Farmer
9. I buy a ... __ ... at the book shop
a. Chalk
c_ Pencil
b. Marker
d. Pen
I 0. My sister writes using .. __ . _
a. Pencil
c. Pen
b. Chalk cl.Ruler
/
.
.
II. Match the left side of the following words into right side
L Pencil (
2. Ruler (
3. Chalk ( )
4. Teacher ( )
Name:
PRE BASIC LEVEL
I. Choose the right answer of the following questiou by crossing A, B, C or D
ャNtセ・@
ウエオ、セョエウ@
write the letter with ...ᄋᄋOセO[Z@
a. Pencll b. Ruler . Mセ@
):!
c. Black board d. Pen
2. J put a ... in the pencil case
a. Pencil b.Pen
c. pencil case d. Pencil sharpener
3. There is a'. ... on the wall
a. Rubber
c. Blackboard
b. Book
d. Ruler
4. Ami uses the ... to sharpen her pencil
a. Book b. Chalk
c. Pen d. Pencil sharpener
5. My ... is in the bag
a. Rubber b. Ruler
c. Chalk d. Book
6. Budi uses ... to write on the blackboard
a. Chalk
c. Pencil
b.Pen
d. Ruler
7. The ... stands in front of the class
a. Nurse
c. Ruler
b. Rubber
d. Teacher
8. The ... is a place for pencil and pen 1
セMMセMMᄋBᄋセ@
a. Pen b. Ruler
c. Chalk d. Pencil case
9. Ida cleans the picture with ...
I 0. Novi borrow a ... to make straight line
セ@
i·, , ; , , , , , , 1J\
a. Pencilc. Pen
b. Chalk
d.Ruler
II. Match the left side of the following words into right side
1. Rubber ( )
2. Pencil case ( )
3. Pencil Sharpener ( )
4. Teacher ( )
5. Chalk ( )
HJ. Arrange the letters to be right words!
LU-L-E-R-R
2. U - B - E - R- B
3.C-A-L-K-H
4. R-E-A-C-H-T-E
5.L-1-P-N-E-C
A.
f!ii·
· .. B.
セ@
..
C.1.;
Mセᄋセ@
. "-.:JS
Nama Lembaga Level
Mata Pelajaran Terna
Waktu
RENCANA PEMBELAJARAN IV : Smart Education Center (S.E.C)
: Pre Besic (Control Class) : Bahasa Inggris
: Tools of school : 90Menit
A Tujuan Pembelajaran Umum (TPU)
Siswa dapat menguasai kosakata dengan menggunakan kata yang tersedia.
B. Tujuan Pembelajaran Khusus (TPK)
I. Siswa dapat menyebutkan nama-nama alat-alat tulis dio sekolah dengan bahasa
Inggris secara lisan. .
2. Si'swa dapat menjawab pertanyaan guru tentang nama-nama alat-alat tulis di sekolah dengan menggunakan bahasa Inggris dengan Iisan.
3, S iswa dapat menyusun kata.
4. Siswa dapat mencocokkan kata-kata dengan gambar.
5. Siswa dapat mengucapkan kata-kata yang diucapkan oleh guru ..
C. Materi Pembelajaran (Terlampir)
D. Buku Panduan
E. Media Pembelajaran
Papan Tulis dan spidol
F. Kegiatan Pembelajaran
I .. Pendahu/uan (25 ')
,- Guru memberi salam dan bertegur sapa. ,. Guru mengabsen kehadiran siswa.
r Guru mengarahkan siswa pada topic yang akan dibahas dengan mengajukan
beberapa pertanyaan.
,. Guru memberikan kertas Iatihan soal tentang materi yang akan di bahas.dan siswa mengerjakannya dengan batas waktu 15 menit. (pre test)
,. Guru menjelaskan tujuan pembelajaran.
r Guru mc1\jelusk11n kepudii
sisw11
kcginllm ynng nknn mernkn lukukun: menghoptll, mengerjakan Iatihan.2. Penyajian ( 60 '.)
• Guru memperkenalkan nama-nama buah dalam bahasa Inggris dengan menulisnya di papan tulis.
• Guru memberikan pertanyaan kepada seluruh siswa yang bcrhubungan dengan nama-nama pekerjaan dalam bahasa lnggris dan siswa di wajibkan menjawab dengan scrempak tanpa melihat catatan mereka.
• Gum mcrnberikan kesempatan untuk bertanya kepada siswa.
0 Guru mcmbcrikan soal-soal dalam kertas Iatihan (post test) yang bcrhubungan
dengan materi · kepada siswa Khususnya contol class.
• Guru mcngumpulkan pekerjaan siswa.
3. Pe1111111p (5)
o Guru mcnanyakan pada mcreka apa yang sudah mereka dapat dari apa yang telah
n1crcka pclajari.
,·J Guru mcngakhiri pelajaran, dengan penutup salarn
G. Waktu
PendahuJ uan Pcnyajian Penutup
(Lily Kart1 rn, S.pd)
: 25 M'enit : 60Menit : 5 Menit
90 Menit
Mengctahui
Jakarta, J uni 2005
Pcnulis
Name:
I choose the right answer of the following question by crossing A, B, C or D
I .The teacher write on the ... (Papan tulis hitam)
a. Pencil b. Ruler c. Black board d.Pen
2.
r
put the pencil in the ... (Tempat pensil)a. Pencil b.Pen c. pencil case d. Pencil sharpener
3. The students write the exercise on the ... (Buku)
a. Rubber b. Book c. Blackboard d. Ruler
4. Nita sharpens the pencil using ... (Peruncing pensil)
a. Book b. Chalk c.Pen d. Pencil sharpener
5. Rani erases the mistake note using ... (Penghapus)
a. Rubber b. Ruler c. Chalk d. Book
6. lbnu writes on the Blackboard using ... (Kapur tulis)
a. Chalk b.Pen c. Pencil d. Ruler
7. To make a line we use ... (Penggaris)
a. Book b. Rubber c. Ruler d. Chalk
8 The ... teaches the student (Guru)
a. Dentist b. Nurse c. Teacher d. Farmer
9. J buy a ... at the book shop (PuJpen)
a. Chalk b. Marker c. Pencil d.Pen
10. My sister writes using ... (Pensil)
a. Pencil b. Chalk c. Pen d.Ruler
ll. Match the left side of the following words into right side
I. Pencil ( ) A. Kapur
2. Ruler ( ) B. Buku
3. Chltlk ( ) C. Penggaris
4. Teacher ( ) D. PensiJ
PRE BASIC LEVEL
Name:
I. Choose the right answer of the following question by crossing A, B, C or D
The students write the letter with ... (Pulpen)
a. Pencil b. Ruler c. Black board d. Pen
2. I put a ... in the pencil case (Pensil)
a. Pencil b. Pen
3. There is a ... on the wall
a. Rubber b. Book
c. pencil case
(Papan tulis)
c. Blackboard
4. Ami uses the ... to sharpen her pencil
a. Book b. Chalk c. Pen
5. My ... is in the bag (Buku)
a. Rubber b. Ruler c. Chalk
6. Budi uses ... to write on the blackboard
a. Chalk b. Pen c. Pencil
7. The ... stands in front of the class (guru)
a. Nurse b. Rubber c. Ruler
d. Pencil sharpener
d. Ruler
(Peruncing pensil)
d. Pencil sharpener
d. Book
(Kapur tulis)
d. Ruler
d. Teacher
8. The ... is a place for pencil and pen (Tempat pensil)
a. Dentist b. Nurse c. Teacher d. Farmer
9. lda cleans the blackboard with ... (penghapus)
a. Chalk b. Rubber c. Pencil
10. Novi borrow a ... to make straight line
a. Pencil b. Chalk c. Pen
d. Pen
(Penggaris)
d.Ruler
IL Match the left side of the following words into right side
1. Rubber ( ) A. Kapur
2. Pencil case
3. Pencil Sharpener
4. Teacher
5. Chalk
( )
( )