ABSTRACT
Tanasale, Inggrit. 2007. Designing a Set of Instructional Speaking Materials Using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the Second Grade of Language Program in SMA Stella Duce 1. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Speaking is a life skill that should be equipped for the students who are prepared to involve in society. Thus, schools should provide the learning situation which makes the students not only learn the subject matter but also learn to be aware of the real context particularly the issues in society such as social, personal, economic, cultural, or political issues covered in teaching learning activities. It leads the students to develop their own critical and creative thinking to solve the problems found.
The writer then, designed the speaking materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning, since this method focuses on integrating material content to real context in order to help the students directly connect and apply their competence in their everyday life. This study dealt with designing a set of instructional speaking materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the second grade of language program in SMA Stella Duce 1. There were two problems discussed in this study. They were: 1) How is a set of instructional speaking materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the second grade of language program at senior high school designed to improve students’ speaking skill? And 2) What will the designed set of materials look like?
To answer the first problem, the writer conducted the research to provide information so as to develop and validate product for school. The writer adapted Educational Research and Development as a research method. The steps of Educational Research and Development employed are: Research and information collection in the form of needs survey, Planning, Preliminary form of product development, Preliminary field testing in the form of feedback gathering, and Main product revision.
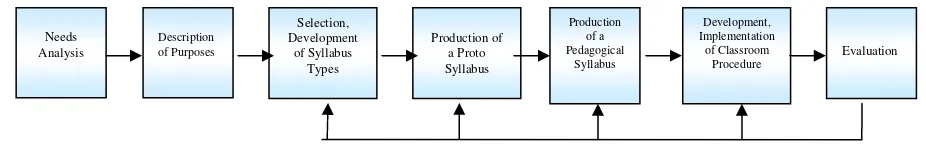
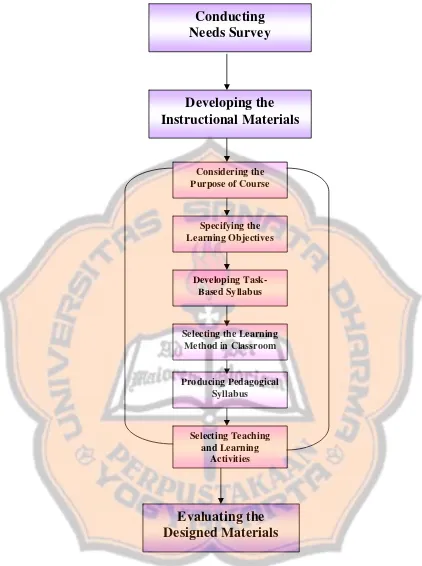
Besides, the writer carried out three main steps to design a set of instructional materials. The steps of the instructional design were chosen by modifying and adapting Newby’s and Yalden’s models. The steps consisted of: 1) Conducting needs survey, 2) Developing the instructional materials, and 3) Evaluating the designed set of materials. In the step of developing the instructional materials, the writer conducted six phases. The phases are: a) Considering the purpose of the course, b) Specifying the learning objectives, c) Developing task-based syllabus, d) Selecting the learning method in classroom, e) Producing pedagogical syllabus, and f) Selecting teaching and learning activities.
In order to present the final version of the designed materials as the answer for number two, the writer distributed questionnaire and the original version of the designed materials to the respondents as the preliminary field testing. The purpose of the questionnaire was to gain feedback from the respondents. The result of the evaluation was in the form of agreement points. The result of statistical data showed that the overall mean was 3,86 out of the scale of 5. It means that most of the respondents considered the designed materials were generally acceptable, yet it still
needed some revisions to make it better. After doing the revision based on the feedback gathering input, the writer concluded that the final version of the designed materials was well appropriate for the second grade of language program in SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta. The final version of designed materials contains eight units. Each of them consisted of six parts, namely: Set Your Goals, Burn Up, Win-win Solution, Get the Big Picture, Grasp the Meaning, and Have a Good Time
As a final point, this study is expected to bring contribution as the alternative method to enhance teaching speaking in classroom as well as to develop teacher’s creativity to make it work.
ABSTRAK
Tanasale, Inggrit. 2007. Designing a Set of Instructional Speaking Materials Using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the Second Grade of Language Program in SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta.Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma
Berbicara adalah ketrampilan hidup yang perlu diperlengkapi kepada siswa ketika mereka dipersiapkan untuk terlibat dalam masyarakat. Oleh karena itu, sekolah harus menyediakan situasi belajar yang tidak hanya membuat siswa belajar pelajaran semata tapi juga belajar untuk peka terhadap konteks realita terkhusus isu-isu dalam masyarakat seperti isu-isu-isu-isu sosial, perseorangan, budaya ataupun politik yang dibungkus dalam kegiatan belajar mengajar. Hal ini mengarahkan siswa untuk mengembangkan pemikiran kritis mereka untuk menyelesaikan masalah yang mereka temukan.
Penulis kemudian merancang materi-materi berbicara dalam bahasa Inggris menggunakan Contextual Teaching and Learning. Penulis memilih metode ini karena metode ini berfokus pada integrasi isi materi dengan konteks realita dalam rangka membantu siswa secara langsung menghubungkan dan mengaplikasikan kompetensi mereka dalam kehidupan sehari-hari.Tujuan dari dilaksanakannya studi ini adalah untuk membuat seperangkat materi berbicara dalam bahasa Inggris dengan menggunakan metode Contextual Teaching dan Learning bagi siswa kelas dua program Bahasa di SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta dalam desain instruksional. Ada dua permasalahan yang dibahas dalam studi ini. Permasalahan tersebut adalah: 1) Bagaimana seperangkat materi pembelajaran berbicara bahasa Inggris dengan menggunakan metode Contextual Teaching dan Learning bagi siswa kelas dua program Bahasa di SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta dalam desain instruksional disusun. Dan 2) Seperti apakah susunan materi-materi pembelajaran itu?
Untuk menjawab masalah pertama, penulis melaksanakan penelitian untuk memperoleh informasi guna mengembangkan dan mensahkan produk untuk sekolah. Penulis mengadaptasi metode Pengembangan dan Penelitian Pendidikan sebagai metode penelitian. Langkah-langkah metode tersebut antara lain: Penelitian dan pengumpulan informasi dalam bentuk penelitian kebutuhan, Perencanaan, Bentuk awal dari pengembangan produk, Tes awal lapangan dalam bentuk pengumpulan umpan balik dan Revisi produk.
Selaim itu, penulis melaksanakan tiga langkah untuk merancang seperangkat materi dalam desain instruksional. Langkah-langkah tersebut dipilih berdasarkan hasil modifikasi model rancangan Yalden dan Newby. Langkah-langkah rancangan instruksional tersebut terdiri dari: 1) Melaksanakan penelitian kebutuhan, 2) Mengembangkan materi instruksional, dan 3) Mengevaluasi materi yang sudah disusun. Dalam langkah kedua yaitu mengembangkan materi instruksional, penulis melaksanakan enam tahap pengembangan materi. Tahap-tahap tersebut antara lain: a) Menentukan tujuan dari program, b) Menentukan tujuan khusus pembelajaran, c) Mengembangkan silabus berbasis tugas, d) Memilih metode pembelajaran di kelas, e) Menghasilkan silbus pedagogis, dan f) Memilih kegiatan belajar mengajar.
Dalam rangka menyajikan bentuk akhir dari materi pembelajaran sebagai jawaban atas masalah kedua, maka penulis mendistribusikan kuesioner beserta dengan bentuk asli dari materi yang dibuat kepada responden. Tujuan dari kuesioner ini adalah untuk memperoleh umpan balik dari responden. Hasil dari evaluasi tersebut diperoleh dalam bentuk poin persetujuan. Hasil data statistik menunjukan bahwa nilai rata-rata yang diperoleh adalah 3,86 dari skala 5. Hal ini berarti bahwa sebagian besar responden menganggap bahwa materi ini layak diterima untuk dipakai. Akan tetapi materi ini masih perlu direvisi untuk menjadikannya lebih baik. Setelah melakukan revisi berdasarkan masukan dari proses pengumpulan umpan balik, maka penulis menyimpulkan bahwa bentuk akhir dari materi ini layak digunakan bagi siswa kelas dua program bahasa di SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta. Bentuk akhir materi yang dirancang mencakup delapan unit. Setiap unit terdiri dari enam bagian, dengan nama: Set Your Goals, Burn Up, Win-win Solution, Get the Big Picture, Grasp the Meaning, and Have a Good Time.
Sebagai penutup, materi ini diharapkan dapat memberi kontribusi untuk meningkatkan kemampuan berbicara siswa dalam bahasa Inggris di kelas seperti juga mengembangkan kreatifitas guru untuk membuat materi ini berhasil di kelas.
DESIGNING A SET OF INSTRUCTIONAL SPEAKING MATERIALS
USING CONTEXTUAL TEACHING AND LEARNING
FOR THE SECOND GRADE OF LANGUAGE PROGRAM
IN SMA STELLA DUCE 1 YOGYAKARTA
A Thesis
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Inggrit O. Tanasale Student Number: 031214082
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
“God will help us when we can not walk,
and He will help us when we find it is hard to walk,
but He cannot help us if we do not want to walk.”
Even though you fall, you must try again,
your God will hold you by the hand.
ABSTRACT
Tanasale, Inggrit. 2007. Designing a Set of Instructional Speaking Materials Using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the Second Grade of Language Program in SMA Stella Duce 1. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Speaking is a life skill that should be equipped for the students who are prepared to involve in society. Thus, schools should provide the learning situation which makes the students not only learn the subject matter but also learn to be aware of the real context particularly the issues in society such as social, personal, economic, cultural, or political issues covered in teaching learning activities. It leads the students to develop their own critical and creative thinking to solve the problems found.
The writer then, designed the speaking materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning, since this method focuses on integrating material content to real context in order to help the students directly connect and apply their competence in their everyday life. This study dealt with designing a set of instructional speaking materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the second grade of language program in SMA Stella Duce 1. There were two problems discussed in this study. They were: 1) How is a set of instructional speaking materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the second grade of language program at senior high school designed to improve students’ speaking skill? And 2) What will the designed set of materials look like?
To answer the first problem, the writer conducted the research to provide information so as to develop and validate product for school. The writer adapted Educational Research and Development as a research method. The steps of Educational Research and Development employed are: Research and information collection in the form of needs survey, Planning, Preliminary form of product development, Preliminary field testing in the form of feedback gathering, and Main product revision.
Besides, the writer carried out three main steps to design a set of instructional materials. The steps of the instructional design were chosen by modifying and adapting Newby’s and Yalden’s models. The steps consisted of: 1) Conducting needs survey, 2) Developing the instructional materials, and 3) Evaluating the designed set of materials. In the step of developing the instructional materials, the writer conducted six phases. The phases are: a) Considering the purpose of the course, b) Specifying the learning objectives, c) Developing task-based syllabus, d) Selecting the learning method in classroom, e) Producing pedagogical syllabus, and f) Selecting teaching and learning activities.
In order to present the final version of the designed materials as the answer for number two, the writer distributed questionnaire and the original version of the designed materials to the respondents as the preliminary field testing. The purpose of the questionnaire was to gain feedback from the respondents. The result of the evaluation was in the form of agreement points. The result of statistical data showed that the overall mean was 3,86 out of the scale of 5. It means that most of the respondents considered the designed materials were generally acceptable, yet it still
needed some revisions to make it better. After doing the revision based on the feedback gathering input, the writer concluded that the final version of the designed materials was well appropriate for the second grade of language program in SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta. The final version of designed materials contains eight units. Each of them consisted of six parts, namely: Set Your Goals, Burn Up, Win-win Solution, Get the Big Picture, Grasp the Meaning, and Have a Good Time
As a final point, this study is expected to bring contribution as the alternative method to enhance teaching speaking in classroom as well as to develop teacher’s creativity to make it work.
ABSTRAK
Tanasale, Inggrit. 2007. Designing a Set of Instructional Speaking Materials Using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the Second Grade of Language Program in SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta.Yogyakarta: Program Studi Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma
Berbicara adalah ketrampilan hidup yang perlu diperlengkapi kepada siswa ketika mereka dipersiapkan untuk terlibat dalam masyarakat. Oleh karena itu, sekolah harus menyediakan situasi belajar yang tidak hanya membuat siswa belajar pelajaran semata tapi juga belajar untuk peka terhadap konteks realita terkhusus isu-isu dalam masyarakat seperti isu-isu-isu-isu sosial, perseorangan, budaya ataupun politik yang dibungkus dalam kegiatan belajar mengajar. Hal ini mengarahkan siswa untuk mengembangkan pemikiran kritis mereka untuk menyelesaikan masalah yang mereka temukan.
Penulis kemudian merancang materi-materi berbicara dalam bahasa Inggris menggunakan Contextual Teaching and Learning. Penulis memilih metode ini karena metode ini berfokus pada integrasi isi materi dengan konteks realita dalam rangka membantu siswa secara langsung menghubungkan dan mengaplikasikan kompetensi mereka dalam kehidupan sehari-hari.Tujuan dari dilaksanakannya studi ini adalah untuk membuat seperangkat materi berbicara dalam bahasa Inggris dengan menggunakan metode Contextual Teaching dan Learning bagi siswa kelas dua program Bahasa di SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta dalam desain instruksional. Ada dua permasalahan yang dibahas dalam studi ini. Permasalahan tersebut adalah: 1) Bagaimana seperangkat materi pembelajaran berbicara bahasa Inggris dengan menggunakan metode Contextual Teaching dan Learning bagi siswa kelas dua program Bahasa di SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta dalam desain instruksional disusun. Dan 2) Seperti apakah susunan materi-materi pembelajaran itu?
Untuk menjawab masalah pertama, penulis melaksanakan penelitian untuk memperoleh informasi guna mengembangkan dan mensahkan produk untuk sekolah. Penulis mengadaptasi metode Pengembangan dan Penelitian Pendidikan sebagai metode penelitian. Langkah-langkah metode tersebut antara lain: Penelitian dan pengumpulan informasi dalam bentuk penelitian kebutuhan, Perencanaan, Bentuk awal dari pengembangan produk, Tes awal lapangan dalam bentuk pengumpulan umpan balik dan Revisi produk.
Selaim itu, penulis melaksanakan tiga langkah untuk merancang seperangkat materi dalam desain instruksional. Langkah-langkah tersebut dipilih berdasarkan hasil modifikasi model rancangan Yalden dan Newby. Langkah-langkah rancangan instruksional tersebut terdiri dari: 1) Melaksanakan penelitian kebutuhan, 2) Mengembangkan materi instruksional, dan 3) Mengevaluasi materi yang sudah disusun. Dalam langkah kedua yaitu mengembangkan materi instruksional, penulis melaksanakan enam tahap pengembangan materi. Tahap-tahap tersebut antara lain: a) Menentukan tujuan dari program, b) Menentukan tujuan khusus pembelajaran, c) Mengembangkan silabus berbasis tugas, d) Memilih metode pembelajaran di kelas, e) Menghasilkan silbus pedagogis, dan f) Memilih kegiatan belajar mengajar.
Dalam rangka menyajikan bentuk akhir dari materi pembelajaran sebagai jawaban atas masalah kedua, maka penulis mendistribusikan kuesioner beserta dengan bentuk asli dari materi yang dibuat kepada responden. Tujuan dari kuesioner ini adalah untuk memperoleh umpan balik dari responden. Hasil dari evaluasi tersebut diperoleh dalam bentuk poin persetujuan. Hasil data statistik menunjukan bahwa nilai rata-rata yang diperoleh adalah 3,86 dari skala 5. Hal ini berarti bahwa sebagian besar responden menganggap bahwa materi ini layak diterima untuk dipakai. Akan tetapi materi ini masih perlu direvisi untuk menjadikannya lebih baik. Setelah melakukan revisi berdasarkan masukan dari proses pengumpulan umpan balik, maka penulis menyimpulkan bahwa bentuk akhir dari materi ini layak digunakan bagi siswa kelas dua program bahasa di SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta. Bentuk akhir materi yang dirancang mencakup delapan unit. Setiap unit terdiri dari enam bagian, dengan nama: Set Your Goals, Burn Up, Win-win Solution, Get the Big Picture, Grasp the Meaning, and Have a Good Time.
Sebagai penutup, materi ini diharapkan dapat memberi kontribusi untuk meningkatkan kemampuan berbicara siswa dalam bahasa Inggris di kelas seperti juga mengembangkan kreatifitas guru untuk membuat materi ini berhasil di kelas.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First and the most, I would like to give my best and greatest praise and worship to my almighty God Jesus Christ. Everything that has been done in my life is all because of His Grace and for one purpose, to glorify Him. May my thesis become an offering which can please Him.
I would also like to give my gratitude to the important people who have helped me in finishing my thesis. First, I would like to thank Yohana Veniranda S.Pd., M.Hum. and Ch. Lhaksmita Anandari S.Pd., M.Ed. as my sponsors. I thank them for their patience, guidance, and support. I would also like to extend my deepest appreciation to all of the lecturers and staff of the English Language Education Study Program. I thank them for their care, guidance, and assistance during my study.
I would also like to give my deep gratitude to Mrs. Indriyanti, Ms. Lina, Ms. Tyas and all the staff and students in second grade of Language Program in SMA Stella Duce 1 for their cooperation and kindness as my respondents.
I would also like to express my never-ending honor and love to my beloved family: my father, Matheis Tanasale, for his trust and support; my mother, Marthina Tupanno, for her love and endless prayer; my sisters, Ella, Icha, Nike, and Yesti for being such wonderful angels for me; my aunty, Nelly Tupanno and my grandma,
Yomima, for their prayer and meaningful guidance. I am so blessed to be born in this family.
My special thanks goes to My GKY’s Family which brings happiness and blessing in my life while I have been in Yogyakarta. I would say big thanks to: G.I. Bagio, G.I. Gracia, G.I. Sumartiwi, k’Yoel, k’Daud, k’Willy, ci’Widia, bu’Er,
mas’Tok, Lia, Joko, Andres, Susan, Siwi, Lisa, and all of my sisters and brothers in Christ. Finally, I have learned the meaning of “My Church is My Family”.
I would like to express my greatest thanks to my ministries; LPMI and
Kambium. I thank them for teaching me to grow in faith. May God bless all their ministries.
I would also say my deepest thanks to all of my “Spaghetti Club”; Santy, c’alenx,k’Ida, Silvy, Dian, k’Dewi, k’Peggy, mba’Ndari, usi Brenda, and usi Cindy. I thank them for all of their sharing, caring, love, cries, laugh and prayer.
I would deliver my thankfulness to my family in Blok M-28; mami Do, pa’De, mba’Yun, mas Anto, and all familyfor their care and support.
I would give my gratefulness to my Christian Students Fellowship Efata;
mas’Bayu, Zuhu, k’Ro, Bayu, Vivi, Christo, Rollie, Pical, Asih, Duon, and all the sisters and brothers in Christ. May all our service bring the pleasure for God.
I also would like to give my best appreciation to my dearly best friends:
Mesya, Kris, Tina, Hana, Ika Amq, Joji, and Wisye for their prayer, love, friendship, and encouragement. Their friendship really colors my life. May all their journey still continue to reach the finish line.
Last, I would like to thank to Giovano Papilaya who has always been there when I need. I thank for his spirit, prayer, love, and encouragement. I am so blessed to have him in my side. I pray for all the best in his life.
Finally, for all who struggle with your thesis and your life, may this word of God can encourage you. “Let no one despise your youth, but be an example to the believer in word, in conduct, in love, in spirit, in faith, in purify”-(1 Tim 4:12).
Inggrit.O Tanasale
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGES ……….……….……… i
APPROVAL PAGES ……….………..………. ii
STATEMENTS OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ……….………....…………. iv
PAGE OF DEDICATION ……….………....……….. v
ABSTRACT ……….……….………..… vi
ABSTRAK ……….…….……...…………...……….…….….. viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ……….…….………....……….. x
TABLE OF CONTENTS ……….………...… xii
LIST OF TABLES ……….………...……… xvii
LIST OF FIGURES ……….…….………….………...….……. xviii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Background ……….……….……..………..……. 1
B. Problem Identification ……….……..………..….… 5
C. Problem Limitation ………....………..…..….…. 5
D. Problem Formulation ….………..………..……….. 6
E. Research Objectives ....……….…..……….. 7
F. Research Benefits ……….……… 7
G. Definition of Terms .………..…...………... 8
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Theoretical Description ...……….………..……… 11
1. Speaking …….……….…… 12
a. The Nature of Speaking ………....….… 12
b. Teaching Speaking ……….………..….. 13
c. Activities in Teaching Speaking …………..………..…… 13
d. Successful Activity for Teaching Speaking ….………..… 14
2. Communicative Competence ………...……..…..… 15
3. Contextual Teaching and Learning ………..……... 16
a. Foundation of Contextual Teaching and Learning …... 17
b. Meaning of Contextual Teaching and Learning ….…... 17
c. Strategies of Contextual Teaching and Learning ………. 18
d. Approaches of Contextual Teaching and Learning …….. 18
1) Problem-Based Learning ………. 19
a) Characteristics of Problem-Based Learning …….. 19
b) The Purpose of Problem-Based Learning ………… 19
c) The Steps of Problem-Based Learning …….…….. 20
2) Cooperative Learning ……….. 20
a) Elements of Cooperative Learning ……….. .21
b) The Significance of Cooperative Learning ………. 21
c) The Role of Evaluation in Cooperative Learning … 22 e. Learning Context Used in Contextual Teaching and Learning ………..………. 22
f. The Role of Teacher and Students in Contextual Teaching and Learning ………..………. 23
4. Competency Based Curriculum ….………....……...…. 24
a. Objectives of English Language Learning
Based on Competence-Based Curriculum ……..…... 24
b. Materials Scope of English Subject Based on Competence-Based Curriculum ...……… 25
c. Principles of CompetenceBased Curriculum …...……. 26
5. The Role of Instructional Materials ………. 26
6. Materials Design Model ……….…….……… 26
7. Syllabus Design ………... 27
8. Design Models ………...….… 28
a. Yalden’s Model ……….….……..…... 28
b. Newby’s Model ………..………. 29
A. Theoretical Framework ……… 32
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Research Method ……….……….……….. 35
B. Needs Survey ……….. 37
1. The Needs Survey Respondents ……….….. 37
2. The Needs Survey Instruments ………. 37
3. The Needs Survey Data ……… 38
4. The Needs Survey Analysis ………. 38
C. Feedback Gathering ……… 39
1. The Feedback Gathering Respondents ………. 39
2. The Feedback Gathering Instruments ……….. 39
3. The Feedback Gathering Data ……….. 40
4. The Feedback Gathering Analysis ……… 40
D. Research procedures ……… 42
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION A. The Steps for Designing a Set of Supplementary Speaking Materials Using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the Second Grade of Language Program in SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta ……….……… 43
1. Conducting Needs Survey ……….………… 43
a. The Needs Survey Respondents ………....…… 44
b. The Needs Survey Data ………. 44
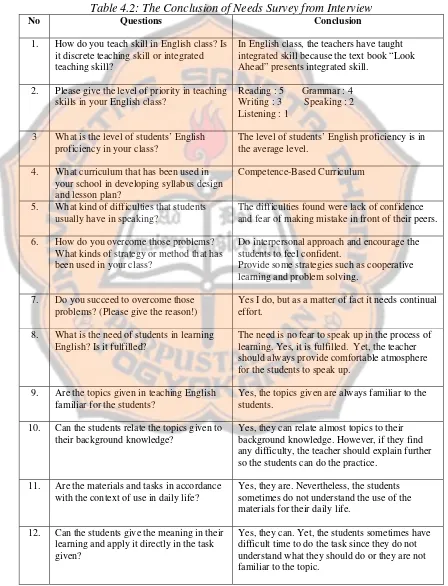
c. The Needs Survey Data Analysis ……….. 47
2. Developing the Instructional Materials ………. 51
a. Considering the Purpose of the Course ………....…. 52
b. Specifying the Learning Objectives ……….. 55
c. Selecting and Developing Syllabus Type ………. 57
d. Selecting the Learning Method ………. 57
e. Producing Pedagogical Syllabus ……… 57
f. Selecting Teaching and Learning Activities ………. 59
3. Evaluating Designed Materials ……….. 59
a. Feedback Gathering Respondents ………....….…… 60
b. Feedback Gathering Data ……….……….……… 60
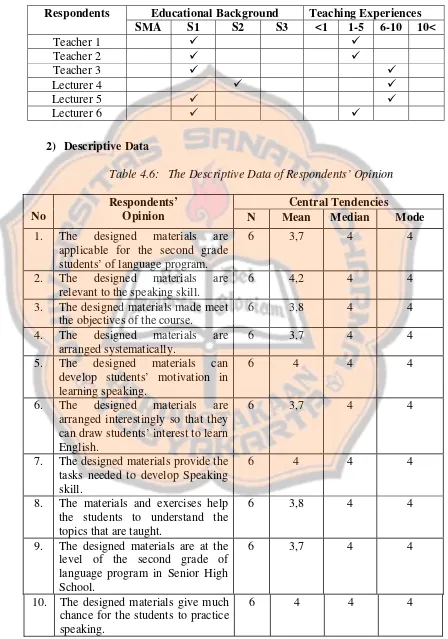
1) Respondents Descriptions ………..……….… 60
2) Descriptive Data ……….….…..………. 61
3) Comments and Criticisms/Suggestions ……...…… 62
c. Feedback Gathering Analysis ……….…… 63
B. The Presentation of a Set of Supplementary Speaking Materials Using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the Second Grade of Language Program in SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta ……….…..… 64
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS A. Theoretical Description ……….……….………. 67
B. Suggestions for English Teachers and Researchers ……… 68
REFERENCES ………. 70
APPENDICES Appendix A: Letter of Permission ………. 72
Appendix B: Verification Letter ………. 73
Appendix C: Questionnaire and List of Interview Questions for Needs Survey ………. 74
Appendix D: Questionnaire for Feedback gathering ………. 80
Appendix E: Raw Data of Feedback Gathering Result ………. ……… 82
Appendix F: Syllabus Design ………..……….. 83
Appendix G : Lesson Plan ………. 87
Appendix H: Presentation of the Designed Materials ………. 111
Appendix I: Teacher’s Manual ……….. 162
LIST OF TABLES
Page
Table 3.1: The Sample of Feedback Gathering Result from Questionnaire …… 40
Table 3.2: The Sample of Descriptive Data of Respondents’ Opinion ……... 40
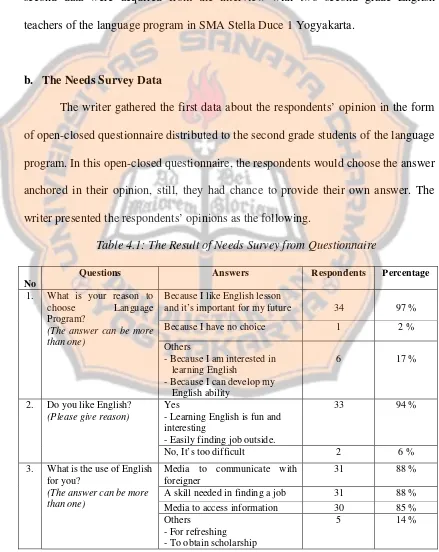
Table 4.1: The Result of Needs Survey from Questionnaire …….……... 44
Table 4.2:The Conclusion of Needs Survey from Interview ………...……... 46
Table 4.3: The Topics and Language Functions
Listed in Designed Materials …….…………..…..………...…. 56
Table 4.4: The Achievement Indicators listed in Designed Materials ………… 56
Table 4.5: The Respondents’ Description of Feedback Gathering ……….…… 62
Table 4.6: The Descriptive Data of Respondents’ Opinion …………...…... 62
Table 4.7: The Criticisms/Suggestions based on Feedback Gathering .…... 63
Table 4.8: The Revision of Designed Materials
Based on Criticisms/Suggestions from Feedback Gathering ………. 64
Table 4.9: The Description of Units in the Designed Materials …..………….... 66
LIST OF FIGURES
Page
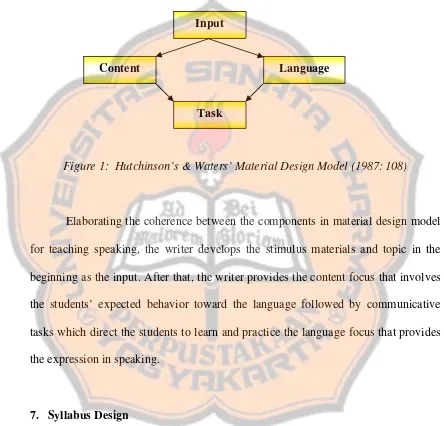
Figure 1: Hutchinson’s & Waters’ Material Design Model …………... 27
Figure 2: Yalden’s Language Program Development ………..…………. 29
Figure 3: Newby’s “Recipe” Model ………...….……….. 31
Figure 4: Steps Used to Design the set of Instructional Materials in
this Study ……..………..………. 34
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter essentially contains the background, the problem identification,
the problem limitation, the problem formulation, the research objective, the research
benefits, and the definition of terms.
A. Background
Education plays an important role to ensure the existence of our nation’s life.
In fact, it has a great responsibility to prepare and shape well-educated and
professional graduates in our country. Education will equip them with life skill to be
creative, adaptive, and communicative in facing their life’s problem and challenge in
the development of human civilization. It means that education not only provides
knowledge but also life skill for graduates to think and adapt in accord with the
demand of society.
To produce skillful graduates, education should serve the curriculum that
supports schools to focus on the achievement of competencies. Competence means
an ability that scopes knowledge, skill, and behavior. The curriculum that
emphasizes on the achievement of students’ competence is Competence-Based
Curriculum. According to Nurhadi, the Competence-Based Curriculum stresses on
shaping the competent graduates who are able to apply their knowledge in real life in
order to solve the problem and fulfill their daily needs (2004: 56).
Besides providing the curriculum, education also gives widely chance for the
students to develop themselves with specific ability in certain field. From the level of
the second grade of senior high school, the students are already divided into three
specific major programs. Those programs are science program (IPA), social program
(IPS), and language program (Bahasa). The students can choose the program that
they are interested to compile with their capability in learning the subjects in that
program.
There is an assumption that the language program is lesser favorite than the
other program in senior high school. It is obviously can be predicted from the few
number of language program classes than the other programs’ classes. The students
consider that the science and social program give much chance to develop their
knowledge in many fields than the language program. The consideration is due to the
belief that in the language program students will only spend much time to learn some
compulsory languages without any chance to learn more about another field.
Nevertheless, learning a language is as much important as learning the other
field. Language is really needed as the media in communication. Language is used to
exchange information and express one’s thoughts, ideas, and feelings in order to
solve the problems in society. Besides our first language Indonesian, English is one
of the foreign languages that are widely used for communication in commerce,
politics technology, and education. English becomes a compulsory subject taught in
school from the level of kindergarten to college. The students are demanded to
master English as active and passive participants to get involved in communication.
Learning English contains four skills; they are listening, speaking, reading,
and writing which are supported by learning pronunciation, spelling, vocabularies,
and grammar. When the speaker learns all those aspects of English, their competence
Wardhaugh (1986: 3), competence refers to what the speaker knows about language;
while performance refers to what the speaker does with language. Being active in
communication, the students should not only be competent in language but also be
able to perform a language. The most obvious way to perform language is by
speaking, since it can convey the competence of the speaker in language. Yet, it is
not easy to speak English because it happens in real time when the speaker faces
another speaker. It also happens naturally, so, the speaker cannot easily correct or
revise what he wishes to say. Thus, the English teacher is challenged to teach the
students not only are able to be competent in language but also are able to perform it
in communication.
When teaching speaking particularly different foreign language like English
in school, the teacher sometimes meets many various kinds of problems in learning.
One of the problems that can arise is when the students are unwilling to take a risk
because they feel that they are unable to speak. Lack of basic linguistic competence
in English makes them feel that they cannot say even any sentence in English.
Another problem occurs when the students are unconfident because the fear of
making mistakes or errors in front of their peers. Dealing with some of these
problems, the teacher should realize at all the times that the students need to feel safe
and comfortable to learn English, which can trigger their courage to speak up.
To enhance students’ communicative skill, Competence-Based Curriculum
gives opportunity for the teacher to develop his or her own teaching and learning
activities. Yet, Competence-Based Curriculum does not provide particular
handbooks or materials to teach speaking or other skills. Competence-Based
Accordingly, it becomes a challenge for the teacher to be aware of students’ needs in
accordance with the society demands for the professional and competent graduates.
In practice, they have to be creative in providing materials which meet the goals of
Competence-Based Curriculum. This approach is to be accommodated effectively by
the method applied in classroom.
For the success of Competence-Based Curriculum implementation, the
method of learning that has been chosen should be compatible with the goal of
Competence-Based Curriculum which equips students with the competencies to
survive in real life (Mulyasa, 2002: 136). One of the methods recently found, that has
been successfully used in United State and Japan schools is Contextual Teaching and
Learning. This method utilizes students’ background and environment as the most
significant factors in the process of learning new knowledge. This method focuses on
integrating material content to real context by connecting with the students’ previous
experience. In other words, the students will not solely learn the subject matter.
Rather, the students will learn to be aware of real context particularly the issues in
society such as social, cultural, political, economic, or personal issues covered in
teaching learning activities to develop their own critical thinking to cope with the
problems found.
SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta is one of the schools that have been using
Competence-Based Curriculum since a year ago. It facilitates the English teachers to
develop their own materials and method to teach English. Based on the primary
observation in SMA Stella Duce 1, particularly in second grade of language program,
it is found that the English teachers in SMA Stella Duce 1 have already taught class
related to social and personal issues. Furthermore, cooperative learning and
problem-based learning have served as the learning strategies in classroom, which are, the
elements of Contextual Teaching and Learning.
Thus, in this study the writer is to design a set of instructional speaking
materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning, which can assist the teacher
particularly in SMA Stella Duce 1 in teaching English particularly speaking skill.
B. Problem Identification
According to the observation of some English text books of language
program, the writer found that although the English teachers teach the integrated
skills, however, their teaching are mainly stressed on reading skill. The students are
exploited with many reading texts regarding the assumption that they are already
able to produce spoken language since they were in junior high school. Rather, they
are expected to be able to produce written language in senior high school. Whereas in
fact, the students in the second grade of language program in SMA Stella Duce 1
have a difficult time to speak in English. Lack of confidence and fear of making
mistakes are some of the factors that make them unwilling to speak English. The
English teacher has to spend much time to persuade the students to express their
language in the form of speaking.
C. Problem Limitation
This study concerns on the designing a set of instructional materials for
teaching speaking using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the second grade of
study on the second grade of language program since the students are considered
being experienced and having a higher level of language proficiency compared to the
other programs in that level. The graduates from the language program are expected
to fulfill the society demand as professional workers who are equipped with one of
communication skills such as English competence.
The writer narrows the study into developing speaking skill without any
purpose to ignore three other skills. Rather, the writer focuses on speaking as the
core of learning which is supported by other skills. So, the design materials will
cover all four skills.
Competence-Based Curriculum is to be employed as a framework since SMA
Stella Duce 1 has used that curriculum in school. The writer will limit the discussion
of approaches in Contextual Teaching and Learning into Problem-Based Learning
and Cooperative Learning. The reason is the writer already discovered in needs
survey that cooperative learning and problem-based learning are the strategies that
have been applied in SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta.
Designing the materials for SMA Stella Duce 1, however, the writer does not
implement these materials since SMA Stella Duce 1 is really strict in their teaching
program to prepare the students for semester exam. Therefore, the writer only
develops and presents the speaking materials and gives chance for the teacher to
implement it.
D. Problem Formulation
Referring to the background and problem limitation above, the writer
1. How is a set of instructional speaking materials using Contextual Teaching
and Learning for the second grade of language program in SMA Stella Duce
1 designed to improve students’ speaking skill?
2. What will the designed set of materials look like?
E. Research Objectives
Based on problem formulation above, the writer formulated two objectives
into the following statements:
1. To find out how a set of instructional speaking materials using Contextual
Teaching and Learning for the second year of language program at senior
high school is designed.
2. To present a set of instructional speaking materials using Contextual
Teaching and Learning for the second year of language program at senior
high school.
F. Research Benefits
By doing this study, the writer expects to produce designed materials which
can be used to enhance students speaking skill. The result of the study is expected to
bring input for the English teachers and future researchers in Indonesia. This study
will open important options for the teacher to learn the method in depth and be a
creative facilitator in developing and applying materials, in which takes students
previous background and contextual condition into consideration. Moreover, the
future researchers can use the topic to develop the further studies for developing
as to enrich our education as well as inventing new kinds of Contextual Teaching and
Learning concept which can work in our education.
G. Definitions of Terms 1. Design
Design is defined as the general arrangement or planning a new set of materials
to guide educational activity in a situation (Houle, 1978: 230). Adopting this
meaning, the writer elaborates the word “design” as a plan how a set of
instructional speaking materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the
second grade of language program at senior high school will look like.
2. Instructional Materials
Instructional materials refer to any materials which are specifically written for the
teachers, instructors and students to achieve the objectives (Dick & Carey, 1937:
127). In this study the writer employs Contextual Teaching and Learning to
develop a set of instructional speaking materials which will be used by the
English teachers in the second grade of senior high school.
3. Speaking
According to Nunan (1991: 43), speaking consists of producing systematic
verbal utterance to convey meaning. In this study, learning speaking is integrated
into Contextual Teaching and Learning. It means that learning speaking is not
only learning the expression but also learning to connect the expression with the
daily context. The students are expected to understand the meaning of language
and its use in the context of daily life and to be able to express it in
4. Contextual Teaching and Learning
Contextual Teaching and Learning is a concept of learning method that helps the
teacher to teach subject matter by placing it in the real context and relating to
students’ previous experience(Nurhadi, 2004: 103). In this study, the writer uses
Contextual Teaching and Learning as a method to teach speaking skill with the
topics taken from real life condition. Henceforth, in this study, Contextual
Teaching and Learning is abbreviated as CTL.
5. Students of Senior High School
Senior high school is a continuation of the education development from junior
high school. This level of education should be finished in three years. The
students are those whose ages about 15-19 years old. Students in senior high
school are assumed as continuing learner of English. They learn English from
elementary to junior high school; so that in senior high school they are expected
to attain informational level of literacy; which means they can access knowledge
using their language.
6. The second Grade of SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta
SMA Stella Duce 1 is located in Jl. Sabirin 1-3 Yogyakarta. Based on statistical
data 2006 for the second year, SMA Stella duce 1 has eleven classes. There are
five classes of science program, five classes of social program, and one class of
language program.
7. The Second Grade of Language Program
In the language program, the students are to learn English, Arabian language, and
Indonesian language as compulsory subjects. They can choose German or
Religion, Anthropology, and Food Science. In the language program, the students
obtain nine hours for learning English, six hours for learning general English
course and three hours for learning English literature course. In general English,
teaching English focuses on learning skills and elements of language. Meanwhile
in literature, the students will learn anything related to literature includes poetry,
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter presents the pertinent theories which become the foundation to
construct the materials. The discussion will be divided into theoretical description
and theoretical framework. The theoretical description provides the theories of
speaking and its elements in teaching, communicative competence, Contextual
Teaching and Learning, Competence-Based Curriculum, instructional materials,
material design model, the task-based syllabus design, and design models of Yalden
and Newby. The theoretical framework describes the steps of designing model
adapted from Yalden’s and Newby’s model.
A. THEORETICAL DESCRIPTION
This section discusses all theories related to the instructional design. The
theories include the theories of speaking and its elements, communicative
competence, Contextual Teaching and Learning, and Competence-Based
Curriculum. In addition, the writer also provides some theories that are relevant to
construct the materials. Those theories are instructional materials, design models, and
task-based syllabus. As a framework that contains steps of doing research, the writer
combined design models of Yalden and Newby.
All the theories provides information about the significance of developing the
speaking materials using Contextual Teaching and Learning for the students in the
second grade of language program at senior high school particularly in SMA Stella
Duce 1 Yogyakarta.
1. Speaking
In this study, the writer will design a set of instructional speaking materials
which employs CTL as a learning method. Therefore, the writer needs to study
further about the theories of speaking and its elements so as to develop the proper
speaking materials that can be useful in teaching and learning speaking.
a. The Nature of Speaking
Speaking is physically situated in face-to-face interaction. The speaker can
see each other and interact through the form of verbal exchange considering the
physical context (Widdowson, 1978: 58). It means that the speaker and the listener
are supposed to take the same place when they want to communicate, which helps
them to understand each other. The information then may be successfully delivered
to the listener. However, speaking can still exist such as communication on the
phone, although the speaker does not meet other speaker. They can understand each
other as long as their communication is in the same topic.
Richards and Rodgers (1999: 48) point out that speaking is always formed in
real time, in which the speaker would speak right away without having any time to
carefully edit and revise it; while the listener is waiting for him or her. It means that
once the speaker gets involved in speaking, he has to prepare to do many things all
together at that moment. The speaker has to be able to understand, think, and say for
unexpected or even predicted topic in the communication.
Here, it is clearly explained that speaking is a natural process. It means that
the speaker produces speaking naturally in real time but it can be understood by
particularly a foreign language that we, as native speakers, are not really familiar
with. Instead of worrying about it, the participants still have the chance to master
speaking skill as long as the participants do some efforts to sharpen their knowledge
of communication and practice in the situation as well.
b. Teaching Speaking
According to Rivers (1968: 160), in teaching speaking, the teacher is
supposed to create conducive situation. In the conducive situation, the teacher can
persuade the students to use the language using their own meaning entitled to the
limits of what they have learned. Rivers also suggests that the teacher should not wait
until the students feel confident to perform the language. In a sense, the teacher
should actively encourage and accustom the students to apply what they have learned
in an act of communication in natural interaction between their friends. As a
consequence, the students are to be motivated to practice their foreign language
exclusively and be familiar with various situational contexts.
c. Activities in Teaching Speaking
A lot of effort has gone into motivating the students to speak; the teacher
could design some stimulating activities to provoke spoken communication in
classroom. Harner (1991: 122) suggests some activities to build the communicative
condition for the students to speak. Those activities are:
1) Information Gap; The students are put into a situation in which they have to share
the information using the target language because one person has information and
2) Role-plays; The students get a particular role where they have to play it in certain
condition by using the target language.
3) Simulation; The students play a role in a simulated environment like in the real
world.
4) Discussion; The students express their idea or opinion in some issues.
5) Problem Solving Task; The students talk together to find a solution to a problem
or task.
The writer develops those activities in learning task and games and integrates those
activities to some issues in society so as to promote the students to speak in those
activities without finding themselves reluctant to do so.
d. Successful Activity for Teaching Speaking
When the students are willing to speak a lot in the target language with the
teacher or other friends, the students should take some steps to succeed in acquiring
speaking skill. According to Davies (1988), there are four characteristics of
successful speaking activity. Firstly, the students have the chance to talk as much as
possible in the limited time given. Secondly, all the students should participate
actively in speaking without any unfairly domination by talkative the students.
Thirdly, the interesting and new topic will be conveyed in learning speaking, to draw
students’ attention and interest to speak. Fourthly, the level of relevancy, accuracy,
and comprehension are required in for the effectiveness of speaking. These steps
could be accommodated effectively if there is a good relationship and cooperation
between the teacher and the students. The teacher becomes the facilitator for the
2. Communicative Competence
To act as the participants in communication, the students are directed to learn
speaking and master language competence model instead. One of the language
competence models developed by Hymes as quoted by Hall (2001: 12) is called
Communicative Competence. In this competence, the individual develops the
competence to use language effectively in speech community by engaging with his
or her prior knowledge of social conditions including setting, participants, and goals
of communication.
There are some components of communicative competence in second or
foreign language learning suggested by Murcia et al. as cited by Hall (2001: 14). The
first component is the ability of knowing, sequencing, and arranging words,
structures, sentences, and utterances to produce cohesive and coherent texts called
Discourse Competence. The second component is the ability of interpreting and
constructing grammatically correct texts and utterances using basic elements of
linguistic system called Linguistic Competence. The third component is the ability of
interpreting and producing direct and indirect speech act called Actional
Competence. The fourth component is the knowledge of encountering breakdowns in
communication by requesting clarification or rephrasing called Strategic
Competence. And the last one is the ability of understanding and contributing in
communicative activity called Sociocultural Competence
Those components above show correlations that complete each other. Murcia
also adds that discourse competence is the main core in communication. The
discourse of communication can be developed when the participants consider the
realize some competences underlies such as linguistic competence, actional
competence, sociocultural competence, and strategic competence. English can be
taught successfully to the students, when all of the competences are taken into
account. These components of communicative competence model will form the
foundation of learning objectives to which the instructional speaking activities for the
students of second grade of language program at senior high school are oriented.
3. Contextual Teaching and Learning
In developing the instructional speaking materials for the second grade of
language program at senior high school, the writer used CTL as a method to facilitate
learning in order to achieve the objective of the course. Therefore, the writer has to
learn the content and features of CTL in depth in order to develop the materials
which have the relevance to the theories of CTL.
a. Foundation of Contextual Teaching and Learning
Contextual Teaching and Learning builds upon bodies of the theory in
constructivism era. According to Zahorik as quoted by Nurhadi, Yasin, and Senduk
(2004: 9), knowledge can be constructed when people bring meaning to their
experience. Since people constantly undergo new experience, therefore knowledge is
always dynamic. Through time, knowledge is developing as well as people are
developing. When people construct knowledge regarding their previous experience,
they have already learned something. The students then are expected to construct
their knowledge based on their experience in learning. The knowledge can help the
Another theory comes from the father of progressivism era, John Dewey. As
quoted by Kohonen, Jaatinen, Kaikkonen, and Lehtovaara (2001: 24), Dewey
explains that learning can be supported by concrete environment. It appears that the
students are able to construct their own knowledge by testing ideas based on their
prior knowledge and experience, applying the ideas to new situations, and integrating
the new knowledge. Hence, the students become active participants in problem
solving and critical thinking regarding constructing knowledge through the activities
in learning which are relevant to their prior knowledge.
Those theories above become the basis for developing the CTL method. CTL
provides the situation or problems as if in the real world covered in issues taken from
society that serve students’ learning experience by developing their critical thinking
to solve the problem.
b. Meaning of Contextual Teaching and Learning
Contextual Teaching and Learning is a learning approach that integrates
academic content with situations or issues that are meaningful to the students. As
Johnson says, as quoted by Nurhadi et.al, that
Contextual Teaching and Learning is a conception of teaching and learning that helps the teacher relates subject matter content to real world situations and motivates the students to make connections between knowledge and its application to their lives as family members, citizens, and workers and engage in the hard work that learning requires. (2004:12)
Apparently, CTL helps the students to construct the knowledge and own
understanding in mind by engaging with their previous experiences and leads the
students to learn by experiencing the learning in created situations like in real life.
learning process, the students are to develop their own critical thinking and creativity
to solve the problems found in society. During the involvement in that experience,
the students will understand the meaning and the importance of that learning by
understanding how to use their knowledge in real life which is associated with their
roles and responsibilities as family members, citizens, students, and workers.
c. Strategies of Contextual Teaching and Learning
According to Centre of Occupational Research and Development at the
University of Wisconsin-Madison as cited by Nurhadi et.al (2004: 23), CTL should
be structured by five essential forms of learning strategy. Firstly, learning must relate
those everyday situations to new information to be absorbed or a problem to be
solved. Secondly, learning stresses on experiencing through exploration, discovery,
and invention. Thirdly, learning takes place when the knowledge is presented in a
useful context. Fourthly, learning occurs in the context of sharing, responding, and
communicating with other learners. Fifthly, learning occurs when the students try to
develop their own knowledge by connecting existing and new knowledge. In this
language instruction using CTL model, the students are required to fulfill these five
essential forms of learning to gain meaningful learning in class and make them as
self-regulated learners. In order to design the effective CTL materials, those five
essential forms of learning will be taken into consideration.
d. Approaches for Implementing Contextual Teaching and Learning
To implement CTL in teaching and learning activities in classroom, some
speaking activities in classroom. According to Berns and Erickson as quoted by
Nurhadi et al. (2004: 19), there are some approaches of Contextual Teaching and
Learning as follows:
1) Problem-Based Learning
Problem-based learning is an approach characterized by the use of “real
world” problems. The problems are employed as a context for the students to learn
critical thinking and problem solving skills by providing some ideas or opinions as
the alternative solutions for solving the problems. The students will gather the
information around a question, discuss, and analyze it. After that, they will present
findings to others. The teacher will role as a facilitator, who provides problem, asks
questions, and facilitates investigation or dialogue.
a) Characteristics of Problem-Based Learning
There are four characteristics of problem-based learning. Firstly, it focuses on
asking questions related to the problem raised. Secondly, it focuses on the
interdisciplinary of context such as social, economic, political, cultural, and personal
context. Thirdly, the student will conduct authentic investigation for the problems.
Fourthly, the student will develop the result and present it to the classroom. Those
characteristics should be covered in problem-based learning.
b) The Purpose of Problem-Based Learning
Problem-based learning is designed to help the students develop three main
skills. Thinking and solving the problem are the first skill to be developed in problem
analyzing and synthesizing the problems. Afterwards, they will interpret their
thinking in terms of solution to the problems. Modeling the role of adult is the
second skill to be sharpened. The students will have the chance to involve in the
phenomenon in real life and learn the important of adult’s role. Learning to think,
interpret, and adapt with that phenomenon are expected from the students. Being an
independent and autonomy learner is the third skill that will be equipped in
problem-based learning. The teacher will encourage and guide the students to ask the
questions and solve the problem on their own. Hence, the students learn to finish
their own task autonomy in their future.
c) The Steps of Problem-Based Learning
There are some steps provided in problem-based learning. Firstly, the teacher
orientates the students to the problem. Secondly, the teacher organizes the students to
define and organize the learning task. Thirdly, the teacher encourages the students to
do group investigation. Fourthly, the teacher helps the students to prepare the
presentation and finally the teacher helps the students to have reflection and
evaluation in the process of solving the problem.
2) Cooperative Learning
Cooperative learning is an approach that organizes instruction using small
learning groups in which the students work together to achieve learning goals
(Slavin, 1995: 4). Cooperative learning can help the students who are willing to work
and succeed as a team. It means that they have to learn cooperatively to get success
Learning. In this team, the students not only do something as a team but also learn
something as a team to achieve the aims of learning.
a) Elements of Cooperative Learning
There are four elements underlying the concept of cooperative learning
suggested by Abdurrahman, as quoted by Nurhadi et al. (2004: 61). The first concept
is the positive interdependence between the members of the team where the students
will motivate each other in their group to achieve the objective of learning. The
second concept is the face-to-face interaction by interacting and sharing the students’
knowledge with other members in the form of dialogue. The third concept is the
individual accountability where the success depends on the individual learning of all
team members. The fourth concept is the skill to develop the interpersonal
relationship by respecting people’s opinions and ideas.
b) The Significance in Cooperative Learning
According to Johnson and Johnson (1984) as cited by Nurhadi et al. (2004:
63), there are some significance in cooperative learning. Besides improving the
aspect of cognition, in cooperative learning, the students will learn to improve their
ability to socialize by adapting with other members of the group and behaving
properly in their group. The students will learn to express their ideas and react to
others criticisms. Yet, the responsibility of each member will be accounted for all the
members of group. Working and Socializing together with their group, self-esteem
and self-acceptance are to be improved in themselves as the individual and social
the condition which makes the student learn to adapt with their partners or
companions and balance the relationship.
c) The Role of Evaluation in Cooperative Learning
To enhance the students’ quality of performance in speaking skill and also
their ability in work cooperatively, evaluation for cooperative learning is required.
There some benefits of using evaluation in cooperative learning as stated by Candler
(2002, in http://www.olc.spsd.sk.ca/html). By employing the evaluation, the teacher
can assess group outcomes as well as individual outcomes. The teacher will know
how the students work from cooperative group-assessment and cooperative
self-assessment. The result becomes the general description of the students’ condition for
the teacher to find the way to improve the students’ learning. Besides, the students
will gain benefits by being able to communicate their work with the teacher and
getting feedback from the teacher in order to produce higher-quality work.
Problem-Based Learning and Cooperative Learning are approaches that are to
be adapted to speaking activities in the classroom. Those approaches are expected to
help the teacher to achieve successful speaking activities in classroom.
e. Learning Context Used in Contextual Teaching and Learning
CTL exploits real context as much as possible related to students’ background
knowledge and experience. It facilitates students’ learning by passing on the
knowledge in stages and pieces that the students are familiar with. The real context
becomes the significant factor of the materials development using CTL. According to
environment. The surroundings and environment are to be recognizable for the
students to learn. There are some contexts that involve in Contextual Teaching and
Learning (Nurhadi et. al, 2004: 4). They are as follows:
1) Cultural Context.
In this context, the students will learn to be aware of the cultural issues raised in
society and learn how to deal with the context.
2) Social, Economic and Political Context.
In these contexts, the students will put themselves as the part of society and
discuss the problem such as social, economic, or political problem found in
society. The students will try to find the solution.
3) Personal Context.
In this context, the students will sharpen their skill to communicate with others
and to take a part as the individual and part of larger community society.
CTL will give chance for the teacher to provide those contexts in learning activities.
The aim is to help the students to see the meaning in the academic materials they are
studying by connecting it with the context of their daily lives, such as personal,
social, economic, political, and cultural context in their society. Furthermore, the
students will learn to be aware of those contexts that exist in real life and the
problems that could be followed.
f. The Role of Teacher and Students in Contextual Teaching and Learning
In CTL, the teacher will act as the facilitator and guide in the process of
teaching and learning activity and assessing the implementation. The teacher is not
risk-taking target language usage. Serving important roles in CTL, the teacher will
support the learning by providing problems, motivation, real life context, and
cooperative learning. The students, meanwhile, are supposed to be the center of
learning. The students should be actively involving as participants in learning by
reinforcing, expanding, and applying their knowledge and skills through the
activities in interdependent group learning to lead them as self-regulated learners.
4. Competence-Based Curriculum
Competence-Based Curriculum is the curriculum that has been applied in
some schools such as SMA Stella Duce 1 Yogyakarta since 2004.
Competence-Based Curriculum focuses on the competence to be performed by the students.
According to Pusat Kurikulum Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Departemen
Pendidikan Nasional (2001: 7-8), in, the students are expected to be able to
communicate in English fluently. Since it views the language as a means of
communication, English learning is expected to function as a means to develop
senior high school students’ personality, knowledge, technology and arts, global
concept, and international communication capability.
a. Objectives of English Language Learning Based on Competence-Based Curriculum
In this curriculum, English lesson has four objectives. Firstly, the students are
able to communicate in English. Secondly, the students are able to understand
English as a language system. Thirdly, the students are able to develop their
knowledge (Pusat Kurikulum Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Departemen
Pendidikan Nasional, 2001: 8). Accordingly, the students are supposed to develop
their English competency integrating with the aspects of life such: arts and culture,
social life, cognitive development, and the like.
b. Materials Scope in English Language Learning based on Competence-Based Curriculum
In an attempt to achieve the objectives stated above, the scope of English
materials for SMA should be determined. The scope of English material should cover
macro skills of English (listening, speaking, reading, and writing), basic language
components (structures, vocabulary, pronunciation, and spelling), and the cultural
aspects such as in English expressions found in various oral and written texts
(Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, 2003: 2).
c. Principles of Competence-Based Curriculum
There are six principles in the Competence-Based Curriculum (Pusat
Penelitian Badan Penelitian dan Pengembangan Departemen Pendidikan Nasional,
2001: 11-12). They are summarized as follows:
1) Knowing what to do according to the purposes and the use of every activity.
2) Integrating the four skills of language (English) competencies.
3) Learning a language is learning how to communicate.
4) Knowing the importance of meaning in teaching.
5) Learning how to do by having much time to practice their knowledge.
5. The Role of Instructional Materials
Materials are one of the important elements needed in developing course
design. Imel states that in CTL, materials should become a tool for helping learners
to reflect on and make changes in their lives (2004, in
http://www.cew.wisc.edu/teachnet/ctl/html). It means that the teacher should be
creative in producing or adapting materials which are comprehensible and
practicable for the students so as to improve their lives. In CTL, the writer will
develop task-based materials. It concerns with the problem-solving task that provided
in cooperative learning. In addition, the task can be also the various kinds of
discussion, presentation, and games that can support the CTL class. The task-based
materials are used in order to give the opportunity for the students to practice the
language use by presenting it in the form of many various kinds of CTL task.
6. Materials Design Model
In designing and writing the materials, Hutchinson and Waters (1987: 108)
propose the materials design model for the teacher. The model is to provide a
coherent framework for the integration of various aspects of learning as well as the
room for teacher’s creativity.
This model consists of four components. The first component is input, which
provides stimulus materials for activities, new language it