Skrining Fraksi Aktif Ekstrak Etanol Akar Pasak Bumi
(Eurycoma longifolia Jack) Sebagai Antioksidan
Vera Nurviana, Nurkhasanah, Laela Hayu Nurani Faculty of Pharmacy, Ahmad Dahlan University
Jl. Prof Soepomo, Janturan, Yogyakarta, e-mail: [email protected]
ABSTRAK
Eurycoma longifolia Jack telah digunakan sebagai obat tradisional untuk menyembuhkan berbagai jenis penya-kit. Tumbuhan tersebut dilaporkan mempunyai aktivitas sebagai antioksidan, antimalaria, antikanker, penambah stamina, dan antiangiogenesis pada beberapa penelitian. Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah skrining fraksi aktif sebagai antioksidan dari ekstrak etanol Eurycoma longifolia Jack. Ekstrak etanol masing-masing difraksinasi meng-gunakan n-heksan, etil asetat, dan metanol. Aktivitas antioksidan yang diamati mengmeng-gunakan metode DPPH. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa semua perlakuan memiliki aktivitas sebagai penangkap radikal bebas, adalah ek-strak etanol dengan nilai ES50 (60.796 ± 0.051 µg/ml) fraksi n-heksana (237.621 ± 1,662 µg/ml) fraksi etil asetat (53.597 ± 0.028 µg/ml), dan fraksi metanol (109760 ± 0,34 µg/ml). Aktivitas antioksidan tertinggi E. longifolia menggunakan metode DPPH adalah fraksi etil asetat.
Kata kunci: Eurycoma longifolia Jack., antioksidan, radikal bebas, DPPH.
ABSTRACT
Eurycoma longifolia Jack has been used as traditional medicines to cure many kinds of diseases. Previous re-searches reported to have antioxidant, antimalaria, anticancer, stamina enhancer, and antiangiogenesis activities. The objective of this research was screen active fraction as antioxidant from ethanolic extract of Eurycoma longi-folia Jack. The ethanolic ectract was fractionated using n-hexan, ethyl acetate, and methanol. Antioxidant cctivity
were observed using DPPH method. The results showed that all the treatments had the activity as scavenging the free radical, with the value ES50 ethanolic extract was (60,796 ± 0,051 µg/ml) fraction of n-hexan (237,621 ± 1,662 µg/ml) ethyl acetate fraction was (53,597±0,028 µg/ml), and methanolic fraction was (109,760±0,34 µg/ ml). The best activity radical scavenging using DPPH method is ethyl acetate fraction.
INTRODUCTION
Antioxidant is a compound that is very important in maintaining good health. Some diseases such as cancer, heart disease, arthritis, diabetes, liver and other degenerative diseases are increasingly being suffered by the people of Indonesia. Such diseases can be caused due to antioxidants present in the body is not able to neutralize the increase of the concentration of free radicals.
If free radicals are not inactivated, their chemical reactivity can damage cellular macro-molecules including proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nucleic acids. Their destructive effect on protein may play a role in the development of diseases, like cataracts. Free radical damage to DNA is also implicated in the development of cancer and its effect on LDL cholesterol is verylikely responsible for heart disease. Free radicals are also responsible for ageing (Bagchi and Puri, 1998).
One way to reduce or prevent oxidative damage to cellular and molecular level is con-suming antioxidant containing food. Concerns about the possible side effects of synthetic an -tioxidants, it is suggested to use natural alter-native antioxidants instead (Sunarni, 2005). Natural antioxidants can be obtained from natural ingredients derived from plants. Indo-nesia as a tropical country has a high biodiver-sity. Based on the survey, Indonesia has 13-15 % of all plant species in the world, or about 35.000-40.000 plants (LIPI, 2011).
One such plant is pasak bumi (Eurycoma longifolia Jack), that is one of the 13 seed plant
set by the government (Budianto dkk., 2004). Eurycoma longifolia Jack has been used as an antioxidant, malaria drugs, increase stamina, anticancer, and aphrodisiac (Nurani, 2013). Eurycomanone was cytotoxic on HeLa cells by inducing apoptosis through the up-regulation of p53 and Bax, and down-regulation of Bcl-2 (Mahfudh and Pihie, 2008). Additionally eury -comanone of the E. longifolia Jack
can inhibit angiogenesis (Salamah et al., 2009).
Compounds contained in E. longifolia
Jack is quasinoid (Miyake, 2009), and alkaloid 9-metoksisantin-6-one (Rosli et al., 2009).
From the roots, several classes of compounds have been identified and they included quassi -noids, cathin-6-one alkaloids, β-carboline al -kaloids, tirucallane-type triterpenes, squalene derivatives, and biphenylneolignans (Lin et al., 2001), and coumarin (7-Hydroxy-6-methoxy-2H-1- benzopyran-2-one) (Nurzaini, 2010).
Previous studies suggested that the methanol extract of the roots of the E. longifolia
Jack has antioxidant activity that is expressed in ES 50 value 423.5135 µg/ml (Filza dkk., 2006). In addition, the ethyl acetate fraction of ethanol extract, as well as the roots of the earth peg 1 isolates of E. longifolia Jack have antioxidant activity as
DPPH free radical catcher with ES50 price of ethanol extract of E. longifolia Jack is 15.636 µg
/ml and ES50 ethyl acetate fraction of ethanol extract of the E. longifolia Jack is 13.948 µg/ml
and 1 isolate of 3.961 µg/ml (Nurani, 2013). The aim of the present study was to evaluate the antioxidant activity of ethanol ex-tract and its derived fraction from E. longifolia
Jack.
MATERIALS AND METHOD Materials
The plant material examined in this study is the root of Eurycoma longifolia Jack obtained from the center of herbal raw mate-rials supplier, Pasar Gede, Solo. Plant material was determined in the Laboratory of Pharma-cognosy, Pharmaceutical Biology Section.
electric stirrer, rotary evaporators, separating funnel, Buchner funnel, vacuum, shacker orbit-al, waterbath, thin layer chromatografi plates. Tool for testing the antioxidant is UV-Vis spec-trophotometer.
Preparation Of The Sample
Extraction
Two kilograms of E. longifolia Jack macerated using 10 L ethanol 96 %. Macera -tion process is optimized with stirring using an electric stirrer for 1 hour, then save for 24 hours at room temperature. The filtrate ob -tained by filtering using a funnel Buchner, in order to obtain maserat. Dregs of the first filter was macerated again using 10 L ethanol 96 %. Maserat II was evaporated using a rotary evap-orator to get thick extract.
Fractionation
Ethanol extract then successively frac-tionated using solvents with different levels of polarity, namely n-hexane, ethyl acetate and methanol. Compounds were dissolved in n-hexane separated called the n-n-hexane fraction and compounds are not soluble in n-hexan then dissolved in ethyl acetate, ethyl acetate soluble fraction called ethyl acetate fraction. Further more insoluble fraction of ethyl acetate then dissolved with methanol (methanol fraction). All fractions obtained and ethanol 96% ex -tracts were analyzed by thin layer chromatog-raphy (TLC).
Thin-layer chromatography (TLC) analysis
Three fractions and ethanol extract were characterized by TLC (silica gel 60 F254, Merk). The extracts were spotted into TLC plate, which then were developed with solu-tion of ethyl acetate:ethanol:water (100:10:1), and then evaluate under uv light at 254 and 360 nm.
2,2- Diphenyl- 1- Picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) Assay
Determination of operating time
Each 1.0 ml of the sample solution is shaken with 1.0 ml of 0.2 mM DPPH solution, then observed
its absorbance for 120 minutes at 516 nm wave lenght.
Determination of Wavelength maximum ab-sorption
Determination of wavelength (ʎ) of maximum absorbance of DPPH solution per -formed as follows: l,0 ml 0.2 mM DPPH solu -tion added 1.0 ml methanol pa, whipped ho -mogeneous, absorbance was measured over a range of wavelength of 400-600 nm.
Absorbance measurements catcher of free radi-cals by DPPH method
Each 1.0 ml of the extract and fractions of E. longifolia Jack added with a solution of DPPH 0.2 mM. The mixture solution was stored dark place during operating time. Then the ab-sorbance was measured The reaction mixture was vortexed thoroughly and left in dark at room temperature for 60 min. The absorbance was measured spectrophotometrically at 516 nm.
Data Analysis
The scavenging ability of the plant ex-tract was calculated using this equation:
Absorbance of negative control – abso bance of the sample
DPPH scavenging = x 100%
activity (%) Absorbance of negative control
Data obtained in the form ES50 analyzed statistically with confidence 95% using the t test.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
DPPH radical scavenging model is wide -ly used method to evaluate antioxidant activity of natural compound and plant extracts. The degree of discoloration indicates the scaveng-ing potential of the antioxidant extract, which is due to the hydrogen donating ability (Barrei -ra et al,. 2008). DPPH is characterized as stable
The violet colour disappears or decrease when an antioxidant is present in the medium. Thus, antioxidant molecules can quench DPPH free radicals and convert them to a colourless prod-uct, resulting in a decrease in absorbance at 517 nm. In this quantitative assay the extract exhibited a notable dose dependent scaveng-ing of the DPPH activity.
Absorbance obtained from these mea-surements are used to calculate the percent capture of free radicals, that is the reduction in absorbance of the solution with the negative control absorbance of the solution of test mate-rial divided by the absorbance of negative con-trol. The absorbance of the negative controls showed the total amount of DPPH in solution. Percent capture of free radicals that illustrate the many DPPH free radicals were arrested or reduced by compounds in the test solution. The results of the calculation of percent DPPH radical arrest by ethanol extract, ethyl acetate fraction of the ethanol extract of E. longifolia
Jack, the fraction of n-hexan, ethyl acetate and methanol fractions can be seen in Tables I and II.
The interaction of a potential antioxi-dant with DPPH depends on its structural con -formation. The number of DPPH molecules that are reduced is correlated with the number of available hydroxyl groups (Brand-Williams
et al., 1995). It is strongly suggested that the
DPPH free radical abstracts the phenolic hydro -gen of the electron-donating molecule and this could be the general mechanism of the scav-enging action of antiperoxidative flavonols, for example.
Medicinal plants antioxidant activity is mainly due to the presence of secondary me-tabolites (Sayed, A et al,. 2011). Ethyl acetate
is The ethyl acetate fraction of eurycoma longi-folia. Jack showed the presence of secondary metabolites like alkaloids, flavonoid, and sterid. Alkaloids have been associated with medicinal uses for centuries and one of their common biological properties
is their cytotoxicity (Nobory, 1994) with pos -sible interaction with cell wall and DNA. In the case of indole alkaloids, many studies have shown to have biological activity such as anti-tumoral, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antioxi -dant, and antimycobacterial effects (Shi et al,. 2011). Flavonoid also inhibit enzymes such as aldose reductase and xanthine oxidase. They are potent antioxidants and have free radi-cal scavenging abilities (Daniel et al,. 2012).
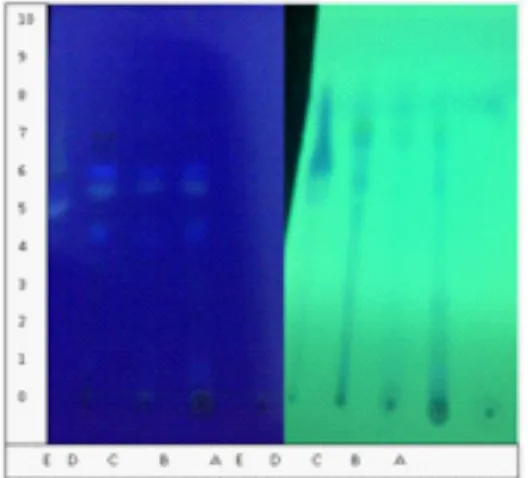
Figure I. TLC of Profil Sample (A= water fraction, B=methanol fraction, C= ethanol 96% ex
-tract, D= ethyl acetate fraction, E= n-hexan fraction).
Based on results obtained from data in Tables I and II as well as those of statistical analysis, we can say that ethanol extracts of E. longifolia Jack showed lower ES50 value than
n-hexan fraction and methanol fraction but higher than ethyl acetate fraction.
The result of thin layer chromatography (TLC)analysis on figure I.
The spots seein in Figure I viewed un-der UV light at 254 and 366 nm suggested that there are antioxidant cmpound contain in ethanolic extract and solvent fractions from E. longifolia Jack root.
CONCLUSION
The best activity of radical of Eurycoma longifolia Jack extract using DPPH method
found in ethyl acetate fraction.
Table 1. Percent DPPH radical arrest by ethanol extract n-hexan fraction, ethyl acetate fraction and methanol fraction of
ethanol extract of E. longifolia Jack
Ethanolic n-hexan Ethyl acetate Methanol extract fraction fraction fraction
Mean ± SD 60.796 ± 237.621 ± 53.597 ± 109.760 ± 0.340
0,051 1.662 0.028
CV 0.0832% 0.6996% 0.0514% 0.3097%
Table 2. Linear regression equation between radical concentration vs. percent arrest
Materials test Linear equation Correlation R table ES50 (r2))
Plants Research Vol. 5(3), pp. 300-308 Mahfudh N. and Pihie AHL., 2008.
Euryc-manone induces apoptosis through the up regulation of P53 in human cervical carcinoma cells. Journal of Cancer Mol-ecules, 4(4): 109-115.
Miyake K., Tezuka Y., Awale S., Li F. and Kadota S., 2009. Quassinoids from Eurycoma longifolia. Journal of Natural Products,
72(12): 2135-2140.
Nobori T, Miurak K, Wu DJ, Takabayashik LA, Carson D A. Deletion of the cyclin-de -pendent kinase- 4 inhibitor gene in multiple human cancers. Nature 1994; 368 (6473): 753-75
Nurani LH., 2013. Isolation and free radicals scavenging activity of isolate-1, ethyl acetate fraction, and ethanolic extract of Pasak Bumi (Eurycoma longifolia
Jack) root. Faculty of Pharmacy Ahmad Dahlan University, Yogyakarta.
Nurzaini RR., 2010. Content analysis of polar fractions roots and stem Pasak Bumi (Eurycoma longifolia Jack.) origin Sin-tang, West Kalimantan. School of Life Sciences and Technology ITB.
Rosli N., Maziah M., Chan KL.and Sreeramanan S., 2009. Factors affecting the accumu -lation of 9-methoxycanthin-6- one in callus cultures of Eurycoma longifolia. J. Forest. Res. 20: 54-58.
S. Arokiyaraj, S.Martin, K. Perinbam, P.Marie Arockianathan, and V. Beatrice., 2008. “Free radical scavenging activity and HPTLC finger print of Pterocarpus san -talinus L, an in vitro study,” Indian Jour-nal of Science and Technology, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 1–3.
Salamah N., Sugiyanto, Hartati MS., Hayati F., J mariyatno F., 2009. Isolation and Iden -tification Of Eurycomanone From Akar Pasak Bumi (Eurycoma Longifolia, Jack) and Its Antiangiogenic Activity. Majalah Farmasi Indonesia, 20(3): 118-126.
REFERENCES
Bagchi K and Puri S, 1998. Free radicals and antioxidants in health and disease. East-ern Mediterranean Health Journal 4(2):
350-360.
Barreira JCM, Ferreira ICFR, Oliveira MBPP, Pereira JA., 2008. Antioxidant activities of the extracts from chestnut flower, leaf, skins and fruit. Food Chem, 107:1106– 1113.
Biology Research Center–LIPI, 2011. Status Keanekaragaman Hayati Indonesia. Bo-gor: LIPI Press. p 7.
Brand-Williams W., Cuvelier ME. and Berset C., 1995. Use of free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol., 28: 25-30.
Budianto R.,Firdaus RT.,ParamitaD.,Vianty TA., Damayanti ED., Suhartono E., 2004. Uji antioksidan tumbuhan pasak bumi ( Eu-rycoma longifolia Jack.) serta peranan-nya sebagai inhibitor kerusakan pro-tein akibat reaksi glikosilasi. Chem. Rev., 7(2): 89-97.
Daniel Seifu, Freshet Assefa and Solomon M. Abay, Medicinal Plants as Antioxidant Agents: Understanding Their Mecha-nism of Action and Therapeutic Effi -cacy, 2012: 97-145 ISBN: 978-81-308-0509-2 Editor: Anna Capasso
Filza MR., Kristanto A., Mayasari DI., Sari NI., P tri DPS., 2006. Pemanfaatan Ekstrak Akar Pasak Bumi (Eurycoma longifo-lia Jack) sebagai Model Antipenuaan In Vitro. Fakultas Kedokteran, Universitas Lambung Mangkurat.
Lin LC.,Peng CY.,Wang HS.,Lee KW.,Paulus WS., 2001. Reinvestigation of the chemical constituents of Eurycoma longifolia.
Chin Pharmaceutical J, 53: 97-106.
Sunarni T., 2005. Aktivitas antioksidan penan kap radikal bebas beberapa kecambah dari biji tanaman familia Papilionaceae.