REPORT
WRITING TECHNIQUES
Dr. Eng. Risdiyono
[email protected] 081325000201 FB : Risdy Adja
Academic
Objective
Write Reports
To give a brief depiction about how to
effectively
Agenda
Framing Motive
Writing Problems and Expectations
Before Writing
Basic Knowledge and Preparations
Writing Skills
Planning, Drafting and Editing
Part 1
Framing Motive
What is the most critical skills an
employee should have?
1. Teamwork
2. Leadership
3. Critical/Analytical Thinking
4. Active Listening
5. Customer Orientation
6. Oral Communication
7. Time Management
8. Written Communication
9. Decission Making
What employers say…
•
1/3 of the employees in America’s top
companies are poorly trained in writing and
cannot compose a coherent business response
(National Commission on Writing)
•
Conscientious employers are retraining
employees to write in the workplace
What does all this mean?
Miscommunication is dangerous
How to be a Good Writer ?
5W + 1H
How to be a Good Writer ?
Learn from the
Samples
given by
Experts
How to be a Good Writer ?
Know the Purpose of your report
Find, Read, Analyze some well known
good reports
Adopt them in your writing
Need to go Faster?
List of Problems in report writing :
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Part 2
Before Writing
Basic Knowledge and
Preparations
2
Before Writing
Basic Knowledge and
Preparations
•
How to write the worst report ?
•
A high quality report
•
Why do reports fail ?
•
Basic Skills
Please List
15
things you
Here are some of the ideas
from a group of participants at
one of training sessions:
•
Too much information
•
No structure
•
Too many technical details no one can
understand
•
Not enough information
•
Use really long words no one can
understand
•
No conclusion
•
Write it on toilet paper
•
No clear aim to the report
•
Not enough paragraphs and bullet
points
•
Report on something everyone knows
about
•
Badly spelled
•
Boring
•
No date or name on it
•
No summary
•
Text too small
•
Weighs 10 kilograms
•
Not sure who you’re writing for
•
Makes rude comments about the
company
A High Quality Report
The report
must be
–
Clear
•
Well structured, clear, concise, suitable for the
intended audience
–
Professional
•
statistically correct, correctly spelled, produced with a
decent word processor
–
Well illustrated
•
illustrations that aid understanding, integrated with
text
5 C’s of Effective Writing
•
Clear
•
Concise
•
Complete
•
Correct
•
Courteous
Clear
(Clarity of Thought)
•
Written in a simple, clear and lucid language.
Its language should not be difficult and
confusing.
•
There should be no ambiguity as regards the
statements made in the report.
•
A reader should be able to understand the
entire report easily, exactly and quickly. In fact,
this is the basic purpose of report writing.
Concise
(Compact but Comprehensive)
•
A lengthy report is not necessarily a good report.
•
In fact, report should be a brief and compact
document.
•
At the same time, it should give complete
picture of the problem under investigation.
Complete
(Self Explanatory)
•
A good report is always a complete and
self-explanatory document.
•
It should give complete information to the
readers in a precise manner.
•
Repetition of facts, figures, information,
conclusions and recommendation should be
avoided.
Correct
(Accurate in all Aspects)
•
A good report is always factual and reliable.
•
The findings, conclusions and recommendations
included in the report should be supported by
information and data collected from reliable
sources and verified.
•
Statistical tables, should support statements
made in the report. Attention needs to be given
to this reliability aspect in report writing
Courteous
(Convenience to read)
•
A good report should be drafted in an impersonal
and impartial manner.
•
The report is prepared for the benefits of a person
who needs it and not for the benefit of the person
who prepares it.
•
Emotions, sentiments, personal views etc. should
be kept away while drafting a report.
•
The approach of report writer should be positive
and constructive.
Part 3
Writing Skills
The challenge
A high quality report vs time constraints
1. Planning
2. Drafting
3. Editing
Adopt a systematic approach
o
Define the problem
o
Gather the necessary information
o
Analyse the information
Organize the information
Write the draft report
•
Check the flow
•
Proof read
•
Finalize
1. Planning
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s
o
Define the problem
o
Gather the necessary information
o
Analyse the information
Organising ideas coherently
Message
New question:
Why?
2. Drafting
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s
Organize the information
Write the draft report
Grouping and summarising
•
Report formats are designed to help you group
and summarise ideas.
•
Designing the structure
first
will save you time
and improve the quality of the report.
Drafting: top tips
•
Write quickly.
•
Write in your own voice
•
Write without interruption.
•
Write without editing.
•
Keep to the plan of your
outline.
Argument: core techniques
•
Deductive
•
Inductive
You should buy if the market is failing to factor element x into McCrackle’s share price.
The market is failing to factor element x into McCrackle’s price.
Buy McCrackle. (and) (therefore)
You should buy McCrackle. McCrackle’s new risk
mitigation system is not factored into its current price.
McCrackle is improving its debt profile rapidly.
Explanation: six types
•
Examples
•
Categorisation
•
Process
•
Definition
•
Cause and effect
•
Comparison and contrast
Effective paragraphs:
1. Unity
2. Topic sentence
3. Coherent support
4. Adequate development
Four characteristics:
1. Unity
•
A paragraph should be about one topic
•
A topic (Greek
topos
, ‘place; location’) is your
position on the subject of the paragraph: your
point of view
•
What do you want to
say
about the subject?
Effective paragraphs:
2. Topic sentences
•
Key characteristics:
–
Single idea
–
What you want to say about the paragraph’s
subject
–
15 words maximum
•
In a draft paragraph, look for a potential topic
3. Coherent support
•
Create coherence by using transitional devices
•
For a list of transitional devices, go to:
http://owl.english.purdue.edu/owl/resource/574/02/
Effective paragraphs:
Use the topic sentence to identify how you will
develop the topic.
•
Are you arguing or explaining in the paragraph?
•
What type of argument or explanation are you
using?
- argument: deductive or inductive?
- explanation: which of the six types?
3. Editing
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s
•
Check the Flow
•
Check the Format
•
Proof read and Finalize
Why edit?
•
To make reading easier
•
To create quality more quickly
•
Because you must
(you can’t get it right first time)
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s
E
di
tin
Editing efficiently
•
Edit on three levels:
- paragraph
- sentence
- word
•
Use a colleague
•
Take a break
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s
E
di
tin
g
A. Checking the FLOW
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s
E
di
tin
FLOW : Editing paragraph sequences
•
Topic sentences should make sense in order
•
Use topic sentences as
–
Margin summaries
–
Sequence of sentences
in the summary black box
–
Supporting text for graphics
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
LO
W
Managing your sentences
Follow the ‘15-25’ rule
•
15 words maximum for all messages, key points and
topic sentences
•
25 words maximum for all other sentences
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
LO
W
Deal with long sentences by:
•
cutting long sentences into
separate sentences
•
separating ‘multiple’ sentences
•
cutting down long sentences
•
making non-sentences
grammatically correct
•
finding strong subjects and verbs
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
LO
W
Plain English
•
Make your average sentence length 15 to 20
words.
•
Use only the words that your reader is most
likely to understand.
•
Use only as many words as you need.
•
Use the strongest, clearest and most specific
verbs you can.
•
Say what you mean.
•
Punctuate clearly and simply.
•
Depend on your focus (what will be
emphasized)
•
Usually, a technical report uses passive
voices
Passive or Active?
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
LO
W
•
ACTIVE FOCUSES
ON THE
PERSON
:
Risdy
used
the Davie
method to test the
oxygen saturation in
all three locations.
•
PASSIVE FOCUSES
ON THE
PROCESS
:
Oxygen saturation
was tested
in all three
locations using the
Davie method.
Active Voice vs. Passive Voice
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
LO
W
•
ACTIVE VOICE
:
Risdy detected
tiny shifts
in blood flow to parts of
the brain with functional
magnetic resonance
imaging.
•
ACTIVE VOICE
: Adam
prepared
a 50ml
solution using distilled
water in volumetric
•
PASSIVE VOICE
:
Tiny shifts in blood flow to
parts of the brain
were
detected
with functional
magnetic resonance
imaging.
•
PASSIVE VOICE
:
A 50ml solution
was
prepared
using distilled
water in volumetric
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
LO
W
Repetition & Signpost
It is important that each part tells the same story
at the appropriate level of detail.
–
Only summary may be read by a manager seeking
an “executive summary”.
–
Only conclusions or introduction may be read by
someone interested in the subject but only
wanting to adopt the main findings.
–
The whole document may be read by someone
wishing to follow-up on the work
•
Repetition
and
signposts
help the reader who
(c) Swansea University. All Rights Reserved.
How to Repeat Yourself
•
Say what you
will say
(
in brief
) in the
Summary
•
Say what you
will say
(
in more detail
) in the
introduction
•
Say what you
have to say
(
in full in the body
)
with signposting
•
Say what you
have said
(
in the conclusions
)
•
Emphasise the good bits in an extended
abstract or executive summary
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
LO
W
(c) Swansea University. All Rights Reserved.
How to Signpost
•
Open each section with a statement of context:
–In the [last section] we ….
–In [this section] we now …
•
Close each section with a statement of context:
–In this [section] we ….
–In the [next section] we will …
•
Provide cross references
–As we saw in [a previous section] …
–As we will show in [a later section] …
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
LO
W
B. Checking the FORMAT
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s
E
di
tin
g
Numbering
•
Numbering important parts of the report helps
with signposting
–Figure 2 shows ….
Better than the figure on page 3 shows
•
Things that should usually be numbered
–Parts, Chapters and Sections
–Figures and Tables
–Equations
•
Things that can be numbered
Using numbers
Use numbers very sparingly.
•
Use no more than
one
number in any topic
sentence of a paragraph.
•
Try to use no more than
two or three
numbers in any other sentence.
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
O
RM
AT
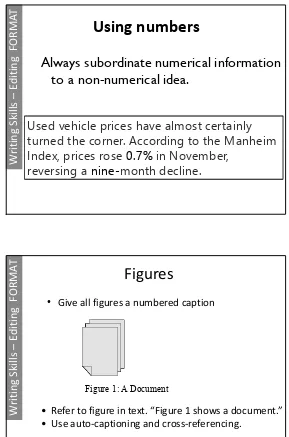
Using numbers
Always subordinate numerical information
to a non-numerical idea.
Used vehicle prices have almost certainly
turned the corner. According to the Manheim
Index, prices rose
0.7%
in November,
reversing a
nine-
month decline.
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
O
RM
AT
Figures and Tables (Floats)
Golden rules for Figures and Tables:
•
Describe float in text (integration), make sure it
matches description
•
Place after the first mention in the text
•
Make sure float conveys the desired message clearly:
keep it simple!
•
Provide informative captions
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
O
RM
AT
Figures
•
Give all figures a numbered caption
• Refer to figure in text. “Figure 1 shows a document.”
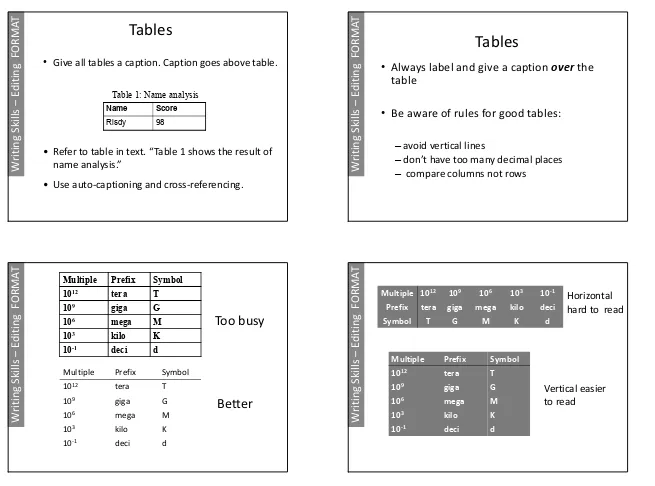
Figure 1: A DocumentTables
•
Give all tables a caption. Caption goes above table.
Table 1: Name analysis
• Refer to table in text. “Table 1 shows the result of
name analysis.”
• Use auto-captioning and cross-referencing.
Name Score Risdy 98
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
O
RM
AT
Tables
•
Always label and give a caption
over
the
table
•
Be aware of rules for good tables:
–
avoid vertical lines
–
don’t have too many decimal places
–
compare columns not rows
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
O
RM
AT
Multiple Prefix Symbol 1012 tera T
109 giga G
106 mega M
103 kilo K
10-1 deci d Multiple Prefix Symbol
1012 tera T
109 giga G
106 mega M
103 kilo K
10-1 deci d
Too busy
Better
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
O
RM
AT
Multiple Prefix Symbol
1012 tera T
109 giga G
106 mega M
103 kilo K
10-1 deci d
Horizontal
hard to read
Vertical easier
to read
Multiple 1012 109 106 103 10-1
Prefix tera giga mega kilo deci
Symbol T G M K d
Busy – too
many DP’s
Better
Number ofProcessors Time (secs)
1 28.35221
4 7.218812
8 3.634951
16 1.929347
Number of
Processors Time (secs) 1 28.35 4 7.21 8 3.63 16 1.92
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
O
RM
AT
Equations
•
Give all equations a label
• Refer to equation in text. “Equation (1) shows
the formula for a quadratic.”
• Use your word processor’s equation editor to
get auto-captioning and cross-referencing.
(1)
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
O
RM
AT
Equation is part of the language
•
Avoid:
We have the following result.
F = ma
( Is F = ma part of the sentence, or a
sentence of its own? )
•
Do:
We have the following result:
F = ma.
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
O
RM
AT
•
Good
•
Bad
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s –
E
di
tin
g
F
O
RM
C. Proof Read and Finalize
W
rit
in
g
Sk
ill
s
E
di
tin
g
Re-Check Technical Issues
•
Sectioning
•
Table of Contents
•
Spelling and Grammar
Sectioning
•
Proper division of your work into sections and
subsections makes the structure clear and the
document easy to follow
•
Use styles in word/ sectioning commands in
Latex
\begin{section}….\end{section}
Table of contents
•
Provides “navigation aid”
•
Make sure TOC agrees with main body of text
Spelling and Grammar
•
Use a style manual/dictionary if in doubt
•
Spell check!!!!
•
Proofread!!!!
Acronyms
•
Avoid UA (useless acronyms)
•
DUAT: Do not use acronyms in titles.
•
DUAA: Do not use acronyms in abstracts.
•
Defined once the first time you encounter it
(“The Nuclear Terminator – henceforth NT –
blew up.")
•
Use sparingly.
Be precise
•
Avoid: “Method A is much better than method B."
•
Do: “Method A is 60% faster than method B.“
•
Avoid : “The speed of test A depends on X."
•
Do: “Test A is faster when X is larger."
Keep It Simple
•
Employ uncomplicated terms.
Be assertive without lying
•
Avoid: “Test A might be the best approach."
•
Do: “We know twelve tests. A is the fastest of
them."
Use strong verbs
•
Avoid: “We made use of categorization."
•
Do: “We categorized."
Begin sentences in English
•
Avoid: “Ω is larger than one"
•
Do: “The parameter Ω is larger than one."
Figures
Write good
Papers
Tables and Figures
•
Tables, figures, references must be referenced in
the main text
What's a good title
•
Must be precise.
•
Must be sexy and compelling.
•
No acronym.
What's an abstract?
•
First sentence is key: avoid rambling.
•
Sexy: why must I read this paper absolutely?
•
The strong points must be there. (Sometimes,
people won't read your paper.)
•
Self-contained: no reference, no hyperlink, no
image.
Recipe for a good 4-sentence abstract
•
State the problem.
•
Why is it interesting?
•
What did you achieve?
Abstract/executive summary
Describes the problem and the solution in a few
sentences. It will be all the big boss reads!
Remember the 2 rules
–
Keep it
short
–
State problem
and
solution
Ex
am
pl
e
GOOD example of Executive Summary
(Accounting & Finance)
• Executive Summary
This report provides an analysis and evaluation of the current and prospective profitability, liquidity and financial stability of Outdoor Equipment Ltd. Methods of analysis include trend, horizontal and vertical analyses as well as ratios such as Debt, Current and Quick ratios. Other calculations include rates of return on Shareholders Equity and Total Assets and earnings per share to name a few. All calculations can be found in the appendices. Results of data analyzed show that all ratios are below industry averages. In particular, comparative performance is poor in the areas of profit margins, liquidity, credit control, and inventory management.
The report finds the prospects of the company in its current position are not positive. The major areas of weakness require further investigation and remedial action by management.
Recommendations discussed include:
• improving the average collection period for accounts receivable
• improving/increasing inventory turnover
• reducing prepayments and perhaps increasing inventory levels
The report also investigates the fact that the analysis conducted has limitations. Some of the limitations include:
forecasting figures are not provided, nature and type of company is not known nor the current economic conditions, data limitations as not enough information is provided i.e. monthly details not known while results are based on past performances not present.
• Executive Summary
This report provides an analysis and evaluation of the current and prospective profitability, liquidity and financial stability of Outdoor Equipment Ltd.
Subject Matter Method of Analysis
Finding
The report finds the prospects of the company in its current position are not positive. The major areas of weakness require further investigation and remedial action by management.
Conclussions
Recommendations
Limitations of the report
Recommendations discussed include:
• improving the average collection period for accounts receivable
• improving/increasing inventory turnover
• reducing prepayments and perhaps increasing inventory levels
The report also investigates the fact that the analysis conducted has limitations. Some of the limitations include: forecasting figures are not provided, nature and type of company is not known nor the current economic conditions, data limitations as not enough information is provided i.e. ...
GOOD example of Executive Summary
(Marketing)
• Executive Summary
This report was commissioned to examine why the sales volume of Choice Chocolate has dropped over the past two years since its peak in 1998 and to recommend ways of increasing the volume.
The research draws attention to the fact that in 1998, the market share of Choice Chocolate was 37%. The shares of their key competitors such as Venus and Bradbury were 22% and 18% respectively. The size of the chocolate market then was $36 million.
Statement of problem/ topic
Key Findings Summarized
Over the next two years, although Choice Chocolate retained its market share the volume of sales in the whole market decreased to $29 million. Further investigations reveal that this market shrinkage coincided with an increase in health awareness amongst consumers who regard the milk and sugar ingredients in chocolate as negative; moreover, since the second half of 1999, an increasing number of rival ‘health candies’ had appeared on the market. These claimed to offer the consumers a healthy alternative. These factors appear to be the major causes of the decreased sales volume of Choice Chocolate.
Key Findings Summarized
Slim Choice is the latest chocolate range put forward by the R & D Department of Choice Chocolate. The report evaluates this range and concludes that it would be an ideal candidate to meet the challenge presented by the market and could satisfy the new consumer demand since it uses significantly reduced milk and sugar ingredients and is endorsed by renowned health experts. According to 97% of the 2000 subjects tested recently, it also retains the same flavor as the original range.
It is recommended:
• that Choice Chocolate take immediate measures to launch and promote Slim Choice alongside its existing product range;
• that Slim Choice adopt a fresh and healthy image;
• that part of the launch campaign contains product endorsement statements by renowned health experts;
• that Slim Choice be available in health food shops as well as in traditional chocolate retail outlets
Recommendation Summarized
POOR example of Executive Summary
(Marketing)
• Executive Summary
Every time a business or consumer purchases products or services they display forms of buyer behaviour that are influenced by many factors. The following report looks at the fast food industry and will analyse four McDonalds’ key products and services. It highlights what type of consumer buying or business buying behaviours are displayed in the purchase of a product or service and explains why each behaviour may occur. This enables a conclusion to be drawn from applying theory to reality. Although a full comprehension of buying behaviour is impossible, since everyone is an individual, it is useful to reflect on common behaviours and attempt to divide behaviours in types and stages. Even McDonalds, a leader in marketing cannot always predict consumer behaviour.
POOR example of Executive Summary
(Marketing)
• Executive Summary
Every time a business or consumer purchases products or services they display forms of buyer behaviour that are influenced by many factors.
The following report looks at the fast food industry and will analyze four McDonalds’ key products and services.
Background to Problem
Report’s aims
It highlights what type of consumer buying or business
buying behaviours are displayed in the purchase of a
product or service and explains why each behaviour
may occur. This enables a conclusion to be drawn from
applying theory to reality.
Although a full comprehension of buying behaviour is
impossible, since everyone is an individual, it is useful to
reflect on common behaviours and attempt to divide
behaviours in types and stages. Even McDonalds, a
leader in marketing cannot always predict consumer
behaviour.
The information in this executive summary is vague
rather than summarizing what the report found.
Presentation Resources
•
Jobling, C. P.,
How to Write a Technical Report
•
Daniel Lemire,
Write good papers
•
Alan Barker,
Writing an equity research report
•
Academic Skills Center, University of Canberra,
Report Writing