vi ABSTRACT
Nugroho, Asep. (2014). Motivation in Learning English and Attitudes Towards Learnin English: A Survey Study. Yogyakarta: English Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Motivation and attitudes are two important factors influencing success or failure in learning English as a foreign language. For senior high school students, the ability of using English will let the students achieve the basic competence of English subject, pass the final examination, and pass the university entrance examination or any other needs that the students have to fulfill. The current study is aimed at investigating the motivation orientations (instrumental and integrative) of the 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok Sleman and their attitudes towards learning English.
There are two research problems stated in this study: (1) What kind of motivation do the 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok have in learning English (2) What is the attitude of the 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok towards learning English?
A survey study was conducted to find out the answers to the research questions. There are two research instruments used in this study, questionnaire and interview. The researcher adapted the questionnaire from the five-point scale format
of Gardner’s Attitude/Motivation Test Battery. The researcher distributed the questionnaire to 3 classes from academic year 2013-2014 in SMK N 1 Depok and only 10 students were involved in the interview.
The quantitative data of the questionnaires were analyzed in terms of frequencies, means, and standard deviation. The research findings show that the 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok are both instrumentally and integrativelly motivated in learning English, but their instrumental motivation outdid their integrative motivation. In reference to the students’ attitudes towards learning English, the results of the study reveal that the 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok Sleman has positive attitudes towards learning English and English-speaking culture and its people.
The findings of this study can help the designers to develop programs and design syllabi and create interesting textbooks which encourage and maintain
students’ interest. Furthermore designers can create an interesting lesson plans by the help of different strategies, techniques, procedures in which the students’ attention is gained.
Key words: motivation, attitudes, 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok
vii ABSTRAK
Nugroho, Asep. (2014). Motivation in Learning English and Attitudes Towards Learnin English: A Survey Study. Yogyakarta: English Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Motivasi dan sikap adalah dua faktor penting yang mempengaruhi keberhasilan atau kegagalan dalam belajar bahasa Inggris sebagai bahasa asing. Untuk siswa SMA , kemampuan menggunakan bahasa Inggris akan membantu siswa mencapai kompetensi dasar mata pelajaran bahasa Inggris, melewati ujian akhir , dan lulus ujian masuk universitas atau kebutuhan lain yang harus mereka penuhi. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menyelidiki orientasi motivasi ( instrumental dan integratif ) siswa kelas 1 SMK N 1 Depok Sleman dan sikap mereka terhadap pembelajaran bahasa Inggris .
Ada dua rumusan masalah dalam penelitian ini : ( 1 ) Apakah siswa kelas 1 SMK N 1 Depok termotivasi instrumental atau integratif terhadap pembelajaran bahasa Inggris? ( 2 ) Bagaimana sikap siswa kelas 1 SMK N 1 Depok terhadap pembelajaran bahasa Inggris?
Sebuah penelitian survey dilakukan untuk mengetahui jawaban rumusan masalah diatas. Ada dua instrumen penelitian yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini , kuesioner dan wawancara . Peneliti mengadaptasi kuesioner dari Gardner (seperangkat tes baterai untuk mengukur Sikap / Motivasi) dalam bentuk skala 5 poin. Peneliti menyebarkan kuesioner ke 3 kelas tahun akademik 2013-2014 di SMK N 1 Depok dan hanya 10 siswa yang terlibat dalam wawancara .
Data kuantitatif dari kuesioner dianalisis dalam bentuk frekuensi, mean, dan standar deviasi. Temuan penelitian menunjukkan bahwa siswa kelas 1 SMK N 1 Depok termotivasi secara instrumental dan integratif dalam belajar bahasa Inggris , tapi motivasi instrumental mereka mengalahkan motivasi integratif mereka. Berdasarkan hasil penelitian untuk sikap siswa terhadap pembelajaran bahasa Inggris , hasil studi ini menunjukkan bahwa siswa kelas 1 SMK N 1 Depok Sleman memiliki sikap positif terhadap belajar bahasa Inggris dan orang yang berbahasa Inggris serta budaya mereka.
Hasil dari penelitian ini dapat membantu para desainer materi untuk mengembangkan desain program dan silabus dan membuat buku yang dapat mendorong dan mempertahankan motivasi siswa. Selanjutnya desainer dapat membuat rencana pembelajaran yang menarik dengan berbagai strategi , teknik , prosedur dimana siswa mempunyai ketertarikan didalamnya.
MOTIVATION IN LEARNING ENGLISH AND ATTITUDES
TOWARDS LEARNING ENGLISH:
A SURVEY STUDY
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By Asep Nugroho
Student Number: 071214153
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
2014
iii
A Sarjana Pendidikan Thesis on
iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work
or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the
v
LEMBAR PERYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH
UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama : Asep Nugroho Nomor Mahasiswa : 071214153
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
Motivation in Learning English and Attitude towards English Learning:
A Survey Study
Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikannya secara terbatas, mempubikasikannya di internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian surat pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
vi ABSTRACT
Nugroho, Asep. (2014). Motivation in Learning English and Attitudes Towards Learnin English: A Survey Study. Yogyakarta: English Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Motivation and attitudes are two important factors influencing success or failure in learning English as a foreign language. For senior high school students, the ability of using English will let the students achieve the basic competence of English subject, pass the final examination, and pass the university entrance examination or any other needs that the students have to fulfill. The current study is aimed at investigating the motivation orientations (instrumental and integrative) of the 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok Sleman and their attitudes towards learning English.
There are two research problems stated in this study: (1) What kind of motivation do the 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok have in learning English (2) What is the attitude of the 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok towards learning English?
A survey study was conducted to find out the answers to the research questions. There are two research instruments used in this study, questionnaire and interview. The researcher adapted the questionnaire from the five-point scale format
of Gardner’s Attitude/Motivation Test Battery. The researcher distributed the questionnaire to 3 classes from academic year 2013-2014 in SMK N 1 Depok and only 10 students were involved in the interview.
The quantitative data of the questionnaires were analyzed in terms of frequencies, means, and standard deviation. The research findings show that the 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok are both instrumentally and integrativelly motivated in learning English, but their instrumental motivation outdid their integrative motivation. In reference to the students’ attitudes towards learning English, the results of the study reveal that the 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok Sleman has positive attitudes towards learning English and English-speaking culture and its people.
The findings of this study can help the designers to develop programs and design syllabi and create interesting textbooks which encourage and maintain
students’ interest. Furthermore designers can create an interesting lesson plans by the help of different strategies, techniques, procedures in which the students’ attention is gained.
vii ABSTRAK
Nugroho, Asep. (2014). Motivation in Learning English and Attitudes Towards Learnin English: A Survey Study. Yogyakarta: English Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Motivasi dan sikap adalah dua faktor penting yang mempengaruhi keberhasilan atau kegagalan dalam belajar bahasa Inggris sebagai bahasa asing. Untuk siswa SMA , kemampuan menggunakan bahasa Inggris akan membantu siswa mencapai kompetensi dasar mata pelajaran bahasa Inggris, melewati ujian akhir , dan lulus ujian masuk universitas atau kebutuhan lain yang harus mereka penuhi. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menyelidiki orientasi motivasi ( instrumental dan integratif ) siswa kelas 1 SMK N 1 Depok Sleman dan sikap mereka terhadap pembelajaran bahasa Inggris .
Ada dua rumusan masalah dalam penelitian ini : ( 1 ) Apakah siswa kelas 1 SMK N 1 Depok termotivasi instrumental atau integratif terhadap pembelajaran bahasa Inggris? ( 2 ) Bagaimana sikap siswa kelas 1 SMK N 1 Depok terhadap pembelajaran bahasa Inggris?
Sebuah penelitian survey dilakukan untuk mengetahui jawaban rumusan masalah diatas. Ada dua instrumen penelitian yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini , kuesioner dan wawancara . Peneliti mengadaptasi kuesioner dari Gardner (seperangkat tes baterai untuk mengukur Sikap / Motivasi) dalam bentuk skala 5 poin. Peneliti menyebarkan kuesioner ke 3 kelas tahun akademik 2013-2014 di SMK N 1 Depok dan hanya 10 siswa yang terlibat dalam wawancara .
Data kuantitatif dari kuesioner dianalisis dalam bentuk frekuensi, mean, dan standar deviasi. Temuan penelitian menunjukkan bahwa siswa kelas 1 SMK N 1 Depok termotivasi secara instrumental dan integratif dalam belajar bahasa Inggris , tapi motivasi instrumental mereka mengalahkan motivasi integratif mereka. Berdasarkan hasil penelitian untuk sikap siswa terhadap pembelajaran bahasa Inggris , hasil studi ini menunjukkan bahwa siswa kelas 1 SMK N 1 Depok Sleman memiliki sikap positif terhadap belajar bahasa Inggris dan orang yang berbahasa Inggris serta budaya mereka.
Hasil dari penelitian ini dapat membantu para desainer materi untuk mengembangkan desain program dan silabus dan membuat buku yang dapat mendorong dan mempertahankan motivasi siswa. Selanjutnya desainer dapat membuat rencana pembelajaran yang menarik dengan berbagai strategi , teknik , prosedur dimana siswa mempunyai ketertarikan didalamnya.
Kata kunci: motivation, attitudes, 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok
viii
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
First of all, I would like to thank my Lord who always accompanied me
and gave me strength in writing and finishing this thesis. I really believed that I
would not finish this thesis without His blessings He has bestowed upon me.
I am deeply indebted to Miss Veronica Triprihatmini, S.Pd., M.Hum.,
M.A. for patiently gave me guidance, suggestions, corrections and encouragement
during the completion of my thesis. My deepest appreciation goes to all lecturers
of the English Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, who had
given me knowledge and guidance during my study in the university.
My sincere gratitude goes to Drs. Eka Setiadi, M.P.d the headmaster of
SMK N 1 Depok Sleman who granted me permission to conduct the research and
collect the data needed to this study. I thank the 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok Sleman for their willingness to be the subject participants of this study.
My greatest gratitude goes to my great parents, Ahmad Dias Pairan and
Mariyam, who never lose faith in me and keep supporting me with their endless
prayer and love. I would like to extend my deepest gratitude to my best friends
Wahyu, Topan and Amri for sharing their love, tears, blood, and everything.
My sincere gratitude also goes to Harry Yudha for being such a good
friend to me and teaches me the meaning of live and to love my Lord more. Many
thanks go to my great friends Hening, Seto, Wendy, Bretya, Bre, Yusak, Asti,
ix
I am very grateful to all staff and all of the lecturers of Program Pasca
Sarjana Universitas Sanata Dharma. I Thank Mbak Dhita, Mbak Desy, Mbak
Lely, Pakde Mul, Chacha, Pita, Diyan, and Lauren for being a great friend to me.
Asep Nugroho
x
TITLE PAGE………... i
APPROVAL PAGES ………... ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY………...
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ……… iv
v
ABSTRACT ……… vi
ABSTRAK………. vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS……….. TABLE OF CONTENTS………. LIST OF TABLES ………... LIST OF FIGURES ………. LIST OF APPENDICES………..
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION
A.Research Background ……….…..
B.Research Problems ……….…...
C.Research Objectives……….….. D.Benefits of the Study……….…. E. Definitions of Terms………..…
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
A.Theoretical Description ………...
1. Motivation ...………. a. Goals ...………... b. Needs ...………...…….……… c. Beliefs about ability ...……… 2. Types of Motivation ... a. Instrumental Motivation ... b. Integrative Motivation ... 3. Attitudes ... 4. Students’ Motivation in Learning English ... B. Review of Related Study ... C.Theoretical Framework ...
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Research Method ………...…
B. Research Participants ...………... C.Research Instruments ...……… D.Data Gathering Technique ………. E. Data Analysis Technique ...……….... F. Research Procedure ...
xi
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
A.SMK N 1 Depok Students Motivation Towards English Language 1. Questionnaire Results ...… a. Domain 1: Degree of Instrumentality ...
b. Domain 2: Degree of Integrativeness ... 2. Interview Results ... a. Instrumental Reasons ... b. Integrative Reasons ...
B.SMK N 1 Depok Students’ Attitudes Towards Learning English
1. Questionnaire Results ... a. Domain 3: Attitudes Towards Learnign English ... 2. Interview Results ...
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS
A.Conclusions ………..
B. Recommendations ………
REFERENCES ……… APPENDICES ………. 27 27 27 28 31 33 34 35 38 38 38 41 44 44 47 48 50
xii
Tables Page
Table 2.1 Three different goal ………. 9
Table 4.2 Frequencies, Percentages, and Mean scores for items of Domain 1 …...
Table 4.3 Frequencies, Percentages, and Mean scores for items of Domain 2 …...
28
31
Table 4.4: Results of the students regarding language course needs ………... 33
xiii
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
Figure 2.1 Maslow’s hierarchy of needs………...………. 10
xiv
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix Page
A- Research Permission Letter ………. 50
B- Questionnaire …...
C- Questionnaire Result ………...
51
55
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, the researcher presents the research background, research
problems, research objectives, benefits of the study, and definition of terms
.
A. Research Background
The aim of teaching English is to enable students to communicate with other
people using the language
.
For senior high school students, the ability of usingEnglish will help them achieve the basic competence of English subject, pass the final
examination, and pass the university entrance examination
.
As mentioned earlier, English is an important subject for senior high school
students
.
This fact can be clearly seen as the researcher served a PPL in SMK N 1Depok. There were some students who failed to achieve an acceptable standard of
competence of the English subject
.
At that particular time, the researcher taught 2classes
.
The students in each class had various characteristics.
One class was verynoisy and the students did not seriously involve themselves in the teaching and
learning activities
.
Another class was really quiet that when the researcher gave themquestions, they kept silent and no one tried to answer the researcher’s questions
.
Thiswas either because they did not understand what was taught or they were simply
discouraged to make an effort to study English
.
The materials given to them were thematerials given in the very beginning of junior high school
.
The researcher was2
wondering why they were not seriously learning English, whereas English is one of
the final examination subjects for senior high school students
.
There are many factorswhich cause the students to fail to achieve certain competence in the English subject
.
One of them might be the students’ motivation towards the English subject
.
Learners’motivation has been widely accepted as the main factor which influences the rate of
success of foreign language learning. McDonough (1983, p
.
142) states that“motivation of the students is one of the most important factors influencing success
or failure in learning the language”
.
Another factor is students’ attitudes towardslearning English
.
Motivation in language learning is affected by the students’attitudes towards learning English
.
Gardner and Lambert (1972, p.
3) state that “thelearner motivation to learn is thought to be determined by his attitudes towards the
other group in particular and by his orientation towards the learning task itself”
.
Inaddition, Lifrieri (2005, p
.
14) states that “attitudes are necessary but insufficientindirect conditions for linguistic attainment
.
Only when paired up with motivationproper do attitudinal tendencies relate to the levels of student engagement in language
learning, and to attainment”
.
Moreover, mastering English, at least passively, will beone of the requirements to apply for a job
.
People learn English with their different motivation of learning, most of them
3
problem occurs when the teacher tries to make an interaction with the students using
the target language, but there are no responses from the students
.
They usually tend tokeep silent, speak softly and unclearly
.
It seems that they are afraid to speak or shyabout saying something since they are not confident of their ability or afraid of
making mistakes
.
Commonly, during a teaching and learning process, students have alot of questions in their mind but they have a hard time to express it in a target
language
.
In another case, the students are busy with themselves when they are notinterested in a certain subject
.
The class becomes very noisy and it is hard for theteacher to control this kind of class
.
Given the importance of identifying learners’ motivation and attitudes towards
learning the English language, the researcher conducted a study to investigate the
SMK N 1 Depok students’ motivation and attitudes towards learning English
.
B. Research Problems
In this study, the researcher intends to find out the answer of the following
research questions:
1. What kind of motivation do the 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok have in learning English?
2. What is the attitude of the 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok towards learning English?
4
C. Research Objectives
As this study is intended to find out the answers to the questions mentioned
earlier in research problems, two research objectives are:
1. To determine what kind of motivation do the 1st grade students of SMK N 1
Depok have in learning English
.
2. To determine what kind of attitude do SMK N 1 Depok students’ have
towards learning English
.
D. Benefits of the study
Gardner and Lambert (1972, p.85) stated that a better understanding of
students' motivation and attitudes may assist ESL/EFL curriculum and instruction
designers to devise language teaching programs that generate the attitudes and
motivation most conducive to the production of more successful ESL/EFL learners.
Additionally, Midraj (2008, p.118) states that a better understanding of students’
motivation and attitudes can help material researchers create and teachers select
activities and tasks that tap students' motivation and attitudes.
For other researchers, hopefully the results of this study can provide them
useful with information for their own study related to this topic
.
They can provide a5
E. Definition of Terms
This section is to define the important terms used in this research
.
It will avoidmisunderstanding about the terms which are used in this study
.
1. Motivation
According to Dornyei and Otto (1998, p.65), motivation can be defined as the
dynamically changing cumulative arousal in a person that initiates, directs,
coordinates, amplifies, terminates, and evaluates the cognitive and motor processes
where by initial wishes and desires are selected, prioritized, operationalized and
(successfully or unsuccessfully) acted out.
Student’s motivation naturally has to do with students' desire to participate in
the learning process (Lumsden, 2009)
.
The students may have their own motivation,and the sources of their motivation may be different from each other
.
Motivation is acrucial factor in learning process
.
In this study, student’s motivation refers to theparticipation of the students while learning English; whether the students of 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok Yogyakarta participate well in the learning process or
not
.
2. Attitude
Gardner (1980, p
.
267), defines the term attitude as "an inference which ismade on the basis of a complex of beliefs about the attitude object"
.
While Ajzan(1988, p
.
4) considers attitudes as “a disposition to respond favorably or unfavorably6
to an object, person, institution, or event”
.
In this study, the attitudes of the studentwould be categorized as positive or negative based on their answer in the
7
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
The discussion of this chapter is divided into three sub-topics
.
First is thetheoretical description which supports the research, the second is the review of
related studies and the last one is the theoretical framework of the research
.
Thefirst sub-topic explains the theories and concepts as the foundations of this
research to solve the problems in this research
.
The second sub-topic providessome studies with a similar topic related to this study. The third sub-topic
summarizes and synthesizes the main theories which the researcher uses to solve
the research problems
.
A. Theoretical Description
The following sub-topic explains the theories about motivation and
attitudes.
1. The Nature of Motivation
Woolfolk (1990, p.302) defines motivation as something which comes
from inside someone’s soul which arouses and directs behavior
.
While anotherpsychologist, Lumsden (1994, p.126) defines motivation as desire to participate or
get involved
.
Both of them are concerned in the involvement or noninvolvementand the desire of doing something to reach certain goals
.
People will energeticallyreach their goal if he or she is highly motivated
.
Woolfolk (1990, p.308) classifiesmotivation into two types: extrinsic motivation (instrumental motivation) and
intrinsic motivation (integrative motivation)
.
Extrinsic motivation is caused byexternal factors or outside rewards which have nothing to do with the learning
situation while Intrinsic Motivation is internal sources of motivation such as the
satisfaction of learning or accomplishment, Woolfolk (1990, p.303)
.
The teacherswould not need any incentives or punishment to make the students work if they
are intrinsically motivated
.
The willingness come from their own and they realizethat they will get something by learning
.
Besides Woolfolk’s extrinsic motivation (instrumental) and intrinsic
motivation (integrative), Cooper and Fishman (1977, p.210) add a type of
motivation named “developmental”
.
Developmental or personal motivation,according to them, refers to motivation relating to personal reason of satisfaction
.
This includes activities such as watching English-dub movies and reading books
in the English language
.
In this section, the researcher discusses the factors which might involve the
students actively in the learning activities
.
Woolfolk (1990, p.312) categorizesthose factors into three main factors
.
In this study, the 1st grade students of SMKN 1 Depok might also be influenced by these factors
.
a. Goals
Making a list of goals can be a starting point to look forward
.
As the goals9
and Johnson as cited in Woolfolk (1990, p.312), explain three different goal
structures
.
Table 2.1 Three different goals
Different Goal Structures
Cooperative Students belief they can reach their goal only if other
students will also reach the goal
.
Competitive Students belief they can reach their goal only if other
students do not reach the goal
Individualistic Students belief their own try to reach a goal is not related
to other students’ tries to reach the goals
.
According to Dweck as cited in Woolfolk(1990, p.313) there are two main
categories of goals, performance and learning
.
When the students are focus onhow they are judged by others, then the goals can be categorized as performance
goal
.
The students who have this paradigm of goal will try to look smart amongtheir friends; they do not want to look incompetent
.
On the other hand, learninggoal is the point to improve, no matter how many mistakes we make, the point is
we have to learn
.
People who have this paradigm of goal tend to see thechallenges and keep doing their best when encountering problems in learning
.
b. Needs
A feel of need can motivate someone to do something
.
The needs willdirectly influence the intrinsic motivation of someone in order to fulfill or satisfy
the needs they have
.
According to Kolesnik as cited in Woolfolk (1990, p.313) aneed can be defined as any type of deficiency in the human organism or the
absence of anything the person needs, or thinks that he need it, for his overall
well-being
.
People who are being motivated by their needs can be seen from theirmovement towards their needs and satisfy those needs
.
Abraham Maslow, as cited in Woolfolk (1990, p.314) sees human needs as
a hierarchy
.
The most essential needs of human being are survival and safety.
Once these needs are fulfilled, the next level of needs will emerge and stimulated
us to fulfill that next level of needs, social needs for belonging and love and needs
for self-esteem
.
When these needs are satisfied, once again, we come to the higherlevel of needs, self-actualization
.
Here is Maslow’s hierarchy of needs in form ofa figure
.
Figure 2.1 Maslow’s hierarchy of needs Self-actualization
Aesthetic appreciation: order, structure, beauty
Self-esteem: approval and recognition Intellectual achievement: understanding and exploring
Survival: food, water, shelter Safety: physical and psychological security
11
Maslow, as cited in Woolfolk (1990, p.314), has called four lower levels of
needs above (for survival, safety, belonging, and self-esteem) as deficiency needs
.
If these needs are not satisfied yet, the motivation to fulfill these needs is
increasing, while when these needs are satisfied, the motivation to fulfill them is
decreasing
.
For the three higher level of needs (intellectual achievement, aestheticappreciation, and self-actualization), Maslow has labeled them as being needs
.
When these being needs are fulfilled, the motivation does not cease. Instead, it
will increase to find further fulfillment of these needs
.
Unlike the deficiencyneeds, being needs can never be completely fulfilled
.
The motivation to achievebeing needs is always change
.
c. Beliefs about ability
According to Woolfolk (1990, p.320), belief about ability is one of the
most powerful attributions which affect motivation in school
.
There are two basicconcepts of ability, entity view of ability and incremental view of ability
.
Anentity view assumes that ability is a stable and uncontrollable trait
.
On the otherhand, incremental view suggests that ability is an unstable and controllable trait
.
Students who have an entity view of ability tend to set performance goals
and they usually look for situations where they can look smart among their
friends
.
In the other hand, students who have an incremental view of ability tendto set learning goals and seek situations where they can improve their skills
.
Intheir paradigm, improving their skills means getting smarter
.
They often set theirgoals in difficult goals level, so it will be boost their motivation to reach those
goals
.
As the theoretical factors are well-established, later it will be useful for the
researcher to achieve the objectives of this study
.
Specifically, those factors willenable the researcher to categorize the types of motivation the 1st grade students of
SMK N 1 Depok have
.
2. Types of Motivation
a. Instrumental Motivation
Gardner (1983, p205) defines instrumental motivation as “learning a
language because of someone else or less clearly perceived utility it might have
for the learner”. Wilkins (1972, p.184) assumes a learner is instrumentally
motivated when he or she wants to learn a language “in order to pass examination,
to use it in one’s job, to use it in holiday in the country, as a change of watching
television, because the educational system requires it”. With instrumental
motivation, the purpose of language learning is more utilitarian, such as meeting
the requirements for school, applying for a job, reading technical material.
b. Integrative Motivation
Gardner (1983, p.203) has explained and clarified what is meant by an
integrative motivation as “learning a language because the learner wishes to
identify himself with or become integrated into the society of target language”.
Additionally, Finnegan (1999, p.568) states that “a learner is integrativelly
13
of the culture and values of the foreign language group, to make contact with the
speaker of the language, to live in the country concerned”. Finnegan also believes
that students who like the people that speak a target language, admire the culture
and have desire to become familiar or even integrate into society in which the
target language is used are most successful in learning that target language. This
form of motivation known as integrative motivation, is believed by Finnegan to
underlies successful acquisition of a wide range of registers and a native like
pronunciation.
Therefore, identifying SMK N 1 Depok students’ motivation will be
related to the reason for which they learn the English language. In other words,
instrumental or integrative reasons will be considered as far as the students’
motivation is concerned. What is important is that the two orientations of
motivation are not mutually exclusive. Some learners learn better if they are
integrativelly oriented while others will be more successful if they are
instrumentally motivated and some learn better if they have both of those
motivations.
3. Attitude
Gardner (1985) defines attitudes as components of motivation in language
learning
.
Gardner states that “motivation refers to the combination of efforts plusdesire to achieve goal of learning the language plus favorable attitudes toward
learning the language”
.
A broader definition of attitudes is stated by Wenden(1991, p.114)
.
Wenden categorizes the term “attitudes” into three components,namely cognitive, affective and behavioral
.
Beliefs and ideas or opinions aboutthe object of the attitude construct the cognitive component
.
The affectivecomponent refers to the feeling and emotions one has towards an object, the
feeling of ‘likes’ or ‘dislikes’ or ‘with’ or ‘against’
.
The behavioral componentrefers to someone’s consisting actions or behavioral intentions towards the object
.
As cited in Gardner (1980, p
.
267), Likert (1932, p.
9) defines attitudes as“an inference which is made on the basis of a complex of beliefs about the attitude
object”
.
From Likert’s definition of attitude, Gardner elaborates it and definesattitude as “the sum total of a man instincts and feelings, prejudice or bias,
preconceived notions, fears, threats, and convictions about any specified topic”
.
While Ajzan (1988, p.4) considers attitudes as “disposition to respond favorably
or unfavorably to and object, person, institution, or event”
.
De Bot, Lowie and Verspoor (2005, p
.
72) who are concerned on themotivation and attitudes in language learning, agreed that a high motivation and
positive attitude towards language learning will help the language learning
process
.
The fact that motivation and attitude towards language learning may playa very crucial role leading to the question, how they could be measured
.
Gardnerand Lambert (1972) in Attitudes and Motivation in Second Language Learning
elaborate the theory in a brief
.
The motivation to learn is determined by theattitudes towards language learning
.
Gardner and Lambert categorize motivation15
in Social psychology and second language learning designed a test battery known
as Attitude and Motivation Test Battery (AMTB)
.
In Gardner’s AMTB, attitude islinked with motivation, a positive attitude increases motivation
.
Later, the descriptions of the attitude logical truths would be used to
analyze the attitudes of students of SMK N 1 Depok towards English language
learning
.
For instance, the definitions would help the researcher finding theanswer of the second research problem about the type of attitudes
.
4. Students’ Motivation in Learning English
Students’ motivation is the crucial thing of a successful teaching and
learning process
.
No matter which the teaching methods are applied in theclassroom, teachers have to make sure that the students are highly motivated, are
eager to learn and have good motivation to involve themselves in the learning
process
.
The motivation to learn comes from various reasons.
It can be assummedthat the students simply love the subject and interested in studying it or there can
be some other practical reasons, such as the students’ eagerness to learn English
so that they can fluently use it as one of the globalization era’s demands
.
Jere Brophy, as cited in Woolfolk (1990, p.328), describes student
motivation to learn as a student’s tendency to find academic activities
meaningful and worthwhile and try to derive the academic advantages from those
activities
.
When the students are motivated to learn, they will do their academicwork more seriously and try to do their best out of it
.
Motivation to learn is important for the students’ success
.
The sources ofmotivation are complex
.
The motivation to learn is personal and comes fromwithin an individual, yet it is influenced by some external factors
.
Frith (2001,p.3) defines motivation as the internal drive directing behavior towards some end
.
Frith also explains the components of the learning motivation into six
components, they are:
a. Curiosity
Human behavior is far more complex, and people are naturally curious
.
They tend to seek something new, they find satisfaction when they can finish a
puzzle, and they are curious about anything
.
Providing students with stimuliwhich are new but not too different from what they already know, will then
develop curiosity within the students
.
Ask the students a question which creates aproblem situation rather than presenting statements of fact
.
b. Self-efficiency
Dividing tasks into chunks and providing students with early success is a
method of developing confidence in the student
.
Drisscoll as cited in Frithdescribes this as performance accomplishments, one of four possible sources of
17
c. Attitude
Attitude is an illusive commodity
.
According to Frith, the attitude of astudent toward learning is very much an intrinsic characteristic and is not always
demonstrated through behavior
.
d. Need
The most well-known and respected classification of human need is
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs
.
Maslow categorizes the human needs into fivelevels, psychological (lower-level), safety (lower-level), love and belongings
(higher need), esteem (higher need), self-Actualization (higher need)
.
Theimportance of this to motivation is the lower-level needs must be satisfied at one
level before the next higher order of needs become predominant in influencing
behavior
.
e. Competence
Competence is an intrinsic motivation for learning which is highly related
to self-efficiency
.
Human being receive more pleasure when doing this well.
External support is important for the student to achieve competence, then the
achievement of competence will be the intrinsic motivation for the student
.
f. External Motivators
In order to create a stimulating environment and combat boredom, an
active participation from the students is needed
.
Therefore learning strategiesshould be flexible, creative, and constantly applied
.
Beside a stimulatingenvironment, grades also have a value as an external motivator
.
B. Review of Related Studies
Atef Saleh Al-Tamini and Munir Shuib was investigating the motivation
and attitudes of the students in learning English at Hadhramout University of
Sciences and Technology (HUST)
.
One of the research objectives of the studywas to investigate and identify the students’ attitudes towards learning English as
their language course for 2 semester in their first year
.
The research sampleconsisted of 81 students who studied in the academic year 2006-2007 in the
Department of Petroleum Engineering (DPE) at HUST
.
To collect the data, theyused questionnaires and interview
.
The result showed that most of the participantshad positive attitudes towards learning English language
.
There was a research conducted in Japan by Benson (1991) who surveyed
over 300 freshmen to investigate their motivation and attitudes towards learning
the English language
.
The results showed that integrative and personal sets of goalwere important factors in motivation among Japanese college students
.
Another study by Sarjit (1993) was carried out to investigate the language
needs of the consultants at a company
.
Learner’s motivation was the main concernin the study
.
The research participants consisted of 26 consultants, one instructorand four directors
.
To gather the data, the researcher used questionnaires,19
motivation was the main reason for learning the English language followed by
personal motivation
.
C. Theoretical Framework
From the discussion in theoretical description, the researcher establishes a
theoretical framework for this research
.
The researcher is concerned with alltheories about motivation
.
Indeed, people will do their best if they are highlymotivated to do something
.
Motivation is an important thing; to gain themotivation is to gain our own desire and our own willingness
.
Based on theresearcher’s experiences in teaching English classes, some students in those
classes tended to be passive and keep silent if the teacher asked them them about
something
.
Only few of them seemed actively involved in each activity given bythe teacher
.
In the theoretical description, from the theories the researcherelaborated motivation into two types, instrumental and integrative
.
The researcheralso elaborates other factors which might affect the motivation of the students of
SMK N 1 Depok Sleman
.
From the discussion of each part, the researcher is ableto design the research instrument to know what type of motivation that the
students of SMK N 1 Depok Sleman have
.
The theories about motivation are usedto answer the first research problem
.
The researcher also elaborates the theoriesabout attitudes towards learning English
.
Mostly, the theories about attitudetowards learning English talk about the types of attitudes and from the discussion
about the attitude theories, the researcher categorizes attitudes towards learning
English into two types, positive and negative
.
The theories about attitudes are21
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter deals with the methodology used in conducting this study
.
Itconsists of research method, research participants, research instruments, data
gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure
.
A. Research Method
This study was conducted to identify SMK N 1 Depok students’
motivational and attitudinal orientations in learning English language
.
To achievethe objective, two research instruments were used, questionnaire and interview
.
The research was conducted in a survey study and made use of quantitative and
qualitative data
.
To get the reliable data to analyze, the researcher had selected togain quantitative data from the questionnaire to be calculated precisely
.
On theother hand, the data from the interview was analyzed using a content analysis
method to get qualitative data
.
B. Research Participants
The research participants of this study were the 1st grade students of SMK
N 1 Depok Yogyakarta
.
The researcher decided the school as the research fieldbecause he had once practiced teaching there for 3 months. Thus the researcher
was quite familiar with the condition of the school
.
The target students’population in this study was all the 1st grade students who studied in the academic
year 2013-2014 in SMK N 1 Depok
.
A random sampling technique was employedby the researcher to select a representative sampling of the subjects in this study
.
There were six classes, each class had 32 students, and the researcher was
randomly selected 3 classes
.
Meanwhile, only 10 students were involved in theinterview
.
The students were selected based on their response to the questionnairein section B
.
In section B of the questionnaire, the students were asked to answera question on whether or not they were interested in attending more English
language training courses to improve their English proficiency
.
10 students whoseresponses were “yes” were selected randomly as interviewee.
C. Research Instruments
The primary instrument used in this study was a questionnaire
.
Thequestionnaire was translated into Indonesian
.
It consisted of three sections: A, Band C
.
In section A, the questionnaire collected the students’ basic information.
Section B consists of two parts which included questions to identify the students’
motivation to learn English language
.
The researcher adapted the questions fromintegrative and instrumental orientation scales of the five-point scale format of
Gardner’s Attitude/Motivation Test Battery (Gardner, 1985), ranging from
‘strongly disagree’ to ‘stronglyagree’
.
It might be worth indicating that Gardner’sinstrumental and integrative types of motivation were adopted because such a
clasification offers “an impetus to the study of languages attitudes and motivation
23
Test Battery (AMTB) is also reported to have good reliability and validity
(Gardner, 1985)
In section B of the questionnaire, the students were asked to answer a
question on whether or not they were interested in attending more English
language training courses to improve their English proficiency
.
The items ofGardner’s AMTB were integrative orientation (item number 1-4) and instrumental
orientation (item number 5-8)
.
Section C of the questionnaire was developed to elicit information
regarding the students’ attitudes towards the English language
.
In this section, thestudents were given ten statements. They were asked to specify their responses to
those statements by using the five-point scale format of Gardner’s
Attitude/Motivation Test Battery, ranging from strongly disagree to strongly
agree
.
It might be worth mentioning that the researcher modified some statementsinto positive (item number 1, 2, 5, 8, 9) and negative (item number 3, 4, 6, 7, 10)
.
Another instrument was in a form of interview. The interview was used to
gain data to cross-validate the students’ responses to the questionnaire
.
Thestudents were asked questions related to their motivation and attitude towards the
English language
.
The questions were: their reasons for learning English, theirinterest to attend English courses, and their attitudes towards the English language
and towards the culture of English speaking world
.
D. Data Gathering Technique
As explained before, this research deals with two major problems
.
Tosolve those problems, this study would gather the data with the following
technique
.
The researcher started to conduct this study at SMK N 1 Depok
Yogyakarta
.
Before distributing the questionnaire, a permission letter to conductthis study was sent to the authorized department at SMK N 1 Depok
.
The studentswere informed about the objectives and the significance of this study when the
researcher distributed the questionnaire
.
They were also asked to state their veryhonest responses and answers
.
The researcher also asked the students if theyneeded any clarifications, they could ask the researcher
.
After the studentsfinished filling out the questionnaire, they were requested to recheck their
responses for incompleteness or missing answers
.
To conduct the interview session, the researcher selected 10 students as
interviewees
.
As explained earlier, those 10 students were selected based on theirresponses to the questionnaire in section B
.
In section B of the questionnaire, thestudents were asked to answer a question on whether or not they were interested
in attending more English language training courses to improve their English
proficiency
.
The 10 students who responded the question by “yes” were selected25
would be treated with complete confidentiality
.
To record the interviewees, theresearcher used a digital voice recorder and a notebook
.
E. Data Analysis Technique
The data collected in the present study was of two types, quantitative and
qualitative
.
The quantitative data of the questionnaires were analyzed in terms offrequencies, means, and standard deviation
.
Frequency shows the number of times an event occurs
.
In this study,frequency was used to analyze how many times a certain item in the instrument
was answered by “strongly agree” or “strongly disagree”
.
The sum of thefrequency would be used to help the researcher answer the research problems
.
Mean also known as average is obtained by dividing the total (sum) of
observed values by the number of observations
.
To calculate mean, the researcheruse this formula:
Later, the mean would be used to calculate the standard deviation
.
A low standarddeviation indicates that the data points tend to be close to the mean, while a high
standard deviation indicates that the data is spread out over large range of values
.
To calculate standard deviation, the researcher used this formula:
For analyzing the qualitative part of the data, a content analysis method
was used
.
In the analysis process, the interviewees’ responses to each questionwere firstly translated into English and then transcribed
.
After that, the responseswere analyzed in terms of themes related to the study objectives
.
F. Research Procedure
This research would be conducted through several steps
.
Beforeadministering the questionnaire to the respondents, the researcher would obtain a
permission letter
.
The letter was used to get permission to do a research in SMKN Depok 1 Sleman
.
The researcher also consulted with the teachers at the schoolabout the research
.
Before distributing the instrument to the subject research, theresearcher tried the instrument out to a sample group of people
.
The researcheralso revised the instrument if there was a mistake during the try out
.
The next stepwas distributing the questionnaires to the sample group and analyzing the data
obtained from the questionnaires which applies calculation as explained earlier
.
After analyzing the data, the researcher would obtain information which can be
27
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter deals with the presentation and discussion of the research
findings which provides answers to the research questions in the problem
formulation stated in chapter I
.
There are two research questions to be answered,first is whether the students of SMK N 1 Depok are motivated instrumentally or
integratively in learning English and second is what the attitudes of the 1st grade
students of SMK N 1 Depok towards learning English are
.
This chapter is dividedinto two parts, namely, SMK N Depok Students’ Motivation Towards Learning
English and SMK N Depok Students Attitudes Towards Learning English
.
Thefirst part of this chapter discusses the results and discussion of the questionnaire
and interview for domain 1: Degree of Instrumentality and domain 2: Degree of
Integrativeness, meanwhile, the second part of this chapter discusses the results
and discussion of questionnaire and interview for domain 3: Attitudes Towards
Learning English
.
A. SMK N 1 Depok Students’ Motivation in Learning English
1. Questionnaire Results
To identify the students’ motivation in learning English, the participants
were asked to answer the questionnaire adapted from Gardner’s Attitude and
Motivation Test Battery (AMTB)
.
In this part, the researcher used 2 domains:degree of instrumentality and degree of integrativeness
.
Originally, Gardner’s AMTB has 12 domains; for the purpose of this
study, the researcher only used 3 domains
.
The data will be prensented in terms ofthe distribution of frequencies/percentages and the total means value for each
domain
.
The means are simply the average calculation of the responses with 1point assigned for “strongly disagree”, 2 for “disagree”, 3for “do not know”, 4 for
“agree”, 5 for “strongly agree”
.
In this part, the researcher presents the results anddiscussion of the questionnaire on domain 1 and 2
.
[image:44.595.103.540.211.728.2]a. Domain 1: Degree of Instrumentality
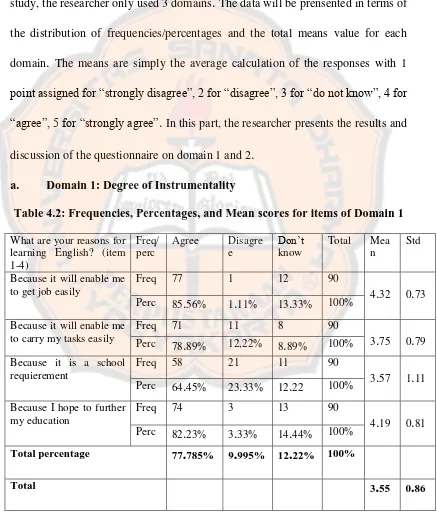
Table 4.2: Frequencies, Percentages, and Mean scores for items of Domain 1
What are your reasons for learning English? (item 1-4)
Freq/ perc
Agree Disagre e
Don’t know
Total Mea n
Std
Because it will enable me to get job easily
Freq 77 1 12 90
4
.
32 0.
73 Perc 85.
56% 1.
11% 13.
33% 100%Because it will enable me to carry my tasks easily
Freq 71 11 8 90
3
.
75 0.
79 Perc 78.
89% 12,22% 8.
89% 100%Because it is a school requierement
Freq 58 21 11 90
3
.
57 1.
11 Perc 64.
45% 23.
33% 12.
22 100%Because I hope to further my education
Freq 74 3 13 90
4
.
19 0.
81 Perc 82.
23% 3.
33% 14.
44% 100%Total percentage 77.785% 9.995% 12.22% 100%
29
Table 4.2 illustrates that 77
.
7 % of the participants are instrumentallymotivated
.
Questionnaire item number 1 which receives the highest mean score4
.
32 and percetage 85.
56 % reveals that the great majority of 1st grade students ofSMK N 1 Depok Sleman learned English because it would enable them to get job
easily, while 82
.
23% of 1st grade students of SMK N 1 Depok Sleman learnedEnglish to further their education, and 78
.
89 of the participants learned Englishbecause it helps them to carry out their tasks more efficiently
.
In brief, the totalmean score (3
.
55) indicates that the largest number of 1st grade students of SMKN 1 Depok Sleman learned English for instrumental reasons such as getting a job
easily, to further their education, and carry out tasks more efficiently, while item
number 3 shows more than 64
.
45 % learned English because it is a schoolrequirement
.
The findings show that the students demonstrated greater emphasis on
instrumental reasons for learning the English language including utilitarian (e
.
g.
enable me to get job easily) and academic reasons (e
.
g.
enable me to carry mytasks more efficiently, it is a school requirement and to further my education)
.
Thestudents see the idea that English is playing a vital role in their recent or future
lives
.
This finding is consistent with Woolfolk’s (1990: 312) view pertaining tothe need factor that can motivate students to learn
.
The needs will directlyinfluence the instrumental motivation of the students in order to fulfill the needs
that they have
.
Gardner defines instrumental motivation as “learning a language [image:45.595.98.517.229.560.2]because of someone else or less clearly perceived utility it might have for the
learner (Gardner, 1983, p
.
203)”.
In other words, a learner is instrumentallymotivated when he/she wants to learn language “in order to pass examination, to
use it in one’s job, because the educational system requires it” (Willkins, 1972, p
.
184)
.
In this case, the students’ needs are in the context of utilitarian andacademic needs
.
For the utilitarian (e.
g.
enable me to get job easily) matter, thestudents of SMK N 1 Depok agreed that it will be their advantages if they are
mastering English language since some job requires the applicant to meet certain
level of English mastery (measured by the TOEFL score)
.
For the academicreasons (e
.
g.
enable me to carry my tasks more efficiently, it is a schoolrequirement and to further my education) the students of SMK N 1 Depok assume
that mastering English will let them to do better for their education
.
English hasbecome the international language of science and technology; students SMK N 1
Depok have to face this fact since some of their learning sources (books, internet
articles, etc
.
) are written in English.
English subject has become one of the mainsubjects in National Examination, the need to pass this examination also play
important role for their motivation in learning English language
.
The studentsconsider this as school requirement that they should accomplish
.
The students ofSMK N 1 Depok also want to further their education by entering the university
31
subjects; indeed this will lead the students to be motivated in learning the English
language
.
[image:47.595.104.554.220.582.2]b. Domain 2: Degree of Integrativeness
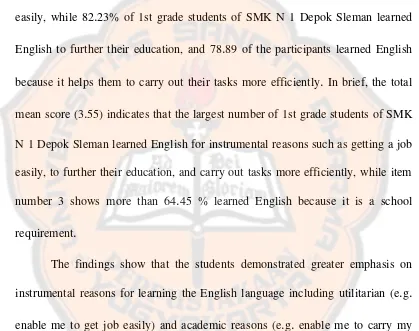
Table 4.3: Frequencies, Percentages, and Mean scores for items of Domain 2
As shown in table 4.3, 74
.
36 % with a total mean score 3.
85 of theparticipants are integratively motivated and thought that English is an important
language
.
Item number 5 receives the highest percentage 94.
44 % with a highestmean score 4
.
36 of the students who said that studying English is importantbecause it will allow them to speak, communicate, and interact more easily with
speaker of English, whereas 76
.
67 % agreed with the idea that if Indonesia had noItem number 5-8 Freq
/perc
Agree Disagre e
Don’t know
Total Mea n
Std
Studying English is important because it will allow me to be more at ease with people who speak English
Freq 85 0 5 90
4
.
36 0.
57 Perc 94.
44% 0% 5.
56% 100%Studying English is important because it will allow me to meet and converse with more and varied people
Freq 61 15 14 90
3
.
69 0.
98 Perc 67.
77% 16.
67% 15.
56% 100%If Indonesia had no contact with English-Speaking countries, it would be a great lost
Freq 69 10 11 90
3
.
97 0.
97 Perc 76.
67% 11.
11% 12.
22 100%Studying English is important because it makes me look smarter than others
.
Freq 53 22 15 90
3
.
39 1.
19 Perc 58.
89% 24.
44% 16.
67% 100%Total percentage 74.365
% 13.055 % 12.502 % 100%
Total 3.85 0.92
contact, it would be a great loss
.
While 67.
77 % of the sample agreed thatstudying English is important, it will allow them to meet and converse with more
and varied people
.
Item number 8 receives the lowest percentage 58.
89 % with alowest mean score 3
.
39 of the students who said that studying English isimportant because it made them look smarter than others
.
The results show that most of the SMK N 1 Depok students learned
English for their needs of communication to the English speaker
.
Gardner (1983,p
.
203) has explained and clarified what is meant by an integrative motivation as“learning a language because the learner wishes to identify himself with or
become integrated into the society of the target language”
.
In other words, alearner is integratively motivated when he/she learns a language because he/she
wants to “know more of the culture and values of the foreign language group…to
make contact with the speakers of the languages…to live in the country
concerned
.
It is believed that the students who are more successful when learninga target language are those who like the people that speak the language, admire
the culture and have desire to become familiar with or even integrate into society
in which the language is used”, Finegan (1999, p
.
568).
The result of questionnaireitem number 8 goes in line with the study proposed by Woolfolk (1990: 320)
about the entity view of ability. Students who have an entity view of ability tend to
set performance goals and they usually look for situation where they can look
33
view of ability tend to set learning goals and seek situations where they can
improve their skills
.
Given the participants’ reasons to learn the English language, these
participants were further asked to specify their own opinions to the idea of
attending more English language training courses that would help improve their
English proficiency
.
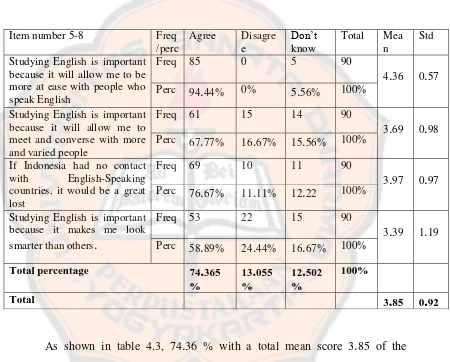
The results in the table 4.4 below indicate that 80 % of them [image:49.595.102.515.229.535.2]responded positively
.
Table 4.4: Results of the students regarding language course needs
Question Yes No Total
n % n % n %
Would you like to attend more English
language courses?
72 80 18 20 90 100
The most reasonable explanation for this might be that the students lacked
the language skills that would enable them to function effectively in their
academic activity
.
Having great desires for learning the language is considered tobe one of the main components of language learning motivation (Gardner, 2006)
.
2. Interview Results
The interview was used to gain data to cross-validate the students’
responses to the questionnaire
.
As explained before, 10 students were selectedrandomly as interviewee based on their response in the section B of the
questionnaire
.
For the sake of confidentiality, the researcher named those 10students by “student 1-10” instead of mention them with their real name
.
Thestudents were asked questions related to their motivation towards learning
English
.
The questions are: 1) their reasons for learning English and 2) theirinterest to attend English courses
.
a. Instrumental reasons
Consistent with the questionnaire results, the majority of the interviewees
agreed that their motivation arises from “more functional or external needs, such
as the need to pass examinations, or posibly, career opportunities” (Skehan, 1989,
p
.
50).
In other words, instrumental motivation is considered as the primary sourceof SMK N 1 Depok Students’ motivation towards learning English
.
Here aresome direct quotes from the interviewees that illustrate those reasons:
Student 8: “because I want to pass the final examination, we all know that English will be one of the main subject in the final examination”
Student 4: “because I want to pass the national examination and I want to go to college I dream about”
Both student 8 and student 4 mentioned about passing the final
examination
.
Moreover, student 4 also mentioned about her willingness to enterthe university that she wants
.
From the two statements above, the instrumentalmotivation arises from academic reason; the need to pass the examination and to
35
arouses their motivation into somehow becomes instrumental motivation for
academic reason
.
Student 3: “because it will be a consideration when I apply a job later” Student 10: “because when I apply a job later, the possibility to get the job will be higher if I master the English language”
Those statements above clearly show us that these students’ motivation
arises from the utilitarian need, which is to get job easily
.
Indeed, masteringEngl