Management
Management
Information Systems,
Information Systems,
10/e
10/e
Raymond McLeod and George
Raymond McLeod and George
Schell
Chapter 9
Chapter 9
Information Security
Learning Objectives
Learning Objectives
►
Understand the organizational needs for information
Understand the organizational needs for information
security & control.
security & control.
►
Know that information security is concerned with
Know that information security is concerned with
securing all information resources, not just hardware &
securing all information resources, not just hardware &
data.
data.
►
Know the three main objectives of information security.
Know the three main objectives of information security.
►Know that management of information security consists
Know that management of information security consists
of two areas: information security management (ISM) &
of two areas: information security management (ISM) &
business continuity management (BCM).
business continuity management (BCM).
►
See the logical relationship among threats, risks &
See the logical relationship among threats, risks &
controls.
controls.
Learning Objectives (Cont’d)
Learning Objectives (Cont’d)
►
Recognize the security concerns of e-commerce &
Recognize the security concerns of e-commerce &
how credit card companies are dealing with them.
how credit card companies are dealing with them.
►
Be familiar with a formal way to engage in risk
Be familiar with a formal way to engage in risk
management.
management.
►
Know the process for implementing an information
Know the process for implementing an information
security policy.
security policy.
►
Be familiar with the more popular security controls.
Be familiar with the more popular security controls.
►Be familiar with actions of government & industry
Be familiar with actions of government & industry
that influence information security.
that influence information security.
►
Know how to obtain professional certification in
Know how to obtain professional certification in
security & control.
security & control.
Organizational Needs for
Organizational Needs for
Security & Control
Security & Control
►
Experience inspired industry to:
Experience inspired industry to:
Place security precautions aimed at
Place security precautions aimed at
eliminating or reducing the opportunity of
eliminating or reducing the opportunity of
damage or destruction.
damage or destruction.
Provide the organization the ability to
Provide the organization the ability to
continue operations after disruption.
continue operations after disruption.
►
Patriot Act & Office of Homeland Security
Patriot Act & Office of Homeland Security
1
1
ststissue is security vs. individual rights.
issue is security vs. individual rights.
Information Security
Information Security
►
System security
System security
focuses on protecting
focuses on protecting
hardware, data, software, computer
hardware, data, software, computer
facilities, & personnel.
facilities, & personnel.
►
Information security
Information security
describes the
describes the
protection of both computer &
protection of both computer &
non-computer equipment, facilities, data, &
computer equipment, facilities, data, &
information from misuse by unauthorized
information from misuse by unauthorized
parties.
parties.
Objectives of Information
Objectives of Information
Security
Security
►
Information security is intended to achieve three
Information security is intended to achieve three
main objectives
main objectives
:
:
Confidentiality:
Confidentiality:
protecting a firm’s data and information
protecting a firm’s data and information
from disclosure to unauthorized persons.
from disclosure to unauthorized persons.
Availability:
Availability:
making sure that the firm's data &
making sure that the firm's data &
information is only available to those authorized to use it.
information is only available to those authorized to use it.
Integrity:
Integrity:
information systems should provide an
information systems should provide an
accurate representation of the physical systems that they
accurate representation of the physical systems that they
represent.
represent.
►
Firm’s information systems must protect data &
Firm’s information systems must protect data &
information from misuse, ensure availability to
information from misuse, ensure availability to
Management of Information
Management of Information
Security
Security
►
Information security management
Information security management
(
(
ISM
ISM
) is
) is
the activity of keeping information resources
the activity of keeping information resources
secure.
secure.
►
Business continuity management
Business continuity management
(
(
BCM
BCM
) is
) is
the activity of keeping the firm & its information
the activity of keeping the firm & its information
resources functioning after a catastrophe.
resources functioning after a catastrophe.
►
Corporate information systems security
Corporate information systems security
officer
officer
(
(
CISSO
CISSO
) is responsible for the firm’s
) is responsible for the firm’s
information systems security.
information systems security.
►
Corporate information assurance officer
Corporate information assurance officer
(
(
CIAO
CIAO
) reports to the CEO & manage an
) reports to the CEO & manage an
information assurance unit.
Information Security
Information Security
Management
Management
►
Concerned with formulating the firm’s information
Concerned with formulating the firm’s information
security policy.
security policy.
►
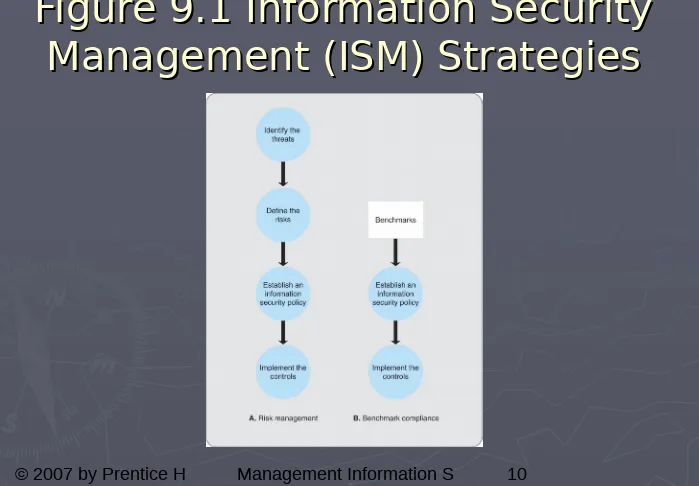
Risk management
Risk management
approach is basing the security of
approach is basing the security of
the firm’s information resources on the risks (threats
the firm’s information resources on the risks (threats
imposed) that it faces.
imposed) that it faces.
►
Information security benchmark
Information security benchmark
is a recommended
is a recommended
level of security that in normal circumstances should
level of security that in normal circumstances should
offer reasonable protection against unauthorized
offer reasonable protection against unauthorized
intrusion.
intrusion.
Benchmark
Benchmark
is a recommended level of performance.
is a recommended level of performance.
Defined by governments & industry associations
Defined by governments & industry associations
What authorities believe to be components of a good
What authorities believe to be components of a good
information security program.
information security program.
►
Benchmark compliance
Benchmark compliance
is when a firm adheres to the
is when a firm adheres to the
information security benchmark & recommended
information security benchmark & recommended
standards by industry authorities.
Figure 9.1 Information Security
Figure 9.1 Information Security
Threats
Threats
►
Information security threat
Information security threat
is a person,
is a person,
organization, mechanism, or event that has
organization, mechanism, or event that has
potential to inflict harm on the firm’s information
potential to inflict harm on the firm’s information
resources.
resources.
►
Internal & external threats.
Internal & external threats.
Internal include firm’s employees, temp. workers,
Internal include firm’s employees, temp. workers,
consultants, contractors, & even business partners.
consultants, contractors, & even business partners.
As high as 81% of computer crimes have been committed
As high as 81% of computer crimes have been committed
by employees.
by employees.
Internal threats present potentially more serious damage
Internal threats present potentially more serious damage
due to more intimate knowledge of the system.
due to more intimate knowledge of the system.
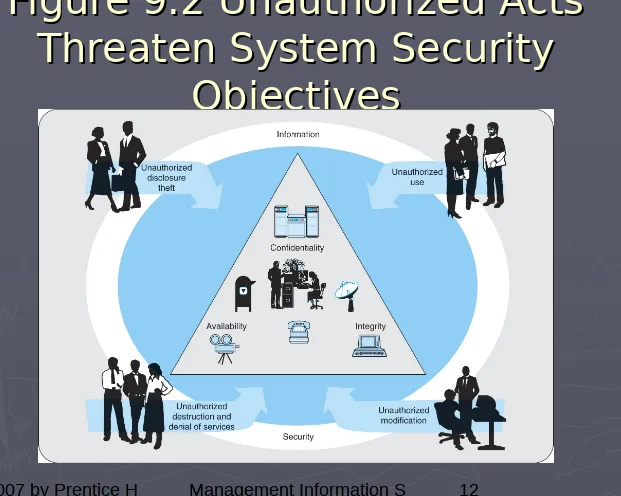
Figure 9.2 Unauthorized Acts
Figure 9.2 Unauthorized Acts
Threaten System Security
Threaten System Security
Types of Threats
Types of Threats
►
Malicious software
Malicious software
(
(
malware
malware
) consists of complete
) consists of complete
programs or segments of code that can invade a
programs or segments of code that can invade a
system & perform functions not intended by the
system & perform functions not intended by the
system owners (i.e. erase files, halt system, etc.).
system owners (i.e. erase files, halt system, etc.).
►
Virus
Virus
is a computer program that can replicate itself
is a computer program that can replicate itself
without being observable to the user & embed copies
without being observable to the user & embed copies
of itself in other programs & boot sectors.
of itself in other programs & boot sectors.
►
Worm
Worm
cannot replicate itself within a system, but it
cannot replicate itself within a system, but it
can transmit its copies by means of e-mail.
can transmit its copies by means of e-mail.
►
Trojan horse
Trojan horse
is distributed by users as a utility &
is distributed by users as a utility &
when the utility is used, it produces unwanted changes
when the utility is used, it produces unwanted changes
in the system’s functionality; can’t replicate nor
in the system’s functionality; can’t replicate nor
duplicate itself.
duplicate itself.
Risks
Risks
►
Information security risk
Information security risk
is a potential
is a potential
undesirable outcome of a breach of
undesirable outcome of a breach of
information security by an information
information security by an information
security threat.
security threat.
all risks represent unauthorized acts.
all risks represent unauthorized acts.
►
Unauthorized disclosure & threats
Unauthorized disclosure & threats
.
.
►
Unauthorized use
Unauthorized use
.
.
►
Unauthorized destruction & denial of
Unauthorized destruction & denial of
service.
E-commerce Considerations
E-commerce Considerations
►
“
“
Disposable” credit card
Disposable” credit card
(AMEX) – an action
(AMEX) – an action
aimed at 60 to 70% of consumers who fear
aimed at 60 to 70% of consumers who fear
credit card fraud arising from Internet use.
credit card fraud arising from Internet use.
►
Visa’s 10 required security practices
Visa’s 10 required security practices
for its
for its
retailers plus 3 general practices for achieving
retailers plus 3 general practices for achieving
information security in all retailers’ activities.
information security in all retailers’ activities.
►
Cardholder Information Security Program
Cardholder Information Security Program
(
Risk Management
Risk Management
►
Defining risks consists of four substeps.
Defining risks consists of four substeps.
Identify business assets to be protected from risks.
Identify business assets to be protected from risks.
Recognize the risks.
Recognize the risks.
Determine the level of of impact on the firm should the risks
Determine the level of of impact on the firm should the risks
materialize.
materialize.
Analyze the firm’s vulnerabilities.
Analyze the firm’s vulnerabilities.
►
Impact severity can be classified as:
Impact severity can be classified as:
Severe impact
Severe impact
puts the firm out of business or severely limits
puts the firm out of business or severely limits
its ability to function.
its ability to function.
Significant impact
Significant impact
causes significant damage & cost, but the
causes significant damage & cost, but the
firm will survive.
firm will survive.
Risk Analysis Report
Risk Analysis Report
►
The findings of the risk analysis should be
The findings of the risk analysis should be
documented in a report that contains detailed
documented in a report that contains detailed
information such as the following for
information such as the following for
each risk
each risk
:
:
A description of the risk.
A description of the risk.
Source of the risk.
Source of the risk.
Severity of the risk.
Severity of the risk.
Controls that are being applied to the risk.
Controls that are being applied to the risk.
The owner(s) of the risk.
The owner(s) of the risk.
Recommended action to address the risk.
Recommended action to address the risk.
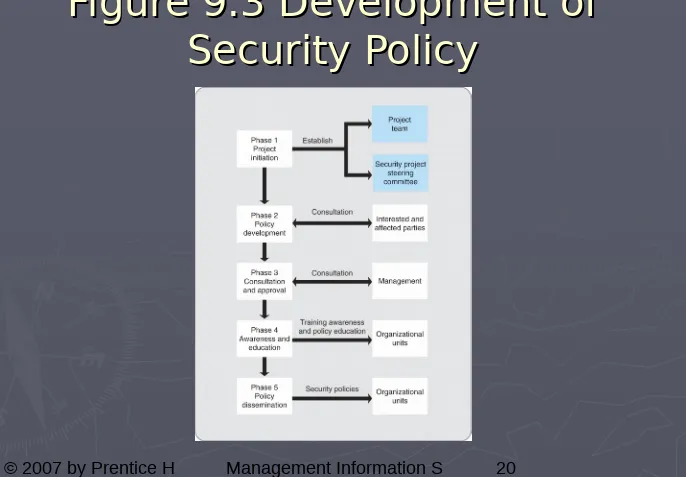
Information Security Policy
Information Security Policy
►
The five phases of implementing:
The five phases of implementing:
►
Phase 1: Project Initiation.
Phase 1: Project Initiation.
►
Phase 2: Policy Development.
Phase 2: Policy Development.
►
Phase 3: Consultation & Approval.
Phase 3: Consultation & Approval.
►
Phase 4:Awareness and Education.
Phase 4:Awareness and Education.
Figure 9.3 Development of
Figure 9.3 Development of
Controls
Controls
►
Control
Control
is a mechanism that is
is a mechanism that is
implemented to either protect the firm
implemented to either protect the firm
from risks or to minimize the impact of
from risks or to minimize the impact of
risks on the firm should they occur.
risks on the firm should they occur.
►
Technical controls
Technical controls
are those that are
are those that are
built into systems by the system
built into systems by the system
developers during the systems
developers during the systems
development life cycle.
development life cycle.
Technical Controls
Technical Controls
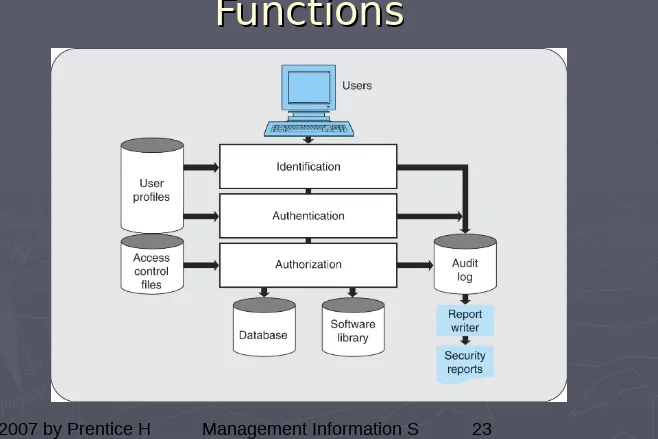
►
Access control
Access control
is the basis for security
is the basis for security
against threats by unauthorized persons.
against threats by unauthorized persons.
►
Access control three-step process includes:
Access control three-step process includes:
User identification
User identification
;
;
User authentication
User authentication
;
;
User authorization
User authorization
.
.
►
User profiles
User profiles
- descriptions of authorized
- descriptions of authorized
users; used in identification &
users; used in identification &
authorization.
Figure 9.4 Access Control
Figure 9.4 Access Control
Technical Controls (Cont’d)
Technical Controls (Cont’d)
►
Intrusion detection systems
Intrusion detection systems
(
(
IDS
IDS
)
)
recognize an attempt to break the security
recognize an attempt to break the security
before
before
it has an opportunity to inflict damage.
it has an opportunity to inflict damage.
►
Virus protection software that is effective
Virus protection software that is effective
against viruses transported in e-mail.
against viruses transported in e-mail.
Identifies virus-carrying message & warns user.
Identifies virus-carrying message & warns user.
►
Inside threat prediction tools
Inside threat prediction tools
classify
classify
internal threats in categories such as:
internal threats in categories such as:
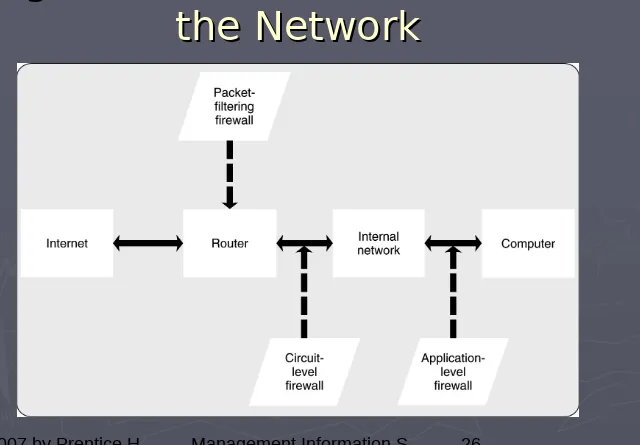
Firewalls
Firewalls
► FirewallFirewall acts as a filter & barrier that restricts the flow of data to & acts as a filter & barrier that restricts the flow of data to &
from the firm & the Internet. Three types of firewalls are: from the firm & the Internet. Three types of firewalls are:
► Packet-filtering Packet-filtering are routers equipped with data tables of IP are routers equipped with data tables of IP
addresses which reflect the filtering policy positioned between the addresses which reflect the filtering policy positioned between the Internet and the internal network, it can serve as a firewall.
Internet and the internal network, it can serve as a firewall.
Router
Router
is a network device that directs the flow of network traffic. is a network device that directs the flow of network traffic. IP addressIP address is a set of four numbers (each from 0 to 255) that is a set of four numbers (each from 0 to 255) thatuniquely identify each computer connected to the Internet. uniquely identify each computer connected to the Internet.
► Circuit-level firewallCircuit-level firewall installed between the Internet & the firm’s installed between the Internet & the firm’s
network but closer to the communications medium (circuit) than the network but closer to the communications medium (circuit) than the router.
router.
Allows for a high amount of authentication & filtering to be Allows for a high amount of authentication & filtering to be
performed. performed.
► Application-level firewall Application-level firewall located between the router & computer located between the router & computer
performing the application. performing the application.
Figure 9.5 Firewall Locations in
Figure 9.5 Firewall Locations in
Cryptographic & Physical
Cryptographic & Physical
Controls
Controls
► CryptographyCryptography is the use of coding by means of mathematical is the use of coding by means of mathematical
processes. processes.
► The data and information can be encrypted as it resides in The data and information can be encrypted as it resides in
storage and or transmitted over networks. storage and or transmitted over networks.
► If an unauthorized person gains access, the encryption makes If an unauthorized person gains access, the encryption makes
the data and information unreadable and prevents its the data and information unreadable and prevents its unauthorized use.
unauthorized use.
► Special protocols such as Special protocols such as SETSET (Secure Electronic Transactions) (Secure Electronic Transactions)
perform security checks using digital signatures developed for perform security checks using digital signatures developed for use in e-commerce.
use in e-commerce.
► Export of encryption technology is prohibited to Cuba, Iran, Iraq, Export of encryption technology is prohibited to Cuba, Iran, Iraq,
Libya, North Korea, Sudan, & Syria. Libya, North Korea, Sudan, & Syria.
►
Physical controls
Physical controls
against unauthorized intrusions such as door against unauthorized intrusions such as doorlocks, palm prints, voice prints, surveillance cameras, & security locks, palm prints, voice prints, surveillance cameras, & security guards
guards
Locate computer centers in remote areas that are less susceptible to Locate computer centers in remote areas that are less susceptible to
natural disasters such as earthquakes, floods, & hurricanes.
Formal Controls
Formal Controls
►
Formal controls
Formal controls
include the establishment
include the establishment
of codes of conduct, documentation of
of codes of conduct, documentation of
expected procedures & practices,
expected procedures & practices,
monitoring, & preventing behavior that
monitoring, & preventing behavior that
varies from the established guidelines.
varies from the established guidelines.
Management denotes considerable time to
Management denotes considerable time to
devising them.
devising them.
Documented in writing.
Documented in writing.
Expected to be in force for the long term.
Expected to be in force for the long term.
Informal Controls
Informal Controls
►
Education.
Education.
►
Training programs.
Training programs.
►
Management development programs.
Management development programs.
►
Intended to ensure the firm’s employees both
Intended to ensure the firm’s employees both
understand & support the security program.
understand & support the security program.
►
Good business practice is not to spend more
Good business practice is not to spend more
for a control than the expected cost of the
for a control than the expected cost of the
risk that it addresses.
risk that it addresses.
Government & Industry
Government & Industry
Assistance
Assistance
► United Kingdom's BS7799. United Kingdom's BS7799. The UK standards establish a set of baseline The UK standards establish a set of baseline
controls. They were first published by the British Standards Institute in 1995,
controls. They were first published by the British Standards Institute in 1995,
then published by the International Standards Organization as ISO 17799 in
then published by the International Standards Organization as ISO 17799 in
2000, & made available to potential adopters online in 2003.
2000, & made available to potential adopters online in 2003.
► BSI IT Baseline Protection Manual. BSI IT Baseline Protection Manual. The baseline approach is also followed The baseline approach is also followed
by the German Bundesamt fur Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik (BSI). The
by the German Bundesamt fur Sicherheit in der Informationstechnik (BSI). The
baselines are intended to provide reasonable security when normal protection
baselines are intended to provide reasonable security when normal protection
requirements are intended. The baselines can also serve as the basis for
requirements are intended. The baselines can also serve as the basis for
higher degrees of protection when those are desired.
higher degrees of protection when those are desired.
► COBIT. COBIT. COBIT, from the Information Systems Audit and Control Association & COBIT, from the Information Systems Audit and Control Association &
Foundation (ISACAF), focuses on the process that a firm can follow in
Foundation (ISACAF), focuses on the process that a firm can follow in
developing standards, paying special attention to the writing & maintaining of
developing standards, paying special attention to the writing & maintaining of
the documentation.
the documentation.
► GASSP. GASSP. Generally Accepted System Security Principles (GASSP) is a product of Generally Accepted System Security Principles (GASSP) is a product of
the U. S. National Research Council. Emphasis is on the rationale for
the U. S. National Research Council. Emphasis is on the rationale for
establishing a security policy.
establishing a security policy.
► ISF Standard of Good Practice. ISF Standard of Good Practice. The Information Security Forum Standard The Information Security Forum Standard
of Good Practice takes a baseline approach, devoting considerable attention to
of Good Practice takes a baseline approach, devoting considerable attention to
the user behavior that is expected if the program is to be successful. The 2005
the user behavior that is expected if the program is to be successful. The 2005
edition addresses such topics as secure instant messaging, Web server
Government Legislation
Government Legislation
►
B
B
oth U.S.
oth U.S.
&
&
U.K. established standards &
U.K. established standards &
passed legislation aimed at addressing the
passed legislation aimed at addressing the
increasing importance of information security.
increasing importance of information security.
►
U.S. Government Computer Security Standards.
U.S. Government Computer Security Standards.
Set of security standards organizations should meet.
Set of security standards organizations should meet.
Availability of software
Availability of software
program that grades users’
program that grades users’
systems & assists them in configuring their systems
systems & assists them in configuring their systems
to meet standards.
to meet standards.
►
U.K. Anti-terrorism, Crime & Security Act
U.K. Anti-terrorism, Crime & Security Act
(ATCSA) 2001.
Professional Certification
Professional Certification
►
Beginning in the 1960s the IT
Beginning in the 1960s the IT
profession began offering certification
profession began offering certification
programs
programs
:
:
Information Systems Audit and Control
Information Systems Audit and Control
Association
Association
(
(
ISACA
ISACA
)
)
International Information System Security
International Information System Security
Certification Consortium
Certification Consortium
(
(
ISC
ISC
)
)
SANS
SANS
(
(
SysAdmin, Audit, Network,
SysAdmin, Audit, Network,
Security
Business Continuity
Business Continuity
Management
Management
►
Business continuity management
Business continuity management
(
(
BCM
BCM
) are
) are
activities aimed at continuing operations after an
activities aimed at continuing operations after an
information system disruption.
information system disruption.
►
This activity was called
This activity was called
disaster planning
disaster planning
, then
, then
more positive term
more positive term
contingency planning
contingency planning
.
.
►
Contingency plan
Contingency plan
is the
is the
key
key
element in
element in
contingency planning; it is a formal written
contingency planning; it is a formal written
document that spells out in detail the actions to
document that spells out in detail the actions to
be taken in the event that there is a disruption,
be taken in the event that there is a disruption,
or threat of disruption, in any part of the firm’s
or threat of disruption, in any part of the firm’s
Contingency Subplans
Contingency Subplans
►
Emergency plan
Emergency plan
specifies those measures that
specifies those measures that
ensure the safety of
ensure the safety of
employees
employees
when disaster strikes.
when disaster strikes.
Include alarm systems, evacuation procedures, & fire-Include alarm systems, evacuation procedures, &
fire-suppression systems. suppression systems.
►
Backup plan
Backup plan
is the arrangements for backup
is the arrangements for backup
computing facilities in the event that the regular
computing facilities in the event that the regular
facilities are destroyed or damaged beyond use.
facilities are destroyed or damaged beyond use.
Backup can be achieved by some combination of
Backup can be achieved by some combination of
redundancy, diversity, & mobility.
redundancy, diversity, & mobility.
►
Vital records
Vital records
are those paper documents,
are those paper documents,
microforms, & magnetic & optical storage media that
microforms, & magnetic & optical storage media that
are necessary for carrying on the firm’s business.
are necessary for carrying on the firm’s business.
►
Vital records plan
Vital records plan
specifies how the vital records will
specifies how the vital records will