www.elsevier.com / locate / bres
Short communication
Expression of CD40 in the brain of Alzheimer’s disease and other
neurological diseases
a,b a ,
*
a a cTakashi Togo
, Haruhiko Akiyama
, Hiromi Kondo , Kenji Ikeda , Masanori Kato ,
b b
Eizo Iseki , Kenji Kosaka
a
Tokyo Institute of Psychiatry, 2-1-8 Kamikitazawa, Setagaya-ku, Tokyo, 156-8585, Japan
b
Department of Psychiatry, Yokohama City University, Yokohama, Japan
c
Soga Hospital, Odawara, Japan
Accepted 12 September 2000
Abstract
We have investigated immunohistochemically the expression of CD40 in post-mortem human brain tissues. In control brain, the blood vessels were stained weakly for CD40. Vascular expression of CD40 was enhanced in the lesions of Alzheimer’s disease and some other neurological diseases. In such diseases, reactive microglia were also positive for CD40. The results of this study suggest that CD40 expression by microglia is up-regulated upon a variety of brain insults and is not limited to lesions with amyloidb-protein deposits.
2000 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.
Keywords: Microglia; Blood vessel; Amyloidb-protein; Inflammation
CD40 is a glycoprotein that belongs to the tumor tem human brain tissues with a variety of degenerative
necrosis factor receptor (TNF-R) family. CD40 was first neurological diseases.
identified as an antigen on the surface of B lymphocytes Brain tissues employed in this study include the
hip-and some carcinoma cells [14]. A number of studies have pocampus and the adjacent temporal isocortex from 18
focused on the role of CD40 for B-lymphocytic functions, cases with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), a case with Down’s
leading to the hypothesis that CD40 and its ligand, syndrome, four cases with schizophrenia and two cases
CD154(gp39), are essential for the development of humor- without neurological complication; the cerebellum from a
al immunity. CD40 is also expressed by such cells as case with dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy (DRPLA);
macrophages [1], Langerhans cells [5], endothelial cells demyelinating lesions from a case with MS and two cases
[10,11] and thymic epithelial cells [6], suggesting in- with adrenoleukodystrophy; and incidentally found
is-volvement of CD40–CD40L(CD154) interactions in a chemic lesions from two cases with AD. Diagnoses were
variety of cell systems. initially made on a clinical basis and were confirmed
In brain, CD40 has been reported to be expressed by post-mortem in every patient by routine neuropathological
microglia in the lesions of multiple sclerosis (MS) [7]. examination. Two cases of AD were complicated with
Inhibition of CD40–CD40L(CD154) interactions was severe systemic infection at the terminal stage and the
shown to retard the development of experimental au- post-mortem examination revealed occurrence of multiple
toimmune encephalomyelitis, an animal model of MS [8]. microabscesses and perivascular infiltration of
mononu-In vitro studies revealed that a pro-inflammatory cytokine, clear cells with activation of microglia throughout the
IFN-g, up-regulates the expression of CD40 by microglia brain parenchyma, the features of bacterial encephalitis. At
[2,13,17]. The purpose of this study is to investigate the autopsy, small blocks of brain tissue were dissected from
immunohistochemical localization of CD40 in post-mor- the hippocampus and other areas that contained brain
lesions. Brain blocks were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde in 0.1 M phosphate buffer, pH 7.4, for 2 days and
*Corresponding author. Tel.: 181-3-3305-5701; fax:
181-3-3329-transferred to 20% sucrose in 0.01 M phosphate-buffered
8035.
E-mail address: [email protected] (H. Akiyama). saline (PBS), pH 7.4. Sections were cut on a freezing
microtome at 30 mm thickness and stored in the same leukodystrophy (Fig. 1E) and multiple sclerosis, and the
solution until stained. cerebellar white matter of DRPLA.
Tissue sections were pretreated with 99% formic acid to In AD brain, round, diffuse deposits of CD40-positive
intensify the staining for CD40. To block the non-specific granules were seen in the cerebral cortex (Fig. 1F).
binding of mouse IgG to microglial Fc receptors, 2% Intensely stained glia-like contours were present in the
human serum was added to the primary antibody solution. center of such round labeling (Fig. 2C). Double
immuno-The primary antibody labeling was detected using the staining for CD40 and HLA-DP/ DQ / DR revealed that the
avidin–biotinylated HRP complex (ABC) system (Vector CD40 deposition occurred around aggregates of reactive
Labs, Burlingame, CA) coupled to a diaminobenzidine microglia and the intense labeling was of microglial
(DAB) reaction intensified with nickel ammonium sulfate aggregates (Fig. 2D). This was also confirmed in two AD
to yield a purple precipitate. For double immunostaining, cases complicated with encephalitis, where microglia were
the second cycle antibody labeling was visualized using extremely activated throughout the brain parenchyma and
DAB without nickel-intensification to yield a brown pre- were stained intensely for CD40 (Fig. 1G). In double
cipitate. Primary antibodies employed in this study are immunostaining for CD40 and amyloidb-protein (Ab), the
summarized in Table 1. CD40 deposition was co-localized with Ab-positive senile
Two antibodies to CD40, LOB7 / 6 and B-B20, labeled plaques (Fig. 2E).
essentially the same structures in post-mortem brain tis- In this study, we have shown that blood vessels and
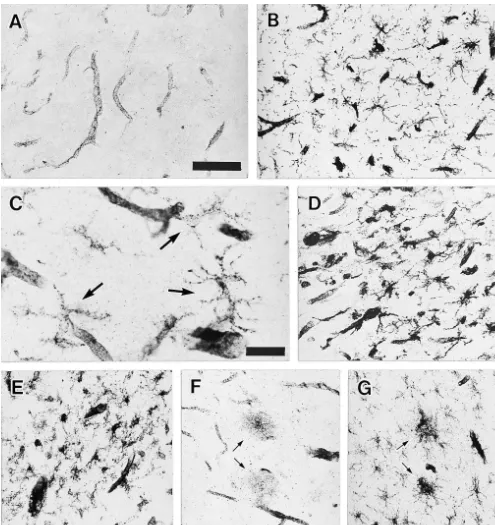
sues. In all tissues examined, the blood vessels were reactive microglia are stained positively for CD40 in
post-stained positively for CD40 (Fig. 1A). In AD and other mortem brain tissues. In control brain, weak expression of
neurological diseases, vascular expression of CD40 was CD40 is detected in the blood vessels. Vascular staining for
enhanced compared with control and schizophrenia cases. CD40 is enhanced in a variety of brain lesions, suggesting
Intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 staining of that CD40 expression is up-regulated. In the lesions of
nearby sections revealed that vascular ICAM-1 expression neurological diseases examined in this study, reactive
was up-regulated in areas with enhanced CD40 expression microglia express CD40. Such results are consistent with
(data not shown). previous in vitro studies, which demonstrated CD40
ex-In addition to the blood vessels, granular staining with pression by vascular endothelial cells [18] and microglia
ill-defined, glia-like contours was seen in the white matter [2,4,9,13].
of all cases. Such glia-like contours were more evident and Round, diffuse deposits of CD40 spread beyond
mi-numerous in the lesions of neurological diseases. Fig. 1B croglial aggregates in some senile plaques. Release of
illustrates the temporal cortex of an AD patient compli- soluble CD40 to culture supernatant was reported in B cell
cated with encephalitis, where a number of glia-like lines [3,12]. It remains to be determined, however, whether
contours are seen stained positively for CD40. At high such extracellular deposition of CD40 is derived from
power magnification, CD40-positive cells showed mor- secretion of soluble CD40 by microglia or represent
phology comparable with microglia (Fig. 1C). Double membrane debris of died microglia.
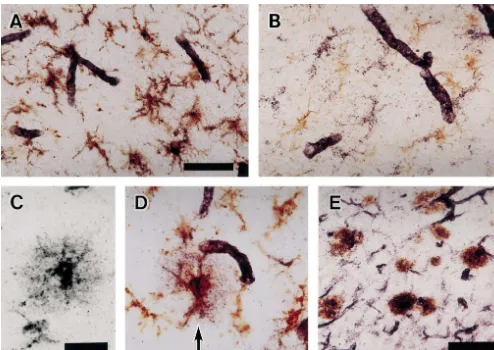
immunostaining for CD40 and HLA-DP/ DQ / DR, a In AD brain, aggregates of reactive microglia express
marker for microglia, or glial fibrillary acidic protein CD40 in senile plaques. Up-regulation of CD40 expression
(GFAP), a marker for astrocytes, confirmed this observa- by microglia is also seen in a variety of brain lesions
tion. CD40-positive glial cells were all positive for HLA- without Ab deposits. They include multiple sclerosis
DP/ DQ / DR (Fig. 2A) whereas they were negative for plaques [7] as well as lesions of adrenoleukodystrophy,
GFAP (Fig. 2B). CD40-positive microglia occurred in the DRPLA, and ischemic strokes. Recently, Abwas shown to
lesions of many neurological diseases regardless of the induce CD40 expression by cultured microglia [16] and
nature of the primary insult. They include ischemic lesions cultured vascular endothelial cells [15,18]. It may be the
(Fig. 1D), demyelinating lesions of an adreno- mechanism by which CD40 expression is up-regulated in
Table 1
Antibodies employed in this study
Antigen Antibody (source) Species, form Concentration
CD40 LOB7 / 6 (Chemicon) Mouse, IgG 1mg / ml
CD40 B-B20 (YLEM) Mouse, IgG 1:50*
HLA-DP/ DQ / DR CR3 / 43 (Dakopatts) Mouse, supernatant 1:200
ICAM-1 84H10 (Immunotech) Mouse, IgG 1mg / ml
GFAP Polyclonal (Dakopatts) Rabbit, Ig 1:10,000*
Amyloidbprotein Polyclonal anti-E50** Rabbit, serum 1:20,000
Fig. 2. (A) Double immunostaining with B-B20 (CD40, purple) and CR3 / 43 (HLA-DP/ DQ / DR, brown). CD40-positive glial cells are all positive for HLA-DP/ DQ / DR. Scale bar550mm. (B) Double immunostaining for CD40 and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) showing CD40-positive glial cells are distinct from GFAP-positive astrocytes. At the same magnification as A. (C) Single staining of a senile plaque for CD40. Around the ill-defined glia like contour, diffuse deposition of CD40-positive round granules is seen. Scale bar525mm. (D) Double immunostaining a section near to C for CD40 (purple) and HLA-DP/ DQ / DR (brown), showing CD40 is deposited beyond the microglial aggregate. At the same magnification as C. (E) Double immunostaining for CD40 (purple) and amyloid b-protein (Ab, brown). Aggregates of CD40-positive microglia and dot-like deposition of CD40 immunoreactivity are co-localized with Ab-positive senile plaques. Scale bar550mm.
regulation by cytokines and activation of monocytes by the ligand
and around senile plaques. However, the results of this
for CD40, J. Exp. Med. 178 (1993) 669–674.
study suggest that CD40 expression is induced upon
[2] F. Aloisi, G. Penna, E. Polazzi, L. Minghetti, L. Adorini, CD40–
multiple stimuli and that CD40–CD40L interactions are CD154 interaction and IFN-g are required for IL-12 but not
involved rather ubiquitously in activation of microglia and prostaglandin E secretion by microglia during antigen presentation2
to Th1 cells, J. Immunol. 162 (1999) 1384–1391.
vascular cells.
¨
[3] P. Bjorck, S. Braesch-Andersen, S. Paulie, Antibodies to distinct epitopes on the CD40 molecule co-operate in stimulation and can be used for the detection of soluble CD40, Immunology 83 (1994)
Acknowledgements 430–437.
[4] M.J. Carson, C.R. Reilly, J.G. Sutcliffe, D. Lo, Mature microglia resemble immature antigen-presenting cells, Glia 22 (1998) 72–85.
This research was supported by grants-in-aid from the
[5] C. Caux, C. Massacrier, B. Vanbervliet, B. Dubois, C. van Kooten, I.
Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan Durand, J. Banchereau, Activation of human dendritic cells through
(10670618). CD40 cross-linking, J. Exp. Med. 180 (1994) 1263–1272.
[6] A.H.M. Galy, H. Spits, CD40 is functionally expressed on human thymic epithelial cells, J. Immunol. 149 (1992) 775–782. [7] K. Gerritse, J.D. Laman, R.J. Noelle, A. Aruffo, J.A. Ledbetter, References W.J.A. Boersma, E. Claassen, CD40–CD40 ligand interactions in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis and multiple sclerosis, Proc. [1] M.R. Alderson, R.J. Armitage, T.W. Tough, L. Strockbine, W.C. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93 (1996) 2499–2504.
J.L. Baron, C.A. Janeway Jr., R.A. Flavell, Requirement for CD40 [14] S. Paulie, B. Ehlin-Henriksson, H. Mellstedt, H. Koho, H. Ben-ligand in costimulation induction. T cell activation, and experimen- Aissa, P. Perlmann, A p50 surface antigen restricted to human tal allergic encephalomyelitis, Science 273 (1996) 1864–1867. urinary bladder carcinomas and B lymphocytes, Cancer Immunol. [9] C.E.G. Havenith, D. Askew, W.S. Walker, Mouse resident microglia: Immunother. 20 (1985) 23–28.
isolation and characterization of immunoregulatory properties with [15] Z. Suo, J. Tan, A. Placzek, F. Crawford, C. Fang, M. Mullan,
1 1
naive CD4 and CD8 T-cells, Glia 22 (1998) 348–359. Alzheimer’s b-amyloid peptides induce inflammatory cascade in [10] D. Hollenbaugh, N. Mischel-Pretty, C.P. Edwards, J.C. Simon, R.W. human vascular cells: the role of cytokines and CD40, Brain Res.
Denfeld, P.A. Kiener, A. Aruffo, Expression of functional CD40 by 807 (1998) 110–117.
vascular endothelial cells, J. Exp. Med. 182 (1995) 33–40. [16] J. Tan, T. Town, D. Paris, T. Mori, Z. Suo, F. Crawford, M.P. [11] K. Karmann, C.C.W. Hughes, J. Schechner, W.C. Fanslow, J.S. Mattson, R.A. Flavell, M. Mullan, Microglial activation resulting Pober, CD40 on human endothelial cells: inducibility by cytokines from CD40–CD40L interaction afterb-amyloid stimulation, Science and functional regulation of adhesion molecule expression, Proc. 286 (1999) 2352–2355.
Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92 (1995) 4342–4346. [17] J. Tan, T. Town, D. Paris, A. Placzek, T. Parker, F. Crawford, H. [12] C. van Kooten, C. Gaillard, J.P. Galizzi, P. Hermann, F. Fossiez, J. Yu, J. Humphrey, M. Mullan, Activation of microglial cells by the Banchereau, D. Blanchard, B cells regulate expression of CD40 CD40 pathway: relevance to multiple sclerosis, J. Neuroimmunol. ligand on activated T cells by lowering the mRNA level and though 97 (1999) 77–85.