Tingkatan 3
Tingkatan 3
(EDISI BAHASA INGGERIS)
(EDISI BAHASA INGGERIS)
Dokumen Standard Kurikulum dan Pentaksiran
Dokumen Standard Kurikulum dan Pentaksiran
Matematik
Matematik
KURIKULUM STANDARD SEKOLAH MENENGAH
KURIKULUM STANDARD SEKOLAH MENENGAH
Matematik
Matematik
Dokumen Standard Kurikulum dan Pentaksiran
Dokumen Standard Kurikulum dan Pentaksiran
Tingkatan 3
Tingkatan 3
(EDISI BAHASA INGGERIS)
(EDISI BAHASA INGGERIS)
Bahagian Pembangunan Kurikulum
Bahagian Pembangunan Kurikulum
APRIL
APRIL 2017
2017
© Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia © Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia
Hak Cipta Terpelihara. Tidak dibenarkan mengeluar ulang mana-mana bahagian artikel, ilustrasi dan
Hak Cipta Terpelihara. Tidak dibenarkan mengeluar ulang mana-mana bahagian artikel, ilustrasi dan isi kandungan buku ini dalam isi kandungan buku ini dalam apa jugaapa juga bentuk dan dengan cara apa jua sama ada secara elektronik, fotokopi, mekanik, rakaman atau cara lain sebelum mendapat kebenaran bentuk dan dengan cara apa jua sama ada secara elektronik, fotokopi, mekanik, rakaman atau cara lain sebelum mendapat kebenaran bertulis daripada Pengarah, Bahagian Pembangunan Kurikulum, Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia, Aras 4-8, Blok E9, Parcel E, bertulis daripada Pengarah, Bahagian Pembangunan Kurikulum, Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia, Aras 4-8, Blok E9, Parcel E, Kompleks Pentadbiran Kerajaan Persekutuan, 62604
Rukun Negara...
Rukun Negara... vv Falsafah Pendidikan Kebangsaan...
Falsafah Pendidikan Kebangsaan... vivi Definisi
Definisi Kurikulum Kurikulum KebangsaaKebangsaan...n... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... viivii Kata Pengantar... Kata Pengantar... ixix Introduction... 1 Introduction... 1 Aims... Aims... ... 22 Objectives... 2 Objectives... 2 The
The Framework Framework of of Secondary Secondary School School Standard-Standard-based based CurriculCurriculum...um... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 44 Focus... 5 Focus... 5 21st
21st Century Century Skills..Skills... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1313 Higher-O
Higher-Order rder ThinkiThinking ng Skills.Skills... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1515 Teaching
Teaching and and Learning Learning StrategiStrategies...es... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 1616 Cross-Curr
Cross-Curricular icular Elements....Elements.... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . . 2020 School
Indices... 31 Indices... 31 Standard
Standard Form...Form... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3535 Consumer
Consumer MathematicMathematics: s: Savings Savings and and Investments, Investments, Credit Credit and and Debt...Debt... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 3939 Scale
Scale DrawingsDrawings... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... . . 4545 Trigonom
Trigonometric etric Ratios...Ratios... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... .... .... 4949 Angles and Tangent
Angles and Tangents of Circles...s of Circles... ... 5353 Plans
Plans and and ElevationElevations...s... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 5757 Loci
Loci in in Two Two DimensioDimensions...ns... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 6161 Straight
Straight Lines....Lines... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 6565 Panel
Panel of of WriterWriters...s... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 6969 Panel
Panel of of TranslaTranslators...tors... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ... 7171 Acknowledgement.
BAHAWASANYA Negara kita Malaysia mendukung cita-cita hendak:
BAHAWASANYA Negara kita Malaysia mendukung cita-cita hendak:
Mencapai perpaduan yang lebih erat dalam
Mencapai perpaduan yang lebih erat dalam kalangan seluruh masyarakatnya;
kalangan seluruh masyarakatnya;
Memelihara satu cara hidup demokratik;
Memelihara satu cara hidup demokratik;
Mencipta satu masyarakat yang adil di
Mencipta satu masyarakat yang adil di mana kemakmuran negara
mana kemakmuran negara
akan dapat dinikmati bersama secara adil
akan dapat dinikmati bersama secara adil dan saksama;
dan saksama;
Menjamin satu cara yang liberal
Menjamin satu cara yang liberal terhadap tradisi-tradisi
terhadap tradisi-tradisi
kebudayaannya yang kaya dan berbagai corak;
kebudayaannya yang kaya dan berbagai corak;
Membina satu masyarakat progresif yang akan menggunakan
Membina satu masyarakat progresif yang akan menggunakan
sains dan teknologi moden;
sains dan teknologi moden;
MAKA KAMI, rakyat Malaysia, berikrar akan
MAKA KAMI, rakyat Malaysia, berikrar akan menumpukan seluruh tenaga dan usaha
menumpukan seluruh tenaga dan usaha
kami untuk mencapai cita-cita tersebut berdasarkan prinsip-prinsip yang berikut:
kami untuk mencapai cita-cita tersebut berdasarkan prinsip-prinsip yang berikut:
KEPERCAYAAN KEPADA TUHAN
KEPERCAYAAN KEPADA TUHAN
KESETIAAN KEPADA RAJA DAN NEGARA
KESETIAAN KEPADA RAJA DAN NEGARA
KELUHURAN PERLEMBAGAAN
KELUHURAN PERLEMBAGAAN
KEDAULATAN UNDANG-UNDANG
KEDAULATAN UNDANG-UNDANG
KESOPANAN DAN KESUSILAAN
KESOPANAN DAN KESUSILAAN
“Pendidikan di Malaysia adalah suatu usaha berterusan ke arah
“Pendidikan di Malaysia adalah suatu usaha berterusan ke arah lebih
lebih
memperkembangkan potensi individu secara menyeluruh dan bersepadu
memperkembangkan potensi individu secara menyeluruh dan bersepadu
untuk melahirkan insan yang seimbang dan harmonis dari segi intelek,
untuk melahirkan insan yang seimbang dan harmonis dari segi intelek,
rohani, emosi dan jasmani, berdasarkan kepercayaan dan kepatuhan
rohani, emosi dan jasmani, berdasarkan kepercayaan dan kepatuhan
kepada Tuhan. Usaha ini
kepada Tuhan. Usaha ini adalah bertujuan untuk melahirkan warganegara
adalah bertujuan untuk melahirkan warganegara
Malaysia yang berilmu pengetahuan, berketerampilan, berakhlak mulia,
Malaysia yang berilmu pengetahuan, berketerampilan, berakhlak mulia,
bertanggungjawab dan berkeupayaan mencapai kesejahteraan diri serta
bertanggungjawab dan berkeupayaan mencapai kesejahteraan diri serta
memberikan sumbangan terhadap keharmonian dan kemakmuran
memberikan sumbangan terhadap keharmonian dan kemakmuran
keluarga, masyarakat dan negara”
keluarga, masyarakat dan negara”
Sumber: Akta Pendidikan 1996 (Akta 550)
Sumber: Akta Pendidikan 1996 (Akta 550)
3.
3. Kurikulum
Kurikulum Kebangsaan
Kebangsaan
(1)
(1)
Kurikulum
Kurikulum Kebangsaan
Kebangsaan ialah
ialah suatu
suatu program
program pendidikan
pendidikan yang
yang termasuk
termasuk
kurikulum dan kegiatan kokurikulum yang merangkumi semua pengetahuan,
kurikulum dan kegiatan kokurikulum yang merangkumi semua pengetahuan,
kemahiran, norma, nilai, unsur kebudayaan dan kepercayaan untuk membantu
kemahiran, norma, nilai, unsur kebudayaan dan kepercayaan untuk membantu
perkembangan seseorang murid dengan sepenuhnya dari segi
perkembangan seseorang murid dengan sepenuhnya dari segi jasmani, rohani,
jasmani, rohani,
mental dan emosi serta untuk menanam dan mempertingkatkan nilai moral yang
mental dan emosi serta untuk menanam dan mempertingkatkan nilai moral yang
diingini dan untuk menyampaikan pengetahuan.
diingini dan untuk menyampaikan pengetahuan.
Sumber: Peraturan-Peraturan Pendidikan (Kurikulum Kebangsaan) 1997 Sumber: Peraturan-Peraturan Pendidikan (Kurikulum Kebangsaan) 1997 [PU(A)531/97.] [PU(A)531/97.]
Kurikulum Standard Sekolah Menengah (KSSM) yang Kurikulum Standard Sekolah Menengah (KSSM) yang dilaksanakan secara berperingkat mulai tahun 2017 akan dilaksanakan secara berperingkat mulai tahun 2017 akan menggantikan Kurikulum Bersepadu Sekolah Menengah (KBSM) menggantikan Kurikulum Bersepadu Sekolah Menengah (KBSM) yang mula di
yang mula dilaksanakan pada laksanakan pada tahun 1989. tahun 1989. KSSM KSSM digubal bagidigubal bagi memenuhi keperluan dasar baharu di bawah Pelan Pembangunan memenuhi keperluan dasar baharu di bawah Pelan Pembangunan Pendidikan Malaysia (PPPM) 2013-2025 agar kualiti kurikulum Pendidikan Malaysia (PPPM) 2013-2025 agar kualiti kurikulum yang dilaksanakan di sekolah menengah setanding dengan yang dilaksanakan di sekolah menengah setanding dengan standard an
standard antarabangsa. tarabangsa. Kurikulum Kurikulum berasaskan berasaskan standard yangstandard yang menjadi amalan antarabangsa telah dijelmakan dalam KSSM menjadi amalan antarabangsa telah dijelmakan dalam KSSM menerusi penggubalan Dokumen Standard Kurikulum dan menerusi penggubalan Dokumen Standard Kurikulum dan Pentaksiran (DSKP) untuk semua mata pelajaran yang Pentaksiran (DSKP) untuk semua mata pelajaran yang mengandungi Standard Kandungan, Standard Pembelajaran dan mengandungi Standard Kandungan, Standard Pembelajaran dan Standard Prestasi.
Standard Prestasi.
Usaha memasukkan standard pentaksiran di dalam dokumen Usaha memasukkan standard pentaksiran di dalam dokumen kurikulum telah mengubah landskap sejarah sejak Kurikulum kurikulum telah mengubah landskap sejarah sejak Kurikulum Kebangsaan dilaksanakan di bawah Sistem Pendidikan Kebangsaan dilaksanakan di bawah Sistem Pendidikan Kebangsaan.
Kebangsaan. Menerusinya murid dapat ditaksir secaMenerusinya murid dapat ditaksir secara berterusanra berterusan untuk mengenal pasti tahap penguasaannya dalam
untuk mengenal pasti tahap penguasaannya dalam sesuatu matasesuatu mata pelajaran, serta membolehkan guru membuat tindakan susulan pelajaran, serta membolehkan guru membuat tindakan susulan bagi mempertingkatkan pencapaian murid.
bagi mempertingkatkan pencapaian murid.
DSKP yang dihasilkan juga telah menyepadukan enam tunjang DSKP yang dihasilkan juga telah menyepadukan enam tunjang Kerangka KSSM, mengintegrasikan pengetahuan, kemahiran dan Kerangka KSSM, mengintegrasikan pengetahuan, kemahiran dan nilai, serta memasukkan secara eksplisit Kemahiran Abad Ke-21 nilai, serta memasukkan secara eksplisit Kemahiran Abad Ke-21 dan Kem
dan Kemahiran Bahiran Berfikir erfikir Aras Aras Tinggi (KBTinggi (KBAT). AT). PenyepaduanPenyepaduan tersebut dilakukan untuk melahirkan insan
tersebut dilakukan untuk melahirkan insan seimbang dan harmonisseimbang dan harmonis dari segi intelek, rohani, emosi
dari segi intelek, rohani, emosi dan jasmani sebagaimana tuntutandan jasmani sebagaimana tuntutan Falsafah Pendidikan Kebangsaan.
Falsafah Pendidikan Kebangsaan.
Bagi menjayakan pelaksanaan KSSM, pengajaran dan Bagi menjayakan pelaksanaan KSSM, pengajaran dan pembelajaran (PdP) guru perlu memberi penekana
pembelajaran (PdP) guru perlu memberi penekanan n kepada KBATkepada KBAT dengan memberi fokus kepada pendekatan Pembelajaran dengan memberi fokus kepada pendekatan Pembelajaran Berasaskan Inkuiri dan Pembelajaran Berasaskan Projek, supaya Berasaskan Inkuiri dan Pembelajaran Berasaskan Projek, supaya murid dapat menguasai kemahiran yang diperlukan dalam abad murid dapat menguasai kemahiran yang diperlukan dalam abad ke-21.
ke-21.
Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia merakamkan setinggi-tinggi Kementerian Pendidikan Malaysia merakamkan setinggi-tinggi penghargaan dan ucapan terima kasih kepada semua pihak yang penghargaan dan ucapan terima kasih kepada semua pihak yang terlibat dalam penggubal
terlibat dalam penggubalan KSSM. an KSSM. Semoga pelaksanaan KSSemoga pelaksanaan KSSMSM akan mencapai hasrat dan matlamat Sistem Pendidikan akan mencapai hasrat dan matlamat Sistem Pendidikan Kebangsaan.
Kebangsaan.
Dr. SARIAH BINTI ABD. JALIL Dr. SARIAH BINTI ABD. JALIL Pengarah
Pengarah
Bahagian Pembangunan Kurikulum Bahagian Pembangunan Kurikulum
INTRODUCTION INTRODUCTION
Mathematics KSSM is a core subject that must be learned Mathematics KSSM is a core subject that must be learned by allby all pupils under the National Education System. In Malaysia, each pupils under the National Education System. In Malaysia, each pupil gets the opportunity to go through at least six years of basic pupil gets the opportunity to go through at least six years of basic education in primary school and five years in secondary school. education in primary school and five years in secondary school. Mathematics programme at the secondary school level is divided Mathematics programme at the secondary school level is divided into Mathematics at lower secondary, Mathematics at upper into Mathematics at lower secondary, Mathematics at upper secondary and Additional Mathematics at
secondary and Additional Mathematics at upper secondary.upper secondary.
The secondary school Mathematics content is essentially a The secondary school Mathematics content is essentially a continuation of knowledge and skills learnt at the primary school continuation of knowledge and skills learnt at the primary school level.
level. Its aims, amonIts aims, among others, are to develg others, are to develop the knowledge andop the knowledge and skills of the pupils to enable them to solve problems in their daily skills of the pupils to enable them to solve problems in their daily lives, further their studies to a higher level and able to function as lives, further their studies to a higher level and able to function as an effective workforce.
an effective workforce.
Rearrangement of Mathematics KSSM takes into
Rearrangement of Mathematics KSSM takes into consideration theconsideration the continuity from primary school to secondary school and onto a continuity from primary school to secondary school and onto a higher level of education.
higher level of education.
In addition, benchmarking of the Mathematics Curriculum in In addition, benchmarking of the Mathematics Curriculum in Malaysia with high performing countries in the international Malaysia with high performing countries in the international
assessments has been carried out. This measure is to
assessments has been carried out. This measure is to ensure thatensure that the Mathematics Curriculum in Malaysia is relevant and at
the Mathematics Curriculum in Malaysia is relevant and at par withpar with other countries in the world.
other countries in the world.
In the effort to develop potential and increase the level of In the effort to develop potential and increase the level of individual’s
individual’s intellectual and human development, Mathematics isintellectual and human development, Mathematics is the best medium because of its nature that encourages logical and the best medium because of its nature that encourages logical and systematic thinking. Thus, the development of the Mathematics systematic thinking. Thus, the development of the Mathematics curriculum, besides based on the needs of
curriculum, besides based on the needs of developing the country,developing the country, also takes into consideration factors that contribute to the also takes into consideration factors that contribute to the development of individuals who can think logically, critically, development of individuals who can think logically, critically, analytically, creatively and innovatively. This is
analytically, creatively and innovatively. This is consistent with theconsistent with the need to provide adequate mathematical knowledge and skills to need to provide adequate mathematical knowledge and skills to ensure that the country is able to compete internationally and to ensure that the country is able to compete internationally and to meet the challenges of
meet the challenges of the 21st century. The different the 21st century. The different backgroundsbackgrounds and abilities of the pupils are given special attention in determining and abilities of the pupils are given special attention in determining the knowledge and skills learned in
AIMS AIMS
Mathematics KSSM aims to produce individuals who are Mathematics KSSM aims to produce individuals who are mathematically
mathematically fikrahfikrah, which means individuals who can think, which means individuals who can think mathematically, creative and innovative as well as competent in mathematically, creative and innovative as well as competent in applying mathematical knowledge and skills effectively and applying mathematical knowledge and skills effectively and responsibly to solve problems and make decisions, based on the responsibly to solve problems and make decisions, based on the attitudes and values so that they are able to deal with challenges attitudes and values so that they are able to deal with challenges in their daily lives, in line with the development of science and in their daily lives, in line with the development of science and technology as well as the
technology as well as the challenges of the 21st century.challenges of the 21st century.
OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES
Form 3 Mathematics KSSM enables pupils to achieve the f
Form 3 Mathematics KSSM enables pupils to achieve the f ollowingollowing objectives:
objectives: 1.
1. Develop Develop an an understanding understanding of of the the concepts, concepts, laws, laws, principlesprinciples and theorems related to Number and Operations,
and theorems related to Number and Operations, Measurement and Geometry, Relationship and Algebra, Measurement and Geometry, Relationship and Algebra, Statistics and Probability, and Discrete Mathematics. Statistics and Probability, and Discrete Mathematics. 2.
2. Develop Develop capacity capacity in:in:
formulating situations into formulating situations into mathematical forms.mathematical forms.
using concepts, facts, procedures and using concepts, facts, procedures and reasoning.reasoning.
interpreting, applying and evaluating mathematicalinterpreting, applying and evaluating mathematical outcomes.
outcomes.
3.
3. Apply Apply the the knowledge knowledge and and skills skills of of mathematics mathematics in in makingmaking reasonable judgements and decisions to solve problems in a reasonable judgements and decisions to solve problems in a variety of contexts.
variety of contexts. 4.
4. Enhance Enhance mathematical mathematical skills relaskills related to ted to Number Number andand Operations, Measurement and Geometry, Relationship and Operations, Measurement and Geometry, Relationship and Algebra, S
Algebra, Statistics tatistics and Probabiand Probability, and lity, and Discrete MDiscrete Mathematicsathematics such as:
such as:
collecting and handling data.collecting and handling data.
representing and interpreting data.representing and interpreting data.
recognising relationship and representing themrecognising relationship and representing them mathematically.
mathematically.
using algorithms and relationship.using algorithms and relationship.
making estimation and approximation.making estimation and approximation.
measuring and measuring and constructing.constructing.
5.
5. Practise Practise the the mathematicmathematical al process process skills skills consistently consistently whichwhich include problem solving, reasoning, mathematical include problem solving, reasoning, mathematical communication, making connection and
communication, making connection and representation.representation.
6.
6. Cultivate Cultivate the the use use of of mathematical mathematical knowledge knowledge and and skills skills inin making reasonable judgements and decisions effectively and making reasonable judgements and decisions effectively and responsibly in daily life.
7.
7. Realise Realise that that mathematical mathematical ideas ideas aare re inter-related,inter-related, comprehensive and integrated body of knowledge, and are comprehensive and integrated body of knowledge, and are able to relate mathematics with other disciplines of able to relate mathematics with other disciplines of knowledge.
knowledge.
8.
8. Use tecUse technology hnology in conin concept buicept building, malding, mastery stery of skillsof skills,, investigating and exploring mathematical ideas and solving investigating and exploring mathematical ideas and solving problems.
problems.
9.
9. Foster Foster and and practice practice good good moral moral valuesvalues,, positive attitudes positive attitudes
towards mathematics and appreciate the importance and the towards mathematics and appreciate the importance and the beauty of
beauty of mathematics.mathematics.
10.
10. Develop higher-order, critical, creativDevelop higher-order, critical, creative and innovativee and innovative thinking.
thinking.
11.
11. Practise anPractise and furthed further develop r develop generic skilgeneric skills to ls to face challface challengesenges of the 21st century.
KSSM is built on the basis of six fundamental strands which are KSSM is built on the basis of six fundamental strands which are Communication; Spiritual; Attitude and Values; Humanities; Communication; Spiritual; Attitude and Values; Humanities; Personal Competence; Physical Development and
Personal Competence; Physical Development and Aesthetics; andAesthetics; and Science and Technology. These six strands are the main domain Science and Technology. These six strands are the main domain that support one another and are integrated with critical, creative that support one another and are integrated with critical, creative and innovative thinking. The integration aims to produce human and innovative thinking. The integration aims to produce human
capital who appreciate values based on spiritual practices, capital who appreciate values based on spiritual practices, knowledge, personal competence, critical and creative as well as knowledge, personal competence, critical and creative as well as innovative thinking as shown in Figure 1. The Mathematics innovative thinking as shown in Figure 1. The Mathematics curriculum is developed based on the six strands of the KSSM curriculum is developed based on the six strands of the KSSM Framework.
Framework. THE FRAMEWORK OF
Mathematical Mathematical SkillsSkills
2121stst Century Skills Century Skills
Higher-Order Higher-Order ThinkingThinking Skills
Skills FOCUS
FOCUS
Mathematics KSSM focuses on developing individuals who Mathematics KSSM focuses on developing individuals who internalise and practise mathematical
internalise and practise mathematical fikrahfikrah. The Mathematics. The Mathematics Curriculum Framework as illustrated in Figure
Curriculum Framework as illustrated in Figure 2, is fundamental to2, is fundamental to the implementation of the mathematics curriculum in the the implementation of the mathematics curriculum in the classroom.
classroom.
Four key elements which contribute to the development of human Four key elements which contribute to the development of human that posses mathematical
that posses mathematicalfikrahfikrahare:are:
Learning Learning areasareas
Values Values
Skills Skills
Mathematical Mathematical processesprocesses
Mathematical ValuesMathematical Values
Universal valuesUniversal values
Number & OperationsNumber & Operations
Measurement & GeometryMeasurement & Geometry
Relationship & AlgebraRelationship & Algebra
Statistics & ProbabilityStatistics & Probability
Discrete Discrete MathematicsMathematics
Problem SolvingProblem Solving ReasoningReasoning CommunicationCommunication RepresentationRepresentation ConnectionConnection LEARNING AREAS LEARNING AREAS VALUES VALUES
SKILLS
SKILLS
PROCESSES
PROCESSES
Number Number & & OperationsOperations
Measurement & Measurement & GeometryGeometry
Relationship & Relationship & AlgebraAlgebra
Statistics & Statistics & ProbabilityProbability
Discrete Discrete MathematicsMathematics
Mathematical Mathematical ValuesValues
Universal Universal valuesvalues
Mathematical Mathematical SkillsSkills
2121stst Century Skills Century Skills
Higher-Order Higher-Order ThinkingThinking
Problem Problem SolvingSolving Reasoning Reasoning Communication Communication Representation Representation Connection Connection
Mathematical MathematicalFikrahFikrah
In the Fourth Edition of Kamus Dewan (2005),
In the Fourth Edition of Kamus Dewan (2005), fikrahfikrahhas the samehas the same meaning as the power of thinking and thought. In the context of meaning as the power of thinking and thought. In the context of mathematics education, mathematical
mathematics education, mathematical fikrahfikrahrefers to the quality ofrefers to the quality of pupils to be developed through the
pupils to be developed through the national mathematics educationnational mathematics education system. Pupils who acquired mathematical
system. Pupils who acquired mathematical fikrahfikrah are capable ofare capable of doing mathematics, understanding mathematical ideas, and doing mathematics, understanding mathematical ideas, and applying the knowledge and skills of mathematics responsibly in applying the knowledge and skills of mathematics responsibly in daily life, guided by good attitudes and values
daily life, guided by good attitudes and values..
Mathematical
MathematicalFikrahFikrahalso intends to produce individuals who arealso intends to produce individuals who are creative, innovative and well-equipped to face the challenges of the creative, innovative and well-equipped to face the challenges of the 21st century, as the country is highly dependent on the ability of 21st century, as the country is highly dependent on the ability of human capital to think and generate
human capital to think and generate new ideas.new ideas.
Learning Area Learning Area
The content of Mathematics covers five main learning areas The content of Mathematics covers five main learning areas thatthat
are
areinter-relatedinter-related,,namely:namely:
Numbers Numbers and and OperationsOperations
Measurement Measurement and and GeometryGeometry
Relationship Relationship and and AlgebraAlgebra
Statistics Statistics and and ProbabilityProbability
Discrete Discrete Mathematics.Mathematics.
Mathematical Processes Mathematical Processes
Mathematical processes that support effective and meaningful Mathematical processes that support effective and meaningful teaching and learning are:
teaching and learning are:
Problem Problem solvingsolving
Reasoning Reasoning
Mathematical Mathematical communicationcommunication
Making Making connectionconnection
Representation. Representation.
These five inter-related mathematical processes need to be These five inter-related mathematical processes need to be implemented and integrated across the
implemented and integrated across the curriculum.curriculum.
Problem solving
Problem solving is the heart of mathematics. Hence, problem- is the heart of mathematics. Hence, problem-solving
solving skills need to be developed comprehensively andskills need to be developed comprehensively and integrated across the mathematics curriculum. In accordance with integrated across the mathematics curriculum. In accordance with the importance of problem solving, mathematical processes are the the importance of problem solving, mathematical processes are the backbone of the teaching and learning of mathematics and should backbone of the teaching and learning of mathematics and should be able to produce pupils who are creative, innovative and capable be able to produce pupils who are creative, innovative and capable of using a variety of problem-solving strategies and higher order of using a variety of problem-solving strategies and higher order thinking skills. Teachers need to design teaching and learning thinking skills. Teachers need to design teaching and learning
sessions that make problem solving the focus of discussion. sessions that make problem solving the focus of discussion. Activities c
Activities carried out shouarried out should engage the pupils ld engage the pupils actively by actively by posing aposing a diversity of questions and tasks that contain not
diversity of questions and tasks that contain not only the routine butonly the routine but routine questions as well. Solving problems involving routine questions as well. Solving problems involving non-routine questions needs thinking and reasoning at a higher level. routine questions needs thinking and reasoning at a higher level. These skills should be consistently cultivated by the teachers to These skills should be consistently cultivated by the teachers to produce pupils who are able to compete at a global level.
produce pupils who are able to compete at a global level.
The following problem-solving steps should be emphasised so that The following problem-solving steps should be emphasised so that pupils can solve
pupils can solve problems systematically and effectively:problems systematically and effectively:
Understanding Understanding and and interpreting interpreting problemsproblems
Devising Devising a a strategystrategy
Implementing Implementing the the strategystrategy
Doing Doing reflection.reflection.
The application of various strategies in problem solving including The application of various strategies in problem solving including the steps involved
the steps involved has to be used widely. Among the strategieshas to be used widely. Among the strategies commonly used are drawing
commonly used are drawing diagrams, identifying patterns, makingdiagrams, identifying patterns, making tables/charts or systematic lists; using algebra, trying simpler tables/charts or systematic lists; using algebra, trying simpler cases, reason out logically, using trial and improvement, making cases, reason out logically, using trial and improvement, making simulation, working backwards as well as using analogies. simulation, working backwards as well as using analogies.
The following are some of the
The following are some of the processes that need to beprocesses that need to be emphasised and developed through problem solving, that is to emphasised and developed through problem solving, that is to develop
develop pupils’ capacity in:pupils’ capacity in:
Formulating Formulating situations situations involving involving various various contexts contexts such assuch as personal, community, scientific and occupation
personal, community, scientific and occupation mathematically.
mathematically.
Using aUsing and appnd applying clying concepts, oncepts, facts, facts, procedures procedures andand reasonings in solving
reasonings in solving problems.problems.
Interpreting, Interpreting, evaluating evaluating and and reflecting reflecting on ton the she solutions olutions oror decisions made and determining whether they are reasonable. decisions made and determining whether they are reasonable. Reflection is an important step in
Reflection is an important step in problem solving. Reflection allowsproblem solving. Reflection allows pupils to see, understand and appreciate perspectives of others pupils to see, understand and appreciate perspectives of others from different angles as well as enables pupils
from different angles as well as enables pupils to consolidate theirto consolidate their understanding of the concepts learned.
understanding of the concepts learned.
Reasoning
Reasoning is an important basis for understanding mathematics is an important basis for understanding mathematics more effectively and meaningfully. The development of more effectively and meaningfully. The development of mathematical reasoning is closely related to pupils’
mathematical reasoning is closely related to pupils’ intellectual intellectual development and communication. Reasoning does not only development and communication. Reasoning does not only develop the capacity of logical thinking but also increases the develop the capacity of logical thinking but also increases the capacity of critical thinking that is fundamental in understanding capacity of critical thinking that is fundamental in understanding mathematics in depth and
mathematics in depth and meaningfully. Therefore, teachers needmeaningfully. Therefore, teachers need to provide space and opportunity through designing teaching and to provide space and opportunity through designing teaching and
learning activities that require pupils to do mathematics and be learning activities that require pupils to do mathematics and be actively involved in discussing
actively involved in discussing mathematical ideas.mathematical ideas.
The elements of reasoning in the teaching and learning prevent The elements of reasoning in the teaching and learning prevent pupils from considering mathematics as just a set
pupils from considering mathematics as just a set of procedures orof procedures or algorithms that should be followed to obtain a solution without algorithms that should be followed to obtain a solution without understanding the actual mathematical concepts in depth. understanding the actual mathematical concepts in depth. Reasoning not only changes
Reasoning not only changes the paradigm of pupils’ consciousthe paradigm of pupils’ conscious procedural knowledge but also gives thought and intellectual procedural knowledge but also gives thought and intellectual empowerment when pupils are guided and trained to make and empowerment when pupils are guided and trained to make and validate conjectures, provide logical explanations, analyze, validate conjectures, provide logical explanations, analyze, evaluate and justify the mathematical activities. Such training evaluate and justify the mathematical activities. Such training would enhance
would enhance pupils’ confidence and courage, in line with the aimpupils’ confidence and courage, in line with the aim of developing powerful mathematical thinkers.
of developing powerful mathematical thinkers.
Communication in mathematics
Communication in mathematics is the process of expressing is the process of expressing ideas and understanding inverbal, visual or written form using ideas and understanding inverbal, visual or written form using numbers, notations, symbols, diagrams, graphs, pictures or numbers, notations, symbols, diagrams, graphs, pictures or words.words. Communication is an important process in learning mathematics Communication is an important process in learning mathematics because mathematical communication helps pupils to clarify and because mathematical communication helps pupils to clarify and reinforce their understanding of mathematics. Through reinforce their understanding of mathematics. Through communication, mathematical ideas can be better expressed and communication, mathematical ideas can be better expressed and understood. Communication in mathematics, either verbally, in understood. Communication in mathematics, either verbally, in written form or using symbols and visual representations (charts, written form or using symbols and visual representations (charts,
graphs, diagrams, etc), help pupils to understand and apply graphs, diagrams, etc), help pupils to understand and apply mathematics more effectively.
mathematics more effectively.
Teachers should be aware of the opportunities that exist during Teachers should be aware of the opportunities that exist during teaching and learning sessions to encourage pupils
teaching and learning sessions to encourage pupils to express andto express and present their mathematical ideas by using
present their mathematical ideas by using appropriate questioningappropriate questioning techniques. Communication that involves a variety
techniques. Communication that involves a variety of perspectivesof perspectives and points of view helps
and points of view helps pupils to better improve their mathematicalpupils to better improve their mathematical understanding whilst enhancing their self-confidence.
understanding whilst enhancing their self-confidence.
The significant aspect of mathematical communication is the ability The significant aspect of mathematical communication is the ability to provide effective explanation as well as to
to provide effective explanation as well as to understand and applyunderstand and apply the correct mathematical notations. Pupils should use the the correct mathematical notations. Pupils should use the mathematical language and symbols correctly to ensure that a mathematical language and symbols correctly to ensure that a mathematical idea can be explained precisely.
mathematical idea can be explained precisely.
Effective communication requires an environment that is always Effective communication requires an environment that is always sensitive to the needs of pupils
sensitive to the needs of pupils so that they feel comfortable whileso that they feel comfortable while speaking, asking and answering questions, explaining and speaking, asking and answering questions, explaining and justifying
justifying their their views views and and statements statements to to their their classmates classmates andand teachers. Pupils should be given the opportunity to communicate teachers. Pupils should be given the opportunity to communicate actively in a variety of settings, for example while doing
actively in a variety of settings, for example while doing activities inactivities in pairs, groups or while giving
Representation
Representation is an important component of mathematics and is an important component of mathematics and often used to represent real-world phenomena. Therefore, there often used to represent real-world phenomena. Therefore, there must be a similarity between the aspects of the world that is must be a similarity between the aspects of the world that is represented and the world that
represented and the world that is representing. Representation canis representing. Representation can be defined as any
be defined as any notations, letters, images or concrete objects thatnotations, letters, images or concrete objects that symbolise or represent something else.
symbolise or represent something else. At
At the the secondary secondary school school level, level, representing representing ideas ideas andand mathematical models generally make use of symbols, geometry, mathematical models generally make use of symbols, geometry, graphs, algebra, figures, concrete representations and dynamic graphs, algebra, figures, concrete representations and dynamic softwares. Pupils must be able to change from one form of softwares. Pupils must be able to change from one form of representation to another and recognize the relationship between representation to another and recognize the relationship between them, and use various representations, which are relevant and them, and use various representations, which are relevant and required to solve problems.
required to solve problems.
The use of various representations helps pupils to understand The use of various representations helps pupils to understand mathematical concepts and relationships; communicate their mathematical concepts and relationships; communicate their thinking, reasoning and understanding; recognise the relationship thinking, reasoning and understanding; recognise the relationship between mathematical concepts and use mathematics to model between mathematical concepts and use mathematics to model situations, physical and social phenomena. When pupils are able situations, physical and social phenomena. When pupils are able to represent concepts in different ways, they will be flexible i to represent concepts in different ways, they will be flexible i n theirn their thinking and understand that there are a variety of ways to thinking and understand that there are a variety of ways to represent mathematical ideas that enable problems to be solved represent mathematical ideas that enable problems to be solved more easily.
more easily.
Connection
Connection between areas in mathematics such as counting, between areas in mathematics such as counting, geometry, algebra, measurement and statistics is important for geometry, algebra, measurement and statistics is important for pupils to learn concepts and skills integratedly and meaningfully. pupils to learn concepts and skills integratedly and meaningfully. By recognizing how the concepts or skills of different areas are By recognizing how the concepts or skills of different areas are related to each other, mathematics will be seen and studied as a related to each other, mathematics will be seen and studied as a discipline that is comprehensive, connected to each other thus discipline that is comprehensive, connected to each other thus allowing abstract concepts to be understood easily.
allowing abstract concepts to be understood easily.
When mathematical ideas are connected to daily life experiences When mathematical ideas are connected to daily life experiences within and outside the classroom,
within and outside the classroom, pupils will be more aware of thepupils will be more aware of the use, the importance, the strength and
use, the importance, the strength and the beauty of mathematics.the beauty of mathematics. Besides, they are also able to use mathematics contextually in Besides, they are also able to use mathematics contextually in other disciplines and in their daily lives. Mathematical models are other disciplines and in their daily lives. Mathematical models are used to describe real-life situations mathematically. Pupils will used to describe real-life situations mathematically. Pupils will realise that this method can be used to
realise that this method can be used to solve problems or to predictsolve problems or to predict the likelihood of a
the likelihood of a situation based on the mathematical model.situation based on the mathematical model. In implementing the Mathematics Curriculum, the opportunity to In implementing the Mathematics Curriculum, the opportunity to make connections should be established so that pupils can relate make connections should be established so that pupils can relate conceptual knowledge to procedural knowledge and be able to conceptual knowledge to procedural knowledge and be able to relate topics in mathematics in particular
relate topics in mathematics in particular and relate mathematics toand relate mathematics to other fields in general. This will increas
other fields in general. This will increas e pupils’ understanding ofe pupils’ understanding of mathematics; making it clearer, more meaningful and
Mathematics Process Standards Mathematics Process Standards
The following are the
The following are the process standards to be achieved by pupilsprocess standards to be achieved by pupils through the implementation of this
through the implementation of this curriculum.curriculum.
Table 1:
Table 1: Mathematics Process StandardsMathematics Process Standards PROBLEM SOLVING
PROBLEM SOLVING
Understand the problems.Understand the problems.
Extract relevant information in a given situation andExtract relevant information in a given situation and organise information
organise information systematicallysystematically..
Plan various strategies to Plan various strategies to solve problems.solve problems.
Implement the strategies according to the plan.Implement the strategies according to the plan.
Generate solutions to meet the requirements of theGenerate solutions to meet the requirements of the problem.
problem.
Interpret the solutions.Interpret the solutions.
Review and reflect upon the solutions and Review and reflect upon the solutions and strategiesstrategies used.
used. REASONING REASONING
Recognise reasoning and proving as fundamentals toRecognise reasoning and proving as fundamentals to mathematics.
mathematics.
Recognise patterns, structures, and similarities withinRecognise patterns, structures, and similarities within real-life situations and symbolic representations. real-life situations and symbolic representations.
Choose and use various types of Choose and use various types of reasoning andreasoning and
methods of proving. methods of proving.
Make, investigate and verify mathematical conjectures.Make, investigate and verify mathematical conjectures.
Develop and evaluate mathematical arguments andDevelop and evaluate mathematical arguments and
proofs. proofs.
Make decisions and justify the decisions made.Make decisions and justify the decisions made. COMMUNICA
COMMUNICATION TION IN MATHEMATICSIN MATHEMATICS
Organise and incorporate mathematical thinking throughOrganise and incorporate mathematical thinking through communication to clarify and strengthen the
communication to clarify and strengthen the understanding of
understanding of mathematics.mathematics.
Communicate mathematicCommunicate mathematical thoughts and al thoughts and ideas clearlyideas clearly
and confidently. and confidently.
Use the language of mathematics to expressUse the language of mathematics to express mathematical ideas precisely.
mathematical ideas precisely.
Analyse and evaluate the mathema Analyse and evaluate the mathematical thinking andtical thinking and strategies of others.
strategies of others.
REPRESENTATION REPRESENTATION
Illustrate mathematical ideas using various types Illustrate mathematical ideas using various types ofof representations.
representations.
Make interpretations from given Make interpretations from given representations.representations.
Choose the appropriate types of Choose the appropriate types of representations.representations.
Use various types of Use various types of mathematical representationmathematical representations to:s to: i)
i) simplify simplify complex complex mathematical mathematical ideasideas ii)
ii) assist in assist in problem solvproblem solvinging
iii) develop models and interpret mathematical iii) develop models and interpret mathematical
phenomena phenomena
iv) make connections between various types of iv) make connections between various types of
representations. representations.
CONNECTION CONNECTION
Identify and use Identify and use the connection between mathematicalthe connection between mathematical ideas.
ideas.
Understand how mathematical ideas are Understand how mathematical ideas are inter-relatedinter-related
and form a cohesive unity. and form a cohesive unity.
Relate mathematical ideas to daily life and Relate mathematical ideas to daily life and other fields.other fields.
Skills Skills
The skills that must be developed and instilled amongst pupils The skills that must be developed and instilled amongst pupils through the teaching of this subject include the
through the teaching of this subject include the Mathematical Skills,Mathematical Skills, 21st Century Skills and Higher Order Thinking
21st Century Skills and Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS).Skills (HOTS). The mathematical skills refer to, among others, the skills of The mathematical skills refer to, among others, the skills of measuring and constructing, estimating and rounding, collecting measuring and constructing, estimating and rounding, collecting and handling data, representing and
and handling data, representing and interpreting data, recognisinginterpreting data, recognising relationships and representing mathematically, translating real-life relationships and representing mathematically, translating real-life situations into mathematical models, using the precise language situations into mathematical models, using the precise language ofof mathematics, applying logical reasoning, using algorithms and mathematics, applying logical reasoning, using algorithms and relationships, using mathematical tools, solving
relationships, using mathematical tools, solving problems, makingproblems, making decisions and so on. In addition, the curriculum also demands the decisions and so on. In addition, the curriculum also demands the development
development of pupils’ mathematicalof pupils’ mathematical skills in aspects related to skills in aspects related to creativity, the needs of originality in their thinking and
creativity, the needs of originality in their thinking and the ability tothe ability to
see things around them with new and different perspectives in see things around them with new and different perspectives in order to develop creative and innovative individuals. The use of order to develop creative and innovative individuals. The use of mathematical tools strategically, accurately and effectively is mathematical tools strategically, accurately and effectively is strongly emphasised in the teaching and
strongly emphasised in the teaching and learning of mathematics.learning of mathematics. The mathematical tools include papers and pencils, rulers, The mathematical tools include papers and pencils, rulers, protractors, compasses, calculators, electronic spreadsheets, protractors, compasses, calculators, electronic spreadsheets, dynamic softwares and so on.
dynamic softwares and so on.
The rapid progress of various technologies in todays’ life has The rapid progress of various technologies in todays’ life has resulted in the use of technologies as an essential element in the resulted in the use of technologies as an essential element in the teaching and learning of mathematics. Effective teachers will teaching and learning of mathematics. Effective teachers will maximise the potential and technological capabilities so that pupils maximise the potential and technological capabilities so that pupils can build understanding and increase their proficiency and interest can build understanding and increase their proficiency and interest in mathematics. Due to the capacity and effectiveness of in mathematics. Due to the capacity and effectiveness of technology in the teaching and learning of mathematics content, technology in the teaching and learning of mathematics content, teachers need to embrace the use of technology, particularly teachers need to embrace the use of technology, particularly scientific calculators, graphing calculators, computer softwares like scientific calculators, graphing calculators, computer softwares like Geometer's Sketchpad, Geogebra, electronic spreadsheets, Geometer's Sketchpad, Geogebra, electronic spreadsheets, learning softwares (courseware), the Internet and others.
learning softwares (courseware), the Internet and others.
However, technology must be used wisely.
However, technology must be used wisely. Calculator for exampleCalculator for example is not to be used to the extent that the importance of mental is not to be used to the extent that the importance of mental calculations and basic computations is neglected. Efficiency in calculations and basic computations is neglected. Efficiency in carrying out the calculations is important especially in the lower carrying out the calculations is important especially in the lower
level and pupils should not totally rely on calculators. For example, level and pupils should not totally rely on calculators. For example, although the graphing calculator helps pupils to visualize the nature although the graphing calculator helps pupils to visualize the nature of a function and its graph, fundamentally the use of paper and of a function and its graph, fundamentally the use of paper and pencil is still the learning outcome to be achieved by all pupils. pencil is still the learning outcome to be achieved by all pupils. Similarly, in seeking the roots of the quadratic equations, the basic Similarly, in seeking the roots of the quadratic equations, the basic concept must first be mastered by the pupils. Technology should concept must first be mastered by the pupils. Technology should be used wisely to help pupils form concepts, enhance be used wisely to help pupils form concepts, enhance understanding, visualize concepts and so on while enriching understanding, visualize concepts and so on while enriching pupils’pupils’ learning experiences.
learning experiences.
Specifically, the skills in using technology that need to be nurtured Specifically, the skills in using technology that need to be nurtured among the pupils through the
among the pupils through the teaching and learning of Mathematicsteaching and learning of Mathematics are the pupils
are the pupils’’ ability in:ability in:
Using technoUsing technology to logy to explore, carry explore, carry out researout research, constch, constructruct mathematical modelling, and hence form a deep
mathematical modelling, and hence form a deep understandingunderstanding of the mathematical concepts
of the mathematical concepts
Using technoloUsing technology to helgy to help in calculatp in calculations to solions to solve problemsve problems effectively
effectively
Using Using technology, technology, especially especially electronic electronic and diand digital gital technologytechnology to find, manage, evaluate
to find, manage, evaluate and communicate informationand communicate information
Using Using technology technology responsibly responsibly and and ethically.ethically.
The use of technology such as dynamic softwares, scientific The use of technology such as dynamic softwares, scientific calculators, graphing calculators, the Internet and so on needs to calculators, graphing calculators, the Internet and so on needs to
be integrated into the teaching
be integrated into the teaching and learning of mathematics to helpand learning of mathematics to help pupils form deep understanding of concepts especially abstract pupils form deep understanding of concepts especially abstract concepts.
concepts.
Values in Mathematics Education Values in Mathematics Education
Values are affective qualities intended to be formed through the Values are affective qualities intended to be formed through the teaching and learning
teaching and learning of mathematics using appropriate contexts.of mathematics using appropriate contexts. Values are usually taught and learned implicitly through the Values are usually taught and learned implicitly through the learning sessions. Good moral values develop
learning sessions. Good moral values develop great attitudes. Thegreat attitudes. The application of values and attitudes in the teaching and learning of application of values and attitudes in the teaching and learning of mathematics are meant to produce individuals who
mathematics are meant to produce individuals who are competentare competent in terms of knowledge and skills as well as
in terms of knowledge and skills as well as having good characters.having good characters. Embracing good moral values would produce a virtuous young Embracing good moral values would produce a virtuous young generation with noble personal qualities and good
generation with noble personal qualities and good attitudes.attitudes. Values that need to be developed in pupils through the teaching Values that need to be developed in pupils through the teaching and learning of mathematics are:
and learning of mathematics are:
Mathematical Mathematical valuesvalues – – values within the knowledge of values within the knowledge of mathematics which include emphasis on the properties of the mathematics which include emphasis on the properties of the mathematical knowledge; and
mathematical knowledge; and
Universal Universal values - values - universal noble universal noble values that values that are appliedare applied across all the subjects.
The development of values through teaching and learning of The development of values through teaching and learning of mathematics should also involve the elements of divinity, faith, mathematics should also involve the elements of divinity, faith, interest, appreciation, confidence, competence and tenacity. interest, appreciation, confidence, competence and tenacity. BeliefBelief in the Power and Greatness of God can basically be nurtured in the Power and Greatness of God can basically be nurtured through the content of the curriculum. The
through the content of the curriculum. The relationship between therelationship between the content learned and the real world enables pupils to see and content learned and the real world enables pupils to see and validate the Greatness and the Power of the Creator of the validate the Greatness and the Power of the Creator of the universe.
universe.
The elements of history and patriotism should also be inculcated The elements of history and patriotism should also be inculcated through relevant topics to enable pupils to
through relevant topics to enable pupils to appreciate mathematicsappreciate mathematics as well as to boost interest and confidence in mathematics. as well as to boost interest and confidence in mathematics. Historical elements such as certain events involving Historical elements such as certain events involving mathematicians or a brief history of a concept or symbol are also mathematicians or a brief history of a concept or symbol are also emphasised in this
emphasised in this curriculum.curriculum.
21st Century Skills 21st Century Skills
One of the aims of KSSM is to produce pupils who possess the One of the aims of KSSM is to produce pupils who possess the skills of the 21st century by focussing on thinking skills, living skills skills of the 21st century by focussing on thinking skills, living skills and career guided by the
and career guided by the practice of good moral values.practice of good moral values.
21st Century Skills aim to produce pupils who have the 21st Century Skills aim to produce pupils who have the characteristics specified in the pupils’
characteristics specified in the pupils’ profile as in Table profile as in Table 2, so that2, so that they are able to compete at a global level. The mastery of the they are able to compete at a global level. The mastery of the Content Standards and the Learning Standards in
Content Standards and the Learning Standards in the Mathematicsthe Mathematics Curriculum contributes to the acquisition of the 21st Century Skills Curriculum contributes to the acquisition of the 21st Century Skills among the pupils.
among the pupils.
Table 2: Pupils Table 2: Pupils’’ ProfileProfile
PUPILS PUPILS’’ PROFILE PROFILE DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION Resilient Resilient
Pupils are able to face
Pupils are able to face and overcome difficultiesand overcome difficulties and challenges with
and challenges with wisdom, confidence,wisdom, confidence, tolerance, and empathy.
tolerance, and empathy.
Competent Competent communicator communicator
Pupils voice out and express their thoughts, Pupils voice out and express their thoughts, ideas and information confidently and
ideas and information confidently and creatively,creatively, in verbal and in written form, using various media in verbal and in written form, using various media and technology.
PUPILS PUPILS’’ PROFILE PROFILE DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION Thinker Thinker
Pupils think critically, creatively and
Pupils think critically, creatively and innovatively;innovatively; are able to
are able to solve complex problems and makesolve complex problems and make ethical decisions. They think about learning and ethical decisions. They think about learning and themselves as learners. They generate
themselves as learners. They generate questions and be open
questions and be open towards othertowards other individual’s and
individual’s and communities’ perspectives,communities’ perspectives, values, and traditions. They are confident and values, and traditions. They are confident and creative in handling new learning
creative in handling new learning areas.areas.
Team Work Team Work
Pupils can co-operate effectively and Pupils can co-operate effectively and harmoniously with others. They shoulder harmoniously with others. They shoulder responsibilities together as well as respect and responsibilities together as well as respect and appreciate the contributions from each
appreciate the contributions from each membermember of the team. They acquire interpersonal skills of the team. They acquire interpersonal skills through collaborative activities, and this through collaborative activities, and this makesmakes them better leaders and
them better leaders and team members.team members.
Inquisitive Inquisitive
Pupils develop natural inquisitiveness to explore Pupils develop natural inquisitiveness to explore new strategies and ideas. They learn
new strategies and ideas. They learn skills thatskills that are necessary for inquiry-learning and research, are necessary for inquiry-learning and research, as well as display independent traits in learning. as well as display independent traits in learning. The pupils continuously enjoy life-long l
The pupils continuously enjoy life-long l earningearning experiences.
experiences.
Principled Principled
Pupils have a sense
Pupils have a sense of integrity and sincerity,of integrity and sincerity, equality, fairness and respect the dignity of equality, fairness and respect the dignity of individuals, groups and community. They are individuals, groups and community. They are responsible for their actions, consequences and responsible for their actions, consequences and decisions. decisions. PUPILS PUPILS’’ PROFILE PROFILE DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION Informed Informed
Pupils obtain knowledge and develop a Pupils obtain knowledge and develop a broadbroad and balanced understanding across the various and balanced understanding across the various disciplines of knowledge. They explore
disciplines of knowledge. They explore
knowledge efficiently and effectively in terms of knowledge efficiently and effectively in terms of local and global contexts. They understand local and global contexts. They understand issues related to ethics or laws
issues related to ethics or laws regardingregarding information acquired.
information acquired.
Caring Caring
Pupils show empathy, compassion and Pupils show empathy, compassion and respectrespect towards the needs and feelings of
towards the needs and feelings of others. Theyothers. They are committed to serve the society and ensure are committed to serve the society and ensure the sustainability of the
the sustainability of the environment.environment. Patriotic
Patriotic Pupils demonstrate their love, support andPupils demonstrate their love, support and respect for the country.
HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) are explicitly stated in the Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) are explicitly stated in the curriculum so that teachers are able to translate into their teaching curriculum so that teachers are able to translate into their teaching and learning to promote a
and learning to promote a structured and focused thinking amongstructured and focused thinking among students. Explanation of HOTS focuses on four levels of thinking students. Explanation of HOTS focuses on four levels of thinking as shown in Table 3.
as shown in Table 3.
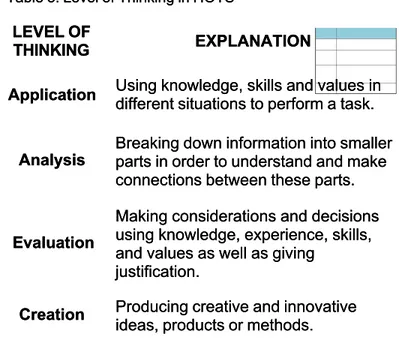
Table 3: Level of Thinking in HOTS Table 3: Level of Thinking in HOTS
LEVEL OF
LEVEL OF
THINKING
THINKING
EXPLANATION
EXPLANATION
Application
Application
Using knowledge, skills and values in
Using knowledge, skills and values in
different situations to perform a task.
different situations to perform a task.
Analysis
Analysis
Breaking down information into smaller
Breaking down information into smaller
parts in order to understand and make
parts in order to understand and make
connections between these parts.
connections between these parts.
Evaluation
Evaluation
Making considerations and decisions
Making considerations and decisions
using knowledge, experience, skills,
using knowledge, experience, skills,
and values as well as giving
and values as well as giving
justification.
justification.
Creation
Creation
Producing creative and innovative
Producing creative and innovative
ideas, products or methods.
ideas, products or methods.
HOTS is the ability to apply knowledge, skills and values to make HOTS is the ability to apply knowledge, skills and values to make reasoning and reflection to solve problems, make decisions, reasoning and reflection to solve problems, make decisions,
innovate and able to create something. HOTS includes critical and innovate and able to create something. HOTS includes critical and creative thinking, reasoning and thinking
creative thinking, reasoning and thinking strategies.strategies.
Critical thinking skills
Critical thinking skills is the ability to evaluate a certain idea is the ability to evaluate a certain idea logically and rationally in order to make sound judgements using logically and rationally in order to make sound judgements using logical reasoning and evidences.
logical reasoning and evidences. Creative thinking skills
Creative thinking skills is the ability to produce or create is the ability to produce or create something new and worthy using authentic imagination and something new and worthy using authentic imagination and thinking out of the box.
thinking out of the box. Reasoning skills
Reasoning skills is an individual’s ability to make logical andis an individual’s ability to make logical and rational considerations and evaluations.
rational considerations and evaluations. Thinking strategies
Thinking strategies is a structured and focused way of thinking is a structured and focused way of thinking toto solve problems.
solve problems.
HOTS can be applied in classrooms through reasoning, HOTS can be applied in classrooms through reasoning, inquiry-based learning, problem solving and projects. Teachers and pupils based learning, problem solving and projects. Teachers and pupils need to use thinking tools such as thinking maps and mind maps need to use thinking tools such as thinking maps and mind maps as well as high-level questioning techniques to
as well as high-level questioning techniques to encourage pupils toencourage pupils to think.