TOPIC 1 INTRODUCTION TO INTERACTIVE
MEDIA
T.J. Iskandar Abd. Aziz
INTRODUCTION
Welcome to topic 1 of the course, CBMI4103 Interactive Media. Before we begin with the topic, do you know what interactive media is? Do you notice that our world is changing, and information and communication technology are among the factors contributing to this change. Rapid development of digital and other technologies in recent years has been focusing on combining and integrating multiple media such as text, character, sound, and image information into interactive media applications that allow greater interaction between a user and the medium.
Digital interactive media have revolutionised the information society. Multi-channel and interactive televisions are no longer the only interactive media easily available to everybody. More and more people can gain access to the Internet, through personal computers, televisions, mobile phones, and now even through games consoles. The choice of services available is greater than ever before. High-speed phone lines and communication infrastructures give households access to a whole new range of media communications services and experiences. Using their TV sets, people are able to email, shop from home, and devise their own personal viewing schedules.
This topic discusses the important terms and concept related to interactive media, the history of traditional print and electronic mass media such as newspaper, radio and television, the convergence of each media into interactive digital media with the birth of personal computing and the advantages and disadvantages of interactive media.
OBJECTIVES
By the end of this topic, you should be able to:
1. identify the terms and concepts of interactive media;
2. define the terms and concept of digital convergence;
3. describe the history of media industry;
4. define the requirements needed for interactive media; and
MIND MAP
1.1 CONCEPTS OF INTERACTIVE MEDIA
Briefly, compare media industry before and after the birth of computer.
What are the factors contributing to the development of digital interactive media?
Before we proceed with the rest of the topic, it is important for us to clearly define the terms and concepts of “media” and “interactive” from different perspectives and adopt the most suitable term as our main point of reference.
According to www.Wikipedia.org (2005):
Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary, 6th ed. (2000) defines media as:
“The main ways that large numbers of people receive information and entertainment, that is television, radio and the newspaper”.
In this context, media is addressed as print and electronic mass media that we encounter in our everyday lives such as newspaper, radio and television.
Mass media is the term used to represent a section of the media specifically conceived and designed to reach a very large audience, typically at least as large as the whole population of a nation state. The term mass media was coined in the 1920s with the advent of nationwide radio networks and of mass-circulation newspapers and magazines.
1.1.1 What is Multimedia?
Another related word is multimedia. Although there are many different definitions to its meaning, generally the word multimedia can be divided into two parts that is “multi” and “media”. “Multi” means many; while “media” refers to the tools used as a channel for communication, like the newspaper, radio, television and the Internet.
According to Halimah Badioze Zaman (1996),
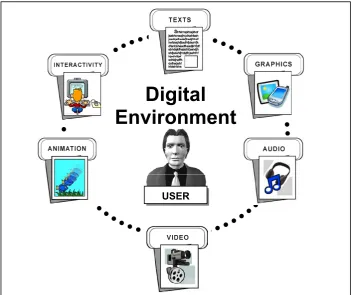
This definition is very relevant to the concept of interactive media where all of the media are integrated seamlessly in a digital environment. These media will be interactive if the user is given power to control whatever elements he or she wants and accesses it non-sequentially (as illustrated in Figure 1.1).
Figure 1.1: Elements of interactive media
“Multimedia can be defined as the integration of multiple media: texts, numeric, graphics, image, video, animation, and audio in a digital environment that offer interactivity to allow a user to access information in a non-linear fashion”
Digital
Environment
Multimedia has been around for a long time. Its origins is far older than computers. Books which include texts and pictures can be considered as multimedia. For example, during the 1970s, some of the universities in the United States of America had already had their so called multimedia system; teaching using text books, study guides, television, radio programmes, cassette tapes and video tapes, all without the involvement of any computer. These media systems was not interactive multimedia, since the interactions were provided by people.
1.1.2 What is Interactive?
The next important term that requires our understanding is interactive. What do we actually mean when we say that a program or a media is interactive?
According to Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary, 6th ed. (2000), interactive can be defined as:
Interactivity, therefore, is the potential of a medium that distinguishes it from earlier media technology innovations such as slides, film, and video. Where interaction formerly was limited to "Off" and "On", interactive media or multimedia may provide a "hook" to help transform users from passive recipients of information to active participants in their own perspective.
The term interactive media or multimedia has taken on different meaning over the past several years. As understood by common people, though not directly expressed, multimedia is an application, product or experience that features multiple media such as text, graphics, sound, video and animation which are displayed on a personal computer to a user. Interactive features and navigational control are among the necessary features to be integrated in an interactive media system.
Users become active participants instead of passive onlookers and they will have control of the event, thus creating an interactive experience for them. Interactive media offers multiple choices or scenarios which sequences or subjects to explore can be chosen by the viewers. The presentation "interacts" with the viewer by responding to these choices.
1.1.3 What Is Interactive Media?
We have discussed the definition of media, multimedia and interactive, let us take a look at the main definition, which is interactive media.
“A system that allows information to be passed continuously and in both directions between a computer and the person who uses it”.
According to Philip Van Allen (1996),
Whereas Graham (1999) defines interactive media as:
Flew (2002) defines interactive media as:
We can conclude from all these definitions that interactive media involves:
x Combining multiple digital media into a convergent product
x Using different types of medium
x Providing users with different level of interactivity or participation
x Customisation of features and interactivity by the users of the system
In order for interactive media to really works, we need to understand what is digital convergence and its relation to interactive media. What do we really expect convergence to offer us in terms of the forward progress of interactive media?
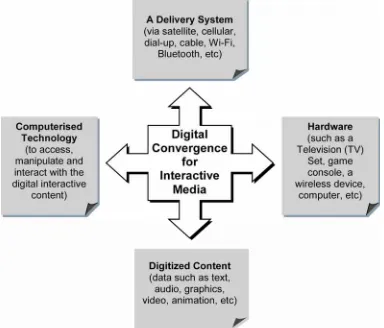
The convergence of media and technology makes possible a variety of new electronic products and services, bussiness opportunities and expanded marketplace for interactive media. In order for convergence to be successful, there are four elements needed, as illustrated in Figure 1.2.
“Interactive media is an integrated presentation of multiple media that requires audience participation.
For the author, it's a digital medium where the author can manipulate media during the presentation, define linkages between media, and have a dialog with the audience.
For the audience it's a nonlinear medium where the audience is an active catalyst in the development of the narrative.
In-between the author and audience is a distributed and dynamic medium, where elements of the presentation can be at different locations on a network, may change over time, and may have different authors.”
"Interactive media involves interactivity with some forms of digital presentation. A combination of different media types may include graphics, animation, video, sound, typography, and virtual reality."
Figure 1.2: Four elements of digital convergence
Out of the four elements of digital convergence, the most important is the content itself. The content must be available in digital form. The merging of technology and media is also known as digital media integration.
Basically, there are three common types of media that can be found in the market nowadays:
x Printed media such as newspapers, magazines, and books.
x Electronic mass media such as radio, television, film, videos, long plays. x Digital media such as digital video, CD-ROMs, DVDs, CDs.
All of these types of media and the related technologies will be discussed in details in the next topic.
1.2 HISTORY OF INTERACTIVE MEDIA
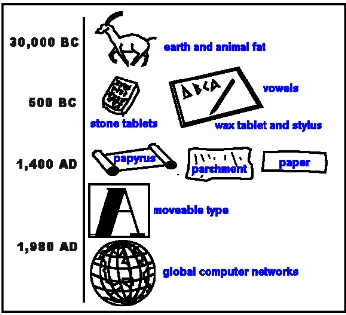
Figure 1.3: Evolusion of media
Source:http://www.december.com/present/mediaev.html
Take a look at Figure 1.3. What can we say about the evolution of media that has taken place for thousands of years? Since the dawn of time, people have had the need to communicate with one another. This created what we called as communication media.
The earliest form of media is through oral and scribal culture. The use of inscriptions, Paleolithic painting on the cave, and language and storytelling, were all the traditional form or media used in communication. This includes written language, where symbols were marked on paper, stone, or whatever materials available.
After thousands of years passed, and people who wanted to share their ideas with people had to do a lot of writing, writing machine was invented. This machine is called the printing press. Gutenberg's invention of the printing press is widely thought of as the origin of mass communication – as it marked the Western culture's first viable method of disseminating ideas and information from a single source to a large and far-ranging audience.
Along with this print media, printing and publishing industry, journalism, photography and advertising were introduced to the arena.
The invention of the telephone has resulted in the rapid dissemination of technical and scientific information. It saved countless lives through links to emergency services, made the emergence of modern cities possible through telephonic connections; which increased the speed of information exchanges and accelerated the rate of scientific and technological change as well as growth in industry.
Table 1.1(a) and (b) will give you a more comprehensive cover of the history of media.
According to Steve Heath (1999),
We have had multimedia in a linear fashion, non-computer-based forms for quite some time. From musical drama to film that utilises live band or orchestra that plays the score and special effects, traditional media has been conceived as multimedia. But it is the personal computer technology that has really created worldwide interest in interactive media.
Without computers, interactive media or digital entertainment could not exist. Video games, Multiplayer Online Games, interactive TV, wireless entertainment and virtual reality would never be possible.
Nowadays, the number of computers have increased tremendously, so does the power and usefulness of these devices. Plus, prices and size have also diminished and this technological revolution plays a significant part in the development of interactive entertainment.
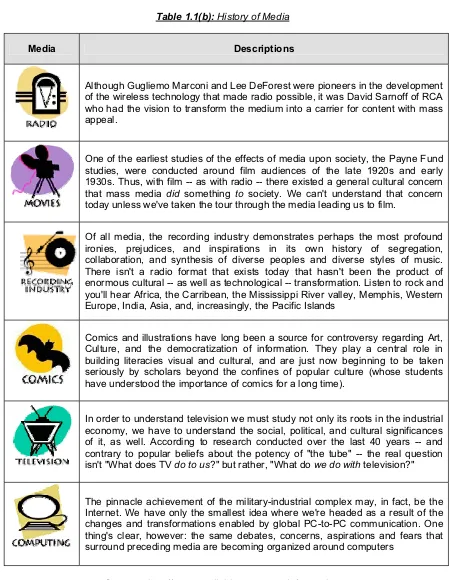
Table 1.1(a): History of Media
Media Descriptions
From ancient cave paintings to writing, the development of means for recording culture was a transformation that led, ultimately, to an unprecedented control over and organization of knowledge, power, and natural resources.
According to media historians, ethnographers, and other social scientists, the transition from oral- to print-based culture had major impacts upon nearly every facet of life. With the proliferation of printing presses, literacy, and printed materials, the epistemologies, cultural and religious identities, and social and political organizations that had emerged during the Middle Ages were significantly transformed. The Renaissance and the Enlightenment -- and the later Industrial Revolution -- all share roots with the evolution of printing.
Telegraph lines were built alongside the railroads -- a factor that helped establish standardized time zones across the U.S. Telegraphy also had a major impact upon journalistic conventions that had emerged during the late 1700s and early 1800s -- the "inverted pyramid" style of reportage is just one of the legacies of the era. Also, telegraphy was central to the modification of economic practices, as the price of goods became less dependent upon place and more dependent upon time.
Initially, the telephone was thought to be a convenience only for businesses -- and the rich. Its threat to social custom lies in its ability to enable isolated people to converse -- without the watchful eyes of society, family, community and other socializing forces looking on.
Journalism in the US began with pamphleteering, and its predominant narrative style has always been one of advocacy, rather than objectivity. In fact, the development of standards of objectivity is dependent, indeed, upon previous cultural and technological transformations that began with the print revolution.
During the late 1800s through the early decades of the 20th century, successive waves of immigrants arrived in the US, and found themselves mingling among new social groups. Advertising helped to create a new national identity, and played an important role in building a sense of community out of the melting pot. But, these new communities were organized around consumption rather than based on cultural traditions -- and that, of course, changed everything.
Table 1.1(b): History of Media
Media Descriptions
Although Gugliemo Marconi and Lee DeForest were pioneers in the development of the wireless technology that made radio possible, it was David Sarnoff of RCA who had the vision to transform the medium into a carrier for content with mass appeal.
One of the earliest studies of the effects of media upon society, the Payne Fund studies, were conducted around film audiences of the late 1920s and early 1930s. Thus, with film -- as with radio -- there existed a general cultural concern that mass media did something to society. We can't understand that concern today unless we've taken the tour through the media leading us to film.
Of all media, the recording industry demonstrates perhaps the most profound ironies, prejudices, and inspirations in its own history of segregation, collaboration, and synthesis of diverse peoples and diverse styles of music. There isn't a radio format that exists today that hasn't been the product of enormous cultural -- as well as technological -- transformation. Listen to rock and you'll hear Africa, the Carribean, the Mississippi River valley, Memphis, Western Europe, India, Asia, and, increasingly, the Pacific Islands
Comics and illustrations have long been a source for controversy regarding Art, Culture, and the democratization of information. They play a central role in building literacies visual and cultural, and are just now beginning to be taken seriously by scholars beyond the confines of popular culture (whose students have understood the importance of comics for a long time).
In order to understand television we must study not only its roots in the industrial economy, we have to understand the social, political, and cultural significances of it, as well. According to research conducted over the last 40 years -- and contrary to popular beliefs about the potency of "the tube" -- the real question isn't "What does TV do to us?" but rather, "What do we do with television?"
The pinnacle achievement of the military-industrial complex may, in fact, be the Internet. We have only the smallest idea where we're headed as a result of the changes and transformations enabled by global PC-to-PC communication. One thing's clear, however: the same debates, concerns, aspirations and fears that surround preceding media are becoming organized around computers
1.2.1 Convergent Technologies
The birth of modern digital interactive media has been made possible by the following convergent technologies:
x The invention of digital communicationsduring the late 1940s has created a new era of digital innovation and services, although it is very limited at that time.
x The invention of the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol ((TCP/IP) in the late 1960s paved the way for distributed media environment like the Internet.
x ARPANET's creation of the Internet during the early 1970s.
x The invention of the personal computer (PC) in the late 1970s.
Beside the four technologies listed above, the following advancement in technology had also helped toward the popularity of interactive media:
x The invention of the Hypertext Transport Protocol (HTTP) in the late 1980s enabled active text or hypertext to be transferred easily throughout the world.
x The opening of the Internet to the public in 1992 created worldwide excitement when people all over the net were able to share information freely, creating borderless world concept.
x The invention of the Mosaic browser software in that same year (1992) enabled netizens to develop and promote their own GUI-based websites.
These and other technological innovations converged to create a new interactive communications medium that has characteristics inconceivable even a decade ago.
Few years after the introduction of the first Internet browser, the year 1994 can be considered as the first of the Multimedia Era, with multimedia information communications beginning to take hold in numerous fields, such as cable TV, for which experiments in bidirectional services and user interactivity had already begun.
Today, in the home, transmission and exchange of video via personal computer made communications network possible, as in home shopping using bidirectional cable TV. In addition, "video-on-demand" TV programming (in which individual viewers can select from cable suppliers the specific programs that they want to watch) is being tested.
1.3 INTERACTIVE
MEDIA
REQUIREMENTS
Basically, there are several important factors that affect how interactive media works (Heath, 1999).
(a) Demands from the Customer
Developers of interactive media often overlook this issue. Consumer plays an important part in determining whether the multimedia technology and services provided are accepted. If a cable TV company wants to provide 500 channels to be selected by the consumers, the company should at the same time provide users with some tools to manage the vast amount of program information and decide which programs or channels to watch.
(b) Compression Techniques
Digital interactive media like audio and video data consumes a large amount of bandwidth and needs to be compressed significantly. Mpeg-4 compression codec for video streaming application on the net is a good example of compression techniques. These techniques usually require optimum processing power from fast machines. These video compression codec will be discussed in later topics.
(c) Processing Power
Interactive media involves data compression/decompression for it to work. Video and audio streaming, are some of the application of interactive media that require real-time processing. As such, powerful hardware and software support, plus a fast processor is needed to handle the compress/decompress processes effectively.
(d) Standards
Appropriate International standards needed to guarantee interoperability and of course to ensure financial returns and incentives are viable for industry. Broadcasting standards for Interactive television (iTV) is among those that receive greater attention and discussion.
(e) Bandwidth
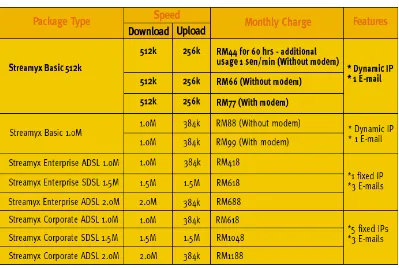
This is the most critical area for a multimedia system or interactive media. Sufficient bandwidth are needed to run the system to ensure the Quality Of Service is not degraded. This is especially true for Video on Demand (VoD) services where guaranteed bandwidth is very important to users. Malaysian nowadays, through Internet broadband services like the TMNet Streamyx, could enjoy greater bandwidth from 512 kbps up to 2 Mbps that enables them to have fast unlimited access to the Internet; and streaming audio and video through the services provided. TMNet streamyx brings the web's rich multimedia content to life, at up to 100 times the speed of an ordinary Internet connection, allowing interactive media and data to be distributed or utilised. Not only that the connection is always on, the price is also affordable for a wider market of users. Refer to Table 1.2 for a sample of the latest streamyx packages as of 1st January 2005.
(f) Internal Distribution
and not all could afford it, thus limiting the scope of interactive media. The best example is like when you want to use ASTRO in Malaysia, you will need to pay for the installation fee and the monthly fee, and to some, it is just too expensive.
Table 1.2: TMNet Streamyx Packages (Effective 1st January 2005)
Source:http://www.tm.net.my/html/htm/product_streamyx/packages.htm#
One of the requirements of interactive media is sufficient bandwidth. Based on your experience on using broadband services such as TMNet Streamyx, Jaring and others,which service provider do you prefer? Does your favourite broadband service provider have sufficient bandwidth?
1.4 IMPACTS OF INTERACTIVE MEDIA
The birth of the Internet and digital interactive media change everything, from societies to politics and even cultural values. These interactive media should be developed in such a way that they maximise learning and exploring opportunities for the users and encourage regular, ongoing interaction between the user and the system. Interactivity in this context refers not only to the interaction and communication among users and the system, but also to the interaction between users and the environment.
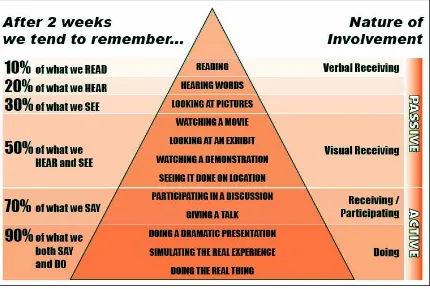
Figure 1.3: Edgar Dale’s cone of learning
Source:http://www.intech.com/education/pdf/ConeOfLearning-Flyer.pdf
Interactivity in an interactive media that allows transfer of power to users to become active participants instead of passive. Users are allowed to explore a multimedia program as how they wants it.
Interactive media is both praised and harshly criticised by some. Either way the boat floats, media has impacted how we see the world today. It has projected things like a propaganda which is a crucial part of our history. Sometimes, media is purposely shown in a certain sequence or omits certain events to keep the audiences attention. A "new perspective" on a controversial news report can use real footage, real news experts, but change the idea of the point altogether.
Everyday, the media has an impact on us in some way or another. For some people, the media has such an impact that they set their schedules up so that nothing will interfere with their favourite television shows. For others, media functions as a device to catch up with the world’s events. In either case, we depend on the media for something.
learned from media. Sadly, these examples may include naming a popular brand of alcholic drinks, striking a "sexy" pose, or play fighting. Children only have to put a movie into the VCR/VCD player, open a magazine, click on a website, or watch TV to experience all kinds of messages.
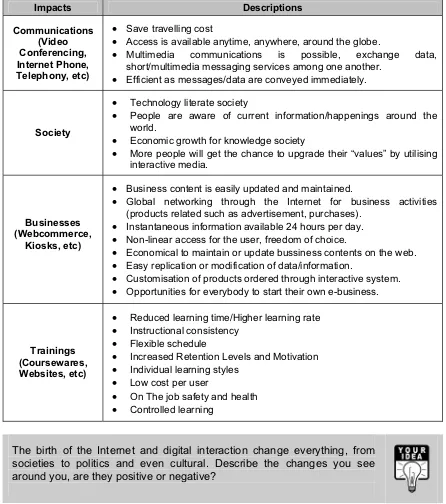
Media offers entertainment, culture, news, sports, and education. They are an important part of our lives and have much to teach. But some elements taught may not be what we want the viewers especially children to learn. In general, we can safely conclude that Interactive media brings about certain changes or impacts to users, regardless of the age factor (see Table 1.3).
Table 1.3: Impacts of Interactive Media
Impacts Descriptions
x Access is available anytime, anywhere, around the globe.
x Multimedia communications is possible, exchange data, short/multimedia messaging services among one another.
x Efficient as messages/data are conveyed immediately.
Society
x Technology literate society
x People are aware of current information/happenings around the world.
x Economic growth for knowledge society
x More people will get the chance to upgrade their “values” by utilising interactive media.
Businesses (Webcommerce,
Kiosks, etc)
x Business content is easily updated and maintained.
x Global networking through the Internet for business activities (products related such as advertisement, purchases).
x Instantaneous information available 24 hours per day. x Non-linear access for the user, freedom of choice.
x Economical to maintain or update bussiness contents on the web. x Easy replication or modification of data/information.
x Customisation of products ordered through interactive system. x Opportunities for everybody to start their own e-business.
Trainings (Coursewares,
Websites, etc)
x Reduced learning time/Higher learning rate x Instructional consistency
x Flexible schedule
x Increased Retention Levels and Motivation x Individual learning styles
x Low cost per user
x On The job safety and health x Controlled learning
For more information on social impact of media evolution visit: http://www.textuality.com/talks/kiep-1/
Exercise 1.1
1. How does the Internet support the use of interactive media?
2. What are the most important elements of digital convergence? Justify.
3. List TWO (2) advantages of using an interactive media.
SUMMARY
Digital convergence between different types of media and technology has given birth to a new concept of media, an interactive media which allows for greater user-medium interaction. In order to create and use interactive media, there are a number of important elements and factors that need careful consideration. Communication over distances which has become much more feasible with the invention of the telephone, computer, and the Internet has made such an impact on our society. Now, we are able to view tremendous multitudes of information from our own living room. The history of modern communication media is still on going, and will continue to progress far into the future.
GLOSSARY
Internet Publicly available worldwide system of interconnected computer networks that transmit data using a standardised Internet Protocol (IP). It carries various information and services, such as electronic mail, online chat and the interlinked web pages and other documents of the World Wide Web.
Multimedia The integration of multiple media: texts, numeric, graphics, image, video, animation, and audio in a digital environment that offer interactivity to allow user to access information in a non-linear fashion.
TEST 1
Instructions: Answer all questions within 15 minutes.
1. Define the term interactive media.
(3 marks)
2. State THREE (3) examples of interactive media.
(3 marks)
3. What is digital convergence? Provide examples to explain the concept.
(4 marks)
4. Give TWO (2) important factors that need to be considered when developing an interactive media system.
(4 marks) 5. What is the main differences between analog and digital media?
(4 marks)
TEST 2
Instructions: Answer all questions within 30 minutes.
1. Elaborate the meaning of multimedia as defined by Halimah Badioze Zaman (1996).
(4 marks)
2. Explain briefly how digital convergence helps to promote the use of interactive media.
(6 marks)
3. List THREE (3) common types of media widely available in the market nowadays. (3 marks)
4. Discuss briefly the following requirements of interactive media:
(i) Compression techniques (ii) Processing power
(iii) Bandwidth
(6 marks)
5. What do you understand by the Cone Of Learning by Edgar Dale? Elaborate.