HOME ABOUT LOG IN REGISTER SEARCH CURRENT ARCHIVES
Nit hin T Abraham , Shaem a Lizbet h Mat hew , C.A Pradeep Kum ar 4900- 4904
Com m unicat ion and Calibrat on of Sensing Met er s
Harr ouz Abdelkader, Om ar Harrouz, Ali Benat iallah 4905- 4914
Sensit iv it y Fact or Based Opt im al Locat ion of SVC on Tr ansm ission Net w or k
T. D. Sudhakar 4915- 4923
Modeling of Tunnel Junct ion ( GaAs) in t he Cascade Solar Cell
Dennai Benm oussa, Benslim ane H, Helm aoui A, Hem m ani A 4924- 4927
Theoret ical St udy of Mult iple Solar Cells Syst em as a Funct ion of Tem perat ure
Ben Slim ane Hassane, Ben Moussa Dennai, Helm aoui Abderr achid 4928- 4933
Behavior of DFI G Wind Turbine Dur ing Unbalanced Grid Volt age
Om er Elfak i, Wang Zezhong, Liu Qihui 4934- 4943
St udy on t he Accept ance Test Specificat ion of Grid- connect ed Micr o- gr id
Le Jian, Tao Mao, Yang Zhichun, Liu Yang, Liu Kaipei 4944- 4953
A Reliabilit y Ev aluat ion of High Speed Railw ay Tract ion Subst at ion Based on t he GO- FLOW Met hodology
Li Liang, Feng Zhao, Sihua Wang 4954- 4962
Resear ch on Zigbee Net w or k Tem perat ur e Sensor in I nt elligent High- Volt age Sw it ch Cabinet
Xin- bo Huang, Yang Zhao, Xiao- hui Zhao, Zhi- j un Liao 4963- 4972
Shor t - Ter m Predict ion of Wind Pow er Based on an I m proved PSO Neur al Net w or k
Hong Zhang, Guo Zhao, Lix ing Chen, Bailiang Liu 4973- 4980
An appr oach for Assessing Harm onic Em ission Lev el Based on Robust Par t ial Least Squares Regr ession
Xiang Li, Minyou Chen, Yongw ei Zheng, Shan Cheng, Feng Li 4981- 4987
Elect rom agnet ic- t herm al Scale Model of Gas- I nsulat ed Bus Bars
Hongt ao Li, Naiqiu Shu, Ling Li, Hui Peng, Zipin Li 4988- 4995
A Design of Rapid Pulsed I nt elligent Charging Cir cuit
Zhang Lefang, Li Xiaohong, Ren Zhihong 4996- 5002
Three- Dim ensional Ther m al Analy sis of Three- Phase Enclosed GI S Bus Bar s
Hongt ao Li, Naiqiu Shu, Ling Li 5003- 5010
Analy sis of Weak Posit ion in Ov er head line under Heav y I cing Condit ion by Finit e Elem ent Met hod
Gan Yan, Liu Chao, Ruan Jiangj un, Li Jinliang, Du Zhiy e, Hu Yuanchao 5011- 5021
A Nov el SSR Mit igat ion Met hod Based on GCSC in DFI G w it h Series Connect ed Com pensat or
Zakieldeen Elhassan, Li Yang, Tang Yi 5022- 5036
Dy nam ic char act erist ics analy sis of WEDM based on Ansys and LMS
Jingx ing Qi, Changt ao Cai, Zhixing Mao, Dongdong Luo 5037- 5043
The 3D Modeling of Cut t ing For ce in High- speed Milling for Flat Mill
Mult i- Area Aut om at ic Gener at ion Cont r ol Schem e including Renew able Energy Sources
Sandeep Bhongade, Bar j eev Tyagi, H.O. Gupt a 5052- 5070
Effect of Cont am inat ion on Elect r ic Field Dist ribut ion of DC Volt age Divider
Caibo Liao, Ruan Jiangj un, Du Zhiye, Liu Chao 5071- 5077
A Har m onic Analy sis Met hod Based on Harr is Window for Digit al
Herm agasant os Zein, Yusr a Sabri, Er win Derm aw an 5086- 5095
Tr ansform er St at e Assessm ent Met hod Based on Fuzzy and Ev idence Theories
Xie Jianghong, Wang Haipeng, Nie Dexin, Song You, Cai Wei 5096- 5103
I m plem ent at ion of Sm ar t Met ering Syst em s: Challenges and Solut ions
Hossein Shahinzadeh, Ay la Hasanalizadeh- Khosr oshahi 5104- 5109
An Exact Model for Rot or Field- Or ient ed Cont rol of Single- Phase
I nduct ion Mot or s PDF
Moham m ad Jannat i, Ali Monadi, Saj ad A. Anbaran, Nik Rum zi Nik I dris, Mohd Junaidi Abdul Aziz
5110- 5120
Solut ion Traj ect or ies for a Single- Phase Pr ogr am m ed PWM I nv er t er
Ayong Hiendro, Sy aifur rahm an Syaifurr ahm an, Dedi Triyant o, Junaidi Junaidi 5121- 5128
I nv est igat ing t he Effect of Differ ent PWM Modes on Ripple Reduct ion in
Five- Phase BLDC Mot or w it h New Met hod PDF
Sey ed Mohsen Mirbagheri, Sey ed Saj j ad Salehi GHalehsefid, Sey ed Moham m ad Hossein Mousav i
5129- 5136
dsPI C33 Based Cont r ol for PV- Grid Syst em w it h a Buck- Boost MPPT
Slam et Riyadi 5137- 5143
Direct Virt ual Pow er Cont r ol
Li Xiang, Han Minx iao 5144- 5153
Pow er Loss Research on I GCT- applied NPC Thr ee- level Conv er t er
Dong Xu, MinXiao Han, Lei Wan 5154- 5162
Design and Sim ulat ion Low Volt age Single- Phase Tr ansform er less Phot ov olt aic I nv er t er
Raj endra R Aparnat hi, Ved Vy as Dw ivedi 5163- 5173
Cir cuit Design of Digit al Closed Loop Cont rol Syst em for FOG
Qiudong Sun, Yufeng Shao, Jiancun Zuo, Liandong Wang, Lin Gui 5174- 5184
The Tr ansm ission Pr oper t ies of Coat ed THz Teflon Tube
Wu Pan, Tian bo Duo, Zichen Liu, Jun Chen 5185- 5190
Digit al I m age St or age Sy st em Based on USB and NAND Flash
Yongj un Cui, Wei Liu 5191- 5196
Design of 3- Bit ADC in 0.18 µm CMOS Process PDF
Moham m ad Marufuzzam an, Syar izal Z. Abidin, Mam un Bin I bne Reaz, Labonnah Farzana Rahm an
5197- 5203
An I m prov ed A Low Pow er CMOS TI Q Com par at or Flash ADC
A Al, Mam un B. I bne Reaz, J. Jalil, Mohd. Alauddin Bin Mohd. Ali 5204- 5210
Red ( SrCa) AlSiN3: Eu2+ Nit ride Phosphor Par t icle Size of Phosphor Conv er t ed War m Whit e LEDs
Peng Hui Yuen, Hsien Shiung Hw ang, Mut har asu Devaraj an 5211- 5216
Opt im al Feedback Cont r ol of Vehicle Vibr at ion w it h Eight Degr ees of Freedom
Ali Hem at i, Mehdi Taj dar i, Ahm adr eza Khoogar 5217- 5224
Sim plificat ions of t he Rule base for t he st abilizat ion of I nver t ed Pendulum Syst em
Tharw at O. S. Hanafy , Moham ed K Met w ally 5225- 5234
Wav elet Kernel Based on I dent ificat ion for Nonlinear Hy br id Syst em s
Edw in Albert Um oh 5251- 5260
I dent ificat ion of Nonlinear Sy st em Based on Fuzzy Model w it h Enhanced Gradient Sear ch
Arbab Nighat Khizer, Dai Yaping, Am ir Mahm ood Soom ro, Xu Xiang Yang 5261- 5267
A New Ant i- Windup PI Cont roller for Direct Tor que Cont rol Syst em
Li Qi Meng, Miao Jing Li 5268- 5274
Dy nam ic Sliding Mode Cont rol of Ship Rudder - fin Joint Nonlinear Syst em
Han Yao zhen 5275- 5283
Adapt ive Neural Net w ork Appr oach for a Class of Uncert ain Non- affine Nonlinear Syst em s
Hui Hu, Yingj un Wang, Xilong qu 5284- 5292
SI SO P- I LC Algorit hm for Out put Dat a Dropout s and I t s Applicat ion in Wast ew at er Biological Treat m ent Plant
Gu Qun, Hao Xiaohong, Li Zhuoyue, Wang Hua 5293- 5297
Wind- I nduced Vibrat ion Analy sis of Overhead Wor king Truck
Hongqi Jiang, Shuncai Li, Xianbiao Mao 5298- 5304
Ant i- int erference Tr acking Met hods of Maneuver ing Target for St r uct ur e Random Jum p Syst em s
Jianfeng Wu, Shucai Huang, Xiaoyan Wu, Yu Zhong, Hongxia Kang, Chengj ing Li 5305- 5315
Algor it hm of Mult i Sensor Dat a Fusion based on BP Neural Net w or k and Mult i- scale Model Pr edict iv e Cont rol
Guo Wang, Dong Dai 5316- 5323
Sensor Fusion v ia Br ain Em ot ional Learning for Ground Vehicle
Alv aro Vargas- Clara, Sangram Redk ar 5324- 5330
A Vir t ual Physics- based Approach t o Mult iple Odor Sour ces Localizat ion
Xiaoping Ma, Yuli Zhang, Yanzi Miao 5331- 5341
Dy nam ic Er ror Analysis of CMM Based on Variance Analy sis and I m proved PLSR
Zhang Mei, Cheng Fang, Li Guihua 5342- 5349
Design of Decent ralized Cont roller for I nt eract iv e Pr ocesses t hrough Relat ive Fr equency Ar ray
R.Hanum a Naik, D.V. Ashok Kum ar, K.S.R. Anj aneyulu 5350- 5361
Cont rolled Synchr onizat ion by Lim it ed Capacit y Com m unicat ion Channel
Ziqi Dong, Yongchun Liu, Da Lin 5362- 5367
Charact erist ics Analysis and Det ect ion Algor it hm of Mosquit oes
Jahangir Alam S. M., Hu Guoqing, Cheng Chen 5368- 5378
Mult i- user Det ect ion Based on Gaussian Sum Par t icle Filt er in I m pulsiv e Noise
Li Zhihui, x ian Jin- Long 5379- 5386
St udy on Mahalanobis Discr im inant Analy sis of EEG Dat a
Yuan Shi, Linlin Yu, Fang Qin 5387- 5391
Resear ch on Operat ing Condit ion Effect on t he Shock Pulse Met hod
Ruifeng Zhang, Jianshe Kang, Lishan Hao, Xinghui Zhang, Hongzhi Teng, Haiping Li 5392- 5398
Resear ch of Blind Forensics Algor it hm on Digit al I m age Tam per ing
Hongying Jin 5399- 5407
A New Digit al I m age Hiding Algorit hm Based on Wav elet Pack et Tr ansform and Singular Value Decom posit ion
Yueli Cui, Shiqing Zhang, Zhigang Chen, Wei Zheng 5408- 5413
The Nav el Orange Sugar and Acidit y Quant it at ive Predict ion Model Opt im izat ion Resear ch by Second Gener at ion Wavelet Tr ansfor m
Zhao Ke, Yang Han, Wang Zhong, Wang Qi 5414- 5419
St udy of Addit iv e Dit her on Rest r aining Signal Tr uncat ion Err or
Tao Liu, Shulin Tian, Zhigang Wang, Lianping Guo 5420- 5429
St ochast ic Sy nchr onizat ion of Neut r al- Type Chaot ic Mar kovian Neur al Net w or ks w it h I m pulsive Effect s
Cheng- De Zheng, Xix i Lv 5430- 5437
Waheed Ullah, Yang Fengfan, Abid Yahy a 5448- 5457
Perform ance Analysis of A Hy brid Mim o Technique for High Rat e Wir eless Com m unicat ion Syst em
Kehinde Odeyem i, Er ast us Ogunt i 5458- 5468
Rat eless Codes Design Schem e Based on Tw o St ages
Yunj i Li, Xiaolong Yang, Keping Long 5469- 5475
An I CVBPNN Algor it hm for Tim e- var ying Channel Track ing and Pr edict ion
Sufang Li, Mingyan Jiang, Dongfeng Yuan 5476- 5483
A Surv ey on Clust er ing Rout ing Pr ot ocols Based on PSO in WSN
Enyan Sun 5484- 5490
Var iable St ep Size Blind Equalizat ion based on Sign Gradient Algorit hm
Ying Xiao, Fuliang Yin 5491- 5498
Spat ial Char act erist ics of Wir eless Channel in Tunnel w it h I m perfect Walls
Yi Zhang, Zhao Xu, Bo- Ming Song, Yu Huo 5499- 5507
Analy sis and Design of Com plem ent ary Ring Type Met am at erial Filt er in THz Wave Dom ain
Wu Pan, Jun Chen, Tianbo Duo, Zichen Liu 5508- 5513
A St udy of Cognit ive Technology OFDM Syst em and Fr am e St ruct ure
Hua Hou, Wei Zhang 5514- 5521
Mat hem at ical Pr ogr am m ing Model on Joint and Recovery of Paper Scr ap
Zhixia JI ANG, Haifeng LUO, Jianj un YANG, Zhengqiang WEN 5522- 5528
Sequence Clust er ing Algor it hm Based on Weighed Sequent ial Pat t er n Sim ilar it y
Di Wu, Jiadong Ren 5529- 5536
Perform ance Analysis of Pat hfinding Algorit hm s Based On Map Dist r ibut ion
Yan Li, Zhenhua Zhou, Wenj u Zhao 5537- 5545
Fuzzy c- Means and Mean Shift Algor it hm for 3DPoint Clouds Denoising
Tongguang Ni, Xiaoqing Gu, Hongy uan Wang 5546- 5551
Measur em ent Met hod of t he Gr ain Quant it y Based on The Gr ound Pr essure
Fan Chao, Zhang Dex ian, Yang Tiej un, Fu Hongliang 5552- 5558
I nt uit ionist ic Fuzzy Set Based Task Scheduling w it h QoS Pr efer ence Aw ar eness
Juan Wang 5559- 5566
Reduct ion on Pr oposit ional Logic Set based on Cor relat ion Analysis
Zhi Huilai 5567- 5574
Const ruct ion of Geological Knowledge- based Syst em s of Railw ay Rout e Select ion
Lv Xikui, Zhou Xiaoping, He Bin 5575- 5584
Polygraph Surv ey and Evaluat ion Based on Analyt ic Hier archy Process
Zhixia Jiang, Yibo Liu, Pinchao Meng 5585- 5590
Const ruct ion Prot ocol of Wir eless Sensor Net w or k based on Cent r alized Clust ering Rout ing and Tim e Division Mult iplex ing MAC Pr ot ocol
Shit ao Yan, Mianrong Yang 5591- 5598
Key I nt ernet of Things Technology and Applicat ion Resear ch
Xu Bing 5599- 5602
I m plem ent at ion of I nput - Pr ocess- Out put Model for Measur ing I nfor m at ion Sy st em Pr oj ect Success
A'ang Subiy akt o, Abd. Rahm an Ahlan 5603- 5612
Det ect ing Rice Grow t h Using ALOS Mult ispect ral and Synt het ic Apert ure Radar
Bam bang Hendro Trisasongko, Dyah Ret no Panuj u, La Ode Sy am sul I m an 5613- 5620
Obj ect Tr acking Based on Mult iple Feat ur es Adapt ive Fusion
Jie Cao, Leilei Guo, Jinhua Wang, Di Wu 5621- 5628
Digit al I m age St abilizat ion Based on I m pr ov ed Scale I nvariant Feat ur e Tr ansform
Xiaoran Guo, Shaohui Cui, Dan Fang 5645- 5654
Sket ching Exper t Sy st em for Crim e I nvest igat ion Pur poses
Bagus Yudist ira, I Ket ut Gede Darm a Put r a, Anak Agung Kom pyang Oka Sudana 5655- 5660
Key Technology on Middlew are- based Dynam ic Tr affic I nform at ion Plat for m
Lei Wu, Tai Yang, Licai Yang 5661- 5568
Hy per t ension Expert Syst em w it h C5.0 Algor it hm and Fuzzy Logic PDF
Yang Bensehng, Yuan Xiangm eng, Huang Xiaoguang 5678- 5684
Applicat ion of Boost ing Algorit hm in Spam Filt r at ion
Wencheng Gu 5685- 5692
Par t it ioning of Oracle Applicat ion in St r uct ur ed Elect ronic Medical Records
Chaundi Pan, Jiandong Hu, Jian Shi 5693- 5698
I SSN: 2087- 278X
CONTACT:
Inst it ut e of Advanced Engineering and Science (IAES) email: info@iaesj ournal.com, admin@iaesj ournal.com.
Copyright© 2012 IAES Int it ut e of Advanced Engineering and Science
TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering Vol.12, No.7, July 2014, pp. 5669 ~ 5677
DOI: 10.11591/telkomnika.v12i7.5723 5669
Received February 1, 2013; Revised March 21, 2014; Accepted April 14, 2014
Hypertension Expert System with C5.0 Algorithm and
Fuzzy Logic
I Gusti Made Ngurah Ardi Yasa*1, I Ketut Gede Darma Putra2, Ni Md Ika Marini Mandenni3 Department of Information Technology, Udayana University, Bali, Indonesia
Bukit Jimbaran, Badung, Bali, Indonesia, Telp. 0361-7853533
*Corresponidng author, e-mail:[email protected], [email protected], [email protected]
Abstract
Expert System is a knowledge-based system which is its knowledge is coming from the experts itself. This system is expected to help users to take best decisions in solving the problems they face. This expert system can be applied in various fields of knowledges. Medical field is one area where expert system is needed in case of taking decision, such as diagnosing and treatment.Hypertension is one of medical disease that can be diagnosed from looking at the patient’s physical characteristics and the patient’s lifestyle. Beside using the experts knowledge in diagnosing process, we also combine it with C5.0 algorithms and fuzzy logic to get precise result. C5.0 algorithm is used to create a decision tree based on the experts, while fuzzy logic used to categorize the type of hypertensive disease that suffered by the patient and increase the level of accuracy of the diagnosing system. The accuracy of the combination between c5.0 algorithm and fuzzy logic is about 97.19%.
Keywords: expert system, hypertension, C5.0 algorithms, fuzzy logic
Copyright © 2014 Institute of Advanced Engineering and Science. All rights reserved.
1. Introduction
As many as 1 billion people worldwide suffer from hypertension. In the United States, nearly 1 in 3 adults (approximately 73 million people) have some degree of high blood pressure. Hypertension is a contributing factor to many other diseases including myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, heart failure, renal failure, and retinopathy, and is a leading cause of death [1].
Awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension are suboptimal. Only two-thirds of patients with hypertension are aware of their status, which means that a large segment of the population has hypertension that is unrecognized and untreated. Even in patients with known hypertension, some are not treated for various reasons; including physician and patient under-recognition of the importance of treatment.To minimize the impact of hypertension, the need for an expert system for early diagnosing patients with hypertension. Expert systems are computer programs that attempt to achieve the level of performance in a way that is comparable to solve problems with a human expert in taking a decision [2].
An Expert system is a computer program that simulates the judgment and behavior of a human being or an organization that has expert knowledge and experience in a particular field. Typically, such a system contains a knowledge base of accumulated experience and a set of rules for applying the condition to each particular situation that is described in the program. Sophisticated expert systems can be enhanced with additions to the knowledge base or to the set of rules. In other words, it is a software based system which makes or evaluates decisions based on rules established within the software [3]. Compared to the knowledge of human experts, the Expert System Knowledge has the advantages of permanent, easy to transfer, easy to edit, compatible, moderate and well suited for fault diagnosis [4].
ISSN: 2302-4046
TELKOMNIKA Vol. 12, No. 7, July 2014: 5669 – 5677 5670
Machine learning systems can be used to develop the knowledge bases used by expert systems. Given a set of clinical cases that act as examples, a machine learning system can produce a systematic description of those clinical features that uniquely characterise the clinical conditions. This knowledge can be expressed in the form of simple rules, or often as a decision tree [7].
Hypertension is a condition in which a person experiences an increase in blood pressure above normal. Hypertension is estimated to cause 4.5% of the global disease burden and is as prevalent in many developing countries as in developed countries. Worldwide, seven million premature deaths have been attributed to hypertension. In recent decades, it has become increasingly clear that the development of stroke, ischemic heart disease, and renal failure have been attributed by hypertension [8].
Many people have hypertension for years without even knowing it. According torecent estimates, one in four adults in the United States have hypertension, but, because there are few symptoms, nearly onethird of these people don’t know they have it. That is why it is called the “silent killer” [9].
2. Research Method
The type of disease that is created as the object of research is hypertension. Hypertension is classified into several types: Pre Hypertension, Stage I Hypertension and Stage II Hypertension [1]. Expert’s knowledge is obtained from literature sources such as library books and internist. Basic Informations based on the results of clinical examination and laboratory tests. This system’s knowledges is representated by using the C5.0 Algorithm and Fuzzy Logic. The system is developed into web-based system which giving the users ease of access. The output produced by this system is the belief of the illness and the stage of the hypertension.
2.1. C.50 Algorithm
C5.0 model done by splitting the sample based on the field that provides the maximum information gain. In C5.0 algorithms, the selection of the attributes processed using information gain. Attributes selected heuristically to find purest attributes, which is giving the most net node. If one of the branches of a decision tree derived from one class, then this branch is called pure [10]. Information gain is the main criteria that is used. So in selecting attributes for splitting objects in some classes, we should select the attributes that produce the best information gain [11].
The size of the information gain is used to select the test attributes at each node in the tree. This size is used to select the attributes or nodes on the tree. Attribute with the highest information gain value will be selected as the parent for the next node [12]. The formula to get the information gain value is:
, , … , ∑ (1)
S is a set that consists of s sample data. known as class attribute, m defines the classes in it, Ci (for i = 1, ..., m), S1 the number of samples of S in class Ci. To classify the samples that going to be used, Use the rule (1) above to obtain the required information. According to rule (1) above, pi is a proportion of the output class, same as the class Ci and estimated by si /s. Attribute A has specific values {a1, a2, ..., av}. Attribute A can be used for partition S into v subsets, {S1, S2, ..., Sv}, where Sj contains samples on S worth aj in A [11].
If A is chosen as the test attribute (for example, the best attribute for split), then this subset will be related to the branch of node set S. Sij is the number of samples in class Ci in a subset Sj. To get the value of a subset of the attribute A, then use formula (2),
∑ … , … , (2)
…
is the number of subsets j divided by the number of samples in S. To get the value of the gain, then used the formula [11].
TELKOMNIKA ISSN: 2302-4046
Hypertension Expert System with C5.0 Algorithm and Fuzzy… (I Gusti Made Ngurah Ardi Yasa) 5671
Having the first branch determined, the next process is to do the second iteration. In the second iteration, the attributes of the first branch will not be used in this process. The process of determining the second branch is the same as the previous method of determining branch. The iterative process will continue until the data can not be solved anymore. From the various existing branches will form a scheme that will end in an initial hypothesis.
2.2. Fuzzy Logic
Basically, Fuzzy Logic is a multivalued logic, that allows intermediate values to be defined between conventional evaluations like true/false, yes/no, high/low, etc. Notions like rather tall or very fast can be formulated mathematically and processed by computers, in order to apply a more human-like way of thinking in the programming of computers [13].
2.2.1. Knowledge Representation
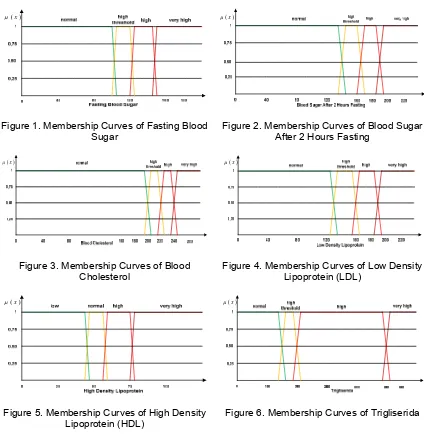
Knowledge of clinical symptoms and laboratory results of the patient is necessary for the representation of these facts along with an explanation of the question [14]. The question scheme of the system is obtained from the decision tree through C50 algorithm. The questions scheme will be ended by giving the result about which type the hypertension is. Laboratory results will represented by a fuzzy set with a membership function. Some fuzzy sets model shown below.
) ( x
( x)
Figure 1. Membership Curves of Fasting Blood Sugar
Figure 2. Membership Curves of Blood Sugar After 2 Hours Fasting
) ( x
( x)
Figure 3. Membership Curves of Blood Cholesterol
Figure 4. Membership Curves of Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
) ( x
( x)
Figure 5. Membership Curves of High Density Lipoprotein (HDL)
ISSN: 2302-4046
TELKOMNIKA Vol. 12, No. 7, July 2014: 5669 – 5677 5672
Membership functions of Fasting Blood Sugar:
,, ,
Membership functions of the Blood Sugar After Fasting 2 Hours:
,,
Membership functions of Blood Cholesterol:
,,
Membership functions of Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
,,
Membership functions of High Density Lipoprotein (HDL):
TELKOMNIKA ISSN: 2302-4046
Hypertension Expert System with C5.0 Algorithm and Fuzzy… (I Gusti Made Ngurah Ardi Yasa) 5673
Calculation of the degree of fuzzy membership for each symptom is determined by the value assigned by the user [15].
Table 1. Fuzzy Rule Rule
Number Rule Value
R000001 IF Parental history of suffering from hypertension is YES THEN CF = 0.90
R000002 IF Eat Food With High Salt Levels is often AND Stress is often THEN CF = 0.70
R000003 IF Eat Food With High Salt Levels is often AND Sleep Apnea is often THEN CF = 0.75
R000014 IF Stress is often AND vertigo is often THEN CF = 0.65
R000035 IF Smoking is very often AND Vertigo is often THEN CF = 0.72
R000045 IF Sistolic Blood Pressure Normal AND Diastolic Blood Pressure Normal THEN CF = 0.50
R000057 IF Sistolic Blood Pressure High AND Diastolic Blood Pressure High THEN CF = 0.90
R000068 IF Sistolic Blood Pressure High Threshold AND Diastolic Blood Pressure Very High
THEN CF = 0.85
Based on the degree of membership, calculate the implication function with MIN function [16]-[18].μ(x) is the degree of membership for x and wi is the result of implication.
, (4)
The process of composition is made to obtain the value zi of each rule. The certainty value from expert of each rule is value of zi [14].
2.2.3. Defuzzification
Defuzzification process is done using weighted average method defuzzification by calculating the average value of zi [16-18].
∑∑ (5)
wi is the result of implication and zi is the result of composition [14]. The results of defuzzification demonstrate the value of the belief for the syndrome experienced by patients.
2.2.4. Certainty Factor Calculation
The result of defuzzification process will be used to calculate the value of belief for the diagnosis. Firstly, will be calculated certainty factor (CF) sequential as follows [16].
, ∗ (6)
CF(x,y) is result of certainty factor sequential, CF(x) is result of defuzzification and CF(y) is the expert certainty value of each rule. In this study, CF sequential multiplies with the weight value of each phase of disease. CF sequential from several rules generated combined using the following calculation of the combined CF as follows [17].
ISSN: 2302-4046
TELKOMNIKA Vol. 12, No. 7, July 2014: 5669 – 5677 5674
The results of combined CF suggest the diagnosis of the disease to the symptoms experienced by patients [14].
3. Results and Discussion
The main objective of this research is to create an expert system which can be used for diagnosing hypertension. The expectation of this system is to help users to overcome the effects of hypertension by telling them early about their condition.
3.1. Knowledge Acquisition
The Knowledge Acquisition role is transferring knowledge that gained from completing a variety of literature and experts knowing into a knowledge base. This knowledge base will be the most important part of an expert system for storing all the knowledge to be used as a standard for decision making.
3.2. Knowledge Representation
The first thing that is done in representing the knowledge is started from generating a decision tree using C5.0 algorithm. The process of forming a decision tree start from selecting the initial tree branches. This branch is obtained from the value of the attribute that has the highest gain of all the existing attributes. In this case we use 15 attributes that will be used in generating a decision tree. The decision tree made up three-pronged branches, that in every branch later is the result of the question in the previous branch.
Figure 7. Decision Tree
After determining the first branch, the process continues to the next iteration. In the second iteration, the first branch attributes will not be used in this process. The process of determining the second branch is the same as the previous method to determine the first branch. Iterative process will continue until the data can not be solved again. From the various existing branches will form a scheme that will ended up by giving an initial hypothesis.
TELKOMNIKA ISSN: 2302-4046
Hypertension Expert System with C5.0 Algorithm and Fuzzy… (I Gusti Made Ngurah Ardi Yasa) 5675
The fuzzification process in the diagnosing hypertension is divided into 2 phases. The first phase begins with processing the data proximity of the decision tree with the data from the knowledge base that has undergone the fuzzification process. The data were fed by the user will be matched with hypotheses that have been made by fuzzy logic. The next process is processing the result of a laboratory data that may be owned by the user. Data from a laboratory results in numbers will be grouped into several classes.
Figure 9. Consultation User Interface With Fuzzy Logic
Results from each of these classes will be processed by implicating classes from every existing laboratory results.
3.3. System Performance
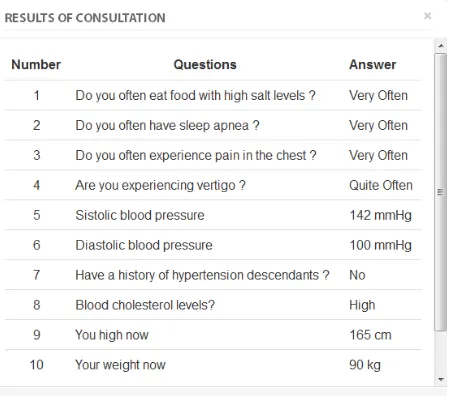
The performance of the expert system is obtained from the comparison of the results of the diagnosis made by a real expert with the diagnoses given by the expert system. Based on the structure of the system above, this expert system was tested in many different cases. One example of consultation and diagnosis of the system is given in Figure 10.
Figure 10. Results of Consultation
ISSN: 2302-4046
TELKOMNIKA Vol. 12, No. 7, July 2014: 5669 – 5677 5676
Table 2. Expert Systems Performance with C5.0 algorithm
Scheme Case Total Cases Same Case With Scheme Correct Wrong Accuracy (%)
1 900 50 44 6 88
Average of the difference result 95.57
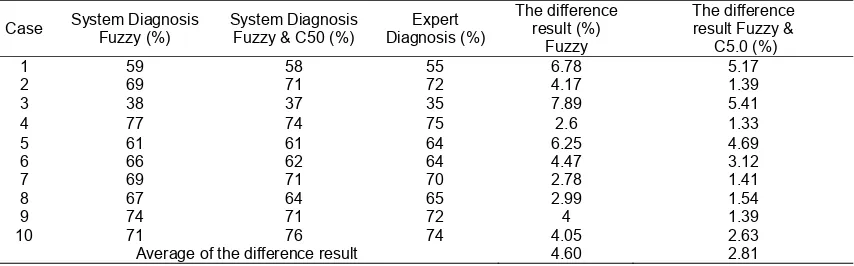
Expert System Performance with a combination of C5.0 and fuzzy logic algorithm has a better accuracy rate than the use of two methods separately. The combination can improve the accuracy of diagnoses predicted by the expert system. The expert system performance with a combination of C5.0 algorithms and fuzzy logic can be seen in Table 3.
Table 3. Performance with a Combination of C5.0 Algorithms and Fuzzy Logic
Case System Diagnosis Fuzzy (%)
Average of the difference result 4.60 2.81
4. Conclusion
Expert system for diagnosing Hypertension has been developed into a web-based platform to receive feed in a form of physical symptoms and laboratory test results. the questions systematic that arises is a decision tree derived from processing the required data by using the C5.0 algorithm. Fuzzy rules relating each disease symptoms using expert certainty. This system provides an output of hypertension illness possibility that suffered by users. The combination of C50 with fuzzy logic algorithm increase the expert system hypotheses accuracy. From statistical Performance accuracy of c5.0 is 95.7% and Fuzzy logic 95.4%. Test results with a combination of c5.0 algorithm with fuzzy logic system shows that the developed expert system has 97.19% accuracy of the similarity to a real expert.
References
[1] Jeffery Martin. Hypertension Guidelines: Revisiting the JNC 7 Recommendations. The Journal of Lancaster General Hospital. 2008; 3(3): 91-97.
[2] Joseph, Hans-D. Web-Based Expert System for Classification of Industrial and Commercial Waste Products. Journal of Emerging Trends in Computing and Information Sciences. 2011; 2(6): 357-262. [3] Josephine, Jeyabalaraja. Expert System and Knowledge Management for Software Developer in
Software Companies. International Journal of Information and Communication Technology Research. 2012; 2(3): 243-247.
[4] Feng Yongxin, Yang Tao.Study of Fault Diagnosis Method for Wind Turbine with Decision Classification Algorithms and Expert System. TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering. 2012; 10(5): 905-910.
TELKOMNIKA ISSN: 2302-4046
Hypertension Expert System with C5.0 Algorithm and Fuzzy… (I Gusti Made Ngurah Ardi Yasa) 5677
[6] Santosh Kumar, Dipti Prava. An Expert System for Diagnosis of Human Diseases. International Journal of Computer Applications. 2010; 1(13): 71-73.
[7] Prasadl, Krishna. An Approach to Develop Expert Systems in Medical Diagnosis Using Machine Learning Algorithms (Asthma) and A Performance Study. International Journal on Soft Computing (IJSC). 2011; 2(1): 26-33.
[8] Syer Ree Tee, Xin Yun Teoh. The Prevalence of Hypertension and Its Associated Risk Factors In Two Rural Communities In Penang, Malaysia. IeJSME. 2010: 4(2): 27-40.
[9] Christine Laine ed. Living With Hypertension. American College of Physicians and Microlife Corporation. Report number: 4. 2004.
[10] Prof. Nilima Patil, Prof Rekha. Comparison of C5.0 & CART Classification algorithms using pruning technique. International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT). 2012; 1(4): 1-5. [11] Ernawati. Prediksi Status Keaktifan Studi Mahasiswa Dengan Algoritma C5.0 Dan K-Nearest
Neighbor Thesis. Bogor: Postgraduate IPB. 2008.
[12] Mehmed Kantardzic. Data Mining: Concepts, Models, Methods, and Algorithms. IEEE Press, A john Wiley & Sons, Inc, Publication. 2003: 177-178.
[13] LA Zadeh. Making computers think like people. IEEE. Spectrum.1998; 21(8) 26-32.
[14] Darma Putra. Fuzzy Expert System for Tropical Infectious Disease by Certainty Factor. TELKOMNIKA Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering. 2012; 10(4): 825-836.
[15] Putu Manik Prihatini, Katut Gede Darma Putra. Expert knowledge based system with uncertainity for Tropical Infections Dieseased Diagnosis. IJSCSI. 2012; 3(4): 157-163.
[16] Sivanandam SN, Sumathi S, Deepa SN. Introduction to Fuzzy Logic using MATLAB. New York: Springer. 2007.
[17] Negnevitsky Michael. Artificial Intelligence A Guide to Intelligent Systems Second Edition. England: Pearson Education. 2002