Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- Rick Graziani
- Allan Johnson
- Pengajar:
- Mark Taub, Editor-in-Chief
- Brett Bartow, Product Line Manager
- Ronald Fligge, Business Operation Manager, Cisco Press
- Mary Beth Ray, Executive Editor
- Sandra Schroeder, Managing Editor
- Ellie C. Bru, Project Editor
- Mandie Frank, Copy Editor
- Celia McCoy, Technical Editor
- Bob Vachon, Editorial Assistant
- Vanessa Evans, Designer
- Chuti Prasertsith, Composition
- Cheryl Lenser, Indexer
- Jaikumar, Proofreader
- Sekolah: Cisco Networking Academy
- Mata Pelajaran: Computer Networking
- Topik: Introduction to Networks v6 Companion Guide
- Tipe: companion guide
- Tahun: 2017
- Kota: Indianapolis
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. Introduction
The 'Introduction to Networks v6 Companion Guide' serves as a vital resource for students enrolled in the Cisco Networking Academy's Introduction to Networks course. It aligns closely with educational objectives, providing a structured approach to understanding networking concepts, technologies, and protocols. The guide emphasizes practical applications, ensuring learners can design, install, operate, and maintain networks effectively. Its comprehensive coverage of topics prepares students for further courses and certifications, fostering a robust foundation in networking principles.
II. Chapter 1: Explore the Network
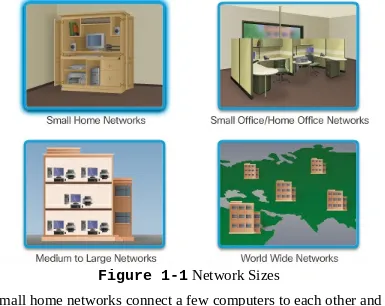
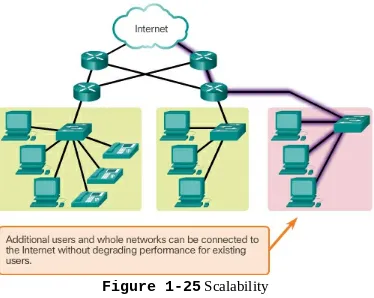
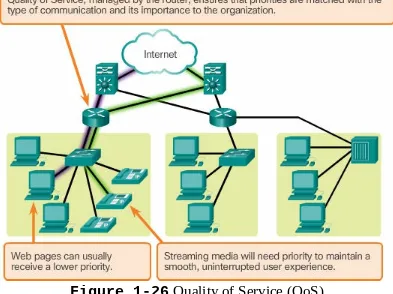
This chapter introduces the concept of networks and their significance in daily life. It discusses how networks enhance communication, learning, and work by providing connectivity. The chapter also explores different types of networks, including LANs and WANs, and highlights the importance of network components. By understanding these foundational elements, students can appreciate the role of networks in modern society and their impact on various sectors.
2.1 Networking Today
The section emphasizes the omnipresence of networks in daily activities, showcasing their role in facilitating communication and resource sharing. It highlights the transformation in human interaction due to networking technologies, underlining the necessity for students to grasp these dynamics.
2.2 Types of Networks
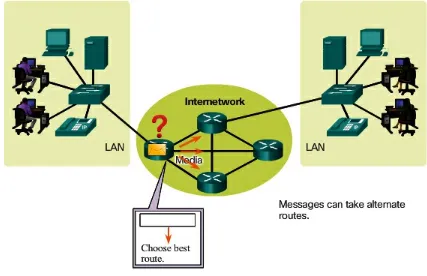
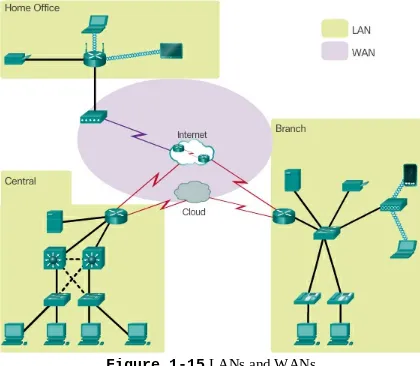
This subsection categorizes networks into LANs, WANs, and the Internet, explaining their unique characteristics and applications. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for students as they design and manage networks tailored to specific needs.
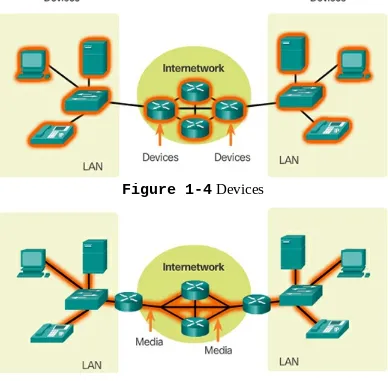
2.3 Network Components
This part covers the various components that make up a network, including end devices and intermediary devices. By familiarizing themselves with these components, students can better understand network architecture and functionality.
III. Chapter 2: Configure a Network Operating System
This chapter focuses on the Cisco IOS, the operating system for Cisco devices. It introduces students to the basic functions and access methods for IOS, alongside command-line navigation and configuration. Understanding IOS is essential for effective network management and troubleshooting, equipping students with practical skills necessary for real-world applications.
3.1 IOS Bootcamp
Students learn about the purpose and access methods of Cisco IOS, which is fundamental for configuring network devices. This foundational knowledge is critical for anyone pursuing a career in networking.
3.2 Basic Device Configuration
This section covers the essential steps for configuring devices, including setting hostnames and securing access. Mastery of these skills enables students to ensure device integrity and security.
IV. Chapter 3: Network Protocols and Communications
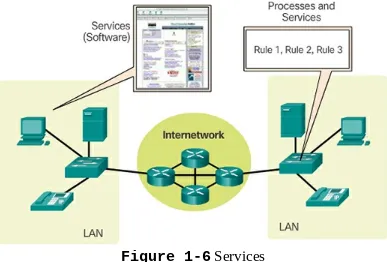
This chapter delves into the protocols that govern network communications, emphasizing the OSI and TCP/IP models. It provides insights into how these protocols facilitate data transfer and communication across networks. A solid understanding of network protocols is crucial for students, as it forms the basis for effective network design and troubleshooting.
4.1 Rules of Communication
This section outlines the fundamental principles of communication in networking, including message encoding and delivery options. Grasping these rules is essential for students to design efficient communication systems.
4.2 Protocol Suites
Students explore various protocol suites, particularly TCP/IP, and their role in enabling communication. This knowledge is vital for understanding how different protocols interact within a network.
V. Chapter 4: Network Access
This chapter introduces the physical and data link layers of networking, focusing on how data is transmitted over various media. It discusses the encapsulation processes and the importance of understanding physical media characteristics. Knowledge of network access is critical for students, as it affects the performance and reliability of network communications.
5.1 Physical Layer Protocols
This subsection covers the physical connections and media used in networking, essential for students to understand how data travels across networks.
5.2 Data Link Layer Protocols
Students learn about the data link layer's role in providing reliable communication over physical media. This understanding is crucial for ensuring data integrity and network performance.
VI. Chapter 5: Ethernet
This chapter examines Ethernet, a predominant LAN protocol. It explains how Ethernet operates and its interaction with the TCP/IP suite. Understanding Ethernet is vital for students, as it forms the backbone of most local area networks and is fundamental for effective network design.
6.1 Ethernet Protocol
The section discusses the structure and function of Ethernet frames, providing students with insights into data encapsulation and addressing.
6.2 LAN Switches
This subsection covers the role of switches in LAN environments, emphasizing their importance in managing data traffic efficiently.
VII. Chapter 6: Network Layer
This chapter introduces the network layer and the concept of routing. It covers the role of routers and how they manage data packets between networks. A solid understanding of the network layer is essential for students to design and troubleshoot complex networks effectively.
7.1 Routing
Students learn about the routing process, including how routers make forwarding decisions based on IP addresses. This knowledge is crucial for managing network traffic.
7.2 IPv4 and IPv6
This section covers the differences between IPv4 and IPv6 addressing, preparing students for the transition to newer protocols in modern networking.
VIII. Chapter 7: IP Addressing
This chapter focuses on IP addressing, including both IPv4 and IPv6. It explains the structure of IP addresses and the importance of subnetting. Mastery of IP addressing is critical for students, as it affects network design and communication.
8.1 IPv4 Address Structure
Students learn about the components of IPv4 addresses, including network and host portions, which are essential for effective network segmentation.
8.2 IPv6 Addressing
This subsection discusses the need for IPv6 and its addressing scheme, preparing students for future networking challenges.
IX. Chapter 8: Subnetting IP Networks
This chapter examines subnetting techniques to optimize IP address usage. It explains how to create subnets based on network requirements. Understanding subnetting is crucial for students to enhance network performance and manage IP addresses effectively.
9.1 Subnetting Techniques
Students learn various methods for subnetting, including classful and classless approaches, which are essential for network efficiency.
9.2 Variable Length Subnet Masking
This section covers VLSM, allowing students to allocate IP addresses more efficiently based on specific network needs.
X. Chapter 9: Transport Layer
This chapter introduces the transport layer protocols, focusing on TCP and UDP. It discusses their roles in data transportation and reliability. A strong grasp of transport layer concepts is essential for students to ensure effective communication in networks.
10.1 TCP and UDP
Students explore the characteristics and differences between TCP and UDP, which helps them choose the appropriate protocol for various applications.
10.2 Port Numbers
This section explains the significance of port numbers in networking, enabling students to understand how applications communicate over the network.
XI. Chapter 10: Application Layer
This chapter covers application layer protocols and services, including HTTP, DNS, and DHCP. It emphasizes their roles in enabling robust communication across networks. Understanding the application layer is vital for students as it directly impacts user experience and application performance.
11.1 Application Protocols
Students learn about key application protocols and their functions, which are crucial for developing and managing network applications.
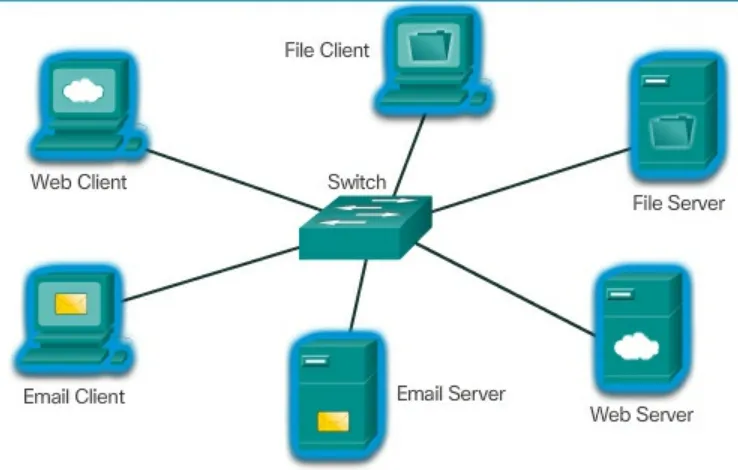
11.2 Client-Server Model
This subsection discusses the client-server model, helping students understand how services are provided and consumed in a networked environment.
XII. Chapter 11: Build a Small Network
This chapter synthesizes the knowledge gained throughout the guide by guiding students in building a small network. It covers design considerations, security threats, and troubleshooting methods. This practical application reinforces learning outcomes and prepares students for real-world networking challenges.
12.1 Network Design
Students learn about the components and topology of small networks, which is essential for effective network planning.
12.2 Network Security
This section addresses security threats and mitigation strategies, preparing students to protect their networks from vulnerabilities.
XIII. Appendix A: Glossary
The glossary provides definitions for key terms encountered throughout the guide. It serves as a valuable reference for students, aiding in the retention of essential networking vocabulary.