xvii ABSTRACT
Jatiningsih, Arum. 2008. Multiple Intelligences Based Integrated Materials for an Extracurricular Activity for the Fifth Grade Students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
There are two main reasons why the writer conducted this study. The first reason is in the English extracurricular activity, the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School are given monotonous activities which most of the activities only develop students’ linguistic intelligence. The second reason is the need of a set of English instructional materials for the extracurricular activity for fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School that can develop students’ multiple intelligences.
There were two problems formulated in this study. They were: 1) How is a set of Multiple Intelligences based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity for the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School designed? 2) What does the design a set of Multiple Intelligences based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity for the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School look like?
The writer applied Research and Development method in this study. In order to answer the first problem, the writer designed a set of instructional materials by combining Kemp’s and Yalden’s models. The steps were: 1) conducting needs survey, 2) stating the goals, topics and general purposes, 3) formulating the learning objectives, 4) developing the syllabus, 5) specifying the subject contents, 6) determining the teaching learning activities, resources and intelligences being developed, 7) evaluating the designed materials. To answer the second problem, the writer designed the materials. The designed materials consisted of eight units. Each unit was divided into three main parts, namely:Start to Think, What Should You Do? and Do it Again. Start to Think was the pre-activity. What Should You Do? was the main activity. Do it Again was the post activity. Each unit developed various intelligences. Nevertheless, the distribution of the intelligences that were developed in each unit was different, it depended on the topic. They were 4 up to 7 intelligences that were developed in each unit. Although the distribution of the intelligences was different in each unit, the designed materials had covered eight intelligences.
The preliminary field testing showed that the total mean for the designed materials is 4.06. It meant that the designed materials were good and acceptable.
xviii ABSTRAK
Jatiningsih, Arum. 2008. Multiple Intelligences Based Integrated Materials for an Extracurricular Activity for the Fifth Grade Students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Ada dua alasan utama mengapa penulis melakukan penelitian ini. Alasan pertama adalah dalam kegiatan ekstrakurikuler bahasa Inggri, siswa kelas lima SD Kanisius Kalasan diberikan kegitan yang monoton dimana sebagian besar kegiatannya hanya dapat mengembangkan kecerdasan linguistik. Alasan kedua adalah kebutuhan satu set materi pembelajaran untuk kegiatan ekstrakurikuler bahasa Inggris siswa kelas lima SD Kanisius Kalasan yang dapat mengembangkan kecerdasan majemuk siswa.
Ada dua permasalahan yang diformulasikan dalam studi ini. Permasalahan tersebut yaitu: 1) Bagaimana satu set materi terpadu untuk kegiatan ekstrakurikuler kelas lima SD Kanisius Kalasan yang berdasarkan Kecerdasaan Majemuk di desain? 2) Seperti apakah penyajian satu set materi terpadu untuk kegiatan ekstrakurikuler kelas lima SD Kanisius Kalasan yang berdasarkan Kecerdasan Majemuk tersebut?.
Penulis menerapkan metode Riset dan Pengembangan dalam studi ini. Untuk menjawab permasalahan yang pertama, penulis mendesain materi dengan mengkombinasikan model Kemp dan Yalden. Langkah-langkahnya: 1) mengadakan survey kebutuhan siswa, 2) menentukan sasaran, topik, dan tujuan umum 3) merumuskan indikator, 4) mengembangkan silabus, 5) menspesifikkan subjek isi, 6) menentukan aktifitas belajar mengajar, sumber dan kecerdasan yang dikembangkan, 7) evaluasi materi. Untuk menjawab permasalahan yang kedua, penulis mendesain materinya. Materi yang didesain terdiri dari delapan unit. Setiap unit dibagi dalam tiga bagian utama, yaituStart to Think, What Should You Do? dan Do it Again.Start to Think adalah aktifitas pembuka. What Should You Do? adalah aktifitas utama. Do it Again adalah aktifitas penutup. Setiap unit mengembangkan berbagai macam kecerdasan. Namun demikian, distribusi kecerdasan yang dikembangkan tiap unit berbeda-beda, hal ini tergantung pada topiknya. Ada 4 sampai 7 kecerdasan yang dikembangkan pada tiap unit. Meskipun distribusi kecerdasan berbeda-beda pada setiap unitnya, materi yang didesain telah mencakup delapan kecerdasan.
Evaluasi pra-area menunjukkan bahwa nilai rata-rata total pada materi yang didesain adalah 4,06. Hal ini berarti bahwa materi yang didesain baik dan dapat diterima.
MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES BASED INTEGRATED MATERIALS FOR AN EXTRACURRICULAR ACTIVITY
FOR THE FIFTH GRADE STUDENTS
OF KANISIUS KALASAN ELEMENTARY SCHOOL
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain theSarjana PendidikanDegree
in English Language Education
By
Arum Jatiningsih Student Number: 031214007
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
MULTIPLE INTELLIGENCES BASED INTEGRATED MATERIALS FOR AN EXTRACURRICULAR ACTIVITY
FOR THE FIFTH GRADE STUDENTS
OF KANISIUS KALASAN ELEMENTARY SCHOOL
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain theSarjana PendidikanDegree
in English Language Education
By
Arum Jatiningsih Student Number: 031214007
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
2008
iv
Courageous Smile
Seema Chowdhury
Face your life and its trials
With a quiet mind and courageous smile
And know that courage is what we need
To perform for us all heroic deeds
So with cheer and tons of hope
Go forward and never mope
And burn the little candle's light
To make your surroundings all bright
And all this can be done with faith
And the gift of courage from God great
So come forward and face life's trial
With a quiet mind and courage's smile
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Firstly, I would like to express my greatest praise and gratitude to dearest Jesus Christ for His blessing and guidance during the completion of my thesis. Everything that God has planned for me is amazing and great. He never leaves me alone in all circumstances.
My greatest gratitude and honor also go to my major sponsor, F.X. Ouda Teda Ena, S.Pd., M.Pd. who has given me guidance, advice, and courage to finish this thesis. I also thank my co-sponsor,Christina Kristiyani, S.Pd., M.Pd. who has given me time, patience, knowledge, and guidance during the process of accomplishing this thesis.
The next gratitude is given to Y. Hariyanta, the headmaster of SD Kanisius Kalasan, for allowing me doing my research. I also thank Y. Krisna Winursito, S.Pd.,the English extracurricular teacher,who has given me his time, help, and willingness to evaluate my designed materials.
viii
I also express my deep gratitude to Bapak and Ibu Bangun Sugiarto, S.H. for supporting me to finish this thesis and giving me warm and sweet relationship. I thank my “little sister”,Dik Putri, for her help, support, pray, and love.
I would like to give my love and gratitude to all friends who have been so kind and helpful in the process of thesis accomplishment, especially for Nita, Nila, Ratri, Febri, Monci, Yuan, Paul, Lala, Gaby, Vivi, Mbak Ayu, Ipad, AyuandLintang.I thankBani for the beautiful pictures and fatherJ.J. Spillane, S.J.for his willingness to be the speaker for the listening material.
My sweet thanks are also directed to ex- Narada’s members,Amel,Kristi, Maria, and Nina. I also give my sweet thanks to my friends in GKJ Bantul, Mbak Indah, Dolly, Kunto, Mas Jarot, Thia, Mbak Kris, Pak Juni, Ibu Retno, Mbak Eny, Mas Banu, Mas Joko, Mbak Sulis, Sari, Mbak Suryanti, Tutik, Gilang and Wawan.I thank them for the sweet and beautiful friendship.
I would like to give my deepest love and thank to my dearest one, Mas Aan. I thank him for his never ending love and support. He gives me motivation to always do my best.
ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES ... ii
BOARD OF EXAMINERS ... iii
PAGE OF DEDICATION ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S OF ORIGINALITY ... v
PAGE OF PUBLICITY ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... ix
LIST OF TABLES ... xiv
LIST OF FIGURES ... xv
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xvi
ABSTRACT ... xvii
ABSTRAK ... xviii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION A. Research Background ... 1
B. Problem Formulation ... 3
C. Problem Limitation ... 3
D. Research Objectives ... 4
E. Research Benefits ... 4
x
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
A. Theoretical Description ... 7
1. Theories of Designing Instructional Materials ... 7
a. Kemp’s Model ... 7
b. Janice Yalden’s Model ... 9
2. Child Development and Characteristics ... 11
3. Foreign Language Teaching to Children in Middle Childhood Period ... 12
a. Children’s Ability to Grasp Meaning ... 13
b. Children’s Instinct for Play and Fun ... 13
c. The Role of Imagination ... 13
d. The Instinct for Interact and Talk ... 14
4. The Nature of Multiple Intelligences Theory ... 14
a. Linguistic Intelligence ... 14
b. Logical-Mathematical Intelligence ... 15
c. Spatial Intelligence ... 15
d. Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence ... 16
e. Musical Intelligence ... 16
f. Interpersonal Intelligence ... 16
g. Intrapersonal Intelligence ... 17
h. Naturalist Intelligence ... 17
i. Existential Intelligence ... 18
5. Integrated Material ... 18
xi CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY
A. Methods ... 21
1. Research and Information Collecting ... 22
2. Planning ... 22
3. Developing Preliminary Form of Product ... 23
4. Preliminary Field Testing ... 23
5. Final Product Revision ... 23
B. Research Participants ... 24
C. Research Instrument ... 24
1. Questionnaire ... 24
2. Interview Checklist ... 25
D. Data Gathering Techniques ... 25
1. Data Gathering for the Participants Needs ... 25
2. Data Gathering for the Evaluation ... 25
E. Data Analysis Techniques ... 26
1. Participants’ Needs ... 26
2. Evaluation on the Design ... 27
a. Descriptive Statistics of Respondents’ Opinion on the Designed Materials ... 27
b. Respondents’ Comments and Suggestions ... 28
F. Research Procedures ... 29
1. Research and Information Collecting ... 29
2. Planning ... 29
xii
4. Preliminary Field Testing ... 30
5. Final Product Revision ... 30
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION A. The Designing Process of the Multiple Intelligences Based Integrated Materials ... 31
1. Needs Survey ... 31
a. Students’ Needs based on the Questionnaire .. 32
b. Students’ Needs based on the Interview ... 34
2. The Goals, Topics, and General Purposes ... 34
3. The Learning Objectives ... 36
4. The Syllabus ... 37
5. The Subject Content ... 37
6. The Teaching Learning Activities, Resources, and Intelligences Being Developed ... 38
7. The Designed Materials ... 38
B. Findings and Discussion on the Designed Materials Evaluation ... 39
1. Preliminary Field Testing ... 39
a. The Discussion of the Designed Materials ... 41
b. Respondents’ Comments and Suggestions on the Designed Materials ... 41
2. Final Product Revision ... 42
xiii
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
A. Conclusions ... 45
B. Suggestions ... 46
1. English Extracurricular Teacher ... 46
2. Future Researchers ... 47
xiv
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
3.1 The Format of Descriptive Statistic of the Respondents’
Opinions (blank) ……….. ... 28
4.1 The Goals and General Purposes of the Designed Materials…………... 35
4.2 The Topics ... 36
4.3 The Indicators of the Students’ Performance in Each Skill ... 36
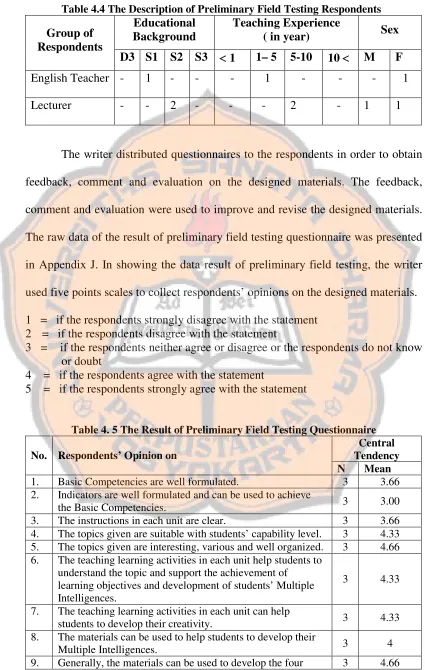
4.4 The Description of Preliminary Field Testing Respondents ... 40
xv
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
1.1 Kemp’s Model: The Relationship of Each Step in the Plan
xvi
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page
Appendix A Letters of Permission ... 50
Appendix B Questionnaire on the Needs Survey ... 52
Appendix C The Result of the Questionnaire on the Needs Survey ... 55
Appendix D The Result of the Interview on the Needs Survey ... 57
Appendix E Indicators in Each Topic ... 58
Appendix F Syllabus ... 63
Appendix G Learning Activities and Intelligences Being Developed ... 73
Appendix H Topics, Titles, Sections and Subsections of the Designed Materials ... 78
Appendix I Questionnaire on the Evaluation ... 80
Appendix J The Result of the Questionnaire on the Evaluation ... 82
Appendix K General Description of the Designed Materials ... 83
xvii ABSTRACT
Jatiningsih, Arum. 2008. Multiple Intelligences Based Integrated Materials for an Extracurricular Activity for the Fifth Grade Students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
There are two main reasons why the writer conducted this study. The first reason is in the English extracurricular activity, the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School are given monotonous activities which most of the activities only develop students’ linguistic intelligence. The second reason is the need of a set of English instructional materials for the extracurricular activity for fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School that can develop students’ multiple intelligences.
There were two problems formulated in this study. They were: 1) How is a set of Multiple Intelligences based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity for the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School designed? 2) What does the design a set of Multiple Intelligences based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity for the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School look like?
The writer applied Research and Development method in this study. In order to answer the first problem, the writer designed a set of instructional materials by combining Kemp’s and Yalden’s models. The steps were: 1) conducting needs survey, 2) stating the goals, topics and general purposes, 3) formulating the learning objectives, 4) developing the syllabus, 5) specifying the subject contents, 6) determining the teaching learning activities, resources and intelligences being developed, 7) evaluating the designed materials. To answer the second problem, the writer designed the materials. The designed materials consisted of eight units. Each unit was divided into three main parts, namely:Start to Think, What Should You Do? and Do it Again. Start to Think was the pre-activity. What Should You Do? was the main activity. Do it Again was the post activity. Each unit developed various intelligences. Nevertheless, the distribution of the intelligences that were developed in each unit was different, it depended on the topic. They were 4 up to 7 intelligences that were developed in each unit. Although the distribution of the intelligences was different in each unit, the designed materials had covered eight intelligences.
The preliminary field testing showed that the total mean for the designed materials is 4.06. It meant that the designed materials were good and acceptable.
xviii ABSTRAK
Jatiningsih, Arum. 2008. Multiple Intelligences Based Integrated Materials for an Extracurricular Activity for the Fifth Grade Students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Ada dua alasan utama mengapa penulis melakukan penelitian ini. Alasan pertama adalah dalam kegiatan ekstrakurikuler bahasa Inggri, siswa kelas lima SD Kanisius Kalasan diberikan kegitan yang monoton dimana sebagian besar kegiatannya hanya dapat mengembangkan kecerdasan linguistik. Alasan kedua adalah kebutuhan satu set materi pembelajaran untuk kegiatan ekstrakurikuler bahasa Inggris siswa kelas lima SD Kanisius Kalasan yang dapat mengembangkan kecerdasan majemuk siswa.
Ada dua permasalahan yang diformulasikan dalam studi ini. Permasalahan tersebut yaitu: 1) Bagaimana satu set materi terpadu untuk kegiatan ekstrakurikuler kelas lima SD Kanisius Kalasan yang berdasarkan Kecerdasaan Majemuk di desain? 2) Seperti apakah penyajian satu set materi terpadu untuk kegiatan ekstrakurikuler kelas lima SD Kanisius Kalasan yang berdasarkan Kecerdasan Majemuk tersebut?.
Penulis menerapkan metode Riset dan Pengembangan dalam studi ini. Untuk menjawab permasalahan yang pertama, penulis mendesain materi dengan mengkombinasikan model Kemp dan Yalden. Langkah-langkahnya: 1) mengadakan survey kebutuhan siswa, 2) menentukan sasaran, topik, dan tujuan umum 3) merumuskan indikator, 4) mengembangkan silabus, 5) menspesifikkan subjek isi, 6) menentukan aktifitas belajar mengajar, sumber dan kecerdasan yang dikembangkan, 7) evaluasi materi. Untuk menjawab permasalahan yang kedua, penulis mendesain materinya. Materi yang didesain terdiri dari delapan unit. Setiap unit dibagi dalam tiga bagian utama, yaituStart to Think, What Should You Do? dan Do it Again.Start to Think adalah aktifitas pembuka. What Should You Do? adalah aktifitas utama. Do it Again adalah aktifitas penutup. Setiap unit mengembangkan berbagai macam kecerdasan. Namun demikian, distribusi kecerdasan yang dikembangkan tiap unit berbeda-beda, hal ini tergantung pada topiknya. Ada 4 sampai 7 kecerdasan yang dikembangkan pada tiap unit. Meskipun distribusi kecerdasan berbeda-beda pada setiap unitnya, materi yang didesain telah mencakup delapan kecerdasan.
Evaluasi pra-area menunjukkan bahwa nilai rata-rata total pada materi yang didesain adalah 4,06. Hal ini berarti bahwa materi yang didesain baik dan dapat diterima.
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter covers six parts of the thesis: research background, problem formulation, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits and definition of terms.
A. Research Background
Philosophically, students must have opportunities for the creative exploration of their individual interests and talents while they are also learning valued skills and concepts. Linda Campbell, Bruce Campbell and Dee Dickinson (1996: xxi) state that ”not all children exhibit the same intelligences profile, nor they share the same interests”. In other words, the major intelligences in each child may be different.
Gardner (1985) states that students tend to have several major intelligences, but they can be helped to develop other intelligences through education and the teacher (in Suparno, 2004: 15). It means that each student should be given opportunities to learn through many kinds of intelligences. By learning through many kinds of intelligences, the students can improve their major intelligences and develop other intelligences that they have less.
Teaching language, especially teaching English is not just a matter of delivering knowledge. It also leads students to apply the language in real situation. The problem is most of English materials which are developed by many publishers only focus on the language competence. However, in teaching English to the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School for the
extracurricular activity, the problem is that the teacher does not have special set of English materials to teach the students.
As far as the writer noticed, the students are given monotonous activities during the extracurricular class. The activities only develop students’ linguistic intelligence. The other reason is that the students tend to use teacher-based learning. It means that the students become passive learners because the students have difficulty in developing their creativity and intelligences. Related to this problem, the writer noticed that English as an extracurricular activity is important to be conducted. This activity is an opportunity for the teacher to teach English materials that can be used to develop student’s intelligences, talents and interests by providing many activities. This activity will be difficult to be conducted in regular class because the teacher has already had a fixed set of materials. So, the English teacher needs to use a set of English material that provides students with opportunities in learn English while developing many kinds of intelligences in extracurricular class.
Based on Multiple Intelligences Theory proposed by Howard Gardner there are nine intelligences possessed by human, namely: linguistic intelligence, logical-mathematical intelligence, spatial intelligence, bodily-kinesthetic intelligence, musical intelligence, interpersonal intelligence, intrapersonal intelligence, naturalist intelligence and existential intelligence (in Suparno, 2004: 19). It means that each person has all of the nine intelligences, but these intelligences develop differently in each person (in Suparno, 2004: 45).
activity for the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. The writer hopes that the result of this study will provide a reference that is not monotonous in content and can be used to develop children’s intelligences.
B
.
Problem FormulationThe problems of the research are formulated as follows:
1. How is a set of Multiple Intelligences based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity for the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School designed?
2. What does the design a set of Multiple Intelligences based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity for the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School look like?
C. Problem Limitation
existence, such as reflection. The fifth grade students of Elementary School may not understand the human existence yet. Third, the instructional materials are designed for an extracurricular activity of the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. English extracurricular activity in Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School is provided for the fifth and sixth grade. The writer only designs the materials for the fifth grade because the extracurricular activity for the sixth grade is used to train students with exercises in order to prepare for the National Examination. The writer did not design materials for the regular class because the teacher has already had a fixed set of materials.
D. Research Objectives
There are two objectives of this study.
1. The first objective is to find out how a set of Multiple Intelligences based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity for the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School is designed.
2. The second objective is to design a set of Multiple Intelligences based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity for the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School.
E. Research Benefits
1. The fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School
The students will experience various activities that can stimulate their intelligences by applying the materials. The students are able to develop their talents, interests, and intelligences, and to improve their ability in learning English based on multiple intelligences theory.
2. The English extracurricular teacher of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School It will be useful for the English extracurricular teacher to use the designed materials because the teacher has not had the fixed material to be given to the students. The instructional materials also help the teacher to teach using multiple intelligences theory and the teacher can improve their strategy in teaching English.
3. Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School
The writer hopes that the designed will give the effective, meaningful and useful materials so the English extracurricular activity can be done successfully.
4. Other researchers
The study has limitation because it is only designing not implementing. The writer hopes that other researchers are willing to evaluate and make the design better.
F. Definition of Terms
1. Integrated Materials
Integration is “the act or process of organizing with various parts into a whole or wholes and systematically arranging wholes, usually in the order of their importance” (Dictionary of Linguistics, 1975: 102). This study tries to integrate four skills; speaking, reading, writing, and listening. So, in this study, an integrated material is a set of materials that integrate speaking, reading, writing and listening skills.
2. Multiple Intelligences
Multiple Intelligences refer to “a learner-based philosophy that characterizes human intelligence as having multiple dimensions that must be acknowledged and developed in education” (Richard & Rodgers, 1986: 115). Multiple Intelligences consist of nine intelligences, namely linguistic intelligence, logical-mathematical, spatial intelligence, bodily-kinesthetic intelligence, musical intelligence, interpersonal intelligence, intrapersonal intelligence, naturalist intelligence, existential intelligence (Suparno, 2004: 25-44). In this study, the writer only uses eight intelligences. They are linguistic intelligence, logical-mathematical intelligence, spatial intelligence, bodily-kinesthetic intelligence, musical intelligence, interpersonal intelligence, intrapersonal intelligence and naturalist intelligence.
3. Extracurricular Activity
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This section discusses the theories and concepts that support the study. There are two major sections in this chapter. The first is theoretical description and the second is theoretical framework.
A. Theoretical Description
Theoretical description consists of the theories of designing instructional materials, child development and characteristics, foreign language teaching to children in middle childhood period, the nature of Multiple Intelligences theory, and integrated materials.
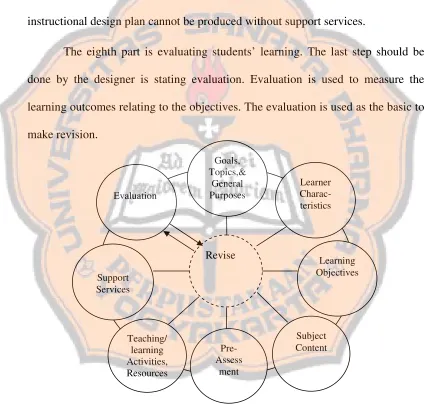
1. Theories of Designing Instructional Materials a. Kemp’s Model
Based on Kemp’s model, the plan of designing instructional materials consists of eight parts. The first part is considering goals, topics and general purposes. All educational programs are based on broadly stated goals. Most of the designers start with the formulation of the goals before designing the materials. After establishing its goals, the designer lists the major topics to be treated within the content area. The topics will become the basis for the instruction. Topics are sequenced from simple to the complex level. Next, the designer writes the general purposes. A single topic may have more than one purpose.
The second part is enumerating learners’ characteristics. In this step, the designer should obtain information about the students’ capabilities, needs and
interests. Kemp states that there are four factors influenced the students’ characteristics; those are academic factors, social factors, learning conditions and learning styles. Knowing the learners’ characteristics is very important. It is important because it will support the achievement of the goals, topics, and general purposes that have been stated in the first step.
The third part is specifying learning objectives. The designer specifies the learning objectives to be achieved by the students. Kemp states that objectives tell students about what goals they must attain. It means that all activities in teaching learning process must be able to support the achievement of the learning objectives.
The fourth part is listing the subject content. Kemp states that students’ learning experiences must involve subject content. The designer makes the subject content that is closely related to the objectives and the students’ needs. It means that the subject content should be included in the steps of designing the materials because it is closely connected with the objectives and students’ need.
The fifth part is developing pre-assessments. Kemp states that the designer develops pre-assessment in order to know whether the students are ready to study the topic or not. The other reason is to know the students’ competence in some of the stated objectives. Pre-assessment can be done through a placement and diagnostic test. It can be said that placement and diagnostic test will be helpful to re-examine the topics and the stated objectives in order to help the designer to group the students based on their background knowledge.
designer selects materials to provide learning experiences. So, it will utilize the content associated with each objective.
The seventh part is coordinating support services. The designer should also consider the support services such as budget, personnel, facilities, equipment, and schedules. Those support services are used to carry out the instructional plan. The instructional design plan cannot be produced without support services.
The eighth part is evaluating students’ learning. The last step should be done by the designer is stating evaluation. Evaluation is used to measure the learning outcomes relating to the objectives. The evaluation is used as the basic to make revision.
Figure 2.1 Kemp’s Model: The Relationship of Each Step in the Plan to Other Steps (Kemp, 1977)
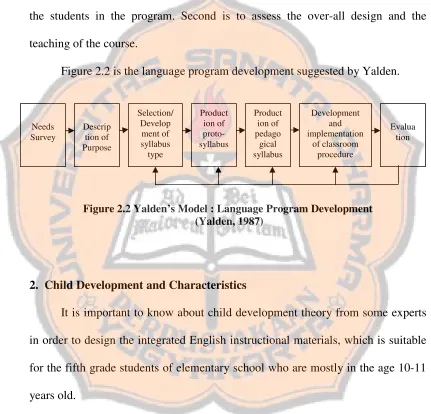
b. Janice Yalden’s Model
There are seven stages in planning a syllabus based on Janice Yalden (1987: 88). The first stage is needs survey. According to Yalden, when a needs
Revise
Subject Content
Learning Objectives
Teaching/ learning Activities, Resources Support
Services
Pre-Assess
ment Evaluation
Learner Charac-teristics Goals,
survey is being undertaken there is potentially a great deal of information to be gathered. It means that a needs survey is important to be conducted to understand who are the learners. A needs survey is also used as the basic to establish realistic and acceptable objectives.
The second stage is description of purpose. This stage is conducted after the designer did the needs survey because the information from needs survey becomes the basis in developing the purpose of the program. It is the step where the designer clarifies the purpose of the language program. This will establish the foundation for the major decision facing the language course designer in the next step, selection of syllabus type.
The third stage is selection of syllabus type. In this stage, the designer should choose the most appropriate a syllabus type based on the result of the needs survey and the purpose of the program. The designer can combine more than one syllabus in order to make course design more reliable.
The fourth stage is production of a proto syllabus. This stage describes the language itself and language use to be converted in the program. In the other words, the designer should describe and determine the content of the syllabus.
The fifth stage is production of a pedagogical syllabus. According to Yalden, in production of pedagogical syllabus stage, the designer develops the teaching learning approaches. The designer also implies the syllabus into the teaching and learning activities.
preparation of the lesson plans, preparation of the weekly schedules. Yalden also states about the teacher training in this stage, such as creation of teaching material. The seventh stage is evaluation and recycling stage. Yalden states that evaluation and recycling stage has two broad aspects. First is to evaluate or test the students in the program. Second is to assess the over-all design and the teaching of the course.
Figure 2.2 is the language program development suggested by Yalden.
Figure 2.2 Yalden’s Model : Language Program Development (Yalden, 1987)
2. Child Development and Characteristics
It is important to know about child development theory from some experts in order to design the integrated English instructional materials, which is suitable for the fifth grade students of elementary school who are mostly in the age 10-11 years old.
Craig (1979: 396) states that “middle childhood ( ages 6 – 12) is the time before adolescence when the child is adjusting to the new environment of school, is forming close ties with people outside the home, and is developing work and play habits along with many new interests”. It means that during this time, children experience many developmental ideas and attitudes toward their society.
They like doing something new and interact with new society. They like to make experiments. It is time for children to explore their ideas and creativity.
According to Watson and Lindgren (1973: 363) ” the middle childhood and early later childhood runs from about 6 to 12 for girls and from 6-14 for boys. This is a period in which children begin a major involvement in the world outside the family and the immediate neighborhood”. Related to those statements, the fifth grade students are included in the middle childhood. Middle childhood is a period where children must be given opportunity to develop their creativity and ideas. They are also given freedom to express their feeling and communicate with others.
According to Jean Piaget, as quoted by Medinnus and Johnson (1969: 124) “from the age of seven or eight to the age of 11 or 12, the child is concerned with concrete ideas. He also adds, in this age the formation of concepts is felt to involve operational groupings concerning subjects that can be manipulated or known through the senses”. It means that in the fifth grade students of elementary school who are in the age 10 or 11 is the time to form concepts and try to express in real situation. They focus on the real and concrete ideas.
a. Children’s Ability to Grasp Meaning
Haliwell (1992: 3) states “that children can learn through intonation, demonstration, gesture, facial expressions, actions and circumstances to understand the unknown words and phrases”. It means that the teacher should understand this point. When children encounter a new language, the teacher can help them by using some points above. The teacher should understand the students’ difficulties in learning English. To help the students to grasp the meaning of the English words, phrases or sentences, the teacher should be able to teach in various ways. It means that teaching English for children is not only by teaching the linguistics aspect but also by revealing the real expressions or conditions.
b. Children’s Instinct for Play and Fun
Haliwell (1992: 6) states “that children have an enormous capacity for finding and making fun”. It means that the teacher should understand that the children should be provided with materials and activities that can build children’s interests. One of the ways is by giving them games. Those statements related to the interesting activities that should be given to the children when they learning English. By activating the students kinesthetic ability, hopefully children more interested to learn English.
c. The Role of Imagination
learning language, in this case learning English. By giving materials which can build their imagination, the children can learn English easily.
d. The Instinct for Interaction and Talk
Halliwell states that “children’s capability for interact and talk is one of the most powerful motivators for using the language “ (1992: 8). It means that the teacher should understand that children can learn the language, but the effective way to learn it is to use it. The teacher should be able to provide the materials and activities that encourage children to talk and interact with others. It is important for children to learn English by building their ability in socializing and interacting in their environment.
4. The Nature of Multiple Intelligences Theory
There are many experts who state about Multiple Intelligences. Some experts state that Multiple Intelligences consist of seven intelligences. Some state that it consists of eight intelligences. There are also experts who said that it consists of nine intelligences.
Howard Gardner (1985) states that Multiple Intelligences consist of nine intelligences (in Suparno, 2004: 19). The nine intelligences are linguistic intelligence, logical-mathematical intelligence, spatial intelligence, bodily-kinesthetic intelligence, musical intelligence, interpersonal intelligence, intrapersonal intelligence, naturalist intelligence, and existential intelligence. a. Linguistic Intelligence
accomplish certain goals or purposes (Armstrong, 2000). It means that linguistic intelligence closely related to listening, speaking, reading and writing activity.
According to Campbell and Dee Dickinson (1996: 4), they are some characteristics possessed by people who have high degrees of linguistic intelligence, such as they use listening, speaking, writing and reading to remember, communicate, discuss, explain, and persuade to others. They also listen effectively what has been said, read effectively what has been read, speak effectively to a variety of audiences and write effectively to understand grammar, spelling, and punctuation.
b. Logical-Mathematical Intelligence
Logical-mathematical intelligence involves the ability to analyze problems logically. This intelligence is also related to the usage of numbers and mathematic thinking (Armstrong, 2000). It means that logical-mathematic intelligence is closely related to activities to count, classify and categorize.
According to Campbell and Dee Dickinson (1996: 5), they are some characteristics possessed by people who have high degrees of logical-mathematic intelligence, such as they are familiar with the concept of quantity, time, and cause and effect. They also think mathematically by gathering evidence, making hypotheses, formulating models, and building strong arguments.
c. Spatial Intelligence
Spatial intelligence involves the potential to recognize and use patterns of wide area (Armstrong, 2000). It means that spatial intelligence is related to shapes, patterns and colors.
such as they learn by seeing and observing. They recognize objects, shapes, colors, and details. They also use visual image to get information and they enjoy drawing, painting, sculpting, or otherwise reproducing objects in visible forms. d. Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence
Bodily-kinesthetic intelligence is the ability to use mental abilities to coordinate body movements (Armstrong, 2000). It means that the body movements are used to express the ideas and feelings.
According to Campbell and Dee Dickinson (1996: 68), they are some characteristics possessed by people who have high degrees of bodily-kinesthetic intelligence, such as they explore the environment and objects through touch and movements. They also enjoy learning experiences such as participating in role play, games, or physical exercises.
e. Musical Intelligence
Musical intelligence involves skill in the performance, composition, and appreciation of musical patterns (Armstrong, 2000). It means that musical intelligence closely related to melody, rhythm, and tone.
According to Campbell and Dee Dickinson (1996: 135), they are some characteristics possessed by people who have high degrees of musical intelligence, such as they listen and respond variety of sounds including the human voice, environmental sound and music. They enjoy hearing music in the learning environment. They also develop the ability to sing or play an instrument alone or with others.
f. Interpersonal Intelligence
that this intelligence asks people to be able to know other people well and build close relationship with the society.
According to Campbell and Dee Dickinson (1996: 160), they are some characteristics possessed by people who have high degrees of interpersonal intelligence, such as they are interested to interact with others. They perceive feelings, thoughts, motivations, behaviors, and lifestyles of others. They also understand and communicate effectively in both verbal and nonverbal ways. g. Intrapersonal Intelligence
Intrapersonal intelligence refers to the ability to understand oneself, to appreciate one’s feeling, fears and motivations (Armstrong, 2000). It is the ability to understand who they are.
According to Campbell and Dee Dickinson (1996: 196, 231), they are some characteristics possessed by people who have high degrees of intrapersonal intelligence, such as they like to attempt to understand inner experience. They also like to work independently.
h. Naturalist Intelligence
Naturalist intelligence enables human beings to recognize, categorize features of the environment (Armstrong, 2000). It means that is related to understand the nature or surroundings. This intelligence makes human able to classify and indentify animals and plants.
i. Existential Intelligence
Existential intelligence enables people to answer problems about human’s existence (Armstrong, 2000). It means that it includes ability to reflect about the value of life.
People who developed their existential intelligence well exhibit specific characteristics. First, they like to reflect about human existence in this world. Second, they reflect what has been done (in Suparno, 2004: 54).
5. Integrated Materials
According to Brown (2001: 234), the integration of four skills is “the only plausible approach within communicative and interactive framework”. It means that the integration of four skills is the integration of listening, speaking, reading and writing skills. Reading and listening are parts of receptive skills, while speaking and writing are parts of productive skills. There was a time when the terms “passive” referred to “receptive skills” and “active” referred to “productive skills” (Nunan, 2003: 24).
Integrated material is ”material that focuses on the mastery of integrated communicative skills rather than a mere mastery of the rules in target language” (Richard and Rodgers, 1988: 64). It means that the integrated material is designed for communicative competence. There is an integrated relationship or unity in each part of its activities.
B. Theoretical Framework
and Yalden’s Instructional Design Model. The writer also employs Multiple Intelligences Theory and Integrated Language Instruction. The writer does not apply all elements of these theories. The writer selects some of the elements which can contribute to the processes of designing a set of Multiple Intelligence based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity for the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School.
Since this study focuses on designing integrated instructional materials, the writer applies the integration of four skills; listening, speaking, reading and writing. Each unit of the design materials integrates the four skills. The integrated materials are to offer a variety of content, resources and language experiences.
The writer also applies Multiple Intelligences theory as the philosophical education of the design. The writer applies eight from nine intelligences that are included in Multiple Intelligences Theory. The eight intelligences are: linguistic intelligence, logical-mathematical intelligence, spatial intelligence, bodily-kinesthetic intelligence, musical intelligence, interpersonal intelligence, intrapersonal intelligence, and naturalist intelligence. The materials of the design focus on the development of those intelligences, although the development of the intelligences in each unit is random and different.
In designing the materials, the writer needs to know about the children’s development and characteristics, and the principles in teaching foreign language for children in middle childhood period. It is important to know because the materials designed are for the fifth grade students of elementary school whose ages are around 10-11 years old and have special characteristics.
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY
This chapter discusses the detailed information about the methodology used to accomplish the study. In this study, the writer answers two questions stated in chapter one. First, this study is intended to find out how a set of Multiple Intelligences based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity of the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School was designed. Second, this study is intended to present the design of a set of Multiple Intelligences based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity of the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. These two problems are discussed into seven sections, namely methods, research participants, research instruments, data gathering techniques, data analysis techniques, and research procedures.
A. Methods
The research was aimed at designing a set of Multiple Intelligences based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity for the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. In this study, the writer used Research and Development (R & D) method. According to Borg and Gall (1983), Educational Research and Development (R&D) was a process used to develop and validate educational products. The steps of this process were usually referred to as the R & D cycle, which consisted of research and information collecting, planning, developing preliminary form of product, preliminary field testing, main product revision, main field testing, operational product revision, operational field testing, final product revision, dissemination and implementation.
The writer did not use all steps in R & D cycle. The writer only used research and information collecting, planning, developing preliminary form of product, preliminary field testing, and final product revision. The writer only used those steps because of the time limitation. This writer only designed the materials not implemented the materials.
1. Research and Information Collecting
In this stage, the writer aimed to gain the information by using three ways; review of related literature, interview & questionnaire. The first was review of related literature. Review of related literature was gathered from library survey. The second was an informal interview. The writer conducted an informal interview with the English extracurricular teacher of the fifth class of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. The informal interview was done to gather information related to the need analysis of the students and to support the data. The third was questionnaire. The questionnaire was given to the students. The purpose was to know the students’ needs. In other words, the writer conducted needs survey (Yalden, 1987) in research and information collecting stage.
2. Planning
develop their interest but still considering the content of materials. In this study, the writer used Multiple Intelligences theory as the educational philosophy.
3. Developing Preliminary Form of Product
The writer made the preliminary form of the design by determining the teaching learning activities, resources, and intelligences being developed (Kemp, 1977). The writer found the sources of the materials from many books and internet. The writer also prepared the evaluation instruments, which were questionnaires.
4. Preliminary Field Testing
In this step, the writer distributed questionnaires to the English extracurricular teacher of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School and two English lecturers of the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. They were asked to give their opinions whether they agreed with the designed materials or not. The writer also considered that to obtain valid feedback of the designed materials was not enough by only giving the questionnaires to the respondents. The respondents were interviewed in order to criticize and to give feedback of the designed materials so the writer could revise the designed materials. In other words, the writer conducted evaluation to the designed materials (Yalden, 1987) in the preliminary field testing stage.
5. Final Product Revision
B. Research Participants
In doing this study, the writer used two groups of participants. The first group was the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. They were the participants in research and information collecting stage. The writer used purposive sampling. There were two classes namely class V A and class V B. The total numbers of students were 72 students. The second group was the English extracurricular teacher of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School and two lecturers of the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. They were participants in preliminary field testing stage.
C. Research Instruments
In order to obtain the data, there were two instruments in this study. They were questionnaire and interview checklist.
1. Questionnaire
According to Ary et al (1979:175), there were two types of questionnaires namely “structured or closed form” and “unstructured or open form”. In this study, the writer used closed form questionnaire in gathering data of participants’ needs and open form questionnaire in gathering respondents’ evaluation on the designed materials.
2. Interview Checklist
The writer conducted an informal interview with the English extracurricular teacher of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. The interview was conducted before designing the materials to obtain additional information. Several additional information that were gained through interview were the students’ needs and interest, the background and characteristics of the students, the teaching strategies and English learning, materials resources and evaluation, and problem faced by the students.
D. Data Gathering Techniques
There are two important points in gathering the data. They are data gathering for the participants’ needs and data gathering for the evaluation.
1. Data Gathering for the Participants’ Needs
In gathering the data for the participants’ needs, the writer distributed questionnaires to the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. The writer also interviewed the teacher of English extracurricular activity of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School to know further about the students’ needs. 2. Data Gathering for the Evaluation
Kalasan Elementary School and two lecturers of the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. The writer distributed the questionnaires after the writer had finished the designed materials.
E. Data Analysis Techniques
After the questionnaires were collected, the data were recorded. There were two important points to be discussed in the data analysis techniques. The analyses were conducted to know participants’ needs and evaluation on the design.
1. Participants’ Needs
The participants’ needs were reached by analyzing the questionnaires that were distributed in research and information collecting stage. The data gathered in the closed form were calculated by percentage. The result was obtained by dividing the number of the students who chose certain topic with the total number of the students, then multiplied by 100%.
100% n
N
Note :
N : the number of students who choose certain topic
n : the total number of students
2. Evaluation on the Design
The data for the evaluation were divided into two categories. The first category was about the respondents’ opinions that were shown statistically. The second one was the respondents’ comments and suggestions that were explained in sentences.
a. Descriptive Statistics of Respondents’ Opinion on the Designed Materials To calculate the data from questionnaires, the writer used three major measures of central tendency proposed by Brown and Rodger, namely: ”mean, median and mode” (Brown and Rodger, 2004:128). The mean, median and mode were usually used to describe the average performance among a group of scores. The writer counted the mean of the respondents’ answers. The mean or average point ( X ) was obtained by counting the sum of the respondents’ answer (∑x) divided by the number of the respondents (N).
The formula was:
Note:
point average the
X
x = the sum of respondents’ answer N = the number of respondents
To calculate the data, the assessment of the respondents’ opinion toward the designed materials used “Likert Scale”, in which the respondents were asked to register their responses on 5 points of agreement, namely:
1 = if the respondents strongly disagree with the statement 2 = if the respondents disagree with the statement
3 = if the respondents neither agree or disagree or the respondents do not know or doubt
4 = if the respondents agree with the statement
5 = if the respondents strongly agree with the statement
Table 3.1: The Format of Descriptive Statistic of the Respondents’ Opinions (blank)
Frequency of the Point of Agreement
Central Tendency
No Statement N
Mean Median Mode
In the preliminary field testing, the data showed whether the designed materials were good and acceptable or not. The assessment of the mean is classified as follows:
0.0 X 2 = the designed materials were poorly designed 2.01 X 3 = the designed materials were fairly designed
3.01 X 4 = the designed materials were good, but need crucial revisions 4.01 X 5 = the designed materials were well designed and acceptable, but
need few revisions
b. Respondents’ Comments and Suggestions
F. Research Procedures
In the following section, the writer discusses how the study was conducted. The writer adopted the research procedure from the Research and Development cycle, Kemp’s and Yalden’s Model. The research procedures in this study were research and information collecting, planning, developing preliminary form of product, preliminary field testing, and final product revision.
1. Research and Information Collecting
This step could be considered as needs survey. The writer asked permission to conduct the study in Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. After obtained the permission to do the study, the writer had an informal interview with the English extracurricular teacher. To know the students’ needs related to the Multiple Intelligences, the writer distributed questionnaires to the students.
2. Planning
The writer analyzed the data from the questionnaires and an interview checklist. Data from the instruments were used to state the goals, topics and general purposes of the study. In this step, the writer also formulated the learning objectives, selected and developed the syllabus and specified the subject content. 3. Developing Preliminary Form of Product
4. Preliminary Field Testing
Having finished designing the materials, the writer conducted preliminary field testing. The preliminary field testing was conducted by distributing the designed materials and the second questionnaires to two lecturers of the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University and the English extracurricular teacher of the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School in order to evaluate the designed materials.
5. Final Product Revision
The writer analyzed the results of the questionnaires. The writer revised and improved the designed materials based on the feedback from the respondents that was stated in the distributed questionnaire. The writer presented the final version of the designed materials. The final version of the designed materials was a set of Multiple Intelligence based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity of the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School.
Figure 3.1 Research Procedures Research and Information Collecting
Preliminary Field Testing Planning
Developing Preliminary Form of Product
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter describes the findings and discussion of the study and the presentation of the designed materials. This chapter is divided into three main parts. The first part is the designing process of the Multiple Intelligences based integrated materials. The second part is the findings and discussion on the designed materials evaluation. The third part is the designed Multiple Intelligences based integrated materials for an extracurricular activity for the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School.
A. The Designing Process of the Multiple Intelligences Based Integrated Materials
The writer applied seven steps in designing Multiple Intelligences Based Integrated Materials for an Extracurricular Activity for the Fifth Grade Students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. The seven steps are the combination of two instructional design models, Kemp and Yalden models. They are conducting needs survey, stating the goals, topics, and general purposes, formulating the learning objectives, developing the syllabus, specifying the subject contents, determining the teaching learning activities, resources and intelligences being developed, evaluating the designed materials.
1. Needs Survey
In order to obtain the data of the students’ needs, the writer distributed the questionnaire to the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan elementary school and interviewed the English extracurricular teacher.
a. Students’ Needs based on the Questionnaire
There were two classes namely class V A and class V B. The total numbers of students were 72 students. The raw data of the result of the questionnaire on the needs survey were presented in Appendix C.
From the result of needs analysis, 62.5% of the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan elementary school liked listening activity, 41.66 % of them liked reading and writing, and only 29.16% of them who liked speaking. There was 51.39% of the students who thought that writing was the most difficult subject to learn, 15.27% of them met difficulties in grammar, 13.89% of them met difficulties in reading, 8.33% of them met difficulties in pronunciation. There was only 4.17% of them who met difficulties in listening and vocabulary, and 2.78% of them who met difficulties in speaking.
There was 62.5% of the students who said that they rarely learned English by using creative activities such as discussion, drawing, drama, singing, group games, individual games, or out door activity in extracurricular class, 25% of them said sometimes, 8.33% of them said never. There was only 4.17% of them who said often. It meant that the teaching learning activities in English extracurricular class of the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan elementary school was rarely to apply various and creative activities.
The table also showed that most of the students (66.66%) liked to work individually in learning English in extracurricular class. It was also found that 56.94% of them liked to learn outside the class, 45.83% of them liked to memorize the vocabularies, 41.66% of them liked to work with friends, 31.94% of them liked to learn English through singing English songs. There was only 15.27% of them who liked to draw, color and explain the pictures, 8.33% of them who liked to listen to the teacher’s explanation, while the rest (4.16%) of the students liked to the group discussion.
Concerning to the media that were used in English extracurricular class, 55.55% of the students said that they rarely used media in learning English, 36.11% of them said sometimes, only 8.34% of them said often and none of them said never. It meant that the English extracurricular activity in Kanisius Kalasan elementary school was rarely to use media in teaching learning activity. Based on the students’ point of view, 59.72% of them felt more interested and enthusiastic if they used media in learning English, 27% of them felt okay and only 2.78% of them who disliked using media to learn English.
Related to the students’ opinion, 79.17% of them thought that the topics that were given in English extracurricular class were okay, 12.5% of them thought that the topics were easy to learn and 8.33% of them thought that the topics were difficult to learn.
and only 8.33% of them who disagreed to learn English used materials that could develop their intelligences and talents.
b. Students’ Needs based on the Interview
The writer interviewed the English teacher who taught the extracurricular activity of the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School. He also taught in regular class of the fifth grade students. The English extracurricular teacher said that most of the fifth grade students of Kanisius Kalasan Elementary School were active students. They liked to move and talk. They were also difficult to focus on their teacher. The teacher mostly used traditional technique (explanation) to teach the students because it would be easier for the teacher to handle the students. The teacher sometimes also asked the students to do role play. There were several problems that were faced by the students in learning English. First, the students’ willingness to learn English was low. Second, the teacher gave monotonous techniques and activities during the teaching learning activities. To solve the students’ difficulties, the students should be given interesting activities. The teacher also said that he sometimes used TV and tape recorder in teaching learning activity. At last, the teacher agreed if English extracurricular activity implemented Multiple Intelligences theory. The teacher stated that teaching learning through Multiple Intelligences provided students opportunity to develop their talents. Students were able to learn English in interesting situation and activities. The data from the interview were presented in Appendix D.
2. The Goals, Topics, and General Purposes
reading, and writing. Having determined the goals, the writer specified the general purposes that were stated as Basic Competence. The goals and general purposes of the designed materials were presented in Table 4.1.
Table 4.1 The Goals and General Purposes of the Designed Materials
NO. SKILLS GOALS
(COMPETENCE STANDARD)
GENERAL PURPOSES (BASIC COMPETENCE) 1. Listening Understand simple instruction
in daily life context
The students are able to: 1. Respond simple instruction
with correct action.
2. Listen the recording and respond the instruction by completing the texts, conversations, and poems. 2. Speaking Express simple instruction and
information in daily life context
The students are able to: 1. Give and respond simple
instruction correctly. 2. Give simple information
correctly. 3. Reading Understand simple English
vocabularies, phrases, sentences and texts in daily life context
The students are able to: 1. Read vocabularies simple
phrases, sentences, and texts using correct intonation and spelling. 2. Understand the meaning
and message from the vocabularies, phrases, sentences, texts and pictures.
4. Writing Write words, simple phrases and sentences in daily life context
The students are able to: Write words, simple phrases and sentences accurately.
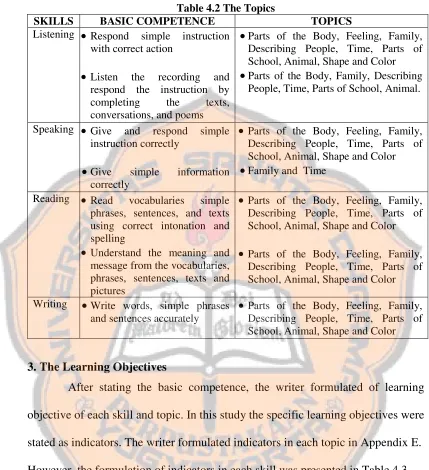
Table 4.2 The Topics
SKILLS BASIC COMPETENCE TOPICS
Listening Respond simple instruction with correct action
Listen the recording and respond the instruction by completing the texts, conversations, and poems
Parts of the Body, Feeling, Family, Describing People, Time, Parts of School, Animal, Shape and Color
Parts of the Body, Family, Describing People, Time, Parts of School, Animal.
Speaking Give and respond simple instruction correctly
Give simple information correctly
Parts of the Body, Feeling, Family, Describing People, Time, Parts of School, Animal, Shape and Color
Family and Time
Reading Read vocabularies simple phrases, sentences, and texts using correct intonation and spelling
Understand the meaning and message from the vocabularies, phrases, sentences, texts and pictures
Parts of the Body, Feeling, Family, Describing People, Time, Parts of School, Animal, Shape and Color
Parts of the Body, Feeling, Family, Describing People, Time, Parts of School, Animal, Shape and Color
Writing Write words, simple phrases and sentences accurately
Parts of the Body, Feeling, Family, Describing People, Time, Parts of School, Animal, Shape and Color
3. The Learning Objectives
After stating the basic competence, the writer formulated of learning objective of each skill and topic. In this study the specific learning objectives were stated as indicators. The writer formulated indicators in each topic in Appendix E. However, the formulation of indicators in each skill was presented in Table 4.3.
Table 4.3 The Indicators of the Students’ Performance in Each Skill
No Skill Indicators
1 Listening The students are able to:
1.Respond the instruction about Parts of the Body, Feeling, Family, Describing People, Time, Parts of School, Animal, Shape and Color with correct action. 2.Listen to the recording and complete the text about Parts
of the Body and Parts of School correctly.
3.Listen to the recording and complete the conversation about Describing People and Time correctly.
4.Listen to the recording and complete the poem about Family and Animal correctly.
2 Speaking The students are able to :
1.Respond the instruction by pronouncing the words, phrases, or sentences about Parts of the Body, Feeling, Family, Describing People, Time, Parts of School, Animal, Shape and Color correctly.
2.Respond the instruction by singing song, imitating, and saying.
3.Give simple instruction to friends about Parts of the Body, Feeling and Family correctly.
4. Give simple information to friends and teacher about Family and Time correctly.
3 Reading The students are able to:
1. Read vocabularies about Parts of the Body, Feeling, Family, Describing People, Time, Parts of School, Animal, Shape and Color using correct intonation and spelling
2. Read simple phrases and sentences about Parts of the Body, Describing People, Family, Animal, Shape and Color using correct intonation and spelling.
3. Read simple texts about Parts of the Body, Family, Parts of School, Shape and color using correct intonation and spelling.
4. Answer the question of the meaning of vocabularies about Parts of the Body, Feeling, Family, Describing People, Time, Parts of School, Animal, Shape and Color correctly.
5. Answer the question of the meaning and message about simple phrases, sentences and text about Parts of the Body, Describing People, Family, Parts of School, Animal, Shape and Color correctly.
4 Writing The students are able to:
Write words, simple phrases, sentences and texts about Parts of the Body, Feeling, Family, Describing People, Time, Parts of School, Animal, Shape and Color using correct alphabet and structure.
4. The Syllabus
Having finished stating the goals, topics, general purposes, and the learning objectives, the writer modified the syllabus. The syllabus was modified from 2006 Curriculum (KTSP).The syllabus was developed to help the teacher to apply the materials. The syllabus was presented in Appendix F.
5. The Subject Contents
contents into three parts in each section. In this designed materials, the writer used term “Start to Think” for pre-activity, “What Should You Do?” for main activity and “Do it Again” for post- activity.
Start to Think was pre- activity to activate students’ prior knowledge and to introduce the topic. What Should You Do? was a part where students were provided with various tasks that could activate students’ intelligences and learn the four skills. In this part students also learned theories that was written in particular instruction namely “Study the Pattern”. Nevertheless, not all units contained “Study the Pattern”. Do it Again was post activity that provided students with simple and entertaining activities. It was also used to remind students with the materials that they had already learned. Some units also provided list of vocabularies related to the topic namely Words to Remember. Words to Remembercould be found inStart to ThinkorWhat Should You Do?. 6. The Teaching Learning Activities, Resources and Intelligences Being
Developed
The writer developed and determined the teaching learning activities that could develop students’ multiple intelligences and their ability in listening, speaking, reading, writing skills. The explanation of the learning activities and distribution of the intelligences being developed in each unit in the designed materials was presented in Appendix G.
7. The Designed Materials
order to evaluate the designed materials. The respondents were expected to give their evaluation and feedback on the designed materials. Then, the writer conducted some revisions based on the evaluations and feedback proposed by the respondents to make the final version of the designed materials.
B. Findings and Discussion on the Designed Materials Evaluation
The writer realized that the designed materials still need some improvements. The writer distributed the second questionnaire to the respondents in order to obtain evaluation, comment and feedback. The respondents were two lecturers of the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University and an English extracurricular teacher of Kanisius Kalasan elementary school. There were two main parts of the findings and discussion, those were preliminary field testing and final product revision.
1. Preliminary Field Testing
Gambar

Dokumen terkait
The Implementation of Cooperative Integrated Reading Composition (CIRC) Through a Set of Reading Instructional Materials to Teach Reading to the Fifth Grade Students of
A Study on the Implementation of Task -Based Learning to Teach Vocabulary for the Second Grade Students of Kanisius Notoyudan Elementary School in Yogyakarta.. Yogyakarta: English
It was proven by the formulated problem of this research as what the researcher had mentioned before about what the appropriate materials for English extracurricular of Pangudi
There was only one research problem of this study “what do speaking materials using task-based learning for the seventh grade students of English Extracurricular
Therefore, this study is intended to design reading instructional materials using games for the fifth grade students of Santa Maria Elementary School Magelang.. There are
Based on the explanations above the writer choose At the Zoo game in teaching vocabulary to young learners especially elementary school students fifth grade.. At the Zoo game is one of
Adi Putra, Tri, Syahrilfuddin, Content Analysis Of Mathematical Literacy Skills Of Fifth Grade Elementary School Page | 46 from the interviews results with students S15 and S22: R
The purpose of this research and development is to produce and find out the effectiveness of mathematics learning devices about flow rate material in fifth- grade elementary school