DAFTAR PUSTAKA
Acevedo E, Fereres E. 1993. Resistance to abiotic stresses. Di dalam Hayward MD, Bosemark NO, Romagosa I, editor. Plant Breeding: Principles and Prospects. London: Chapman & Hall. hlm 406-421.
Ahn SW, Amir M. 1986. Rice blast management under upland conditions. Di dalam. Progress in Upland Rice Research. Los Banos, Phillippines: IRRI hlm 363-374 Akatsuka T, Kodama O, Sekido H, Kono Y, Takeuchi S. 1985. Novel phytoalexins
(Oryzalexin A, B and C) isolated from rice blast leaves infected with Pyricularia oryzae. Agric Biol Chem 49: 1689-1694.
Alluri K. 1986. Screening rice varieties in acid upland soils. Di dalam. Progress in Upland Rice Research. Los Banos, Phillippines: IRRI. hlm 263-270.
Aluko GK, Oard JH. 2004. Evaluation of discriminant analysis as tool for rapid identification of marker associated with drought resistance in rice. Di dalam Rockefeller Foundation Workshop. hlm 83-84.
Amir M, Anggiani, Santoso. 1999. Uji ketahanan varietas/galur padi terhadap penyakit blas (Pyricularia grisea) di lapang. Prosiding Kongres Nasional XV dan Seminar Ilmiah Perhimpunan Fitopatologi Indonesia: Purwokerto, 16-18 Sep 1999. hlm 153-157
Amir M, Kardin MK. 1991. Pengendalian penyakit jamur. Di dalam Soenarjo E, Damardjati DS, Syam M, Editor. Padi. Buku 3. Bogor: Puslitbangtan. Departemen Pertanian. hlm 825-844.
Amir M, Nasution A. 1995. Status dan pengendalian blas di Indonesia. Di dalam Syam M, Hermanto, Musaddad A, Sunihardi, editor. Kinerja Penelitian Tanaman Pangan Bogor: Pusat Penelitian dan Pengembangan Tanaman Pangan. hlm 583-592.
Amir M, Santoso, Nasution A, Kustianto B. 2003. Pemetaan Pyricularia grisea di daerah endemik blas di sentra produksi padi sawah dan padi gogo. [Laporan Akhir]. Sukamandi: Balitpa, Balitbangtan, Departemen Pertanian.
Amir M. 2002. Strategi penyelamatan padi gogo dari ancaman penyakit blas. Di dalam. Hermanto, Kasim H, Adil WH, editor. Risalah Seminar 2000-2001 Pusat Penelitian dan Pengembangan Tanaman Pangan. Bogor: Pusat Penelitian dan Pengembangan Tanaman Pangan. hlm 68-76.
Aniol AM. 1995. Physiological aspects of aluminum tolerance associated with the long arm of chromosome 2D of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) genome. TAG 91: 510-516. Anonymous. 2007. Ketahanan pangan: substansi beras dilupakan. Kompas 27 April 2007:
halaman 1 dan 15 (kolom 1-5).
Archambault DJ, Zhang G, Taylor GJ. 1996. Accumulation of Al in root mucilage of an Al-resistant and Al-sensitive cultivar of wheat. Plant Physiol 112:1471-1478.
Asfaruddin. 1997. Evaluasi ketegangan galur-galur padi gogo terhadap Al dan efisien dalam penggunaan K. [tesis]. Bogor: Program Pascasarjana, Institut Pertanian Bogor. Baligar VC, Pitta GVE, Gama EEG, Schaffer RE, de Bahia Filho, Clark RB. 1997. Soil
acidity affects on nutrient use efficiency in exotic maize genotypes. Plant Soil 192: 9-13.
Banzinger M, Betran FJ, Lafitte HR. 1997. Efficiency of high-nitrogen selection environments for improving maize for low-nitrogen target environments. Crop Sci 37: 1103-1109.
Barcelo J, Guevara P, Poschenrieder, CH. 1993. Silicon amelioration of aluminum toxicity in teosinte (Zea mays L. ssp. mexicana). Plant Soil 154: 249-255.
Basyir A, Punarto S, Suyamto, Supriyatin 1995. Padi Gogo. Malang: Balai Penelitian Tanaman Pangan.
Blamey FPC, Dowling AJ.1995. Antagonism between aluminum and calcium for sorption by calcium pectate. Plant Soil 171: 137-140.
Blum A. 1988. Plant Breeding for Stress Environments. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. Bonman JM, Estrada BA, Bandong JM.1989. Leaf and neck blast resistance in tropical
lowland rice cultivars. Plant Dis 73:388-390.
Bonman JM. 1992a. Blast. Di dalam Webster RK, Gunnel PS, editor. Compendium of Rice Diseases. St Paul: American Phytopathological Society. hlm: 14-16.
Bonman JM. 1992b. Durable resistance to rice blast disease-environmental influences. Euphytica 63:115-123.
Bouchez A, Gallais A. 2000. Efficiency of the use of doubled-haploids in recurrent selection for combini ng ability. Crop Sci 40: 23-29.
[BPS] Biro Pusat Statistik. 2007. Statistik Indonesia 2005/2006. Jakarta: Biro Pusat Statistik.
Brancourt-Hulmel M, Heumez E, Pluchard P, Beghin D, Depatureaux C, Giraud A, Le Gouis J. 2005. Indirect versus direct selection of winter wheat for low-input or high-input levels. Crop Sci 45: 1427-1431.
Calhoun DS, Gebeyehou G, Miranda A, Rajaram S, van Ginkel M. 1994. Choosing evaluation environments to increase wheat grain yield under drought conditions Crop Sci 34: 673-678.
Cartwright DW, Langcake P, Pryce P, Leworthy DP, Ride JP. 1981. Isolation and characterization of two phytoalexins from rice as momilactones A and B. Phytochemistry 20: 535-537.
Carver BF, Ownby JD. 1995. Acid soil tolerance in wheat. Adv Agron 54:117-173. Ceccarelli S. 1996. Adaptation to low/high input condition. Euphytica 92: 203-214.
Chahal GS, Gosal SS. 2002. Principles and Procedures of Plant Breeding: Biotechnological and Conventional Approaches. New Delhi: Narosa Publishing House.
Chao CT, Moldenhauer KAK, Ellingboe AH. 1999. Genetic analysis of resistance/susceptibility in individual F3 families of rice against strains of Magnaporthe grisea containing different genes for avirulence. Euphytica 109: 183-190.
Chozin MA 2006. Peran ekofisiologi tanaman dalam pengembangan teknologi budidaya pertanian.Orasi Ilmiah Guru Besar Tetap Ilmu Agronomi. Bogor: Fakultas Pertanian Institut Pertanian Bogor, 24 Juni 2006.
Chumley FG, Valent B. 1990. Genetic analysis of melanin-deficient, non-pathogenic mutants of Magnaporthe grisea. MPMI 3: 135-143.
Chung GS. 1992. Anther culture for rice improvement in Korea. Di dalam. Zheng K, Murashige T, editor. Anther Culture for Rice Breeders. Seminar and Training for Rice Anther Culture. Hangzhou, China September 1992. Hangzhou: China National Rice Research Institute. hlm: 8-37.
Clark RB, Flores CL, Gourley LM, Duncan RR. 1990. Mineral element concentrations and grain yield of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) and pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) grown on acid soil. Di dalam ML van Beusichem, editor. Plant Nutrition-Physiology and Application. Netherlands: Kluwer Acad Publ. hlm 391-396.
Clark RB, Gourley. 1988. Mineral element concentrations of sorghum genotypes grown on tropical acid soil. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 19: 1019-1029.
Cocker KM, Evans DE, Hodson MJ. 1998a. The amelioration of aluminum toxicity by silicon in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): malate exudation as evidence for an in planta mechanisms. Planta 204: 204-318.
Cocker KM, Evans DE, Hodson MJ. 1998b. The amelioration of aluminum toxicity by silicon in higher plant: Solution chemistry or an in planta mechanisms? Plant Physol 104: 608-614.
Coronel VP, Akita S, Yoshida S. 1990. Aluminum toxicity tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L) seedlings. Di dalam. ML van Beusichem, editor. Plant Nutrition-Physiology and Application. Netherlands: Kluwer Acad Publ. hlm: 357-373.
Correa-Victoria FJ, Zeigler RS. 1995. Stability of partial and complete resistance in rice to Pyricularia grisea under rainfed upland conditions in Eastern Colombia. Phytopathology 85: 977-982.
Datta SK. 2005. Androgenic haploids: factors controlling development and its application in crop improvement. Current Sci 89: 1870-1878.
Degenhardt J, Larsen PB, Howell SH, Kochian LV. 1998. Aluminum resistance in the Arabidopsis mutant alr-104 is caused by aluminum-induced increase in rhizospere pH. Plant Physiol 117: 19-27.
Departemen Pertanian. 2007. Statistik Pertanian 2006. Jakarta: Pusat Data dan Informasi Pertanian, Departemen Pertanian RI.
Derent CW, Datnoff LE, Snyder GH, Martin FG. 1994. Silicon concentration, disease response, and yield components of rice genotypes grown on flooded organic histosols. Crop Sci 34: 733-737.
Dewi IS, Hanarida I, Rianawati S. 1996. Anther culture and its application for rice improvement program in Indonesia. Indon Agric Res Dev J 18: 51-56.
Dewi IS, Purwoko BS. 2001. Kultur antera untuk mendukung program pemuliaan tanaman padi. Bul Agron 29: 59-63.
Dewi IS. 2003. Peranan fisiologis poliamin dalam regenerasi tanaman pada kultur antera padi (Oryza sativa L.). [disertasi]. Bogor: Program Pascasarjana, Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Dillon VM, Overton J, Grayer RJ, Harborne JB. 1997. Differences in phytoalexin response among rice cultivars of different resistance to blast. Phytochemistry 44: 599-603. Dobermann A, Fairhurst T. 2000. Rice Nutrient Disorders and Nutrient Management.
Manila: IRRI/Potash & Phosphate Institute of Canada.
Epstein E. 1999. Silicon. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Mol Biol 50: 641-664.
Everitt BS, Dunn G. 1991. Applied Multivariate Data Analysis. London : Edward Arnold. Fageria NK, Wright RJ, Baligar VC. 1988. Rice cultivar response to aluminum in nutrient
solution. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 19: 1133-1142.
Falconer DS, Mackay TFC. 1996. Introduction to Quantitative Genetics. Fourth Edition. London: Longman
Farid N, Syakhril, Asfaruddin, Trikoesoemaningtyas, Jagau, Y, Soepandi D, Makmur M. 1997. Preliminary study on variability of nutrient element efficiency under aluminum stress condition in upland rice (Oryza sativa L.). Proceeding of the International Symposium on Plant Responses to Ionic Stress: Aluminum and Others Ions. Kurashiki, Japan: 19-20 September, 1997.
Farid N. 1997. Pengujian plasma nutfah padi gogo untuk ketenggangan terhadap tanah masam dan ketahanan terhadap penyakit blas. [tesis]. Bogor: Institut Pertanian Bogor, Program Pascasarjana
Fehr WR. 1987. Principles of Cultivar Development: Theory and Technique. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Filippi MC, Prabhu As. 1997. Integrated effect of host plant resistance and fungicidal seed treatment on rice blast control in Brazil. Plant Dis 81:351355.
Galvez L, Clark RB, Gourley LM, Maranville JW. 1987. Silicon interactions with manganese and aluminum toxicity in sorghum J Plant Nutr 10: 1139-1147.
Ganesan K, Sankaranarayanan C, Balakumar T. 1993. Physiological basis of differential aluminum tolerance in rice genotypes. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 24:2179-2191. Giaveno CD, Filho JB. 2002. Selection methods for maize seedlings in greenhouse as
related to aluminum tolerance. Scienticia Agricola 59: 807-810.
Gomez KA, Gomez AA. 1995. Prosedur Statistik untuk Penelitian Pertanian. Ed-2. Sjamsuddin E, Baharssjah J, penerjemah; Jakarta: UI Press. Terjemahan dari: Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research.
Gupta US. 1997. Crop Improvement: Stress Tolerance. Volume 2. New Hampshire: Science.
Hai TV, Houben V, Mbouti CN, Dufey JE. 1993. Early diagnosis of aluminum toxicity to rice cultivars (Oryza sativa L.). Agronomie 13: 853-860.
Hammond KE, Evands DE, Hodson MJ. 1995. Aluminum/silicon interactions in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seedlings. Plant Soil 173:89-95.
Hanarida I, Ambarwati AD, Apriana A. 2002. Induksi kalus dan regenerasi tanaman melelui kultur antera pada silangan padi tipe baru. Penelitian Pertanian Tanaman Pangan 21: 20-23.
Hara T, Gu MH, Koyama H. 1999. Ameliorative effect of silicon on aluminum injury in the rice plant. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 45: 929-936.
Harahap Z, Amir M, Azwar, R. 1986. Blast breeding methodologies in Indonesia. Di dalam. Progress in Upland Rice Research. Los Banos, Philippines: IRRI hlm: 327-333.
Hardjowigeno S. 2003. Ilmu Tanah. Jakarta: Academika Presindo.
Haynes RJ. 1990. Active ion uptake and maintenance of cation-anion balance; A critical examination of their role in regulating rhizosphere pH. Plant Soil 126: 247-264. Hiradate S, Taniguchi S, Sakurai K. 1998. Aluminum speciation in aluminum-silica
solutions and potassium chloride extracts of acid soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 62: 630-636.
Horst WJ, Schmohl N, Kollmeier M, Baluska F, Sivaguru M. 1999. Does aluminum affect root growth of maize through interaction with the cell wall-plasma membrane-cytoskeleton continuum? Plant Soil 215: 163-174.
Howard RJ, Valent B.1996. Breaking and entering host penetration by fungal rice blast pathogen Magnaphorte grisea. Annu Rev Microbiol 50: 491-515.
Howeler RH, Cadavid LV. 1976. Screening of rice cultivar for tolerance to Al-toxicity in nutrient solution as compared with a field screening method. Agron J 68: 551-555. Hu H. 1988. In-vitro induced haploids in higher plant. Di dalam. Genetic Manipulation in
Crops. Proceedings of the International Symposium on Genetic Manipulation in Crops: the 3rd International Symposium on Haplody. Beijing, Oktober 1984. Manila, Phlippines: IRRI and Sinica Acad. hlm: 8-12
Huang JS. 2001. Plant Pathogenesis and Resistance: Biochemistry and Physiology of Plant-Microbe Interactions. London: Kluwer Acad.
Huang JW, Shaff JE, Grunes DI, Kochian LV. 1992. Aluminum effect on calcium fluxes at the root apex of aluminum-tolerant and aluminum-sensitive wheat cultivars. Plant Physiol 98: 230-237.
Irawan. 2005. Analisis ketersediaan beras nasional: suatu kajian simulasi pendekatan sistem dinamis. Di dalam Husen E, Racman A, Irawan, Agus F, editor. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Multifungsi Pertanian dan Ketahanan Pangan. Bogor: Pusat Penelitian dan Pengembangan Tanah dan Agroklimat, Departemen Pertanian hlm 107-130.
[IRRI] International Rice Research Institute. 1996. Standard Evaluation System for Rice. Manila: International Rice Research Institute.
Ishikawa S, Wagatsuma T, Sasaki R, Ofei-Manu P 2000. Comparison of the amount of citric and malic acids in Al media of seven plant species and two cultivars each in five plant species. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 46: 751–758.
Ishikawa S, Wagatsuma T. 1998. Plasma membrane permeability of root-tip cells following temporary exposure to Al ions is a rapid measure of Al tolerance among plant species. Plant Cell Physiol 39:516-525.
Jagau Y. 2000. Fisiologi dan pewarisan sifat efisiensi nitrogen dalam keadaan terceka m Al pada padi gogo. [disertasi]. Bogor: Program Pascasarjana, Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Jan VVS, Mecado CC, Kinet JM, Bauharmount J. 1997. Selection of Al-resistant plants from a sensitive rice cultivar, using somaclonal variation, in vitro and hydroponics cultures. Euphytica 97: 303-310.
Jensen CJ. 1986. Haploid induction and production in crop plant. Di dalam. Horn W, editor. Genetic Manipulation in Plant Breeding. Berlin: Walter de Gruyer.hlm: 231-256.
Jones DL, Kochian LV.1995. Aluminum inhibition of the inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate signal transduction pathway in wheat roots: a role in aluminum toxicity? Plant Cell 7: 1913–1922
Kaltjens WG, Ulden PSR. 1987. Effect of Al on nitrogen (NO3- and NH4+) uptake, nitrate reductase activity and proton release in two cultivars differing in Al tolerance. Plant Soil 104: 227-234.
Kamprath EJ. 1970. Exchangeable aluminum as a criterion for liming leached mineral soils. SSA Proc 34: 252
Kataoka T, Nakanishi TM. 2001. Aluminium distribution in soybean root tip for a short time Al treatment. J Plant Physiol: 58: 731–736
Khatiwada SP. Senadhira D, Carpena AL, Zeigler RS, Fermandez PG. 1996. Variability and genetics of tolerance for aluminum toxicity in rice. TAG 93: 738-744.
Khush GS, Virmani SS, 1996. Haploids in plant breeding. Di dalam. Jain SM Sopory SK, Veilleux RE, editor. In Vitro Haploid Production in Higher Plant. The Netherlands: Kluwer Acad. hlm 11-33.
Kim SG, Kim KW, Park EW, Choi D. 2002. Silicon-induced cell wall fortification of rice leaves: A possible cellular mechanism of enhanced host resistance to blast. Phytophatology 92: 1095-1103.
Kinraide TB, Ryan PR, Kochian LV. 1994. Al3+-Ca2+ interactions in aluminum rhizotoxicity. II. Evaluating the Ca2+-displacement hypothesis. Planta 192:104-109. Kiyosawa S. 1982. Genetic and epidemiological modelling of breakdown of plant disease
resistance. Annual Review of Plant Phytopathology 20: 93-117.
Kobayashi T. Kanda E, Ishiguro K, Torigoe Y. 2001. Detection of panicle blast with multispectral radiometer and the potential of using airborne multispectral scanners. Phytopathology 91: 316-323.
Kochian LV, Heokenga OA, Pineros MA. 2004. How do crop plants tolerate acid soils? Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance and phosphorous efficiency. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55 : 459-493.
Kochian LV, Pineros MA, Heokenga OA. 2005. The physiology, genetics and molecular biology of plant aluminum resistance and toxicity. Plant Soil 274: 175-195.
Kochian LV. 1995. Cellular mechanisms of aluminum toxicity and resistance in plant. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Mol Biol 46: 273-260.
Koga J, Shimura M, Oshima K, Ogawa N, Yamauchi T, Ogasawara N. 1995. Phytocassanes A, B, C and D, novel diterpene phytoalexins from rice, Oryza sativa L. Tetrahedron 51: 7907-7918.
Kollmeier M, Felle HH, Horst WJ. 2000. Genotypic differences in aluminum resistance of maize are expressed in the distal part of the transition zone. Is reduced basipetal auxin flow involved in inhibition of root elongation by aluminum? Plant Physiol 122: 945-956.
Koyama H, Kawamura A, Kihara T, Hara T, Takita E, Shibata D. 2000. Over expression of mitochondrial citrate synthase in Arabidopsis thaliana improved growth on a phosphorus-limited soil. Plant Cell Physiol 41: 1030-1037.
Kustianto B, Amir M, Suwarno. 1993. Studi genetika sifat keta hanan blas pada beberapa varietas padi gogo. Penelitian Pertanian. 13 : 21-24.
Lazof DB, Goldsmith JG, Rufty TW, Lintin RW.1996.The early entry of Al into cells of intact soybeans roots. Plant Physiol 112: 1289-1300.
Lewis CF, Chistiansen MN. 1981. Breeding plants for stress environments. Di dalam Frey KJ, editor. Plant Breeding II. Ames: The Iowa State University Press. hlm 151-178. Li CC. 1975. Path Analysis: A Primer. California: Boxwood Press.
Li MF. 1992. Anther culture breeding of rice Di dalam. Zheng K, Murashige T, editor. Anther Culture for Rice Breeders. Seminar and Training for Rice Anther Culture. Hangzhou, China September 1992. Hangzhou: China National Rice Research Institute.hlm 75-86.
Liu DY, Wang SD, Ding SL, Zhang MG. 1983. The utilization of anther culture method in the breeding of rice. Di dalam. Shen JH, Zhang ZH, Shi SD, editor. Studies on Anther Culture Breeding in Rice. Beijing: Agricultural Press. hlm: 32-38.
Liu K, Luan S. 2001. Internal aluminum block of plant inward K+ channels. Plant Cell 13: 1453-1465.
Ma JF .2004. Role of silicon in enhancing the resistance of plant to biotic and abiotic stress. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 50 : 11-18
Ma JF, Hiradate S, Matsumoto H. 1998. High aluminum resistance in buckwheat II. Oxalic acid detoxifies aluminum internally. Plant Physiol 117: 753-759.
Ma JF, Hiradate S, Nomoto K, Iwashita T, Matsumoto H. 1997a. Internal detoxification mechanism of Al in hydrangea: Identification of Al form in leaves. Plant Physiol. 113: 1033-1039.
Ma JF, Hiradate S. 2000. Form of aluminum for uptake and translocation in buckwheat (Fogopyrum sculentum Moench). Planta 211: 355-360.
Ma JF, Ryan PR, Delhaize E .2001. Aluminum tolerance in plants and the complexing role of organic acids. Trends in Plant Science 6:273-278.
Ma JF, Sasaki M, Matsumoto H. 1997b. Al-induced inhibition of root elongation in corn, Zea mays L. is overcome by Si addition. Plant Soil 188:171–176.
Ma JF, Shen R, Zhao Z, Wissuwa M, Takeushi Y, Ebitani T, Yano M. 2002. Response of rice to Al stress and identification of quantitative trait loci for Al tolerance. Plant Cell Physiol 43:652-659.
Ma JF, Takahashi E. 1993. Interactions between calcium and silicon in water-culture rice plants. Plant Soil 148:107-113.
Ma JF, Zheng SJ, Li XF, Takada K, Matsumoto H. 1997c. A rapid hydrophobic screening for aluminum tolerance in barley. Plant Soil 191:133-137
Ma JF,.Shen R, Nagao S, Tanimoto E. 2004. Aluminum targets elongating cells by reducing cell wall extensibility in wheat roots. Plant Cell Physiol 45:583-589.
Ma JF. 2000. Role of organic acids in detoxification of aluminum in higher plants. Plant Cell Physiol 41:383-390
Ma JF. 2005. Plant root responses to three abundant soil minerals: Silicon, Aluminum and Iron. Critical Reviews in Plant Science 24: 267 – 281.
Makmur A. 2001.Pemuliaan Tanaman Bagi Lingkunan Spesifik. Bogor: IPB Press. Mangoendidjojo W. 2003. Dasar-dasar Pemuliaan Tanaman. Yogyakarta: Kanisius. Marchetti MA. 1983. Dilatory resistance to rice blast in USA rice. Phytopathology 73:
645-649.
Mariano ED, Jorge RA, Keltjens WG, Menossi M. 2005. Metabolism and root exudation of organic acid anions under aluminum stress. Braz J Plant Physiol 17:157-172. Marschner H. 1995. Mineral Nutrition in Higher Plant. San Diego: Acad Press.
Martinez CP, Correa-Victoria F, Amezquita MC, Tulande E, Lema G, Zeigler RS. 1996. Comparison of rice lines derived through anther culture and pedigree method in relation to blast (Pyricularia grisea Sacc.) resistance. TAG 92:583-590.
Matsumoto H, Yamamoto Y, Kasai M. 1992. Changes of some properties of plasma membrane-enriched fraction of barley roots related to aluminum stress: Membrane-associated ATPase, aluminum and calcium. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 38: 411-419.
Matsumoto H. 2000. Cell biology of aluminum toxicity and tolerance in higher plants. Int
Rev Cytol 2000: 200:1-46.
Mitani N, Ma JF, Iwashita T. 2005. Identification of the silicon form in xylem sap of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Physiol 46:279-283.
Mogi S, Sugandhi Z, Baskoro SW, Edwina R, Cahyadi I. 1991. Establishment of differential variety series for pathogenic race identification of rice blast fungus and distribution of race based on the new differential Indonesia. Karawang, Jatisari: Rice Diseases Study Group Report.
Mukherjee SG. 1999. Discovery of haploid production by anther culture. In vitro Plant 35: 357-360.
Nagata T, Hayatsu M, Kosuge N. 1992. Identification of aluminum in tea leaves by 27Al NMR. Phytochemistry 31: 1215-1218.
Narasimhamoorty B, Blancaflor EB, Bouton JH, Payton ME, Sledge MK. 2007. A comparison of hydroponics, soil and root staining methods for evaluation of aluminum tolerance in Medicago truncatula (Barrel Medic) germplasm. Crop Sci 47: 321-328.
Nasution A, Santoso, Amir M, Kustianto B. 2004. Studi dinamika populasi dan dominasi ras patogen blas. [Laporan Akhir Tahun]. Sukamandi: Balitpa, Balitbangtan.. Departemen Pertanian
Nasution I, Suhartini T. 1991. Evaluasi metode uji ketahanan kultivar padi gogo terhadap tanah masam. Di dalam. Macmud M, Kosim M, Gunarto L, editor. Prosiding Lokakarya Penelitian Komoditas dan Studi Khusus. Bogor: Puslitbang, hlm 65-80.
Nguyen, VT, Burow MD, Nguyen HT, Le BT, Le TD, Paterson AH. 2001. Molecular mapping of genes conferring aluminum tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). TAG 106:1002-1010.
Notteghem Jl. 1986. Blast resistance methodology in the Ivory Coast. Di dalam. Progress in Upland Rice Research. Los Banos, Phillippines: IRRI hlm 305-316
Notteghem JL. 1993. Durable resistance to rice blast disease. Di dalam Jacobs Th, Parlevit JE, editor. Durability of Disease Resistance. London : Kluwer Acad Publ. London. hlm: 125-134.
Nursyamsi D. 2000. Aluminum tolerance of tropical crops. [thesis]. Hokkaido: Graduate School of Agriculture, Hokkaido University.
Okada K, Fischer AJ, Ferez-Salasar FA, Canon-Romero Y. 2003. Difference in retention of Ca and Al as possible mechanisms of Al resistance in upland rice. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 49:889-895.
Oku H. 1994. Plant Pathogenesis and Disease Control. Boca Raton: Lewis Ou SH. 1985. Rice Diseases. Kew Surrey: Commonwealth Mycological Institute.
Poehlman JM, Sleper DA. 1995. Breeding Field Crops. Ames: Iowa State University Press.
Polle EA, Konzak CF, Kittrick JA. 1978. Visual detection of aluminum tolerance levels in wheat by hematoxylin staining of seedling roots. Crop Sci. 18: 823-827.
Polle EA, Konzak CF. 1990. Genetics and breeding of cereals for acid soils and nutrient efficiency. Di dalam. Baligar VC, Duncan RR, editor. Crops as Enhancers of Nutrient Use. New York: Academic Pr. hlm: 81-130.
Prasetiyono J. 2003. Identifikasi marka mikrosatelit yang terpaut dengan sifat toleransi terhadap keracunan aluminium pada padi persilangan Dupa x ITA131. [tesis]. Bogor: Program Pascasarjana , Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Purwoko BS, Hanarida I, Dewi IS, Santosa E. 2000. Penggunaan poliamin untuk meningkatkan regenerasi tanaman hijau pada kultur antera padi dan aplikasinya dalam program pemuliaan padi. Laporan Hibah Bersaing VIII/2. Jakarta; Depdiknas. Purwoko BS, Usman AW, Dewi IS. 2001. Poliamin meningkatkan regenerasi tanaman
hijau pada kultur antera padi (Oryza sativa L.) cv. Taipei 309. Hayati 8: 117-130. [Puslitbangtan] Pusat Penelitian dan Pengembangan Tanaman Pangan. 2006. Laporan
Tahunan 2005 Penelitian dan Pengembangan Tanaman Pangan. Jakarta: Badan Penelitian dan Pengambangan Pertanian.
Rahman MT, Kawamura K, Koyama H, Hara T. 1998. Varietals differences in the growth of rice plants in response to aluminum and silicon. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 44: 423-431. Ramli M. 2000. Ketahanan dan dinamika ketahanan selama pertumbuhan beberapa
genotipe padi terhadap blas daun dan blas leher malai. [tesis] . Bogor: Program Pascasarjana, Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Rengel Z, Robinson DL. 1989. Competitive Al3+ inhibition of net Mg2+ uptake by intact Lolium multiflorum roots. I. Kinetics. Plant Physiol 91: 1407-1413.
Rodrigues FA, McNally DJ, Datnoff LE, Jones JB. 2004. Silicon enhances the accumulation of diterpenoid phytoalexins in rice: a potential mechanism for blast resistance. Phytopathology 94:177-183.
Rodrigues FA, McNally DJ, Datnoff LE, Jones JB. 2005. Silicon influences cytological and molecular events in compatible and incompatible rice Magnaporthe grisea interactions. PMPP 66:144-159.
Rossman AY, Howard RJ, Valent B. 1990. Pyricularia grisea, the correct name for the rice blast disease fungus. Mycologia 82: 509-512.
Roumen EC. 1993. Selection for partial resistance in rice blast. Di dalam. Jacobs T, Parlevliet JE, editor. Durability of Disease Resistance. London: Kluwer Acad. London. hlm:195-200.
Rout GR, Samantaray S, Das P. 2001. Aluminum toxicity in plants: a review. Agronomie 21: 3-21.
Roy D. 2000. Plant Breeding: Analysis and Exploitation of Variatian. New Delhi: Narosa Publishing House.
Rusdiansyah, Rohaeni N, Trikoesoemaningtyas. 2001. Evaluasi beberapa kultivar padi gogo asal Kalimantan Timur untuk ketahanan terhadap aluminium menggunakan metode kultur hara. Bul Agron 29: 73-77.
Rusdiansyah. 2002. Introgresi sifat-sifat agronomi dari spesies padi liar serta studi pewarisan sifat ketenggangan aluminium dan ketahanan penyakit blas daun pada populasi keturunan silangbalik Oryza glumaepatula. [disertasi]. Bogor: Program Pascasarjana, Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Samac DA, Tasfaye M. 2003. Plant improvement for tolerance to aluminum in acid soils. Plant Cell Tissue and Organ Culture 75: 189-207.
Santoso. 2005. Analisis ketahanan 28 genotipe padi terhadap penyakit blas daun dan hubungannya dengan keberadaan gen Pi-b dan Pi-ta1. [tesis] Bogor: Sekolah Pascasarjana, Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Sarkarung S. 1986. Screening upland rice for aluminum tolerance and blast disease. Di dalam Progress Report in Upland Rice Research. Los Banos: IRRI. hlm 271-281. Sasmita P. 2006. Karakterisasi dan evaluasi toleransi padi gogo haploid ganda hasil kultur
antera terhadap naungan. [disertasi]. Bogor: Sekolah Pascasarjana, Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Seebold KW, Kucharek TA, Datnoff LE, Correa-Victoria FJ, Marchetti MA. 2001. The influence of silicon on components of resistance to blast in susceptible, partially resistant and resistant cultivars of rice. Phytopathology 91: 63-69.
Setijono S. 1982. Lime estimation of Indonesia acid mineral soil and its significantion to crop production. [tesis doktor] Bogor: Fakultas Pascasarjana, Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Shen JH, Li MF, Chen YO, Zhang ZA. 1983. Improving rice by anther culture. Di dalam. Cell and Tissue Culture Techniques for Cereal Crop Improvement. Beijing: Science Pr/ International Rice Research Institute.hlm 183-205.
Silue D, Notteghem JL, Tharreau D. 1992. Evidence for a gene-for-gene relationship in the Oryza sativa-Magnaporthe grisea pathosystem. Phytopathology 82: 577-580.
Silva IR, Smyth TJ, Moxley DF, Carter TE, Allen NS, Rufty TW. 2000. Aluminum accumulation at nuclei of cells in the root tip. Fluorescence detection using lumogallion and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Plant Physiol 123: 543-552 Singh M, Ceccarelli S, Hamblin J. 1993. Estimation of heritability from varietals trials
data. TAG 86: 437-441.
Singh RK, Chaudhary RD. 1979. Biometrical Methods in Quantitative Genetic Analysis. New Delhi: Kalyani Press.
Siregar H. 1981. Budidaya Tanaman Padi. Jakarta: Sastra Hudaya.
Sivaguru M, Fujiwara T, Samaj J, Baluska F, Yang Z, Osawa H, Maeda T, Mori T, Volkmann D, Matsumoto H. 2000. Aluminum-induced 1? 3-ß-D-glucan inhibits cell-to-cell trafficking of molecules through plasmodesma. A new mechanism of aluminum toxicity in plants. Plant Physiol 124: 991-1005.
Sivaguru M, Paliwal K. 1993. Differential aluminum tolerance in some tropical rice cultivars II. Mechanism of aluminum tolerance. J Plant Nutr 16: 1717-1732.
Snape JW. 1989. Double haploid breeding: Theoretical basis and practical applications. Di dalam Mujeeb-Kazi A dan Stich LA, editor. Review of Advances in Plant Biotechnology 1985-1988. Manila, Philippines: International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center/ International Rice Research Institute. hlm 19-30.
Spehar CR, Sauza LAC. 2006. Selection for aluminum tolerance in tropical soybeans, Pesquisa Agropecuária Tropical 36: 1-6.
Sudir, Suprihanto, Guswara A, Toha, HM. 2002. Pengaruh genotipe, pupuk dan fungisida terhadap penyakit blas leher pada padi gogo. Penelitian Pertanian Tanaman Pangan 21:39-42.
Sulaeman, Supato, Eviati. 2005. Analisis Kimia Tanah, Tanaman, Air dan Pupuk. Bogor: Balai Penelitian Tanah.
Sutaryo B, Purwantoro A, Nasrullah. 2005. Seleksi beberapa kombinasi persilangan padi untuk ketahanan terhadap keracunan aluminium. Ilmu Pertanian 12: 20-31.
Syakhril 1997. Evaluasi reaksi galur-galur padi gogo terhadap Al dan kekurangan nitrogen. [tesis] . Bogor: Program Pascasarjana, Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Tabuchi A, Matsumoto H. 2001. Change in cell-wall properties of wheat (Triticum aestivum) roots during aluminum-induced growth inhibition. Plant Physiol 112: 353-358
Takahashi, E. 1997. Uptake mode and physiological functions of silica. Dalam: Tanane M, Yuzo M, Fumio K, Hikoyuki Y, editor. Science of Rice Plant. Physiology. Volume 2. Tokyo: Food and Agriculture Policy Research Center. hlm: 420-433.
Tan K, Keltjens WG, Findenegg GR. 1993. Aluminum toxicity with sorghum genotypes in nutrient solution and its amelioration by magnesium. J Plant Nutr 155:81-86.
Tasfaye M, Temple SJ, Allan DL, Vance CP, Samac DA. 2001. Over expression of malate dehydrogenase in transgenic alfalfa enhances organic acid synthesis and confers tolerance to aluminum. Plant Physiol 127: 1836-1844.
Taylor GJ, McDonald-Stephens JL, Hunter DB, Bertsch PMN, Elmore D, Rengel Z, Reid RJ. 2000. Direct measurement of aluminum uptake and distribution in single cell of Chara corallina. Plant Physiol 123: 987-996.
Toda T, Koyana H, Hori T, Hara T. 1999. Aluminum tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana under hydroponics and soil culture conditions. Soil Sci Plant Nutr 45:419-425. Trikoesoemaningtyas. 2002. Fisiologi dan pewarisan sifat efisiensi kalium dalam keadaan
tercekam Aluminium pada padi gogo (Oryza sativa L.). [disertasi]. Bogor: Program Pascasarjana, Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Ud-Din N, Caever BF, Clutter AC. 1992. Genetic analysis and selection for wheat yield in drought-stressed and irrigated environment. Euphytica 62: 89-96.
Utami DW, Amir M, Moeljopawiro S. 2000. Analisis RFLP kelompok ras dan haplotipe isolat blas dengan DNA pelacak MGR 586. J Biotek Pertanian 5: 28-33.
van der Plank JE. 1963. Plant Disease: Epidemics and Control. New York: Academic Press.
Villagarcia MR, Carter TE, Rufty TW, Niewoehner AS, Jennette MW, Arrellano C. 2001. 2001. Genotypic rankings for aluminum tolerance of soybean roots grown in hydroponics and sand culture. Crop Sci. 41: 1499-1507.
Vitorello VA, Capaldi FR, Stefanuto VA. 2005. Recent advances in aluminum toxicity and resistance in higher plants. Braz J Plant Physiol 17: 129-143.
Wang Y, Stass A, Horst WJ. 2004. Apoplastic binding of aluminum is involved in silicon-induced amelioration of aluminum toxicity in maize. Plant Physiol 136: 3762-3770. Wang Z, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM. 1989. Inheritance of partial resistance to blast in indica
rice cultivars. Crop Sci 29:848-853.
Watanabe T, Okada K. 2005a. Physiological mechanisms of aluminum resistance of rice varieties and the development of rapid screening method for resistant genotypes. Di dalam. JIRCAS, Research Highlights 2003. Tsukuba, Ibaraki: Japan International Research Center for Agricultural Sciences. hlm 28-29.
Watanabe T, Okada K. 2005b. Interactive effects of Al, Ca and others cations on root elongation of rice cultivars under low pH. Ann Bot 95: 379-385.
Watanabe T, Osaki M, Yoshihara T, Todano T. 1998. Distribution and chemical speciation of aluminum in the Al accumulator plant, Melastoma malabatricum L. Plant Soil 201: 165-173..
Watanabe T, Osaki M, Yano H, Rao I. 2006. Internal mechanisms of plant adaptation to aluminum toxicity and phosphorus starvation in three tropical forages J Plant Nutr 29: 1243-1255.
Wenzel G, Graner A, Fadel F, Zitzlsperger J, Wehr BF. 1992. Production and use of haploids in crop improvement. Di dalam Moss JP, editor. Biotechnology and Crop Improvement in Asia. India: International Crop Research Institute for Semi -Arid Tropics. hlm 169-179.
Wu P, Liao CY, Hu B, Yi KK, Jin WZ, Ni JJ, He C. 2000. QTL and epistasis for aluminum tolerances in rice (Oryza sativa L.) at different seedling stages. TAG 100: 1295-1303.
Wu P, Zhao B, Yan J, Lou a, Wu Y, Senadihra D. 1997. Genetic control of seedling tolerance to aluminum toxicity in rice. Euphytica 97: 289-293.
Yamamoto Y, Kobayashi Y, Devi SR, Rikiishi S, Matsumoto H. 2003. Oxidative stress triggered by aluminum in plant roots. Plant Soil 255:239-243.
Yang Q, Wang Y, Zhang J,Shi W,Qian C, Peng X. 2007. Identification of alumi num-responsive proteins in rice roots by a proteomic approach: Cysteine synthase as a key player in Al response. Proteomics 7: 737-749.
Yeh WH, Bonman JM. 1986. Assessment of partial resistance to Pyricularia oryzae in six rice cultivars. Plant Pathol 35:319-323.
Yoshida S, Nevasero SA, Ramirez EA. 1969. Effects of silica and nitrogen supply on some leaf characters of the rice plant. Plant Soil 31: 49-56.
Yoshida S. Forno DA, Cock JH, Gomez KA. 1976. Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice. Los Banos, Philippines: IRRI.
Zen S. 1995. Heritabilitas, korelasi genotipik dan fenotipik karakter padi gogo. Zuriat 6: 25-31.
Zhang ZH. 1989. The practicability of anther culture breeding in rice. Dalam Mujeeb-Kazi dan Stich LA, editor. Review of Advances in Plant Biotechnology 1985-1988. Manila, Philippines: International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center/ International Rice Research Institute. hlm: 31-42.
Zheng SJ, Yang Jl, He YF, Yu XH, Zhang L, You JF, Shen RF, Matsumoto H. 2005. Immobilization of aluminum with phosphorus in roots is associated with high aluminum resistance in buckwheat. Plant Physiol 138: 297-303.
Zhu YY, Fang H, Wang YY, Fan JX, Yangg SS, Mew TW, Mundt CC. 2005. Panicle blast and canopy moisture in rice cultivar mixtures. Phytopathology 95: 433-438.
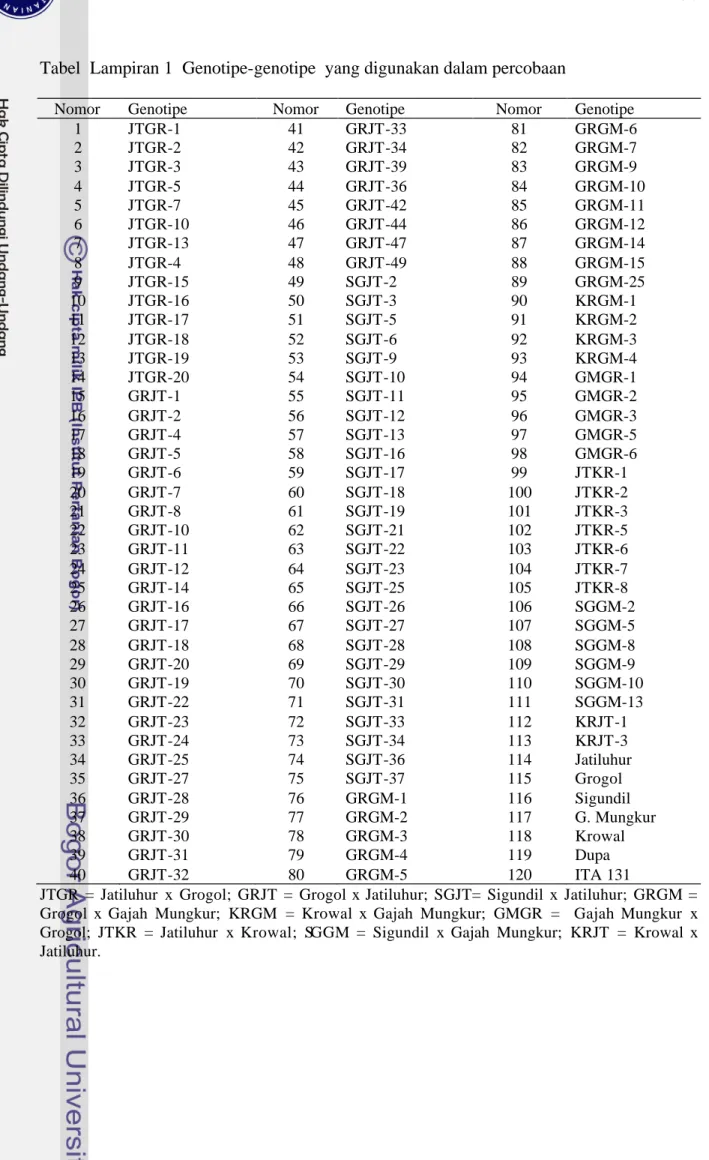
Tabel Lampiran 1 Genotipe-genotipe yang digunakan dalam percobaan
Nomor Genotipe Nomor Genotipe Nomor Genotipe
1 JTGR-1 41 GRJT-33 81 GRGM-6 2 JTGR-2 42 GRJT-34 82 GRGM-7 3 JTGR-3 43 GRJT-39 83 GRGM-9 4 JTGR-5 44 GRJT-36 84 GRGM-10 5 JTGR-7 45 GRJT-42 85 GRGM-11 6 JTGR-10 46 GRJT-44 86 GRGM-12 7 JTGR-13 47 GRJT-47 87 GRGM-14 8 JTGR-4 48 GRJT-49 88 GRGM-15 9 JTGR-15 49 SGJT-2 89 GRGM-25 10 JTGR-16 50 SGJT-3 90 KRGM-1 11 JTGR-17 51 SGJT-5 91 KRGM-2 12 JTGR-18 52 SGJT-6 92 KRGM-3 13 JTGR-19 53 SGJT-9 93 KRGM-4 14 JTGR-20 54 SGJT-10 94 GMGR-1 15 GRJT-1 55 SGJT-11 95 GMGR-2 16 GRJT-2 56 SGJT-12 96 GMGR-3 17 GRJT-4 57 SGJT-13 97 GMGR-5 18 GRJT-5 58 SGJT-16 98 GMGR-6 19 GRJT-6 59 SGJT-17 99 JTKR-1 20 GRJT-7 60 SGJT-18 100 JTKR-2 21 GRJT-8 61 SGJT-19 101 JTKR-3 22 GRJT-10 62 SGJT-21 102 JTKR-5 23 GRJT-11 63 SGJT-22 103 JTKR-6 24 GRJT-12 64 SGJT-23 104 JTKR-7 25 GRJT-14 65 SGJT-25 105 JTKR-8 26 GRJT-16 66 SGJT-26 106 SGGM-2 27 GRJT-17 67 SGJT-27 107 SGGM-5 28 GRJT-18 68 SGJT-28 108 SGGM-8 29 GRJT-20 69 SGJT-29 109 SGGM-9 30 GRJT-19 70 SGJT-30 110 SGGM-10 31 GRJT-22 71 SGJT-31 111 SGGM-13 32 GRJT-23 72 SGJT-33 112 KRJT-1 33 GRJT-24 73 SGJT-34 113 KRJT-3 34 GRJT-25 74 SGJT-36 114 Jatiluhur 35 GRJT-27 75 SGJT-37 115 Grogol 36 GRJT-28 76 GRGM-1 116 Sigundil 37 GRJT-29 77 GRGM-2 117 G. Mungkur 38 GRJT-30 78 GRGM-3 118 Krowal 39 GRJT-31 79 GRGM-4 119 Dupa 40 GRJT-32 80 GRGM-5 120 ITA 131
JTGR = Jatiluhur x Grogol; GRJT = Grogol x Jatiluhur; SGJT= Sigundil x Jatiluhur; GRGM = Grogol x Gajah Mungkur; KRGM = Krowal x Gajah Mungkur; GMGR = Gajah Mungkur x Grogol; JTKR = Jatiluhur x Krowal; SGGM = Sigundil x Gajah Mungkur; KRJT = Krowal x Jatiluhur.
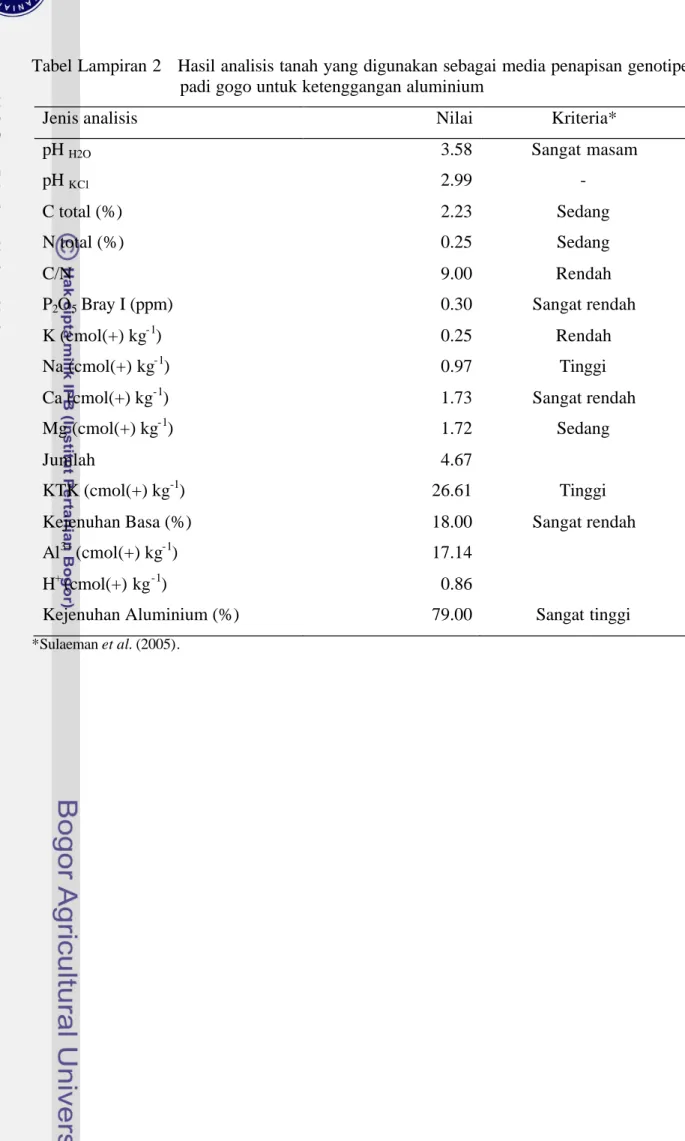
Tabel Lampiran 2 Hasil analisis tanah yang digunakan sebagai media penapisan genotipe padi gogo untuk ketenggangan aluminium
Jenis analisis Nilai Kriteria*
pH H2O 3.58 Sangat masam
pH KCl 2.99 -
C total (%) 2.23 Sedang
N total (%) 0.25 Sedang
C/N 9.00 Rendah
P2O5 Bray I (ppm) 0.30 Sangat rendah
K (cmol(+) kg-1) 0.25 Rendah
Na (cmol(+) kg-1) 0.97 Tinggi
Ca (cmol(+) kg-1) 1.73 Sangat rendah
Mg (cmol(+) kg-1) 1.72 Sedang
Jumlah 4.67
KTK (cmol(+) kg-1) 26.61 Tinggi
Kejenuhan Basa (%) 18.00 Sangat rendah
Al3+ (cmol(+) kg-1) 17.14
H+ (cmol(+) kg-1) 0.86
Kejenuhan Aluminium (%) 79.00 Sangat tinggi
Tabel Lampiran 3 Skala ketahanan tanaman terhadap blas berdasarkan bercak pada daun
Skala Adanya bercak pada daun
0 Tidak ada bercak
1 Bercak sebesar ujung jarum (0,5%) dan berwarna coklat, tanpa ada pusat sporulasi
2 Bercak nekrotik keabu-abuan, bundar sampai sedikit memanjang berdiameter sekitar 1-2 mm, dengan pinggir berwarna coklat. lebih besar dari ujung jarum. Becak umumnya dijumpai pada bagian bawah daun (luas daun terserang 1%)
3 Tipe bercak sama seperti pada skala 2, tetapi jumlah bercak nyata lebih banyak pada bagian atas daun (luas daun terserang 2%).
4 Bercak tipe rentan, khas blas (belah ketupat dengan pusat abu-abu), panjang 3 mm atau lebih panjang, menginfeksi kurang dari 4% luas daun 5 Bercak tipe rentan, khas blas (belah ketupat dengan pusat abu-abu),
menginfeksi 4 -10 % luas daun.
6 Bercak tipe rentan, khas blas (belah ketupat dengan pusat abu-abu), menginfeksi 11-25 % luas daun.
7 Bercak tipe rentan, khas blas (belah ketupat dengan pusat abu-abu), menginfeksi 26-50 % luas daun.
8 Bercak tipe rentan, khas blas (belah ketupat) dengan pusat abu-abu, menginfeksi 51-75 % luas daun dan beberapa daun mulai mati.
9 Menginfeksi lebih dari 75 % luas daun.
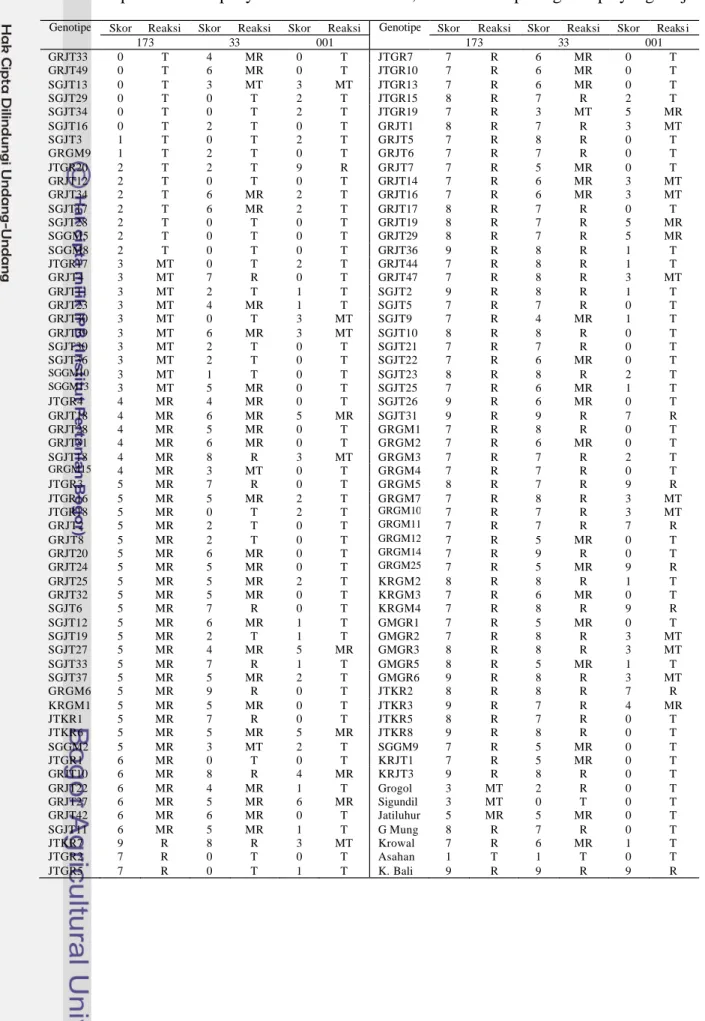
Tabel Lampiran 4 Skala penyakit blas daun ras 173, 033 dan 001 pada genotipe yang diuji Genotipe Skor Reaksi Skor Reaksi Skor Reaksi Genotipe Skor Reaksi Skor Reaksi Skor Reaksi
173 33 001 173 33 001 GRJT33 0 T 4 MR 0 T JTGR7 7 R 6 MR 0 T GRJT49 0 T 6 MR 0 T JTGR10 7 R 6 MR 0 T SGJT13 0 T 3 MT 3 MT JTGR13 7 R 6 MR 0 T SGJT29 0 T 0 T 2 T JTGR15 8 R 7 R 2 T SGJT34 0 T 0 T 2 T JTGR19 7 R 3 MT 5 MR SGJT16 0 T 2 T 0 T GRJT1 8 R 7 R 3 MT SGJT3 1 T 0 T 2 T GRJT5 7 R 8 R 0 T GRGM9 1 T 2 T 0 T GRJT6 7 R 7 R 0 T JTGR20 2 T 2 T 9 R GRJT7 7 R 5 MR 0 T GRJT12 2 T 0 T 0 T GRJT14 7 R 6 MR 3 MT GRJT34 2 T 6 MR 2 T GRJT16 7 R 6 MR 3 MT SGJT17 2 T 6 MR 2 T GRJT17 8 R 7 R 0 T SGJT28 2 T 0 T 0 T GRJT19 8 R 7 R 5 MR SGGM5 2 T 0 T 0 T GRJT29 8 R 7 R 5 MR SGGM8 2 T 0 T 0 T GRJT36 9 R 8 R 1 T JTGR17 3 MT 0 T 2 T GRJT44 7 R 8 R 1 T GRJT4 3 MT 7 R 0 T GRJT47 7 R 8 R 3 MT GRJT11 3 MT 2 T 1 T SGJT2 9 R 8 R 1 T GRJT23 3 MT 4 MR 1 T SGJT5 7 R 7 R 0 T GRJT30 3 MT 0 T 3 MT SGJT9 7 R 4 MR 1 T GRJT39 3 MT 6 MR 3 MT SGJT10 8 R 8 R 0 T SGJT30 3 MT 2 T 0 T SGJT21 7 R 7 R 0 T SGJT36 3 MT 2 T 0 T SGJT22 7 R 6 MR 0 T SGGM10 3 MT 1 T 0 T SGJT23 8 R 8 R 2 T SGGM13 3 MT 5 MR 0 T SGJT25 7 R 6 MR 1 T JTGR4 4 MR 4 MR 0 T SGJT26 9 R 6 MR 0 T GRJT18 4 MR 6 MR 5 MR SGJT31 9 R 9 R 7 R GRJT28 4 MR 5 MR 0 T GRGM1 7 R 8 R 0 T GRJT31 4 MR 6 MR 0 T GRGM2 7 R 6 MR 0 T SGJT18 4 MR 8 R 3 MT GRGM3 7 R 7 R 2 T GRGM15 4 MR 3 MT 0 T GRGM4 7 R 7 R 0 T JTGR3 5 MR 7 R 0 T GRGM5 8 R 7 R 9 R JTGR16 5 MR 5 MR 2 T GRGM7 7 R 8 R 3 MT JTGR18 5 MR 0 T 2 T GRGM10 7 R 7 R 3 MT GRJT2 5 MR 2 T 0 T GRGM11 7 R 7 R 7 R GRJT8 5 MR 2 T 0 T GRGM12 7 R 5 MR 0 T GRJT20 5 MR 6 MR 0 T GRGM14 7 R 9 R 0 T GRJT24 5 MR 5 MR 0 T GRGM25 7 R 5 MR 9 R GRJT25 5 MR 5 MR 2 T KRGM2 8 R 8 R 1 T GRJT32 5 MR 5 MR 0 T KRGM3 7 R 6 MR 0 T SGJT6 5 MR 7 R 0 T KRGM4 7 R 8 R 9 R SGJT12 5 MR 6 MR 1 T GMGR1 7 R 5 MR 0 T SGJT19 5 MR 2 T 1 T GMGR2 7 R 8 R 3 MT SGJT27 5 MR 4 MR 5 MR GMGR3 8 R 8 R 3 MT SGJT33 5 MR 7 R 1 T GMGR5 8 R 5 MR 1 T SGJT37 5 MR 5 MR 2 T GMGR6 9 R 8 R 3 MT GRGM6 5 MR 9 R 0 T JTKR2 8 R 8 R 7 R KRGM1 5 MR 5 MR 0 T JTKR3 9 R 7 R 4 MR JTKR1 5 MR 7 R 0 T JTKR5 8 R 7 R 0 T JTKR6 5 MR 5 MR 5 MR JTKR8 9 R 8 R 0 T SGGM2 5 MR 3 MT 2 T SGGM9 7 R 5 MR 0 T JTGR1 6 MR 0 T 0 T KRJT1 7 R 5 MR 0 T GRJT10 6 MR 8 R 4 MR KRJT3 9 R 8 R 0 T GRJT22 6 MR 4 MR 1 T Grogol 3 MT 2 R 0 T GRJT27 6 MR 5 MR 6 MR Sigundil 3 MT 0 T 0 T GRJT42 6 MR 6 MR 0 T Jatiluhur 5 MR 5 MR 0 T SGJT11 6 MR 5 MR 1 T G Mung 8 R 7 R 0 T JTKR7 9 R 8 R 3 MT Krowal 7 R 6 MR 1 T JTGR2 7 R 0 T 0 T Asahan 1 T 1 T 0 T JTGR5 7 R 0 T 1 T K. Bali 9 R 9 R 9 R
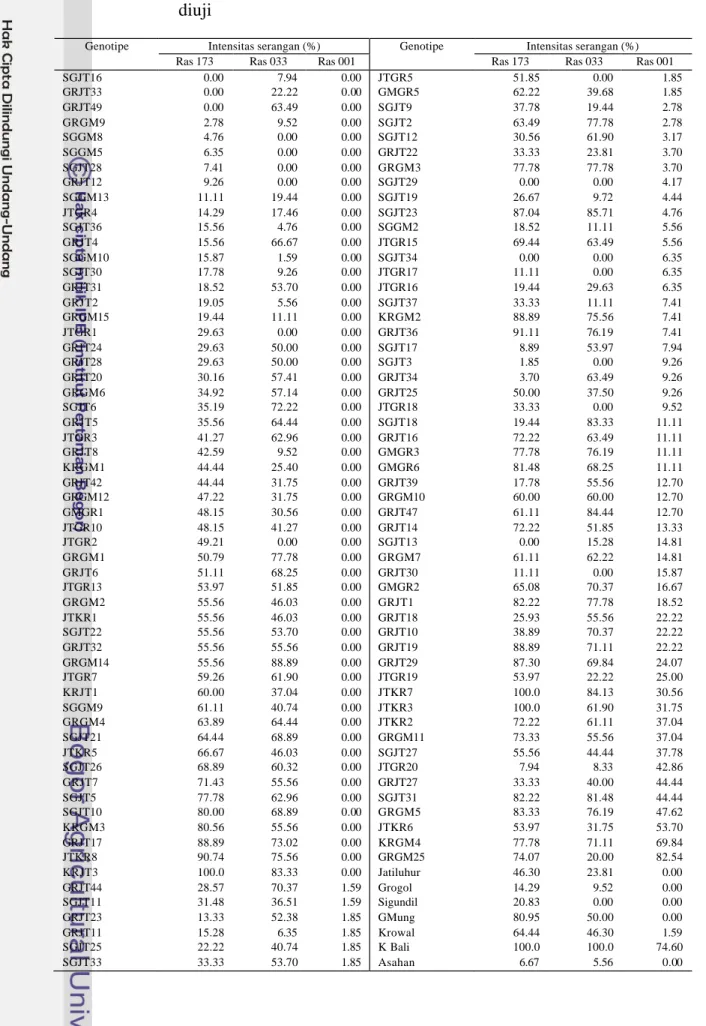
Tabel Lampiran 5 Intensitas serangan blas daun ras 173, 033 dan 001 pada genotipe yang diuji
Genotipe Intensitas serangan (%) Genotipe Intensitas serangan (%) Ras 173 Ras 033 Ras 001 Ras 173 Ras 033 Ras 001
SGJT16 0.00 7.94 0.00 JTGR5 51.85 0.00 1.85 GRJT33 0.00 22.22 0.00 GMGR5 62.22 39.68 1.85 GRJT49 0.00 63.49 0.00 SGJT9 37.78 19.44 2.78 GRGM9 2.78 9.52 0.00 SGJT2 63.49 77.78 2.78 SGGM8 4.76 0.00 0.00 SGJT12 30.56 61.90 3.17 SGGM5 6.35 0.00 0.00 GRJT22 33.33 23.81 3.70 SGJT28 7.41 0.00 0.00 GRGM3 77.78 77.78 3.70 GRJT12 9.26 0.00 0.00 SGJT29 0.00 0.00 4.17 SGGM13 11.11 19.44 0.00 SGJT19 26.67 9.72 4.44 JTGR4 14.29 17.46 0.00 SGJT23 87.04 85.71 4.76 SGJT36 15.56 4.76 0.00 SGGM2 18.52 11.11 5.56 GRJT4 15.56 66.67 0.00 JTGR15 69.44 63.49 5.56 SGGM10 15.87 1.59 0.00 SGJT34 0.00 0.00 6.35 SGJT30 17.78 9.26 0.00 JTGR17 11.11 0.00 6.35 GRJT31 18.52 53.70 0.00 JTGR16 19.44 29.63 6.35 GRJT2 19.05 5.56 0.00 SGJT37 33.33 11.11 7.41 GRGM15 19.44 11.11 0.00 KRGM2 88.89 75.56 7.41 JTGR1 29.63 0.00 0.00 GRJT36 91.11 76.19 7.41 GRJT24 29.63 50.00 0.00 SGJT17 8.89 53.97 7.94 GRJT28 29.63 50.00 0.00 SGJT3 1.85 0.00 9.26 GRJT20 30.16 57.41 0.00 GRJT34 3.70 63.49 9.26 GRGM6 34.92 57.14 0.00 GRJT25 50.00 37.50 9.26 SGJT6 35.19 72.22 0.00 JTGR18 33.33 0.00 9.52 GRJT5 35.56 64.44 0.00 SGJT18 19.44 83.33 11.11 JTGR3 41.27 62.96 0.00 GRJT16 72.22 63.49 11.11 GRJT8 42.59 9.52 0.00 GMGR3 77.78 76.19 11.11 KRGM1 44.44 25.40 0.00 GMGR6 81.48 68.25 11.11 GRJT42 44.44 31.75 0.00 GRJT39 17.78 55.56 12.70 GRGM12 47.22 31.75 0.00 GRGM10 60.00 60.00 12.70 GMGR1 48.15 30.56 0.00 GRJT47 61.11 84.44 12.70 JTGR10 48.15 41.27 0.00 GRJT14 72.22 51.85 13.33 JTGR2 49.21 0.00 0.00 SGJT13 0.00 15.28 14.81 GRGM1 50.79 77.78 0.00 GRGM7 61.11 62.22 14.81 GRJT6 51.11 68.25 0.00 GRJT30 11.11 0.00 15.87 JTGR13 53.97 51.85 0.00 GMGR2 65.08 70.37 16.67 GRGM2 55.56 46.03 0.00 GRJT1 82.22 77.78 18.52 JTKR1 55.56 46.03 0.00 GRJT18 25.93 55.56 22.22 SGJT22 55.56 53.70 0.00 GRJT10 38.89 70.37 22.22 GRJT32 55.56 55.56 0.00 GRJT19 88.89 71.11 22.22 GRGM14 55.56 88.89 0.00 GRJT29 87.30 69.84 24.07 JTGR7 59.26 61.90 0.00 JTGR19 53.97 22.22 25.00 KRJT1 60.00 37.04 0.00 JTKR7 100.0 84.13 30.56 SGGM9 61.11 40.74 0.00 JTKR3 100.0 61.90 31.75 GRGM4 63.89 64.44 0.00 JTKR2 72.22 61.11 37.04 SGJT21 64.44 68.89 0.00 GRGM11 73.33 55.56 37.04 JTKR5 66.67 46.03 0.00 SGJT27 55.56 44.44 37.78 SGJT26 68.89 60.32 0.00 JTGR20 7.94 8.33 42.86 GRJT7 71.43 55.56 0.00 GRJT27 33.33 40.00 44.44 SGJT5 77.78 62.96 0.00 SGJT31 82.22 81.48 44.44 SGJT10 80.00 68.89 0.00 GRGM5 83.33 76.19 47.62 KRGM3 80.56 55.56 0.00 JTKR6 53.97 31.75 53.70 GRJT17 88.89 73.02 0.00 KRGM4 77.78 71.11 69.84 JTKR8 90.74 75.56 0.00 GRGM25 74.07 20.00 82.54 KRJT3 100.0 83.33 0.00 Jatiluhur 46.30 23.81 0.00 GRJT44 28.57 70.37 1.59 Grogol 14.29 9.52 0.00 SGJT11 31.48 36.51 1.59 Sigundil 20.83 0.00 0.00 GRJT23 13.33 52.38 1.85 GMung 80.95 50.00 0.00 GRJT11 15.28 6.35 1.85 Krowal 64.44 46.30 1.59 SGJT25 22.22 40.74 1.85 K Bali 100.0 100.0 74.60 SGJT33 33.33 53.70 1.85 Asahan 6.67 5.56 0.00
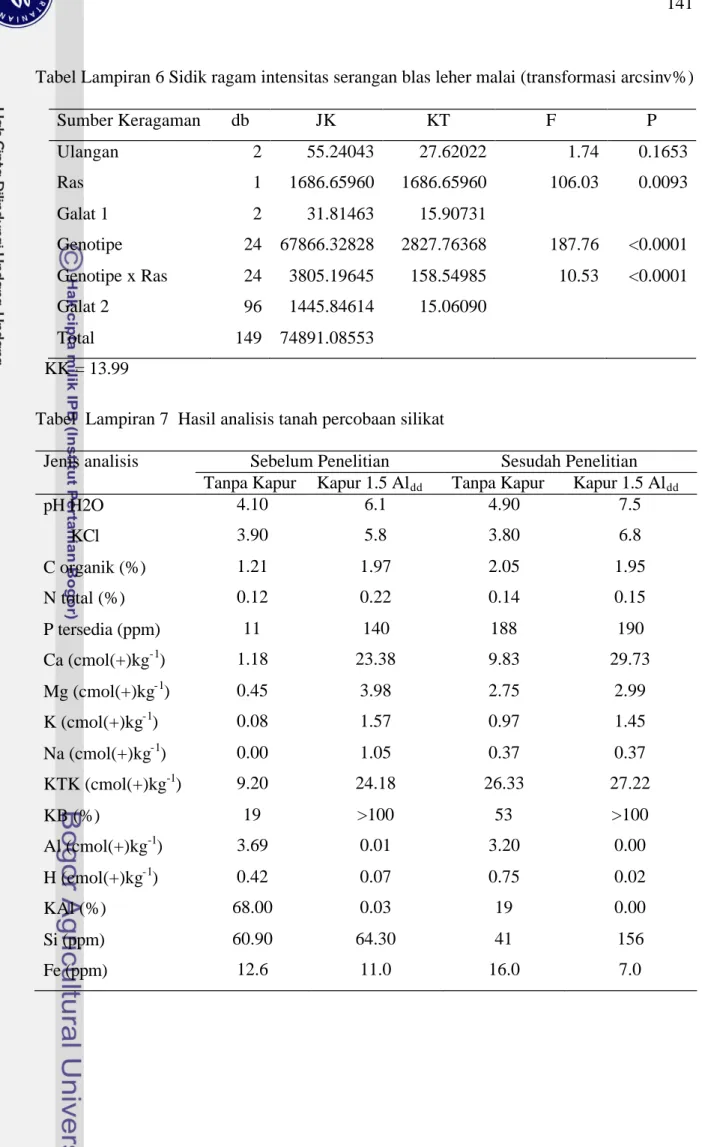
Tabel Lampiran 6 Sidik ragam intensitas serangan blas leher malai (transformasi arcsinv%) Sumber Keragaman db JK KT F P Ulangan 2 55.24043 27.62022 1.74 0.1653 Ras 1 1686.65960 1686.65960 106.03 0.0093 Galat 1 2 31.81463 15.90731 Genotipe 24 67866.32828 2827.76368 187.76 <0.0001 Genotipe x Ras 24 3805.19645 158.54985 10.53 <0.0001 Galat 2 96 1445.84614 15.06090 Total 149 74891.08553 KK = 13.99
Tabel Lampiran 7 Hasil analisis tanah percobaan silikat
Jenis analisis Sebelum Penelitian Sesudah Penelitian Tanpa Kapur Kapur 1.5 Aldd Tanpa Kapur Kapur 1.5 Aldd
pH H2O 4.10 6.1 4.90 7.5 KCl 3.90 5.8 3.80 6.8 C organik (%) 1.21 1.97 2.05 1.95 N total (%) 0.12 0.22 0.14 0.15 P tersedia (ppm) 11 140 188 190 Ca (cmol(+)kg-1) 1.18 23.38 9.83 29.73 Mg (cmol(+)kg-1) 0.45 3.98 2.75 2.99 K (cmol(+)kg-1) 0.08 1.57 0.97 1.45 Na (cmol(+)kg-1) 0.00 1.05 0.37 0.37 KTK (cmol(+)kg-1) 9.20 24.18 26.33 27.22 KB (%) 19 >100 53 >100 Al (cmol(+)kg-1) 3.69 0.01 3.20 0.00 H (cmol(+)kg-1) 0.42 0.07 0.75 0.02 KAl (%) 68.00 0.03 19 0.00 Si (ppm) 60.90 64.30 41 156 Fe (ppm) 12.6 11.0 16.0 7.0
Tabel Lampiran 8 Hasil analisis tanah untuk pengujian ketengangan Al lapangan Jasinga
Jenis analisis Nilai Kriteria*
pH H2O 4.10 Sangat masam
pH KCl 3.90
C organik (%) 1.21 Rendah
N total (%) 0.12 Rendah
P tersedia (ppm) 11 Sedang
Ca (cmol(+)kg-1) 1.18 Sangat rendah
Mg (cmol(+)kg-1) 0.45 Rendah
K (cmol(+)kg-1) 0.08 Sangat rendah
Na (cmol(+)kg-1) 0.00 Sangat rendah
KTK (cmol(+)kg-1) 9.20 Rendah
KB (%) 19 Sangat rendah
Al (cmol(+)kg-1) 3.69
H (cmol(+)kg-1) 0.42
KAl (%) 68.00 Sangat tinggi
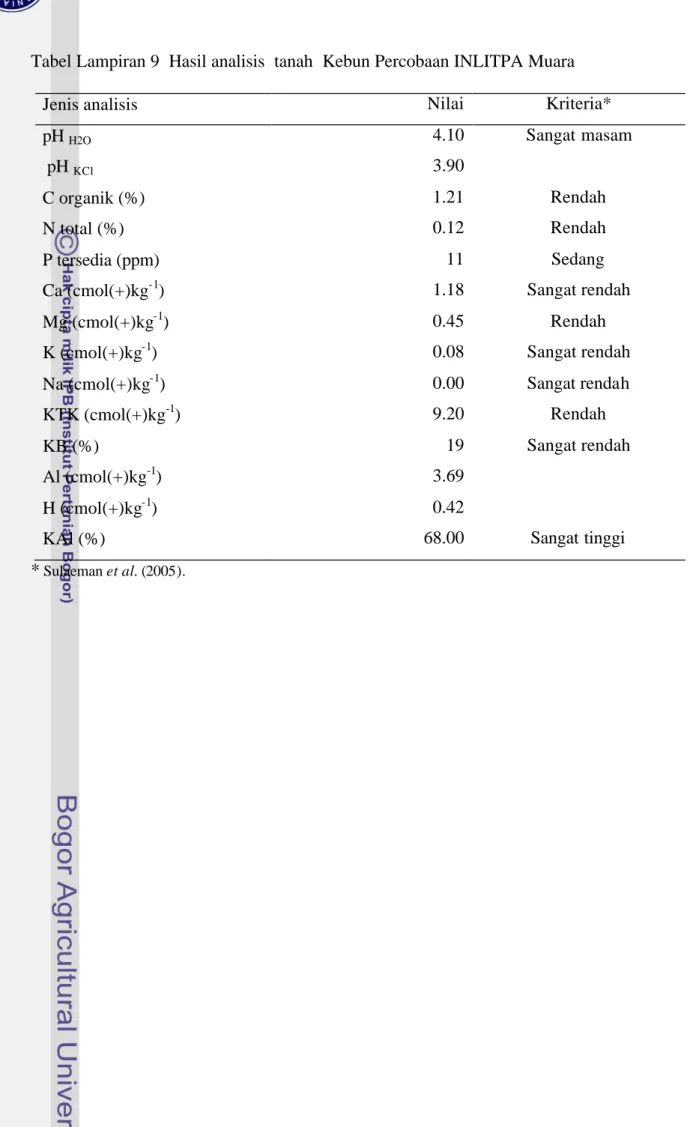
Tabel Lampiran 9 Hasil analisis tanah Kebun Percobaan INLITPA Muara
Jenis analisis Nilai Kriteria*
pH H2O 4.10 Sangat masam
pH KCl 3.90
C organik (%) 1.21 Rendah
N total (%) 0.12 Rendah
P tersedia (ppm) 11 Sedang
Ca (cmol(+)kg-1) 1.18 Sangat rendah
Mg (cmol(+)kg-1) 0.45 Rendah
K (cmol(+)kg-1) 0.08 Sangat rendah
Na (cmol(+)kg-1) 0.00 Sangat rendah
KTK (cmol(+)kg-1) 9.20 Rendah
KB (%) 19 Sangat rendah
Al (cmol(+)kg-1) 3.69
H (cmol(+)kg-1) 0.42
KAl (%) 68.00 Sangat tinggi
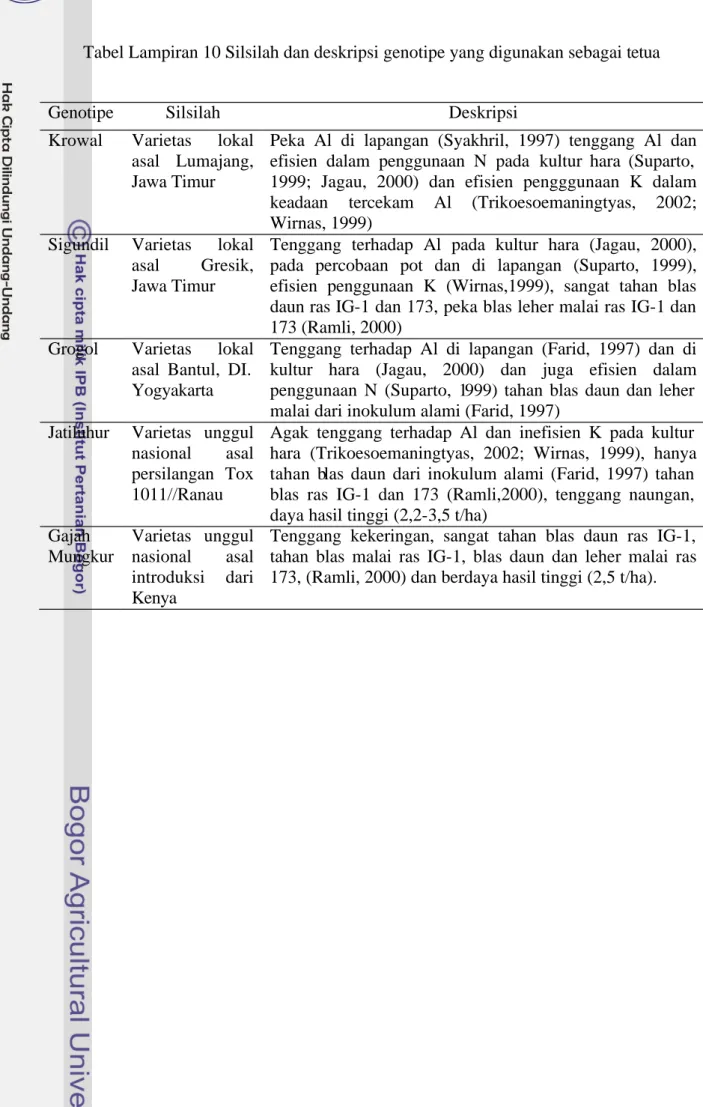
Tabel Lampiran 10 Silsilah dan deskripsi genotipe yang digunakan sebagai tetua
Genotipe Silsilah Deskripsi
Krowal Varietas lokal asal Lumajang, Jawa Timur
Peka Al di lapangan (Syakhril, 1997) tenggang Al dan efisien dalam penggunaan N pada kultur hara (Suparto, 1999; Jagau, 2000) dan efisien pengggunaan K dalam keadaan tercekam Al (Trikoesoemaningtyas, 2002; Wirnas, 1999)
Sigundil Varietas lokal asal Gresik, Jawa Timur
Tenggang terhadap Al pada kultur hara (Jagau, 2000), pada percobaan pot dan di lapangan (Suparto, 1999), efisien penggunaan K (Wirnas,1999), sangat tahan blas daun ras IG-1 dan 173, peka blas leher malai ras IG-1 dan 173 (Ramli, 2000)
Grogol Varietas lokal asal Bantul, DI. Yogyakarta
Tenggang terhadap Al di lapangan (Farid, 1997) dan di kultur hara (Jagau, 2000) dan juga efisien dalam penggunaan N (Suparto, 1999) tahan blas daun dan leher malai dari inokulum alami (Farid, 1997)
Jatiluhur Varietas unggul nasional asal persilangan Tox 1011//Ranau
Agak tenggang terhadap Al dan inefisien K pada kultur hara (Trikoesoemaningtyas, 2002; Wirnas, 1999), hanya tahan blas daun dari inokulum alami (Farid, 1997) tahan blas ras IG-1 dan 173 (Ramli,2000), tenggang naungan, daya hasil tinggi (2,2-3,5 t/ha)
Gajah Mungkur Varietas unggul nasional asal introduksi dari Kenya
Tenggang kekeringan, sangat tahan blas daun ras IG-1, tahan blas malai ras IG-1, blas daun dan leher malai ras 173, (Ramli, 2000) dan berdaya hasil tinggi (2,5 t/ha).
Tabel Lampiran 11 Deskripsi varietas Gajah Mungkur
Identitas/Karakter Keterangan
Nomor : IRAT 112
Asal : Introduksi dari Kenya
Golongan : Cere, kadang-kadang berbulu
Umur : 90-95
Bentuk tanaman : Tegak
Tinggi tanaman : 90-100 cm
Anakan produktif : Sedang (6-8 batang)
Warna kaki : Hijau tua
Warna batang : Hijau tua
Warna telinga daun : Hijau
Warna lidah daun : Tidak berwarna
Warna daun : Hijau
Muka daun : Licin
Posisi daun : Tegak sampai miring
Daun bendera : Tegak
Bentuk gabah : Medium
Warna gabah : Kuning keemasan
Kerontokan : Agak tahan
Kerebahan : Sedang
Tekstur nasi
Kadar amilosa : 23,20%
Bobot 1000 butir : 36 g
Potensi hasil : 2,5 ton/ha gabah kering
Ketahanan/toleransi : Tahan blas dan cukup toleran terhadap kekeringan Penciri : Muka daun licin, warna gabah kuning keemasan
Baik ditanam sebagai padi gogo di daerah beriklim kering
Pemulia : Z. Harahap, Erwina Lubis, Murdani Diredja
Tahun dilepaskan : 1994
Tabel Lampiran 12 Deskripsi varietas Jatiluhur
Identitas/Karakter Keterangan
Nomor : --
Asal : Persilangan Tox 1011/Ranau
Golongan : Cere (Indica)
Umur : 110 - 115 hari
Bentuk tanaman : Tegak
Tinggi tanaman : 95-100 cm
Anakan produktif : Sedang (6-8 batang)
Warna kaki : Ungu
Warna batang : Bergaris ungu
Warna telinga daun : Tidak berwarna Warna lidah daun : Tidak berwarna
Warna daun : Hijau tua
Muka daun : Kasar
Posisi daun : Tegak sampai miring
Daun bendera : Miring
Bentuk gabah : Bulat besar
Warna gabah : Kuning kotor
Kerontokan : Agak tahan
Kerebahan : Sedang
Tekstur nasi : Pera
Kadar amilosa : 27,60 %
Bobot 1000 butir : 27 g
Potensi hasil : 2,5-3,5 ton/ha gabah kering Ketahanan/toleransi : Tahan blas dan toleran naungan
Penciri : Baik ditanam untuk padi lahan kering (gogo) sampai ketinggian 500 m dpl
Pemulia : Erwina Lubis, Murdani Diredja, Suwarno, Susanto Tw, Hadi S
Tabel Lampiran 13 Deskripsi varietas Asahan
Identitas/Karakter Keterangan
Nomor : --
Asal : Persilangan IR 1561-228-1.IR1737//CR 94-15 Golongan : Cere (Indica), kadang-kadang berbulu
Umur : 115 – 125 hari
Bentuk tanaman : Tegak
Tinggi tanaman : 95-110 cm
Anakan produktif : Sedang (10-15 batang)
Warna kaki : Hijau tua
Warna batang : Hijau tua
Warna telinga daun : Tidak berwarna Warna lidah daun : Tidak berwarna
Warna daun : Hijau tua
Muka daun : Kasar
Posisi daun : Tegak
Daun bendera : Tegak sampai miring
Bentuk gabah : Ramping
Warna gabah : Kuning bersih, ujung gabah sewarna
Kerontokan : Sedang
Kerebahan : Tahan
Rasa nasi : Enak seperti ketan
Kadar amilosa : 16 %
Rendemen gabah-beras : 65,5 %
Potensi hasil : 4,0 - 4,5 ton/ha gabah kering lebih tinggi dari PB26
Ketahanan terhadap hama : Tahan wbc biotipe 1 dan 2, cukup tahan wbc biotipe 3, peka wbc hijau, peka wewreng punggung putih dan ganjur
Ketahanan terhadap penyakit : Tahan terhadap virus kerdil rump ut tungro, HDB, Cercospora, cukup tahan terhadap vierus kerdil hampa dan blas
Penciri : Baik ditanam untuk padi sawah dataran rendah Tahun dilepaskan : 8 Juni 1978