ABSTRACT
Malasari, Susanti. 2017. Android Application to Improve Senior High School Students’ Speaking Skill. Yogyakarta: The Graduate Program in English Language Studies, Sanata Dharma University.
Being able to communicate in English fluently is the concern of every individual in this world because it gives some advantages in this life. For example, a fluent English speaker can get more opportunities to study or work overseas. The importance of being fluent in English influences the Senior High School students to improve their speaking fluency. In order to be able to communicate in English fluently, the students should practice it frequently. However, they have limited English exposures and opportunity to use English. In the classroom, the opportunity to use English is limited because of the limited time. In addition, the students rarely have chances to use English outside the school because the environment has limited English exposure. Therefore, the writer is interested in designing an Android application for Senior High school students. The application can be used as the supplementary materials for the students to practice their speaking both inside and outside the school.
There are two questions formulated in the problem formulation, they are: (1) What does the Android application for Senior High School students look like? (2) How does the Android application improve Senior High School students’ speaking skill?
In order to answer the problems, the research combined ADDIE model with Borg and Gall’s (1983) R & D cycle. The quantitative and qualitative data were used as the main data of this study. The quantitative data were obtained from qustionnaire; while the qualitative data were obtained from the open ended questions in the questionnaire and interview.
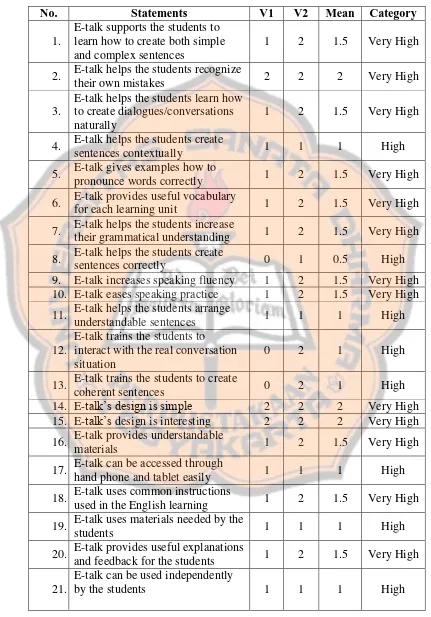
The answer of the first question shows the description of the Android application. The application is named e-talk. E-talk is an English learning application which is aimed to improve Senior High School students’ speaking skill. This application consists of five main features: vocabulary, grammar, expression, conversation and project which are developed based on the speaking theories proposed by Harmer (2001), Goh and Burns (2012) and Louma (2004). On the other hand, the application was designed based on the principles of mobile learning proposed by Elias (2011) and Egbert and Handson-Smith (1999). Each feature in the application provides some activities based on the aspects of speaking which is developed based on the learning objectives stated in the syllabus. The answer of the second question concerns with how the application improve the Senior High School students’ speaking skill. The result shows that the application eases speaking practice by the mean score 1.5 out of 2. It helps the students improve their vocabulary, pronunciation, fluency and comprehension through the features and activities provided in the applications
ABSTRAK
Malasari, Susanti. 2017. Aplikasi Android untuk Meningkatkan Kemampuan Speaking Siswa Sekolah Menengah Atas. Yogyakarta: Program Pascasarjana Kajian Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Berbahasa Inggris secara lancar menjadi perhatian setiap individu di seluruh dunia karena memberikan beberapa keuntungan. Contohnya, seseorang yang dapat berkomunikasi dengan Bahasa Inggris mempunyai kesempatan yang lebih banyak untuk dapat belajar maupun bekerja di luar negeri. Pentingnya berbahasa Inggris dengan lancar mempengaruhi siswa Sekolah Menengah Atas untuk meningkatkan kemampuan berhahasa Inggrisnya. Untuk itu, siswa perlu mempraktikkannya secara rutin. Akan tetapi, mereka mempunyai kesempatan terbatas untuk menggunakan Bahasa Inggris. Di kelas, siswa hanya mempunyai sedikit kesempatan untuk praktik karena keterbatasan waktu. Sedangkan di luar kelas, siswa jarang menggunakan Bahasa Inggris karena mereka tidak bersosialisasi dengan Bahasa Inggris. Oleh karena itu, penulis tertarik untuk mendesain sebuah aplikasi Android yang dapat digunakan para siswa sebagai materi tambahan untuk praktik berbahasa Inggris baik di dalam maupun di luar kelas.
Terdapat dua pertanyaan yang dinyatakan dalam rumusan masalah, yaitu: (1) Seperti apakah aplikasi Android untuk Siswa Sekolah Menengah Atas? (2) Bagaimanakah aplikasi Android tersebut meningkatkan kemampuan speaking siswa Sekolah Menengah Atas?
Untuk menjawab pertanyaan tersebut, penelitian ini menggabungkan model instruksional ADDIE dan siklus Penelitian dan Pengembangan milik Borg dan Gall (1983). Data kuantitatif dan kualitatif digunakan sebagai data utama pada penelitian ini. Data kuantitatif diperoleh dari kuesioner, sedangkan data kualitatif diperoleh dari pertanyaan uraian yang terdapat pada kuesioner serta wawancara.
Jawaban dari pertanyaan pertama adalah deskripsi aplikasi Android. Aplikasi tersebut diberi nama e-talk. E-talk adalah aplikasi pembelajaran Bahasa Inggris yang ditujukan untuk meningkatkan kemampuan speaking siswa Sekolah Menengah Atas. Aplikasi ini terdiri dari lima fitur utama, yaitu: vocabulary, grammar, expression, conversation dan project yang dikembangkan berdasarkan teori-teori speaking yang dikemukakan oleh Harmer (2001), Goh dan Burns (2012) dan Louma (2004). Sedangkan aplikasi tersebut didesain berdasarkan prinsip-prinsip pembelajaran mobile yang dikemukakan oleh Elias (2011) dan Egbert dan Handson-Smith (1999). Setiap fitur pada aplikasi tersebut
menyediakan aktivitas-aktivitas berdasarkan aspek-aspek speaking yang dikembangkan berdasarkan tujuan pembelajaran pada silabus. Jawaban dari pertanyaan kedua membahas tentang bagaimana aplikasi tersebut membantu siswa Sekolah Menengah Atas meningkatkan kemampuan speakingnya. Hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa aplikasi tersebut meningkatkan kemampuan speaking dengan skor rerata 1.5 dari skor maksimal 2. Aplikasi tersebut membantu siswa
ANDROID APPLICATION TO IMPROVE SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ SPEAKING SKILL
A Thesis Presented to
The Graduate Program in English Language Studies in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
for the Degree of
Magister Humaniora (M. Hum.)
in English Language Studies
by
Susanti Malasari Student Number: 136332038
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
i
ANDROID APPLICATION TO IMPROVE SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL STUDENTS’ SPEAKING SKILL
A Thesis Presented to
The Graduate Program in English Language Studies in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
for the Degree of
Magister Humaniora (M. Hum.)
in English Language Studies
by
Susanti Malasari Student Number: 136332038
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
DEDICATION PAGE
life is about to choose ...
... whether you want to be strong or weak...
happy or sad ...
whatever your choice is, live your life fully ...
because your life depends on how you shape it ...
This thesis is gratefully dedicated to
My beloved parents
My younger brother and his family
My friends and Colleagues
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to praise my God, Allah SWT, for the Most Gracious love, mercy and guidance. His strength empowers me to face this life especially in writing my thesis.
My greatest gratitude goes to my thesis advisor, Dr. B. B. Dwijatmoko, M. A. for his time, advice, ideas, comments, suggestions and also his patience in guiding me during the writing process of my thesis. I would also thank F. X. Mukarto, Ph. D. for his best guidance, advice and support for SEAMOLEC students. My deepest gratitude goes to all the lecturers of The Graduate Study Program Of English Language Studies for sharing their knowledge and helping me broaden my knowledge and skill. My gratitute also goes to the Director of SEAMOLEC, Dr. Ir. Gatot Hari Priowirjanto, and SEAMOLEC for funding and sharing useful knowledge about technology for the future education. A great appreciation goes to Henny Herawati, S. Pd., M. Hum. for inspiring my life through her drawings and poems. My deepest thank goes to all the staff at secretariat and Pak Mul for their help during my study. I would also thank Sanata Dharma University librarians for their kindness in helping me finding references that were useful for my study and my thesis.
viii
spending their time to be my research validators. Your suggestions and advice are very useful for the process of writing my thesis. I thank Mas Oki and Ika for helping me dealing with the Android application. I also appreciate Grade X3 students of SMAN 3 Bantul for their willingness to be my research participants.
My gratitude goes to my family: My Father, Murjoko Maiyanto, my mother, Warsih, my younger brother, Ari, my sister-in-law, Dhesi and my little niece, Meisya. I thank them for their love, support, prayers and encouragement. I also thank for every smile, every joke, every great moment in my life and everything they have given to me. May God always give us a great amount of peace so that we can have such a great live in this world.
My special thanks go to my colleagues in my office for coloring my working days. They all have been so nice and great friends in the office. I also thank Rizal for his help and support. My deepest thanks go my SEAMOLEC and KBI 2013 friends, who are so friendly and kind. I would express my gratitude for Mbak Pipit, Anin and Askar for encouraging me to finish this study. I also thank Mas Kasan Kurdi for the photo that beautifies my dedication page.
Last but not least I would like to express my deepest thanks to everybody who has helped and supported me in writing my thesis and for those who have come and beautified my life. I cannot mention one by one but I truly thank them for everything they have given to me. May God bless you all.
ix
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... vii
x
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 50
A. Research Method ... 50
B. Research Design ... 52
C. Research Setting and Participants ... 55
1. Research Setting ... 55
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS ... 66
A. The Processes of Developing the Learning Media (ETALK) ... 66
1. Information Collecting ... 66
a. Syllabus Analysis ... 67
b. Need Analysis Questionnaire and Interview Script Design ... 70
c. The Need Analysis from Questionnaire Results ... 72
d. The Need Analysis from Interview Results ... 80
2. Planning ... 84
3. Development ... 87
a. Developing the Materials ... 87
b. Developing the Storyboard and Flowchart ... 89
c. Developing the Application Using App Inventor ... 91
d. Building the Application into.apk File ... 93
xi
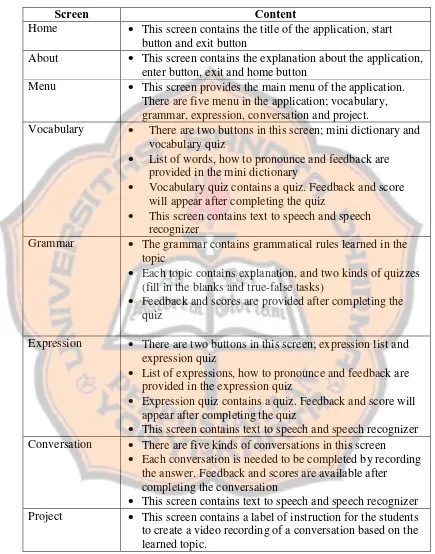
2. Introductory Page of the Application ... 114
3. The Menu of the Application ... 115
4. The Vocabulary Feature ... 116
5. The Grammar Feature ... 120
6. The Expression Feature ... 124
7. The Conversation Feature ... 129
8. The Project Feature ... 131
C. How E-talk Improves Senior High School Students’ Speaking Skill ... 132
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 137
A. Conclusions . ... 137
B. Suggestions ... 139
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 141
xii
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1 Micro Skills of Oral Communication ... 11
Table 2.2 Four Categories of Speaking Skill ... 13
Table 3.1 The Combined Model of R & D and ADDIE Model ... 51
Table 3.2 The Description of the Expert Validators ... 56
Table 3.3 Stages, Instruments, Participants, Data and Aims ... 56
Table 3.4 The Description of Need Analysis Questionnaire Results ... 62
Table 3.5 The Conversion Table of the Raw Scores into Converted Score ... 63
Table 3.6 The CRE Scales ... 63
Table 3.7 The Description of the Validation Questionnaire Results ... 65
Table 4.1 The Competency Standard and the Basic Competence of Speaking Skill for Grade X ... 67
Table 4.2 Grade Tenth’s Semester 1 and 2 Speaking Materials ... 68
Table 4.3 The Selected Speaking Materials for the Application ... 69
Table 4.4 The Working Concepts of Need Analysis Questionaire and Interview Script ... 70
Table 4.5 The Teaching of Speaking in the Classroom ... 73
Table 4.6 The Students’ Speaking Strategies ... 75
Table 4.7 The Media Used by the Students to Practice Speaking ... 76
Table 4.8 The Students’ Aspects of Speaking ... 78
Table 4.9 The Topics, Materials, Activities and Learning Objectives ... 85
Table 4.10 Features and Activities ... 86
Table 4.11 The Parts and the Contents of Each Part in e-talk ... 90
Table 4.12 The Descriptive Statistics of Material Experts’ Opinion ... 95
Table 4.13 The Descriptive Statistics of Media Experts’ Opinion ... 96
Table 4.14 The Description of the Categorization of the Scores ... 98
Table 4.15 The Comments and Suggestions from the Experts ... 103
Table 4.16 The Students’ Opinion about the Materials ... 106
Table 4.17 The Students’ Opinion about the Media ... 107
xiii
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 2.1 Android System Architecture ... 29
Figure 2.2 The Designer Interface ... 34
Figure 2.3 The Blocks Editor ... 35
Figure 2.4 The Emulator ... 35
Figure 2.5 The ADDIE Model ... 39
Figure 2.6 The Dick and Carey Model ... 42
Figure 2.7 Theoretical Framework Model ... 48
Figure 3.1 The Writer’s Combined Model of ADDIE and R & D ... 54
Figure 4.1 Home page of e-talk ... 113
Figure 4.2 E-talk Introductory Page 1 ... 114
Figure 4.3 E-talk Introductory Page 2 ... 114
Figure 4.4 Menu Screen of E-talk ... 116
Figure 4.5 The Vocabulary Screen of E-talk ... 116
Figure 4.6 The Vocabulary Topic Screen of E-talk ... 117
Figure 4.7 The Vocabulary List ... 118
Figure 4.8 The Pronunciation Practice ... 118
Figure 4.9 The Pronunciation Drill Feedback ... 119
Figure 4.10 Vocabulary Quiz Screen ... 120
Figure 4.11 The Feedback and Score ... 120
Figure 4.12 The Grammar Topic ... 121
Figure 4.13 The Grammar Activity ... 121
Figure 4.14 The Grammar Explanation Screen ... 121
Figure 4.15 The Grammar Exercise 1a ... 122
Figure 4.16 The Grammar Exercise 1b ... 122
Figure 4.17 The Grammar Exercise 1 Score ... 123
Figure 4.18 The Grammar Exercise 2a ... 124
Figure 4.19 The Grammar Exercise 2b ... 124
Figure 4.20 The Grammar Exercise 2 Feedback and Score ... 124
Figure 4.21 The Expression Screen of E-talk ... 125
Figure 4.22 The Expression Topic Screen of E-talk ... 126
Figure 4.23 The Expression List ... 127
Figure 4.24 The Pronunciation Practice Screen ... 127
Figure 4.25 The Pronunciation Drill Feedback ... 127
xiv
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1 English Syllabus of Senior High School Grade X ... 146
Appendix 2 The Blueprint of Questionnaires ... 154
Appendix 3 The Flowchart and Storyboard of E-talk ... 160
Appendix 4 Need Analysis Questionnaire ... 183
Appendix 5 Experts Validation Questionnaire ... 188
Appendix 6 Users Validation Questionnaire ... 194
Appendix 7 Interview Guidelines ... 197
Appendix 8 The Results of Need Analysis Questionnaire ... 199
Appendix 9 The Results of Experts Evaluation Questionnaire ... 203
Appendix 10 The Results of Users Validation Questionnaire ... 210
Appendix 11 Interview Transcription ... 216
Appendix 12 Photo Documentation ... 229
xv ABSTRACT
Malasari, Susanti. 2017. Android Application to Improve Senior High School Students’ Speaking Skill. Yogyakarta: The Graduate Program in English Language Studies, Sanata Dharma University.
Being able to communicate in English fluently is the concern of every individual in this world because it gives some advantages in this life. For example, a fluent English speaker can get more opportunities to study or work overseas. The importance of being fluent in English influences the Senior High School students to improve their speaking fluency. In order to be able to communicate in English fluently, the students should practice it frequently. However, they have limited English exposures and opportunity to use English. In the classroom, the opportunity to use English is limited because of the limited time. In addition, the students rarely have chances to use English outside the school because the environment has limited English exposure. Therefore, the writer is interested in designing an Android application for Senior High school students. The application can be used as the supplementary materials for the students to practice their speaking both inside and outside the school.
There are two questions formulated in the problem formulation, they are: (1) What does the Android application for Senior High School students look like? (2) How does the Android application improve Senior High School students’ speaking skill?
In order to answer the problems, the research combined ADDIE model with Borg and Gall’s (1983) R & D cycle. The quantitative and qualitative data were used as the main data of this study. The quantitative data were obtained from qustionnaire; while the qualitative data were obtained from the open ended questions in the questionnaire and interview.
The answer of the first question shows the description of the Android application. The application is named e-talk. E-talk is an English learning application which is aimed to improve Senior High School students’ speaking skill. This application consists of five main features: vocabulary, grammar, expression, conversation and project which are developed based on the speaking theories proposed by Harmer (2001), Goh and Burns (2012) and Louma (2004). On the other hand, the application was designed based on the principles of mobile learning proposed by Elias (2011) and Egbert and Handson-Smith (1999). Each feature in the application provides some activities based on the aspects of speaking which is developed based on the learning objectives stated in the syllabus. The answer of the second question concerns with how the application improve the Senior High School students’ speaking skill. The result shows that the application eases speaking practice by the mean score 1.5 out of 2. It helps the students improve their vocabulary, pronunciation, fluency and comprehension through the features and activities provided in the applications
xvi ABSTRAK
Malasari, Susanti. 2017. Aplikasi Android untuk Meningkatkan Kemampuan Speaking Siswa Sekolah Menengah Atas. Yogyakarta: Program Pascasarjana Kajian Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Berbahasa Inggris secara lancar menjadi perhatian setiap individu di seluruh dunia karena memberikan beberapa keuntungan. Contohnya, seseorang yang dapat berkomunikasi dengan Bahasa Inggris mempunyai kesempatan yang lebih banyak untuk dapat belajar maupun bekerja di luar negeri. Pentingnya berbahasa Inggris dengan lancar mempengaruhi siswa Sekolah Menengah Atas untuk meningkatkan kemampuan berhahasa Inggrisnya. Untuk itu, siswa perlu mempraktikkannya secara rutin. Akan tetapi, mereka mempunyai kesempatan terbatas untuk menggunakan Bahasa Inggris. Di kelas, siswa hanya mempunyai sedikit kesempatan untuk praktik karena keterbatasan waktu. Sedangkan di luar kelas, siswa jarang menggunakan Bahasa Inggris karena mereka tidak bersosialisasi dengan Bahasa Inggris. Oleh karena itu, penulis tertarik untuk mendesain sebuah aplikasi Android yang dapat digunakan para siswa sebagai materi tambahan untuk praktik berbahasa Inggris baik di dalam maupun di luar kelas.
Terdapat dua pertanyaan yang dinyatakan dalam rumusan masalah, yaitu: (1) Seperti apakah aplikasi Android untuk Siswa Sekolah Menengah Atas? (2) Bagaimanakah aplikasi Android tersebut meningkatkan kemampuan speaking siswa Sekolah Menengah Atas?
Untuk menjawab pertanyaan tersebut, penelitian ini menggabungkan model instruksional ADDIE dan siklus Penelitian dan Pengembangan milik Borg dan Gall (1983). Data kuantitatif dan kualitatif digunakan sebagai data utama pada penelitian ini. Data kuantitatif diperoleh dari kuesioner, sedangkan data kualitatif diperoleh dari pertanyaan uraian yang terdapat pada kuesioner serta wawancara.
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter consists of five major parts. The first part, background of the study, explains the writer‟s reasons in choosing the topic. The second part, problem
identification, formulates the problems that the writer wants to discuss. The third part, research questions, presents the questions to be answered in this study. The fourth part, research goals, presents the goals of this study. In addition, the last part, research benefits, explains some benefits of this study.
A. BACKGROUND OF THE STUDY
2 1996). Speaking consists of producing systematic verbal utterances to convey meaning (Nunan, 2003).
There are four components underlying speaking competency proposed by Canale and Swain (1980); grammatical competence, sociolinguistic competence, discourse competence and strategic competence. Grammatical competence deals with the construction of grammatical sentences including vocabulary and pronunciation. Sociolinguistic competence deals with how the utterances are produced and understood in different contexts. Discourse competence deals with the rules of cohesion and coherence. Strategic competence deals with how the speaker uses the language to achieve the communicative goals. Those four aspects are important points for English learners to consider if they want to be able to speak English well.
3 The development of technology makes significant changes in people‟s life.
Technology helps people to be more efficient by providing some tools which ease people‟s work. Technology can also help people in the educational systems such
as teaching English as a foreign language. Since the object of the study is Senior High School Students, technology is used to facilitate them because they are enthusiastic about technology. In addition, they like spending their time to use gadgets to play games, listen to music, and mingle with friends in social media. This is an opportunity for teachers to develop technology in teaching and learning processes.
In this case, technology can be used as a tool which can help teachers to teach English easily and practically by using the mobile technology in language learning. Mobile learning as an educational activity makes sense only when the technology in use is fully mobile and when the users of the technology are also mobile while they learn (El-Hussein and Cronje 2010). It means that mobile learning enables students to have a mobile learning process which can be accessed anytime and anywhere. The use of technology in English language learning also enables English learners to have an enjoyable learning because it provides the learners with some interesting features which will make the learners become more motivated and become independent learners.
4 Hardware support, Multi-touch, Multi-tasking, Flash support and Tethering (Li, 2012). Those features makes android has similar systems to computer systems. Therefore, it enables teachers to use android to make teaching media which can make English teaching and learning processes easier; especially speaking skill.
By using Android, teachers can make interesting and interactive speaking activities which can motivate students to practice their English. The more the students practice their speaking, the better English communication they have. Therefore, it would be more effective to learn through practicing rather than attending lectures or trying to understand theories. The Android application will provide accessible English exposures which enable the students to practice their English anytime and anywhere to facilitate the students to improve their speaking skill.
B. PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION
5 students have difficulties in acquiring the language which have bad effects for their speaking skill.
C. RESEARCH QUESTIONS
There are two research questions in this study. They are listed as follows:
1. What does the Android application for Senior High School students look like? 2. How does the Android application improve Senior High School students‟
speaking skill?
D. RESEARCH GOALS
In this study, there are two objectives that the writer wants to achieve. The first is goal is the final version of the iconic model of the Android application. The materials provided in the android application model are designed according to the Senior High School learning objectives stated in Curriculum 2006. The model will provide the students with various kinds of learning materials such as vocabulary, grammatical rules and also conversation practice. The Android application model is designed to help the students improve their speaking skill.
6 E. RESEARCH BENEFITS
The writer hopes that this research is beneficial for some groups of people such as English teachers, students and further writers. The Android application made by the writer will help English teachers facilitate the students to practice their speaking skill both inside and outside the classroom since they have limited time to practice their English at school. The Android application will help teachers to teach useful expressions, vocabulary and grammatical rules needed by the students in order to improve their speaking skill. This android application will also ease the teachers in teaching pronunciation because it provides features which enable the students to practice how to pronounce words.
The Android application will also be beneficial for the students because it can help the students to practice their English everywhere. The students will be able to learn and practice various kinds of English expressions, vocabulary and also grammar. It is hoped that students will have more practical, interesting and easier English learning which can motivate them to practice their English. The Android application model made by the writer will help the students to have enough English exposures that can help them improve their speaking skill.
7 CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
This chapter includes the theories that the writer takes in the research to support the analysis of the formulated problems stated in chapter I. This chapter is divided into three parts. They are theoretical review, review on related studies and theoretical framework. Theoretical review covers the theories of speaking, mobile learning, Android, Instructional Design and English for Senior High School. Review on related studies presents the similar studies conducted by some previous writers. In addition, theoretical framework describes the application of all theories used in this study.
A. THEORETICAL REVIEW
The theoretical review consists of four concepts. They are speaking, mobile learning, Android and Instructional Design. The concepts are described as follows.
1. Speaking
Since the writer attempts to design an Android application to improve Senior High School students‟ speaking skill, the writer provides some theories of
8 a. The Nature of Speaking
Speaking is one of four English skills that people usually want to learn because they want to be able to communicate in English. Speaking is the basic language which is developed in early stages or in a childhood. Tarigan (1990) defines that speaking is a language skill that is developed in child life, is preceded by listening skill, and at that period speaking skill is learned. This statement is supported by Brown (2000) who stated that from communicative, pragmatic view of the language classroom, listening and speaking skills are closely intertwined which especially apply to conversation.
Speaking is a verbal language which is used to communicate with others. Speaking consists of producing verbal utterances to convey meaning (Nunan, 2003). Speaking is not merely verbal utterances that convey meaning but it is also defined as the process of expressing ideas and information to the listener. This statement is supported by Brown and Yule (1983), who state that speaking is to express the needs-request, information, service and etc. In this context, the speakers say what they have in mind as well as the information they want to convey to the listeners.
9 the event it also includes the individual participants‟ goal. This is the expected outcomes and the personal goals of accomplishing particular occasions. A stands for Act sequence; refers to the form and the content of the speech acts. It contains the words used, how they are used and the relationship of the topic and what is said. K stands for Key; refers to the tone, manner, or spirit of act. I stands for instrumentalities or it is called as the channel or the mode and form of speech. N stands for Norms; refers to the norms of interpretation and norms of interaction. In addition, G stands for Genre, refers to categories or types of the utterance such as poems, proverbs, etc.
10 appropriateness, the use of a language to signal social relationships, etc.). Discourse competence is the mastery of rules concerning cohesion and coherence of various kinds of discourse in second language (e.g., use of appropriate pronouns, synonyms, conjunctions, substitution, repetition, marking of congruity and continuity, topic-comment sequence, etc.). Strategic competence is the mastery of verbal and non-verbal communication strategies in second language used when attempting to compensate for deficiencies in the grammatical and sociolinguistic competence or to enhance the effectiveness of communication (e.g., paraphrasing, how to address others when uncertain of their relative social status, slow speech for rhetorical effect, etc.) to help the learners to be good at English communication.
b. Microskills of Speaking
11 Table 2.1. Micro Skills of Oral Communication Adapted from Brown (2000)
1. Produce chunks of language of different lengths.
2. Orally produce differences among the English phonemes and allophonic variants.
3. Produce English stress patterns, words in stressed and unstressed positions, rhythmic structure, and intonational contours.
4. Produce reduced forms of words and phrases
5. Use an adequate number of lexical units (words) in order to accomplish pragmatic purposes.
6. Produce fluent speech at different rates of delivery
7. Monitor your own oral production and use various strategic devices-pauses, fillers, self-corrections, backtracking-to enhance the clarity of the message. 8. Use grammatical words classes (nouns, verbs, etc), systems (e.g. tense,
agreement, pluralization) word order, patterns, rules and elliptical forms. 9. Product speech in natural constituents-in appropriate phrases, pause groups,
breath groups, and sentences.
10.Express a particular meaning in different grammatical forms. 11.Use cohesive devices in spoken discourse.
12.Accomplish appropriately communicative functions according to the situations, participants, and goals.
13.Use cohesive devices in spoken discourse.
14.Convey links and connections between events and communicate such relations as main idea, supporting idea, new information, given information, generalization, and exemplification.
15.Use facial features, kinesics, body language, and other nonverbal cues along with verbal language to convey meanings
16.Develop and use a battery of speaking strategies, such as emphasizing key words, rephrasing, providing a context for interpreting the meaning of words, appealing for help, and accurately assessing how well your interlocutor is understanding you
c. Speaking Aspects
12 affects the appropriate communication in conversation. Second, vocabulary is a speaking aspect which is also important for good speaking ability. The more vocabulary that English learners have, they more they will be able to find appropriate diction for their conversation which results to the speaking effectiveness. Third, grammar, it is the aspect which is related to the structure or rules of the language such as word order, inflection and derivation of the meaningful features of English. Calce Murcia (1987) states that grammar is essential to the communicative language in teaching. Fourth, fluency, it is the ability to speak smoothly and easily without any hesitation of what is being spoken. Fluent speakers can speak fluently even though they make some grammatical or pronunciation mistakes. Fluency has a big role in speaking because it will influence the speakers‟ confidence in their speaking performance.
Fifth, comprehension is the ability to comprehend the meaning of what is said. Comprehension becomes one of the aspects of good speaking ability because it influences the conversation process. If both speakers comprehend what they are speaking, they will be able to grasp the information conveyed.
13 Table 2.2 Four Categories of Speaking Skill
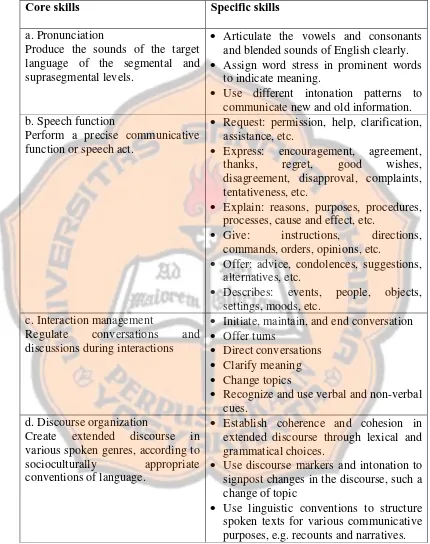
Core skills Specific skills
a. Pronunciation
Produce the sounds of the target language of the segmental and suprasegmental levels.
Articulate the vowels and consonants and blended sounds of English clearly. Assign word stress in prominent words
to indicate meaning.
Use different intonation patterns to communicate new and old information. b. Speech function
Perform a precise communicative function or speech act.
Request: permission, help, clarification, assistance, etc.
Express: encouragement, agreement, thanks, regret, good wishes, disagreement, disapproval, complaints, tentativeness, etc.
Explain: reasons, purposes, procedures, processes, cause and effect, etc.
Give: instructions, directions, commands, orders, opinions, etc.
Offer: advice, condolences, suggestions, alternatives, etc.
Describes: events, people, objects, settings, moods, etc.
c. Interaction management
Regulate conversations and discussions during interactions
Initiate, maintain, and end conversation Offer turns
Direct conversations Clarify meaning Change topics
Recognize and use verbal and non-verbal cues.
d. Discourse organization
Create extended discourse in various spoken genres, according to socioculturally appropriate conventions of language.
Establish coherence and cohesion in extended discourse through lexical and grammatical choices.
Use discourse markers and intonation to signpost changes in the discourse, such a change of topic
Use linguistic conventions to structure spoken texts for various communicative purposes, e.g. recounts and narratives.
14 such as fluency, accuracy, interaction and coherence. First, fluency is the ability to express comprehensible language smoothly. Fluent speakers will speak without any hesitation and many pauses in their communication. They will express the information communicatively, „effectively and naturally. Second, accuracy, refers to the speakers‟ ability to produce correct sentences including grammar,
vocabulary and pronunciation. Third, interaction refers to the situation between the speakers and listeners. Interaction plays a big role in speaking. In influences the atmosphere of the conversation created by both speaker and listener. It will create new topics to be discussed that can encourage the speaker and listener to communicate to one another. Fifth, coherence refers to the appropriateness of the discourse in the conversation. In this case, coherence is closely related to how the speakers use appropriate cohesive devices.
d. Types of Classroom Speaking Performance
15 Intensive speaking is designed to practice some phonological or grammatical aspect of language. It can be done by doing the activity both individually or in groups where learners are practicing certain forms of language. It is described as short replies to teacher or student-initiated questions or comments. This responses are usually sufficient and do not extend into dialogue. It is usually authentic and meaningful.
The transactional language is aimed to convey or exchange specific information or it is called as the extended form of responsive language. In this case, conversation may have more of negotiative nature that responsive speech. The interpersonal dialogue is aimed to maintain social relationship than to transmit facts and information. These kind of conversations can involve a casual register, colloquial language, emotionally charged language, slang, ellipsis, sarcasm or a covert agenda. The extensive speech refers to the planned extended monologues usually in the form of oral reports, summaries or short speeches. These monologues are often planned and formal.
e. Teaching Speaking
Speaking nowadays becomes a standalone subject with little attention paid to its process of learning. There are seven stages of learning activities presented by Goh and Burns (2012) highlighting the importance of the teacher‟s role in facilitating learning and providing input and feedback for the learners. Those stages are presented as follows.
16 In the first stage, the learner‟s metacognitive awarness about second language is developed. In this stage, the learners are encouraged to have a self-observation on their speaking performace and development.
2) Provide input and / or guide planning
This is the stage where the learners are given some support to prepare what they are going to do/say and how they will say it. In this stage, the learners are given appropriate vocabulary related to their speaking needs. They are also explained about the social and linguistic conventions of speech and speakers‟ roles and relationships for particular contexts.
3) Conduct speaking tasks
In this stage, the learners are provided with context where they can practice speaking. The learners are also encouraged to develop their speaking fluency in expression of meaning.
4) Focus on language / skills / strategies
Stage four of the cycle is aimed to create the learners‟ opportunity to improve their language accuracy and enhance the use of skills and strategies effectively. In this stage, the learners are also encouraged to select the language features of the fluency task they have completed such as pronunciation, grammar, text structures and vocabulary.
5) Repeat speaking task
17 done. These repetitions can improve the learners‟ confidence because they have at least one attempt at a task.
6) Direct learners‟ reflection on learning
In the stage six, the learners are encouraged to monitor and evaluate what they have learned in overall stages.
7) Facilitate feedback on learning
In this final stage, the learners are given important feedback on their performances in the previous stages of the cycle. It is explained that the feedback does not always given by the teacher but it can be a form of peer feedback.
18 According to Harmer (2001), knowledge of language features and the ability to process information „on the spot‟ are two elements of speaking that the learners should master in order to speak fluently. To improve the knowledge of language features, teachers should develop the learners‟ connected speech, help
them to be able to deploy some suprasegmental features and devices, supply a variety of phrases for different functions, and help the learners to structure discourse. In addition, the success of speakers‟ productive ability also depends on the rapid processing skills that talking necessitates which expected the teachers to help learners to process the language to be comprehensible, understandable, interactive and convey the intended meaning of a communication.
f. Teaching Speaking with Technology
Since English becomes an international language, more people want to be able to communicate in English. As a result, more people are interested in learning English either in formal or informal institution in order to improve their English communication skill. Some people might be good at written English communication however; they are not good at oral English communication. For those who are not good at oral English communication, they usually hesitate to express their ideas to others because the feel unconfident. This unconfident feeling is not merely caused by the lack of vocabulary of the speakers but it might be caused by other aspects such as, grammatical accuracy or pronunciation. This condition will create a problem in English teaching.
19 social condition. Richard and Renandya (2002) state that speaking is used for many different purposes involving different skills. They state that these different purposes for speaking implies knowledge of the rules that account for how spoken language reflects the context or situation in which speech occurs, the participants involved and their specific roles and relationship, and the kind of activity the speakers are involved in. However, it is hard for teachers to teach their students if their students have lack of confident to practice their speaking ability in the classroom. In this case, teachers must be able to create a learning atmosphere which encourages their students to practice their speaking and enable them to build their speaking performance. Therefore, teachers must be able to create tools for their students to enable them to practice their speaking ability anytime and anywhere without having direct interaction with other speakers.
20 2. Mobile Learning
Mobile learning is now widely used in education in order to make learners have a portable device to learn (El-Hussein and Cronje, 2010). Advanced mobile devices such as smart cellular telephones are very popular among people primarily because they are wireless and portable. These functionalities enable users to communicate while on the move. The popularity of these devices is therefore a consequent of their ability to function at multiple levels.
a. The Nature of Mobile Learning
21 However, the demand for learning anytime and anywhere encourages people to invent a new type of learning which is called m-learning. O‟Malley et al. (2003) defines that mobile learning is when the learners are not in a fixed location and they use mobile technologies as their learning opportunities. It can be stated that m-learning is a learning that use any kinds of portable learning which usually related to the most recent technologies. Mobile learning as learning environmental based on mobility of technology, mobility of learners and mobility of learning that augments the higher educational landscape (El-Hussein and Cronje, 2010). Mobile learning becomes one of the distance learning alternatives which enable learners to have an easy access of learning. It gives learners more learning opportunities since they can learn anytime and anywhere. Geddes (2004) states that m-learning is identified by being available anywhere, anytime and by the tools used. Mobile learning gives learners flexibility of learning since they can access it anytime and anywhere. This kind of learning eases learner to learn inside or outside the school. Mobile device is a pervasive medium that may assist us in combining work, study and leisure time in meaningful ways (Turunen, et al. 2003). It is any educational provision where the sole or dominant technologies are handheld or palmtop devices (Traxler, 2005).
22 encourages „anywhere, anytime‟ learning. Mobile devices allow students to
gather, access, and process information outside the classroom. They can encourage learning in a real-world context, and help bridge school, after school, and home environments. Second, it reaches underserved children. Handheld devices can help advance digital equity, reaching and inspiring populations „at the edges‟ – children from economically disadvantaged communities and those from
developing countries because of their relatively low cost and accessibility in low-income communities. Third, it improves twenty-first century social interactions. Mobile technologies have the power to promote and foster collaboration and communication, which are deemed essential for twenty-first century success.
Fourth, it fits with learning environments. Mobile devices can help overcome many of the challenges associated with larger technologies, as they fit more naturally within various learning environments. At last, it enables a personalized learning experience. Not all children are alike; instruction should be adaptable to individual and diverse learners. There are significant opportunities for genuinely supporting differentiated, autonomous, and individualized learning through mobile devices.
23 range of people abilities, preferences, schedules, level of connectivity and choices in methods. Third, simple and intuitive. It means that the design must be simple and intuitive. Any kinds of complicated design should be eliminated. Fourth, perceptible information. It means that the the content should be clear. Fifth, tolerance of error; means that the design should minimize the errors in the software operation. This can be done by designning learning environment with a tolerance of error. Sixth, low physical and technical effort. It means that the design requires a low physical and technical error such as providing the learners with the simple way of inputting text into the device. Seventh, community of learners and support. It means that the learners should be facilitated with a community which can support one another. This kind of community can reduce the sense of missing out on specific delivery features. At last, instructional climate. It means that the instructor should interact with the learners in various ways to generate discussions and get feedback from the students.
b. MALL
24 that MALL is the formal or informal learning of a foreign language with the assistance of mobile devices. A similar definition is stated by to Miangah and Nezarat (2012) who describe MALL as the use of mobile technology in language learning. According to Miangah and Nezarat (2012) MALL can help the students have the opportunity study a second language using the mobile device when they want and where they are. MALL is a way to promote the learners to have a convenient learning environment that can support the learning needs difference which help the learners to achive their personal success. Chen (2013) describes that the study with mobile phones can be used to foster grammatical accuracy, improve speech fluency, learn vocabulary, promote reading comprehension, etc. On the other hand, Miangah and Nezarat (2012) state that MALL can develop different aspects of language learning such as vocabulary, listening, grammar, phonetics, reading comprehension etc. Besides helping the students learning the languange, there are some advantages offered by MALL devices. It fosters self-study which can increase the acquisition of the language. According to Hulme and Shield (2008) in Small, language learners who study individually outside the classroom develop such language skills and areas. Next, it provides the material which can be accessed anytime and anywhere and mobile device is a fast language learning tool because there is no time to wait for the computer to boot up (Stockwell, 2008).
25 software. The social networks can be used as a tool for the students to foster community and provide language practice outside the classroom, guide the conversation and grammar. The SMS texting can be used to help the learners learn vocabulary. Lu (2008) explains that the students can memorize, practice literating meaning, and check the words in the dictionary if they are not sure just using the mobile phone to verify the information. The videos can help the students practice listening skills. The virtual worlds help the students learn new words and expressions, improve their language skills and provide more English exposure to the students. The voice recognition can help the learners practice the pronunciation. According Godwin-Jones, (2009) the voice recognition software is a helpful tool in language learning because it let the learners listen to language learners practicing pronunciation and repeat back the correct pronunciation spoken by the learner. At last, the blackboard virtual learning software can offer a collaborative learning environment for the students.
26 action but it can also help the learners have the idea of when and how frequently they would receive the reminders. This idea can disturb the learners‟ activities,
especially when they are in the workplace. Therefore, a reccomendation is to allow the learners to plant and control when these push events occur. Fourth, strive for maintain equity. It means that it is important to know whether the learner have a mobile device, what kind of device the learners has, the connectivity and the expense is for using the device for the planned operation. Fifth, acknowledge and plan for accomodating language learner differences. It means that the mobile learning should facilitate learners with various learning styles. Sixth, be aware of language learners‟ existing uses and culture of use. The learners often use their mobile devices for personal and social use rather than as educational tools. Therefore, the task or application provided should be consistent based on their needs. Seventh, keep the mobile learning activities and tasks short and succinct. The short and succinct tasks will make the application accessible for the students. Eighth, let the language learning task with the technology and vice versa. The task should consider the learners‟ mobility and also the technology.
27 3. Android
Android is now widely used by people because it has many features which are similar to the computer‟s features. Those features enable android to be used in
education to make people have mobile learning which is practical and portable for learners.
a. The Nature of Android
Android is a kind of operating system which is popular recently. Android is an operating system based on Linux with a Java programming interface which is developed by Google (Vogel, 2013). It provides all necessary tools to develop Android applications such as compiler, debugger , emulator and virtual machine to run Android programs. “Android allows background processing, provides a rich user interface library, supports 2-D and 3-D graphics using the OpenGL libraries, access to the file system and provides an embedded SQLite database” (Vogel, 2013). Android is a comprehensive platform designed for mobile devices, championed by Google and owned by Open Handset Alliance (Gargenta, 2011).
28 under business-friendly licenses (Apache/MIT) which does not need license. Therefore, it can be freely extended, modified and used for variety purposes. Android is a purpose-built platform for mobile devices which can run on all sorts of physical devices. Since Android is portable, it doesn‟t make any assumptions about a device‟s screen size, resolution, chipset, etc. Android is an operating
system designed for low powered devices that run on battery and are full of hardware such as Global Positioning System (GPS) receivers, cameras, light and orientation sensors, WiFi and UMTS (3Gtelephony) connectivity and a touchscreen (Brahler, 2010).
Android enables applications to make use of the hardware features through abstraction and provide a defined environment for applications. Android
29 The Android software stack can be subdivided into five layers: The kernel and low level tools, native libraries, the Android Runtime, the framework layer and on top of all the applications (Brahler, 2010).
Figure 2.1 Android system architecture
The kernel in use is a Linux 2.6 series kernel, modified for special needs in
30 Android Runtime consists of the Dalvik virtual machine and the Java core libraries. The Dalvik virtual machine is an interpreter for byte code that has been transformed from Java byte code to Dalvik byte code. Dalvik itself is compiled to native code whereas the core libraries are written in Java, thus interpreted by Dalvik. Frameworks in the Application Framework layer are written in Java and provide abstractions of the underlying native libraries and Dalvik capabilities to applications. Android applications run in their own sandboxed Dalvik VM and can consist of multiple components: Activities, services, broadcast receivers and content providers. Components can interact with other components of the same or a different application via intents.
b. Android Features
There are many features provided in the android operating system. All of the features can support the information and technology. Lee (2012) states that Android is open source and freely available to manufacturers for customization, there are no fixed hardware or software configurations. Android supports some important features such as storage, connectivity, messaging, web browser, media support, hardware support, multi-touch, multi-tasking, flash support and tethering. Storage uses Uses SQLite, a lightweight relational database, for data storage. Connectivity supports GSM/EDGE, IDEN, CDMA, EV-DO, UMTS, Bluetooth (includes A2DP and AVRCP), Wi-Fi, LTE, and WiMAX. Messaging supports both SMS and MMS. Web browser is based on the open source WebKit, together with Chrome‟s V8 JavaScript engine. Media support includes support for the
31 AMR-WB (in 3GP container), AAC, HE-AAC (in MP4 or 3GP container), MP3, MIDI, Ogg Vorbis, WAV, JPEG, PNG, GIF, and BMP. Hardware support is accelerometer Sensor, Camera, Digital Compass, Proximity Sensor, and GPS. Multi-touch supports multi-touch screens. Multi-tasking supports multi-tasking applications. Flash support such Android 2.3 supports Flash 10.1. In addition, tethering supports sharing of Internet connections as a wired/wireless hotspot.
c. MIT App Inventor
App Inventor is widely used by Android developer to create Android application because it is a simple mobile applications builder. “App Inventor is a visual, drag-and-drop tool for building mobile apps on the Android platform” (Wolber et all, 2011). In the App Inventor, the visual appearance of Android application is designed by using a web-based graphical interface builder. The application‟s behavior is set by using the puzzle bocks which contain programming tools provided by the App Inventor. There are many activities provided by App Inventor. First, People can play using the App Inventor because App Inventor promotes exploration and discovery. Users can simply open App Inventor, connect the phone and start putting together blocks. By doing this, users can immediately see and interact with the app that is built on the phone. Second, users can build a quick prototype; incomplete and unrefined working models of idea. “Expressing an idea in text is like writing to a friend or loved one with
32 (Wolber et all, 2011). Third, users can build apps with personal utility. App Inventor can be used to build an app exactly how users want it. Fourth, users can develop complete applications. Since App Inventor is not just a prototyping system or an interface designer, users can build complete, general-purpose applications. It is simple for the users to build complete applications because App Inventor the fundamental programming language provided in App Inventor in block form. At last, users can teach and learn using App Inventor. App Inventor is a great teaching and learning tool for students for any kinds of subjects such as computer science, math, physics, and entrepreneurship). The learning experience provided in App Inventor is creating and building applications or multimedia quizzes.
There are many different types of applications that users can build by using App Inventor. First, users can build games. Users can start building simple games and learn to build the more complex ones. Second, users can build educational software. App Inventor can be used to build quiz applications that can help students to study. Third, users can build location-aware applications. Since App Inventor provides access to a GPS-location sensor; users can build applications to know where the users‟ the location is. App Inventor can also be used to help users remember where they parked their car, an app that shows the location of friends or colleagues at a concert or conference, or user‟s own custom tour app of user‟s school, workplace, or a museum. Fourth, App Inventor can be
33 orientation and acceleration, take pictures, and make phones calls. Fifth, users can build SMS applications. Sixth, users can build applications that control robots such as using the phone as a remote control, or programming it to be a “brain” of a robot. The robot and phone communicate via Bluetooth, and App Inventor‟s Bluetooth components let you create similar apps that control other Bluetooth devices. Seventh, App Inventor enables users to build complex applications App Inventor dramatically lowers the entrance barrier to programming and lets you build flashy, high-tech apps within hours. But the language also provides loops, conditionals, and other programming and logic constructs necessary to build apps with complex logic. At last, App Inventor provides users with Web-enabled apps; a way for the user‟s applications to communicate with the Web.
Another definition of App Inventor is proposed by The university of Queensland Australia. It defines that MIT App Inventor is an application that is built in Java and run in a web browser which lets users to create Android mobile applications without writing a single line of code or hacking a single esoteric configuration file. After designing the application and adding behavior to the
application, it can be tested in the Android Emulator. However, when it is going to be tested on a mobile phone, users must create an .APK application file that can
34 and their basic look and feel, as well as layout tools for arranging them horizontally or vertically in the interface.
Figure 2.2 The Designer Interface
35 Figure 2.3 The Blocks Editor
Third, The Android Device Emulator; it is a virtual version of an Android smartphone including touch-screen, hardware keys, and typical functions. The Android Device Emulator is a way to build to build and test the application built. It can also be used to make a change the design or blocks, switch to the emulator and test the results immediately.
36 d. The Advantages of Applying Android in Education
There are some advantages of applying Android in Education. http://www.educause.edu/ir/library/pdf/ELI7067.pdf (n. d) states that might hasten the integration of mobile technology into the learning experience and give students and faculty new ways to interact with content. Many of the tools that support mobile learning are often better suited to communication and data-gathering than to creative reports like writing a paper, putting together a video retrospective, building a series of charts and graphs, or making a class presentation. Like Apple‟s iOS products, Android can integrate with devices
including laptops, netbooks, and tablets, though in the case of Android, the list of connectable devices is longer. This interconnectivity provides an easy way for students to move data from their smart phones to locations where it can be shared with others and used in the construction of individual and group projects.
4. Instructional Design
37 definition is presented by Spector and Muraida (1997), who state that instructional design is structuring of the learning environment in order to increase the learning effectiveness. On the other hand, Smith and Ragan (2005) state that instructional design is the whole process of creating learning activities. In this case, the whole process consists of defining the learning needs and goals, developing the materials and activities and evaluating all the of the instruction and learning activities. In addition, Elly (1996) defines the term instructional design by differentiating it into two terms; instructional technology and educational technology. The instructional technology refers to the process of teaching and learning by using the teaching and learning strategies while the educational technology refers to the use of technology in any aspects of the educational system.
There are many instructional design models that are based on a long process of the researches on learning processes. Each component of the model is based on theories and researches that shows the effectiveness of the components. The models bring the concept of variety educational situations and it shows the procedures that are used to create effective learning media. There are two instructional models that are used as the references for this study; ADDIE and Dick and Carey model (2009). The discussion of those two models are decribed as follows.
a. ADDIE Model
38 evaluation of each phase may lead the instructional designer back to any previous phase. The end product of one phase is the starting product of the next phase. The ADDIE model consists of five steps; analysis, design, development, implementation and evaluation (Rodgers, 2002).
Analysis is the phase in which the writer define and identify the problem and determine the solution of the problem. The analysis is the stage where the writer does need analysis and determine the goals of the research in order give input for the design. Design phase is the outline of the goals of the research. In this phase, the writer conducts a learning analysis, write objectives, select delivery systems and sequence instruction. This is the input for the development phase. Development phase is the phase when the writer develops the instruction and media that will be used. The purpose of this phase is to generate the lesson plans and lesson materials.
39 This type of evaluation assesses the overall effectiveness of the instruction. Data from the Summative Evaluation is often used to make a decision about the instruction as whether to purchase an instructional package or continue/discontinue instruction). Tomonori states that each of the steps provided in the ADDIE model are linked to one another which starts from analysis and ends with evaluation. He adds that the revision can occur within the process; therefore the feedback is stemming from the evaluation stage. The five steps of ADDIE model mentioned above can be seen in the following figure.
Figure 2. 5 The ADDIE Model b. Dick and Carey Model
40 evaluation of instruction, revise instruction, design and conduct summative evaluation (Dick and Carey, 2009). The first step is identifying instructional goals. In this step, the writer determines new information skill that is going to be developed. The instructional goals might be taken from needs assessment, performance analysis, etc. The second step is conducting instructional analysis. In this step, the writer determines the action on performing the goal and look at the skills needed to complete the goal. The final step of this phase is to determine the skills, knowledge and attitude needed by learners in the new instruction. The third step is analyzing learners and contexts. In order to analyze the instructional goal, there is an analysis of the context to learn the skill ad context to be used. The learners‟ skills, preferences and attitude are determined with the characteristics of
the instructional setting and the setting that is going to be used. The fourth step is writing performance objectives. In this step, the writers write the statements of the learners‟ expected skill when they complete the instruction. The fifth step is
developing assessment instruments. These instruments are written based on the written objectives and they are aimed to measure the learners‟ ability to perform
what the writers have described in the objectives.
The sixth step is developing instructional strategy. This instructional strategy is identified based on the information from the preceding five steps which is aimed to achieve the goal. The strategy is emphasized on the components to improve the students‟ learning. This strategy is based on the theories of learning,