Mood and Modality Analysis on 2014 Indonesian Pre Presidential Election in
The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe Editorials
THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment
of the Requirements for the Degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan
Patrisius Wogananda Rusmawan
112014701
FACULTY OF LANGUAGE AND LITERATURE
SATYA WACANA CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
PUBLICATION AGREEMENT DECLARATION
As a member of the (SWCU) Satya Wacana Christian University, I verify that:
Name : Patrisius Wogananda Rusmawan
Student ID Number : 112014701
Study Program : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
Faculty : Faculty of Language and Literature Kind of Work : Undergraduate Thesis
In developing my knowledge, I agree to provide SWCU with a non exclusive royalty free rights for my intellectual property and the contents there in entitled:
Mood and Modality Analysis on 2014 Indonesian Pre Presidential Election in The
Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe Editorials
Along with any pertinent equipment
With this non exclusive royalty free rights, SWCU maintains the rights to copy,
reproduce, copy, print, publish, post, display, incorporate, store in or scan into a retrieval system or database transmit, broadcast, barter or sell my intellectual property in whole or in part without my express written permission, as long as my name is still included as the writer.
This declaration is made according to the best of my knowledge. Made in : Salatiga
Date :
Verified by Signee
Approved by:
Dian Toar Y. G. Sumakul, MA Christian Rudianto, M.Appling.
COPYRIGHT STATEMENT
This thesis contains no such material as has been submitted for examination in any course or accepted for the fulfillment of any degree or diploma in any university. To the best of my knowledge and my belief, this contains no material previously published or written by any other person except where due reference is made in the text.
Copyright@ 2015. Patrisius Wogananda Rusmawan and Dian Toar Sumakul
All rights reserved. No part of this thesis may be reproduced by any means without the permission of at least one of the copyright owners or the Faculty of Language and Literature, Satya Wacana Christian University, Salatiga
Mood and Modality Analysis on 2014 Indonesian Pre Presidential Election in The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe Editorials
Patrisius Wogananda Rusmawan 112014701
Abstract
The basic function of editorial is giving information to their readers. The information is usually in the form of opinions. The newspaper through their editors/journalists delivers the information in the form of attitude and opinion toward an issue to their readers. However, editorial might contain other intentions. Other intentions that might appear are persuasion and offer. This paper analyzed mood and modality of newspaper editorials, especially on their stand on Indonesian general election in 2014. This paper used two editorial texts from The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe that contain the attitude of the two newspapers in Indonesian presidential election 2014. Looking at the Mood and Modality used in the texts, the writer investigates how the two editorials were different in terms of functions. From the Mood data, this paper found that The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe Editorials is exchanging information to their readers. However, there were differences in exchanging good and service. The Jakarta Post tended to demand more information through the command speech role to their reader than The Jakarta Globe. This function was also supported by the Modality data. The editorial in The Jakarta Post has more obligation and has more high value modality compared to the editorial in The Jakarta Globe. These functional elements support the underlying purpose of each text.
Keywords: Editorial, Systemic Functional Linguistics, Discourse Analysis, Mood, Modality
Introduction
One of basic functions of language that Halliday (2004) suggested is acting out our social relationships. It is included in one of his metafunctions of language that he calls it interpersonal metafunction. This is in line with what Thompson (2004) said that one of the main purposes of
communicating is to interact with other people; to establish and maintain appropriate social links with them. In newspaper editorial, journalist interacts with other people through written article.
article that presents the newspaper's opinion on an issue. The editorial is an important article since it conveys not only one journalist’s attitude, but the whole newspaper’s attitude. The
newspaper attitude can be analyzed using Halliday’s mood and modality in interpersonal
metafunction. By looking at the mood, we can analyze the form they use the most, whether it is indicative or imperative. From modality, we can get whether it is mostly modalization or
modulation. This is in accordance with two most fundamental kinds of speech roles that Halliday (2004) mentioned, which were giving and demanding. Indicative in mood and modalization in
modality has function as giving (information) while imperative in mood and modulation in modality has function as demanding (good and service).
There are three important previous studies to put here. The first previous relevant study
found that actually newspaper is mostly giving information. This is revealed by Simarmata and R. John Pieter (2007). They said, “having probability type as the most dominant feature indicates
that editorial writer has certainty in giving the information through the text”. The second finding which is also related to mood and modality is from Alireza Bonyadi (2011). He stated that “editorial writers inclined to thematize modality possibly to increase its persuasive effect”. This
revealed that modality has relation with persuasive. The third finding suggests that mood and modality should be consolidated as Roseline Abonego Adejare (2014) stated “examining mood
and modality together has revealed fresh facts about the similarities and differences between both systems. This should be consolidated”.
competing English online newspapers (which also have hard paper circulation) in Indonesia; The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe. Before presidential election, The Jakarta Globe took a stand
to be neutral in their editorial. One day after The Jakarta Post publication, The Jakarta Post took a stand to endorse on one presidency candidate. Even though it was clear that The Jakarta Globe chose to be neutral and The Jakarta Post chooses to be on one candidate side, their journalists
had different ways in presenting their opinion toward their choices. Roger Fowler (1991) stated that language in the press is not neutral but a highly constructive mediator. Their choices of
modality words can determine their function of the text, whether they are exchanging good and service or not, particularly on command and offer to their reader. This analysis intended to show how mood and modality influence the function of editorial text. This study could also serve as
the model of functional analysis when it deals with editorials. From this approach, we can analyze the differences of mood and modality between the editorials in Jakarta Post and Jakarta
Globe. We can also analyze how the differences in mood and modality show the differences of the editorials in Jakarta Post and Jakarta Globe in terms of communicative functions.
Systemic Functional Linguistics
In 1960, Halliday introduced Systemic Functional Linguistic term in the UK and later in
Australia. Many researchers (e.g.: Thompson, 2004; Graham Lock, 1996; Martin White, 2003; Roger Fowler, 2013; and Palmer, 2001) use this approach, particularly in language education and discourse analysis. Thompson added an easier definition of mood and modality, while Graham
Halliday proposed 3 metafunctions: ideational, interpersonal, and interactional metafunctions. In ideational metafunctions, language provides a theory of human experience in
communication. It includes certain resources of the every language lexicogrammar.
The second is textual metafunction. It is related to the construction of text. Besides enabling or facilitating communication function, it is also construing experience and enacting
interpersonal relations such as being able to build up sequences of discourse, organizing the discursive flow and creating cohesion and continuity as it moves along.
The third function is interpersonal metafunction. This function sees language more as an
action. It is enacting our personal and social relationships with other people around us. This function includes when we inform or question, give an order or make an offer, and express our
appraisal of and attitude towards anyone we are addressing and what we are talking about. Mood and modality were discussed in this paper belong to interpersonal metafunction
Mood
The component of the clause that consists of Subject and Finite is called Mood. The
general principle behind the expression of MOOD in the clause is the position of Subjec and Finite. The declarative form, which is the characteristic expression of a statement, has subject in
front of the finite: S^F (Subject^Finite). Interrogative form, which is the characteristic expression of a question, has finite location before the subject: F^S (Finite^Subject). Imperative form, which is the characteristic expression of a command, does not have subject or finite (no Subject or
Table 1. Mood and Form
Adapted from Graham Lock (1996, p.177, 179)
There is an anomaly when the Mood does not serve as usual expression for example a declarative that does not characteristically express statement but command. This kind of anomaly is called Non Congruent in this paper.
Table 2. Giving or Demanding, Goods-&-Services or Information
Role in exchange Commodity exchanged giving and demanding. Giving means ‘inviting to receive’, while demanding means ‘inviting to
Mood Form
Declarative Subject^Finite
Wh - Interrogative wh-Finite^Subject
Yes No Interrogative Finite^Subject
Imperative Predicator in V(base) does not
give’. There are four kinds of expression that appear, depending on the commodity that is
exchanged. If it is goods and services and the role in exchange is giving, the expression is offer.
If it is demanding, then the expression is command. If the commodity exchanged is information and the role in exchange is giving, then the expression is statement. If it is demand, then the expression is question. Thompson (2004) stated that statements are most naturally expressed by
declarative clauses, questions by interrogative clauses, and commands by imperative clauses.
The Finite element, as its name implies, has the function of making the proposition finite. This can be done in either of two ways. The first is Reference to the time of speaking (primary
tense). Primary tense means past, present or future at the moment of speaking; time relative to
‘now’. Take an example: an old man was crossing the road. The second is Reference to the
judgment of the speaker (Modality). Modality means likely or unlikely (for a proposition), desirable or undesirable (for a proposal). The example is can’t in it can’t be true.
Modality
Modality is a part of MOOD in the finite element. What the modality system does is to construe the region of uncertainty that lies between ‘yes’ and ‘no’ (Halliday, 2004). Halliday
classified two kinds of modality. First is propositions or modalization. Other researcher prefers to use modalization and modulation than propositions and proposals. Halliday did not mention
that modalization acts as exchanging information but Thompson did. Modalization has two members, which are probability and usuality. Another kind of modality is proposals or
degrees of obligation: ‘allowed to/supposed to/required to’ and in an offer, it represents degrees
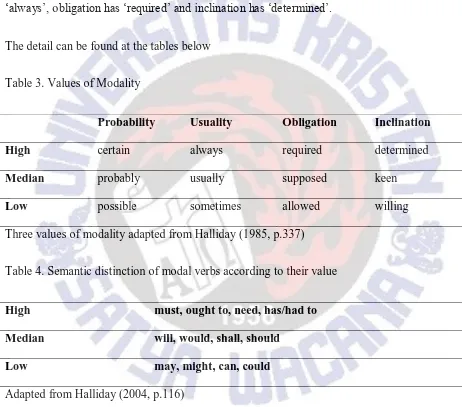
of inclination: ‘willing to/anxious to/determined to’. Another important aspect is the value of
modality. Halliday divided modality into three values:high, median and low. Every type of modality has those three values. Take example, high probability has ‘certain’, usuality has
‘always’, obligation has ‘required’ and inclination has ‘determined’.
The detail can be found at the tables below
Table 3. Values of Modality
Probability Usuality Obligation Inclination High certain always required determined
Median probably usually supposed keen
Low possible sometimes allowed willing
Three values of modality adapted from Halliday (1985, p.337)
Table 4. Semantic distinction of modal verbs according to their value
High must, ought to, need, has/had to Median will, would, shall, should
Low may, might, can, could
Adapted from Halliday (2004, p.116)
Thompson (2004) relates value of modality with responsibility. Using value of modality, it can
Previous Studies on Mood and Modality on Editorial
Having probability type as the most dominant modality indicates that editorial writer has certainty in giving the information through the text. The use of modality in the texts is related to
the context of situation and culture. Congruent realization indicates that the editorial writer does not use a wide range of variants for the expression of modality in the clause. In terms of value,
the closeness between low and high indicates that the expressions are both closer to positive or negative polar. It is the most probable modality to be executed or the least probable one to be done. (Simarmata, R. John Pieter, 2007)
In general, expressing modality mainly through modal auxiliary verbs confirmed the findings of the study conducted by Morley (2004) who acknowledged the greater importance of modals in
editorials compared with news reports. More frequent use of generic phrases like that is looking less likely … for expressing modality in both newspapers (cf. Tables no. 2,4) revealed that
editorial writers inclined to thematize modality possibly to increase its persuasive effect (Alireza Bonyadi, 2011).
In terms of modality, te study found that with a frequency of 7 in 1000 words and 5.11 in 1000
words, will and can far exceeded the reported 4.2 and 3.5 occurrences in 1 000 words by 67 and 46 percent respectively and that shall was rarer still with a frequency of 1 in 10 000 words. As
physics shows, there are strong indications that a text’s subject matter dictates the pattern of
modality marking. The need to predict relationships and results of mathematical operations made
similarities and differences between both systems. This should be consolidated (Roseline Abonego Adejare, 2014).
The Study
Research Question
The research tried to answer the following research questions:
1. What are the types of the Mood used in the editorials of The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe?
2. What are the types of the Modality used in the editorials of The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe?
3. How do the Mood and Modality influence the function of the editorials of The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe?
Context of study
This study analyzed The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe editorial differences in presenting their tone before the presidential election 2014. As commonly understood, the backgrounds of
these two newspapers were different in terms of their supports to the Presidential candidates. Therefore, through these editorials, the writers could take sides, supporting or opposing Jokowi
as the President. Looking at the chosen of Mood and Modality used in both texts, this study would analyze how the functions of the texts were different
Text editorials about Joko Widodo in The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe. The text in The Jakarta Post was published on 4th of July, 2014while the text in The Jakarta Globe was published
on 3rd of July, 2014.
Instruments of Data Collection
Halliday (2004, p. 106) states that clause has a meaning as an exchange, and this could be
observe through the existence of Subject and Finite. The data were collected based on reading every main clause that had meaning as an exchange based their Subjects and Finites. It means,
the clauses that were looked at were finite clauses.
Data Collection Procedure
First, the texts were taken from newspaper online editorial, The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe that contained news about Joko Widodo. After that, the text were analyzed using
Halliday’s Mood and Modality. The mood and modality were counted based on the type of
modality to determine the tone of editorial. The data were analyzed by focusing on the functions of the texts. The functions of each editorial was later compared. Based on the functions, finally,
the writer would see the mood and modality that influenced the tone of each editorial.
Data analysis
The data were analyzed using Halliday’s systematic functional linguistic especially in
presenting their tone of the topic. This tone difference was analysed based on the functions of the editorials determined by the mood and modality used in the texts.
Finding and Discussion
In this section, this paper will show and discuss the findings on mood and modality that appeared on two editorial text, The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe editorials. In addition, this paper will also discuss the communicative function of the texts.
Mood
Mood consists of two components, subject and finite. From the position of subject and finite, we can determine the expression of the mood whether it is indicative or imperative. Indicative has a function as giving information while imperative has a function as demanding
Table 5. Mood Finding
From the table above, declarative dominates the text. The Jakarta Post text has 92% and The Jakarta Globe has 100%. For example, “We were not silent during reformasi” is a declarative
sentence. The subject is ‘we’ and the finite is ‘were’. Subject precedes the finite position. Therefore, the structure is S^F, a typical pattern of a declarative form. The declarative form that appears on The
Jakarta Globe text is “This decision guarantees legal certainty, circumventing second-round
conflicts”. ‘This decision’ is subject and ‘guarantees’ is finite. Therefore, the structure is S ^ F, a
typical pattern of a declarative form.
However, The Jakarta Post has deviation if we compare with The Jakarta Globe text. It has 8% of imperative. An example of imperative clause on The Jakarta Post is “Stand firm in rejecting
the tide of sinister forces”. There is no subject and finite in it. Therefore, the structure is S F, a
typical pattern of an imperative form.
The two texts from two different newspapers above display declarative as the most often expression appeared. Teun A. van Djik (1995) stated that editorial in the press is generally expected to express opinions. This is in line with Alan Weintraut (n.d.) as he defines editorial as
often expression that occurs. The newspaper wants to inform their opinion of an issue to their readers.
Modality
Modality is reference to the judgment of the speaker and it is construing the region of
uncertainty that lies between ‘yes’ and ‘no’. It has modalization and modulation. modalization is
like mood’s indicative that functions as giving information and modulation is like mood’s
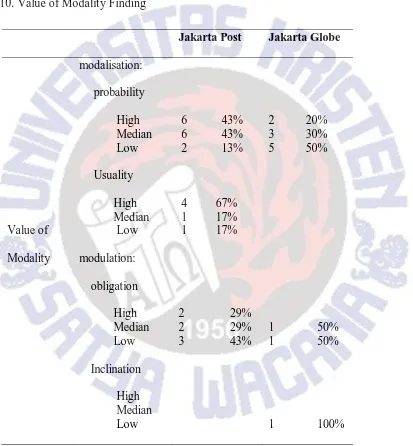
The table above illustrates that modalization is dominant. The Jakarta Post has 74% and The Jakarta Globe has 77% of modalization that consists of probability and usuality. For
example, sentence “The quake of uncertainty could produce tremors of conflict across the country” has ‘could’ as modality. The meaning of the sentence when it deals with modality is that ‘it is likely to be true’ that the quake of uncertainty produces tremors of conflict across the country. The
meaning is on probability that belongs to modalization. Another example from The Jakarta Globe is
“The quake of uncertainty could produce tremors of conflict across the country”. This sentence has
‘could’ as modality. The meaning when it deals with modality is that “it is likely to be true” that the
quake of uncertainty produce tremors of conflict across the country. The meaning is on probability that belong to Modalization.
The difference between The Jakarta Post text and The Jakarta Globe text in modality is that the proportion on modulation in The Jakarta Post text is more than The Jakarta Globe text. The Jakarta Post text has 26% and The Jakarta Globe has 23%. Furthermore, The Jakarta Post’s
modulation concentrates on all obligation without inclination. This is different from The Jakarta Globe text that has inclination.
Mood and modality data on the majority data occurred on the two texts are the same. In mood, declarative that belongs to indicative which function as giving information is the most often
expression appeared. In modality, the most often modality kind appeared is the modalization. Modalization also has function as giving information. Like what stated before. Alan Weintraut defined editorial as an article that presents the newspaper's opinion on an issue. From the
Communicative Function
Communicative function is related to mood and modality, especially in giving information and demanding good and service. This section will explain the minor data that appear in mood and
modality in both texts. The minor data will explain us the differences between The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe in term of communicative function. The first difference is on imperative and the
non congruent of declarative on mood. The second is on obligation in modality and the value of modality.
Imperative
The imperative is the mood that has function as exchanging goods-&-services and has the
characteristic expression of a command. The Jakarta Post text has 8% of imperative in mood and The Jakarta Globe text has no imperative at all.
Table 7. Imperative Finding
The imperative is the mood that has function as exchanging goods and services. From the data above, The Jakarta Post has 8% of imperative and The Jakarta Globe has no imperative.
and services while The Jakarta Globe does not demand at all. If we take a look at the headlines of both texts, The Jakarta Post endorses one candidate whereas The Jakarta Globe chooses to be
neutral. The Jakarta Post from this section had a possibility to demand their reader to choose the same candidate. On the other hand, The Jakarta Globe does not have imperative. This is in line with their choice to be neutral.
Non Congruent Speech Role
Table 8. Non Congruent of Declarative Finding
Jakarta Post Jakarta Globe example in The Jakarta Post: “But in an election like no other, we are morally bound to not stand by and do nothing”. In this sentence, the main clause is “we are morally bound to not stand by
and do nothing”. The pattern is S^F. Therefore, it is a declarative sentence. However, it does not
merely function as delivering statement. This sentence is more on delivering command than delivering statement. The command is that the writer indirectly wants the readers to choose what the newspaper chooses because “But in an election like no other, we are morally bound to not
stand by and do nothing” sentence contains moral word”moral” word. Another example is taken
coverage and discussion”. In this sentence, the main clause is “we maintain equal balance in
coverage and discussion”. The pattern is S^F. Therefore, it is declarative sentence. However, it
does not merely function as delivering statement. This sentence is more on delivering offer than delivering statement. The offer is that the writer indirectly gives the readers equal balance in coverage and discussion on news reporting.
The majority of non-congruent data in TJP is declarative command. This is different from the data of TJG that shows more on offer, in this declarative offer. Command shows that the writer demands the readers to perform certain goods and services, while an offer indicates the
provision of goods and services by the writer. This difference on non-congruent data shows that TJP article, besides providing information to the readers, also asking the readers to provide certain services to satisfy or fulfill the writer’s opinion or ideas. This is an indication, in terms of
tone, that the TJP article is more on demanding goods and service compared to TJG article.
Obligation functions as demanding good and service. Different from the imperative and the non congruent
The Jakarta Post obligation is 26% and The Jakarta Globe is 15%. This is a sign that The Jakarta Post demands more on good and service than The Jakarta Globe.
High Value of Modality
Thompson (2004) relates value of modality with responsibility. Using value of modality,
If the value of modality is high, then the speaker accepts the responsibility for the attitude of being expressed is also high.
An example from The Jakarta Post Modalization, especially in probability, is “The
Jakarta Post in its 31-year history has never endorsed a single candidate or party during an
election.” This is high value of modality by using “never”. The Jakarta Post is really sure that
they has not been endorsed a single candidate in its 31-year history. The Jakarta Post’s responsibility on saying that statement is high. Another example from The Jakarta Globe
Modalization “The press is the fourth estate of democracy, and we believe our neutrality permits
us to better carry out our role, reminding both sides to behave with fairness and integrity”. The
high value of modality is on ‘we believe’. The paper categorizes ‘we believe’ as high modality
because it has only two measurements, either ‘we believe’ or ‘we don’t believe’
The interesting examples come are from modulation area. Let’s take a look from The
Jakarta Post example: “our journalism has always stood on the belief of the right moral ground when grave choices must be made”. This sentence has two modality. The first is on ‘always’. This is part of modalization, especially on high value of probability. The second one is on ‘must’. ‘Must’, according to Halliday (2004), is included in high value of modality. This
becomes high value of modulation because of the words “the right moral ground”. This is a high
suggestion for the readers to choose on the newspaper belief to stand on “the right moral
ground”. Different type of high modulation appears on The Jakarta Globe text. There is no
obligation type on The Jakarta Globe. It is inclination and unfortunately there is no high value of
Inclination but median one. For example, “we will continue to provide critical coverage of the
included in medium value of modality. This sentence belongs to inclination because its offers to provide critical coverage of the government for the benefit of the Indonesian people.
The high value of modality, if we relate it to communicative function, has two functions.
The high value of modalization shows that the newspaper is highly responsible on information they share. The high value of modulation displays that the newspaper is highly responsible on
good and service they demand.
The Jakarta Post’s majority data in modalization and modulation is on median to high value of modality. This is an indicator that The Jakarta Post has high responsibility about
information they share and good and service they demand. This is different with The Jakarta Globe that put their responsibility on median to low value of modality.
The differences on the value of Modality are caused by the intention of the text. The two texts have the same topic but different intention. The mostly median to high value is good for
The Jakarta Post because of the responsibility they take in inform and demand is high. This is different with The Jakarta Globe. It might be not necessary to be highly responsible on the information and good and service and the share and demand since they inform their neutrality.
Conclusion
By doing mood and modality analysis, the two editorials have the same pattern, that they
both mostly give information, although they have different standing in the general election. This also indicated that mood and modality have similarity in meaning between indicative and modalization. This can be an indication that the basic function of editorial is to give information.
The differences between The Jakarta Post and The Jakarta Globe are in the appearance of imperative and rhe non-congruent of declarative. The imperative and the non-congruent of
declarative in this two editorials match with their tone of editorials. The Jakarta Post editorial has imperative and the most non-congruent of Declarative is Command, which match with the tone of endorsing on one candidate. The Jakarta Globe has 100% declarative and the most non
congruent of declarative is offer, which match with their tone of editorial in choosing to be neutral.
The obligation data and the value of modality data are also different. On obligation, The Jakarta Post has bigger percentage than The Jakarta Globe. The Jakarta Post has a tendency in demanding more on good and service than The Jakarta Globe. The Jakarta Post has another
intention, which is to persuade their readers to choose what TJP choose. This is also in line with the endorsing tone of TJP editorial.
This research can open the eyes of people, especially educated people, that editorial has give and demand function. This research also deepens the understanding of students in
This research is still lack of mood subject analysis and subjectivity/objectivity. Further research can add them to make the analysis better. The readers’ comment on editorial website is
also beneficial. It can be analyzed if the researcher looks for two-ways communication.
References
Adejare, R. A. (2014). The Manifestation of Mood and Modality in Texts. English Linguistics
Research, 3(1), p18.Bell, A., & Garrett, P. (Eds.). (1998). Approaches to media discourse.
Wiley-Blackwell.
Bonyadi, A. (2011). Linguistic manifestations of modality in newspaper editorials. International Journal of Linguistics, 3(1), E30.
Fowler, R. (2013). Language in the News: Discourse and Ideology in the Press. Routledge.
Halliday, M.A.K. 1994. An Introduction to Functional Grammar (2nd Ed).London: Edward ArnoldHalliday, M.A.K. and Christian M.I.M Matthiesen. 2004. An Introduction to Functional
Grammar (3rd Ed). London: Hodder Arnold
Halliday, M. A. K., & Matthiessen, C. M. (2013). Halliday's Introduction to Functional Grammar
4th Edition. Routledge.
Halliday, M. A. K. (2002). On grammar (Vol. 1). Bloomsbury Publishing.
Halliday, M. A. K. (2003). On language and linguistics (Vol. 3). A&C Black.
Lock, G. (1996). Functional English grammar: An introduction for second language teachers. Cambridge University Press.
Thompson, G. (2004). Introducing Functional Grammar 2nd Edition. Hodder Education Palmer, F. R. (2001). Mood and modality. Cambridge University Press.
Van Dijk, T. A. (1995, December). Opinions and ideologies in editorials. In 4th International Symposium of Critical Discourse Analysis, Language, Social Life and Critical Thought,
Athens (pp. 14-16).
Acknowledgement
I am willing to present my thanks for everyone who has helped me, especially in this paper. All of honors are just for Jesus Christ, The Almighty, with His grace this paper could be done.My Beloved Parents. Thank you so much for your affection and help in all my life, your
love is beyond any words. My Advisor, Dian Toar Y. G. Sumakul, MA for his valuable advice, and suggestion which are very helpful in finishing this paper. Thank you very much for your
time to share your great knowledge and great experiences to me. My Examiner Christian Rudianto, M.Appling who has guided me with his worthy correction and suggestion to improve
the paper’s quality. The Dean of Faculty Language and Literature, Victoria Usadya Palupi,
MA-ELT, for her contribution and attention. All lecturers of Faculty of Language and Literature SWCU, who have transferred much knowledge to me. My Beloved friends of SEVENERS.
Thanks for our togetherness and your attention to me. The last, this paper is far from being perfect, but it is expected that this skripsi will be useful not only for the researcher, but also the readers. For this reason, constructive thought full suggestion and critics are well come to make
this paper better.
Salatiga, May 2015