ALEL DAN GEN GANDA
MonoHibrid pada Hewan:Warna Rambut Hitam: (gen A):
AA (hitam) x aa (albino)
Aa (Hitam)
Gen A:
1 Kali mutasi : -- >alel a
Gen Ganda:
Bbrp kali mutasi---) bbrp alel: a1,a2,a3, dst
However, it is possible to have several
different allele possibilities for one gene.
The ABO
blood system
• This is a controlled by a tri-allelic gene
• It can generate 6 genotypes
• The alleles control the production of antigens on the surface of the red blood cells
• Two of the alleles are codominant to one another and both are dominant over the third
• Allele IA produces antigen A
• Allele IB produces antigen B
• Allele i produces no antigen
© 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
• About 30% of the genes in humans are di-allelic, that is they exist in two forms, (they have two alleles)
• About 70% are mono-allelic, they only exist in one form and they show no variation
A L E L
G A N D A
Pengertian:
Gen (virgin) kalau bermutasi membentuk Alel ( A --
a)
Banyak Gen mengalami mutasi berulang-ulang, menimbulkan
banyak macam alel (lebih dari 2, disebut alel Ganda)
Contoh: Gen pigmentasi bulu kelinci (Gen C, pigmentasi hitam), memiliki 3 alel:
1. c : albino (tak ada pigmentasi)
2. cch: pigmentasi terang, bulu pigmentasi gelap pada ujung (Chinchilla)
3. ch: pigmentasi bagian ujung-ujung tubuh, bagian lain putih
(H= himalaya)
Certain types of rabbits…
…
can either be brown, white, have a chinchilla pattern, or have a himalayan patternC causes fully brown coat cc causes albino (white) cch
causes a chinchilla pattern
ch
causes a Himalayan pattern
The alleles are arranged in the following pattern
C > cch > ch > c
• Himalayan rabbit – color in certain parts of the body; dominant only to c; chc or chch
• Albino rabbit – no color – allele is recessive to all other alleles; cc
Full color rabbit – alleles are dominant to all others; CC, Ccch, Cch,
or Cc
Chinchilla rabbit – partial defect in pigmentation cch allele dominant to all
other alleles except C;
Kelinci Gelap:
CC, Cc, Ccch, Cch
Kelinci lebih terang; Chinchila:
cch cchh; cch, ch; ccchc
Kelinci Himalaya:
c h ch; ch,c
Kelinci Albino: cc
P; Cch Cch X Ch Ch
F1: Cch Ch X Cch Ch
F2: Cch Cch
Cch Ch
Cch Ch
Ch Ch
P ; CC x Cch Cch
F1 : C Cch x c c
F2: Cc
Multiple alleles
Each gene locus can have more than 2 alleles.
An allele may be dominant to some alleles but recessive to others.
This situation produces more than 2 different phenotypes. Each individual has 2 alleles present in their cells at any one time.
BB or Bb or Bbl
blbl
In this case both A and B are dominant to O (recessive).
A and B are codominant (both expressed)
So... there are four human blood types
AA, AO A blood type BB ,BO B blood type AB AB blood type
or
OO O blood type
Genotypes Phenotypes (Blood types)
IA IA A
IA IB AB
IAi A
IB IB B
IBi B
Sistem Golongan Darah A-B-O. (K. Landsteiner, 1868
–
1943)
Gen Asli I (Isoagglutinogen), :
1. Alelnya : Ia, Ib, I
2. Urutan dominan: Ia = Ib >i
Golongan (Fenotip)
Genotip
A Ia Ia atau Ia i
B Ib Ib; atau Ib i
AB Ia Ib
O ii
Contoh: Gol A x Gol B
(Ia Ia; Ia I) x ( Ib Ib; Ib I)
1. Ia Ia x Ib Ib AB
2. Ia Ia x Ib I AB; A
3. Ia I x Ib I AB; B
Crossing Over dan
Rekombinan
• Sometimes in meiosis, homologous chromosomes exchange parts in a process called crossing-over.
Structure of Chromosomes
– Homologous chromosomes are identical pairs of chromosomes.
– One inherited from mother and one from father
– made up of sister chromatids joined at the centromere.
21 Apr 2002 11
Crossing Over Basics
•
Occurs at One or More Points Along
Adjacent Homologues
•
Points contact each other
•
DNA is Exchanged
•
Menaikkan var.Genetik
Recombination During Meiosis
•
How crossing over
leads to genetic
recombination
•
Nonsister
chromatids break
in two at the same
spot
•
The 2 broken
chromatids join
together in a new
way
Figure 8.18B
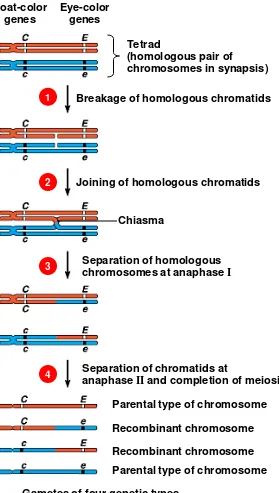
Tetrad
(homologous pair of
chromosomes in synapsis)
Breakage of homologous chromatids
Joining of homologous chromatids
Chiasma
Separation of homologous chromosomes at anaphase I
Separation of chromatids at
anaphase II and completion of meiosis Parental type of chromosome Recombinant chromosome Recombinant chromosome Parental type of chromosome Gametes of four genetic types
•
A segment of one
chromatid has
changed places with
the equivalent
segment of its
nonsister homologue
•
If there were no
crossing over meiosis
could only produce 2
types of gametes
Figure 8.18B
Tetrad
(homologous pair of
chromosomes in synapsis)
Breakage of homologous chromatids
Joining of homologous chromatids
Chiasma
Separation of homologous chromosomes at anaphase I
Separation of chromatids at
anaphase II and completion of meiosis Parental type of chromosome Recombinant chromosome Recombinant chromosome Parental type of chromosome Gametes of four genetic types
TEORI PELUANG
:
The Principles of Probability
•
The Principles of probability can be used to
predict
the
outcomes
of genetic crosses
•
Alleles segregate by complete randomness
•
Similar to a coin flip!
Genetics & Probability
• Mendel’s laws:
–
segregation
–
independent assortment
reflect same laws of probability
that apply to tossing coins or
rolling dice
Probability & genetics
•
Calculating probability of
making a specific gamete is
just like calculating the
probability in flipping a coin
–
probability of tossing heads?
–
probability making a B gamete?
50%
100%
BB
B
B
Bb
B
b
Determining probability
• Number of times the event is expected
Number of times it could have happened
• Probabilitas pedet lahir jantan dari 10 kelahiran ?. Sex rasio 5:5 The probability is 5:10.
• Or you can express it as a fraction: 5/10. Since it's a
fraction, why not reduce it? The probability that you will pick an odd number is 1/2.
• Probability can also be expressed as a
percent...1/2=50% Or as a decimal...1/2=50%=.5
GENETIKA: PERAMALAN KETURUNAN
DENGAN HUKUM PELUANG
Prinsip dasar: Pemindahan gen dari orang tua kpd keturunannya
Berkumpulnya kembali gen-gen dalam sigot
Kakek (Aa)
Org tua: JTN (a)
Org tua: BTN: A
Anak: Aa Konsep Peluang
Analogi pemindahan satu gen (A/a) dari sepasang Gen (Aa) = pelemparan mata uang yang memiliki dua sisi:
-Gambar
-Huruf.
Aa X Aa
F1
mis Peluang muncul aa?
Calculating probability
sperm egg1/2
1/2
offspring=
x
1/4
P
P
PP
P
p
P
p
1/2
x
1/2
=
1/4
p
p
pp
p
P
P
p
x P
p
P
p
male / sperm
P
p
fem al e / eggs
PP
P
p
P
p
pp
1/2
x
1/2
=
1/4
1/2
x
1/2
=
1/4
1/2
+
• Chance that 2 or more independent events will occur together
– probability that 2 coins tossed at the same time will land heads up
– probability of Pp x Pp pp
Rule of multiplication
1/2
x
1/2
=
1/4
1/2
x
1/2
=
1/4
P
p
P
p
Calculating probability in crosses
Use rule of multiplication to predict crosses
YyRr
x
YyRr
yyrr
?%
Yy
x
Yy
Rr
x
Rr
1/4
1/4
1/16
yy
rr
x
Apply the Rule of Multiplication
Got it? Try this!
AABbccDdEEFf
x
AaBbccDdeeFf
AabbccDdEeFF
Bb
x
Bb
bb
cc
x
cc
cc
Dd
x
Dd
Dd
EE
x
ee
Ee
Ff
x
Ff
FF
AA
x
Aa
Aa
1/2
1/4
1
1/2
1
1/4
1/64
Rule of addition
•
Chance that an event can occur
2 or more different ways
–
sum of the separate probabilities
–
probability of
Bb
x
Bb
Bb
sperm egg offspring
1/2
x
1/2
=
1/4
B
b
Bb
1/2
x
1/2
=
1/4
b
B
Bb
1/4
1/4
+
1/2
DASAR TEORI PELUANG
I. Terjadinga sesuatu yang diinginkan = sesuatu yang diinginkan ---keseluruhan kejadian
P (X) = X/(X+Y)
Contoh : P (gambar) = 1/ 1+1 = ½ = 50 %
P (lahir anak jantan) = lahir jantan/ (lahir JTN + BTN ) = ½ = 50 %.
II. Peluang terjadinya 2 persitiwa /lebih yang masing-masing berdiri sendiri
P. (X,Y) = P (X) x P (Y)
contoh: Peluang dua anak pertama laki-laki P (Kl, LK) = (1/2) x ( ½) = ¼.
Aplikasi dalam pewarisan
sifat
Contoh: Gen resesif a (Albino)
P: Aa x Aa
normal normal
F1. AA : Normal
Aa : Normal
Aa ; Normal
aa : albino (1/4)
Peluang anak laki-laki albino ???
Butawarna : gen resesif c
X –linked.
P: Cc x
C-normal normal
F1 : CC: F,
Normal
Cc: F,
Normal
C- : M,
Normal
c- : M
III. Peluang Terjadinya dua persitiwa /lebih yang saling mempengaruhi
P ( X atau Y) = P (x) + P (Y)
Contoh Pelempran dua mata uang bersama
Peluang muncul dua gambar atau 2 huruf = ¼ + ¼ = ½.
PENGGUNAAN RUMUS BINOMIUM: (a+b)2
a, b = DUA KEJADIAN YANG TERPISAH
n = banyaknya kejadian
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
Pelemparan 3 mata uang ( n= 3) ; (a+b) 3 = a3 + 3 a2b + 3 ab2 + b3
Peluang I G , 2 H = 3 ab2 = 3 ((1/2)(1/2)2
= 3/8.
n=3
‘(2G, 2 H)= ? N = 2
(a2+2ab+b2)
2 ab = 2 (1/2) (1/2) = 1/2
Penggunaan Rumus Binomium: Peluang pewarisan sifat Albino
Jika suatu perkawinan mempunyai 4 anak ( n = 4) Maka
Peluang semua anak normal ?
Rumus (a+b)4 = a4+ 4 ab3+6a2b2+4ab3+b4
Peluang 4 anak normal (a4) = (3/4)4 = 81/256
JTN : Aa x BTN Aa
¾ Normal ¼ Albino
Aplikasi lain teori peluang dalam genetika
Pada suatu perkawinan:
Genotip diketahui, mis : Aa Bb Cc X Aa Bb Cc
aabbCc aa = 1/4 bb = ¼ Cc = 1/2
Peluang (aabbCc) = 1/4x1/4x1/2 = 1/32
AaBbCcDdEe X AaBbCcDdEe
AABbccDdEE ? = 1/2x1/2x1/4x1/2x1/4 = 1/256
Contoh Pada dua sifat : GEN: Dominan dan Resesif
-mata Merah Dominan thd Putih (M) -Kuliut Albino Resesif (a) Genotip Mm Aa X mm Aa
Fenotip
Aa X Aa A A
a a
AA F1 ??? Aa
Aa
aa = 1/4 Bagaimana Peluang Gen Sifat tsb diwariskan
pada anak anaknya?
M = ½
a = ¼ = 1/8 Mm x mm
M m
m m
Mm
Mm
mm
Y X
X X
Fertilisation Possible
Offsprings PEJANTAN
Father
Sex cells
Meiosis
INDUK Mother
XX XY
Chance of a Female 50%
Chance of a Male 50%
X Y X XX XY X XX XY
© 2007 Paul Billiet ODWS
The inheritance of Gender
Summary:
Males and females have different purposes defined by their gametes
Development of sexes is dependent on:
genes
hormones environment
Mengapa Seks Penting: Kasus Keseimbangan Hormonal,
penentuan jenis kelamin menjadi tidak sederhana
Contoh: PIG betina
Awal bunting
Lahir : Jantan normal
Betina : ??? (alat kelm + Jantan)
Testoteron
Dewasa
Injeksi hormon betina
(Progesteron + Estrogen)
Tetap tidak menunjukkan perilaku betina normal
Injeksi hormon jantan
(Testoteron)
Perilaku jantan jelas, fungsi seks jantan
Crocodile Sex Determination
Incubating temperature
30oC all female 32oC all male
31oC 50% female, 50% male
http://a.abcnews.com/images/Sports/rt_thailand_ 080514_ssh.jpg
Hasil Analisis Kariotyping:
Metode:
Disusun besar- kecil Besar,bentuk, homolog Urutan:
Besar—kecil
Besar dan kesamaan bentuk
Letak/bentuk acak
Jumlah dapat dihitung
Manfaat : Penentuan Sex
Manfaat:
R I N G K A S A N
1. MAMALIA : XY --- Betina : XX
Jantan : XY
2. BELALANG : XO --- Betina : XX
Jantan: XO/ X- (tak ada krom Y)
3. UNGGAS/
BURUNG: ZW--- Betina ZW atau ZO
Jantan ZZ (burung) atau ZZ (Ayam)
4. LEBAH : haploid/diploid Betina : 2n : 32 buah
Jantan : n : 16 buah Catatan : 1,2,3 dasar kromosom seks
1,3 ada perbedaan (berbalikan)
4 dasar jumlah kromosom
Dasar: Kariotyping untuk menentukan seks (X-Y Kromosom)
Manfaat: Pre-derterminasi seks (deteksi dan manipulasi seks)
R I N G K A S A N II
1. JANTAN Heterogametik:
a. Mamalia, Manusia : krom Y == JANTAN
betina : XX Jantan : XY
b. Heminiptera (Kepik, belalang) Betina : XX
Jantan : X0 (tak ada krom Y)
2. BETINA Heterogametik : burung, Ikan , Kupu a. Burung : betina kromosom mirip Y spt manusia
betina : ZW : bukan penentu seks yg kuat Jantan: ZZ
b. Spesies lain (unggas/ayam/itik) : mirip XO Betina : ZO
Tipe XY: Drosophla, manusia, mamalia
Sex Drosophila Manusia
Jantan 2 XY + 6 A 2 XY + 44 A
Betina 2 XX 2 XX
Contoh : drosophila 6 autosome : bentuk sama
2 seks kromosom: bentuk beda :XX, XY
X batang lurus, Y sedikit bengkok di salah satu ujungnya
Munculnya kelainan kromosom
Normal:
XX x XY
X X , Y
XX XY
Abnormal: non disjunction, meiosis ,
pembt sel kelamin jantan/betina pd drosophila X X x XY
ND Normal
XX O X Y
XXX XXY XO YO
Kelainan kromosom pada manusia
: sindrom turner : wanita sindrom klinefelter: priasindrom down: autosom/mongolisme
XX X XY
ND
X XY O
XXY XO
Klinefelter (47) : Turner (45)
• testis tak berkembang -ovary tak berkembang, tak menstruasi
•Mandul dll - kelj. Mammae tak berkembang baik dll.
Peran Krom:
Manusia Drosophila
X Menentukan sifat wanita Menentukan sifat betina
Menentukan kehidupan, YO = lethal
Y Pemilik gen sifat laki-laki (asal ada Y = laki-laki
Teori indeks kelamin pada drosophila: krn adanya ND Oleh C.B. BRIDGES: faktor penentu seks
jantan pada kromosome, betina pada autosome
Indeks = Jmlh. Kromosome X = X/A Jmlh. pasangan autosom
Contoh:
Normal BTN 3 AA XX = X/A = 2/2 = 1.0
JTN 3 AA XY = X/A = ½ = 0.5
Population Genetics
•
mempelajari tingkah laku gen dalam populasi
(perubahan
frekuensi gen)
•
Mekanisme pewarisan sifat pada kelompok ternak
(populasi), Pada sifat kuantitatif dan kualitatif
•
how often or frequent genes and/or alleles appear in the
population
Populasi
:
Kelompok ternak t.a. bangsa/spesies yang sama, di daerah tertentu dimana antara anggota terjadi saling kawin satu dgn yang lainPerlu estimasi frekuensi gen (merugikan) bagi generasi
mendatang
( Mis. Ekspresi gen-gen yang mengalami
mutasi
, dll)
Perbedaan Genetika Individu dan Populasi
INDIVIDU
POPULASI
1.LINGKUNGAN: 1
tempat/1 lingkungan
1.banyak tempat/banyak lingkungan
2.WAKTU:
terbatas satu generasiMasa panjang, generasi ke generasi tumpang tindih.
3. GENOTIP:
satu sampel genetik khas.Susunan gen tetap
Tak ada variasi/ satu ukuran Tidak terjadi evolusi
Gen pool
Population Genetics
•
Is simply, the study of Mendelian genetics in
populations of animals
•
Basic foundation is the Hardy-Weinberg law
•
Usually limited to inheritance of qualitative traits
influenced by only a small number of genes
•
Important to understand why characteristics, desirable
or not, can be fixed or continue to exhibit variation in
natural populations
•
Principles applied to the design of selection strategies
to increase the frequencies of desirable genes or
KONSEP-KONSEP DASAR
:
FREK. GEN Frek Genotip Frek. fenotip
Konsep Genetik: bahwa setiap indv. mempunyai dua lokus .untuk setiap pasang gen
Contoh: Sifat Kualitatif (Warna kulit), dikontrol sepasang Gen R-r Kemungkinan Genotip: RR, Rr, rr (mis sapi Short Horn)
(Fenotip: ?)
Frek. Gen (R ) = p; alelnya ( r ) = q
Frek gen R = p = juml. Gen R/ juml. Gen (R + r) Frek gen r = q = juml. Gen r/Jumlh gen (R + r)
Pendekatan:
:The study of the change of allele
SEBAB SEBAB MODIFIKASI GENETIK
Terjadinya modifikasi genetik, perubahan dalam frekuensi gen:
-Adaptasi agar dpt survive dlm pop
-Lingkungan berubah
-Terjadi evolusi
Perilaku Gen dalam Populasi: HK. Hardy Weinberg:
APAPUN JENIS GENOTIP/FREKUENSI AWAL AKAN TERCAPAI KESEIMBANGAN DARI SATU GENERASI
KE GERASI BERIKUTNYA
Syarat Hk. H. Weinberg:
1. Tidak ada kekuatan yang mampu merubah frek.gen (mutasi, dll)
2. Pada pop. Berlaku Hk Mendel 3. Populasi besar
Jadi terjadi keseimbangan, maka frek.gen/alel dll dapat ditentukan dalam populasi
Mis : frek A = p, Frek a = q , maka p + q = 1
Jika terjadi perkw. Acak: Jumlah total: p2 (AA)+2pq (Aa) + q2(aa)
Gamet
(frek)
A
(p)
a
(q)
A (p)
Genotip
(frek)
AA
(p
2)
Aa
(pq)
a (q)
Genotip
(frek)
Aa
(pq)
Aa
(q
2)
Only one of the populations below is in
genetic equilibrium. Which one?
Population sample Genotypes Gene frequencies
AA Aa aa A a
100 20 80 0 0.6 0.4
100 36 48 16 0.6 0.4
100 50 20 30 0.6 0.4
100 60 0 40 0.6 0.4
Contoh Perhitungan Frek . Gen/ (Kodominan):
Fenotip
Merah
Roan
Putih
Genotip
RR
Rr
rr
Jika diketahui dalam populasi sapi short horn: 900 (merah);
450 (Roan) dan 150 (putih)
Brp. Frek (RR); Frek (R) ) ?
F (RR)) = jml. Indv. RR/ Juml tot indv. = 900/1500 = 0.6 = 60 %
F (R ) = jml R/ Total geg
Contoh : DOMINANSI PENUH
:Pada pop 100 ekor sapi FH ditemukan 1 sapi berwarna kemerahan Brp frekuensi FH yang hitam heterosigot?
H = p
M = q ; maka frek gen HH + HM + MM = 1
Atau p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1 berasal dari ( p + q = 1)
Diketahui q2 = 0.01 –maka q = 0.1---p = 0.9
2 pq = 2 (0.1) (0.9) = 0.18
LATIHAN/ DISKUSI/HOMEWORK
:Fenotip
Genotip
j.indv.
j.gen R
J. Gen r
Merah
RR
80???-Roan
Rr
???-
50 50Putih
rr
20???-Total
???-
210 90EXAMPLE ALBINISM IN THE INDO. BUFFALO POPULATION
Frequency of the albino phenotype = 1 in 20 000 or 0.00005
Phenotypes Genotypes Hardy Weinberg frequencies
Observed frequencies
Normal AA p2
0.99995
Normal Aa 2pq
Albino aa q2 0.00005
A = Normal skin pigmentation allele Frequency = p
a = Albino (no pigment) allele Frequency = q
Normal allele = A = p = ?
Albino allele = q =
HOW MANY buffalo IN Indonesia/Toraja
ARE CARRIERS FOR THE ALBINO
ALLELE (Aa)?
a
allele = 0.007
=
q
A
allele
=
p
But
p + q = 1
Therefore
p
= 1- q
= 1
–
0.007
= 0.993 or 99.3%
The frequency of heterozygotes (
Aa
)
=
2pq
= 2 x 0.993 x 0.007
= 0.014 or 1.4%
• Genotype Number Number of A1
• A1A1 4 2 X 4
• A1A2 41 41
• A2A2 84
• A1A3 25 25
• A2A3 88
• A3A3 32
• Total 274
• f(A1) = ((2 X 4) + 41 + 25) ÷ (2 X 274)
• = (8 +41 + 25) ÷ 548
• = 74 ÷ 548
• = 0.135
SUMMARY
•
Genetic drift
•
Mutation
•
Mating choice
•
Migration
•
Natural selection
All can affect the
transmission of genes
from generation to
generation
Genetic Equilibrium
If none of these factors is operating then the relative
proportions of the alleles (the
GENE
FREQUENCIES
) will be constant
Factors causing genotype frequency
changes
•
Selection
= variation in fitness; heritable
•
Mutation
= change in DNA of genes
•
Migration
= movement of genes across populations
•
Recombination
= exchange of gene segments
•
Non-random Mating
= mating between neighbors
rather than by chance
•
Random Genetic Drift
= if populations are small
enough, by chance, sampling will result in a different
FAKTOR-FAKTOR YG MAMPU
MERUBAH KESEIMB. FREK GEN
1. MUTASI: Gen mpj sifat “dpt bermutasi”, Gen R ____> r (frekuensi Gen r meningkat dlm pop).
Gen-gen terdapat dalam berbagai bentuk sbg alel yang berlainan forward mutation (maju) mengurangi gen tipe liar back mutation (surut)
Akibat : menimbulkan polymorfisma : (banyak alel dari gen yg sama)
.2. SELEKSI: Kekuatan besar pengaruhnya terhadap frek alel seleksi buatan
3.
iNBREEDING
: Perkawinan Keluarga dan tidak
acak ,
ekspresi gen resesif meningkat
• Penurunan variabilitas genetik
• Peningkatan homosigotik
Manfaat : bagi para breeder
Hewan yang mempj persamaan ciri dikawinkan (inbreeding) dihasilkan suatu strain/purebreed yang homogen
Prinsip dasar: mempertahankan gen-gen tertentu pd frekuensi tinggi, sementara gen-gen lain dapat dihilangkan
(mengekalkan/mempertahankan sifat yang diinginkan)
Aa X Aa
AA Aa
Aa
aa
Homosigot 2/4 = 50 %
Homosigot resesif:
¼
= 25 %
AA X AA Aa X Aa aa X aa
AA,AA AA,Aa,Aa,aa aa, aa
Homosigot : 6/8= 75, %
4
.
REPROD. SEXUAL
dan
rekombinasi
gen:
variabilitas meningkat dg perkw. Acak
(pilihan acak dr gen 2 parent, cenderung memprod.
Keturunan lebih bervariasi scr genetik), karena:
•
Adanya pilihan acak sel benih (meiosis)
•
Fenomena rekombinasi gen dalam kromosom
5. MIGRASI: perpindahan gen( ke dalam/keluar pop) Mis . Adanya import ternak sapi perah
(frekuensi fenotip/genotip sapi perah meningkat dalam pop)
Migrasi penduduk (becana alam/perang) merubah frek gen dari populasi yang asli/yang didatangi.
6. ARUS GENETIK: random genetic drift
Perubahan scr acak frek.gen dari
generasi ke generasi oleh teori PELUANG, A a X Aa mis Aa -- peluang teoritis sama mewaris