i
INTEGRATING BASIC PRONUNCIATION MATERIAL IN SPEAKING
CLASS FOR XI GRADE STUDENTS OF SMA BOPKRI 2 YOGYAKARTA
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN FINAL PAPER
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
Gressiana Soik
Student Number: 081214117
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAMME DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
v
I dedicate this final paper to my LORD, Jesus Christ.
T he LORD the Shepherd of His People
A Psalm of David
T he L ORD is my sheperd;
I shall not want.
H e makes me to lie down in green pastures;
H e leads me beside the still waters.
H e restores my soul;
H e leads me in the paths of righteousness
F or H is name’s sake.
Yea, though I walk through the valley of the shadow of death,
I will fear no evil;
F or You are with me;
Your rod and Your staff, they comfort me.
You prepare a table before me in the presence of my enemies;
You anoint my head with oil;
M y cup runs over;
Surely goodness and mercy shall follow me
All the days of my life;
And I will dwell in the house of the L ORD forever.
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to express my thanks to God that I could
finish this thesis. In doing this paper, God helped me a lot. I would not have been
able to finish my paper without the help of God. Therefore, I really thank God for
His blessing and grace He gave.
I would like to express my gratitude to Christina Kristiyani, S.Pd.,
M.Pd. for her guidance during the moment of final paper writing. She was very
patient in commenting my paper and giving so many helpful advices so that I
could revise and revise my paper. I would express my gratitute also for all PBI
lecturers who had given their best in teaching me as their student. I would like to
thank them all for the knowledge and experienced they had shared to me.
I would like to thank Ibu Sri Rahayuningsih as the headmaster of
SMA BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta, Ibu Ariatmi PH as one of the English teachers in
that school and also all the students who were involved in my research. I would
like to thank them for the help in the process of completing my paper.
My thanks also for my beloved parents, my father and my mother for
the support and advices during the time I studied in Sanata Dharma University. I
am proud to be their daughter. I would like to thank them for all the best they gave
to me. I also thank my sisters and brothers for their support and motivational
words they always gave to me. I would also thank my lovely boyfriend for his
viii
My thanks also go to all my friends. I really enjoy my time working
together with my friends. I thank them all for being good friends for me. I really
learned many things from them all. May God bless them all.
ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGE... ii
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY... iv
DEDICATION PAGE... v A. Review of Related Literature... 8
A.1. Dick and Carey’s Model of Instruction... 9
A.2. Kemp’s Model of Instruction... 12
A.3. Pronunciation... 17
A.4.c. Strategy in Teaching Speaking... 23
B. Findings... 23
B.1. Identify Instructional Goals... 24
B.2. Analyze Learners and Contexts... 24
B.3. Write Perofmance Objectives... 24
x
B.5. Develop and Select Instructional Material... 26
B.5.a. The speaking material... 26
B.5.b. Exercise for the students... 27
B.5.c. Pronunciation... 28
CHAPTER III CONCLUSION... 31
REFERENCES... 33
APPENDICES APPENDIX 1 Designed Material for Teacher... 36
APPENDIX 2 Designed Material for Students... 45
xi
LIST OF TABLES
xii
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 2.1Dick and Carey System Approach Model for Designing Instruction... 9
xiii ABSTRACT
Soik, Gressiana. 2012. Integrating Basic Pronunciation Material in Speaking Class for XI Grade Students of SMA BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program. Department of Language and Arts Education. Faculty of Teachers Training and Education. Sanata Dharma University.
In learning a language, learners have to deal with the language aspects. One of the language aspects is pronunciation. Pronunciation deals with the way words sound. English is one of the languages that have differences in the way the words are spelled and pronounced. Therefore, pronunciation is considered to be important to be learned by English learners.There are some benefits that the learners may achieve in learning pronunciation. The learner will be able to differenciate the minimal difference of two sounds. By knowing the phonetic alphabets, the learners will also know how to read phonetic transcriptions of English words. It will also help the learners in listening.
Based on those considerations, the writer was interested in designing a pronunciation material for the students. The writer chose XI grade students of SMA BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta to be the respondents. The writer integrated the basic pronunciation material in speaking class. There was a research problem to answer. “What does the basic Pronunciation material look like? The writer tried to find out what the basic pronunciation material look like.
In designing the material, the writer used Educational Reseach and Development as the method. The writer used the steps in designing material based on Dick and Carey’s Model of Instruction and Kemp’s Model of Instruction. The writer combined those two models by using the strenght of each model.
The final product of this research is a unit of speaking material that contains basic pronunciation material. The topic of the material is “Asking and Giving Opinion”. The material is divided into three main points. That are: the speaking material about “Asking and Giving Opinion”, the exercises for the students, and pronunciation material. Pronunciation material is also divided into five parts. They are consonants, vowels, diphthongs, phonetic transcription and practicing part. The writer hopes this material will be useful for the teacher and students of SMA BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta.
xiv
ABSTRAK
Soik, Gressiana. 2012. Integrating Basic Pronunciation Material in Speaking Class for XI Grade Students of SMA BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program. Department of Language and Arts Education. Faculty of Teachers Training and Education. Sanata Dharma University.
Dalam pembelajaran bahasa, pelajar harus mengetahui aspek-aspek bahasa tersebut. Salah satu aspek dari bahasa adalah pengucapan. Pengucapan selalu berkaitan dengan bagaimana bunyi dari suatu kata. Bahasa Inggris adalah salah satu bahasa yang memiliki perbedaan pada cara penulisan dan pengucapan kata-katanya. Sehingga, pengucapan sangatlah penting untuk dipelajari oleh pelajar bahasa Inggris. Ada beberapa manfaat yang dapat diperoleh dari belajar pengucapan. Pelajar akan mampu mengetahui perbedaan sederhana dari dua bunyi. Dengan mengetahui fonetik alfabet, pelajar pun secara tidak langsung bisa membaca transkripsi fonetik. Hal ini juga dapat membantu pelajar dalam mendengarkan.
Berdasarkan pertimbangan diatas, penulis tertarik untuk mendesain materi mengenai cara pengucapan bahasa Inggris. Penulis memilih siswa kelas XI dari SMA BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta sebagai subjek dan sasaran penelitian. Penulis mengintegrasikan materi mengenai cara pengucapan bahasa Inggris dalam pelajaran berbicara bahasa Inggris. Adapun rumusan masalahnya adalah “Seperti apakah bentuk materi pengucapan bahasa Inggris?” Penulis mencoba menemukan jawaban atas permasalan tersebut.
Dalam mendesain materi ini, penulis mengunakan metode penelitian dan pengembangan berbasis pendidikan. Penulis mengunakan langkah-langkah menyusun materi sesuai dengan teori menyusun instruksi yang dikemukakan oleh Dick and Carey dan Kemp. Penulis menggabungkan kedua model tersebut dengan mengambil kelebihan dari masing-masing model.
Produk akhir dari penelitian ini adalah satu unit materi berbicara bahasa Inggris yang disertai materi mengenai cara pengucapan bahasa Inggris. Topik dari materi ini adalah “Meminta dan Memberikan Pendapat”. Materi ini dibagi menjadi tiga bagian utama yaitu materi berbicara, latihan siswa, dan materi pengucapan. Materi pengucapan juga dibagi lagi kedalam lima bagian yaitu konsonan, vocal, diftong, transkripsi fonetik dan praktek siswa. Penulis berharap, materi ini dapat berguna bagi guru dan siswa SMA BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta.
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter includes the background information of the study in which
the writer explains the investigated problem, the importance of the study and the
overview of the study strategy. It also involves the research method of the study.
A. Background
In studying a language, the learners have to deal with the language aspects.
According to Syafei (1988), the language aspects include “pronunciation,
grammar, lexis (vocabulary and idiom), style (appropriate to the situation),
function, and discourse. Pronunciation is stated as one of language aspects that
students need to learn and master. Pronunciation deals with the way words sound.
Dardjowidjojo (2009) said that people often get confused with the
difference of sounds and letters. He emphasized, “sounds are not letters” (p.16).
Although sounds are represented graphycally by letters, it does not mean that it is
synonymous with a letter. (Dardjowidjojo, 2009, p.16). Besides that, Traugott and
Pratt (1980) said that for English, there are differeces between the way words are
spelled and the way words are pronounced. Therefore, the English learners will
have to face the problem dealing with pronunciation. Syafei (1988) also stated
that the diffuculties for English learners to master pronunciation is because of the
According to Syafei (1988), “Pronunciation is a two fold process. It
involves the recognition of sounds as well as the production of sounds.” (p.1).
Lado and Fries (1954) also agreed that the students have problem in recognizing
the significant sounds of the language before finally they can learn how to
produce it.
In the School Based Curriculum (Government Regulation number 22 of
year 2006), the English subject is divided into four skills such as listening,
speaking, reading and writing. Grammar, vocabulary and pronunciation are the
elements of language. It means those elements cannot be separated from the
language. There are two ways of teaching those elements according to Syafei
(1988). The first is to integrate it to other skills (listening, speaking, reading and
writing). The second is to teach it separately from those skills which means the
teacher will focus more on those elements. (Syafei, 1988, p.1)
Based on the writer’s observation in SMA BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta,
pronunciation is not taught to the students. The teacher did not use any
pronunciation material to teach to the students. In fact, in the School Based
Curriculum, the competent standard for speaking is “to express the meaning of
formal and sustained transactional conversations (to get things done) and
interpersonal conversations (to socialize) accurately, fluently, and acceptably
using various oral expressions in daily context by involving speech acts:....”
(Government Regulation number 22 of year 2006). By having a good
Most teachers in SMA BOPKRI 2 had tried to involve pronunciation in
those four skills, but they did not have the specific materials to teach it. The
teachers only tried to correct the wrong pronunciation of their students and the
students only remembered the pronunciation of the words from the teacher. In
fact, the students did not know how to pronounce the words by themselves.
Therefore, the students were dependent on the teacher.
The fact that pronunciation is not taught to the SMA BOPKRI 2 students
really interested the writer. As what has been mentioned, pronunciation is one of
the English language elements. Pronunciation cannot be separated from the
English language itself. Therefore, the writer is going to integrate basic
pronunciation material in speaking class for XI grade students of SMA BOPKRI 2
Yogyakarta. The writer is going to design the basic pronunciation material that
will be integrated to Speaking.
The reason for the writer to choose SMA BOPKRI 2 was that, the writer
has seen the need of the students to master pronunciation based on the writer’s
observation when the writer did teaching practice there. The writer has already
known the students’ level of pronunciation. Based on the writer’s observation, the
writer made a conclusion that the students’ abilities in pronouncing the English
words were not good enough. The writer really wanted to help the students to
make their pronunciation better.
The students can obtain many benefits of learning pronunciation. Lado and
differences of sounds. By knowing the basic pronunciation materials, the students
will be able to differenciate two different sounds that seem similar. For example
the sounds /I/ in “fill” and /i:/ in “feel”, /ʃ/ in “sheet” and /s/ in “seat”, etc. Besides
that, Lado and Fries (1954) also said that knowing the phonetic alphabet can give
the students memory clue to know how to read each symbol. It means, if the
students know how to read phonetic alphabet, the students will be able to
pronounce words correctly by consulting dictionary. It is essential because
different pronunciation can lead to different meaning.
Knowing how English words sound can also help the students in listening.
According to Lado and Fries (1954), most students have problem dealing with
understanding spoken language. He said that most students fail in interpreting
what the speaker says. It is because of inability of the students in recognizing the
sounds of the language. Therefore, it is important for the students to learn the
word sounds. By knowing the word sounds, the students can easily guess what the
speaker says to them. The students will also understand easily what the speaker
says. It really helps them in comunicating using English. The students can also
write what the speaker says to them. It is needed if the students have to write
information from the speaker.
This study is also aimed to help the teacher of SMA BOPKRI 2
Yogyakarta in combining Pronunciation material with speaking material. The
writer expects that this research will also be useful for the XI grade students of
Pronunciation. The writer hopes, it will also build the students’ motivation to
learn and speak English. Therefore, in this research the writer formulated one
problem to be solved. That is what does the basic Pronunciation material look
like?
B. Research Method
This research was conducted using Educational Research and
Development method. It is a method used in developing material. It is aimed to
identify educational problems that are needed to be solved by educational
products, like textbook, syllabus, instructional media, etc. The writer used this
method because the writer wanted to analyze the students’ problems in speaking
especially in pronunciation and to design speaking material involving basic
pronunciation material based on the students’ needs. According to Galls and Borg
(2007):
Research and Development is an industry-based development model in which the findings of research are used to design new products and procedures, which then are systematically field-tested, evaluated, and refined until they meet specified criteria of effectiveness, quality, or similar standards. (p. 589)
This research was also based on Dick and Carey’s system approach model
for designing instruction. Dick and Carey’s system approach model is mainly
about a plan and a course development in designing the material. Dick and Carey
(2005) mentioned ten steps in designing instructions. Besides that, the writer also
use Kemp’s model of instruction. Kemps mentions eight steps. Kemps’s model is
more flexible. Therefore, the teacher can move from one step to another step
writer only used some steps to design the material. The writer did not design
assessment for the students.
In conducting this research, the steps based on Dick and Carey’s system
approach model of Educational Research and Development (2005) and Kemps
Model of Instuction (1977) were used. Those steps would be elaborated more
below.
1. Identify instructional goals
The first step the writer had to do was to identity the instructional goals. It
was about what the writer wanted the students to be able to do after they had
completed the writer’s instruction. In this step the writer tried to select the topic
and list the general purposes.
2. Analyze learners and contexts
The writer would analyze the learners’ needs by gathering the data from
the learners. The writer tried to analyze the learning condition and learning styles
of the students so that the writer could make the suitable material for the students.
It is the material based on the students’ need.
3. Write performance objectives
This was the step when the writer decided the goals. The writer had to
write the goals in form of statements. It is what the students should be able to do
after the students had compeleted the instruction.
4. Develop instructional strategy
The writer would identify the strategy that would be used in the writer’s
components of students learning including pre-instructional activities,
presentation of contents, learner participation and assessments.
5. Develop and select instructional materials
The writer would use the instructional strategy to develop the instructional
8 CHAPTER II
DISCUSSION
This chapter includes the elaboration of the related literature used in the
research and the findings as well as the interpretation of the findings.
A. Review of Related Literature
In this research the writer used several theories as the basic theories to
design the material. Those theories are about Dick and Carey’s model of
instruction, Kemp’s model of instruction, pronunciation and speaking. Dick and
Carey’s models of instruction and Kemp’s model of instruction were used as the
basic theories to design the material which contained some steps the writer had to
follow in designing the material. The writer chose some steps in Kemp’s theory
and combined it to Dick and Carey’s Theory. There are five steps that the writer
chose. It had beed elaborated more in the methodology in the first chapter. By
following those steps, the writer would finally come to the developing and
selecting the material. Therefore, the writer would need theory about
pronunciation to be integrated as the basic pronuncation material. The writer took
some examples of words that consisted of phonetic alphabet that included
consonants, vowels and diphthongs to be put in the material. The writer made the
speaking material as the main material to teach. In this case, the theory about
speaking was needed. It was needed by the writer to know the difficulties that the
material and activities for the teacher and the students. All of those theories will
be elaborated more in the following points:
1. Dick and Carey’s Model of Instruction
According to Dick and Carey (2005), “instruction process itself can be
viewed as a system” (p. 2). The components of system include the learners, the
instructor, the instructional materials, and the learning environment. Teachers are
supposed to be able to design material because one of the components of system is
the instructional material. There are ten steps that the teachers should follow to
design instruction based on Dick and Carey’s model of instruction, which can be
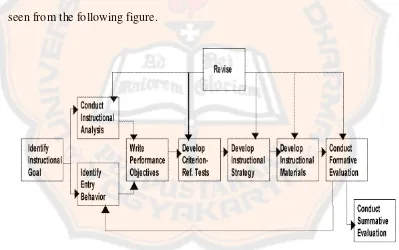
seen from the following figure.
The procedure of figure 2.1 will be elaborated below.
a. Identify instructional goals
Instructional goals deal with what the designer wants the students to be
able to do after they have completed the instruction. It can be the lists of goals. It
means the designer can make more than one goal of instruction. (p. 6)
b. Conduct instructional analysis
Conducting instructional analysis is needed “to determine step-by-step
what the students were doing when they performed that goal” (p. 6). This included
the determination of the skills, knowledge, and attitudes that were required for the
learners to be able to begin the instruction (p. 6).
c. Analyze learners and contexts
It is stated that “there is a parallel analysis of the learners, the context in
which they will learn the skills, and the context in which they will use them” (p.
6). It means there is a relation between the learners, their skills and the context
which they use their skills. It is also stated that “Learner’s current skill and
preferences, and attitudes are determined along with the characteristics of the
instructional setting and the setting in which the skills will eventually be used” (p.
6). The learners’ skills depend on the context.
d. Write performance objectives
This is the step to write the statements of the goals. It can be written
“based on the instructional analysis and the statements of entry behaviours” (p. 6).
condition under which the skill must be performed, and the criteria for successfull
performance” (p. 6).
e. Develop assessment instruments
This step is to design assessment istrument. It is designed to measure the
learners’ ability to perform what had been written in the objectives (p. 6). This
will emphasize more on the skills describe in the objectives (p. 6).
f. Develop instructional strategy
It is the step to identify the strategy that would be used in the instruction in
order to achieve the terminal objective (p. 6). This would involve several
components of students learning including pre-instructional activities,
presentation of contents, learner participation and assessments (p. 6).
g. Develop and select instructional materials
This step is to use the instructional strategy to develop the instructional
material (p. 7). It includes “the instructor’s guides, students’ modules, overhead
transparancy, video-taped, computer-based multimedia formats, and web-paged
for distance learning” (p. 7).
h. Design and conduct formative evaluation of instruction
This step is to design the formative evaluation. There are three types of
formative evaluation to be refered to, which are “one-to-one evaluation,
small-group evaluation, and field-trial evaluation” (p. 7).
i. Revise instruction
After finished with the 9 steps mentioned before, the next step is to revise
summarized and interpreted to find out the difficulties experienced by the learners
in achieving the objectives” (p. 7). The designer will revise the instruction based
on the result of formative evaluation.
j. Design and conduct summative evaluation
Within this step, the designer has to design the summative evaluation to
assess the students’ ability. It is stated that summative evaluation is “an evaluation
of the absolute and/or relative value of worth of the instruction and occurs only
after the instruction has been formatively evaluated and sufficiently revised to
meet the standard of the designer” (p. 8).
This system approach can be used to identify “what is to be taught”,
determine “how it will be taught” and evaluate “the instruction” (p. 9). The
system approach provides the guidelines for the writer to design material. It helps
the writer to focus on what the learner are supposed to be able to do as it is stated
in Dick and Carey’s book “The Systematic Design of Instruction” (2005: p. 8).
2. Kemp’s Model of Instruction
Kemp’s model of instruction is more flexible. Teacher can choose
whichever component to start first. The teacher can also move from one
component to another component freely. There are only eight steps in Kemp’s
model of instruction. The relationship among the components can be seen from
Figure 2.2 Kemp’s Model of Instruction
The components of Kemps’ Model of Instruction can be described below.
a. Goals, Topics, and General Purposes
Kemp began with stating a question, which is “what do you want to
accomplish in teaching each topic?” (p. 13). This part is divided into three which
will be elaborated based on Kemp’s theory.
1) Identifying Goals
The goals can be derived from society, students and subject area.
“Statements of goals should recognize changes in learners’ needs and interests, as
well as changes in the needs of society and its institutions” (p. 14).
2) Selecting Topics
After recognizing the goals, the designer has to list the major topics. The
this point it become necessary to decide how many topics should be treated and to
what depth” (p. 15).
3) Listing General Purposes
General purpose is accepted as a starting point for the planning (p. 16).
Some expressions can be used to state the general purposes. They are used to
“signifying broadly what the teacher wants to accomplish in the topic” (p. 16).
Some of the expressions that are commonly used are:
to acquire a skill to comprehend to learn to appreciate to determine to like to become aware of to enjoy to master to become familiar with to grasp the significance of to perceive to be introduced to to have the feeling for to understand to be believe in to know to use
b. Learner Characteristics
Kemp stated a question to be answered that is, “what factors do you want
to know about the student group or individual learners that will affect plans for
their learning?” (p. 18). In order to design an instructional plan, the teacher should
know some factors that will contribute information about the learners. The
information can be gotten from two areas.
1) Learning Condition
It is stated that “learning condition refers to a group of factors that can
affect a person’s ability to concentrate, absorb, and retain information” (p. 19).
Each person has different responds to environment. As an example, the students’
responses to music while studying are different. Some students enjoy studying
2) Learning styles
Different person has different learning style. “Some profit more from
visual approach; others from verbal (listening and/or reading) experiences; and
still others from physical activities and the manipulation of objects” (p.20)
c. Learning Objectives
Kemp proposed one question dealing with learning objective, which is
“what should students know or be able to do, or in what ways should they behave
differently, after studying this topic?” (p. 23). The objective can be categorized as
cognitive, psychomotoric and affective.
In writing objective, there will be some difficulties. Therefore, there has to
be a procedure to be followed. Starting with defining an action verb, followed by
the content reference that describe the subject being treated, followed by the
performance standards, and finally it is followed by criteria or conditions under
which the learning must take place. (p. 29)
The level of objectives has to be considered. There are 6 levels that are
stated by Kemp which are knowledge as the lowest level, comprehension,
application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation as the highest level. (p. 31)
d. Subject Content
This part starts with a question “what subject content should be treated?”
or “what subject content support each objective?” (p. 43). There are two steps that
should be accomplished, which are organizing content and task analysis.
Organizing the content based on the topics that have been decided and making the
e. Pre-Assessment
To check the students existing knowledge, pre-assessment can be used.
There are two kinds of pre-assessment, which are prerequisite testing and
pretesting. “A prerequisite test determines whether students have the appropriate
private background preparation for the topic” (p. 51). Meanwhile pretesting test is
used to “determine which of the objectives students may already have achieved”
(p. 51)
f. Teaching/Learning Activities Resources
It deals with the instructional method and instructional resources to
accomplish the objectives (p. 55). There are many methods that can be used in
teaching and learning activity. Some of the examples are group presentation,
individual learning, and interaction between teacher and students (pp. 60-70).
g. Support Service
It includes the support services that are required to implement the design
plan. In order to define the support service, the teacher has to know the budget
during development and during implementation (p. 85). Besides that, defining
facilities, equipments, time and schedule and coordinating with other activities are
also needed.
h. Evaluation
This is the last part of designing instruction. The final step to do is to
evaluate the students whether the students really achieve the goal or not. This is
3. Pronunciation
The theory about pronunciation is needed by the writer to design basic
pronunciation material. There is one of the terms used in theory about
pronunciation that will be elaborated more by the writer. The term is ‘”phonetics”.
Phonetics is also known as the sound of language. According to
Dardjowidjojo (2009), “phonetics is a science that deals with the sound of human
language” (p. 12). Dardjowidjojo divided phonetics into acoustic phonetics,
auditory phonetics, and articulatory phonetics.
Dardjowidjojo (2009) said, “Acoustic phonetics deals with the study of the
physical properties of sounds in the form of sound waves that result from the
production of the sounds” (p.12). Meanwhile “Auditory phonetics deals with how
sound are perceived by our brains” (p.13). As the speaker speaks, the sounds the
speaker produces will create sound waves that will be catch by the ears of the
listener. Dardjowidjojo (2009) stated, “Articulatory phonetics also deals with the
sound of language, but it focuses on how the sounds are produced” (p. 14). It also
deals with the speech mechanism. It includes several things that have role in
producing sounds.
In this paper, the writer focused on articulatory phonetics. Jurafsky and
Martin (2009) also stated that articulatory phonetics deals with “how speech
sounds are produced by articulators in the mouth” (p.216). He also said that
articulatory phonetics deals with the production of sounds by the various organs in
the mouth, throat, and nose which modify the airflow from the lungs
Wray, Trott and Bloomer (1998) said that, if someone is focusing on
pronunciation, it will be clear that he/she needs “a means of transcribing sounds in
some details” (p. 195).The learners need to be able to demonstrate the sounds on
the paper so that they can see the differences between the sounds. Traugott and
Pratt (1980) also stated that in studying a language, “it’s important to have some
way to write down sounds unambiguously” (p. 46). For these reason, International
Phonetic Alphabet (IPA) was developed in late 1880s with the aim of transcribing
the sounds of human language (stated in Traugott and Pratt, 1980, p.46, and
Jurafsky and Martin, 2009, p 216). Syafei (1988) said that, “Phonetic alphabets
are based on the principle that one symbol is always used to represent a given
sound, and each sound is represented by one symbol only” (p. 3). Syafei (1998)
also said, “Writting down the pronunciation of an utterance with these symbols is
known as transcription” (p. 3). Therefore, the term “phonetic transcription” is also
used to refer to the combination of phonetic alphabets from the sound of a word.
According to Indriani (2005), the English speech sounds can be classified
into two which are consonants and vowel (p. 8). However, there is one more
English speech sound which is diphthong or gliding vowels.
a. Consonants
Consonant deals with many speech mechanisms. To define the sound of a
consonant, the learner has to know the anatomy of a consonant. It includes the
airstream mechanism, oral or nasal, the manner of articulation, airflow central or
Fromkin, Rodman and Hyams (2007), there are 25 consonants in English which
can be seen from the following table.
Table 2.1 Some Phonetic Symbol for American English Consonant
Bilabial Labiodental Interdental Alveolar Palatal Velar Glottal Stop (oral)
alveolar, palatal, velar and glottal are classified into the place of articulation. It is
classified based on the articulators which are moving when the certain sounds are
produced. Table 1.1 also has stop, nasal, fricative, affricative, glide and liquid as
the manner of articulation. According to Fromkin, Rodman and Hyams (2007),
the manner of articulation deals with the way the airstream flows out of the lungs.
The airstream can flow from the lungs up and out of the mouth which is called
“oral sound” or out of the nose which is called “nasal sound”. The vocal cords
not vibrate which means of producing “voiceless sounds”. (Fromkin, Rodman and
Hyams, 2007, p.229)
It is better for the students to know the theory of consonants. If the students
master the sounds of consonants and each symbol, they will find it easier to read
the symbol or write down the symbol in form of phonetic transcription. Besides
that, by knowing the consonants, the students will be able to recognize the
minimal difference of the consonants. For example the difference between voiced
and voiceless consonants.
b. Vowels
Vowels are voices that escape freely from the mouth without any fricative.
According to Jurafsky and Martin (2009), “vowels can be characterized by the
position of the articulators as they are made” (p.222). There are 12 vowels in
English according to Indriani (2005, p. 13).
1. /i/ - tea 4. /œ/ - sad 7. /a:/ - art 10. /ʊ/ - foot
2. /I/ - sit 5. /3:/ - bird 8. /ʌ/ - up 11. /ᴐ:/ - war 3. /e/ - pen 6. /ә/ - ago 9. /u:/ - food 12. /ɒ/ - not
The theory about vowel will help the student differenciate two similar vowel
sounds. For example, the diferrence between /i:/ and /I/, /ᴐ:/ and /ɒ/, /u: / and /ʊ/,
etc.
c. Diphthongs
According to Fromkin, Rodman and Hyams (2007), “diphthong is a
some people agree to have 9 diphthongs meanwhile some agree to have 8
diphthongs because they consider the diphthong /ᴐә/ as /ᴐ:/.
1. /aI/ - like 4. /Iә/ - hear 7. /ᴐә/ - more
2. /eI/ - day 5. /ʊә/ - doer 8. /aʊ/ - down
3. /ᴐI/ - boy 6. /ɛә/ - care 9. /әʊ/ - show
This diphthongs theory is aslo essential to be learned by the students. The
students will know some combination of vowels sounds. The students can also
know the difference between vowels and diphthongs.
Those three elements of speech sounds are really important for the
students to be able to master basic pronunciation material. By knowing each of
those elements, the students will be able to recognize sounds they are listening.
They can also write the sounds they are listening as of phonetics transcription.
Indirectly, the students will know how to read phonetics transcriptions of English
words. They can consult dictionary to find out how a certain word sounds.
4. Speaking Skill
In mastering a language, the students have to be able to communicate
using the language. One important skill to master is speaking. There are three
main parts in speaking that will be viewed theoretically.
a. Nature of Speaking
Speaking is one skill that can be acquired naturally. When a baby is born,
then grows up, the baby will learn speaking firstly, and it happens naturally. As
language is used for communicative purpose, speaking is considered as an
According to Richards and Rodgers (2001), “language can be called as
interactional view” (p. 21). It sees language as a tool in the relation of
“interpersonal relation” and “the performance of social transactions between
individuals” (p 21). In relation to interpersonal relation, speaking takes a bigger
role than the other three skills as it is viewed as a tool to express meaning (p. 21).
The importance of knowing the nature of speaking is to make the writer
sees the language as communication tool in speaking class. The students need to
speak and to use the language to communicate with others. It also makes the
writer sees that speaking skill can be acquired by the students naturally if the
students keep practicing.
b. Nature of Teaching Speaking
In teaching speaking, there are many problems that teachers should deal
with. According to Ur (1999: 121), “some fundamental problems that appear in
the speaking class include inhibition, complete silence, and low participation” (as
cited in Sinatra, 2010, p. 15). Learners are often afraid of making mistake and
being criticized by others. They also feel shy to be the centre of attention when
they are speaking. Some learners also complain that they do not have something
to talk or even they do not know how to say. Therefore, some learners prefer
using mother tongue because it is easier (Sinatra, 2010, p. 15-16).
In the School Based Curriculum (Government Regulation number 22 of
year 2006), each meeting of English teaching and learning is 2 times 45 minutes.
It means the students are limited by time. If some students are active in the class,
problem comes up dealing with the passive students. The passive students will
only have very little time to talk (Sinatra, 2010, p. 16).
By knowing the possible problems that may appear in speaking class, the
writer can make the strategy to overcome the problems. The writer can aslo make
the materials and activities that suitable for speaking class.
c. Strategy in Teaching Speaking
Dealing with the problems in teaching speaking, the teachers are expected
to design activity that will be able to overcome the problems (Sinatra, 2010, p.
15-16). Ur (1999, p. 120) suggests four characteristics of successful speaking class.
First, the teacher should provide much time for the learners to talk. Second,
classroom activity should not be dominated by the active students who are
talkative. Third, interesting topic will make the learners eager to speak. The last,
the teacher should provide material that is relevant and comprehensible. (cited in
Sinatra, 2010, p. 16).
These strategies are needed by the writer to design activities so that all the
students can be active in class with no exception. All students should have enough
chances and time to speak in class. Therefore all students will have enough
speaking practice.
B. Findings
In this part, the writer would explain what the writer had got and done
during this research. As the writer had mentioned in the methodology, the writer
There were 5 steps the writer had followed. All of those steps will be elaborated
as follows:
1. Identify Instructional Goals
In this part the writer selected the topic based on the competent standard of
English for XI grade of senior high school students for semester one according to
School Based Curriculum. The writer chose one topic for speaking that was
“Asking and Giving Opinion”. The writer chose this topic because the writer
wanted to design the pronunciation material from the basic. It means that it should
be put at the begining of the semester.
2. Analyze Learners and Contexts
The learners were the XI grade students of SMA BOPKRI 2 Yogyakarta.
There are 3 classes of Science program, 4 classes of Social program and 1 class of
Language program. The English speaking ability of Language students was better
than Science and Social students. The English speaking ability of Science students
was also better than Social students. Their speaking ability included the ability of
pronouncing the English words correctly, the mastery of vocabulary, sentence
structure and grammar. All of those students still needed to learn pronunciation
especially the Social students.
3. Write Performance Objectives
From the learners characteristics, the writer tried to make the goals based
on the students’ needs. The writer tried to fulfill the students’ needs of speaking,
especially in Pronunciation aspect. The goals of the materials can be listed as
a) The students are able to recognize the expression of asking and giving
opinion correctly.
b) The students are able to identify the expression of asking and giving opinion
correctly.
c) The students are able to use the expression of asking and giving opinion
correctly.
d) The students are able to recognize the English consonants, vowels and
diphthongs correctly.
e) The students are able to write and read phonetic transcription of English
sounds correctly.
f) The students are able to pronounce English words correctly.
4. Develop Instructional Strategy
The writer had made the list of activities that had been put in the lesson
plan. The list of the activities were the pre-activities, whilst activities and post
activities. The whilst activities were divided into three parts which are
exploration, elaboration and confirmation. Exploration means the students try to
get the information about the material which is given by the teacher. The students
explore the material to get the information that they need. For examples: the
students listen to the teacher’s explanation, the students read the conversation, etc.
Elaboration means the students elaborate the material they have got from the
teacher. The students can work in group or work individually to do the exercises
given. For example: the students are asked to complete the conversations.
the material by doing the exercises that are given by the teacher. In this part, the
students are able to produce something. For example: the students are able to
make short dialogues about asking and giving opinion.
5. Develop and Select Instructional Material
The writer designed the material about Asking and Giving Opinion. It
would be for one meeting of teaching and learning. The writer divided it into three
main parts.
a. The speaking material
The material was based on Competent Standard of XI grade students of
Senior High School for semester one. This part was about the explanation of the
expression used in asking and giving opinion and the example of it in form of
dialogue. The writer provided some examples of expression so that the students
could get the idea of the expression. In this part, the function of the teacher was to
give the model to the students so that later they would be able to work by
themselves to produce something. One example of the expressions of asking
opinion was “What do you think about...?” One example of the expressions of
giving opinion was “Well, I think....” In this part, the students completed the goal
of being able to indentify the expression of asking and giving opinion.
The writer also provided the examples of using the expressions in 2
dialogues with the aim to give the students idea on how to use the expression in a
dialogue. The teacher would ask two students to read each of the conversations.
While the students read, the teacher corrected the student’s pronunciation. The
giving opinion that were used in the conversation. In this step, the students
completed the goal of being able to recognize the expression of asking and giving
opinion. One of the examples that were used in the dialogue was “What do you
think about it?” the answer was “Well, I think it’s cute”.
b. Exercise for the students
The second part was exercise for the students to practice completing the
dialogues with the right expression they had learned. The exercise was given to
the students so that they could practice what they got from the teacher. For
example:
Conversation 1
Shinta : Hi Ana, what do you think about my new haircut?
Ana : ________________________________________________________
Shinta : Thanks.
In this conversation, the students were asked to work in pairs to fill in the blank
space with the appropriate expression of giving opinion. Then, they had to practie
the conversation with their partners.
The students were also asked to make their own dialogues using the
expression that they had learned. They had to work in pairs. It was aimed to make
the students able to use the expressions in a daily conversation. In this step, the
students completed the goal of being able to use the expression of asking and
giving opinion.
The writer chose pair work because of the effectiveness. According to
target language with partners” (p. 15). Hammer (2001) also said, “If we allow
forty students in the class to concentrate on pair work and partner exercises,
twenty students will be actively speaking instead of just one, as would be common
in the lockstep approach” (cited in Maher, p. 16).
c. Pronunciation
This part was divided into five subparts. The first was to learn English
consonants. The writer provided all the English consonants the students should
learn. The teacher would pronounce the consonants and the words consisted of the
consonants. The students were supposed to listen and repeat it. For example /p/ -
performance, /b/ - big and /t/ - try. The writer also focused on four consonant
sounds that were /v/, /z/, /ʃ/ and /Ӡ/. The writer also provided the example of it in a
short dialogue.
Andy : What do you think about my new friend Fery? /f/
Mery : He is very smart. /v/
The second part was about the English vowels. The writer also provided
the kinds of English vowels. The teacher would read, and the students would
listen and repeat. The examples of vowels were /ʌ/ - cut and /œ/ - bad, and /a:/ -
cart. The writer focused on two vowel sounds that were /i:/ and /I/. The writer
provided the example of a short dialogue using some of those words containing
English vowels. The example is as follows.
Andy : What do you feel about living together with this little family?/i:/ and /I/
The third part was about English diphthongs. The writer provided the
English diphthongs that the learners should learn. The example of it were /ᴐi/ -
boy, /eә/ - care, /aʊ/ - how, /әʊ/ - show, /eI/ - make, and / ʊә/ - fluent. The writer
focused on two diphthong sounds that were /әʊ/ and /ʊә/. The writer also
provided the example of some words containing English diphthongs in form of a
short dialogue that can be seen below.
Mery : Any comment about Ina’s boyfriend? /ᴐi/
Andy : I think he doesn’t care for her. /eә/
Mery : How do you know? /aʊ/ and /әʊ/
Andy : I saw him walking with another girl last day. /eI/
Mery : Are you sure? / ʊә/
Andy : Yes.
For the first, second and third parts, the students were asked to listen and
repeat. In these parts the students will try to recognize the sound they are listening
and try to produce it in their speaking. Odisho (2007) proposed traditional
monosensory teaching of pronunciation with exclusive reliance on the auditory
sensory modality. It is the teaching of pronunciation which is affected by “ear
training”. Ear training means the students are given model, then the students listen
to it after that they pronounce it (Odisho, 2007, p.6).
The writer used a kind of drills in Audiolingual Method (Richards and
Rodgers, 2001, p.60) which is stated by Brooks (1964, p 156-161). Brook said
that in repetition, “the student repeats an utterance aloud as soon as he has heard
it” (cited in Richards and Rodgers, 2001, p.60). By repeating what the teacher
(Richards and Rodgers, 2001, p.60). In these parts the students complete the goal
of being able to recognize the English consonants, vowels and diphthongs.
The fourth part was about the full phonetic transcription of English words
containing English consonants, vowels and also diphthongs. The students were
asked to listen and repeat what the teacher said. The examples were /boIfrend/ -
boyfriend and/kɒment/ - comment.
The last part was exercise part. The students were asked to write the
phonetics transcription of the words that were given. They had to consult their
dictionary. After that, they had to practice reading the phonetic transcription of
those words with their friends. In this step the students completed the goal of
being able to write and read the phonetic transcription of English sounds.
The material designed with the purpose to make the students know how to
pronounce English words correctly. If the students know the English consonants,
vowels and also diphthongs’ sounds, they will know how to read phonetics
transcriptions of English words in dictionary. Indirectly, they will become
31 CHAPTER III
CONCLUSIONS
In this chapter the writer is going to summarize the major finding of the
problem. The writer had designed material for speaking class that included basic
pronunciation material. The writer used some steps of Dick and Carey’s model of
instruction and Kemp’s model of instruction to design the material. There were 5
steps the writer had to follow.
The designed products were a unit of teacher guideline and a unit of
material. The material was designed for XI Grade students of SMA BOPKRI 2
Yogyakarta. The material was designed with the aim at helping the teacher to find
out the specific material to teach pronunciation and helping the students to better
their pronunciation. The students can get many benefits of learning pronunciation
as what the writer has written in the previous part. The writer made a unit of
teacher guideline as a guideline for the teacher who wants to use this designed
material. By using the teacher’s guideline, the writer hopes that the teacher will
know how to teach the students using the designed material.
The material was about Asking and Giving Opinion based on Competent
standard of XI grade students of Senior High School for semester one. Basically,
this material consisted of three main parts. The first part was about the
explanation of the material and examples of it. The second part was the practicing
part. The last part was the pronunciation part which was divided into 5 subparts
Phonetic Transcripton, and practicing part. It was designed with the aim to let the
students know how to read phonetic transcription of English words so that the
students could learn pronunciation independently by consulting dictionary.
The writer really hopes this material will be useful for the teachers and the
students who use it. The writer also hopes this material can help the teachers in
33
REFERENCES
Dardjowidjojo, S. (2009). English phonetics & phonology for Indonesians. Jakarta: Yayasan Obor Indonesia.
Dick, W., Carey, L., Carey, J.O. (2005). The systematic of instruction. Boston: Allyn and Bacon.
Fromkin, V., Rodman, R., & Hyams, N. (2007). An introduction to language (8th ed). Wadsworth: Thomson.
Gall, M.D., Gall, J.P., Borg, W.R. (2007). Educational research: An introduction. Boston: Pearson.
Indriani, M.I. (2005). English pronunciation: The English speech sounds theory & practice. Jakarta: PT Gramedia Pusaka Utama.
Jurafsky, D. & Martin, J. H. (2009). Speech and language processing: An introduction to natural language (2nd ed). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Kemp, J. E. (1977). Instructional design. Belmot: Fearon Pitman Publishers.
Lado, R. & Fries, C. C. (1954). Exercises in sound segments, intonation, and rhythm. New York: The University of Michigan Press.
Maher, K.M. (n.d.). Intricacies of pair work. Retrieved June 12, 2012, from http://www.keiwa-c.ac.jp/kenkyu/kiyo/doc/kiyo20-2.pdf
Odisho, E. Y. (2007). A multisensory, multicognitive approach to teaching pronunciation. Linguística - Revista de Estudos Linguísticos da Universidade do Porto, 2, 3-28. Retrieved June 12, 2012 from http://ler.letras.up.pt/uploads/ficheiros/6862.pdf
Richard, J.C. & Rodgers, T. S. (2001). Approach and methods in language teaching. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Sinatra, A. F. (2010). The teaching of English language skills and English language components: Designing a task based activity for teaching speaking. Malang: State University of Malang Press.
Syafei, A. (1988). English pronunciation theory and practice. Jakarta: Departemen Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan.
35
36 APPENDIX 1
36
English
is
Fun
(
Teacher’s Guideline)
Designed by
Gressiana S oik
PREFACE
First of all, t he w rit er w ould like t o t hank Jesus Christ for His blessings t hat t he w rit er could finish designing t his mat erial. The w rit er w ould also express her grat it ude t o Christ ina Krist iyani, S.Pd., M .Pd. for her guidance during t his mat erial making.
Being aw are of t he import ance of English pronunciat ion t o be learned by Senior High School St udent s, t he w rit er t ried t o design a basic pronuncat ion mat erial t hat w as int egrat ed int o Speaking mat erial. This mat erial w as designed w it h t he aim at helping t he t eacher in t eaching pronunciat ion t o XI grade st udent s of Senior High School w ho are in semest er one. This mat erial w as also designed w it h t he aim at improving st udent s abilit y of pronouncing t he English w ords.
The w rit er hopes t his mat erial w ill be useful for t he t eacher in SM A BOPKRI 2 Yogyakart a and also t he st udent s w ho are st udying t here. The w rit er also hopes t his
mat erial can give benefit s t o t hose w ho are reading it .
The w rit er is aw are of t he lim inat ion of t his mat erial. Therefore, t he w rit er w ill be happy t o accept every suggest ion and advice for t he sake of revising t he mat erial. Thank you and having fun w it h “ English is Fun” .
The Writer
Gressiana Soik
36
Asking and Giving Opinion
A.
Table of Expr essions of Asking and Giving Opinion
Asking Opinion Giving Opinion
What do you think about...? Well, I think ...
What's your opinion about ...? In my opinion I think ... How do you feel about ...? I feel that we should ...
Example 1:
Read this conversation and try to find the expression used by underlying it!
Read this conversation and try to find the expression used by underlying it!
Andi : Hi Rina! Rina : Hi Andi!
Andi : I heard Mila has a new boyfriend. Rina : Oh, yeah. I know it already.
Andy : What’s your opinion about her boyfriend?
Rina : In my opinion, he is a good guy. He is smart and diligent.
Andy : That’s good.
B.
Let ’s Pr act ice!
Work in pair, and do these exercises below!
1. Complete these conversation! After you have completed it, practice it with your parner.
Conversation 1
Shinta : Hi Ana, what do you think about my new haircut?
Meri : Hi Nia, any comments on my performance last night?
2. Please make a conversation of asking and giving opinion with your partner. Use the expressions given in the table!
C. Pronunciat ion
Let ’s learn t he phonet ic alphabet of English consonant sounds.
List en and r epeat ! Read the words consisting of the consonant sounds loudly. Let the students repeat it.
Read it loudly. Focus on the difference between /f/ and /v/. Dialogue I
Dialogue II
List en and r epeat ! Read the words consisting of the vowel sounds loudly. Let the students repeat it.
Read the minimal pairs of the words to show the students the difference between /i:/ and /I/. For example eden –eaten, leave-live, etc.
/i:/ - / I/
Read it loudly. Focus on the difference between /i:/ and /I/. Dialogue I
Andy : What do you feel about living together with this little family?/i:/ and /I/
Mery : It’s just awesome.
Read it loudly. Focus on the difference between /i:/ and /I/.
Dialogue II
Mery : What do you think about the person who steals your money? /i:/ Ina : The person must be a bad guy. You have to get him to police station. Mety : Yeah, but I still forgive him. /I/
List en and r epeat ! Read these words consisting of diphthong sounds loudly. Let the students repeat it.
/eI/ - make /aʊ/ - how /ɛә/ - care
/aI/ - like /әʊ/ - show /ʊә/ - fluent
/ᴐI/ - boy /Iә/ - near
Let ’s f ocus on t hese dipht hong sounds.
Read these words consisting of /әʊ/ and /ʊә /loudly. Let the students repeat it.
/әʊ/ /ʊә/ show sure only pure open cruel note fluent home cure know tour
Read it loudly. Focus on the difference between /ᴐI/, /eә/, /әʊ/, /eI/, and / ʊә/. Dialogue I
Mery : Any comment about Ina’s boyfriend? /ᴐI/
Andy : I think he doesn’t care for her. /eә/ Mery : How do you know? /aʊ/ and /әʊ/
Andy : I saw him walking with another girl last day. /eI/
words!
List en and Repeat ! Read these words loudly. Let the students repeat it.
Performance /pәfᴐ:mәns/ Friend /frend/ My /maI/
Boyfriend /boIfrend/ Very /veri/ Night /naIt/
Time /taIm/ The /ðә/ Think /θIŋk/
Diligent /dIlIʤәnt/ Thanks /θœŋks/
Comment /kɒment/ Care /keә(r)/ Good /gʊd/ Joke /dʒәʊk /
Smart /sma:t/ She /ʃi:/ Zoo /zu:/ Pleasure /pleӠә(r)/
Let ’s Pract ice!
Find the phonetics transcriptions of the words below by looking at your dictionary! Try to pronouce these words with your partner by reading the phonetic transcriptions.
1. About : /әbaʊt/ 2. What : /wɒt/ 3. Opinion : /әpɪnjәn/
4. Already : /ɔːlredi/
5. And : /ænd/ 6. Book : bʊk/ 7. New : /njuː/
8. These : /ðiːz/
9. Haircut : /ˈheә.kʌt/
10.Should : /ʃʊd/
45 APPENDIX 2
45
English
is
Fun
Designed by
Gressiana S oik
PREFACE
First of all, t he w rit er w ould like t o t hank Jesus Christ for His blessings t hat t he w rit er could finish designing t his mat erial. The w rit er w ould also express her grat it ude t o Christ ina Krist iyani, S.Pd., M .Pd. for her guidance during t his mat erial making.
Being aw are of t he import ance of English pronunciat ion t o be learned by Senior High School St udent s, t he w rit er t ried t o design a basic pronuncat ion mat erial t hat w as int egrat ed int o Speaking mat erial. This mat erial w as designed w it h t he aim at helping t he t eacher in t eaching pronunciat ion t o XI grade st udent s of Senior High School w ho are in semest er one. This mat erial w as also designed w it h t he aim at improving st udent s abilit y of pronouncing t he English w ords.
The w rit er hopes t his mat erial w ill be useful for t he t eacher in SM A BOPKRI 2 Yogyakart a and also t he st udent s w ho are st udying t here. The w rit er also hopes t his
mat erial can give benefit s t o t hose w ho are reading it .
The w rit er is aw are of t he lim inat ion of t his mat erial. Therefore, t he w rit er w ill be happy t o accept every suggest ion and advice for t he sake of revising t he mat erial. Thank you and having fun w it h “ English is Fun” .
The Writer
Gressiana Soik
45
Asking and Giving Opinion
A.
Table of Expr essions of Asking and Giving Opinion
Asking Opinion Giving Opinion
What do you think about...? Well, I think ...
What's your opinion about ...? In my opinion I think ... How do you feel about ...? I feel that we should ...
Example 1:
Read this conversation and try to find the expression used by underlying it!
Read this conversation and try to find the expression used by underlying it!
Andi : Hi Rina! Rina : Hi Andi!
Andi : I heard Mila has a new boyfriend. Rina : Oh, yeah. I know it already.
Andy : What’s your opinion about her boyfriend? Rina : In my opinion, he is a good guy. He is smart
and diligent. Andy : That’s good.
B. Let ’s Pract ice!
Work in pair, and do these exercises below!
3. Complete these conversation! After you have completed it, practice it with your parner.
Conversation 1
Shinta : Hi Ana, what do you think about my new haircut?
Meri : Hi Nia, any comments on my performance last night?
Nia : _______________________________________________________ Meri : Yes, of course.
Nia : Well, I think_____________________________________________ Meri : Thank you.