ABSTRACT
DEVELOPING STUDENTS’ LISTENING SKILL THROUGH DICTOGLOSS AT THE FIRST YEAR STUDENTS’ OF SMAN 1 NATAR
By
Nurul Puspita
Listening can be considered as the first step in learning a language. Thus, listening plays a very important role in students’ success of learning language skills.
Therefore, the objectives of this research are to improve (1) students’ listening skill in getting the gist of the text and reconstruct it (2) students’ listening activity and (3) the quality of teacher’s performance.
The subject of this research is the first year students of SMAN 1 NATAR, class X.9. The research was conducted from January 6th until 16th 2012. An action research was carried out in order to improve students’ listening skill by using Dictogloss in listening class.
vocabulary in the first cycle. In the second cycle, all of the students could focus and reconstruct the text well. They became more active in listening class it was because the students were given summary Dictogloss in the second cycle. In this cycle, the students were given a flow chart which helped the students reconstruct the text.
Additionally, teacher’s performance result account as one of the main points observed by the researcher. In cycle 1 the researcher could not emphasize the use of English and coordinated learning process. It was because the students were lacking of vocabulary. The students did not understand the meaning of the
teacher’s explanation. In cycle 2, the researcher used simple vocabulary and made some vocabulary games. Thus, the students could catch what the researcher meant. The researcher also proposed the students a reinforcement instead of verbal reprimand or even a punishment.
Based on the data, it can be concluded that there is an improvement of the
students’ listening skill after being taught using Dictogloss. Therefore, Dictogloss is recommended to be used by English teachers to improve their students’
listening skill and teacher’s performance. However, since students have
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter discusses several points, i.e., background of the problem, research problem, objective of the research, uses of the research, scope of the research, and definition of term, as follows:
1.1 Background
The demand in English curriculum of SMA states that SMA/MA students should be able to use language in informational level. Arriving at informational level means that the students are expected to be able to access knowledge and
information from the target language (English) by their language skills. There are
four skills of language to be taught by English teachers of SMA/MA, i.e., listening, speaking, reading, and writing (Depdiknas, 2006:307). The learners should be trained to be able to use English in real communication so that they master these four skills.
demonstrated, remember what is shown or told, and then practice speaking to gain functional skill in active communication.
If the students have good listening skill, they may easily understand what is being said or heard. Moreover, they will be able to communicate about the information they have heard. Conversely, if the students lack of listening skill, they might have many difficulties to going through the next steps of acquiring other language skills such as speaking, reading, and writing. Therefore, listening plays a very important role for students’ success of learning English.
Margaret (1988) also states that listening can be considered as the first step in learning a language. It means that language learning, initially, highly depends on listening skill. It provides aural input that serves as the basis for language acquisition and enables its learners to interact in spoken communication and continue to the next skills. So, the students should have good skill in listening to develop their ability in English. More practice in listening makes them know new vocabulary and are able to send a message to others. By developing their ability to listen, they become independent learners and are able to listen accurately i.e. they are much more likely to be able to reproduce sentence accurately, refine their understanding of grammar and develop their own vocabulary.
information from the text. Obviously they have difficulties in getting information even though they know what to be listened.
The result of the pre observation done by the researcher in the 1st semester of the 1st grade also shows similar case. The teacher just gives some exercises from tape recorder and discusses the answer together. He only gives the students multiple choice questions, then asks them to answer it, while students were listening, teacher walks around the class and observes the students activities. This activity does not make the students know what they listen because their focus only to answer the question and get the best score. Thus, it is not interesting for the students.
From the fact above, it can be revealed that there are several problems of teaching listening i.e., the low listening achievement especially in getting the gist and reconstruct the text, inappropriateness of teaching technique used by the teacher in teaching listening. Therefore, it should be an appropriate technique to be applied for the students to increase their listening achievement.
speech is as the main learning strategies. Therefore, the researcher proposes Dictogloss as an alternative technique.
Dictogloss offers a context-rich method of assessing how much students know about the topic of the text. The dictogloss has been proposed as a procedure that encourages students to reflect on their own output (Wajnryb, 1990). In a
dictogloss the emphasis is on the students’ ability to communicate in order to re-convey the meaning of the text, as opposed to re-producing it word for word. The use of dictogloss are that students are encouraged to focus some of their attention on form and that all four language skills – listening (to the teacher read the text and to groupmates discuss the reconstruction), speaking (to note taking while listening to the teacher, the group’s reconstruction, and the original text), reading (note taking while listening to the teacher, the group’s reconstruction, and the
original text), and writing (the reconstruction) – are involved.
Furthermore, dictogloss can be used as a mediator that is useful for listening bottom-up and top down. Teacher will find out the individual items in text (bottom-up strategy). However, in small group discussion, some of the top-down strategy perhaps is used. In this strategy, teacher will integrate student’s
background knowledge. By using this technique teacher is able to make prediction, make inferences about the things in text, find out the topic, and be familiar with kinds of text.
Considering the statement above, the writer would like to propose dictogloss as a technique in teaching listening. The writer hopes that dictogloss will be helpful to
1.2 Formulation of The Problem
In reference to the background above, the research problem can be formulated as follow:
1. How can dictogloss improve students’ listening skill in getting the gist of the text and reconstruct the text?
2. How can dictogloss improve students’ listening activity in teaching listening process?
3. How can dictogloss improve the quality of teacher’s teaching performance?
1.3 Objective of the Research
In relation to the problem formulated above, the objectives of the action research are to:
1. Improve students’ listening skill in getting the gist of the text and reconstruct text through dictogloss.
2. Improve students’ listening activity in teaching listening process through dictogloss.
3. Improve the quality of teacher’s teaching performance through dictogloss.
1.4 Uses of the Research
This result of the research can be used as follow:
Theoretical uses:
2. To be used as a reference for the next researcher who will concentrate on students’ listening comprehension, students’ participation in teaching learning process of dictogloss and teacher’s teaching performance.
Practical uses:
1. As a help to English teacher in finding appropriate technique in improving students listening skill and teacher’s performance.
2. As a help to students in improving their listening skill.
3. As a consideration in making policy related to the development of teaching learning English subject especially listening skill.
1.5 Scope of the Research
1.6 Definition of Terms
There are some terms that will be useful in the research. The terms below will guide the reader in reading and understanding the research.
Dictogloss
It refers to a technique where the learner receives some spoken input, hold this in their memory for short time, and then write what they heard by using their own word.
Developing Listening skill
It refers to a series of actions in the class interrelate to increase the students’ listening skill through dictogloss.
Listening skill
It refers to the activity of paying attention and trying to grasp the meaning of something we hear from the spoken passage.
Action research
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW
There are some concepts related to the research. In literature review, the section
discusses several concepts such as concept of listening, concept of teaching
listening, concept of dictogloss, kinds of dictogloss, procedure of using dictogloss,
advantages and disadvantages of dictogloss, and theoretical assumption.
2.1 Concept of Listening
Listening is an active process requiring participation on the part of listener.
Margaret (1988:19) states that listening is an active process in which the listener
plays a very active part in constructing the overall message that is actually
exchanged between the listener and speaker. The idea above indicates that the
listeners are actually playing an active role because they should have ability to
digest the message of the speaker. Therefore, the listener should listen to the
speaker carefully.
According to Howatt and Dakin in Saricoban (1999:1), listening is the ability to
identify and understand what others are saying. Morley (1991:2) states that
listening is the most common communicative activity in daily life; we can expect
to listen twice as much as we speak, four times more than we read, and five times
more than we write. Moreover, Underwood (1985:1) defines listening as the
activity of paying attention and trying to grasp the meaning of something we hear.
the other skills. A listener must listen to something before he or she starts to
speak, and this activity involves understanding the speaker’s accent or
pronunciation, his grammar and vocabulary and then grasping his meaning.
There are several types of listening Syque (2002:5):
1. Discriminative listening
Discriminative listening is the most basic type of listening, whereby the difference
between different sounds is identified. We learn to discriminate sounds and
phonemes of the language, and to discriminate between muscle and skeletal
movements that signify different meaning.
2. Comprehension listening
In comprehension listening, we try to make sense the meaning or to comprehend
what others are really saying, and through understanding body language, voice,
etc help us understand what other person really mean. In communication,
comprehension often benefits from drawing out of key facts and items from long
spiel.
3. Evaluative listening
In evaluative listening, we make judgments about what the other person is saying,
whether something is good, bad, worthy, or unworthy. It is particularly pertinent
4. Appreciative listening
In appreciative listening, we seek certain information which will meet our needs
and goals. For example when we are listening to good music, poetry or stirring
words of great leader.
5. Empathetic listening
In empathetic listening, we seek to understand beliefs, models, emotions and goals
of other people. This requires excellent discrimination and close attention to the
nuances of emotional signals. We show the expose we get by demonstrating our
empathy in our demeanor toward them.
6. Therapeutic listening
In therapeutic listening, we are not only empathizing with the speaker but also to
use this deep connection in order to help the speaker understand, change or
develop in some way.
7. Dialogic listening
In dialogic listening, we learn through conversation and engaged interchange of
ideas and information in which we actively seek to learn more about the person
and how they think.
In terms of the skills of listening, there are two main divisions Hughes
(1991:134):
1. Macro skill
In macro skill, to understand what someone says, a listener has to involve with
listener should get the general idea of the information, following instructions or
directions.
2. Micro skill
In micro skill, to understand what someone says, a listener has to interpret
intonation pattern (e.g. recognize stress and rhythm), recognition of function of
structures (interrogative as request, imperatives e.g. sit down!), cohesive devices
e.g. such as and which, detect sentence constituents, e.g. subject, verb, object,
prepositions), recognizing discourse markers (e.g. Well; Oh, another thing is;
Now, finally).
In this research, the students were required to concentrate on comprehension
listening that was to understand the information they hear and belong to macro
skill. The research was focused on the macro skill since the researcher used
Dictogloss that measured the specific information and the gist of the text that the
students should get from the text.
Malkina (1995:41) states comprehension can be described as the process which
enables the receiver to make meaning from verbal and non-verbal information.
Non-verbal information may include background knowledge based on experience
or visual information (mental pictures). According to James (2006:1) listening
comprehension refers to understanding the spoken language. Testing for listening
comprehension must be grade-level appropriate.
Furthermore, James (2006:1) divided listening comprehension into two levels,
1. Lower levels of listening comprehension
This level would include understanding only the facts explicitly stated in a spoken
passage and has very simple syntax and uncomplicated vocabulary.
2. Advanced levels of listening comprehension
This level would include implicit understanding and drawing inferences from
spoken passage with more complicated syntax and advanced vocabulary.
Thus, listening comprehension refers to the ability to grasp idea from a spoken
passage we hear. Therefore, in this research, to suit with the students
understanding of a spoken passage, the researcher refers to the advanced level of
listening comprehension to get ideas and to comprehend information that was
explicitly and implicitly stated in a spoken passage which belongs to macro skill.
2.2 Concept of Teaching Listening
Language learning depends on listening. Listening provides the aural input that
serves as the basis for language acquisition and enables learners to interact in
spoken communication. Effective language instructors show students how they
can adjust their listening behavior to deal with a variety of situations, types of
input, and listening purposes. They help students develop a set of listening
strategies and match appropriate strategies to each listening situation.
According to Swift (2007:18), teaching listening suggest that we need to take a
more active approach to improve listening abilities, by focusing on the specific
problems that the students have and planning listening activities, which will help
There are two approaches involved in listening according to Swift:
1. Bottom-up processing
The bottom-up approach sees comprehension as a matter of listeners first
decoding (or understanding) the smallest elements of what they hear-the elements
of sounds.
2. Top-down processing
The top-down approach sees understanding as starting from the listener’s
background knowledge of the non-linguistic context and of working down
towards the individual sounds. Listeners will actively interpret what they hear in
terms of their understanding of the situation and the world in general.
According to Wong (2005:4), way of treating the teaching and learning of
listening by focusing on how to get the main ideas, the gist or the meaning in
listening materials even when it is clear that the learners have not been able to
identify a lot of the speech sounds is often called the top-down processing
approach.
Brown (1990:255) states that the objectives of teaching listening are producing
good listeners who construct reasonable interpretations on the basis specified
input and recognize when specific information is required. In addition, it was
necessary for the teacher to follow stages in teaching listening with hope the
students will be able to comprehend the story.
Garvie in Malkina (1995:4) sees the following stages of development in a child’s
1. The learner picks up “clues”
In this stage, the learner found some clue to comprehend through words or picture,
which helps them to construct meaning.
2. The learner develops coping skills
After having the clues, the students will then grasp and manage the information
they have heard.
3. The learners get the gist or general picture of the message and much of the
supporting detail.
Thus, teaching listening is a process of giving the students chances to learn the
language through information, in which through the stages of comprehending in
teaching listening, the students will be able to obtain and to understand general
idea of the information.
2.3 Concept of Dictogloss
In the Dictogloss, a short passage, designed to practice a particular grammatical
feature, is read twice at normal speed by the teacher. Students individually try to
write down as much as they can, and subsequently work in small groups to
“reconstruct” the text; that is, the goal is not to reproduce the original, but to
“gloss” it using their combined linguistic resources (Wajnryb 1990: 12).
Dictogloss is a technique where the learner receives some spoken input, hold this
in their memory for short time, and then write what they heard (Ruth Wajnryb,
Dictogloss can be defined as two words, “dicto” and “glossary” means that a
technique in teaching listening process by dictating the students and asking the
students to make a sentence and rewrite the text by giving them glossary in related
by the text.
Dictogloss can develop student’s listening skill, because they listen what teacher
dictates in a short piece of text. It also highlights student’s grammatical
competence through reconstruction, paraphrase and analysis of the text. In
addition, it also uses as both a diagnostic tool, to find out what students do and do
not know about the specific topic, as well as a tool to build knowledge of a topic,
through communicative strategies.
Dictogloss represents a major shift from traditional dictation. When implemented
conscientiously, Dictogloss embodies sound principles of language teaching
which include: learner autonomy, cooperation among learners, curricular
integration, and focus on meaning, diversity, thinking skills, alternative
assessment, and teachers as co learners. These principles flow from an overall
paradigm shift that has occurred in second language education (Jacobs & Farrell,
2001). The principles can be described like the following;
1. Learner Autonomy. In Dictogloss, as opposed to traditional dictation, students
reconstruct the text on their own after the teacher has read it aloud to them just
twice at normal speed, rather than the teacher reading the text slowly and
repeatedly. The students need to help each other to develop a joint reconstruction
of the text, rather than depending on the teacher for all the information.
they may need to improve. The students gain insights into their own linguistic
shortcomings and develop strategies for solving them by working through
reconstruction with a partner. They also can ask for a pause in the dictation and
elaborate the text.
2. Cooperation Among learners. This make students cooperate with their friends.
They work with their team to reconstruct the text.
3. Curricular Integration. All four language skills i.e., listening, speaking, reading,
and writing are utilized in Dictogloss. In dictation the text, the students will use
their listening skill, after that they will discuss their reconstruction with the
partner, then reading the text in front of the class to compare with the original text
and the last write down the reconstruction.
4. Focus on Meaning. In this research, the students focus in getting the specific
information of the text. They grasp the meaning of idea in the text.
5. Diversity. The students who have larger vocabularies and greater content
knowledge in the topic of the text can help with that part of the reconstruction,
and those whose interpersonal skills are better developed may often help
coordinate the group’s interaction.
6. Alternative Assessment. Dictogloss offers a context-rich method of assessing how
much students know about writing and about the topic of the text. The text
reconstruction task provides learners with opportunities to display both their
knowledge of the content of the text as well as of the organizational structure and
language features of the text (Derewianka, 1990). As students discuss with each
other during Steps 4 and 5, teachers can listen in and observe students’ thinking as
greater insight than does looking at the product after they have finished. In this
way, Dictogloss supplies a process -based complement to traditional
product-based modes of assessment. Furthermore, students are involved in self assessment
and peer assessment.
7. Teachers as Co-learners. The students are not only work with the researcher but
their friends too. The researcher is not as all knowing sages but they can discuss
with their group in reconstructing the text.
In this research the researcher would integrated all of those principle.
2.4 Kinds of Dictogloss
The following types of dictogloss are based on theories exposed by Sarieva (2004)
they are:
2.4.1 Variation A: Dictogloss Negotiation
In Dictogloss Negotiation, rather than group members discussing what they heard
when the teacher has finished reading, students discuss after each section of text
that has been read. Sections can be one sentence long or longer, depending on the
difficulty of the text relative to students’ proficiency level.
a. Students sit with a partner, desks face-to-face rather than side-by-side. This
encourages discussion. After reading the text once while students listen, during
the second reading, the teacher stops after each sentence or two, or paragraph.
During this pause, students discuss but do not write what they think they heard.
As with standard Dictogloss, the students’ reconstruction should be faithful to the
b. One member of each pair writes the pair’s reconstruction of the text section. This
role rotates with each section of the text.
c. Students compare their reconstruction with the original as in Step 5 of the
standard procedure.
So, in this variation they will work in pair to reconstruct the text that they have
heard. Then, it will compare with the original text.
2.4.2 Variation B: Student -Controlled Dictation
In Student -Controlled Dictation, students use the teacher as they would use a tape
recorder. In other words, they can ask the teacher to stop, go back, i.e., rewind,
and skip ahead, i.e., fast-forward. However, students bear in mind that the aim of
dictogloss is the creation of an appropriate reconstruction, not a photocopy.
a. After reading the text once at normal speed with students listening but not taking
notes, the teacher reads the text again at natural speed and continues reading until
the end if no student says “stop” even if it is clear that students are having
difficulty. Students are responsible for saying “stop, please” when they cannot
keep up and “please go back to (the last word or phrase they have written).” If
students seem reluctant to exercise their power to stop us, we start reading very
fast. We encourage students to be persistent; they can “rewind” the teacher as
many times as necessary. The class might want to have a rule that each student
can only say “please stop” one time. Without this rule, the same few students –
almost invariably the highest level students - may completely control the pace.
b. The lower proficiency students might be lost, but be too shy to speak. After each
member of the class has controlled the teacher once, anyone can again control one
and should control the teacher if they need help, this rule need not be followed
absolutely.
c. Partner conferencing (Step 4 in standard dictogloss) can be done for this variation
as well. Student-Controlled Dictation can be a fun variation, because students
enjoy explicitly controlling the teacher.
d. Another way of increasing student control of dictation is to ask them to bring in
texts to use for dictation or to nominate topics.
The main point on this variation is the rule. The students can control the teacher
whether to stop, pause, and then continue. Teacher is the only source of sound
here. And the task of the students is reconstructing not photocopy or write down
all the text.
2.4.3 Variation C: Student-Student Dictation
Rather than the teacher being the one to read the text, students take turns to read to
each other. Student-Student Dictation works best after students have become
familiar with the standard dictogloss procedure. This dictogloss variation involves
key elements of cooperative learning, in particular equal participation from all
group members, individual accountability (each member takes turns controlling
the activity) and positive interdependence as group members explore meaning and
correctness together.
a. A text - probably a longer than usual one - is divided into four or five sections.
Each student is given a different section. Thus, with a class of 32 students and a
text divided into four sections, eight students would have the first section, eight
understand it. If the text is challenging, students with the same section can
initially meet in groups of three or four to read and discuss the meaning.
b. In their original groups, students take turns reading their section of the text as the
teacher would for standard dictation while their group mates take notes.
c. Students work with their partners to reconstruct the text, with the students taking
the role of silent observer when the section they read is being reconstructed.
d. For the analysis, Step 5 of the standard procedure, each student plays the role of
the teacher when the section they read is being discussed. Every group member
eventually plays the role of teacher.
Student-Student Dictation can also be done by students bringing in the own texts
rather than using a text supplied by the teacher. So, the teacher should make sure
that the students really understand with the rule of dictogloss. Then, this activity
will run well.
2.4.4 Variation D: Dictogloss Summaries
While in the standard dictogloss procedure students attempt to create a
reconstruction of approximately the same length as the original, in Dictogloss
Summaries, students focus only on the key ideas of the original text.
a. Steps 1, 2, and 3 are the same as in standard dictogloss, although to encourage
summarizing rather than using the words of the original text, the teacher might ask
students not to take any notes.
b. Students work with a partner to summarize the key points of the text. Here, as
well as in other dictogloss variations, we can provide visual cues (sketch, flow
comprehension and may help students structure their reconstruction. Additionally,
students can create visuals to accompany their reconstructions, as another means
to demonstrate comprehension and to promote unique reconstructions.
So, the students should build the same length in reconstruct the text from the
original text. Although, it doesn’t use the original text, but use such kind of clues
then it will summarize.
2.4.5 Variation E: Scrambled Sentence Dictogloss
Scrambled Sentences is a popular technique for teaching a number of language
skills. Scrambled Sentences Dictogloss employs this technique to raise the
difficulty level of dictogloss and to focus students’ attention on how texts fit
together.
a. The teacher jumbles the sentences of the text before reading it to students.
b. When students reconstruct the text, they first have to recreate what they heard and
then put it into a logical order.
c. When analyzing students’ reconstructions, the class may decide that there is more
than one possible correct order. This fits with the overall spirit of dictogloss, i.e.,
that there is no one correct way to achieve a communicative purpose, although
there are certain conventions that should be understood and considered.
This variation is quite difficult for the student. They will hear a jumble text. So,
their task is reconstructing a jumble text into a logical order. Then, there will be
variation answer too. It will develop based on their opinion. So, there will be more
2.4.6 Variation F: Elaboration Dictogloss (Airey, 2002)
In Elaboration Dictogloss, students go beyond what they hear to not just recreate a
text but also to improve it.
a. This dictogloss method may be preceded by a review of ways to elaborate, such as
adding adjectives and adverbs, examples, facts, personal experiences, and causes
and effects.
b. After taking notes on the text read by the teacher, as in Step 3 of the standard
procedure, students reconstruct the text. Then, they add elaborations. These can be
factual, based on what students know about the topic of the text or research they
do, or students can invent elaborations. For instance, part of the text read by the
teacher might be: Today, many students use bicycles. Students could simply
elaborate by adding a word or two: Today, many Japanese college students use
bicycles. Or, a sentence or two could be added: Today, many students use bicycles.
This reduces air pollution and helps students stay fit. However, bicycle riding in a
crowded city can be dangerous.
Before doing this activity the teacher might give such kind of background
knowledge to the students or builds up their schemata. It will help the students to
elaborate the text that will be heard by them. After hearing the text they can
reconstruct the text then elaborate it. The text can elaborate by adding the adverb
and adjective.
2.4.7 Variation G: Dictogloss Opinion
In Dictogloss Opinion, after students reconstruct the text, they give their opinion
on the writers’ ideas. These opinions can be inserted at various points in the text
throughout the text, it promotes a kind of dialogue with the original authors of the
text.
The type of this variation is quite unique. Beside, reconstructing the text the
students also should give their opinion about the text. They can give all off their
opinion and write down the opinion after the reconstruct text.
The researcher would use standard Dictogloss in cycle 1. By using this variation
students’ can discuss with their pair after each section of the text that has been
read, then in cycle 2 it was changed into summary Dictogloss.
2.5 Procedures of Teaching Listening through Dictogloss
According to Jacob (1990), the basic format of teaching listening through
Dictogloss can be cited as follows:
1. The class engages in some discussion on the topic of the upcoming text. This
topic is one on which students have some background knowledge and, hopefully,
interest. The class may also discuss the text type of the text, e.g., narrative,
procedure, or explanation, and the purpose, organizational structure, and language
features of that text type.
2. The teacher reads the text aloud once at normal speed as students listen but do not
write. The text can be selected by teachers from newspapers, textbooks, etc., or
teachers can write their own or modify an existing text. The text should be at or
below students’ current overall proficiency level, although there may be some
new vocabulary. It may even be a text that students have seen before. The length
3. The teacher reads the text again at normal. Students are not trying to write down
every word spoken; they could not even if they tried, because the teacher is
reading at normal speed. In this case, they only listens teacher dictation and try to
get the gist of the text. Later teacher read the text again. Here students can take a
note and write down important word.
4. Students work in pair to reconstruct the text in full sentences, not in point form
(also known as bullet points). This reconstruction seeks to retain the meaning and
form of the original text but is not a word-for-word copy of the text read by the
teacher. Instead, students are working together to create a cohesive text with
correct grammar and other features of the relevant text type, e.g., procedure, or
rhetorical framework, e.g., cause and effect, that approximates the meaning of the
original.
5. Students, with the teacher’s help, identify similarities and differences in terms of
meaning and form between their text reconstructions and the original, which is
displayed on an overhead projector or shown to students in another way.
This procedure takes from one of the variation of the Dictoglos. It is standard
Dictogloss. So, in her research the researcher will use this way in cycle 1 and it
was changed into summary Dictogloss in cycle 2. The text was narrative which is
suitable with students’ proficiency. In this research the target is first grade of
senior high school students.
2.6 Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Dictogloss
2.6.1 Advantages of using Dictogloss
2.6.1.1 For teacher
a. Dictogloss involves the whole class, no matter how large it is. Since, teacher read
the text automatically students in the class involves themselves to listen the text
carefully. It is because Dictogloss need more concentration in listening. Students
are forced to listen because in Dictogloss they reconstruct the text with their own
word. For example, teacher read the text loudly and clearly, while teacher read the
text, students write down the inferences. So, it can involve the whole class.
b. Correction can be done by the students, because all students have the same topic
about the text, so they can do pair correction.
c. Dictogloss can be prepared for mixed ability groups, for example in reconstruct
the text. They are divided into some group without any discrimination. It is to
avoid in one group all the member have a good students and in contrast in one
group all of the member are not quite good students.
d. Teacher can move about giving individual attention. Therefore he or she may
know the weaknesses and strongest each individual.
e. Dictogloss can provide access to interesting text, by introducing a topic, example,
or summarizing it.
2.6.1.2 For students
These technique also have advantages for the students, they are:
a. Dictogloss can help the students to develop their four language skill.
b. Dictogloss helps to develop short-term memory.
c. Dictogloss helps the students in active learning.
2.6.2 Disadvantages of using dictogloss
a. Dictogloss just gives short-term memory not long term memory.
b. Dictoglos just reconstruct the text without focus on grammar.
2.7 Theoretical Assumption
Teacher might make some goal to success the learning process. He could choose
the appropriate technique in their teaching listening, so that the students could
reach the target. By using Dictogloss in developing listening skill, students might
be able to develop their four integrative ways. The reason was because they used
their background knowledge before learning. Finally, it could be assumed that by
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter discusses certain points; research design, general description of the
research, research procedures, indicator of the research, instrument of the
research, and data analysis, as follow:
3.1 Research Design
In this research, the researcher used an action research. Action research was
characterized by problems and actions done by using cycle to solve the problems.
In doing the research, the researcher (acted as the teacher) collaborated with the
English teacher of that school (collaborator) to improve the students’ listening
skill through dictogloss. The researcher and the collaborator would also carry out
reflection after knowing the result of the analysis. The function of the collaborator
in this action research was as a resource to find the problem in order that the
researcher could see the improvement when do this technique and also, as the
second observer to get the data.
This research was done at the first year of SMAN 1 Natar. It was done based on
the problem faced by the students and the teacher when they were in class. Based
on the problem found by the researcher, the researcher examined the cause of the
problem and then finds the solution for that problem.
The subject of this action research was the students of the first year students of
so active when they were learning Listening especially in getting the gist of the
text and reconstruct the text. The students were only good at listening text in
simple text and answer the multiple choices in simple question too. According to
the researcher’s pre-observation towards those students, the researcher concludes
that most of the students have low listening achievement.
In this research, the researcher acted as the teacher by implementing Dictogloss
since this was a kind of research that was based on the teacher’s problem and how
the teacher solve the problem by herself; meanwhile the English teacher of SMAN
1 NATAR acted as collaborator and also observed the students since the
researcher did not know the ability of each students exactly. The researcher makes
the lesson plan and performs in the class based on it. So, during the research, the
researcher and the collaborator observed everything that occurred in the
classroom.
3.2 General Description of the Research
The research was an action research which was conducted based on the problem
faced by the students and the English teacher. In doing the research, the researcher
does collaboration with the English teacher to improve the students’ listening skill
trough Dictgloss technique.
While the teacher was applying Dictogloss in the classroom, the collaborator
observed the teaching learning process and makes some necessary points from
that process. In that process, the teacher also hold listening test by giving the
students listening test of a narrative text. The focus of analyzing was on getting
After that, the researcher and the collaborator analyze the result of the
observation, and also the listening test. The researcher and the collaborator also do
reflection after knowing the result of the analysis. Based on the analysis and
reflection, it was decided whether the next cycle would be held or not, and the
next cycle would be focused on eradicating the weaknesses in the previous cycle.
3.3 Research Procedures
In this action research, the researcher implement two cycles depending on the
result of the analysis and reflection in the first cycle. The first cycle was based on
the problem of the research. The main steps of each cycle were as follows:
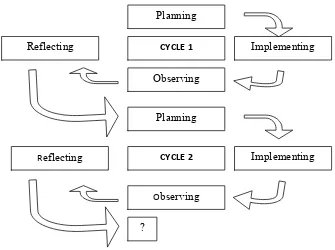
3.3.1 Planning
Planning was the stage where the problem causes were identified. By knowing the
causes, the focus of the problem could be formulated in the importance of the
implementation that would be given. After deciding what the problem and the
causes were, the appropriate technique was selected. And based on the problem
and the teaching technique, the materials and teaching aids and the type of test
were planned. To get a complete series of data, a rater was involved to observe the
teaching-learning process
3.3.2 Implementing
In this step, the researcher implements the material by using Dictogloss technique
while she was teaching listening. The researcher read the text and asked the
students to listen. After that researcher asked students to reconstruct the text, by
their own words, to make them meaningfully. In teaching, the researcher involves
teaching learning process. The collaborator observed the situation in the class and
made some necessary notes.
3.3.3 Observing and Interpreting
The collaborator observed the activities happened in the classroom in every cycle
and wrote the result of the observation in the observation sheets. The researcher
also interpreted the result of the observation. This step was started when teaching
learning process was occurring.
3.3.4 Reflecting
In this step, the researcher and the collaborator analyze the result of the listening
test of the students as the learning product. The researcher also analyzed
everything occurs in the teaching learning process based on the observation
sheets. It was done to find out the improvement after the teacher implements
Dictogloss in the classroom. In analyzing, the researcher together with the
collaborator do reflection to discover the weakness and strength of the
implementation of Dictogloss, and also to know the problems faced by both
teacher and students during teaching and learning process. By doing so, the
researcher and the teacher know what should be improved for the next cycle. If
the indicators of the research haven’t been fulfilled in the first cycle, the
researcher together with the collaborator would plan the next step to make
betterment in the next cycle. On the other hand, if the indicators were already
Figure 1. The cycles of the classroom action research. Adapted from Arikunto, 2006:16.
3.4 Indicators of the Research
In order to see whether dictogloss could develop students listening skill, then
researcher determine the indicator dealing with the learning process and learning
product.
3.4.1 Learning Process
In the learning process, there were two aspects which become the focus of this
research, that is, the students’ learning activities and the teacher’s teaching
performance.
The target determined by the researcher concerning the students’ activities
whether there were a problems or not in the cycle. The researcher would observe
Observing
CYCLE 2 Implementing Planning
Reflecting
Observing
CYCLE 1 Implementing Planning
Reflecting
students’ activities in the class from pre-activity to post-activity. If there was not a
significant problem during in the class, it meant that the activities of the students’
were good. To set the target of the success of this action research, the researcher
also did a discussion with the English collaborator.
Besides observing the students’ activities, the collaborator also observed the
teacher’s teaching performance during the teaching and learning process. It was
expected that the teacher could get score 70 in her teaching performance after
implementing dictogloss techniques. So, if the teacher could reach that target, it
means that the teacher’s teaching performance was good. For the teaching
performance, there were some aspects scored, that is, the teacher’s activities in pre
activity, while activity, and post activity.
3.4.2 Learning Product
Dictogloss technique was able to develop students’ listening skill. It would be
seen in the score when the teacher gives listening test in each cycle. So, the
dictogloss technique is regarded as applicable to develop students’ listening skill.
In giving score of reconstructing the text in listening test, the researcher uses the
scoring criteria is adopted from Andrich, D (2002: 103-121).
a. Score 86 – 100
All primary information is given, correct, and have accurate message.
b. Score 70 – 85
All primary is given, correct, and correctly show the relationships among the
c. Score 56 – 69
Most of the primary information is given and correct, but the message maybe
missing one or two pieces of primary information.
d. Score 0 – 39
One or more pieces of primary information were given and correct, but the
message may also include primary information is incorrect.
e. Score 0
No information is given that is correct.
There would be another indicator in giving the score. In giving score of getting the
gist of the text, the writer uses the scoring criteria is adopted from Andrich, D
(2002: 103-121).
a. Score 5
All information is present and correct.
b. Score 4
Response correct in that all important is given and is correct, may be missing
subtle details, may have incorrect details that do not interfere with central
meaning.
c. Score 3
Response substantially correct, all information that is present is correct, may be
missing a few pieces of information.
d. Score 2
Some pertinent information, some information may be incorrect, but sketch of the
e. Score 1
Minimal pertinent information provides either the gist of the situation or clue
regarding a source of further information.
f. Score 0
No meaningful information or totally inaccurate information.
3.5 Instruments of the Research
The data would be collected until there was a consistency of the data, so there was
no exact time to gather it. Moreover, to make the data was valid the writer would
use triangulation. Triangulation was a way of collecting the data by combining
two or more methods. According to Setiyadi (2006:246) the use of triangulation
was to describe the subject in a complete description. Actually there were many
kinds of triangulation but this research would use methodological triangulation.
To gain the data, the researcher applies four kinds of instruments. The instruments
were the listening test, observation sheet, questionnaire, and interview.
3.5.1 Listening Test
The first instrument used in getting the data was listening test. In order to make
data accurate, dictation is applied. In this research, the students would be asked to
reconstruct the text in form of writing which was given to them. This test was
aimed at knowing students’ improvement in listening skill. For example:
Instruction:
a. Write your name and your class clearly on the paper.
b.Use your time efficiently (2×45 minutes).
a. Listen the text cwerefully.
b. Write down the important information that you get from the text in box 1
individually.
c. Write down the important information that you get from the text in box 2 with
your friend.
d. Reconstruct the text based on the information that you get from box 1 and box 2
with the whole class; you may used your own word to reconstruct the text.
The validity of the test would be measured by face validity, content validity, and
construct validity. Face validity would be gotten from printing of instruction and
direction in the test. Content validity would obtained by choosing the text based
on the level of the students and the curriculum. While construct validity would be
achieved by focusing the test in getting the gist and reconstruct the test to show
the students skill.
The researcher would always try that in collecting the data is reliable. In this
research basically there were many ways to collect the data reliable. The
reliability would be gotten by using some data collection, such as observation
sheet, interview, and questionnaire. So, by using that way hopefully the data
would be consistence.
3.5.2 Observation sheet
Observation was conducted in every cycle during the teaching learning process.
When teaching and learning process was occurring, the researcher observed the
process happened in the classroom. The researcher used structured observation to
So there were two kinds of observation sheets that were filled out by the
researcher, that were the observation sheet for the students’ activities and the
observation sheet for the teacher’s performance. Besides, the researcher also
makes some necessary notes in the observation sheet concerning the students’
activities and teacher’s performance.
3.5.3 Questionnaire
The questionnaires were used to support the data gain from observation about the
students’ opinion. Questionnaire is made suitable with everything which related
with the answer is needed by the observer as additional data to support the
research. In this action research, the researcher would use open-ended questions.
Open-ended questionnaire could be used to help the researcher in selecting data
because the respondents were free to express their answer (Setiyadi,2006). By
using open ended questionnaire, the researcher hopefully would find the important
data which could not imagine before.
3.5.4 Interview
The interview was addressed to the students to know the ordinary method of
learning listening that they dealt with and also the students’ knowledge.
And after implementing the method, the writer would interview the students to get
the complimentary data by preparing some questions. Interview was done
structurally it was used as a basis research question. Questions which were
proposed related with the developing of dictogloss. The purpose of interviewing
people was to find out their mind, what they thought or how they felt about this
3.6 Data Analysis
Data analysis needs careful thinking since data analysis was aimed at organizing
the data. It was done to make the readers were able to understand the result of the
research. Data analysis was the process of organizing the data in order to gain the
regularity of the pattern and form of the research. The term interpretation could be
defined as procedure of giving meaning ob the result of analytical process. Data
analysis was done to create understanding for the data after following certain
procedure final of result of the students could be presented by the researcher to the
readers (Setiyadi, 2001).
In this research, the researcher validates the data by using, listening test and
observation. After get the data from the test and observation, the teacher would
analyze the data based on the limitation of the problems and objectives of the
research.
In analyzing and interpreting the data, the first step was that the teacher would
make description of all data. Then the teacher selects the data related to the
research question. The next step, the teacher arranges all collected data by
classifying the data. The data of the learning process and learning product were
gathered by means speaking test, observation sheet, interview, and questionnaire.
The last step is making the report. Having taken the data, she interprets all the
collected data and described them into conclusion. And based on the analysis and
reflection, it would be decided whether to conduct three cycles.
The data analysis that was done for the learning product and learning process is as
3.6.1 Learning product
To know the learning product, the researcher uses listening test to collect the data.
There were some steps used to analyze the data got from the test:
3.6.1.1 Giving the listening scores to the students
After giving the test, the researcher checks the result of students’ test to give the
score. Besides that, the researcher analyzed the result to know the errors mostly
made by the students. This was very useful for betterment in the next cycle.
3.6.1.2 Calculating students’ total score
There were two steps that must be done in calculating the total scores:
Calculating the scores from 1st and 2nd rater.
X=
Note:
X: Total score
X1: Score from 1st rater (the researcher as the teacher)
X2: score from 2nd rater (the English teacher as the collaborator)
3.6.2 Learning process
To get the data from the learning process, the researcher uses observation sheets
and questionnaire. The result of the observation sheet and questionnaire were
analyzed after every cycle is conducted.
Since the observation was done for observing the students’ activities and also the
teacher’s performance, the researcher analyzed the result of the observation
3.6.2.1 Students’ Learning Activities
In analyzing the data get from observing the students’ learning activities, the
researcher analyzed the problem that is faced in the cycle.
3.6.2.2 Teacher’s Teaching Performance
Meanwhile, in analyzing the data get from observing the teacher’s performance,
the researcher does the following steps:
1. Counting the total score
In this step, the researcher counts the sum of scores from all aspects. The aspects
that were scored cover the teacher’s activities in pre-activity, while-activity, and
post-activity.
2. Making a description from the data that have been analyzed.
It is similar to analyze the students’ activities, to analyze the teacher’s
performance the researcher also make a description from the collected data which
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
In reference to the result and discussion of the research, the researcher tried to
give conclusion and suggestion as follows:
5.1 Conclusion
Considering all data gathered from action research, the researcher has drawn up
some conclusion. They were as follow:
1. Dictogloss can be implemented to improve students’ listening skill. By activating
the students’ three basic schemata, i.e., linguistic, formal, and content schemata,
they can find key word of the text easily. Besides that, being dictated the text; the
students will find new vocabulary. Thus, they will have larger vocabularies which
help them reconstruct the text. in the first cycle, standard Dictogloss is
implemented, then in the second it is changed into summary Dictogloss. It can be
seen that the use of Dictogloss depends on the student’s condition. In this
research, it is proved that summary Dictogloss can improve the students’ listening
skill. Being given a flowchart in the preparation stage of summary Dictogloss, the
students can find key word easily. As a result, they can reconstruct the text well.
To sum up, Dictogloss is considered as a helpful technique that can be used in the
highly exposure of reconstructing text activity which foster the students to grasp
2. Being given the implementation of standard and summary Dictogloss, the students
become more active. In standard Dictogloss they work in pair. As well as that in
standard Dictogloss, in summary Dictogloss, the students are seated in group.
They discuss about reconstruction in their group work. It is deeply shown in the
students’ observation sheets that there are no more problems found during
listening class while the researcher explaining the material. They respond to the
topic well. They can also reconstruct the text from each key word that they have
got from the dictation. In short, Dictogloss also emphasize integratively on the
language skill containing, listening (to the teacher’s reading the text and to
groupmates’ discussing the reconstruction), speaking (during group
reconstruction), reading (in analyzing the reconstruction and in the students’ own
reconstruction), and writing (the reconstruction) which make the students become
more active.
3. Dictogloss contributes a positive effect toward teacher’s teaching performance. It
is showed while the researcher was doing an apperception. She activates the
students’ three basic schemata, i.e., linguistic, formal, and content schemata.
Moreover, in mastering the learning material, the researcher also correlate the
material with other relevant knowledge since in activating the students’ schema
the teacher is asked to be able to relate materials in the classroom with the
students’ real world situation. It is proved when the researcher correlated the text
about snow white to kinds of season. So, the teacher will try to make creative idea
5.2 Suggestion
Based on the conclusions above, the following recommendations were put: 1. For teachers in general and particularly those in SMA Negeri 1 Natar who want to
improve learning product, especially students’ listening achievement, by the
implementation of Dictogloss it is expected that the students are able to construct
their knowledge (entry behavior) based on the students’ real world situation
before going deeper to the materials. Besides, the teachers should be able to create
the interesting materials, of course, based on real situation since it will help the
students easily make a connection between the materials being taught with their
previous knowledge.
2. The researcher may ask the students to bring the dictionary in order that they can
directly check their mistake of diction and spelling and they will not depend too
much on the teacher and their friends in getting information or meaning of words.
The students will be independent and can get more knowledge.
3. In improving students’ activity in teaching and learning process, it is suggested
for the teachers to know well each student’s ability in the classroom because it is
very useful for dividing students in learning community. Additionally, in
correcting students’ error, it is better for the teacher to use peer correction first
than direct correction because some students are afraid of making mistake.
Besides, the interaction will be more active through peer correction.
4. The kinds of dictogloss are used based on students’ condition. In this research, the
second dictogloss is better than first dictogloss. They have their own strength. In
using the first dictogloss, it is better for the teacher more activated students’
schemata so the students will be easy to find key word. The use kind of aid like
students are reconstructing the text. So, the first kind of dictogloss can be
implemented well in listening class.
5. The teacher should motivate students to be active in the classroom by giving them
activities, interesting media, and materials which are related to the students’ real
world situation that can stimulate their interaction during teaching and learning