ABSTRACT
Dwiaji, Belinda Hana. 2016. Easy English Learning Android Application (EEL): An M-Learning Model to learn Speaking Skill for Grade XI Students. Yogyakarta: The Graduate Program in English Language Studies, Sanata Dharma University.
Speaking should be acquired by students since they are supposed to be able to communicate using English both spoken and written. As mobile technology has grown rapidly in educational sector, it creates new opportunities for improving learning experience of students at all levels of education. In addition, the use of mobile technologies has supported the implementation of Mobile Learning (M-Learning). Therefore, the researcher felt necessary to utilize the mobile devices as a learning media to support the XI grade students’ speaking skill by developing a learning model using Android application as a media that were appropriate for research questions, the researcher combined an instructional ADDIE model by Roger (2002) and the steps of R & D cycle by Borg and Gall (1983). The application was designed based on some theories of mobile learning (Elias, 2011), characteristics of well-designed software (Egbert &Hanson-Smith, 1999), principles of MALL (Stockwell & Hubbard, 2013), and aspects of speaking skill (Brown, 2001; Brown, 2004; Nunan, 2003; Richard & Renandya, 2002). The data were in the forms of quantitative and qualitative data. The quantitative data were gathered from questionnaire. Meanwhile, to obtain the qualitative data, open-ended questions in the questionnaires, interviews, and observation were conducted. The research was conducted in SMA Bopkri 2 Yogyakarta.
The result of this research was the iconic model of an Android Application, namely Easy English Android Application (EEL). EEL consists of three main sections in each lesson, namely Let’s Start, Let’s Practice, and Let’s Have Fun. Let’s start contains the materials to build the students’ knowledge about the topics. Let’s practice contains several activities which support their speaking skills. Let’s have fun contains some fun materials to arouse students’ interests. EEL was appropriate for XI grade students to learn speaking skill since it provided activities related to students’ grammatical sentence production, vocabulary mastery, comprehension, pronunciation ability, and fluency (Brown, 2001; Brown, 2004; Nunan, 2003; Richard & Renandya, 2002). The findings showed that EEL was considered as good and useful by the mean score of 1.41 out of (-2) to 2 and useful to help the students in learning speaking. EEL is also flexible and practical, which is in line with the principle of m-learning (Elias, 2011) since the product is easy to operate, simple, and helpful to learn English speaking skill.
ABSTRAK
Dwiaji, Belinda Hana. 2016. Easy English Learning Android Application (EEL): An M-Learning Model to learn Speaking Skill for Grade XI Students. Yogyakarta: Program Pasca-Sarjana Kajian Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Berbicara (speaking) sebaiknya dicapai oleh siswa karena mereka diharuskan mampu berkomunikasi menggunakan bahasa Inggris baik lisan maupun tertulis. Karena mobile technology telah berkembang secara pesat pada sektor pendidikan, hal itu menciptakan kesempatan baru dalam meningkatkan pengalaman pembelajaran siswa di seluruh tingkat pendidikan. Selain itu, penggunaan teknologi mobile telah mendukung penerapan model pembelajaran
Mobile Learning (M-Learning). Oleh karenanya, peneliti perlu memanfaatkan
perangkat mobile sebagai media pembelajaran untuk mendukung kemampuan
speaking siswa kelas XI dengan mengembangkan model pembelajaran aplikasi
Android sebagai media yang sesuai dengan kebutuhan pembelajaran siswa.
Terdapat dua permasalahan inti dalam penelitian ini. Yang pertama adalah seperti apakah model ikonik aplikasi Android untuk siswa kelas XI. Sedangkan, yang kedua adalah bagaimana model ikonik aplikasi Android mendukung kemampuan speaking siswa. Untuk menjawab permasalahan tersebut, peneliti menggabungkan ADDIE model instruksional dari Roger (2002) dengan tahap siklus Penelitian dan Pengembangan dari Borg & Gall (1983). Aplikasi ini didesain berdasarkan teori m-learning (Elias, 2011), karakteristik desain software (Egbert &Hanson-Smith, 1999), prinsip MALL (Stockwell & Hubbard, 2013), dan aspek-aspek speaking (Brown, 2001; Brown, 2004; Nunan, 2003; Richard & Renandya, 2002). Ada dua jenis data dalam penelitian ini, yaitu data kuantitatif dan kualitatif. Data kuantitatif diperoleh dari kuesioner. Sedangkan, untuk mendapatkan data kualitatif, dilakukan pertanyaan kuesioner terbuka, wawancara, dan observasi. Penelitian ini dilaksanakan di SMA Bopkri 2 Yogyakarta.
Hasil penelitian ini merupakan model ikonik aplikasi Android, bernama
Easy English Android Application (EEL). EEL terdiri dari tiga bagian utama pada
setiap lesson, yaitu Let’s Start, Let’s Practice, and Let’s Have Fun. Let’s start berisi materi untuk membangun pengetahuan siswa tentang topik yang akan dipelajari. Let’s Practice berisi beberapa kegiatan yang mendukung kemampuan
speaking. Let’s Have Fun berisi berbagai materi dan kegiatan yang menyenangkan untuk menarik perhatian siswa. Aplikasi ini sesuai untuk siswa kelas XI dalam belajar speaking karena terdapat kegiatan-kegiatan yang berhubungan dengan penggunaan tata bahasa, penguasaan kosakata, pemahaman, kemampuan percakapan, dan kefasihan (Brown, 2001; Brown, 2004; Nunan, 2003; Richard & Renandya, 2002). Hasil penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa aplikasi ini dianggap baik dan berguna dengan skor rerata 1.41 dari (-2) sampai 2 dan bermanfaat untuk membantu siswa dalam belajar speaking. EEL juga fleksibel dan praktis, sesuai dengan prinsip m-learning (Elias, 2011) karena produk tersebut mudah dioperasikan, praktis dan berguna untuk belajar speaking.
Kata kunci: Android, EEL, media pembelajaran, m-learning, siswa kelas XI,
EASY ENGLISH LEARNING ANDROID APPLICATION (EEL): AN M-LEARNING MODEL TO LEARN SPEAKING SKILL FOR GRADE
XI STUDENTS
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements
for the Degree of Magister Humaniora (M.Hum.)
in English Language Studies
by
Belinda Hana Dwiaji
136332032
THE GRADUATE PROGRAM OF ENGLISH LANGUAGE STUDIES SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
iv
I dedicate my thesis for my beloved parents in heaven
Finally, I could finish my thesis, Dad...
Special for my late Father,
No one has ever been given more love, encouragement, and unconditional support than
you have,
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
First and foremost, praise to My Almighty Lord, Jesus Christ for His
blessings, countless love and strength perfectly poured into my life, I could finally
finish my thesis.
I would like to give deepest, sincere, and great appreciation to my thesis
advisor, Dr. B.B. Dwijatmoko, M.A., who is willing to spend his precious time
and giving his greatest advice, support, patience, and guidance during the
accomplishment of my thesis. My deepest gratitude also goes to F.X. Mukarto,
Ph.D., for his precious time guiding us, the SEAMOLEC students. I would also like to thank all lecturers in English Language Studies for sharing invaluable
knowledge, lesson, and experiences that I have got throughout my study. My
deepest gratitude also goes to Director of SEAMOLEC for the funding and their
dedication to introduce how to use technology in education.
I would like to express my gratitude to F. Chosa Kastuhandani, S.Pd.,
M.Hum., Willy Sudiarto Raharjo, S.Kom., M.Cs, and Ronald Adrian, S.T., M.Eng, Ariatmi P.H., S.Pd., and all XI Language Department students of SMA Bopkri 2 Yogyakarta for their willingness to be the research participants during
completing my thesis.
For my late father and late mother in heaven, thank you for endless
love and everything. My one and only sister, Mbak Fani, thank you for
unconditional support and caring, my lovely little brother, Jeremia Sasmita Aji,
and mother, Kitin Sumaryati, thank you for being there for me.
My sincere thanks go to my SEAMOLEC friends, Mbak Marga, Ika,
Mbak Desi, Mas David, Mas Vendi, and Mbak Shanti, thank you for sharing knowledge, wonderful moment, and struggling hard together during our study.I
would also like to express my truly gratefulness to Mbak Mifta and Mbak Pipit,
who always support me to finish my thesis. I also greatly express my deepest
thanks to Oki Wicaksono, who being my tutor, thank you for the time and help in
developing EEL application. My deepest gratitude also goes to Sandy, Mbak
viii
sharing the ideas and discussion during my study. Special thanks to Pak Mul,
Mbak Marni, and Mbak Eli for sharing information and giving help to me. Last but not least, I would also thank to my friends and people whose
names I could not mention, but surely, I cannot complete my thesis without their
ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE... i
APPROVAL PAGE... ii
DEFENSE APPROVAL PAGE... iii
DEDICATION PAGE... iv
STATEMENT OF ORIGINALITY... v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT... vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS... ix
LIST OF TABLES... xi
LIST OF FIGURES... xii
LIST OF APPENDICES... xiii
ABSTRACT... xiv 1. Learning Speaking Skill... a. The Nature of Learning... b. The Nature of Speaking Skill... c. Learning Speaking... d. Learning Speaking using Technology... 2. Android Application Model... a. Mobile Learning (M-Learning)... b. Mobile Assisted Language Learning (MALL)... c. Android... 1) The Nature of Android... 2) Android Development Program... 3. High School Context... a. Students... b. Curriculum... c. Core and Supplementary Materials... 4. Instructional Design Model... B. Review of Related Studies... C. Theoretical Framework... C. Research Setting and Participants... D. Data Collection Technique... E. Data Analysis Technique...
x
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS... A. Process of Developing the Iconic Model... 1. Information Collecting (Analysis)... 2. Planning... 3. Development... a. Develop preliminary form of product... b. Preliminary Field Testing... c. Main Product Revision... 4. Main field Testing... 5. Evaluation... B. The Description of the Iconic Model of Android Application... C. The Description on How EEL Supports the Speaking Skills...
78 78 78 99 104 105 109 128 130 139 140 154 CHAPTER V: CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS...
A. Conclusions... B. Suggestions...
xi
LIST OF TABLES
Page
Table 2.1. Micro-skills and macro-skills of Speaking... 17
Table 2.2. UID Recommendations for M-Learning Adapted from Elias (2011)... 24
Table 2.3. Standard of Competence and Basic Competence of Senior High School grade XI... 42
Table 3.1. The Combined Model of Borg & Gall (R & D) and ADDIE Model... 60
Table 3.2. The Description of the Expert Validators... 66
Table 3.3. The Steps, Data Needed, Participants, Instrument, and Time... 67
Table 3.4. Conversion Table of the Raw Scores into the Converted Scores... 74
Table 3.5. The Description of the Questionnaire Result... 74
Table 3.6. A Scale of Five using a Criterian Reference Evaluation (CRE)/ PAP... 75
Table 4.1. Standard of Competence and Basic Competence of Senior High School grade XI... 79 Table 4.2. The Topics for Speaking Skills of Senior High School Grade XI for Semester 1 and 2... 81 Table 4.3. The Blueprint of the Need Analysis Questionnaire... 82
Table 4.4. The Meaning of Point of Agreement... 83
Table 4.5 The Conversion Table of the Raw Scores into the Converted Score... 84
Table 4.6. The Mean Criteria (Sukarjo, 2006)... 84
Table 4.7. The Need of English and Speaking Skill... 85
Table 4.8. Students and Technology... 94
Table 4.9. The Topics, Activities, and Learning Indicators... 100
Table 4.10. The Description of the Contents and parts of EEL... 106
Table 4.11. The Descriptive Statistics of Materials Experts Opinion... 111
Table 4.12. The Experts Opinions of Media Aspects in the Application... 114
Table 4.13. The Experts’ Comments and Suggestions about the Product... 120 Table 4.14. The Users’ Opinion toward the Materials Aspects... 121
Table 4.15. The Users’ Opinion about the Parts of EEL application... 125
xii
LIST OF FIGURES
Page
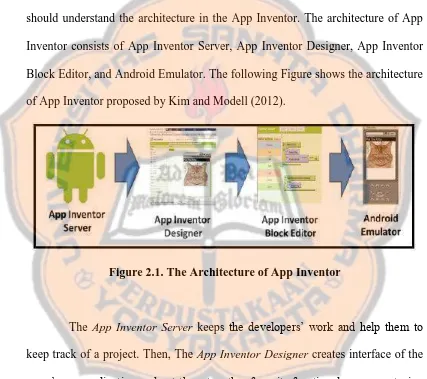
Figure 2.1. The Architecture of App Inventor... 38
Figure 2.2. App Inventor Designer... 39
Figure 2.3. The Blocks of a screen in App Inventor... 40
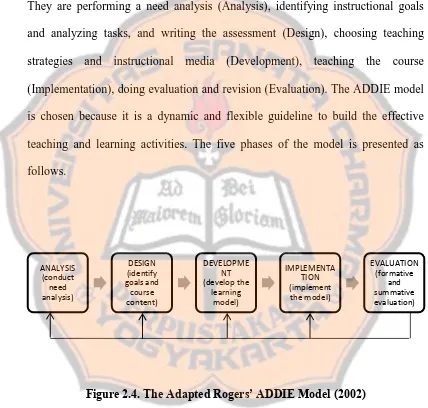
Figure 2.4. The Adapted Rogers’ ADDIE Model (2002)... 45
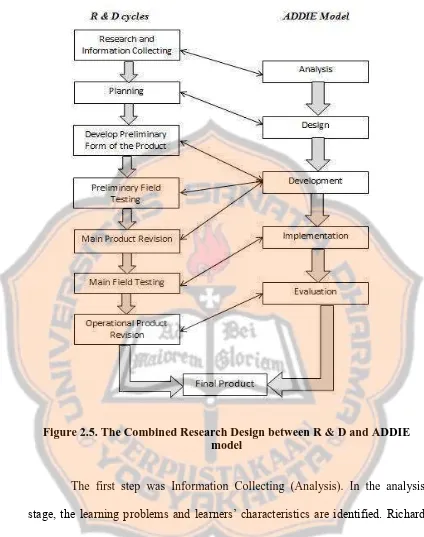
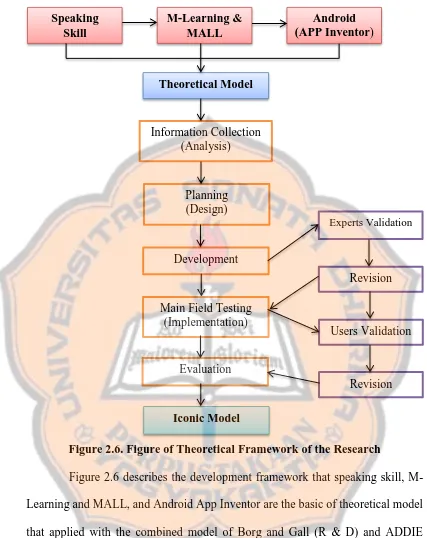
Figure 2.5. The Combined Research Design between R & D and ADDIE model... 47 Figure 2.6. Figure of Theoretical Framework of the Research... 53
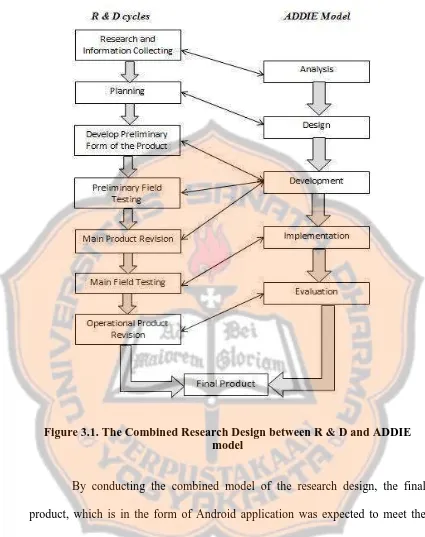
Figure 3.1. The Combined Research Design between R & D and ADDIE model... 64
Figure 4.1. The layout before revision... 129
Figure 4.2. The layout after doing revision... 130
Figure 4.3. The Icon of EEL in handphone screen... 141
Figure 4.4. The Home screen of the Final Version of EEL... 142
Figure 4.5. The Menu Screen of EEL... 143
Figure 4.6. The Section of Lesson Menu Screen of EEL... 144
Figure 4.7. The Let’s Start’s Screen Preview of EEL... 145
Figure 4.8. The Example of the Activities in Let’s Start Section of EEL... 146
Figure 4.9. The Activities in Let’s Practice Section... 148
Figure 4.10. The Scoring System in EEL... 150
xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES
Page
Appendix 1 Syllabus... 172
Appendix 2 Blueprint of Questionnaires... 176
Appendix 3 Interview Guideline... 183
Appendix 4 Flowchart... 185
Appendix 5 Storyboard... 189
Appendix 6 Questionnaires... 196
Appendix 7 The Result of Questionnaires... 211
Appendix 8 Interview Transcription... 223
Appendix 9 Field Note... 238
Appendix 10 Photo Documentation... 241
xiv ABSTRACT
Dwiaji, Belinda Hana. 2016. Easy English Learning Android Application (EEL): An M-Learning Model to learn Speaking Skill for Grade XI Students. Yogyakarta: The Graduate Program in English Language Studies, Sanata Dharma University.
Speaking should be acquired by students since they are supposed to be able to communicate using English both spoken and written. As mobile technology has grown rapidly in educational sector, it creates new opportunities for improving learning experience of students at all levels of education. In addition, the use of mobile technologies has supported the implementation of Mobile Learning (M-Learning). Therefore, the researcher felt necessary to utilize the mobile devices as a learning media to support the XI grade students’ speaking skill by developing a learning model using Android application as a media that were appropriate for research questions, the researcher combined an instructional ADDIE model by Roger (2002) and the steps of R & D cycle by Borg and Gall (1983). The application was designed based on some theories of mobile learning (Elias, 2011), characteristics of well-designed software (Egbert &Hanson-Smith, 1999), principles of MALL (Stockwell & Hubbard, 2013), and aspects of speaking skill (Brown, 2001; Brown, 2004; Nunan, 2003; Richard & Renandya, 2002). The data were in the forms of quantitative and qualitative data. The quantitative data were gathered from questionnaire. Meanwhile, to obtain the qualitative data, open-ended questions in the questionnaires, interviews, and observation were conducted. The research was conducted in SMA Bopkri 2 Yogyakarta.
The result of this research was the iconic model of an Android Application, namely Easy English Android Application (EEL). EEL consists of three main sections in each lesson, namely Let’s Start, Let’s Practice, and Let’s Have Fun.
Let’s start contains the materials to build the students’ knowledge about the topics. Let’s practice contains several activities which support their speaking skills. Let’s have fun contains some fun materials to arouse students’ interests. EEL was appropriate for XI grade students to learn speaking skill since it provided activities related to students’ grammatical sentence production, vocabulary mastery, comprehension, pronunciation ability, and fluency (Brown, 2001; Brown, 2004; Nunan, 2003; Richard & Renandya, 2002). The findings showed that EEL was considered as good and useful by the mean score of 1.41 out of (-2) to 2 and useful to help the students in learning speaking. EEL is also flexible and practical, which is in line with the principle of m-learning (Elias, 2011) since the product is easy to operate, simple, and helpful to learn English speaking skill.
xv ABSTRAK
Dwiaji, Belinda Hana. 2016. Easy English Learning Android Application (EEL): An M-Learning Model to learn Speaking Skill for Grade XI Students. Yogyakarta: Program Pasca-Sarjana Kajian Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Berbicara (speaking) sebaiknya dicapai oleh siswa karena mereka diharuskan mampu berkomunikasi menggunakan bahasa Inggris baik lisan maupun tertulis. Karena mobile technology telah berkembang secara pesat pada sektor pendidikan, hal itu menciptakan kesempatan baru dalam meningkatkan pengalaman pembelajaran siswa di seluruh tingkat pendidikan. Selain itu, penggunaan teknologi mobile telah mendukung penerapan model pembelajaran
Mobile Learning (M-Learning). Oleh karenanya, peneliti perlu memanfaatkan
perangkat mobile sebagai media pembelajaran untuk mendukung kemampuan
speaking siswa kelas XI dengan mengembangkan model pembelajaran aplikasi
Android sebagai media yang sesuai dengan kebutuhan pembelajaran siswa.
Terdapat dua permasalahan inti dalam penelitian ini. Yang pertama adalah seperti apakah model ikonik aplikasi Android untuk siswa kelas XI. Sedangkan, yang kedua adalah bagaimana model ikonik aplikasi Android mendukung kemampuan speaking siswa. Untuk menjawab permasalahan tersebut, peneliti menggabungkan ADDIE model instruksional dari Roger (2002) dengan tahap siklus Penelitian dan Pengembangan dari Borg & Gall (1983). Aplikasi ini didesain berdasarkan teori m-learning (Elias, 2011), karakteristik desain software (Egbert &Hanson-Smith, 1999), prinsip MALL (Stockwell & Hubbard, 2013), dan aspek-aspek speaking (Brown, 2001; Brown, 2004; Nunan, 2003; Richard & Renandya, 2002). Ada dua jenis data dalam penelitian ini, yaitu data kuantitatif dan kualitatif. Data kuantitatif diperoleh dari kuesioner. Sedangkan, untuk mendapatkan data kualitatif, dilakukan pertanyaan kuesioner terbuka, wawancara, dan observasi. Penelitian ini dilaksanakan di SMA Bopkri 2 Yogyakarta.
Hasil penelitian ini merupakan model ikonik aplikasi Android, bernama
Easy English Android Application (EEL). EEL terdiri dari tiga bagian utama pada
setiap lesson, yaitu Let’s Start, Let’s Practice, and Let’s Have Fun. Let’s start berisi materi untuk membangun pengetahuan siswa tentang topik yang akan dipelajari. Let’s Practice berisi beberapa kegiatan yang mendukung kemampuan
speaking. Let’s Have Fun berisi berbagai materi dan kegiatan yang menyenangkan untuk menarik perhatian siswa. Aplikasi ini sesuai untuk siswa kelas XI dalam belajar speaking karena terdapat kegiatan-kegiatan yang berhubungan dengan penggunaan tata bahasa, penguasaan kosakata, pemahaman, kemampuan percakapan, dan kefasihan (Brown, 2001; Brown, 2004; Nunan, 2003; Richard & Renandya, 2002). Hasil penelitian ini menunjukkan bahwa aplikasi ini dianggap baik dan berguna dengan skor rerata 1.41 dari (-2) sampai 2 dan bermanfaat untuk membantu siswa dalam belajar speaking. EEL juga fleksibel dan praktis, sesuai dengan prinsip m-learning (Elias, 2011) karena produk tersebut mudah dioperasikan, praktis dan berguna untuk belajar speaking.
Kata kunci: Android, EEL, media pembelajaran, m-learning, siswa kelas XI,
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
This chapter provides the general explanations of the research. There are
research background, problem identifications, problem limitations, research
questions, research objectives, and research benefits.
A. Background
As English becomes the global language in the world, people’s demand for
mastering English is gradually increasing. The widespread need for English as a
second language or foreign language needs a considerable pressure on the
educational resources of many countries. In countries where English is regarded
as a foreign language not as a second language, for instance in Indonesia, it may
be an important school subject and necessary to pass an examination in English to
enter a school or university. According to Richard, Platt, & Weber (1985:93), as a
foreign language, English has a role as a subject in school but used as a medium
of instruction in education not as a language of communication in government,
business, or industry within the country.
English becomes a compulsory subject taught by most school in Indonesia,
starting from kindergarten, elementary school, junior high school, senior high
school until university. English as one of the subject matters in school covers the
four basic language skills: listening, speaking, reading, and writing. As the main
speaking skill take the highest place as the most important skill to master (Bright
& McGregor, 1970). Speaking, which is said to be one of the productive skills of
a language, is an essential part in learning a language. As stated by Spratt, Mary,
et. al. (2005: 34), speaking is a productive skill, like writing which involves using
speech to express meanings to other people. Therefore, speaking is a productive
skill involves not only an active or productive participation but also receptive
participation.
Speaking is crucial skill that should be acquired by the learners. It is also
as a part of people’s daily life. They have to communicate what they are thinking
to create an interaction with others until there will be a meaningful and purposeful
interaction. In line with Lazarton (Kurniawati, 2013), speaking is an active
interaction between speaker and listener as the process of building and sharing
meaning involving the components of pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary,
fluency and comprehension.
Nowadays people have been living in the globalization era in which the
development of technology in most aspect of life grows rapidly. Consequently,
they try to find a lot of information through the existence of technology for
instance by using internet. People can browse a lot of information and news
through internet. The development of English is related to the growth of
technology as well. Technology can change the way people work, learn, interact,
and spend the leisure time. It also helps to lead the way in improving the teaching
as a learning media as well. It is remarkable when technology is implemented in
teaching and learning process.
The implementation of English curriculum considers the use of
technology. The use of technology is an essential part to support the process of
teaching and learning in order to make it more interesting. So far, video, cassette,
and power point presentation are used in teaching-learning processes. In addition,
it will be one of the teaching and learning instructional that is used either in the
class or outside the class. According to National Research Council (1995),
technology offers new ways of teaching and learning, and provides new ways for
all involved in education to be openly accountable to parents, communities, and
students. The use of technology can facilitate the learners’ achievement since it
provides interesting media to learn English to become more fun and effective.
Technology has an important role in teaching and learning process. Bajcsy
(2002) says that technology in teaching and learning as an enabler and suggests
that technology can work to help organize and provide structure for material to
students; help students, teachers, and parents interact, anytime and anywhere;
facilitate and assist in the authentication and prioritization of Internet material;
and simulate, visualize, and interact with scientific structures, processes, and
models. For instance, the students are able to find the additional materials from
the internet. As stated by Dudeney and Hockly (2007) that internet access is
becoming increasingly available to learners, younger learners are growing in
technology era, and English as an international language is being used in
media to support the teaching and learning materials without the limitation of
time.
As the use of technology grow rapidly in educational sector, many
educational institutions have the opportunity to make use of the internet as a
communication medium for the institution. Previously, the use of internet or
technology is popularly referred to as CALL (Computer Assisted Language
Learning). According to Warschauer (1996) states that CALL is an approach to
teaching and learning foreign languages through which the computer and
computer-based resources such as the internet are used to present, reinforce, and
assess material to be learned. The use of internet has been widely spread
everywhere especially for the students. They can easily browse any kind of
sources they want by using internet not only students who utilize the technology
but also the teachers. Teachers are not merely using textbook to teach their
students, but they can adapt and develop the materials from the internet.
Nowadays, the use of internet can be more easily accessed through mobile
devices. Another term, MALL (Mobile Assisted Language Learning) has come to
its existence to provide independent and effective learning. Kukulska-Hulme and
Shield (2008) define MALL as an access to wireless device network that can
communicate with such networks increase, the use of mobile devices in
supporting language learning becomes more common. They also differ MALL
from CALL related to its use of personal, portable devices that enable new ways
of learning which emphasize access and interaction in different contexts.
(Miangah & Nezarat, 2012). They state that MALL can be considered an ideal
solution to language learning barriers in terms of time and place.
As mobile technology has entered into the mainstream society, it
influences people’s lifestyle in recent years. It changes people’s way of work,
study, and daily act. (Calimag, Miguel and Conde, 2014) state that mobile devices
can facilitate human interaction and access to information resources anytime and
anywhere. People use these smart phones, for instance Android smartphones in
the various ages. Since mobile technology develops, it creates new opportunities
for improving learning experience of students at all level of education. It
facilitates students to access educational resources without need to be present at
the working environment. Mobile devices are a useful tool and a way to access
last recent events in the classroom (Calimag, Miguel and Conde, 2014).
However, related to the English teaching and learning in Senior High
School, the students are supposed to be able to communicate using English both
spoken and written. The problem that has arisen is that the students have less
ability in speaking English. When the teacher triggers a question, the students did
not answer the question whereas the topic had been taught before. Moreover, the
students were lack of vocabulary mastery. The students were not able to express
their ideas in English. They often have difficulties in finding appropriate words to
express their ideas. It shows that they have limited language experiences. Another
problem is sometimes they made pronunciation mistakes because they have rarely
Furthermore, since there are various English learning applications which
can be downloaded in Google play store, the students should utilize the
application since they have Android smart phones in their life style. As we know
that there have been so many speaking application found in Google play store, the
students should utilize the applications to improve their speaking skill to support
their learning environment. They should be able to learn them by themselves. The
learners can get more access to use those applications to give new experience in
learning environment where they are given more opportunity to learn outside the
classroom (Anderson et al., 2008). However, the content of the materials of the
applications provided in the play store do not meet with the students’ needs. They
are only provide general materials and not specifically intended to certain grades.
Besides, the students also rarely use their smartphones effectively. They would
rather use it for the social media rather than for supporting the learning activity.
Considering the facts, the researcher feels necessary to utilize the mobile
devices as a learning media to support the students’ speaking skill by developing a
learning tool using Android application that are intended to the eleventh grade
students and appropriate for their learning needs. The learning media provides
English materials, vocabulary activity, pictures, audio learning, and kinds of tasks,
which is appropriate to syllabus of grade XI. By using android as a media, the
students will be easier to learn English anywhere since it is effective and efficient,
so the students’ can be more frequent to learn English. Therefore, this research
attempts to develop an Android application-learning model of speaking skill to
B. Problem Identification
There are many problems occur faced by senior high school students
related to speaking in teaching and learning process. The problem arises that the
students have less ability in speaking English. The problems will be elaborated in
the following.
First, the students were lack of vocabulary mastery. The students are not
able to express their ideas in English. The students have less ability in speaking
English well. When the teacher triggers a question, the students did not answer the
question whereas the topic had been taught before. They often have difficulties in
finding appropriate words to express their ideas. It shows that they have limited
language experiences. Second, the students often make pronunciation mistakes. It
is because they have rarely practice how to pronounce words. They were also lack
of listening input. Consequently, they are not able to practice speaking with
correct pronunciation and intonation.
The next is since most of students have mobile devices, such as Android
phones in their life style, it has spread and considered as not-an-expensive things
for them. They will be familiar with several Android applications such as social
media, games, and other application. However, the use of Android smartphones in
their life style has not been used effectively to support their learning environment.
They would rather use it for the social media rather than for supporting the
learning activity. Besides, although there are various applications that facilitate
language learning, the content of the materials of the applications provided in the
In conclusion, there is a great opportunity to use technology as a
supporting media to learn English speaking for students. As they are supposed to
be able to communicate in English, they need more exposure and speaking
practice not only in the classroom where they have English lesson, but they are
supposed to be able to get access to English speaking materials anytime and
anywhere. In order to help the students to learn speaking skill, the researcher tried
to develop a learning media as a supporting tool for learning English speaking
which is flexible, portable, and attractive. This is in line with Trifonova &
Ronchetti (2003b) cited in Trifonova, et.al (2014) which state that mobile learning
is a field that recently has attracted the interest of lots of researchers in the
learning domain. Therefore, the researcher would utilize the use of mobile devices
such as smart phones and tablets using Android as the Operating System (Android
OS). Android is an open source mobile operating system that has been supported
by Google Corporation, the world-leading search Engine Company (Cabanban,
2013). By developing such Android application-learning model, the speaking
problems that occurred need to be overcome soon.
C. Problem Limitation
In reference to the identification of the problem above, problems
encountered in the teaching learning process are complex. Therefore, in this
research, there are some limitations of the study. In this research, there is no
experimental study to discover the effect after they have experienced using the
validation. In addition, it concerns with the speaking skill for the eleventh grade
students of Senior High School. As speaking is crucial skill that should be
acquired by the students, they are supposed to be able to communicate with
others. They need more exposure and speaking practices not only in the classroom
when they have English lesson, but also they can learn speaking outside the
classroom anywhere and anytime. Besides, the developed application contains
supplementary materials that in accordance with the syllabus of the eleventh grade
students.
The last, the limitation is the reason why this research focused on
developing Android application as the learning model. Android is selected due to
its flexibility and accessibility that can be downloaded freely by the users. Most
gadgets which is accessible by users is Android. Android is an open source mobile
operating system supported by Google Corporation (Cabanban, 2013). By using
android smartphones or tablets, users can download many applications from
Google play store such as social medias, tools, musics, games, books, etc.
However, most users only use this kind of gadget for entertainment. Therefore,
the researcher intends to utilize this gadgets, especially for students, as a media in
learning English especially to support the eleventh grade students speaking skill.
D. Research Questions
This research proposes two questions to be answered, they are as follows.
1. What does the iconic model of Android application for Senior High School
2. How does the iconic model of Android application for Senior High School
grade XI students support their speaking skill?
E. Research Objectives
In line with the presented research questions, therefore there are two
objectives of this research. First is to present the final version of iconic model of
Android application for Senior High School grade XI students. The researcher
combines the steps in R & D model proposed by Borg and Gall (1983) and
ADDIE model (Roger, 2002) in developing the application. The model is
designed based on the students’ need that consists of several materials and tasks
that support students’ speaking ability. Those are pictures, audio-learning
materials and tasks, multiple-choice tasks, and matching tasks. The construction
of Android-based application learning model will consider the theory and nature
of teaching speaking, Android application inventor, and also curriculum used as a
guideline in designing the materials.
The second objective is to find out how the iconic model of Android
application for Senior High School grade XI students supports their speaking
skills. By implementing Android-based application learning model, the students
will be easier to learn English speaking anywhere since it is effective and
F. Research Benefits
This research is expected to give some benefits to English speaking
learning. The benefits of the study cover theoretical and practical significance.
Theoretically, this study is expected to give contributions as a relevant study to
enrich the educational researches that are related to develop English learning
materials. Moreover, the mobile learning model in the research will support the
implementation of Mobile Assisted Language Learning (MALL).
Kukulska-Hulme and Shield (2008) define MALL as an access to wireless device network
that can communicate with such networks increase, the use of mobile devices in
supporting language learning becomes more common. This research also used
principles in developing and implementing mobile language learning (Stockwell
and Hubbard, 2013). Therefore, the findings of the research are expected to give
more insight in developing the learning materials using mobile technology for
other researchers who carry out same studies in different settings.
Practically, this study provides the learning model that contains materials
that is significant for Senior High School grade XI students. The application is
designed based on students’ need and combined with learning objectives to
achieve their competence. It is expected that the students are able to practice their
speaking skill easily and enjoyably. Moreover, this research encourages the
students to get more English speaking skill practice using technology. By utilizing
this learning model, it is expected that the students are able to use and practice this
learning model without any boundaries of time. The application will be used as
12 CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW
As the main objective of this study is to develop the iconic model of
Android application for senior high school grade XI students to support their
speaking skill, some related theories are presented in this part. This chapter
presents the theoretical review, review of related studies, and theoretical
framework related to learning speaking skill, Android application model, high
school context, and instructional design model. The followings are the discussions
of each item.
A. Theoretical Review
This section is divided into four major parts. They are the theory of
learning speaking skill, EEL Android Application/ Android Application Model,
High School Context, and Instructional Design Model. The further explanation
will be presented as follows.
1. Learning Speaking Skill
This section deals with some points related to learning speaking skills
involving the broad area of interest. They are the nature of speaking, the nature of
speaking skill, learning speaking, and learning speaking using technology. They
are presented as follows.
a. The Nature of Learning
Learning means acquiring knowledge by studying or experiencing
According to Slavin (2003) cited in Brown (2007), learning defines as a change in
an individual caused by experience. Meanwhile, Woofolk (1998:204) says that
learning happens when experience causes a relatively permanent change in an
individual‟s knowledge or behavior. The similar concept that can be drawn from
the definition is “experience” which means that to learn is to experience.
Therefore, learning is when people experience something, there will be a change
related to their knowledge and behavior.
In addition, Brown (2007:8) defines learning as:
1. Learning is acquisition or “getting”.
2. Learning is retention of information or skill.
3. Retention implies storage systems, memory, and cognitive organization.
4. Learning involves active, conscious focus on and acting upon events outside or inside the organism.
5. Learning is relatively permanent but subject for forgetting. 6. Learning involves some form of practice, perhaps reinforced
practice.
7. Learning is a change in behavior.
From the above concepts of learning, it can be inferred that learning is
acquiring the information or skill which involves storage systems, memory,
cognitive organization, recall, motivation, conscious and subconscious learning
styles and strategies, theory of forgetting, reinforcement, and the role of practices
which can change the people‟s behavior.
Furthermore, Gagne (1965) cited in Brown (2007) proposes eight types
of learning. The first is signal learning.which occurs in the total language process.
It means that the learners make a general response of some kind of language
(emotional, cognitive, verbal, or non-verbal). The second is stimulus or response
learning, which is the acquisition of the sound system of a foreign language. In
is the acquisition of phonological sequences and syntactic patterns. The fourth
type of learning is verbal association which differs between verbal and nonverbal
chains. The next is multiple discrimination. In this type, the learners respond to
many different stimuli, which means that each word has several meaning based on
the context. The sixth type is concept learning which includes the relationship
between language and cognition. In this case, the learners should be able to give
common response that identifies the entire class of objects or events. The next
type is principle learning which is the extension of concept learning to the
formation of linguistic system. In this type, the learners try to organize the
experience and behavior. The last type is problem solving which is a kind of
learning which refers to thinking. In this type, the learners faced some problems
which need to be overcome that need creative interaction in solving the problems.
b. The Nature of Speaking Skill
Speaking is a communicative event that includes the use of verbal and
non-verbal language to convey meaning. In line with Chaney (Jondeya, 2011: 28),
speaking is the process of building and sharing meaning through the use of verbal
and non-verbal symbols, in a variety of context. According to this definition,
speaking is aiming at exchanging meanings. To achieve the aim, people use their
articulators to produce language so that they could express meanings to others. In
addition, they also make use of non-linguistic symbols such as facial expressions
and body language in order to make the meanings more clear.
Speaking is communication between two people or more to deliver
feelings, and beliefs by talking it with other people and it usually involves the
speakers‟ physical, physiological, and psychological condition. This is in line with
Hybel (Ardiani, 2013: 10), speaking is any process in which people share
information, ideas, and feeling, it involves all of body language mannerism and
style-anything that adds meaning to a message.
Speaking is a productive skill. As stated by Spratt, et.al. (2005) speaking
involves the speaker to use speech to express meanings to other people. In the
same line, Nunan (2003) says that speaking is a productive oral skill that involves
the production of verbal utterance to comprehend meaning. Chastain in Castillo
(2007) also declares that speaking is a productive skill that involves many
components. It is more than producing the right sounds, choosing the right words
or getting construction of grammatically correct. It includes the background
knowledge of speakers to create opinions or feelings to be communicated with
listeners. Therefore, the listeners often judge others by evaluating and analyzing
the messages of their speaking.
Furthermore, speaking is a productive skill involves not only an active or
productive participation but also receptive participation. Byrne (Jondeya, 2011)
also states that speaking is a two-way process between speakers and listeners and
it involves the productive skills of language and the receptive skills of
understanding. In the same respect, Nunan (2003: 48) supports Byrne‟s statement
saying that speaking is the productive skill that consists of producing systematic
verbal utterances to express meaning. The product of the activity of speaking is
verbal utterances in which people usually have communicative purposes by
feelings, to give commands, to make jokes, to agree or complain about something.
This is also in line with Widdowson (1996: 59) who declares that the skill of
speaking involves both receptive and productive participation. Receptive aspect of
speaking is the skill which is conventionally referred to as‟ listening‟. While,
productive aspect of speaking referred to as „saying‟. It can be concluded that
speaking has a productive part when one participant in an interaction assumes the
active role of speaker.
Speaking is a two-way process between producing language and
receipting it. It is in line with Bygate (1997:5) that there are two ways which
something we do in oral skill. They are motor-perceptive skills and interactional
skills. Motor-perceptive skills involve perceiving, recalling, and articulating in the
correct order of sounds and structures of the language. Then, interactional skill is
a skill that uses the knowledge and basic perceptive skills to achieve the
communication. It involves the making decisions of communication, for example;
what to say, how to say, and whether to develop it, in accordance with one‟s
intentions, while maintaining the desired relations with others. In line with
Bygate, Brown and Yale as quoted by Nunan (1989:26-27) begin their discussion
on the nature of spoken language by distinguishing spoken and written language.
It is stated that written language is characterized by well-formed sentences which
are integrated into highly structured paragraph. Spoken language, on the other
hand, consists of short, often fragmentary utterances, in a range of pronunciations.
In conclusion, speaking is the two-way process of productive and
receptive skill, which include the use verbal and non-verbal language to to deliver
others, they include the process of producing language and receipting messages.
Therefore, speaking is one of important elements of communication because it
could be used as the medium of social interaction.
In mastering speaking, it is necessary to understand some skills that
underline it. There are some micro-skills and macro-skills of speaking which need
to be considered in learning speaking. The micro-skills refer to producing the
smaller chunks of language such as phonemes, morphemes, words, collocations,
and phrasal words. The macro-skills imply the speaker‟s focus on the larger
elements: fluency, discourse, function, style, cohesion, nonverbal communication,
and strategic options. The micro-skills and macro-skills of speaking, according to
Brown (2004: 142-143), are presented on the following table.
Table 2.1. Micro-skills and macro-skills of Speaking Microskills
1) Produce difference among English phonemes and allophonic variants. 2) Produce chunks of language of different lengths.
3) Produce English stress patterns, words in stressed and unstressed positions, rhythmic structure, and intonation contours.
4) Produce reduced forms of words and phrases.
5) Use an adequate number of lexical units (words) to accomplish pragmatic purposes.
6) Produce fluent speech at different rates of delivery.
7) Monitor one‟s own oral production and use various strategic devices -pauses, fillers, self-corrections, backtracking- to enhance the clarity of the message.
8) Use grammatical word classes (nouns, verbs, etc), systems (e.g. tense, agreement, pluralization), word order, patterns, rules, and elliptical forms.
9) Produce speech in natural constituents: in appropriate phrases, pause groups, breath groups, and sentence constituents.
10) Express a particular meaning in different grammatical forms. 11) Use cohesive devices in spoken discourse.
Macroskills
12) Appropriately accomplish communicative functions according to situations, participants and goals.
(Table 2.1 continued)
13) Use appropriate styles, registers, implicature, redundancies, pragmatic conventions, conversation rules, floor-keeping and –yielding, interrupting, and other sociolinguistic features in face-to-face conversations. Convey links and connections between events and communicative such as relations as focal and peripheral ideas, events and feelings, new information and given information, generalization and exemplification.
14) Convey facial features, kinesics, body language, and other nonverbal cues along with verbal language.
15) Develop and use a battery of speaking strategies, such as emphasizing key words, rephrasing, providing a context for interpreting the meaning of words, appealing for help, and accurately assessing how well your interlocutor is understanding you.
The above table shows that the students need to learn language as well as
its function. It is expected that showing the micro-skills and macro-skills of
speaking to them could help them convey and negotiate meaning of language.
Speaking is a very demanding activity for all ages of learner which is
used for oral communication. Speaking skill needs a lot of practice. According to
Pinter (2005), speaking practice starts with practicing and drilling set phrases and
repeating models. Therefore, the learners need to practice with different activities
in classroom in order to encourage them to develop their proficiency in speaking
so that they are able to communicate effectively. Brown (2001) classifies that
there are five basic types of speaking. The first type is imitative. Imitating is for
focusing on some particular element of language form rather than for the purpose
of meaningful interaction. Drills offer students an opportunity to listen and orally
repeat to certain strings of language that may pose some linguistic problems. It
covers the ability to imitate a word of phrase or possibly a sentence. The second
one is intensive. Intensive speaking includes any speaking performance that is
designed to practice some phonological or grammatical aspects of language.
comments. These replies are usually sufficient and do not extend into dialogue. It
includes interaction and comprehension test but at the somewhat limited level of
very short conversations, standard greeting and small talk, simple request and
comments. The stimulus usually happens in a spoken at the appointed time in
order to maintain authenticity.
The next is transactional (dialogue) which has the purpose of conveying
or exchanging specific information. Then, interpersonal (dialogue) is carried out
more for the purpose of maintain and sustaining social relationship than for the
transmission and information. The last type is extensive (monologue). This type
of speaking covers extensive oral production tasks includes oral reports or
presentations, summaries, short speech, and storytelling. In this type, the language
style is frequently deliberative and formal. The five types of speaking that
previously explained can be implemented in classroom speaking activity.
c. Learning Speaking
In learning to speak a foreign language, learners should understand the
context on how the native speakers use the language. Richard and Renandya
(2002) state that learners must acquire the knowledge of how native speakers use
the language in the context of structured interpersonal exchange, in which many
factors interact. In English as a foreign language (EFL) context, speaking is a
crucial part of English language learning and teaching which needs special
attention and instruction. When people communicate with others, their intention to
what they feel and what they think. Nunan (2003) says that in order to
communicate well, people should understand with whom they are speaking.
In learning speaking, learners should be able to determine the purpose of
their speaking so that it might influence the way of their speaking. Richard and
Renandya (2002) define that the purpose of speaking can be describing things,
complaining people‟s behavior, making polite requests, or entertaining people
with jokes or anecdotes. Those different purposes for speaking infers knowledge
of rules on how spoken language reflects the situation in which the speech occurs,
th participants involved and their relationship, and the activities of the speakers
are involved. Therefore, it can be inferred that learners have to be able to
understand the purposes of their speaking in order to be able to speak fluently and
appropriately.
In terms of learning the speaking skills, learning speaking is important to
learners‟ language acquisition and academic learning. People are able to
communicate with language by two ways, acquisition and learning. Krashen and
Terrel (1983) state that language acquisition is knowing the language by
subconscious process while learning language is knowing the language by
conscious process. In this case, learning and teaching are related to each other. To
learn means knowing something while teaching is letting learners know
something. Language cannot be separated from language taching. Brown (2000)
states that teaching cannot be defined apart from learning, teaching is guiding and
facilitating learning. Therefore, in the context of language learning, teachers
should be able to guide and facilitate students in using the language in
speaking, teachers need to show the details of how to convey and negotiate the
meaning of language. It means that the teacher should have good techniques to
teach the students so that they can learn language easily.
The objective of teaching speaking is to help learners communicate in the
target language. The reach the goal, teachers should follow certain principles for
teaching speaking, which could be useful for developing speaking tasks and
materials for them. Nunan (2003: 54-56) sets the principle of teaching speaking.
First, the teachers should be aware of the difference between second and foreign
language. In learning speaking, the teachers should understand the context of
second language and foreign language situation. The second language situation
means the target language that is used in communication in the learners‟ society.
Meanwhile, the foreign language context means the target of language that is not
used in communication in the learners‟ society. Second, the teachers should give
students chances to practice with fluency and accuracy. Next, the teachers should
provide opportunity for students to talk in group or pairs in which teacher‟s talk is
limit. The purpose is to give the opportunity to the students to talk more in order
to facilitate them to communicate with others. Fourth, the teachers should plan
speaking tasks to involve negotiation of meaning. It involves checking to see the
understanding what people said, clarifying the students‟ understanding, and
confirming that someone has understood the meaning. Last, the teachers should
design classroom activities that involve guidance and practice in both
transactional and interactional speaking.
According to the principles above, the teachers should facilitate students
what they know, to produce more language, and to take part in group work
activities. Moreover, the English teachers need to give motivational feedback
when they make mistakes. They should guarantee the students to use the target
language both accurately and fluently. They also should give chance for them to
experience transactional and interactional language. This may help them to
survive in social interaction and professional life.
The principles in teaching speaking are important to enhance speaking in
the teaching and learning process. In order to keep on the intentional
communicative class, the teacher should considers those principles. The principles
also help teacher to design the appropriate materials. Brown (2001: 275-276) also
suggests some principles for designing speaking techniques. First is using
techniques that cover the spectrum of learner needs, from language-based focus
on accuracy to message-based focus on interaction, meaning, and fluency. This
principle concerns with how to make meaningful activities without throwing away
the learners‟ needs. It means that the teacher should maintain balance among
accuracy, fluency, and meaning. The second is providing intrinsically motivating
techniques. It is generally occurred that the students do not understand the
objective of doing tasks giving and benefit of achieving linguistic competence.
The teacher should give them understanding about them in order the students are
interested and motivated to learn better. It means that the teacher should link the
students‟ interest and their need for knowledge to achieve the competence. The
next is encouraging the use of authentic language in meaningful contexts.
Teaching and learning activities will be more interesting if the teacher provides
give the students the materials that are relevant to the students‟ knowledge,
experience, and interest. It means that the meaningful interaction is important to
encourage the students‟ willingness to speak in the target language. The fourth
principle is providing appropriate feedback and correction. The teacher should
give feedback appropriately now since the most EFL students are totally
dependent on the teacher. The next is capitalizing the natural link between
speaking and listening. As the teacher focuses on the speaking goals, listening
goals may naturally precede. Skills in producing language are often initiated
through comprehension.
The sixth is giving students opportunities to initiate oral communication.
It means that the activities should give a lot of opportunities for the students to
initiate the target language. The last principle is encouraging the development of
speaking strategies. This means that the students do not have to worry about their
low level of proficiency since they will build their personal speaking strategies for
accomplishing oral communication purposes. In conclusion, the teaching of
speaking should motivate the students to practice both fluency and accuracy
activities for meaningful purposes. Thus, the English teachers have to use
encouraging and motivating techniques that support the students in learning
speaking.
d. Learning Speaking using Technology
As the development of technology today has given many advantages for
people‟s life style, many experts and educators of institution believe that
learning activities. Technology has a significant role in teaching and learning
process. Bajcsy (2002) says that technology in teaching and learning as an enabler
and suggests that technology can work to help organize and provide structure for
material to students; help students, teachers, and parents interact, anytime and
anywhere; facilitate and assist in the authentication and prioritization of Internet
material; and simulate, visualize, and interact with scientific structures, processes,
and models.
Related to speaking, technology can serve as media for learning speaking
skill. By implementing the use of technology in learning speaking in the
classroom, students will be motivated to learn more. Technology improves
motivation to create authentic task to motivate, and it can be carried out by
creating a reason from speaking in target language, and broadening the audience
base. Technology can also increase communication which equipped with audios,
videos and activities that are boosting the learners‟ ability to speak. In this case,
the students have opportunity to record their performance, they can be able to
evaluate their performance and practice more. In the same line, Banares (2010)
proposes the benefits of recording the students‟ performance for example students
have more speaking practices, the students pay more attention to pronounce the
words since they will be listened to the rest of the group, motivation is high since
the students are digital authors of the course content, shy students are not left
behind. In this case, the students are able to recognize their speaking product. By
recording their performance, the students will know what they do and what they
In regard with advanced development of technology, there is an
opportunity to develop mobile learning model to support the teaching and learning
process. Therefore, the researcher intended to conduct a study by utilizing a
mobile technology to develop learning model to support the students in learning
speaking skill.
2. Android Application Model
In designing the android application model, there are some theories
related to android application model. They are the theory of mobile learning
(m-learning), mobile assisted language learning (MALL), and Android. The
elaboration of each theory will be explained as follows.
a. Mobile Learning (M-Learning)
The advance development of technology grows rapidly in many sectors.
In recent years, mobile technology has entered into the mainstream society which
affecting the people‟s life style. Calimag, et.al. (2014) state that mobile devices
can facilitate human interaction and access to information resources anytime and
anywhere. Since mobile technology develops, it creates new opportunities for
improving learning experience of students at all level of education. As stated by
Tayebinik & Puteh (2012) mobile phones are popular in education due to its
portability and wide access. In addition, mobile phones with high capabilities, i.e.
smart phones have been extensively accessible among the society. Mobile
technologies have been used in the teaching and learning process to facilitate the
students to access educational resources without need to be present at the working
interest in developing learning media. As stated by Trifonova & Ronchetti
(2003b) cited in Trifonova, A. et.al. (2004), mobile learning is a field that recently
has attracted the interest of lots of researchers in the learning domain. The use of
mobile phone as the learning media is familiar with the term mobile learning
(m-learning).
There are some point of views regarding the definition of m-learning.
Cabanban (2013) defines m-learning as a type of e-learning that delivers
educational contents and learning support materials through wireless
communication devices. In the same line, Traxler (cited in Cabanban, 2013)
describes mobile learning as the use of handheld computers in classroom which is
personalized, connected, and interactive. Mobile learning is the implementation of
delivering the educational learning materials through mobile devices. It is also
supported by Trifonova, A. et.al. (2004) that basically m-learning is considered as
any form of studying, teaching or learning that is delivered through a mobile
device or in a mobile environment. Mobile learning includes the use of mobile
phones, MP3 players, Personal Digital Assistants (PDAs) such as Palm hand-held
computers and devices using Windows Mobile Computing platform such as the
iPAQ (Dudeney and Hockly, 2007: 156). This is also in line with O‟Malley, et al.
(2003), m-learning defines as learning that occurs through wireless devices such
as mobile phones, personal digital assistants (PDAs), or laptop computers.
As m-learning becomes a new bridge in doing educational activities, it
enables the learners to do the learning activities without boundary of time.
M-learning has some characteristics which give positive benefits toward the learners.